Survey of Haemosporidian Parasites in Wild Stone-Curlews (Burhinus oedicnemus) in the Canary Islands: First Molecular and Histopathological Evidence of Leucocytozoon sp. Infection
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Climate
2.2. Birds and Tissue Sampling
2.3. Molecular Analysis of Avian Hemosporidia
2.4. Detection and Sequencing of PCR Products and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Histopathological Examination
3. Results
3.1. Birds and Tissue Sampling
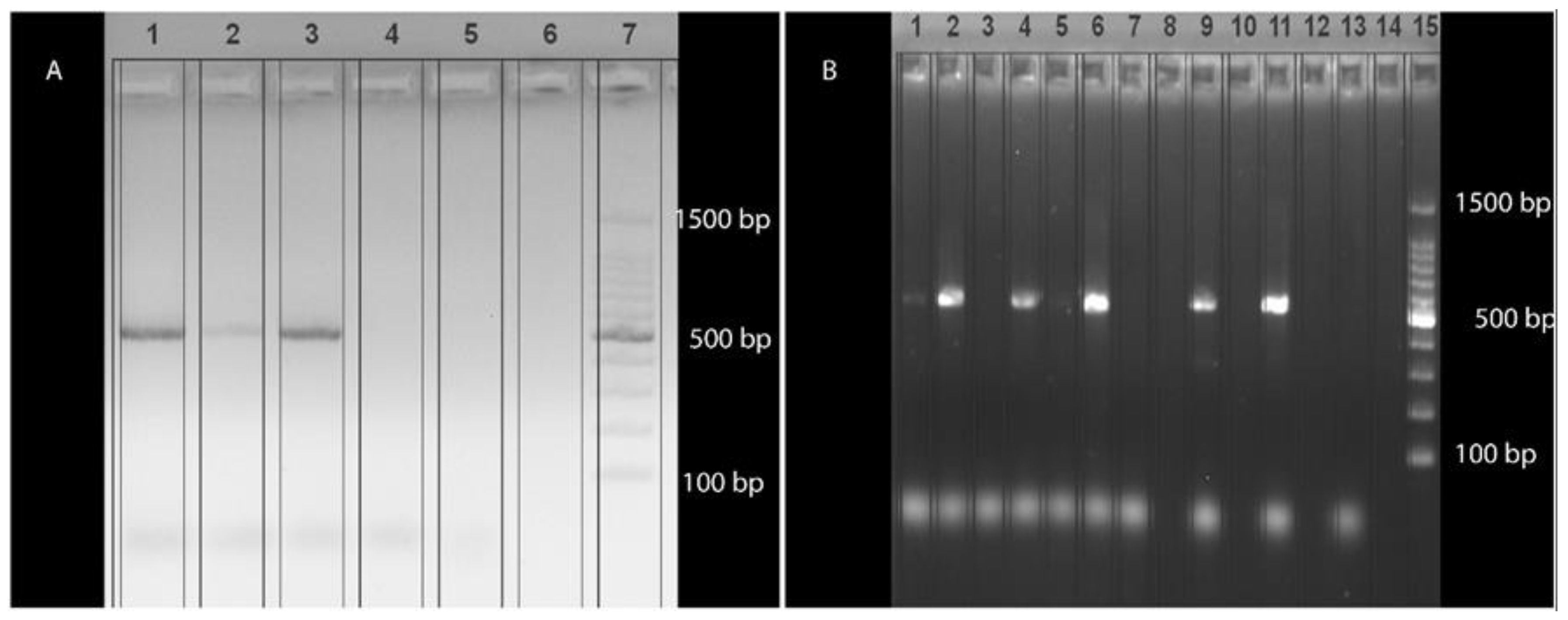
3.2. Detection and Sequencing of PCR Products
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
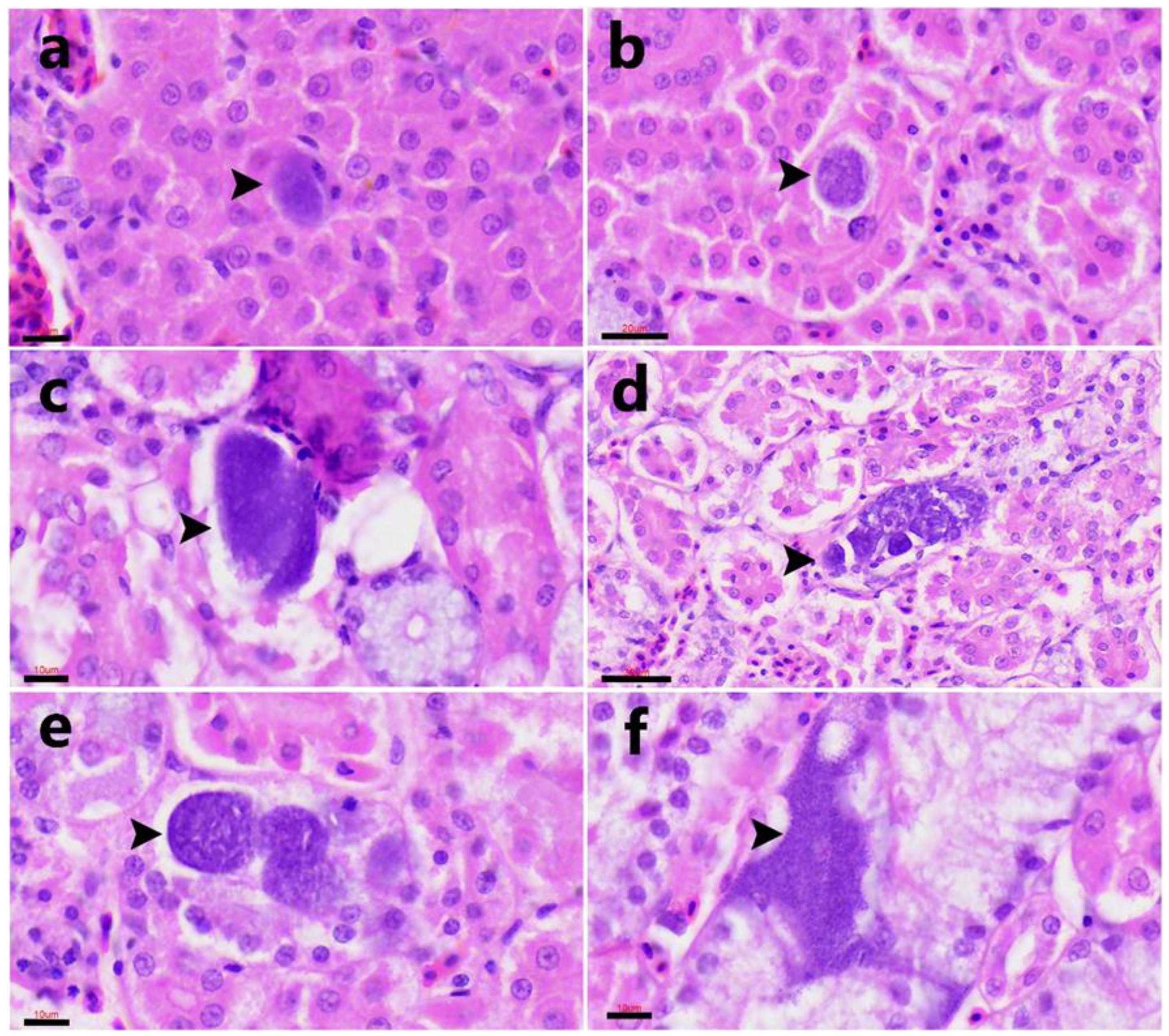
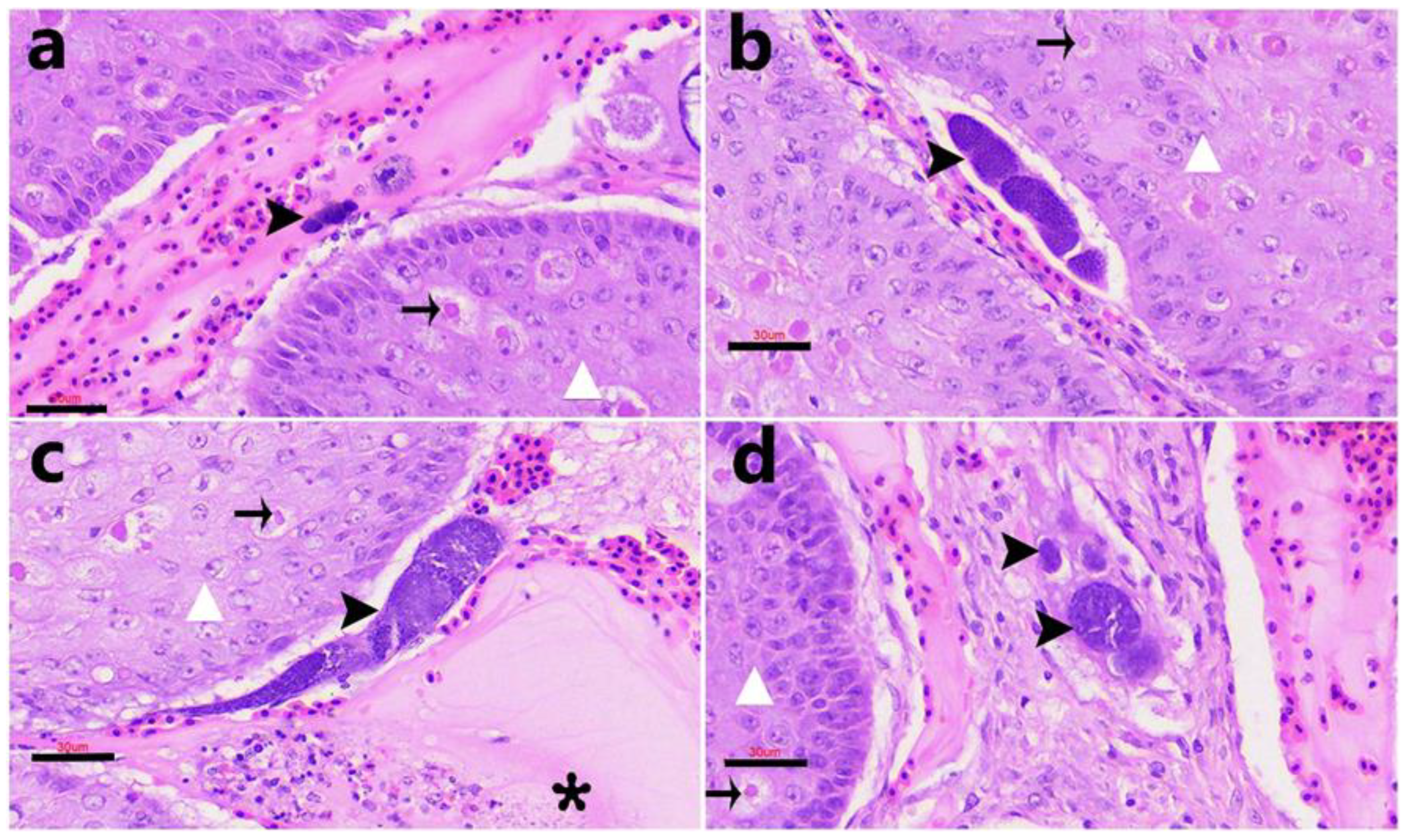
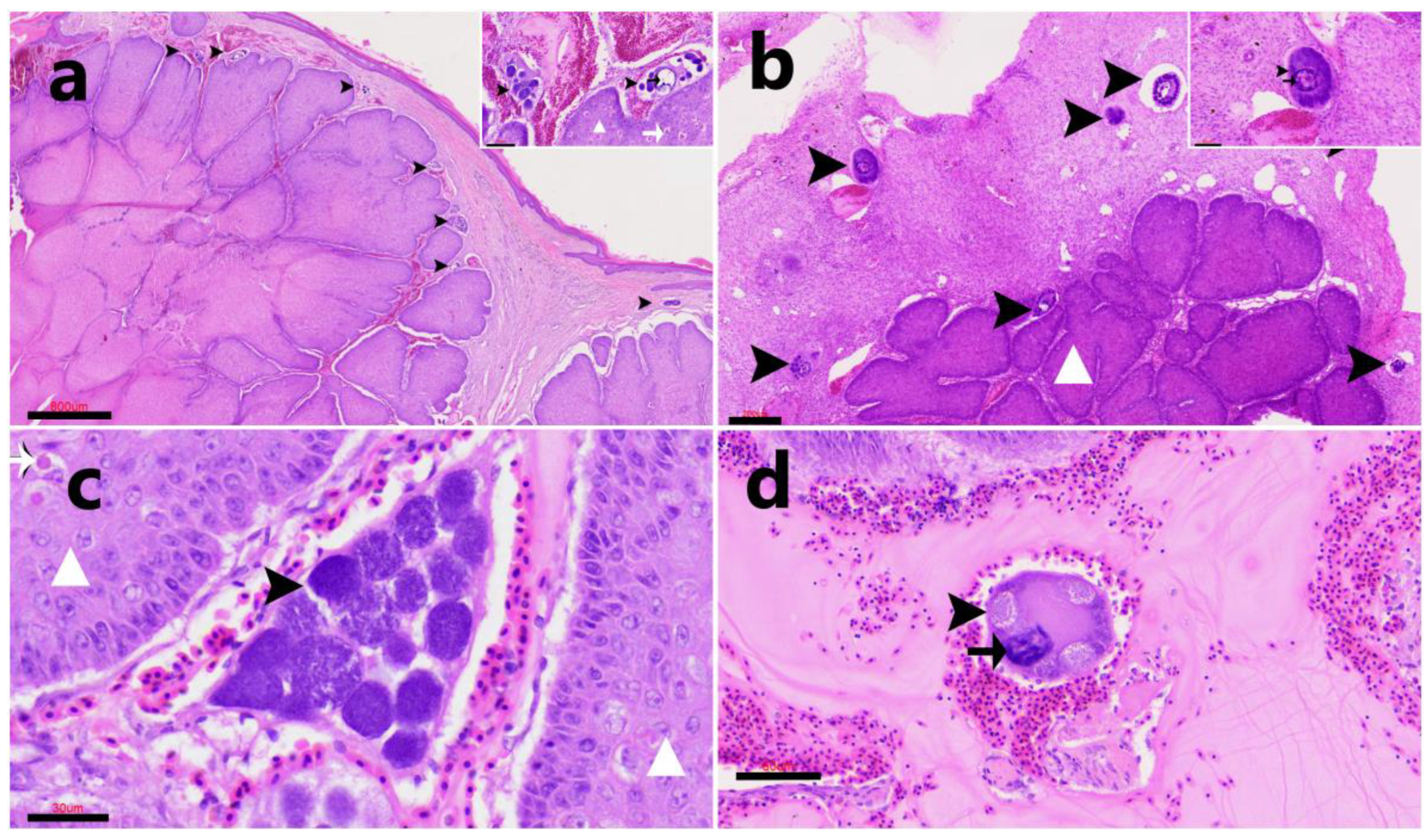
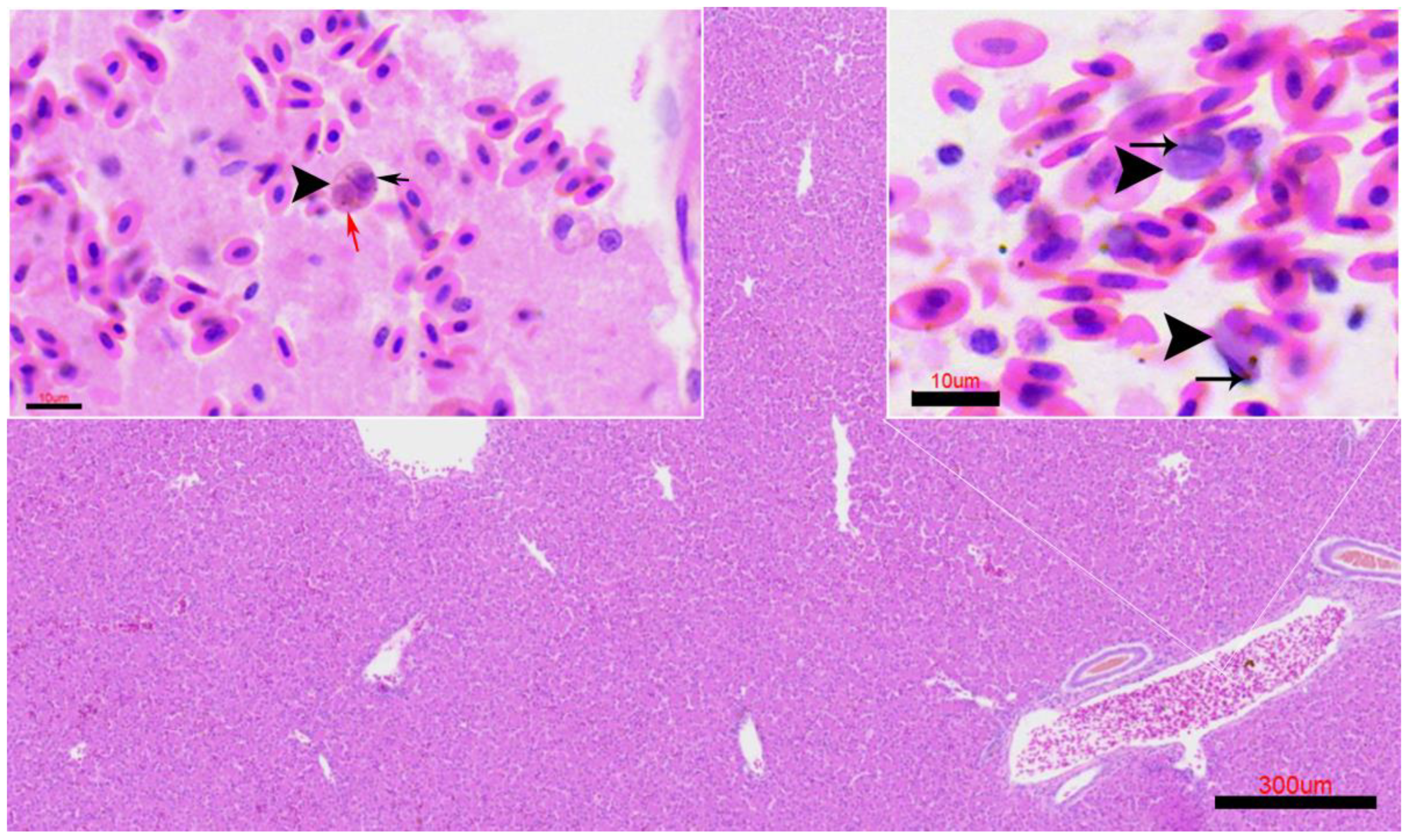
3.4. Histopathological Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IUSA | University Institute of Animal Health and Food Safety |
| ULPGC | University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria |
Appendix A
| ID | Age | Sex | FL | GC | FD | SS | DC | BC | Sample Tested | Haemosporidian PCR Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA324/20 | A | U | L | 29°6′35.86″ N, 13°33′21.72″ W | 30/07/2020 | D | 3 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| SA131/21 | J | F | L | 29°14′51.89″ N, 13°30′44.34″ W * | 08/08/2020 | D | 2 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| SA132/21 | A | F | L | 28°56′57.90″ N, 13°46′16.37″ W * | 03/09/2020 | D | 3 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| SA133/21 | A | F | L | 29°3′49.73″ N, 13°33′55.21″ W * | 24/11/2020 | D | 3 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| SA134/21 | J | M | L | 28°56′37.94″ N, 13°46′47.15″ W * | 04/12/2020 | D | 2 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA255/21 | J | M | F | 28°30′21.84″ N, 13°53′2.39″ W | 20/06/2018 | D | 3 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA334/21 | A | M | GC | 28°6′13.79″ N, 15°41′58.93″ W * | 22/04/2021 | D | 2 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA359/21 | A | U | T | 29°4′34.42″ N, 13°31′19.56″ W | 29/04/2021 | D | 3 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA447/21 | J | U | L | 29°5′31.98″ N, 13°37′24.62″ W | 24/05/2021 | D | 3 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| SA485/21 | A | F | L | 28°59′35.28″ N, 13°36′18.00″ W | 08/04/2021 | D | 2 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA518/21 | J | M | L | 28°59′35.28″ N, 13°36′18.00″ W | 06/04/2021 | D | 2 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA597/21 | J | M | L | 28°56′55.55″ N, 13°36′22.06″ W | 21/12/2018 | D | 2 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA849/21 | J | U | GC | 28°5′1.74″ N, 15°27′18.20″ W | 27/08/2021 | D | 3 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA870/21 | J | M | GC | 28°6′38.85″ N, 15°28′21.07″ W * | U | D | 2 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| SA875/21 | J | F | L | 28°57′55.56″ N, 13°32′52.69″ W * | 07/06/2021 | D | 2 | U | Pool* | - |
| SA876/21 | A | M | L | 28°57′27.70″ N, 13°34′14.15″ W | 08/07/2021 | D | 2 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA877/21 | J | M | L | 29°7′52.43″ N, 13°27′45.56″ W | 29/06/2021 | D | 3 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA994/21 | J | M | L | 29°12′0.67″ N, 13°27′9.54″ W | 31/08/2021 | D | 3 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA1133/21 | A | M | T | 28°28′29.84″ N, 16°20′53.60″ W * | 22/0/2021 | D | 2 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA1156/21 | A | F | F | 28°36′2.63″ N, 13°55′19.53″ W * | 25/10/2021 | D | 3 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA1262/21 | A | F | T | 28°6′37.96″ N, 16°43′51.44″ W * | 04/11/2021 | D | 2 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA1295/21 | J | F | GC | 28°4′8.43″ N, 15°27′13.40″ W | U | D | 3 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA1296/21 | J | F | GC | 28°4′8.43″ N, 15°27′13.40″ W | 18/09/2021 | D | 2 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| SA1297/21 | A | F | GC | 28°4′8.43″ N, 15°27′13.40″ W | 28/09/2021 | D | 2 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA1298/21 | J | F | GC | 28°4′8.43″ N, 15°27′13.40″ W | U | D | 1 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA1411/21 | A | F | T | 28°28′37.20″ N, 16°19′15.71″ W | 30/11/2021 | D | 3 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA1417/21 | A | F | T | 28°28′37.20″ N, 16°19′15.71″ W | 07/09/2021 | D | 2 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA1438/21 | A | F | GC | 28°4′8.43″ N, 15°27′13.40″ W | 12/11/2021 | D | 2 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA1439/21 | A | M | GC | 28°4′8.43″ N, 15°27′13.40″ W | U | D | 2 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA1505/21 | A | U | L | 28°58′44.49″ N, 13°31′4.29″ W | 26/11/2021 | D | 2 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| SA1506/21 | A | F | L | 29°3′50.86″ N, 13°33′20.79″ W * | 10/11/2021 | D | 3 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| SA061/22 | A | M | L | 28°58′22.42″ N, 13°35′7.82″ W | 10/12/2021 | D | 3 | 2 | Lung | - |
| SA301/22 | A | F | L | 29°6′15.60″ N, 13°28′21.07″ W | 27/02/2022 | D | 3 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA1246/22 | C | U | GC | 28°4′8.43″ N, 15°27′13.40″ W | 05/05/2022 | D | 3 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA1267/22 | A | F | GC | 28°7′12.30″ N, 15°28′56.82″ W * | 31/05/2022 | A | 3 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA1269/22 | J | U | GC | 28°6′32.11″ N, 15°27′51.01″ W * | 08/08/2022 | A | 2 | U | Pool* | - |
| SA1277/22 | U | M | GC | 28°7′11.14″ N, 15°28′37.43″ W * | U | D | 2 | Pool* | - | |
| SA1283/22 | J | M | GC | 27°55′14.36″ N, 15°24′50.89″ W | 26/06/2022 | A | 2 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA1365/22 | A | F | H | 27°42′36.42″ N, 17°59′55.14″ W * | U | D | 3 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| SA1508/22 | J | M | GC | 28°6′41.54″ N, 15°29′26.38″ W * | 28/09/2022 | D | 2 | 3 | Pool* | - |
| SA1642/22 | A | M | L | 28°59′51.72″ N, 13°36′13.03″ W * | 03/10/2022 | D | 2 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| FS229/23 | J | U | L | 28°54′0.03″ N, 13°50′1.64″ W | 12/02/2023 | D | 2 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| FS415/23 | A | F | GC | 28°6′10.56″ N, 15°41′59.18″ W * | 05/05/2023 | A | 1 | 1 | Pool*, Liver, kidney, lung, skin | Leucocytozoon. CIAE02 linage. |
| FS0453/23 | A | M | L | 29°5′4.78″ N, 13°39′55.37″ W | 08/04/2023 | D | 2 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| FS0546/23 | A | F | GC | 28°7′6.68″ N, 15°31′21.48″ W * | U | D | 2 | 2 | Pool* | - |
| FS499/24 | A | M | GC | 28°6′27.51″ N, 15°35′0.19″ W * | 03/09/24 | A | 2 | 1 | Pool* | - |
| FS601/24 | A | M | GC | 28°3′53.96″ N, 15°27′44.07″ W | 25/06/24 | A | 2 | 1 | Pool* | - |
References
- Santiago-Alarcon, D.; Palinauskas, V.; Schaefer, H.M. Diptera vectors of avian Haemosporidian parasites: Untangling parasite life cycles and their taxonomy. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 928–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado-Piqueras, A.; Gómez-Muñoz, M.T.; Martín-Maldonado, B. Hemoparasites in Wild Birds: A Systematic Review of Their Ecology and Clinical Implications. Animals 2025, 15, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, C.T.; Thomas, N.J.; Hunter, D.B. Parasitic Diseases of Wild Birds; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–595. [Google Scholar]
- Valkiūnas, G.; Iezhova, T.A. Insights into the Biology of Leucocytozoon Species (Haemosporida, Leucocytozoidae): Why Is There Slow Research Progress on Agents of Leucocytozoonosis? Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecchio, A.; Collins, M.D.; Bell, J.A.; García-Trejo, E.A.; Sánchez-González, L.A.; Dispoto, J.H.; Rice, N.H.; Weckstein, J.D. Bird Tissues from Museum Collections Are Reliable for Assessing Avian Haemosporidian Diversity. J. Parasitol. 2019, 105, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgūnas, M.; Himmel, T.; Harl, J.; Dagys, M.; Valkiūnas, G.; Weissenböck, H. Exo-Erythrocytic Development of Avian Haemosporidian Parasites in European Owls. Animals 2022, 12, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkiunas, G. Avian Malaria Parasites and other Haemosporidia, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; p. 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.T.; Van Atkinson, C., III. Pathogenicity and epizootiology of avian haematozoa: Plasmodium, Leucocytozoon and Haemoproteus. In Bird-Parasite Interactions; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1991; pp. 19–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkiunas, G.; Iezhova, T.A. Exo-erythrocytic development of avian malaria and related haemosporidian parasites. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotta, I.A.; Valkiūnas, G.; Pacheco, M.A.; Escalante, A.A.; Hernández, S.R.; Matta, N.E. Disentangling Leucocytozoon parasite diversity in the neotropics: Descriptions of two new species and shortcomings of molecular diagnostics for leucocytozoids. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, M.R.; Hamer, S.A.; Hartup, B.K.; Snowden, K.F.; Medeiros, M.C.; Outlaw, D.C.; Hamer, G.L. A novel Haemosporida clade at the rank of genus in North American cranes (Aves: Gruiformes). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2017, 109, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabsley, M.J.; Vanstreels, R.E.T.; Martinsen, E.S.; Wickson, A.G.; Holland, A.E.; Hernandez, S.M.; Thompson, A.T.; Perkins, S.L.; West, C.J.; Bryan, A.L.; et al. Parasitaemia data and molecular characterization of Haemoproteus catharti from New World vultures (Cathartidae) reveals a novel clade of Haemosporida. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borner, J.; Pick, C.; Thiede, J.; Kolawole, O.M.; Kingsley, M.T.; Schulze, J.; Cottontail, V.M.; Wellinghausen, N.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Bruchhaus, I.; et al. Phylogeny of haemosporidian blood parasites revealed by a multi-gene approach. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2016, 94, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galen, S.C.; Borner, J.; Martinsen, E.S.; Schaer, J.; Austin, C.C.; West, C.J.; Perkins, S.L. The polyphyly of Plasmodium: Comprehensive phylogenetic analyses of the malaria parasites (Order Haemosporida) reveal widespread taxonomic conflict. R. Soc. Open. Sci. 2018, 5, 171780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outlaw, D.C.; Ricklefs, R.E. Rerooting the evolutionary tree of malaria parasites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13183–13187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinsen, E.S.; Perkins, S.L.; Schall, J.J. A three-genome phylogeny of malaria parasites (Plasmodium and closely related genera): Evolution of life-history traits and host switches. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2008, 47, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellgren, O.; Waldenström, J.; Bensch, S. A new PCR assay for simultaneous studies of Leucocytozoon, Plasmodium, and Haemoproteus from avian blood. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, S.; Hellgren, O.; PÉrez-Tris, J. MalAvi: A public database of malaria parasites and related haemosporidians in avian hosts based on mitochondrial cytochrome b lineages. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchoumbou, M.; Iezhova, T.; Hernández-Lara, C.; Duc, M.; Valkiūnas, G. Unravelling the patterns of exo-erythrocytic development of Haemoproteus parasites (Haemoproteidae, Haemosporida), with a case of abortive tissue stages in a naturally infected bird. Int. J. Parasitol. 2025, 55, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Baldaccini, N.E.; Baratti, M.; Caccamo, C.; Dessi-Fulghueri, F.; Grasso, R.; Pollonara, E.; Rodriguez, F.; Spena, M.T.; Giunchi, D. Preliminary molecular investigation and characterization of subspecies in the Stone Curlew [Burhinus oedicnemus]. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference of the European Ornithologists’ Union, Riga, Latvia, 27–30 August 2011; p. 268. [Google Scholar]
- de Juana, E.; Barros, C.; Rodríguez-Pascual, F.H. Alcaraván Común (Burhinus oedicnemus). In Libro Rojo de las Aves de España; Dirección General para la Biodiversidad—SEO/BirdLife: Madrid, Spain, 2004; pp. 216–223. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, J.A.; Barone, R.; Atienza, J.C. Alcaraván Común (Burhinus oedicnemus insularum). In Libro Rojo de las Aves España; Dirección General para la Biodiversidad—SEO/BirdLife: Madrid, Spain, 2004; pp. 221–223. [Google Scholar]
- Madroño, E.A.; González, C.; Atienza, C. Alcaraván Común (Canarias) Burhinus oedicnemus distinctus. In Libro Rojo de las Aves de España; Dirección General para la Biodiversidad—SEO/BirdLife: Madrid, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, A. Atlas de las Aves Nidificantes en la Isla de Tenerife; Instituto de Estudios Canarios: Tenerife, Spain, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, A.; Baldaccini, N.E.; Baratti, M.; Caccamo, C.; Dessì-Fulgheri, F.; Grasso, R.; Nouira, S.; Ouni, R.; Pollonara, E.; Rodriguez-Godoy, F.; et al. A first assessment of genetic variability in the Eurasian Stone-curlew Burhinus oedicnemus. Ibis 2014, 156, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Giunchi, D.; Rodríguez-Godoy, F.; Grasso, R.; Baldaccini, N.E.; Baratti, M. Multilocus approach reveals an incipient differentiation process in the Stone-curlew, Burhinus oedicnemus around the Mediterranean basin. Conserv. Genet. 2017, 18, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoncini, A.; Ramellini, S.; Falaschi, M.; Brambilla, M.; Martineau, A.; Massolo, A.; Giunchi, D. Steppe-land birds under global change: Insights from the Eurasian Stone-curlew (Burhinus oedicnemus) in the Western Palearctic. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 58, e03478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom-Rivero, A.; Fernández, A.; Marrero-ponce, L.; Padrón-Ramírez, D. Pathological and Molecular Characterization of Avipoxvirus Infection in Burhinus oedicnemus in the Canary Islands. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom-Rivero, A.; Fernández, A.; Marrero-Ponce, L.; Castro-Alonso, A.; Rivero-Herrera, C.; Caballero-Hernández, L.; Suárez-Santana, C.M.; Sierra, E. Molecular detection of a novel herpesvirus in the stone-curlew (Burhinus oedicnemus) from the Canary Islands. Avian Pathol. 2025, 54, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabuig, P.; Casal, A.B.; Camacho, M.; Orós, J. Wildlife: Poxvirus infection in stone curlews in the Canary Islands. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecis, R.; Secci, F.; Antuofermo, E.; Nuvoli, S.; Scagliarini, A.; Pittau, M.; Alberti, A. Multiple gene typing and phylogeny of avipoxvirus associated with cutaneous lesions in a stone curlew. Vet. Res. Commun. 2017, 41, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lierz, M.; Bergmann, V.; Isa, G.; Czerny, C.P.; Lueschow, D.; Mwanzia, J.; Prusas, C.; Hafez, H.H. Avipoxvirus infection in a collection of captive stone curlews (Burhinus oedicnemus). J. Avian Med. Surg. 2007, 21, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Santana, C.M.; Fernández, A.; Quesada-Canales, Ó.; Vela, A.I.; Navarro-Sarmiento, J.; Sierra, E. Bacteremia and Aortic Valvular Endocarditis in a Eurasian Stone-curlew (Burhinus oedicnemus distinctus) due to Streptococcus dysgalactiae. J. Wildl. Dis. 2022, 58, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rioja, L. 100 Aves Nidificantes y Migratorias más Comunes del Archipiélago Canario; SEO/BirdLife: San Cristóbal de La Laguan, Spain, 2018; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, J.A. Atlas de las Aves Nidificantes en el Archipiélago Canario (1997–2003); Dirección General de Conservación de la Naturaleza & Sociedad Española de Ornitología: Madrid, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liebich, H.G. Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th ed.; 5m Publishing: Sheffield, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- König, H.E.; Korbel, R.; Liebich, H.G. Avian Anatomy. Textbook and Colour Atlas, 2nd ed.; 5m Publishing: Sheffield, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rae, M.A. Practical avian necropsy. Semin. Avian Exotic Pet. Med. 2003, 12, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, K.; Matzenauer, C.; Neuhuber, F.; Monticelli, F.; Meyer, H.; Pittner, S.; Gotsmy, W. Suitability of specific soft tissue swabs for the forensic identification of highly decomposed bodies. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2021, 135, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errington, J.; Jones, R.M.; Sawyer, J. Use of tissue swabbing as an alternative to tissue dissection and lysis prior to nucleic acid extraction and real-time polymerase chain reaction detection of Bovine viral diarrhea virus and Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2014, 26, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis Version 12 for Adaptive and Green Computing. Mol Biol Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M.K. Haemoproteus burhinus A new species from the Stone Curlew Burhinus oedicnemus saharae (Reichenow) in Iraq. Bull. Iraq Nat. Hist. Mus. 1996, 8, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zagalska-Neubauer, M.; Bensch, S. High prevalence of Leucocytozoon parasites in fresh water breeding gulls. J. Ornithol. 2016, 157, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, A.; de la Puente, J.; Onrubia, A.; Pérez-Tris, J. Molecular characterization of haemosporidian parasites from kites of the genus Milvus (Aves: Accipitridae). Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krone, O.; Waldenström, J.; Valkiunas, G.; Lessow, O.; Müller, K.; Iezhova, T.A.; Fickel, J.; Bensch, S. Haemosporidian blood parasites in European birds of prey and owls. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harl, J.; Fauchois, A.; Puech, M.P.; Gey, D.; Ariey, F.; Izac, B.; Weissenböck, H.; Chakarov, N.; Iezhova, T.; Valkiūnas, G.; et al. Novel phylogenetic clade of avian Haemoproteus parasites (Haemosporida, Haemoproteidae) from Accipitridae raptors, with description of a new Haemoproteus species. Parasite 2024, 31, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciloglu, A.; Yildirim, A.; Duzlu, O.; Onder, Z.; Dogan, Z.; Inci, A. Investigation of avian haemosporidian parasites from raptor birds in Turkey, with molecular characterisation and microscopic confirmation. Folia Parasitol. 2016, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakarov, N.; Blanco, G. Blood parasites in sympatric vultures: Role of nesting habits and effects on body condition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisi, M.; Mabunda, N.; Gey, D.; Modise, N.O.; de Bruyn, M.; Lécu, A.; Laidebeure, S.; Saillier, A.; Thorel, M.; Iezhova, T.; et al. Diversity of haemosporidian parasites in cranes: Description of Haemoproteus balearicae and its phylogenetic position within the H. antigonis clade. Parasite 2025, 32, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-López, R.; Gangoso, L.; Martínez-De La Puente, J.; Fric, J.; López-López, P.; Mailleux, M.; Muñoz, J.; Touati, L.; Samraoui, B.; Figuerola, J. Low prevalence of blood parasites in a long-distance migratory raptor: The importance of host habitat. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagas, C.R.F.; Duc, M.; Himmel, T.; Eigirdas, V.; Weissenböck, H.; Valkiūnas, G. Exo-erythrocytic development of Leucocytozoon parasites (Haemosporida, Leucocytozoidae) in song thrushes Turdus philomelos. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2023, 22, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desser, S.S.; Fallis, A.M. The cytological development and encapsulation of megaloschizonts of Leucocytozoon simondi. Can. J. Zool. 1967, 45, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, A.; Fallis, A.M. Experimental Studies of the Life Cycle of Leucocytozoon simondi in Ducks in Norway. J. Protozool. 1972, 19, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.G.; Howe, L.; Gartrell, B.D.; Alley, M.R. Prevalence of Leucocytozoon spp, in the endangered yellow-eyed penguin Megadyptes antipodes. Parasitology 2010, 137, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.G. An Investigation of Leucocytozoon in the Endangered Yellow-Eyed Penguin (Megadyptes antipodes). Master’s Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2008; p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Himmel, T.; Harl, J.; Kübber-Heiss, A.; Konicek, C.; Fernández, N.; Juan-Sallés, C.; Ilgūnas, M.; Valkiūnas, G.; Weissenböck, H. Molecular probes for the identification of avian Haemoproteus and Leucocytozoon parasites in tissue sections by chromogenic in situ hybridization. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmel, T.; Harl, J.; Pfanner, S.; Nedorost, N.; Nowotny, N.; Weissenböck, H. Haemosporidioses in wild Eurasian blackbirds (Turdus merula) and song thrushes (T. philomelos): An in situ hybridization study with emphasis on exo-erythrocytic parasite burden. Malar J. 2020, 19, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkiunas, G.; Sehgal, R.N.M.; Iezhova, T.A.; Hull, A.C. Identification of Leucocytozoon toddi group (Haemosporida: Leucocytozoidae), with Remarks on the species taxonomy of leucocytozoids. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.T.; Lease, J.K.; Dusek, R.J.; Samuel, M.D. Prevalence of pox-like lesions and malaria in forest bird communities on leeward Mauna Loa Volcano, Hawaii. Condor 2005, 107, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.J.; Banda, M.; Alley, M.R.; Howe, L.; Gartrell, B.D. The seroprevalence of avipoxvirus and its association with avian malaria (Plasmodium spp.) infection in introduced passerine birds in the southern regions of the North Island of New Zealand. Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illera, J.C.; Emerson, B.C.; Richardson, D.S. Genetic characterization, distribution and prevalence of avian pox and avian malaria in the Berthelot’s pipit (Anthus berthelotii) in Macaronesia. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgin, L.G.; Illera, J.C.; Padilla, D.P.; Richardson, D.S. Biogeographical patterns and co-occurrence of pathogenic infection across island populations of Berthelot’s pipit (Anthus berthelotii). Oecologia 2012, 168, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecchio, A.; Chagas, C.R.F.; Bell, J.A.; Kirchgatter, K. Evolutionary ecology, taxonomy, and systematics of avian malaria and related parasites. Acta Trop. 2020, 204, 105364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Riper, C.; Van Riper, S.G.; Hansen, W.R. Epizootiology and effect of avian pox on Hawaiian forest birds. Auk 2002, 119, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Riper, C., III; Forrester, D.J. Avian Pox. January 2007. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9780470344668.ch6 (accessed on 10 November 2025).
- van der Meer, C.S.; Paulino, P.G.; Jardim, T.H.A.; Senne, N.A.; Araujo, T.R.; dos Santos Juliano, D.; Massard, C.L.; Peixoto, M.P.; da Costa Angelo, I.; Santos, H.A. Detection and molecular characterization of Avipoxvirus in Culex spp. (Culicidae) captured in domestic areas in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellgren, O.; Bensch, S.; Malmqvist, B. Bird hosts, blood parasites and their vectors—Associations uncovered by molecular analyses of blackfly blood meals. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmqvist, B.; Strasevicius, D.; Hellgren, O.; Adler, P.H.; Bensch, S. Vertebrate host specificity of wild-caught blackflies revealed by mitochondrial DNA in blood. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271 (Suppl. S4), 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakarov, N.; Kampen, H.; Wiegmann, A.; Werner, D.; Bensch, S. Blood parasites in vectors reveal a united blackfly community in the upper canopy. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černý, O.; Votýpka, J.; Svobodová, M. Spatial feeding preferences of ornithophilic mosquitoes, blackflies and biting midges. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2011, 25, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, G. Current State of the Blackfly (Simuliidae) Fauna of the Canary Islands, with New Records. Graellsia 2025, 81, e751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, D.P.; Carlos, J.; Gonzalez-quevedo, C.; Villalba, M.; Richardson, D.S. Factors affecting the distribution of haemosporidian parasites within an oceanic island. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gailbreath, K.L.; Oaks, J.L. Herpesviral inclusion body disease in owls and falcons is caused by the pigeon herpesvirus (columbid herpesvirus 1). J. Wildl. Dis. 2008, 44, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrel, S.; Deback, C.; Agut, H.; Boutolleau, D. Genotypic characterization of UL23 thymidine kinase and UL30 DNA polymerase of clinical isolates of herpes simplex virus: Natural polymorphism and mutations associated with resistance to antivirals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4833–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodawatta, K.H.; Synek, P.; Bos, N.; Garcia-del-Rey, E.; Koane, B.; Marki, P.Z.; Albrecht, T.; Lifjeld, J.; Poulsen, M.; Munclinger, P.; et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of avian host—Parasite interactions in the face of biogeographical range expansions. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 2431–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson-Coelho, M.; Silva, G.T.; Santos, S.S.; Miranda, L.S.; Araújo-Silva, L.E.; Ricklefs, R.E.; Miyaki, C.Y.; Maldonado-Coelho, M. Lower Detection Probability of Avian Plasmodium in Blood Compared to Other Tissues. J. Parasitol. 2016, 102, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaver, J.P.; John, S.K.; Seilern-macpherson, K.; Spiro, S.; Cunningham, A.A.; Lawson, B. The lineage diversity, spatiotemporal distribution and pathological significance of Plasmodium and Haemoproteus spp. infection of wild birds in Great Britain. Int. J. Parasitol.: Parasites Wildl. 2025, 28, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, R.E. The Role of Introduced Diseases in the Extinction of the Endemic Hawaiian Avifauna. Condor 2016, 70, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 Positive case).
Positive case).
 Positive case).
Positive case).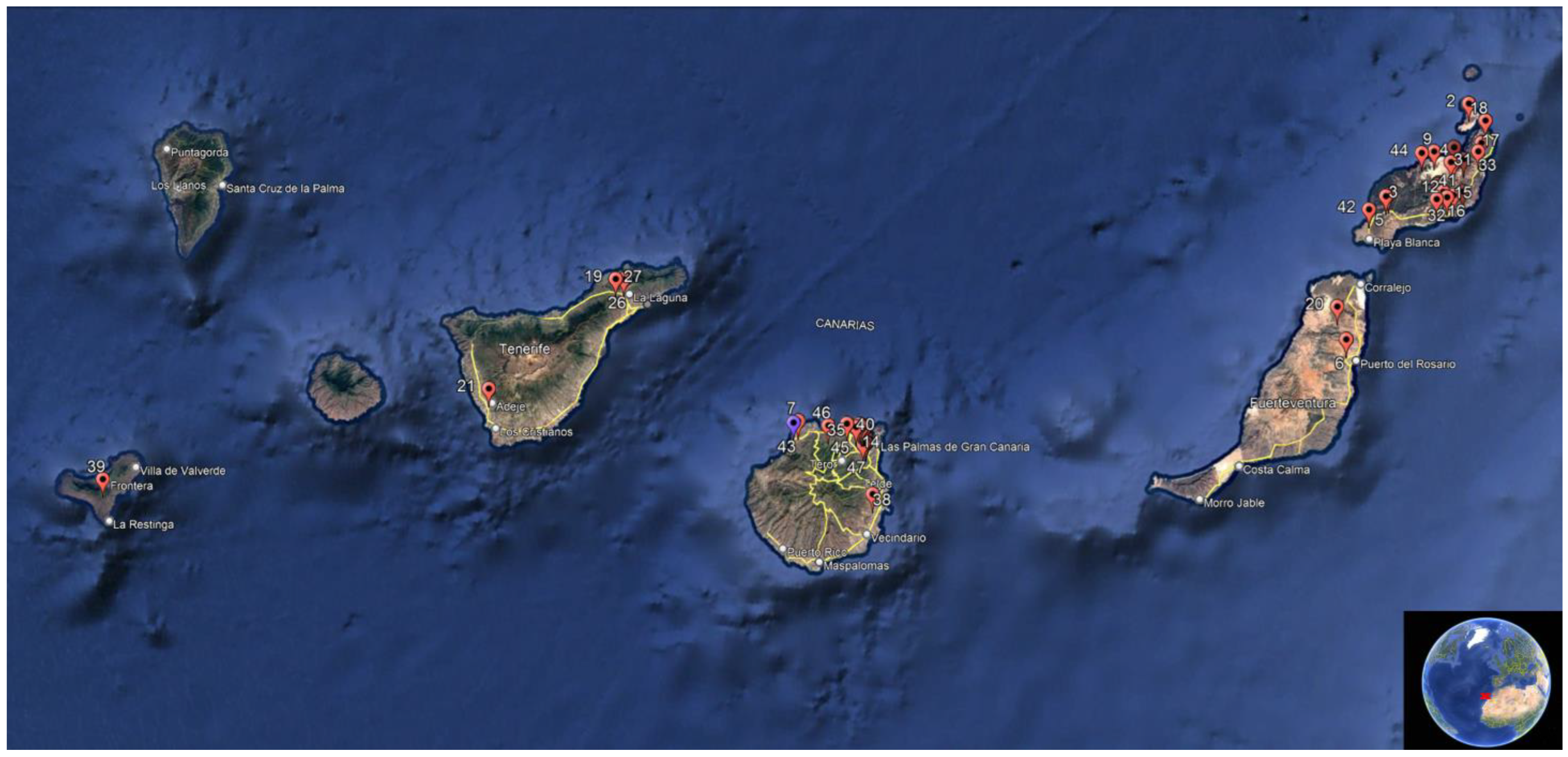

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colom-Rivero, A.; Fernández, A.; Marrero-Ponce, L.; Grandía-Guzmán, R.; Caballero-Hernández, L.; Rivero-Herrera, C.; Suárez-Santana, C.M.; Sierra, E. Survey of Haemosporidian Parasites in Wild Stone-Curlews (Burhinus oedicnemus) in the Canary Islands: First Molecular and Histopathological Evidence of Leucocytozoon sp. Infection. Animals 2025, 15, 3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233381
Colom-Rivero A, Fernández A, Marrero-Ponce L, Grandía-Guzmán R, Caballero-Hernández L, Rivero-Herrera C, Suárez-Santana CM, Sierra E. Survey of Haemosporidian Parasites in Wild Stone-Curlews (Burhinus oedicnemus) in the Canary Islands: First Molecular and Histopathological Evidence of Leucocytozoon sp. Infection. Animals. 2025; 15(23):3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233381
Chicago/Turabian StyleColom-Rivero, Ana, Antonio Fernández, Lucía Marrero-Ponce, Raiden Grandía-Guzmán, Lucía Caballero-Hernández, Candela Rivero-Herrera, Cristian M. Suárez-Santana, and Eva Sierra. 2025. "Survey of Haemosporidian Parasites in Wild Stone-Curlews (Burhinus oedicnemus) in the Canary Islands: First Molecular and Histopathological Evidence of Leucocytozoon sp. Infection" Animals 15, no. 23: 3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233381
APA StyleColom-Rivero, A., Fernández, A., Marrero-Ponce, L., Grandía-Guzmán, R., Caballero-Hernández, L., Rivero-Herrera, C., Suárez-Santana, C. M., & Sierra, E. (2025). Survey of Haemosporidian Parasites in Wild Stone-Curlews (Burhinus oedicnemus) in the Canary Islands: First Molecular and Histopathological Evidence of Leucocytozoon sp. Infection. Animals, 15(23), 3381. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233381







