Identification of Hydatigera Species in Wildcats (Felis silvestris) from Central Spain
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Parasite Species | Definitive Host | Intermediate Host | Country | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. taeniaeformis s.s. | Muridae | Japan | [16] | |
| Felidae (Felis silvestris catus) | Not indicated | Australia | [29] | |
| Muridae | India | [30,31] | ||
| Felidae (Felis silvestris catus) | Korea | [32] | ||
| Felidae (Prionailurus bengalensis) | Not indicated | China | [24] | |
| Canidae | Switzerland | [14] | ||
| Felidae | Australia | [33] | ||
| Muridae | India | |||
| Canidae (Canis lupus familiaris) | Germany | [34] | ||
| Felidae (Felis silvestris catus) | ||||
| Muridae | Kazakhstan, Turkey | [17] | ||
| Canidae (Canis lupus familiaris) | Japan | [15] | ||
| Not indicated | Belgium | [11] | ||
| Felidae (Felis silvestris catus) Stool | USA | [35] | ||
| Muridae | Serbia | [36] | ||
| Felidae (Felis silvestris catus) | Mexico | [37] | ||
| Felidae (Leopardus geoffroyi) | Brazil | [38] | ||
| Not indicated | Finland | [11] | ||
| Japan | ||||
| Muridae | Senegal | [39] | ||
| Muridae | Spain | [21] | ||
| H. kamiyai | Felidae (Felis silvestris catus) | Finland, France, Australia | [21] | |
| Felidae (Felis silvestris silvestris) | Italy | |||
| Felidae (Prionailurus bengalensis) | Russia | |||
| Muridae | Bosnia, Latvia, Russia, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Ethiopia, South Africa | |||
| Cricetidae | Finland, Norway, Russian, Sweden | |||
| Cricetidae | Poland | [40] | ||
| Cricetidae, Muridae, Soricidae | Luxembourg | [41] | ||
| Felidae (Felis silvestris silvestris) | [42] | |||
| Cricetidae, Muridae | Serbia | [36] | ||
| Felidae (Felis silvestris silvestris) | Germany | [43] | ||
| Felidae (Panthera leo) | Namibia | [44] | ||
| Cricetidae | China | [45] | ||
| Cricetidae, Muridae | Czech Republic | [46] | ||
| Not indicated | France | [47] | ||
| Nesomyidae | United Kingdom | [48] | ||
| Hydatigera sp. | Felidae (Felis silvestris catus) | France | [21] | |
| Felidae (Felis silvestris silvestris) | Italy | [20] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Origin
2.2. Initial Processing and Cestode Recovery
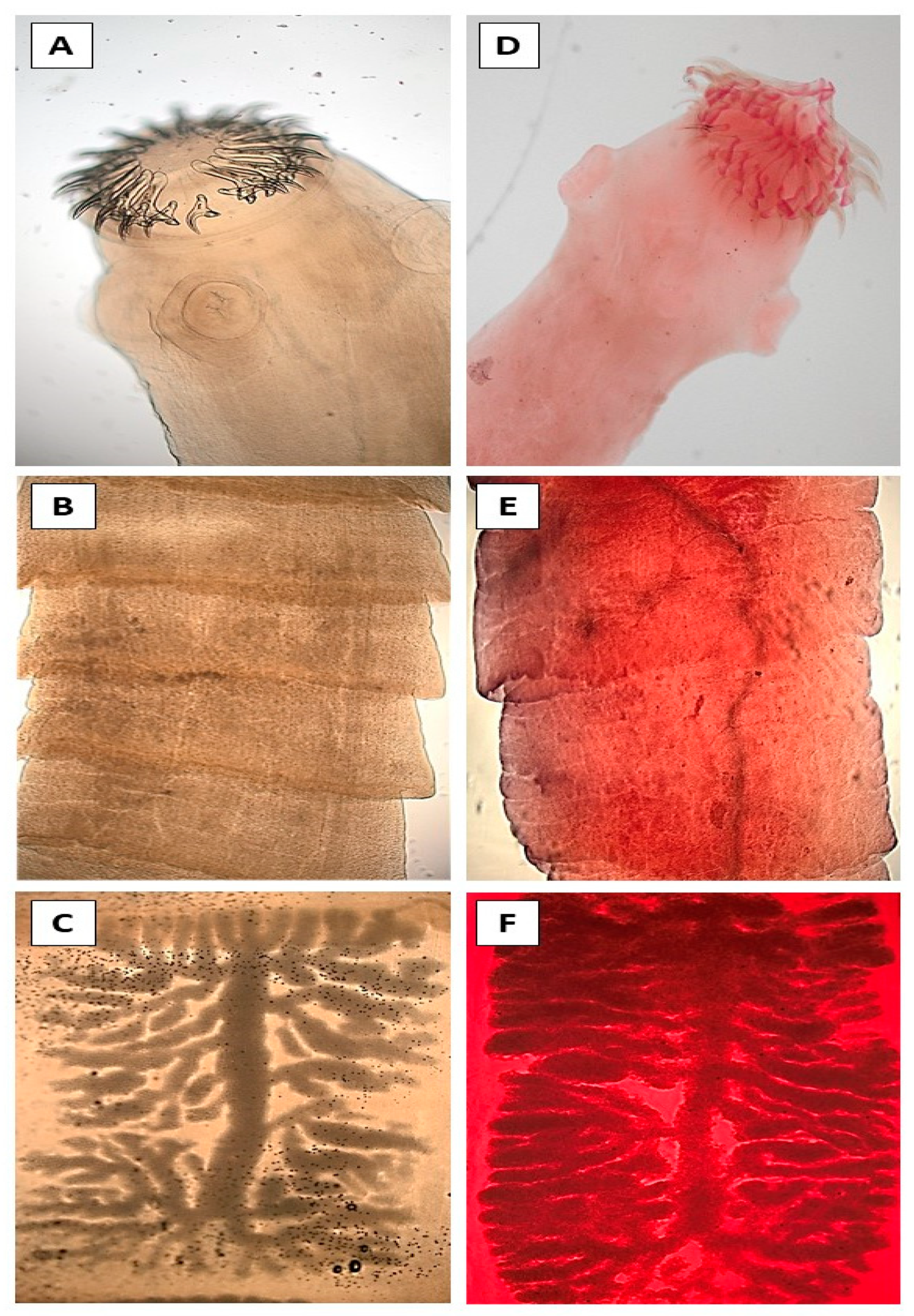
2.3. Staining and Morphological Identification
2.4. DNA Extraction
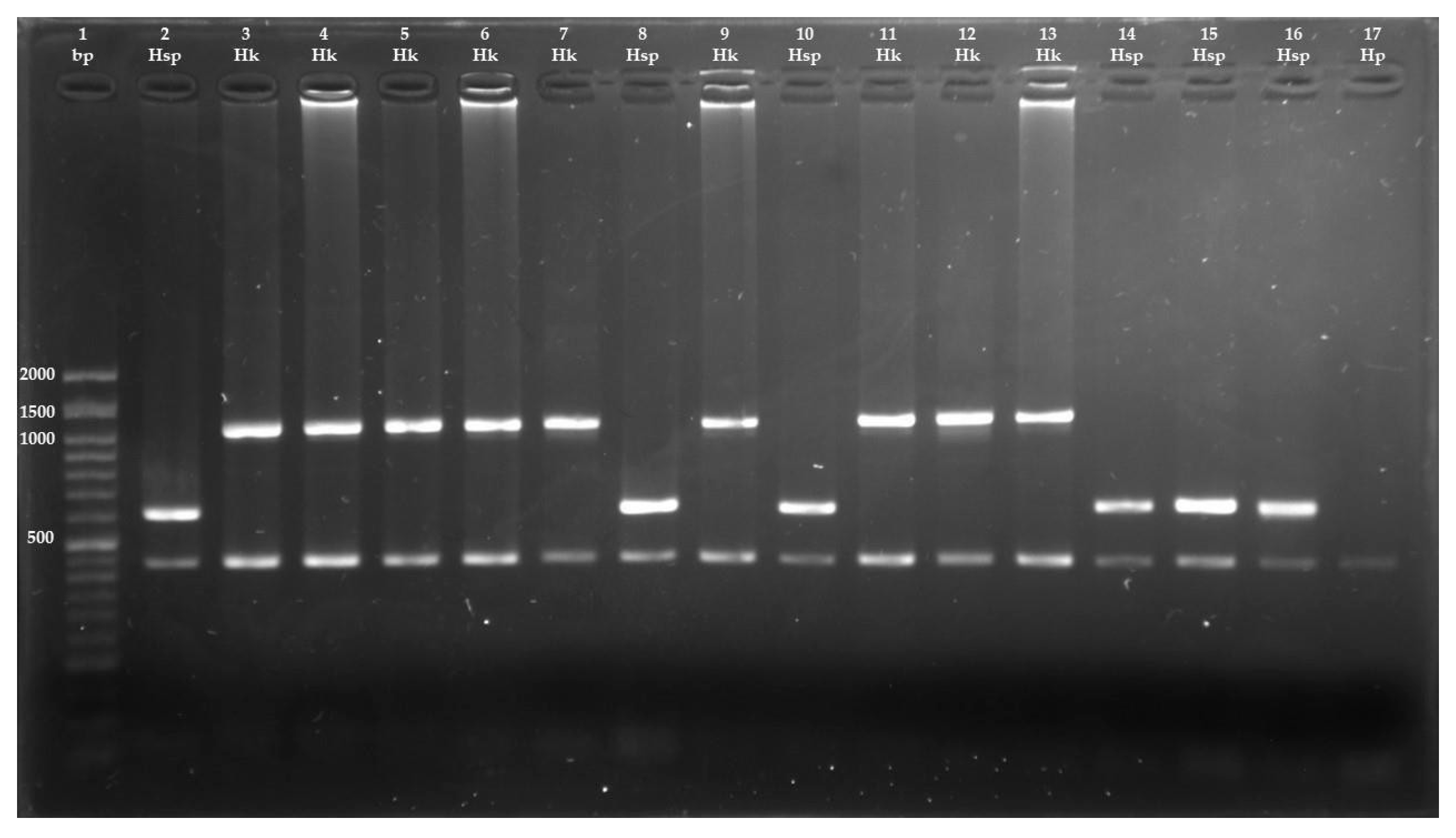
2.5. Molecular Identification of Hydatigera Species
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anile, S.; Bizzarri, L.; Lacrimini, M.; Sforzi, A.; Ragni, B.; Devillard, S. Home-range size of the European wildcat (Felis silvestris silvestris): A report from two areas in Central Italy. Mammalia 2017, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, A. Fauna Ibérica: Mamíferos, 1st ed.; Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales: Madrid, Spain, 1914; 441p. [Google Scholar]
- Palomo, L.J.; Gisbert, J.; Blanco, J.C. Atlas de los Mamíferos Terrestres de España; Dirección General de Conservación de la Naturaleza-SECEM-SECEMU: Madrid, Spain, 2007; 588p. [Google Scholar]
- López-Martín, J.M.; García, F.J.; Such, A.; Virgós, E.; Lozano, J.; Duarte, J.; España, A.J. Felis silvestris Schreber, 1777. In Atlas y Libro Rojo de los Mamíferos de España, 1st ed.; Palomo, J., Gisbert, J., Blanco, J.C., Eds.; Dirección General de Conservación de la Naturaleza-SECEM-SECEMU: Madrid, Spain, 2007; pp. 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Sánchez, J.M.; Barea-Azcón, J.M.; Jaramillo, J.; Herrera-Sánchez, F.J.; Jiménez, J.; Virgós, E. Fragmentation and low density as major conservation challenges for the southernmost populations of the European wildcat. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerngross, P. Felis silvestris: IUCN Red List Assessment; IUCN Red List Threat Species: Cambridge, UK, 2023; p. 8235. [Google Scholar]
- Malo, A.F.; Lozano, J.; Huertas, D.L.; Virgós, E. A change of diet from rodents to rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Is the wildcat (Felis silvestris) a specialist predator? J. Zool. 2004, 263, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, A.M.; Conboy, G.A.; Little, S.E.; Reichard, M.V. Veterinary Clinical Parasitology, 9th ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, D.D. Georgis’ Parasitology for Veterinarians, 11th ed.; Elsevier Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Verster, A. A taxonomic revision of the genus Taenia Linnaeus, 1758 s. str. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1969, 36, 3–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakao, M.; Lavikainen, A.; Iwaki, T.; Haukisalmi, V.; Konyaev, S.; Oku, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Ito, A. Molecular phylogeny of the genus Taenia (Cestoda: Taeniidae): Proposals for the resurrection of Hydatigera Lamarck, 1816 and the creation of a new genus Versteria. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, R.A. The cestode Taenia Krepkogorski (Schuld & Landa, 1934) in the Arabian sand-cat (Felis margarita Loche, 1858) in Bahrain. Bull. Br. Mus. Nat. Hist. Zool. 1972, 24, 183–197. [Google Scholar]
- Loos-Frank, B. An up-date of Verster’s (1969) Taxonomic revision of the genus Taenia Linnaeus’ (Cestoda) in table format. Syst. Parasitol. 2000, 45, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachsel, D.; Deplazes, P.; Mathis, A. Identification of taeniid eggs in the faeces from carnivores based on multiplex PCR using targets in mitochondrial DNA. Parasitology 2007, 134, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Morishima, Y.; Nagahama, S.; Horikoshi, T.; Edagawa, A.; Kawabuchi-Kurata, T.; Sugiyama, H.; Yamasaki, H. A coprological survey of intestinal helminthes in stray dogs captured in Osaka prefecture, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1409–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Bessho, Y.; Kamiya, M.; Kurosawa, T.; Horii, T. Phylogenetic relationships within Taenia taeniaeformis variants and other taeniid cestodes inferred from the nucleotide sequence of the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene. Parasitol. Res. 1995, 81, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavikainen, A.; Haukisalmi, V.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Henttonen, H.; Oksanen, A.; Meri, S. A phylogeny of members of the family Taeniidae based on the mitochondrial cox1 and nad1 gene data. Parasitology 2008, 135, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Lin, R.Q.; Li, M.W.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.G.; Sun, H.Q.; Zhao, G.H.; Zhang, K.X.; Zhu, X.Q. The complete mitchodrial genomes of three cestode species of Taenia infecting animals and humans. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 2249–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Yan, H.; Lou, Z.; Ni, X.; Dyachenko, V.; Li, H.; Littlewood, D.T. Mitochondrial genes and genomes support a cryptic species of tapeworm within Taenia taeniaeformis. Acta Trop. 2012, 123, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimberti, A.; Romano, D.F.; Genchi, M.; Paoloni, D.; Vercillo, F.; Bizzarri, L.; Sassera, D.; Bandi, C.; Genchi, C.; Ragni, B.; et al. Integrative taxonomy at work: DNA barcoding of taeniids harboured by wild and domestic cats. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavikainen, A.; Iwaki, T.; Haukisalmi, V.; Konyaev, S.V.; Casiraghi, M.; Dokuchaev, N.E.; Galimberti, A.; Halajian, A.; Henttonen, H.; Ichikawa-Seki, M.; et al. Reappraisal of Hydatigera taeniaeformis (Batsch, 1786) (Cestoda: Taeniidae) sensu lato with description of Hydatigera kamiyai n. sp. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.D.; Dai, G.D.; Li, L.; Littlewood, D.T.J.; Ohiolei, J.A.; Zhang, L.S.; Guo, A.M.; Wu, Y.T.; Ni, X.W.; Shumuye, N.A.; et al. Expansion of Cyclophyllidea Biodiversity in Rodents of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the “Out of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau” Hypothesis of Cyclophyllideans. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 747484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Cui, X.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shen, Y. Molecular identification of the potential fifth species within genus Hydatigera (Cestoda: Taeniidae) in rodents of Guangdong province, China. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl 2025, 28, 101126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Li, R.; Deng, Y.P.; Liu, G.H.; Fu, Y.T. Comparative Mitochondrial Genomic Analysis Robustly Supported That Cat Tapeworm Hydatigera taeniaeformis (Platyhelminthes: Cestoda) Represents a Species Complex. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 931137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaki, T.; Nonaka, N.; Okamoto, M.; Oku, Y.; Kamiya, M. Developmental and morphological characteristics of Taenia taeniaeformis (Batsch, 1786) in Clethrionomys rufocanus bedfordiae and Rattus norvegicus from different geographical locations. J. Parasitol. 1994, 80, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Casanova, J.C.; Feliú, C.; Gisbert, J.; Manfredi, M.T. Contribución al conocimiento de la cestodofauna de Felis silvestris en la Península Ibérica. RevIbér Parasotol 1989, 49, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Galindo, M.; Martínez-Carrasco Pleite, C.; Pérez-García, J.M.; Candela, M.G. Helmintofauna del gato montés (Felis silvestris silvestris) en el Sureste de la península Ibérica. In Proceedings of the Comunications Scientifiques à lal 37èmes Rencontres du Groupe d’Étude sur l’Ecophatologie de la Faune Sauvage de Montagne, Etroubles, Italy, 13–16 June 2019; p. 18. Available online: https://www.geefsm.eu/fran%C3%A7ais/rencontres-geefsm/2019-etroubles-val-d-aoest-i/ (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Wilcox, R.S.; Bowman, D.D.; Barr, S.C.; Euclid, J.M. Intestinal obstruction caused by Taenia taeniaeformis infection in a cat. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2009, 45, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, R.B.; Zhu, X.; McManus, D.P. NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 and cytochrome c oxidase subunit I sequences compared for members of the genus Taenia (Cestoda). Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh Kumar, J.; Reddy, P.L.; Aparna, V.; Srinivas, G.; Nagarajan, P.; Venkatesan, R.; Sreekumar, C.; Sesikarian, B. Strobilocercus fasciolaris infection with hepatic sarcoma and gastroenteropathy in a Wistar colony. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 141, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; (Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Kolkata, India); Bera, A.K.; (Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Kolkata, India); Konar, A.; (Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Kolkata, India); Bera, B.C.; (Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Kolkata, India); Das, S.K.; Bhattacharya, D.; (Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Kolkata, India). Report of sequence of cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 (CO1) gene of Taenia taeniaeformis isolated from Indian Black Rat (Rattus ratus). GenBank record number EF090612–EF090613. Unpublished work. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.U.; Chun, H.C.; Huh, S. Molecular phylogeny of parasitic Platyhelminthes based on sequences of partial 28S rDNA D1 and mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I. Korean J. Parasitol. 2007, 45, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, M.; Jones, A.; Allsopp, B.A.; Beveridg, I.; Schindler, A.R.; Gasser, R.B. Characterization of Taenia madoquae and Taenia regis from carnivores in Kenya using genetic markers in nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and their relationships with other selected taeniids. Mol. Cell. Probes. 2007, 21, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyachenko, V.; Pantchev, N.; Gawlowska, S.; Vrhovec, M.G.; Bauer, C. Echinococcus multilocularis infections in domestic dogs and cats from Germany and other European countries. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 157, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoggard, K.R.; Jarriel, D.M.; Bevelock, T.J.; Verocai, G.G. Prevalence survey of gastrointestinal and respiratory parasites of shelter cats in northeastern Georgia, USA. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2019, 16, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljević, M.; Rajičić, M.; Umhang, G.; Bajić, B.; Bjelić Čabrilo, O.; Budinski, I.; Blagojević, J. Cryptic species Hydatigera kamiyai and other taeniid metacestodes in the populations of small mammals in Serbia. Parasit. Vectors 2023, 16, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Giles, V.; Hortelano-Moncada, Y.; Torres-Carrera, G.; Gil-Alarcón, G.; Oceguera-Figueroa, A.; García-Prieto, L.; Osorio-Sarabia, D.; Cervantes, F.A.; Arenas, P. Helminths of free-ranging dogs and cats in an urban natural reserve in Mexico City and their potential risk as zoonotic agents. PLoS ONE. 2024, 19, e0310302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignon, J.S.; dos Santos, T.S.; Meireles, G.R.; Martins, K.R.; Zoia, W.A.; Soares, M.P.; de Holleben Camozzato Fadrique, F.; Cunha, R.C.; Monteiro, S.G.; Pappen, F.G.; et al. First record of Hydatigera taeniaeformis in Geoffroy’s cat (Leopardus geoffroyi) in Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2024, 54, 101100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, S.; Bâ, K.; Diouf, N.D.; Léger, E.; Verocai, G.G.; Webster, J.P. Rodents of Senegal and their role as intermediate hosts of Hydatigera spp. (Cestoda: Taeniidae). Parasitology 2019, 146, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, A.; Alsarraf, M.; Dwuznik, D.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Kolodziej-Sobocinska, M.; Behnke-Borowczyk, J.; Banasiak, L.; Grzybek, M.; Tolkacz, K.; Kartawik, N.; et al. Rodents as intermediate hosts of cestode parasites of mammalian carnivores and birds of prey in Poland, with the first data on the life-cycle of Mesocestoides melesi. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, M.; Dumendiak, S.; Gagliardo, A.; Ragazzini, F.; La Rosa, L.; Giunchi, D.; Thielen, F.; Romig, T.; Massolo, A.; Wassermann, M. Echinococcus multilocularis and Other Taeniid Metacestodes of Muskrats in Luxembourg: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Parasite Reproduction, and Genetic Diversity. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mederle, N.; Darabus, G.; Stancu, A.; Pentea, M.; Imre, M.; Luca, I.; Pavlovic, I.; Zdravković, N. Intestinal endo-parasitism in wild cat (Felis silvestris) from Banat area (Romania). Helminthologia 2023, 60, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisterfeld, K.; Raulf, M.K.; Waindok, P.; Springer, A.; Lang, J.; Lierz, M.; Siebert, U.; Strube, C. Endoparasites of peritoneal organs and skeletal muscles of the European wildcat (Felis silvestris) in Germany. Parasit. Vectors 2024, 17, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumendiak, S.; Halajian, A.; Mekonnen, Y.T.; Aschenborn, O.; Camacho, G.J.; Schuster, R.K.; Mackenstedt, U.; Roming, T.; Wassermann, M. Hidden diversity of cestodes in wild African carnivores: I. Non-taeniid cyclophyllideans. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl 2024, 24, 100929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Y. Morphological observation, molecular identification and evolutionary analysis of Hydatigera kamiyai found in Neodon fuscus from the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2024, 123, 105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husák, T.; Čadková, Z.; Máca, O.; Kouba, M.; Klimková, Z.; Sehnal, R.; Nápravníková, J.; Hrabětová, V.; Jankovská, I.; Vadlejch, J.; et al. Molecular identification of zoonotic taeniids metacestodes in several rodent species trapped in Central Europe. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1571082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferte, H.; (Institut de Parasitologie et Pathologie tropicale, Strasbourg, France); Brunet, J.; (Institut de Parasitologie et Pathologie tropicale, Strasbourg, France). Hydatigera kamiyai isolate POC1 cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COX1) gene, partial cds; mi-tochondrial. GenBank record number PV414379. Unpublished work. 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Waeschenbach, A.; (Natural History Museum, London, UK); Griffin, C.; (Natural History Museum, London, UK); Littlewood, D.T.J.; (Natural History Museum, London, UK). Hydatigera kamiyai isolate Worm1_cox1 cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COX1) gene, partial cds; mitochondrial. GenBank record number PQ463655–PQ463656, PA463695–PQ463696, PQ479104–PQ479105. Unpublished work. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Oleinik, Y. Age determination of the wildcat (Felis silvestris): A case study of a sample from the North-Western Black Sea region (Ukraine). Theriol. Ukr. 2024, 28, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Perea, R.; Baquero, R. Age estimation in Iberian wildcats Felis silvestris, by canine tooth sections. Acta Theriol. 1999, 44, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, B.; Biserkov, V.; Genov, T. In toto staining method for cestodes with iron acetocarmine. Helminthologia 1986, 23, 279–281. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, L.F.; Jones, A.; Bray, R.A. Keys to the Cestode Parasites of Vertebrates, 1st ed.; CAB Int.: Wallingford, UK, 1994; p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. The Condensed Protocols. From Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bowles, J.; Blair, D.; McManus, D.P. Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial sequencing. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1992, 54, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, H.; Okamoto, M.; Oku, Y.; Kamiya, M. Intraspecific variation of Taenia taeniaeformis as determined by various criteria. Parasitol. Res. 1995, 81, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabi, M.N.S.; Kapel, C.M.O. First report of Eucoleus boehmi in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in Denmark, based on coprological examination. Acta Parasitol. 2013, 58, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krone, O.; Guminsky, O.; Meinig, H.; Herrmann, M.; Trinzen, M.; Wibbelt, G. Endoparasite spectrum of wild cats (Felis silvestris Schreber, 1777) and domestic cats (Felis catus L.) from the Eifel, Pfalz region and Saarland, Germany. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2008, 54, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Madi, M.A.; Pal, P.; Al-Thani, A.; Lewis, J.W. Descriptive epidemiology of intestinal helminth parasites from stray cat populations in Qatar. J. Helminthol. 2008, 82, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Madi, M.A.; Behnke, J.M.; Prabhaker, K.S.; Al-Ibrahim, R.; Lewis, J.W. Intestinal helminths of feral cat populations from urban and suburban districts of Qatar. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 168, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakou, A.; Migli, D.; Dimzas, D.; Morelli, S.; Di Cesare, A.; Youlatos, D.; Lymberakis, P.; Traversa, D. Endoparasites of european wildcats (Felis silvestris) in Greece. Pathogens 2021, 10, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adalid, R.; Feliu, C.; Somoano, A.; Miñarro, M.; Ventura, J.; Torres, J.; Miquel, J.; Fuentes, M.V. Ecological analysis of the helminth community of Microtus lusitanicus (Gerbe, 1879) (rodentia) in asturias (nw spain). Animals 2021, 11, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, M.V.; Puchades-Colera, P.; Gosálvez, C.; Sáez-Durán, S.; Cholvi-Simó, M.; Ruvira, S.; Sanxis-Furió, J.; Pascual, J.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Franco, S.; et al. The Role of the Norway Rat, Rattus norvegicus, as a Reservoir of Zoonotic Helminth Species in the City of Barcelona (Spain). Animals 2025, 15, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljević, M.; Rajičić, M.; Marco, J.; Blagojević, J.; Rodríguez-Pastor, R.; Bajić, B.; Millán, J. Hydatigera parva population genetics in Iberian rodents provides insights into its introduction from Africa. Parasitology 2025, 152, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdmann, H.; Moks, E.; Talvik, H. Helminth Fauna of Eurasian Lynx (Lynx lynx) in Estonia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2004, 40, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, W.M. Studies on Hydatigera taeniaeformis I. Growth of the Larval Stage. J. Parasitol. 1958, 44, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, D.G.; Scheremeta, R.G.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Sinkoc, A.L.; Pacheco, R.C. Survey of helminth parasites of cats from the metropolitan area of Cuiabá, Mato Grosso, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2013, 22, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantó, G.J.; Guerrero, R.I.; Olvera-Ramírez, A.M.; Milián, F.; Mosqueda, J.; Aguilar-Tipacamú, G. Prevalence of Fleas and Gastrointestinal Parasites in Free-Roaming Cats in Central Mexico. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawy, M.N.; Imam, E.A. Studies on cestodes ofdomestic cats in Egypt with particular reference to species belonging to genera Diplopylidium and Joyeuxiella. J. Egypt. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1978, 38, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, R.K.; Thomas, K.; Sivakumar, S.; O’Donovan, D. The parasite fauna of stray domestic cats (Felis catus) in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.F.; Gaeib, S.Y. Isolation and Identification of different Intestinal Helminthes Groups from Stray Cats in Urban City of Kirkuk. Pakistan J. Med. Health Sci. 2021, 15, 1916–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbabi, M.; Hooshyar, H. Gastrointestinal parasites of stray cats in Kashan, Iran. Trop. Biomed. 2009, 26, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Changizi, E.; Mobedi, I.; Salimi-Bejestani, M.R.; Rezaei-Doust, A. Gastrointestinal Helminthic Parasites in Stray Cats (Felis catus) from North of Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2007, 2, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zibaei, M.; Sadjjadi, S.M.; Sarkari, B. Prevalence of Toxocara cati and other intestinal helminths in stray cats in Shiraz, Iran. Trop. Biomed. 2007, 24, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi-Storm, N.; Mejer, H.; Al-Sabi, M.N.; Olsen, C.S.; Thamsborg, S.M.; Enemark, H.L. Gastrointestinal parasites of cats in Denmark assessed by necropsy and concentration McMaster technique. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 214, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waap, H.; Gomes, J.; Nunes, T. Parasite communities in stray cat populations from Lisbon, Portugal. J. Helminthol. 2014, 88, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircean, V.; Titilincu, A.; Vasile, C. Prevalence of endoparasites in household cat (Felis catus) populations from Transylvania (Romania) and association with risk factors. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 171, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ponce, E.; González, J.F.; De Felipe, M.C.; Hernández, J.N.; Raduan Jaber, J. Epidemiological survey of zoonotic helminths in feral cats in Gran Canaria island (Macaronesian archipelago-Spain). Acta Parasitol. 2016, 61, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, C.; Lucientes, J.; Castillo, J.A.; Estrada, R.; Gracia, M.J.; Peribáñez, M.A.; Ferrer, M. Gastrointestinal helminth parasites in stray cats from the mid-Ebro Valley, Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 75, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchener, A.; Breitenmoser, C.; Eizirik, E.; Gentry, A.; Werdelin, L.; Wilting, A.; Yamaguchi, N.; Abramov, A.V.; Christiansen, P.; Driscoll, C.; et al. A revised taxonomy of the Felidae. The final report of the Cat Classification Task Force of the IUCN/SSC Cat Specialist Group. Cat News 2017, 11, 3–79. [Google Scholar]
| Hydatigera Species | Stage | Host Species | GenBank Accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| H. taeniaeformis s.s. | Adult | Felis catus | FJ597547 |
| Adult | Prionailurus bengalensis | ON055368 | |
| Adult | Not indicated | JQ663994 | |
| H. kamiyai | Adult | Not indicated | NC037071 |
| Adult | Not indicated | PP104554 | |
| Adult | Felis catus | LC008533 | |
| Hydatigera sp. | Larva | Eospolax fontanierii | NC061206 |
| Larva | Eospolax fontanierii | MW808981 | |
| H. parva | Larva | Not indicated | NC021141 |
| H. krepkogorski | Larva | Not indicated | NC021142 |
| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Expected Amplicon Size (bp) | Primer Location in mtDNA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cestodes | JB3 | TTTTTTGGGCATCCTGAGGTTTAT | 450 | cox1 |
| JB4.5 | TAAAGAAAGAACATAATGAAAATG | |||
| H. kamiyai | HD | TATTACTGGTGATACATTAATGCGTG | 1063 | cytb nad4 |
| HKAR | AARTAAAAACGTACCCAACTAGACAG | |||
| Hydatigera sp. | HD | TATTACTGGTGATACATTAATGCGTG | 618 | cytb |
| HSR | ATTAATCTTATCATAACGACAACTAATAATCC |
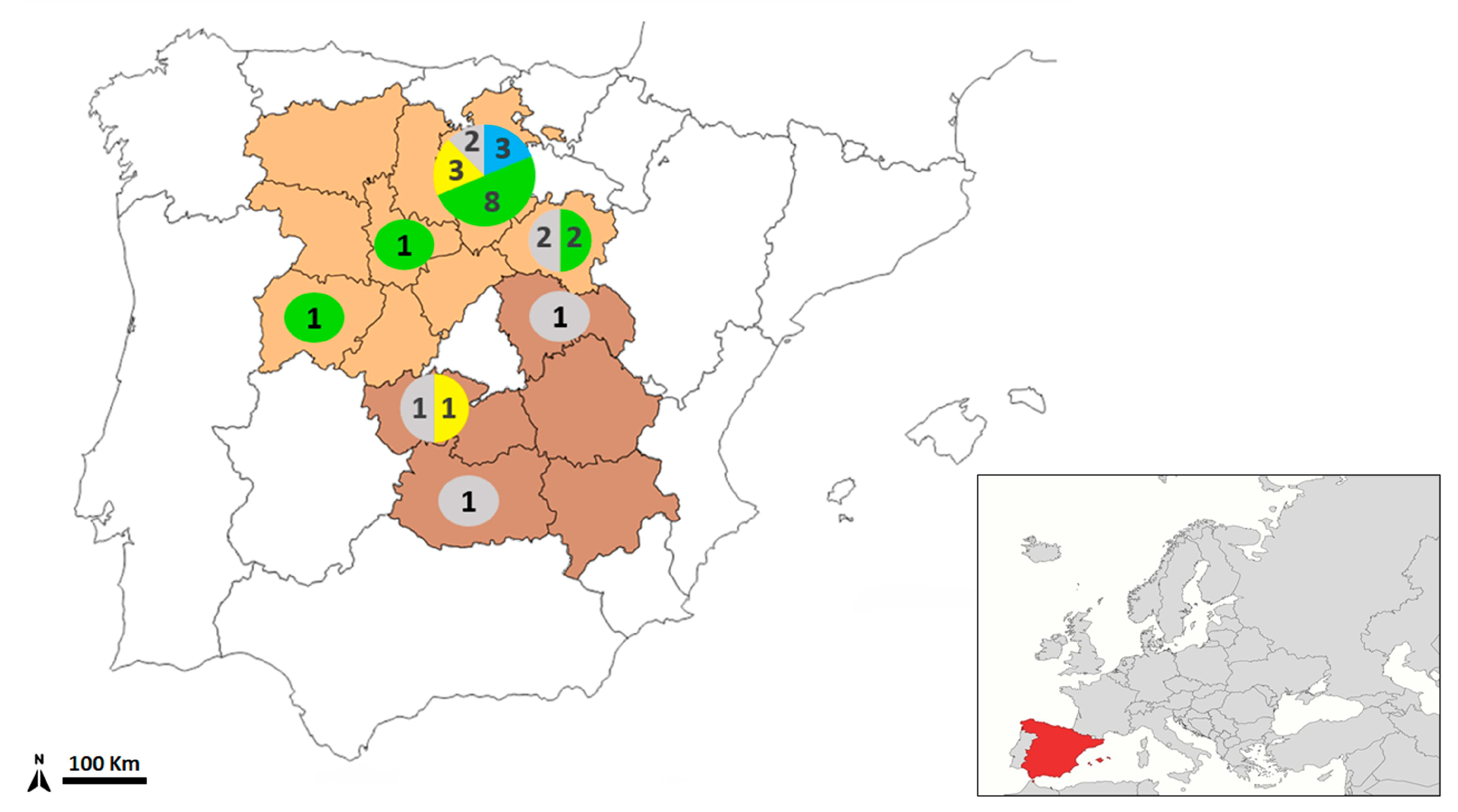
| Wildcat ID | Sex | Location | Hydatigera kamiyai | Hydatigera sp. | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147 | H | Burgos | - | 4 | 4 |
| 180 | M | Burgos | 11 | 6 | 17 |
| 198 | M | Burgos | 11 | - | 11 |
| 199 | M | Burgos | 6 | 4 | 10 |
| 211 | M | Burgos | 7 | - | 7 |
| 212 | M | Burgos | 8 | - | 8 |
| 236 | H | Burgos | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| 237 | H | Soria | 1 | 5 | 6 |
| 262 | M | Burgos | 19 | 1 | 20 |
| 263 | M | Salamanca | 11 | 4 | 15 |
| 268 | M | Burgos | 11 | 11 | 22 |
| 272 | M | Valladolid | 26 | 10 | 36 |
| 275 | M | Burgos | 3 | 7 | 10 |
| 317 | M | Burgos | - | 30 | 30 |
| 365 | M | Burgos | - | 13 | 13 |
| 366 | M | Soria | 2 | 3 | 5 |
| 367 | H | Burgos | 7 | 3 | 10 |
| 376 | H | Burgos | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| 412 | M | Toledo | - | 5 | 5 |
| Total | 5 H/14 M | 128 | 112 | 240 |
| Adults of Our Study (Mean) | Reference Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. kamiyai | Hydatigera sp. | H. kamiyai | H. taeniaeformis s.s. | ||
| Scolex width | 1270 ± 200 | 1470 ± 100 | 1960 ± 200 | 1300 ± 125 | |
| (1100–1580) | (1420–1550) | (1770–2170) | (1190–1440) | ||
| Rostellum diameter | 791 ± 82.7 | 846 ± 21 | 824 ± 89.5 | 736 ± 38 | |
| (700–902) | (817–863) | (731–910) | (703–779) | ||
| Number of hooks | 32 ± 3.2 | 35 ± 0.9 | 33 ± 5 | 38 ± 3 | |
| (28–36) | (34–36) | (30–40) | (36–42) | ||
| Length of large hooks | 421 ± 29 | 409 ± 25 | 426 ± 30 | 429 ± 37 | |
| (380–458) | (375–434) | (396–456) | (393–467) | ||
| Length of small hooks | 269 ± 18 | 254 ± 14 | 253 ± 31 | 266 ± 16 | |
| (266–286) | (247–273) | (213–275) | (249–281) | ||
| TL | 421 ± 29 | 409 ± 25 | 426 ± 30 | 425 ± 37 | |
| (380–458) | (375–434) | (396–456) | (393–467) | ||
| TW | 169 ± 22 | 167 ± 18 | 162 ± 10.5 | 181 ± 12 | |
| Large | (145–205) | (142–184) | (150–171) | (170–194) | |
| hooks | BL | 280 ± 41 | 293 ± 9 | 265 ± 14 | 286 ± 29 |
| (224–322) | (281–302) | (249–277) | (256–314) | ||
| AL | 191 ± 18 | 178 ± 27 | 192 ± 15.5 | 202 ± 8 | |
| (161–208) | (140–203) | (179–210) | (193–209) | ||
| GL | 71 ± 16 | 78 ± 15 | 75 ± 3.5 | 83 ± 11.5 | |
| (54–88) | (56–88) | (71–78) | (72–95) | ||
| GW | 66 ± 7 | 76 ± 8 | 62 ± 4 | 68 ± 13 | |
| (55–75) | (67–86) | (58–66) | (59–85) | ||
| BC | 40 ± 4 | 41 ± 5 | 37 ± 5.5 | 41 ± 7 | |
| (37–43) | (39–47) | (32–43) | (35–49) | ||
| HW | 53 ± 15 | 51 ± 7 | 48 ± 6.5 | 64 ± 12.5 | |
| (32–74) | (41–56) | (42–55) | (53–78) | ||
| TL | 269 ± 18 | 254 ± 14 | 253 ± 31 | 266 ± 16 | |
| (266–286) | (247–273) | (213–275) | (249–281) | ||
| TW | 122 ± 8 | 130 ± 8 | 114 ± 4 | 123 ± 13 | |
| Small | (114–132) | (121–140) | (110–118) | (111–137) | |
| hooks | BL | 155 ± 18 | 156 ± 4 | 126 ± 22 | 150 ± 7 |
| (140–185) | (150–160) | (111–155) | (145–159) | ||
| AL | 142 ± 13 | 145 ± 1 | 141 ± 8.5 | 154 ± 10 | |
| (124–161) | (144–146) | (131–148) | (146–166) | ||
| GL | 55 ± 6 | 61 ± 1 | 55 ± 6 | 55 ± 6 | |
| (47–64) | (59–62) | (50–62) | (48–60) | ||
| GW | 56 ± 5 | 51 ± 11 | 44 ± 11 | 50 ± 11 | |
| (49–62) | (39–65) | (35–57) | (40–62) | ||
| BC | 32 ± 6 | 32 ± 2 | 27 ± 7 | 38 ± 6 | |
| (23–38) | (29–34) | (20–34) | (32–44) | ||
| HW | 34 ± 2 | 33 ± 6 | 31 ± 5 | 34 ± 5.5 | |
| (33–37) | (25–40) | (25–35) | (29–40) | ||
| Sucker size (height × width) | 401 ± 52 × 350 ± 96 (320–460) × (246–456) | 381 ± 14 × 349 ± 38 (365–400) × (295–378) | 445 ± 57 × 399 ± 65 (396–510) × (333–463) | 300 ± 16.5 × 248 ± 20 (288–321) × (228–268) | |
| Number of uterine | 9 ± 1.5 | 9 ± 0.94 | 8 ± 2.5 | 9 ± 3.5 | |
| branches (unilateral) | (8–11) | (8–10) | (6–11) | (5–12) | |
| Host Species * | Prevalence | Origin | Mean Intensity (Range) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lynx pardinus | 2/8 (25%) | Spain | 1.50 (1–2) | [26] |
| Lynx lynx | 1/37 (3%) | Estonia | 1 | [64] |
| Felis silvestris | 8/15 (53%) | Germany | 8 (2–20) | [57] |
| 17/23 (73.9%) | Greece | - | [60] | |
| 7.7% | Scotland | - | [65] | |
| 21/27 (78%) | Spain | 12.6 (1–30) | This study | |
| Felis catus | 1/146 (0.68%) | Brazil | 1 | [66] |
| 14/358 (4%) | Mexico | 3 | [67] | |
| 20/51 (39%) | Egypt | - | [68] | |
| 370/488 (75.8%) | Qatar | - | [58] | |
| 484/658 (73.6%) | Qatar | 33.3 | [59] | |
| 40/240 (16.7%) | United Arab Emirates | 4 (1–79) | [69] | |
| 3/25 (12%) | Irak | - | [70] | |
| 17/113 (15%) | Iran | 0.35 | [71] | |
| 1/50 (2%) | Iran | - | [72] | |
| 13/114 (12.3%) | Iran | - | [73] | |
| 36/99 (36.4%) | Denmark | 8.1 (1–57) | [74] | |
| 5/162 (3.1%) | Portugal | (1–5) | [75] | |
| 11/414 (2.7%) | Romania | - | [76] | |
| 36/48 (75%) | Spain | - | [77] | |
| 5/58 (8.6%) | Spain | - | [78] | |
| Prionailurus bengalensis | 1/1 (100%) | China | 1 | [79] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matas-Méndez, P.; Esteban-Sánchez, L.; Ponce-Gordo, F.; Mateo-Barrientos, M. Identification of Hydatigera Species in Wildcats (Felis silvestris) from Central Spain. Animals 2025, 15, 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223340
Matas-Méndez P, Esteban-Sánchez L, Ponce-Gordo F, Mateo-Barrientos M. Identification of Hydatigera Species in Wildcats (Felis silvestris) from Central Spain. Animals. 2025; 15(22):3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223340
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatas-Méndez, Pablo, Lorena Esteban-Sánchez, Francisco Ponce-Gordo, and Marta Mateo-Barrientos. 2025. "Identification of Hydatigera Species in Wildcats (Felis silvestris) from Central Spain" Animals 15, no. 22: 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223340
APA StyleMatas-Méndez, P., Esteban-Sánchez, L., Ponce-Gordo, F., & Mateo-Barrientos, M. (2025). Identification of Hydatigera Species in Wildcats (Felis silvestris) from Central Spain. Animals, 15(22), 3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223340






