Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Salmonella in Asymptomatic Horses in Eastern Spain: A One Health Perspective
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Epidemiological Data Collection
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Salmonella Isolation
2.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
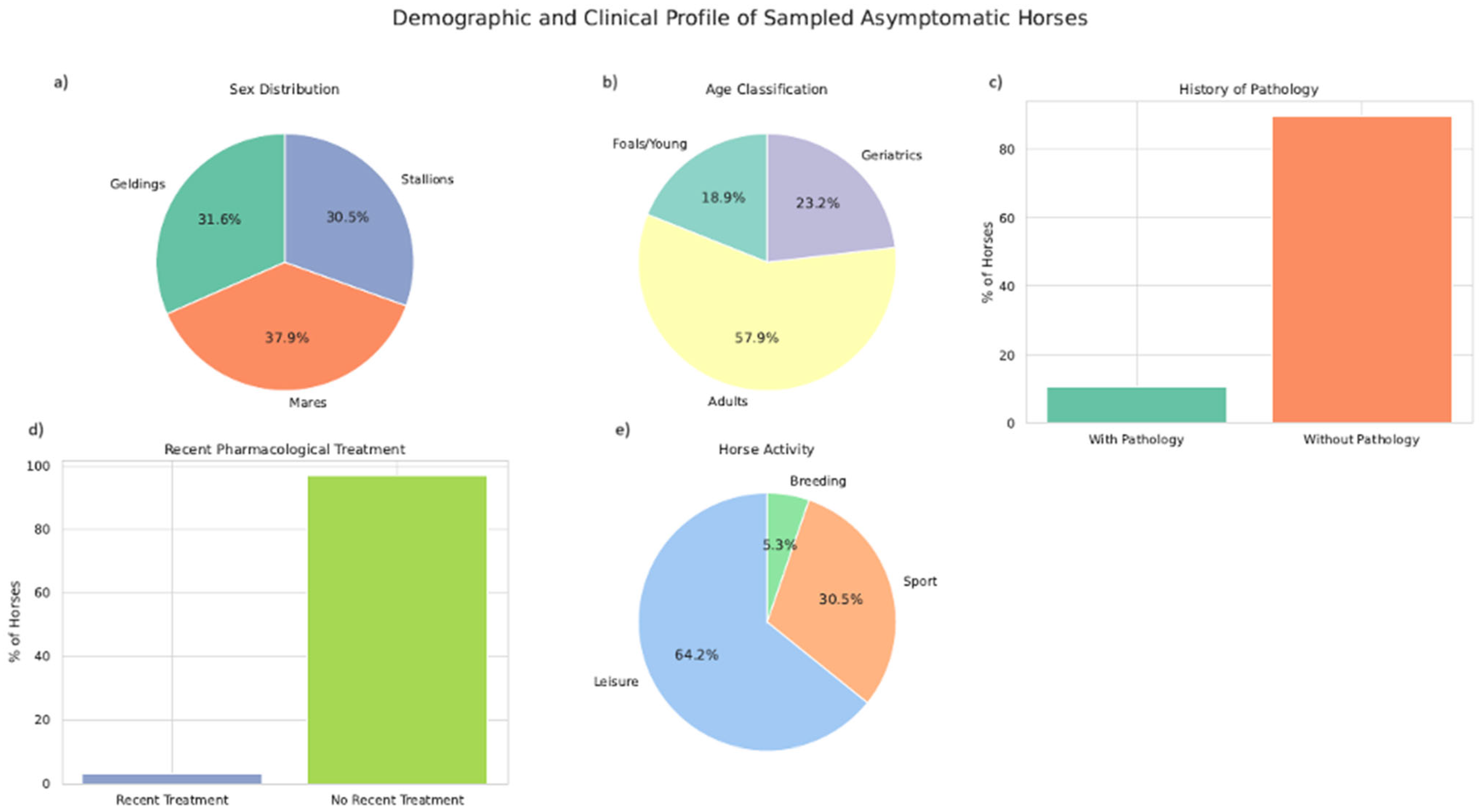
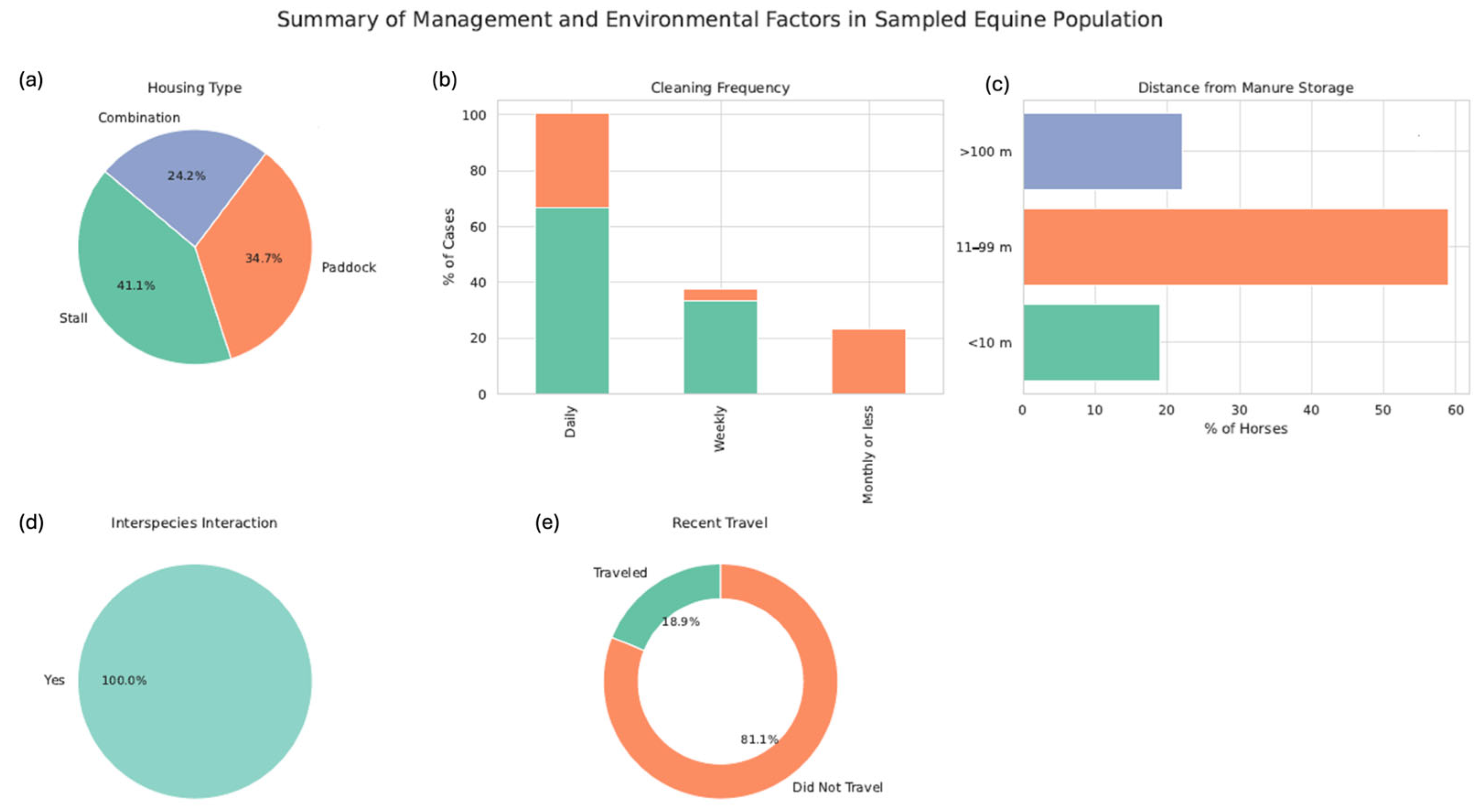
3.1. Epidemiological Data
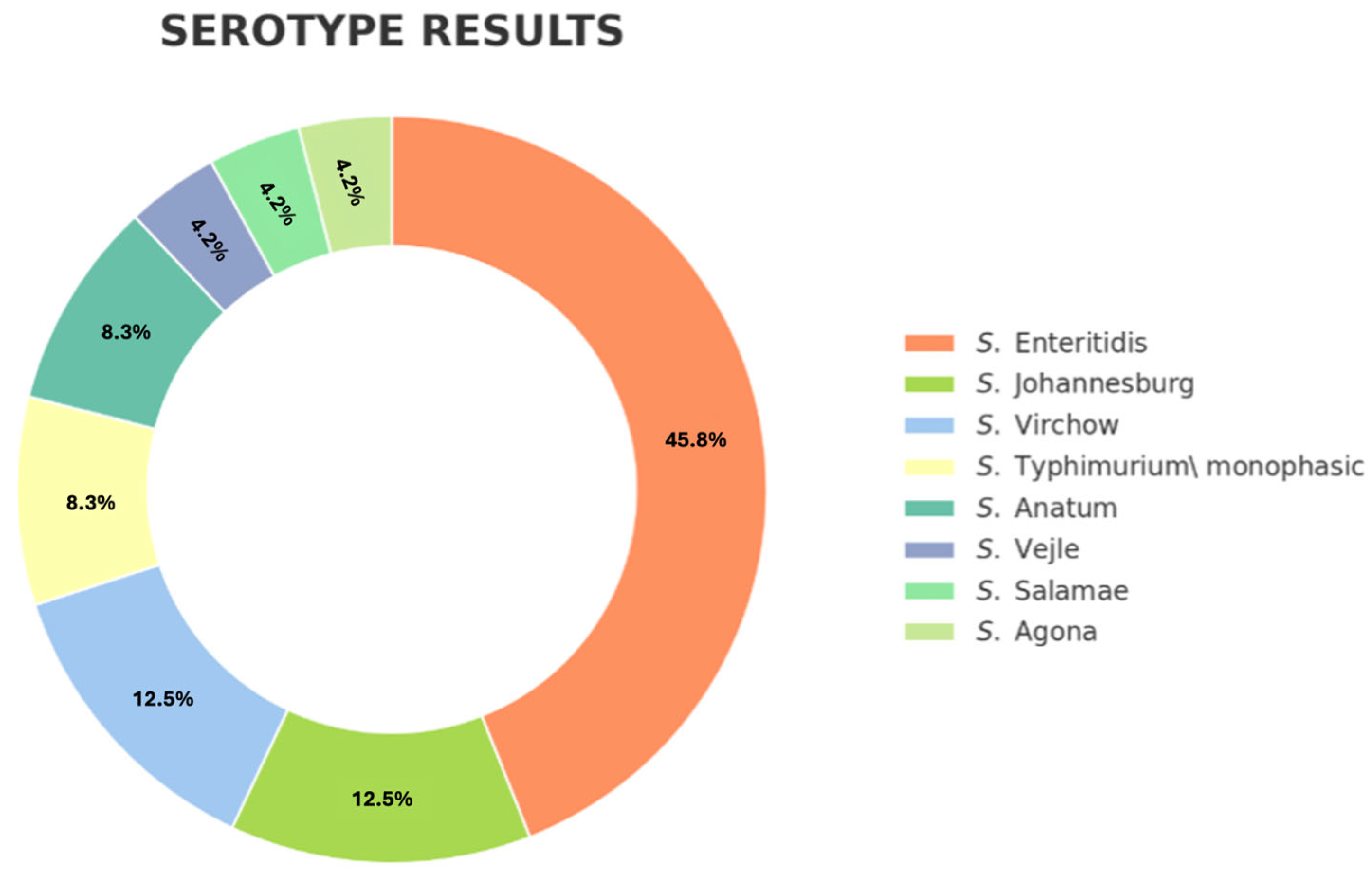
3.2. Salmonella Identification and Serotyping
3.3. Epidemiological Surveys
3.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMI | Amikacin |
| AMR | Antimicrobial Resistance |
| AMP | Ampicillin |
| ASAP | Advanced Software for Analysis of Patterns |
| AZI | Azithromycin |
| BPW | Buffered Peptone Water |
| CEU | Cardenal Herrera CEU University |
| CHL | Chloramphenicol |
| CIP | Ciprofloxacin |
| CIA | Critically Important Antimicrobial |
| COL | Colistin |
| CTA | Cefotaxime |
| CTZ | Ceftazidime |
| EUCAST | European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| EUVSEC3 | European Union Surveillance Sensititre Plate for Salmonella/E. coli |
| FQ | Fluoroquinolone |
| GEN | Gentamicin |
| GLM | Generalized Linear Model |
| HIA | Highly Important Antimicrobial |
| HPCIA | Highest Priority Critically Important Antimicrobial |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| MDR | Multidrug Resistance |
| MER | Meropenem |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MRSA | Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| MSRV | Modified Rappaport Vassiliadis Agar |
| NAL | Nalidixic Acid |
| NSAID | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug |
| NTS | Non-Typhoidal Salmonella |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PRAN | National Antimicrobial Resistance Plan (Spain) |
| R | Statistical Software “R” |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SME | Sulfamethoxazole |
| S. | Salmonella |
| TIG | Tigecycline |
| TET | Tetracycline |
| TRI | Trimethoprim |
| UCH-CEU | Universidad Cardenal Herrera-CEU |
| UELN | Universal Equine Life Number |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| XLD | Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate Agar |
References
- Ministerio de Agricultura Pesca y Alimentación. G de España. SECTOR EQUINO EN CIFRAS. 2024. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/dam/mapa/contenido/ganaderia/temas/produccion-y-mercados-ganaderos/sectores-ganaderos-2/equino/informacion-del-sector/indicadores-economicos/indicadores-economicos-equidos-2024.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- Cummings, K.J.; Perkins, G.A.; Khatibzadeh, S.M.; Warnick, L.D.; Aprea, V.A.; Altier, C. Antimicrobial resistance trends among Salmonella isolates obtained from horses in the northeastern United States (2001–2013). Am. J. Vet Res. 2016, 77, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.A.; Long, M.T.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Besser, T.E. Salmonellosis. In Equine Infectious Diseases, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 321–333.e4. [Google Scholar]
- Dor, Z.; Shnaiderman-Torban, A.; Kondratyeva, K.; Davidovich-Cohen, M.; Rokney, A.; Steinman, A.; Navon-Venezia, S. Emergence and Spread of Different ESBL-Producing Salmonella enterica Serovars in Hospitalized Horses Sharing a Highly Transferable IncM2 CTX-M-3-Encoding Plasmid. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 616032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, P.A.; Methner, U. Salmonella in Domestic Animals, 2nd ed.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2013; pp. 305–317. Available online: https://vetbooks.ir/Salmonella-in-domestic-animals-2nd-edition/ (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union One Health 2023 Zoonoses report. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellow Book|Yellow Book|CDC. 2025. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/yellow-book/index.html (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- Dallap Schaer, B.L.; Aceto, H.; Rankin, S.C. Outbreak of Salmonellosis Caused by Salmonella enterica Serovar Newport MDR-AmpC in a Large Animal Veterinary Teaching Hospital. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, C.P.; Dominguez, J.E.; Garda, D.; Moroni, M.; Pallarols Molinari, N.; Herrera, M.; Chacana, P.A.; Mesplet, M. Multiresistant and blaCTX-M-14-Carrying Salmonella ser. Typhimurium Isolated During a Salmonellosis Outbreak in an Equine Hospital in Argentina. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2021, 99, 103404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Salman, M.D.; Jones, R.L. Epidemiologic study of Salmonellae shedding in the feces of horses and potential risk factors for development of the infection in hospitalized horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1990, 196, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargatz, D.A.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella and nosocomial infections. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2004, 20, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, J.K.; Mainar-Jaime, R.C.; Smith, B.P.; House, A.M.; Kamiya, D.Y. Risk factors for nosocomial Salmonella infection among hospitalized horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1999, 214, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, L.; Morley, P.S.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Salman, M.D.; Gentry-Weeks, C. Factors associated with Salmonella shedding among equine colic patients at a veterinary teaching hospital. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, N.S.; Hernandez, J.A.; MacKay, R.J.; Brown, M.P.; Gaskin, J.M.; Nguyen, A.D.; Giguere, S.; Colahan, P.T.; Troedsson, M.R.; Haines, G.R.; et al. Risk factors associated with fecal Salmonella shedding among hospitalized horses with signs of gastrointestinal tract disease. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 225, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, I.M.; Lawhon, S.D.; Norman, K.N.; Threadgill, D.S.; Ohta, N.; Vinasco, J.; Scott, H.M. Serotype diversity and antimicrobial resistance among Salmonella enterica isolates from patients at an equine referral hospital. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02829-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.G.; Tengelsen, L.A.; Smith, K.E.; Bender, J.B.; Frank, R.K.; Grendon, J.H.; Rice, D.H.; Thiessen, A.M.B.; Gilbertson, C.J.; Sivapalasingam, S.; et al. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium in Four Animal Facilities. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, B.A.; Morley, P.S. Risk factors for shedding of Salmonella enterica among hospitalized large animals over a 10-year period in a veterinary teaching hospital. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astorga, R.; Arenas, A.; Tarradas, C.; Mozos, E.; Zafra, R.; Pérez, J. Outbreak of peracute septicaemic salmonellosis in horses associated with concurrent Salmonella enteritidis and Mucor species infection. Vet. Rec. 2004, 155, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, K.A.; Manzoor, T.; Dar, M.A.; Farooq, A.; Allie, K.A.; Wani, S.M.; Dar, T.A.; Shah, A.A. Salmonella Infection and Pathogenesis. In Enterobacteria; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/80044 (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- Crump, J.A.; Wain, J. Salmonella. Int. Encycl. Public Health 2017, 2, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, B.A. Salmonella in Horses. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2023, 39, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antimicrobial Resistance. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/17-05-2024-who-updates-list-of-drug-resistant-bacteria-most-threatening-to-human-health (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- Johnson, J.A. Nosocomial infections. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2002, 32, 1101–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soza-Ossandón, P.; Rivera, D.; Tardone, R.; Riquelme-Neira, R.; García, P.; Hamilton-West, C.; Adell, A.D.; González-Rocha, G.; Moreno-Switt, A.I. Widespread Environmental Presence of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella in an Equine Veterinary Hospital That Received Local and International Horses. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 537557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgowan, C. Welfare of Aged Horses. Animals 2011, 1, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Arrones Egido, V. Cuidados del Caballo Geriátrico. 2023. Available online: https://www.diarioveterinario.com/t/4290842/cuidados-caballo-geriatrico-equino#:~:text=Hoy%20en%20d%C3%ADa%20se%20considera,o%20senior%20m%C3%A1s%20de%2020 (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- Plana, M.; Farriols, M.M. El Potro y las Etapas de su Desarrollo. 2020. Available online: https://www.ecuestre.es/app/blogs/doma-educativa-y-equitacion-conectada/el-potro-y-las-etapas-de-su-desarrollo (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- Lowther, A. Skeletal Maturity in Horses: Growth Plate Ossification and Age Considerations. 2023. Available online: https://www.horsesinsideout.com/post/skeletal-maturity-in-horses-growth-plate-ossification-and-age-considerations (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.X. WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella. In Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella serovars, 9th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2020/2021. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e07867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 15.0. 2025. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_15.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichner, R.; Sander, A.; Steinrück, H.; Gareis, M. Occurrence of Salmonella spp. and shigatoxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) in horse faeces and horse meat products. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2005, 118, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Garber, L.P.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Ladely, S.; Ferris, K.E. Fecal shedding of Salmonella spp. by horses in the United States during 1998 and 1999 and detection of Salmonella spp. in grain and concentrate sources on equine operations. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 217, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinovi, C.A.; Ward, M.P.; Couëtil, L.L.; Wu, C.C. Risk factors for fecal shedding of Salmonella from horses in a veterinary teaching hospital. Prev. Vet. Med. 2003, 60, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzal, F.A.; Arroyo, L.G.; Navarro, M.A.; Gomez, D.E.; Asín, J.; Henderson, E. Bacterial and viral enterocolitis in horses: A review. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2022, 34, 354–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.P.; Reina-Guerra, M.; Hardy, A.J. Prevalence and epizootiology of equine salmonellosis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1978, 172, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusterla, N.; Byrne, B.A.; Hodzic, E.; Mapes, S.; Jang, S.S.; Magdesian, K.G. Use of quantitative real-time PCR for the detection of Salmonella spp. in fecal samples from horses at a veterinary teaching hospital. Vet. J. 2010, 186, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.C.; O’boyle, D.A. The prevalence and epizootiology of salmonellosis among groups of horses in south east Queensland. Aust. Vet. J. 1981, 57, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, J.A.; Davies, P.R.; Nichols, M.A. The Effect of Fecal Sample Weight on Detection of Salmonella enterica in Swine Feces. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2000, 12, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, B.A.; Morley, P.S. Managing Salmonella in Equine Populations. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2014, 30, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.A.; Fullerton, J.; Barnum, D.A. Effects of transportation, surgery, and antibiotic therapy in ponies infected with Salmonella. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1983, 44, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, D.W.; Casebolt, D.B.; Carter, J.D.; Pappaioanou, M.; Hjerpe, C.A. Risk factors for salmonellosis in hospitalized horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1986, 188, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, W.V.; Sebastian, M.; Hemming, B. Salmonella Antimicrobial Activity of Selected Strains of Enterolactobacillus Species Isolated from the Gastrointestinal Tract of the Horse. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2011, 31, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, J.; Joan, P.; Membrado-Tena, C.; Aparicio, J.V.; Fansa, G.; Antequera, M. Estudios Comarcales de la Provincia de Valencia/Estudis Comarcals de la Província de València. Dirección y Coordinación Técnica/Direcció i Coordinació Tècnica Equipo Técnico/Equip Tècnic: ESTEPA Cartografía/Cartografia. 2018. Available online: https://datos.divaladl.es/userfiles/1078/Documentos/930e90368dEC_bunyol_OK.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Climate change impacts|National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2025. Available online: https://www.noaa.gov/education/resource-collections/climate/climate-change-impacts (accessed on 19 November 2025).
- Brenner, F.W.; Villar, R.G.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.; Swaminathan, B. Salmonella Nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2465–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulford, C.V.; Wenner, N.; Redway, M.L.; Rodwell, E.V.; Webster, H.J.; Escudero, R.; Kröger, C.; Canals, R.; Rowe, W.; Lopez, J.; et al. The diversity, evolution and ecology of Salmonella in venomous snakes. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlangeni, L.N.; Ramatla, T.; Lekota, K.E.; Price, C.; Thekisoe, O.; Weldon, C. Occurrence, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Virulence Profiles of Salmonella Serovars Isolated from Wild Reptiles in South Africa. Int. J. Microbiol. 2024, 2024, 5213895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana-Hernández, K.M.; Rodríguez-Ponce, E.; Medina, I.R.; Acosta-Hernández, B.; Priestnall, S.L.; Vega, S.; Marin, C.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Marco-Fuertes, A.; Ayats, T.; et al. One Health Approach: Invasive California Kingsnake (Lampropeltis californiae) as an Important Source of Antimicrobial Drug-Resistant Salmonella Clones on Gran Canaria Island. Animals 2023, 13, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar, U.; von Lützau, K.; Schlattmann, A.; Rösler, U.; Köck, R.; Becker, K. Zoonotic multidrug-resistant microorganisms among non-hospitalized horses from Germany. One Health 2019, 7, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohnen, A.B.; Wiedenheft, A.M.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Short, D.M.; Cook, K.L.; Lantz, K.; Morningstar-Shaw, B.; Lawrence, J.P.; House, S.; Marshall, K.L.; et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella and Escherichia coli from equids sampled in the NAHMS 2015–16 equine study and association of management factors with resistance. Prev. Vet. Med. 2023, 213, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipangura, J.K.; Chetty, T.; Kgoete, M.; Naidoo, V. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance from bacterial culture and susceptibility records from horse samples in South Africa. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 148, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, I.; Durrani, A.Z.; Khan, M.S.; Mushtaq, M.H.; Ahmad, I. Study of antimicrobial resistance and physiological biomarkers with special reference to Salmonellosis in diarrheic foals in Punjab, Pakistan. Acta Trop. 2017, 176, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feary, D.J.; Hassel, D.M. Enteritis and Colitis in Horses. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2006, 22, 437–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| POSITIVE HORSE | DAY 1 | DAY 2 | DAY 3 | DAY 4 | DAY 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | ||||
| 2 | + | + | |||
| 3 | + | + | |||
| 4 | + | ||||
| 5 | + | + | + | + | |
| 6 | + | ||||
| 7 | + | ||||
| 8 | + | ||||
| 9 | + | ||||
| 10 | + | ||||
| 11 | + | + | |||
| 12 | + | + | |||
| 13 | + | + | |||
| 14 | + | + | + | ||
| 15 | + | + | |||
| 16 | + | ||||
| 17 | + | + | |||
| 18 | + | + | |||
| 19 | + | ||||
| 20 | + | ||||
| 21 | + | + | + | ||
| 22 | + | ||||
| 23 | + | ||||
| 24 | + |
| Epidemiological Data | Classification in Each Group | N of Animals per Group | % of Animals Positive to Salmonella | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Young | 18/95 | 38.88 (7/18) | 0.170 |
| Adult | 55/95 | 18.18 (10/55) | ||
| Geriatric | 22/95 | 31.81 (7/22) | ||
| Sex | Gelding | 30/95 | 23.3 (7/30) | 0.309 |
| Male | 29/95 | 17.24 (5/29) | ||
| Female | 36/95 | 33.33 (12/36) | ||
| Pathology history | Yes | 10/95 | 20 (2/10) | 0.663 |
| No | 85/95 | 25 (22/85) | ||
| Recent pharmacological treatments | Yes | 3/95 | 0 (0/3) | <0.001 |
| No | 92/95 | 26.08 (24/92) | ||
| Horse activity | Reproduction | 5/95 | 60 (3/5) | 0.237 |
| Leisure | 61/95 | 24.5 (15/61) | ||
| Sport | 29/95 | 20.68 (6/29) | ||
| Recent travel | Yes | 18/95 | 22.22 (4/18) | 0.733 |
| No | 77/95 | 25.97 (20/77) | ||
| Horse facility | Box | 39/95 | 17.95 (7/39) | 0.2 |
| Paddock | 33/95 | 36.36 (12/33) | ||
| Both | 23/95 | 21.73 (5/23) | ||
| Manure storage | <10 m | 18/95 | 50 (9/18) | <0.001 * |
| 11–99 m | 59/95 | 25.42 (15/59) | ||
| >100 m | 21/95 | 0 (0) | ||
| Box cleaning frequency | Monthly | 0/95 | 0 (0) | <0.123 |
| Weekly | 22/95 | 28.57 (8/22) | ||
| Daily | 44/95 | 18.18 (8/44) | ||
| Paddock cleaning frequency | Monthly | 22/95 | 18.18 (4/22) | <0.001 * |
| Weekly | 4/95 | 100 (4/4) | ||
| Daily | 32/95 | 28.12 (9/32) | ||
| Contact with other horses and/or animals of other species | Yes | 95/95 | 2.4 (24/95) | |
| No | 0/95 | 0 (0) |
| Antibiotic Group | Antibiotic | % AMR |
|---|---|---|
| Folate-pathway inhibitors | Sulfamethoxazole | 70.8 d ± 10.96 |
| Trimethoprim | 4.2 ab ± 6.88 | |
| Polymyxins | Colistin | 16.7 ab ± 6.88 |
| Quinolones | Nalidixic acid | 16.7 ab ± 12.07 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 25 c ± 12.80 | |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline | 8.3 abc ± 9.35 |
| Glycylcyclines | Tigecycline | 16.7 ab ± 12.8 |
| Carbapenems | Meropenem | 0 a ± 0 |
| Cephalosporins | Ceftazidime | 0 a ± 0 |
| Cefotaxime | ||
| Penicillins | Ampicillin | 4.2 ab ± 6.88 |
| Macrolides | Azithromycin | 0 a ± 0 |
| Amphenicols | Chloramphenicol | 8.3 ab ± 6.88 |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 42.9 c ± 13.22 |
| Amikacin |
| Serotype | n | Folate-Pathway Inhibitors | Polimixins | Quinolones | ||
| Sulfamethoxazole | Trimetoprim | Colistin | 1st Generation | 2nd Generation | ||
| Nalidixic Acid | Ciprofloxacin | |||||
| S. Enteritidis | 11/24 | 4/11 (36.3%) | 1/11 (9.09%) | |||
| S. Johannesburg | 3/24 | 3/3 (100%) | 2/3 (66.75%) | 1/3 (33.3%) | ||
| S. Virchow | 3/24 | 3/3 (100%) | 2/3 (66.7%) | 3/3 (100%) | ||
| S. Typhimurium monofasic | 2/24 | 2/2 (100%) | 2/2 (100%) | 1/2 (50%) | ||
| S. Anatum | 2/24 | 1/2 (50%) | ||||
| S. Vejle | 1/24 | 1/1 (100%) | ||||
| S. Salamae | 1/24 | 1/1 (100%) | ||||
| S. Agona | 1/24 | 1/1 (100%) | 1/1 (100%) | 1/1 (100%) | 1/1 (100%) | |
| Serotype | n | Tetracyclines | Glycylcyclines | Carbapenems | Cephalosporins | Penicillins |
| Tetracycline | Tigecycline | Meropenem | Cefotaxime | Ampicillin | ||
| Ceftazidime | ||||||
| S. Enteritidis | 11/24 | 1/11 (9.09%) | 1/11 (9.09%) | |||
| S. Johannesburg | 3/24 | |||||
| S. Virchow | 3/24 | 3/3 (100%) | 1/3 (33.3%) | |||
| S. Typhimurium monofasic | 2/24 | |||||
| S. Anatum | 2/24 | |||||
| S. Vejle | 1/24 | |||||
| S. Salamae | 1/24 | |||||
| S. Agona | 1/24 | 1/1 (100%) | 1/1 (100%) | |||
| Serotype | n | Macrolides | Amphenicols | Aminoglycosides | ||
| Azithromycin | Chloramphenicol | Gentamicin | Amikacin | |||
| S. Enteritidis | 11/24 | 1/11 (9.09%) | 4/11 (36.3%) | |||
| S. Johannesburg | 3/24 | 1/3 (33.3%) | 3/3 (100%) | |||
| S. Virchow | 3/24 | |||||
| S. Typhimurium monofasic | 2/24 | 2/2 (100%) | ||||
| S. Anatum | 2/24 | 1/2 (50%) | ||||
| S. Vejle | 1/24 | |||||
| S. Salamae | 1/24 | |||||
| S. Agona | 1/24 | 1/1 (100%) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simó-Martínez, M.S.; Marco-Fuertes, A.; Galán-Relaño, Á.; Astorga Márquez, R.J.; Marin, C.; Valero Díaz, A.; Vega, S. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Salmonella in Asymptomatic Horses in Eastern Spain: A One Health Perspective. Animals 2025, 15, 3413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233413
Simó-Martínez MS, Marco-Fuertes A, Galán-Relaño Á, Astorga Márquez RJ, Marin C, Valero Díaz A, Vega S. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Salmonella in Asymptomatic Horses in Eastern Spain: A One Health Perspective. Animals. 2025; 15(23):3413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233413
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimó-Martínez, María Socorro, Ana Marco-Fuertes, Ángela Galán-Relaño, Rafael J. Astorga Márquez, Clara Marin, Antonio Valero Díaz, and Santiago Vega. 2025. "Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Salmonella in Asymptomatic Horses in Eastern Spain: A One Health Perspective" Animals 15, no. 23: 3413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233413
APA StyleSimó-Martínez, M. S., Marco-Fuertes, A., Galán-Relaño, Á., Astorga Márquez, R. J., Marin, C., Valero Díaz, A., & Vega, S. (2025). Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Salmonella in Asymptomatic Horses in Eastern Spain: A One Health Perspective. Animals, 15(23), 3413. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233413









