In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Autochthonous Probiotics and Their Effects on the Mucosal Health of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolation and Culture
2.2. In Vitro Assays
2.2.1. Pathogen Antagonism Assay
2.2.2. Haemolytic Activity
2.2.3. Qualitative Screening for Extracellular Enzyme Activity
2.3. Probiotic Activity in Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions
2.3.1. Pathogen Antagonism Against A. hydrophila in SIJ
2.3.2. Phytate Degradation Activity in Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids
- ε = molar absorptivity constant (µM−1cm−1);
- l = path length (1 cm);
- c = concentration (µM).
2.4. Bacterial Isolate Sequencing and Identification
2.5. Probiotic Diet Preparation
2.6. Experimental Design and Feeding
2.7. Growth Performance, Feed Utilisation, and Carcass Analyses
| Component | Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | PT1 | PT2 | |
| Dry matter | 93.2 ± 0.0 | 93.2 ± 0.1 | 93.2 ± 0.0 |
| Protein * | 43.5 ± 0.4 | 44.4 ± 0.4 | 44.1 ± 0.3 |
| Lipid * | 4.9 ± 0.1 | 5.1 ± 0.2 | 4.9 ± 0.2 |
| Ash * | 4.5 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.1 | 4.6 ± 0.2 |
| NFE *a | 47.1 ± 0.6 | 45.9 ± 0.6 | 46.4 ± 0.3 |
| GE (kJ/g) b | 20.3 ± 0.0 | 20.4 ± 0.0 | 20.3 ± 0.1 |
2.8. Histological and Electron Microscopy Analysis
2.9. Culture-Based Intestinal Microbiological Analysis
2.10. 16S rRNA Gene Metabarcoding Analysis
Diversity Indices
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Assays
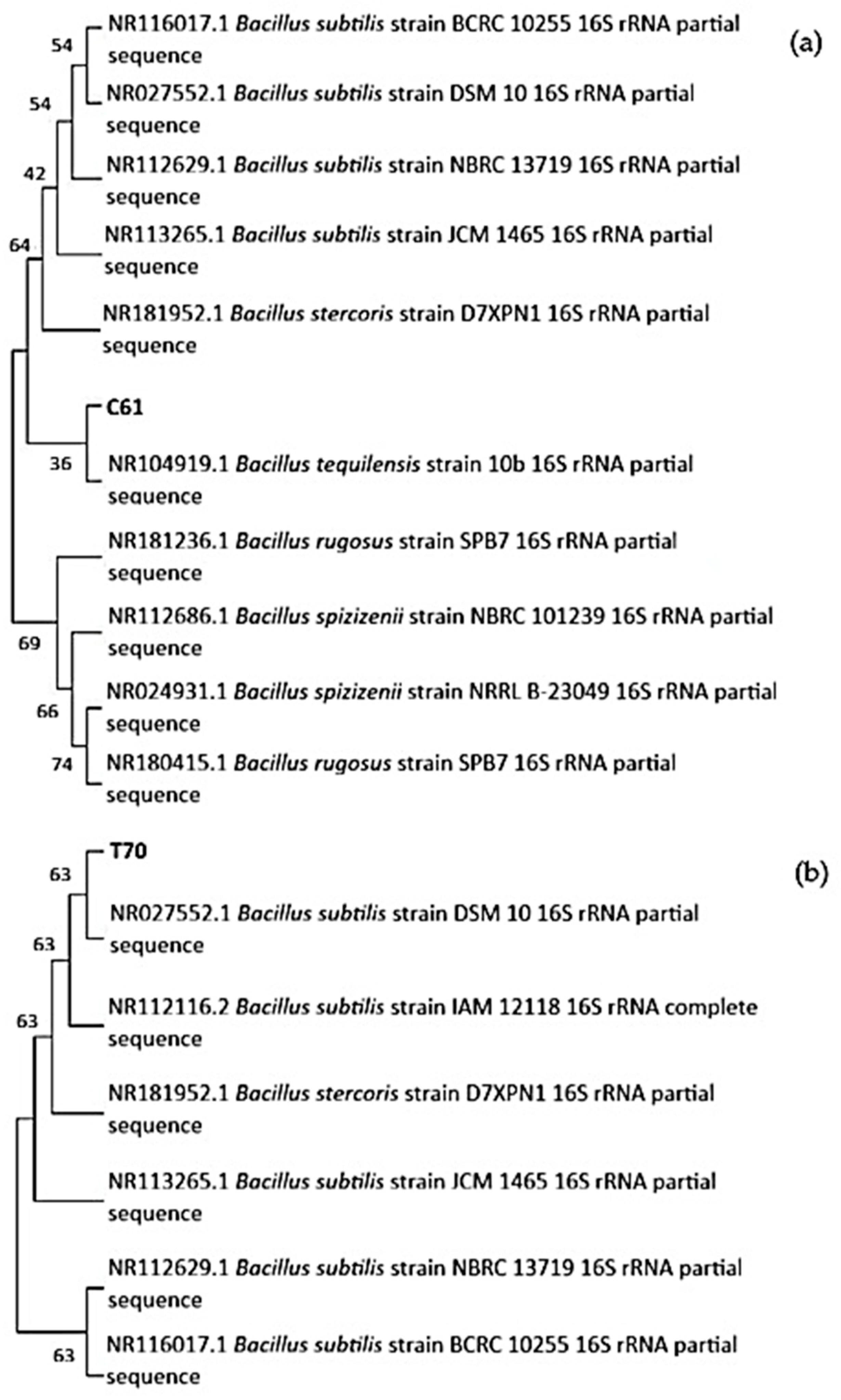
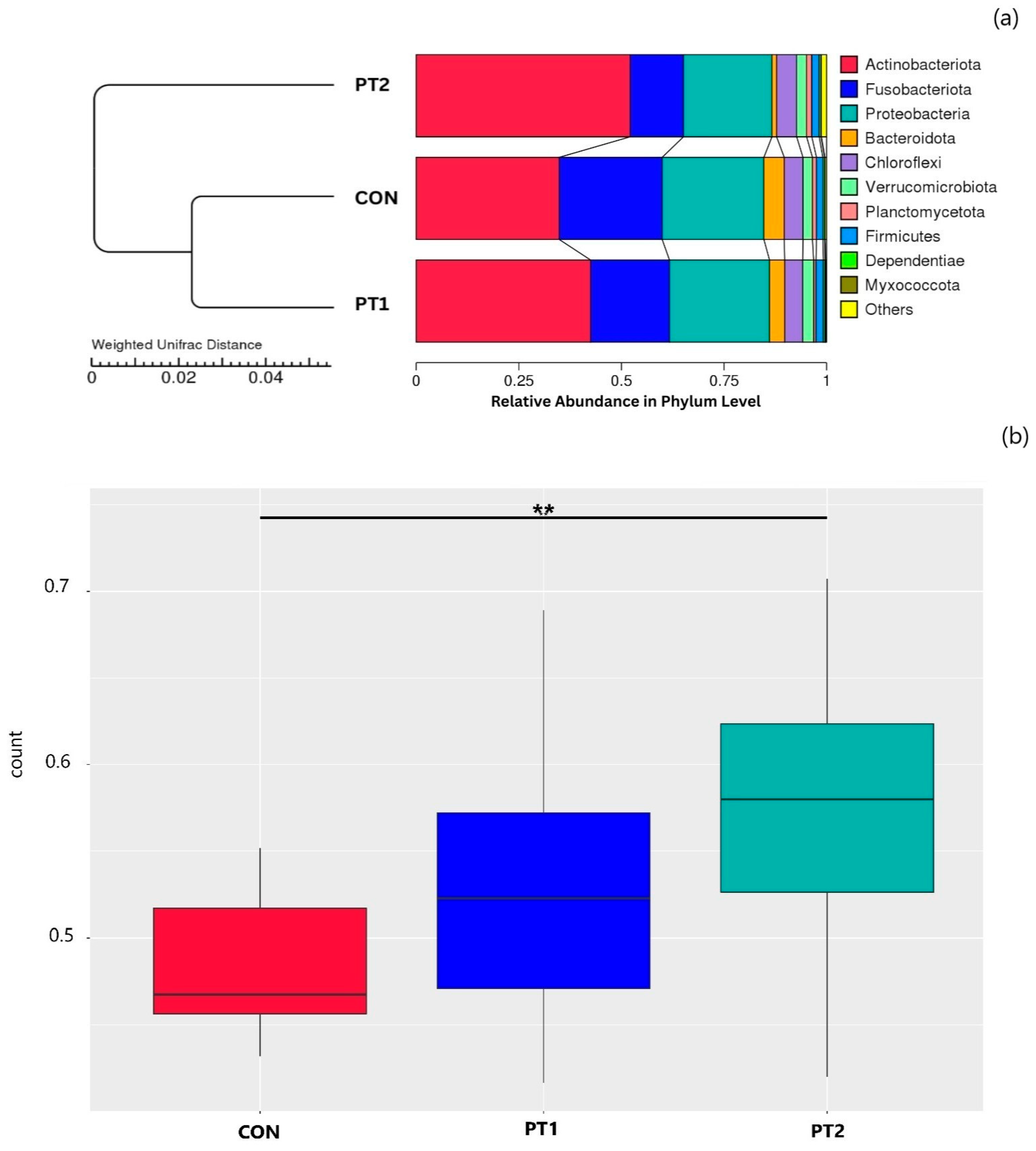
3.2. 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis
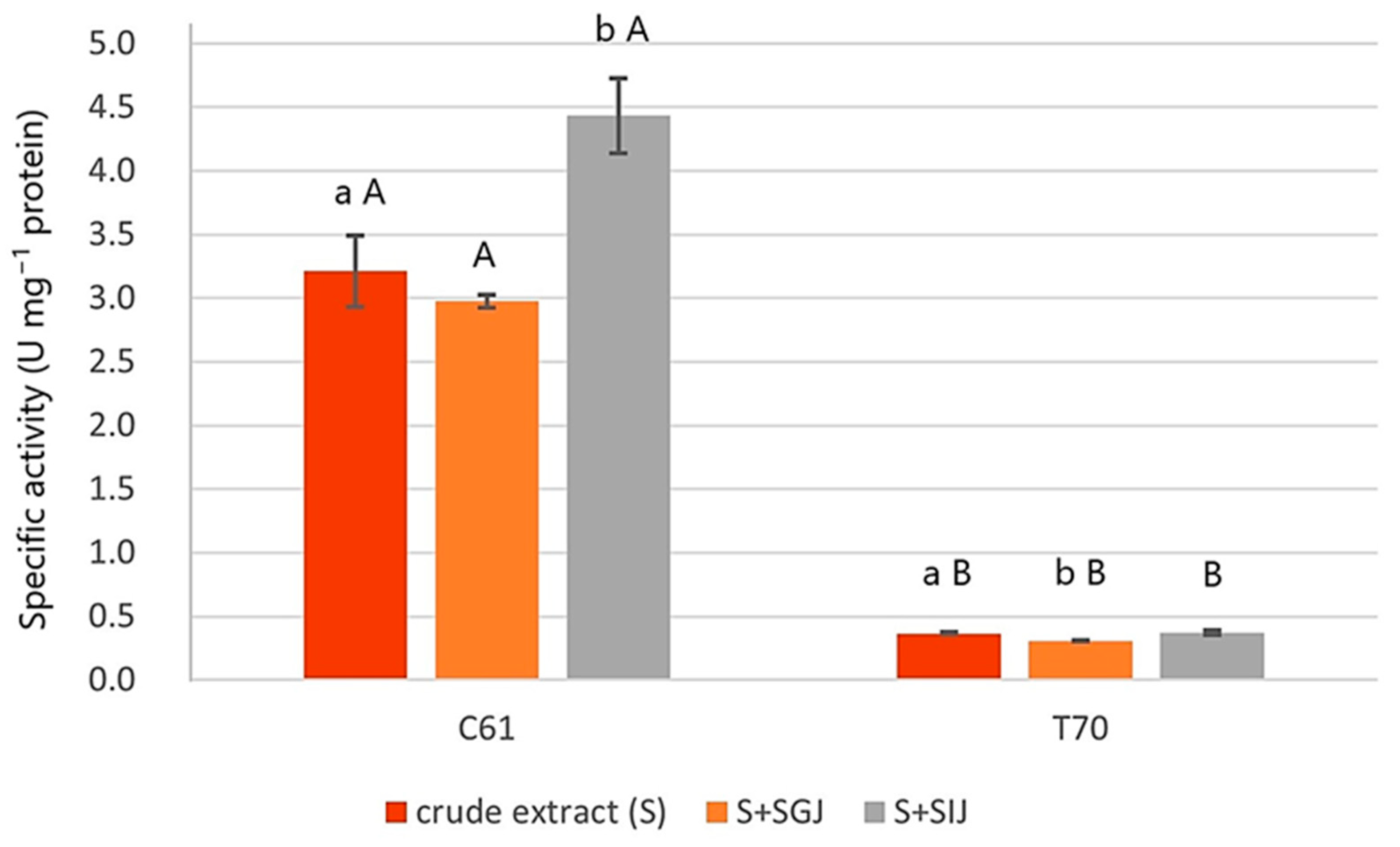
3.3. Probiotic Activity in Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions
3.3.1. Pathogen Antagonism in SIJ
3.3.2. Phytate Degradation Activity in Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids
3.4. Growth Performance, Feed Utilisation, and Carcass Composition
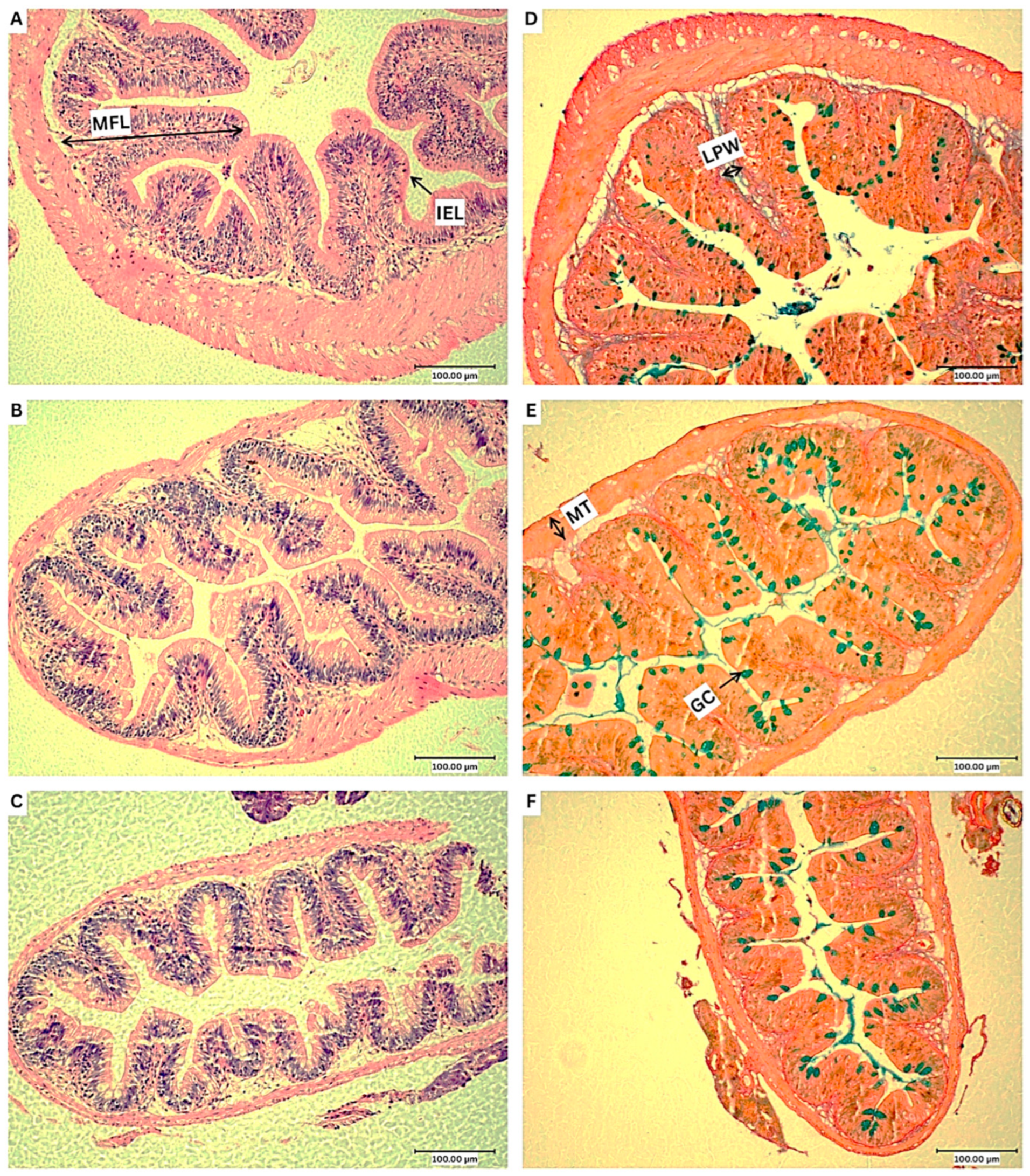
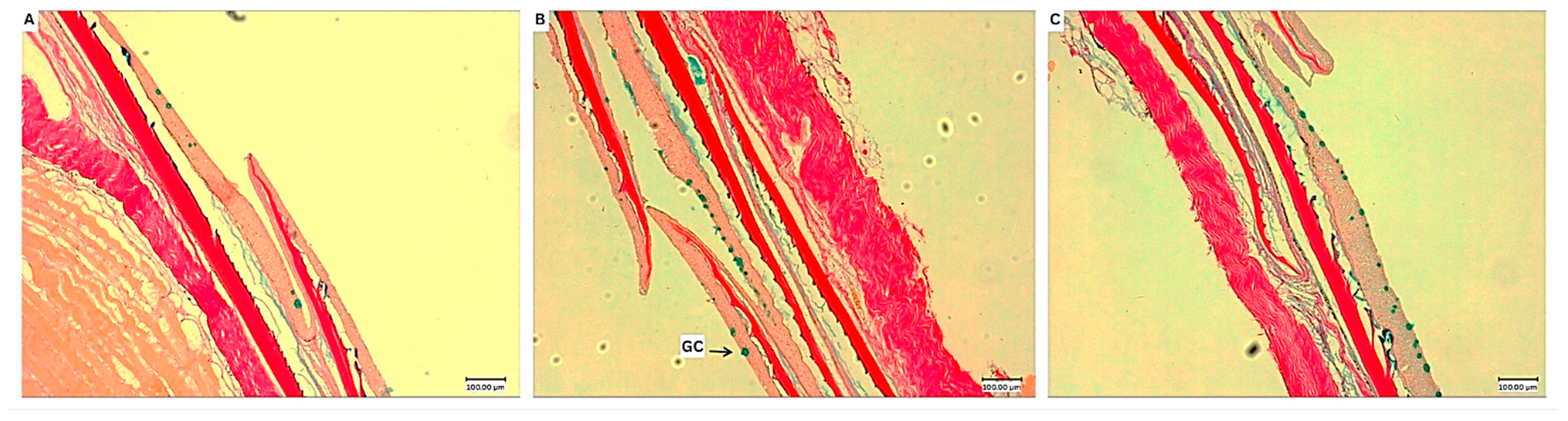
3.5. Histological Analysis
3.6. Intestinal Microbiological Analysis
3.7. Intestinal Microbiota Metabarcoding
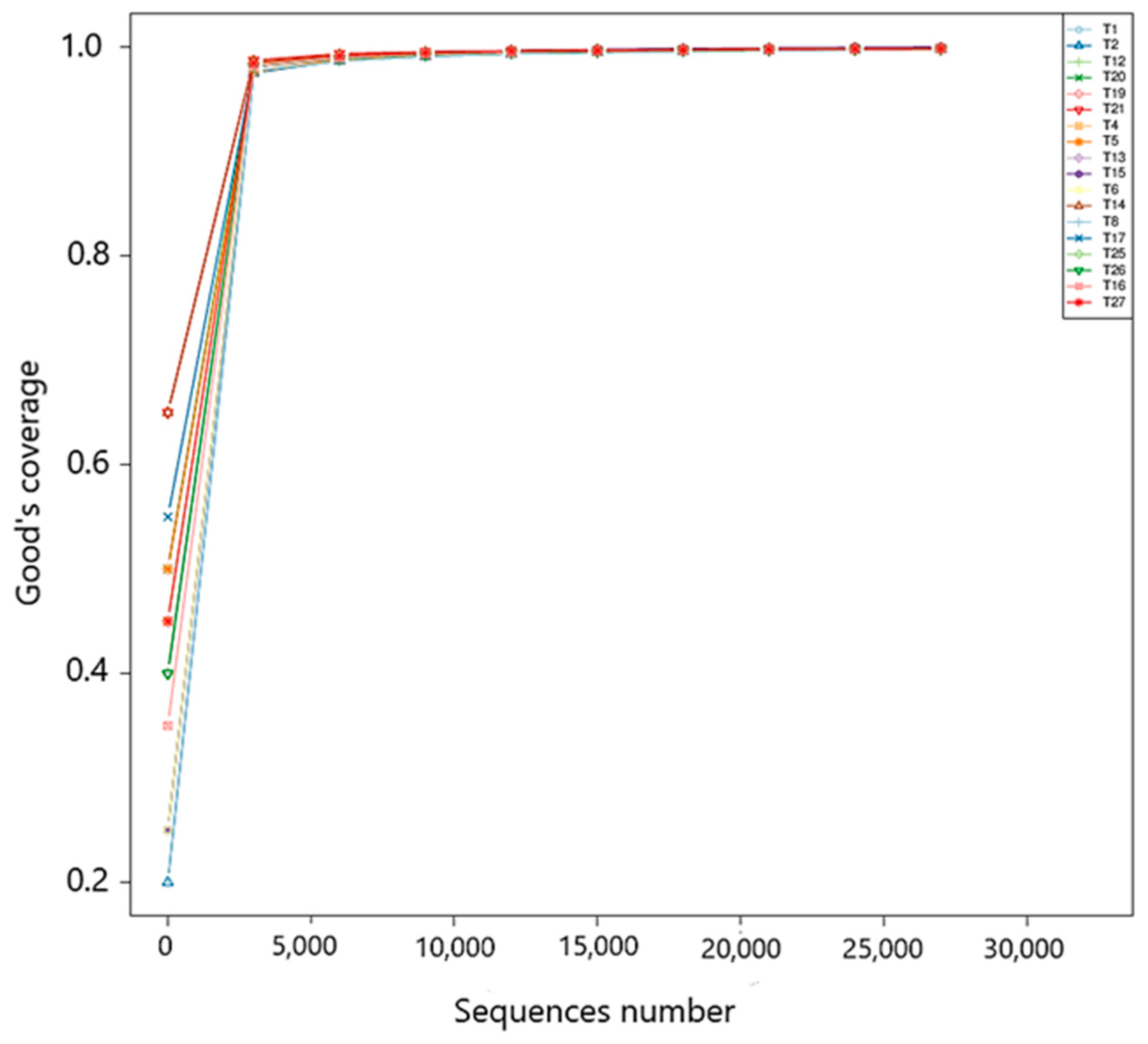
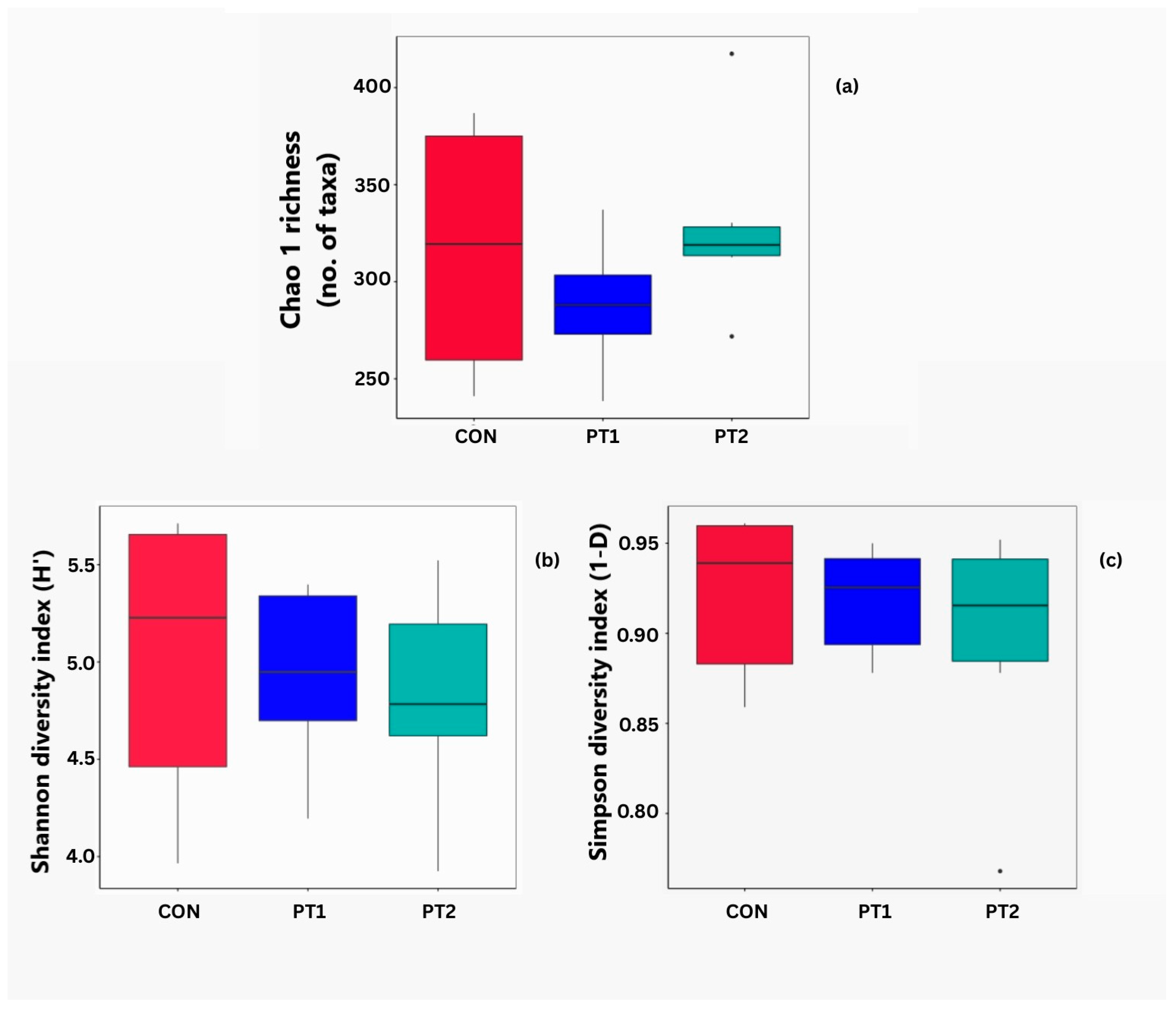
3.7.1. Alpha Diversity Analysis
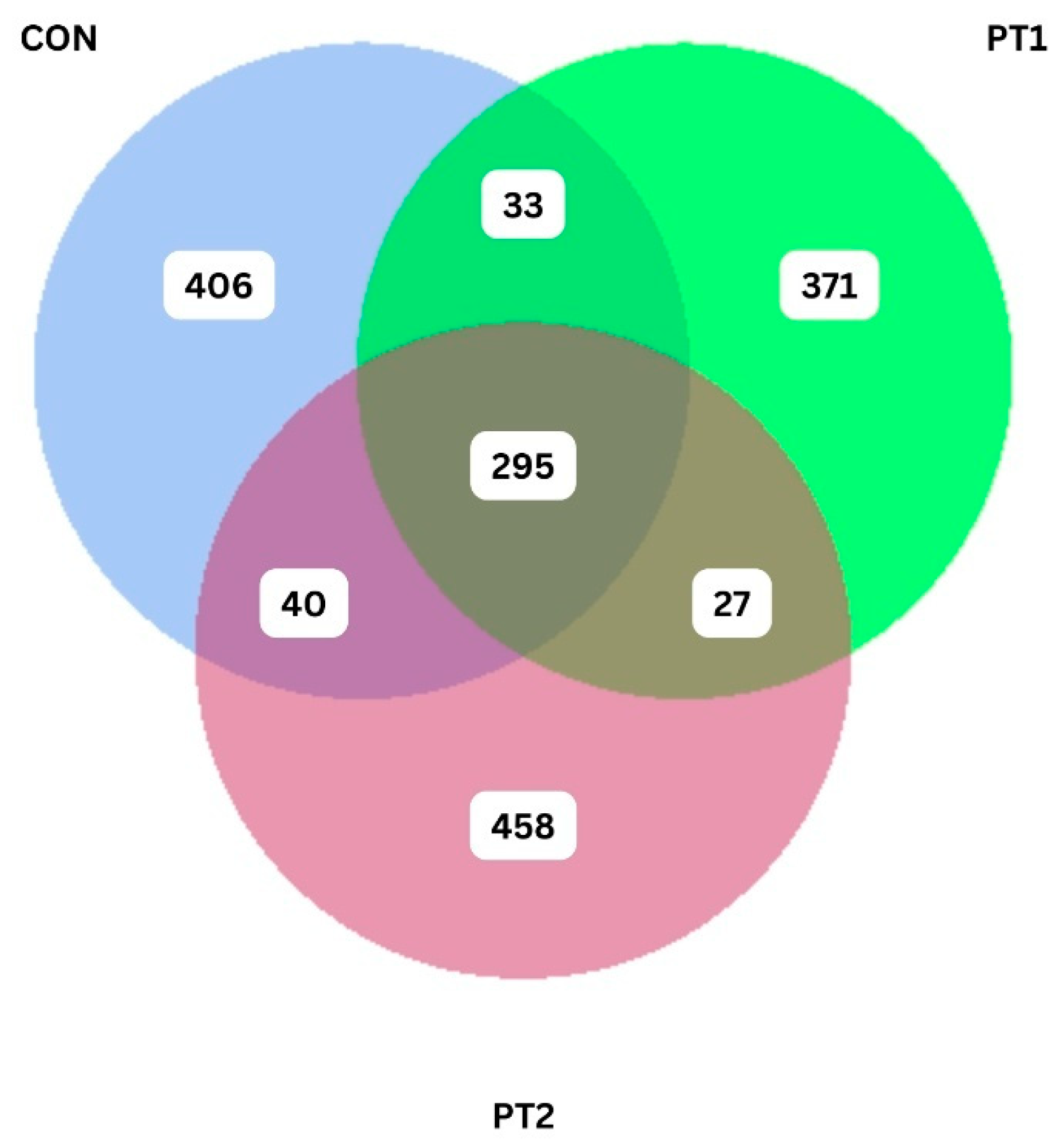
3.7.2. Beta Diversity Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. In Vitro Screening
4.2. In Vivo Trial
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Francis, G.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Becker, K. Antinutritional factors present in plant-derived alternate fish feed ingredients and their effects in fish. Aquaculture 2001, 199, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Metian, M. Feed matters: Satisfying the feed demand of aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2015, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-S.; Liu, C.-H.; Hu, S.-Y. Probiotic Bacillus safensis NPUST1 Administration Improves Growth Performance, Gut Microbiota, and Innate Immunity against Streptococcus iniae in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, S.S.; Satoh, S. Environmental impact of phosphorus and nitrogen from aquaculture. In Feed and Feeding Practices in Aquaculture; Davis, D.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2015; Volume 287, pp. 369–386. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; He, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Jiang, B.; Huang, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, W. Screening and effects of intestinal probiotics on growth performance, gut health, immunity, and disease resistance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Streptococcus agalactiae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 151, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrifield, D.; Ringø, E. Aquaculture Nutrition: Gut Health, Probiotics and Prebiotics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lazado, C.C.; Caipang, C.M.A.; Estante, E.G. Prospects of host-associated microorganisms in fish and penaeids as probiotics with immunomodulatory functions. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Tang, J.; Cai, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, Z.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Afriyie, G. In vivo assessment of the probiotic potentials of three host-associated Bacillus species on growth performance, health status and disease resistance of Oreochromis niloticus against Streptococcus agalactiae. Aquaculture 2020, 527, 735440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kunze, G.; Satyanarayana, T. Developments in biochemical aspects and biotechnological applications of microbial phytases. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 6, 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Noureddini, H.; Dang, J. Degradation of Phytates in Distillers’ Grains and Corn Gluten Feed by Aspergillus niger Phytase. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2008, 159, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ghosh, K. Characterization and identification of gut-associated phytase-producing bacteria in some freshwater fish cultured in ponds. Acta Ichthyol. Et Piscat. 2012, 42, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, T.; Mondal, S.; Ray, A.K. Phytase-producing bacteria in the digestive tracts of some freshwater fish. Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, S.K.; Nandi, A.; Banerjee, G.; Ghosh, P.; Ray, A.K. Purification and Characterization of Extracellular Phytase from Bacillus licheniformis Isolated from Fish Gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sec. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 85, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Dimitroglou, A.; Bradley, G.; Baker, R.T.M.; Davies, S.J. Soybean meal alters autochthonous microbial populations, microvilli morphology and compromises intestinal enterocyte integrity of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Vale Pereira, G.; da Cunha, D.G.; Pedreira Mourino, J.L.; Rodiles, A.; Jaramillo-Torres, A.; Merrifield, D.L. Characterization of microbiota in Arapaima gigas intestine and isolation of potential probiotic bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 1298–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanke, L.J.; Bae, H.D.; Selinger, L.B.; Cheng, K.J. Phytase activity of anaerobic ruminal bacteria. Microbiology 1998, 144, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Dutta, D. Non—Starch Polysaccharide Degrading Gut Bacteria in Indian Major Carps and Exotic Carps. Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 9, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dutta, D.; Ghosh, K. Screening of extracellular enzyme-producing and pathogen inhibitory gut bacteria as putative probiotics in mrigal, Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton, 1822). Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2015, 2, 310–318. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Ninawe, S.; Lal, R.; Kuhad, R.C. Isolation of Three Xylanase-Producing Strains of Actinomycetes and Their Identification Using Molecular Methods. Curr. Microbiol. 2006, 53, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Rana, S.; Beniwal, V.; Salar, R.K. Optimization of tannase production by a novel Klebsiella pneumoniae KP715242 using central composite design. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 7, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, B.; Šušković, J.; Goreta, J.; Matošić, S. Effect of protectors on the viability of Lactobacillus acidophilus M92 in simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2000, 38, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 10th ed.; Approved Standard, (CLSI document M02-A10); Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. EUCAST Disk Diffusion Test Manual (Version 13.0, January 2025). Available online: https://www.eucast.org (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Trivedi, S.; Husain, I.; Sharma, A. Purification and characterization of phytase from Bacillus subtilis P6: Evaluation for probiotic potential for possible application in animal feed. Food Front. 2021, 3, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Córdova, A.F.; Beltrán-Barrientos, L.M.; Santiago-López, L.; Garcia, H.S.; Vallejo-Cordoba, B.; Hernandez-Mendoza, A. Phytate-degrading activity of probiotic bacteria exposed to simulated gastrointestinal fluids. LWT 2016, 73, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, M.C.; Haros, M.; Rosell, C.M.; Sanz, Y. Characterization of an acid phosphatase from Lactobacillus pentosus: Regulation and biochemical properties. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 98, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinonen, J.K.; Lahti, R.J. A new and convenient colorimetric determination of inorganic orthophosphate and its application to the assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 113, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Burnard, D.; Bradley, G.; Davies, S.J.; Baker, R.T.M. Microbial community diversity associated with the intestinal mucosa of farmed rainbow trout (Oncoryhnchus mykiss Walbaum). Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (NRC). Nutrient Requirements of Fish; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Nutrition Specification Database (ASNS), Version 10.0. International Aquafeed Formulation Database. Available online: https://app.iaffd.com/asns (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Home Office. Guidance on the Operation of the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986. 2014. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/operation-of-aspa (accessed on 6 September 2025).
- Konnert, G.D.P.; Gerrits, W.J.J.; Gussekloo, S.W.S.; Schrama, J.W. Balancing protein and energy in Nile tilapia feeds: A meta-analysis. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1757–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawling, M.; Leclercq, E.; Foey, A.; Castex, M.; Merrifield, D. A novel dietary multi-strain yeast fraction modulates intestinal toll-like-receptor signalling and mucosal responses of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroglou, A.; Merrifield, D.L.; Spring, P.; Sweetman, J.; Moate, R.; Davies, S.J. Effects of mannan oligosaccharide (MOS) supplementation on growth performance, feed utilisation, intestinal histology and gut microbiota of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 2010, 300, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.M. Handbook of Microbiological Media, 2nd ed.; Parks, L.C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zaheen, Z.; Farooq War, A.; Ali, S.; Yatoo, A.M.; Ali Md, N.; Bilal Ahmad, S.; Rehman, M.; Paray, B.A. Common bacterial infections affecting freshwater fish fauna and impact of pollution and water quality characteristics on bacterial. In Bacterial Fish Diseases; Hamid Dar, G., Ahmad Bhat, R., Qadri, H., Al-Ghamdy, K., Hakeem, K.R., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 113–145. [Google Scholar]
- Haenen, O.L.M.; Dong, H.T.; Hoai, T.D.; Crumlish, M.; Karunasagar, I.; Barkham, T.; Chen, S.L.; Zadoks, R.; Kiermeier, A.; Wang, B.; et al. Bacterial diseases of tilapia, their zoonotic potential and risk of antimicrobial resistance. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 15 (Suppl. S1), 154–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Roy, M.; Kar, N.; Ringo, E. Gastrointestinal Bacteria in Rohu, Labeo Rohita (Actinopterygii: Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae): Scanning Electron Microscopy and Bacteriological Study. Acta Ichthyol. Et Piscat. 2010, 40, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; Mukherjee, A.; Dutta, D.; Banerjee, S.; Breines, E.M.; Hareide, E.; Ringø, E. Endosymbiotic pathogen-inhibitory gut bacteria in three Indian Major Carps under polyculture system: A step toward making a probiotics consortium. Aquac. Fish. 2021, 6, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Multifaceted applications of probiotic Bacillus species in aquaculture with special reference to Bacillus subtilis. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 862–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del’Duca, A.; Evangelista Cesar, D.; Galuppo Diniz, C.; Abreu, P.C. Evaluation of the presence and efficiency of potential probiotic bacteria in the gut of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) using the fluorescent in situ hybridization technique. Aquaculture 2013, 388–391, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Su, X.; Yun, L.; Shen, Y.; Feng, J.; Yang, G.; Meng, X.; Zhang, J.; Chang, X. Evaluation of probiotic characteristics and whole genome analysis of Bacillus velezensis R-71003 isolated from the intestine of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) for its use as a probiotic in aquaculture. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Dutta, D.; Banerjee, S.; Ringø, E.; Breines, E.M.; Hareide, E.; Chandra, G.; Ghosh, K. Potential probiotics from Indian major carp, Cirrhinus mrigala. Characterization, pathogen inhibitory activity, partial characterization of bacteriocin and production of exoenzymes. Res. Veter Sci. 2016, 108, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, M.; Raja, M.; Perumal, P. Evaluation of probiotic potential of Bacillus spp. isolated from the digestive tract of freshwater fish Labeo calbasu (Hamilton, 1822). Aquac. Rep. 2018, 11, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.R.; Kamilya, D.; Choudhury, T.G.; Tripathy, P.S.; Rathore, G. Deciphering the Probiotic Potential of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens COFCAU_P1 Isolated from the Intestine of Labeo rohita Through In Vitro and Genetic Assessment. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1572–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.-H.; Lu, C.-P. In vivo fish models for visualizing Aeromonas hydrophila invasion pathway using GFP as a biomarker. Aquaculture 2008, 277, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Klesius, P.H. Virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila to channel catfish Ictaluras punctatus fingerlings in the presence and absence of bacterial extracellular products. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 95, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, D.; Li, T.; Gong, X.; Li, A. Does the gastrointestinal tract serve as the infectious route of Aeromonas hydrophila in crucian carp (Carassius carassius)? Aquac. Res. 2013, 46, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Ghosh, K.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Kumar, V.; Lymbery, A.J.; Roy, S.; Ringø, E. Genus Bacillus, promising probiotics in aquaculture: Aquatic animal origin, bio-active components, bioremediation and efficacy in fish and shellfish. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2019, 27, 331–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Ghosh, K. Antagonism against fish pathogens by cellular components and verification of probiotic properties in autochthonous bacteria isolated from the gut of an Indian major carp, Catla catla (Hamilton). Aquac. Res. 2014, 47, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Ringø, E.; Ghosh, K. Extracellular tannase-producing bacteria detected in the digestive tracts of freshwater fishes (Actinopterygii: Cyprinidae and Cichlidae). Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2016, 46, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konietzny, U.; Greiner, R. Bacterial phytase: Potential application, in vivo function and regulation of its synthesis. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2004, 35, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, O.; Igbasan, F. In vitro properties of phytases from various microbial origins. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, A.; Chouayekh, H.; Ben Farhat, M.; Bouchaala, K.; Bejar, S. Gene Cloning and Characterization of a Thermostable Phytase from Bacillus subtilis US417 and Assessment of its Potential as a Feed Additive in Comparison with a Commercial Enzyme. Mol. Biotechnol. 2008, 40, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.W.; Chu, I.S.; Chung, K.S. Purification and Biochemical Characterization of Thermostable Phytase from Newly Isolated Bacillus subtilis CF92. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2011, 54, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookchaiyaporn, N.; Srisapoome, P.; Unajak, S.; Areechon, N. Efficacy of Bacillus Spp. Isolated from Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus Linn. On Its Growth and Immunity, and Control of Pathogenic Bacteria. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, S.; Carrias, A.A.; Williams, M.A.; Liles, M.R.; Terhune, J.S.; Davis, D.R. Effects of Bacillus subtilis Strains on Growth, Immune Parameters, and Streptococcus iniae Susceptibility in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2017, 48, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeoye, A.A.; Yomla, R.; Jaramillo-Torres, A.; Rodiles, A.; Merrifield, D.L.; Davies, S.J. Combined Effects of Exogenous Enzymes and Probiotic on Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Growth, Intestinal Morphology and Microbiome. Aquaculture 2016, 463, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waiyamitra, P.; Zoral, M.A.; Saengtienchai, A.; Luengnaruemitchai, A.; Decamp, O.; Gorgoglione, B.; Surachetpong, W. Probiotics Modulate Tilapia Resistance and Immune Response against Tilapia Lake Virus Infection. Pathogens 2020, 9, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, M.; Gao, F.; Lu, M.; Chen, G. Effects of Dietary Probiotic Supplementation on the Growth, Gut Health and Disease Resistance of Juvenile Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Anim. Nutr. 2020, 6, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panase, A.; Thirabunyanon, M.; Promya, J.; Chitmanat, C. Influences of Bacillus subtilis and Fructooligosaccharide on Growth Performances, Immune Responses, and Disease Resistance of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 1094681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyükdeveci, E.M.; Cengizler, İ.; Balcázar, J.L.; Demirkale, İ. Effects of Two Host-Associated Probiotics Bacillus mojavensis B191 and Bacillus subtilis MRS11 on Growth Performance, Intestinal Morphology, Expression of Immune-Related Genes and Disease Resistance of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Streptococcus iniae. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 138, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcagnile, M.; Quarta, E.; Sicuro, A.; Pecoraro, L.; Schiavone, R.; Tredici, S.M.; Talà, A.; Corallo, A.; Verri, T.; Stabili, L.; et al. Effect of Bacillus velezensis MT9 on Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Intestinal Microbiota. Microb. Ecol. 2025, 88, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, M.C.; Dias, D.d.C.; Araujo, F.v.A.P.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Tachibana, L. Probiotic Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus plantarum in Diet of Nile Tilapia. Bol. Do Inst. De Pesca 2019, 45, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereded, N.K.; Curto, M.; Domig, K.J.; Abebe, G.B.; Fanta, S.W.; Waidbacher, H.; Meimberg, H. Metabarcoding Analyses of Gut Microbiota of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) from Lake Awassa and Lake Chamo, Ethiopia. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, W. Evaluation of Probiotic Strain Bacillus Subtilis C-3102 as a Feed Supplement for Koi Carp (Cyprinus carpio). J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2011, S1, 005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standen, B.T.; Rodiles, A.; Peggs, D.L.; Davies, S.J.; Santos, G.A.; Merrifield, D.L. Modulation of the Intestinal Microbiota and Morphology of Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, Following the Application of a Multi-Species Probiotic. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8403–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ling, H.; Luo, L.; Qi, D.; Feng, L. The Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Clostridium butyricum on the Growth Performance, Immunity, Intestinal Microbiota and Disease Resistance of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Porchas, M.; Preciado-Álvarez, A.; Vargas-Albores, F.; Gracia-Valenzuela, M.H.; Cicala, F.; Martinez-Cordova, L.R.; Medina-Félix, D.; Garibay-Valdez, E. Microbiota Plasticity in Tilapia Gut Revealed by Meta-Analysis Evaluating the Effect of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Biofloc. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Kim, S.H.; Noh, D.-I.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, T.-R.; Hasan, T.; Lee, E.-W.; Jang, W.J. Combination of Host-Associated Rummeliibacillus sp. And Microbacterium sp. Positively Modulated the Growth, Feed Utilization, and Intestinal Microbial Population of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Biology 2023, 12, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kers, J.G.; Saccenti, E. The Power of Microbiome Studies: Some Considerations on Which Alpha and Beta Metrics to Use and How to Report Results. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 796025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Abarike, E.D.; Sakyi, M.E.; Li, Y.; Xie, C.X.; Hlordzi, V. Effects of Three Host-Associated Bacillus Species on Mucosal Immunity and Gut Health of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus and Its Resistance against Aeromonas Hydrophila Infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 97, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Guan, J.; Zhang, H.; Peng, D.; Wen, X.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Q. Effect of Moringa oleifera, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, and Their Combination on Growth Performance, Digestive Enzymes, Immunity, and Microbiota in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Nutr. 2024, 2024, 1755727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Ward, L.R.; Burke, C. Prospects of Using Marine Actinobacteria as Probiotics in Aquaculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 81, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, I.; Schmidt, B.E.; Stokes, C.R.; Lewis, M.; Bailey, M.; Aminov, R.; Prosser, J.I.; Gill, B.P.; Pluske, J.R.; Mayer, C.-D.; et al. Environmentally-Acquired Bacteria Influence Microbial Diversity and Natural Innate Immune Responses at Gut Surfaces. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Hao, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, A. Taxonomic and Functional Characteristics of the Gill and Gastrointestinal Microbiota and Its Correlation with Intestinal Metabolites in NEW GIFT Strain of Farmed Adult Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardman, Z.; Arnosti, C.; Durbin, A.; Ziervogel, K.; Cox, C.; Steen, A.D.; Teske, A. Verrucomicrobia Are Candidates for Polysaccharide-Degrading Bacterioplankton in an Arctic Fjord of Svalbard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3749–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, J.M.; Lepp, D.; Wu, W.; Graf, D.; McGillis, L.H.; Hussain, A.; Carey, C.; Robinson, L.E.; Liu, R.; Tsao, R.; et al. Chickpea-Supplemented Diet Alters the Gut Microbiome and Enhances Gut Barrier Integrity in C57Bl/6 Male Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Song, J.; Peng, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, J.; Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Gong, B. Co-Occurrence Network of Microbes Linking Growth and Immunity Parameters with the Gut Microbiota in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) after Feeding with Fermented Soybean Meal. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 26, 101280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Tan, C.; Xie, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, X. Effects of Enrofloxacin’s Exposure on the Gut Microbiota of Tilapia Fish (Oreochromis niloticus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2023, 46, 101077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huavas, J.; Heyse, J.; Props, R.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Shelley, C. Microbiomes of Tilapia Culture Systems: Composition, Affecting Factors, and Future Perspectives. Aquac. Res. 2024, 2024, 5511461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, C.; Sakata, T.; Sugita, H. Novel Ecological Niche of Cetobacterium somerae, an Anaerobic Bacterium in the Intestinal Tracts of Freshwater Fish. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Qiao, N.; Li, T.; Yu, R.; Zhai, Q.; Tian, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Dietary Supplementation with Probiotics Regulates Gut Microbiota Structure and Function in Nile Tilapia Exposed to Aluminum. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Lara, P.; Hernández-López, J.; Garibay-Valdez, E.; Medina-Félix, D.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; Coronado-Molina, D.; Ortiz-Luna, R.J.; Puerto, J.H.; Gracia-Valenzuela, M.H. Microbiota Attached to and Encapsulated by Granulomas Dissected from Tilapia Spleen: A Case Report. Aquac. Fish Fish. 2022, 3, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonda-Santos, K.; Lara-Flores, M. Detection of Mycobacterium Spp. By Polymerase Chain Reaction in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Campeche, Mexico. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 2785–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Flores, M.; Aguirre-Guzman, G.; Balan-Zetina, S.B.; Sonda-Santos, K.Y.; Zapata, A.A. Identification of Mycobacterium Agent Isolated from Tissues of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 14, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Eding, E.; Kokou, F. Effect of Rearing Systems and Dietary Probiotic Supplementation on the Growth and Gut Microbiota of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Larvae. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatsis, C.; Sipkema, D.; Smidt, H.; Heilig, H.; Benvenuti, G.; Verreth, J.; Verdegem, M. The Impact of Rearing Environment on the Development of Gut Microbiota in Tilapia Larvae. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, S.S.; Shouche, Y.S.; Gade, W.N. Deep Sequencing Reveals Highly Variable Gut Microbial Composition of Invasive Fish Mossambicus Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) Collected from Two Different Habitats. Indian J. Microbiol. 2017, 57, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Hill, N.; Wallace, J. A Perennial Living Mulch System Fosters a More Diverse and Balanced Soil Bacterial Community. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Scicchitano, D.; Palladino, G.; Nanetti, E.; Candela, M.; Furones, D.; Sanahuja, I.; Carbó, R.; Gisbert, E.; Andree, K.B. Microbiome Study of a Coupled Aquaponic System: Unveiling the Independency of Bacterial Communities and Their Beneficial Influences among Different Compartments. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, B.R.P.; Nunez, J.C.B.; Rand, D.M. Characterizing the Cirri and Gut Microbiomes of the Intertidal Barnacle Semibalanus Balanoides. Anim. Microbiome 2020, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yi, M.; Liu, Z.; Ke, X.; Gao, F.; Cao, J.; Lu, M. Effects of Diet on the Gut Microbial Communities of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) across Their Different Life Stages. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 926132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinasyiam, A.; Verdegem, M.C.; Ekasari, J.; Schrama, J.W.; Kokou, F. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Microbial Community Dynamics in Biofloc Systems Supplemented with Non-Starch Polysaccharides. Aquaculture 2024, 594, 741396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, H.S.; Heidarieh, P.; Fatahi-Bafghi, M. Genus Pseudonocardia: What We Know about Its Biological Properties, Abilities and Current Application in Biotechnology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 132, 890–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Shu, Y.; Yan, Y. The Growth-Promoting and Lipid-Lowering Effects of Berberine Are Associated with the Regulation of Intestinal Bacteria and Bile Acid Profiles in Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus Fulvidraco). Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontefract, N.; Sykes, L.; Rawling, M.; Merrifield, D.L. Prebiotic and Probiotic Applications in Fish and Crustaceans. In Feed and Feeding for Fish and Shellfish; Kumar, V., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2025; pp. 213–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntakirutimana, R.; Syanya, F.J.; Mwangi, P. Exploring the Impact of Probiotics on the Gut Ecosystem and Morpho-Histology in Fish: Current Knowledge of Tilapia. Asian J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2023, 25, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Gao, Y.; Yin, P.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L.; Xie, S.; Niu, J. Beneficial Effects on Growth, Haematic Indicators, Immune Status, Antioxidant Function and Gut Health in Juvenile Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by Dietary Administration of a Multi-Strain Probiotic. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Hamidoghli, A.; Choi, W.; Park, Y.; Jang, W.J.; Kong, I.-S.; Bai, S.C. Effects of Bacillus subtilis WB60 and Lactococcus lactis on Growth, Immune Responses, Histology and Gene Expression in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Perez, R.; Amit-Romach, E.; Sklan, D.; Uni, Z. Mucin Dynamics and Microbial Populations in Chicken Small Intestine Are Changed by Dietary Probiotic and Antibiotic Growth Promoter Supplementation. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ho, S.B. Intestinal Goblet Cells and Mucins in Health and Disease: Recent Insights and Progress. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, K.M.; Reda, R.M. Improvement of Immunity and Disease Resistance in the Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, by Dietary Supplementation with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabagh, M.; Mohamed, R.; Moustafa, E.M.; Hamza, A.; Farrag, F.; Decamp, O.; Dawood, M.A.; Eltholth, M. Assessing the Impact of Bacillus strains Mixture Probiotic on Water Quality, Growth Performance, Blood Profile and Intestinal Morphology of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquac. Nutr. 2018, 24, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalwash, H.R.; Salah, A.S.; El-Nokrashy, A.M.; Abozeid, A.M.; Zaki, V.H.; Mohamed, R.A. Dietary Supplementation with Bacillus species Improves Growth, Intestinal Histomorphology, Innate Immunity, Antioxidative Status and Expression of Growth and Appetite-Regulating Genes of Nile Tilapia Fingerlings. Aquac. Res. 2021, 53, 1378–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.S.; Mohammady, E.Y.; Soaudy, M.R.; Elashry, M.A.; Moustafa, M.M.; Wassel, M.A.; El-Garhy, H.A.; El-Haroun, E.R.; Elsaied, H.E. Synergistic Effects of Bacillus pumilus and Exogenous Protease on Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Growth, Gut Microbes, Immune Response and Gene Expression Fed Plant Protein Diet. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 275, 114892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hisnawi, A.; Rodiles, A.; Rawling, M.D.; Castex, M.; Waines, P.; Gioacchini, G.; Carnevali, O.; Merrifield, D.L. Dietary Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici MA18/5M Modulates the Intestinal Microbiota and Stimulates Intestinal Immunity in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2019, 50, 1133–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Torres, A.; Rawling, M.D.; Rodiles, A.; Mikalsen, H.E.; Johansen, L.-H.; Tinsley, J.; Forberg, T.; Aasum, E.; Castex, M.; Merrifield, D.L. Influence of Dietary Supplementation of Probiotic Pediococcus acidilactici MA18/5M during the Transition from Freshwater to Seawater on Intestinal Health and Microbiota of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Cao, H.; Jiang, W.; Hu, B.; Jian, S.; Wen, C.; Kajbaf, K.; Kumar, V.; Tao, Z.; Peng, M. Dietary Supplementation of Bacillus cereus as Probiotics in Pengze Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus Var. Pengze): Effects on Growth Performance, Fillet Quality, Serum Biochemical Parameters and Intestinal Histology. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Hasan, N.A.; Eltholth, M.M.; Saha, P.; Mely, S.S.; Rahman, T.; Murray, F.J. Assessing the Impacts of In-Feed Probiotic on the Growth Performance and Health Condition of Pangasius (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) in a Farm Trial. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawling, M.; Schiavone, M.; Mugnier, A.; Leclercq, E.; Merrifield, D.; Foey, A.; Apper, E. Modulation of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function Fed Different Postbiotics and a Probiotic from Lactobacilli. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, I.; Ramser, A.; Isham, N.; Ghannoum, M.A. The Gut Microbiome as a Major Regulator of the Gut-Skin Axis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S. Interaction Effects of Dietary Supplementation of Heat-Killed Lactobacillus plantarum and β-Glucan on Growth Performance, Digestibility and Immune Response of Juvenile Red Sea Bream, Pagrus major. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, L.H.H.; Barrera, T.C.; Mejía, J.C.; Mejía, G.C.; del Carmen, M.; Dosta, M.; de Lara Andrade, R.; Sotres, J.A.M. Effects of the Commercial Probiotic Lactobacillus casei on the Growth, Protein Content of Skin Mucus and Stress Resistance of Juveniles of the Porthole Livebearer Poecilopsis gracilis (Poecilidae). Aquac. Nutr. 2009, 16, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Estrada, U.; Satoh, S.; Haga, Y.; Fushimi, H.; Sweetman, J. Effects of Inactivated Enterococcus faecalis and Mannan Oligosaccharide and Their Combination on Growth, Immunity, and Disease Protection in Rainbow Trout. J. Appl. Aquac. 2013, 25, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, E.M.; Nguyen, A.T.; Odem, M.A.; Eisenhoffer, G.T.; Krachler, A.M. The Zebrafish as a Model for Gastrointestinal Tract–Microbe Interactions. Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, M.; Lopes, C.; Silva, P. Comparative Histological Description of the Intestine in Platyfish (Xiphophorus maculatus) and Swordtail Fish (Xiphophorus helleri). Tissue Cell 2024, 87, 102306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


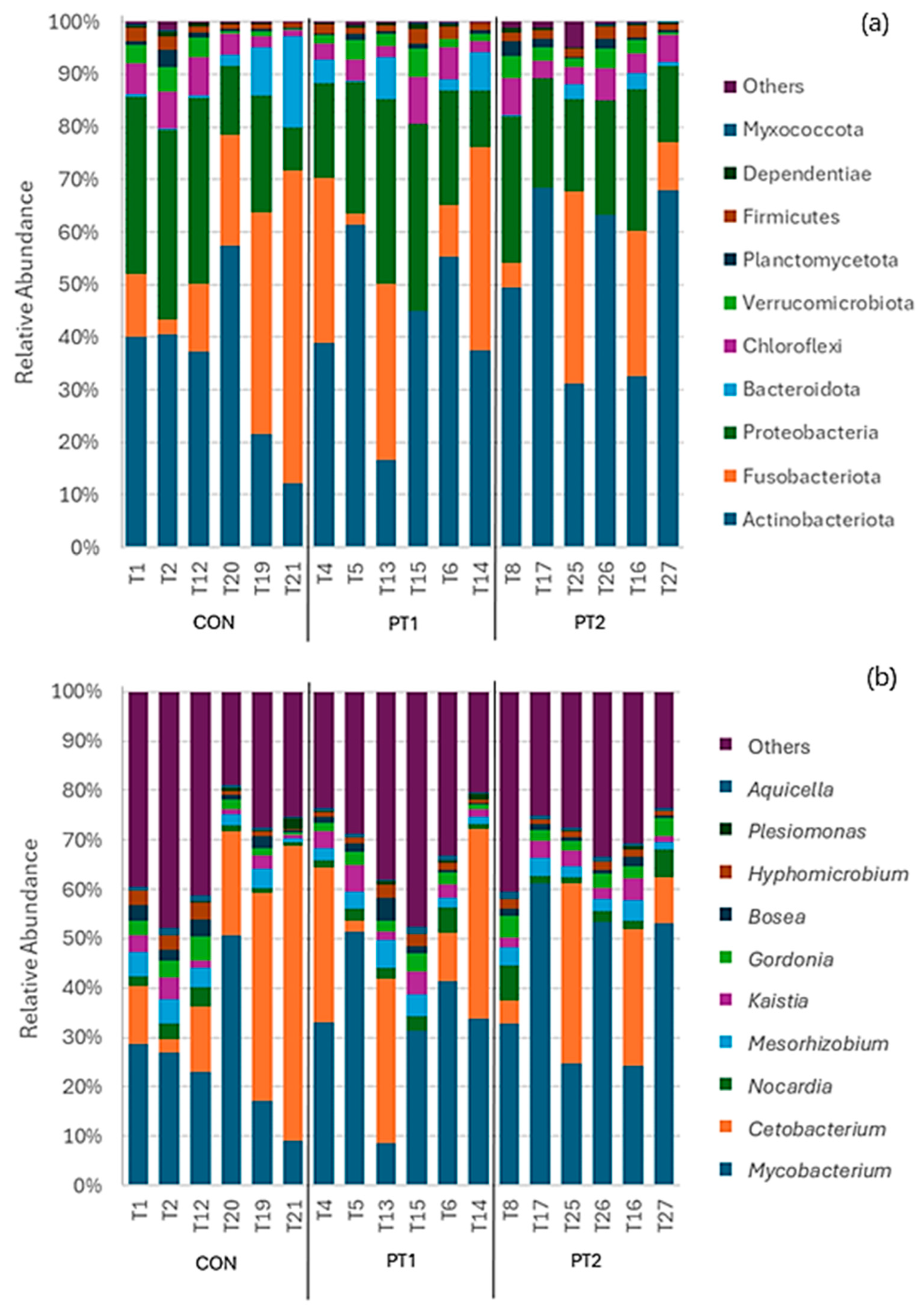
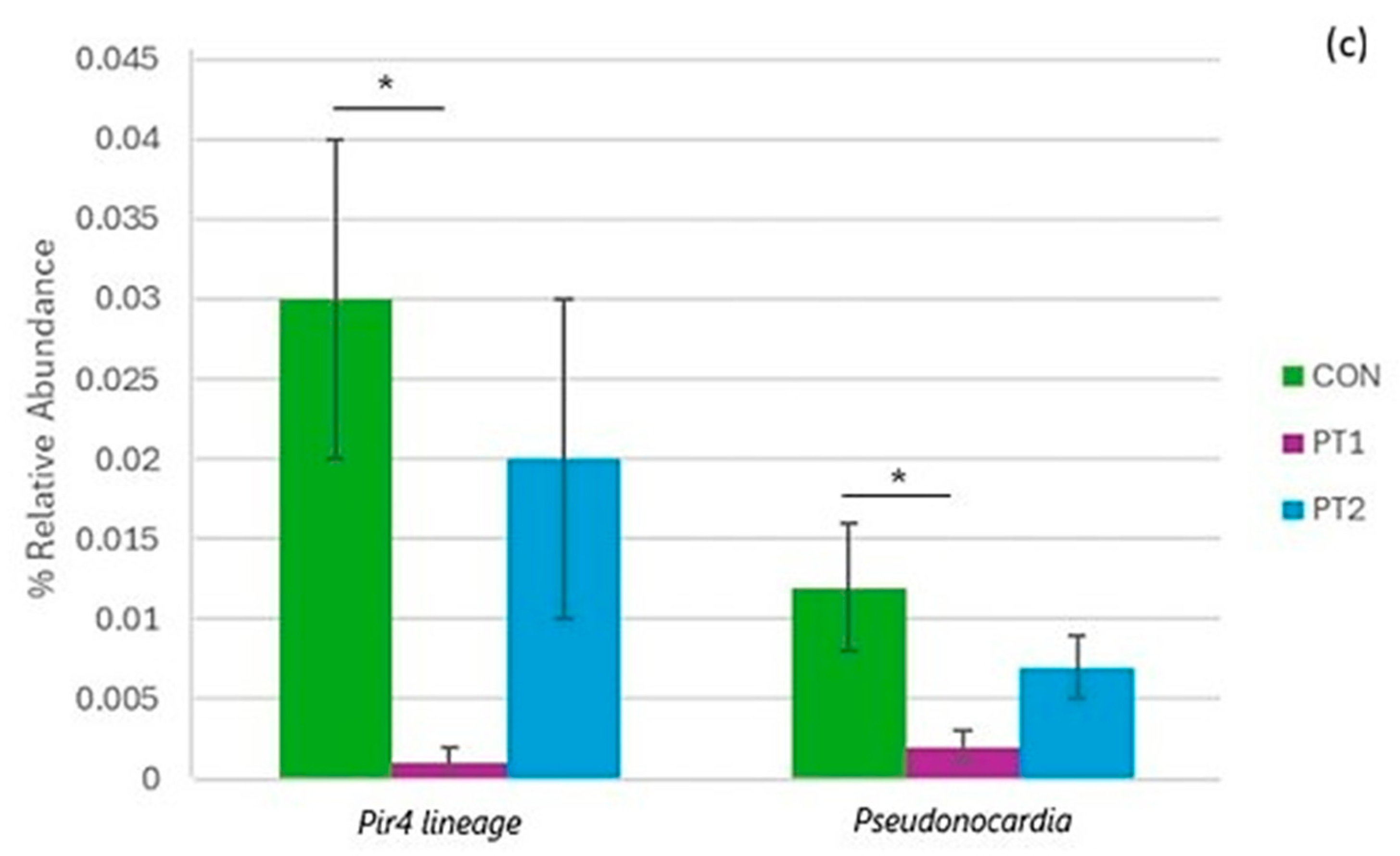
| Ingredient (g/100 g of Diet) | Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | PT1 | PT2 | |
| PT1 concentration * | -- | 7 | -- |
| PT2 concentration * | -- | -- | 7 |
| Soybean meal a | 38.0 | 38.0 | 38.0 |
| Sunflower meal b | 25.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 |
| Corn gluten meal a | 21.7 | 21.7 | 21.7 |
| Cornstarch | 8.7 | 8.7 | 8.7 |
| Sunflower oil | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 |
| Fish meal c | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Fish oil | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Lysine HCl | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Vitamin and mineral premix d | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| CMC-binder | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Gelatin | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Isolate No. | Related Species | Identity (%) | Accession | Pathogen Antagonism | Haemolytic Activity | Extracellular Enzyme Activity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AH | SI | VA | VP | YR | Xylanase | Phytase | Tannase | |||||
| C16 | uncultured Bacilli bacterium | 98.75% | MH375377.1 | + | + | − | − | − | β | + | + | − |
| C22 | Bacillus sp. | 99.89% | OL679725.1; OL679711.1 | + | + | − | − | − | α | + | + | − |
| C24 | Bacillus sp. | 99.89% | MT427735.1 OL679725.1; OL679711.1 | + | + | − | − | − | β | + | + | + |
| C27 | Bacillus subtilis | 100.00% | MZ352777.1 | + | + | + | − | − | α | + | + | − |
| C29 | Bacillus sp. | 100.00% | OL679725.1; OL679711.1 | + | + | − | − | − | α | + | + | + |
| C39 | Bacillus subtilis | 99.51% | KF535143.1; GU193980.1 | + | + | − | − | − | α | + | + | − |
| C54 | Bacillus subtilis | 87.85% | FR849706.1 | + | + | − | − | − | α | + | − | − |
| C61 | Bacillus tequilensis and Bacillus subtilis strains | >99% | NR104919.1 | + | + | + | − | + | α | + | + | − |
| C72 | Pseudomonas mosselii | 99.72% | MT598025.1 | + | − | + | + | + | no growth | + | + | + |
| C80 | Bacillus subtilis | 99.83% | OP904234.1 | + | + | + | − | − | β | + | + | − |
| C122 | Bacillus subtilis | 99.07% | MT538257.1 | + | + | + | − | − | β | + | + | − |
| C123 | Bacillus subtilis | 99.30% | KX426654.1; KX426653.1 | + | + | + | − | − | β | + | + | + |
| C140 | Bacillus sp. | 99.89% | OL679725.1; OL679711.1 | + | + | + | − | − | β | + | + | − |
| C141 | Bacillus velezensis | 99.91% | OP060623.1 | + | + | + | − | − | β | + | + | − |
| C146 | Bacillus subtilis | 99.90% | CP026662.1 | + | + | − | − | − | β | + | + | + |
| C150 | Enterobacter sp. 18A13 | 99.82% | AP019634.1 | + | − | − | − | − | γ | + | + | + |
| T30 | Bacillus stercoris | 99.76% | MN704462.1 | + | − | − | − | − | β | + | + | + |
| T32 | Bacillus subtilis | 96.86% | MN631028.1 | + | − | − | − | − | β | + | − | − |
| T56 | Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis | 96.47% | CP032855.1 | + | + | − | − | − | β | + | + | − |
| T65 | Plesiomonas shigelloides | 94.15% | CP050969.1; LT575468.1; KU517709.1 | − | + | − | − | − | γ | no growth | no growth | no growth |
| T66 | Bacillus subtilis | 98.43% | OM980686.1 | − | + | − | − | − | α | + | + | − |
| T67 | Bacillus subtilis | 95.73% | MN894000.1 | + | + | − | − | − | β | + | + | + |
| T68 | Bacillus subtilis | 100.00% | OP942174.1 | + | + | − | − | − | α | + | + | − |
| T69 | Gottfriedia acidiceleris | 99.66% | MF101038.1 | − | + | − | − | − | no growth | − | − | − |
| T70 | Bacillus subtilis | 99.70% | NR027552.1 | + | + | + | − | − | α | + | + | + |
| T71 | Bacillus thuringiensis | 99.56% | KX822158.1 | − | + | − | − | − | β | no growth | no growth | no growth |
| T72 | Bacillus subtilis | 98.06% | KX426661.1 | − | + | − | − | − | α | + | + | − |
| T103 | Bacillus sp. | 99.35% | OL679725.1; OL679711.1 | − | + | − | − | − | α | + | + | − |
| T105 | Bacillus tequilensis | 99.49% | MK296524.1 | − | + | − | − | − | α | + | + | + |
| T112 | Bacillus subtilis | 95.42% | ON243943.1 | + | − | − | − | − | α | + | + | − |
| T113 | Bacillus tequilensis | 95.73% | JX979116.1 | + | + | - | - | - | α | + | + | - |
| Isolate | Zone of Inhibition (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Without SIJ Exposure | With SIJ Exposure | |
| C61 | 15.33 ± 0.58 | 14.67 ± 0.58 |
| T70 | 16.33 ± 0.58 a | 14.00 ± 1.00 b |
| Parameter | Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | PT1 | PT2 | |
| IW (g fish−1) | 5.4 ± 0.0 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 5.4 ± 0.0 |
| FW (g fish−1) | 11.8 ± 0.5 | 11.8 ± 0.5 | 12.5 ± 0.6 |
| NWG (g fish−1) | 6.4 ± 0.5 | 6.5 ± 0.4 | 7.1 ± 0.6 |
| SGR (% day−1) | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| FI (g fish−1) | 9.3 ± 0.4 | 9.5 ± 1.0 | 9.7 ± 0.4 |
| FCR (g g−1) | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.1 |
| PER | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.1 |
| CF | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.0 | 1.7 ± 0.0 |
| % Survival | 98.5 ± 2.6 | 95.5 ± 7.9 | 97.0 ± 5.3 |
| Component (%) | Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | PT1 | PT2 | |
| Moisture | 73.6 ± 0.9 | 74.4 ± 1.2 | 74.4 ± 0.8 |
| Protein | 57.4 ± 0.9 | 58.0 ± 3.1 | 59.0 ± 0.5 |
| Lipid | 25.9 ± 2.7 | 24.9 ± 3.4 | 23.6 ± 1.1 |
| Ash | 10.6 ± 0.8 | 10.4 ± 0.9 | 10.6 ± 0.4 |
| Parameter | Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | PT1 | PT2 | |
| Mucosal fold length (µm) | 120.6 ± 29.5 a | 166.0 ± 27.5 b | 123.0 ± 27.1 a |
| Lamina propia width (µm) | 22.1 ± 5.6 | 21.0 ± 8.2 | 18.3 ± 4.0 |
| Muscularis thickness (µm) | 21.7 ± 11.3 a | 22.5 ± 9.5 a | 11.3 ± 3.3 b |
| Goblet cell count (n/70 µm) | 5.6 ± 2.6 a | 9.3 ± 2.4 b | 8.1 ± 2.8 ab |
| % Goblet cell coverage (n/70 µm) | 5.5 ± 4.5 | 6.8 ± 3.4 | 6.7 ± 2.8 |
| IEL count (n/70 µm) | 25.8 ± 2.7 | 29.5 ± 11.1 | 32.6 ± 10.1 |
| Microvilli density (AU) | 30.1 ± 6.3 | 24.1 ± 12.3 | 27.7 ± 11.7 |
| Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | PT1 | PT2 | |
| allochthonous | 7.0 ± 0.4 | 6.9 ± 0.4 | 7.1 ± 0.2 |
| Bacillus spp. | 5.4 ± 0.3 | 5.5 ± 0.4 | 4.9 ± 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abarra, S.T.; Maulu, S.; Odu-Onikosi, S.G.; Momoh, T.A.; Eynon, B.; Emery, M.; Rawling, M.; Merrifield, D.L. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Autochthonous Probiotics and Their Effects on the Mucosal Health of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Animals 2025, 15, 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223296
Abarra ST, Maulu S, Odu-Onikosi SG, Momoh TA, Eynon B, Emery M, Rawling M, Merrifield DL. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Autochthonous Probiotics and Their Effects on the Mucosal Health of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Animals. 2025; 15(22):3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223296
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbarra, Sherilyn T., Sahya Maulu, Sheu G. Odu-Onikosi, Taofik A. Momoh, Benjamin Eynon, Matthew Emery, Mark Rawling, and Daniel L. Merrifield. 2025. "In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Autochthonous Probiotics and Their Effects on the Mucosal Health of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)" Animals 15, no. 22: 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223296
APA StyleAbarra, S. T., Maulu, S., Odu-Onikosi, S. G., Momoh, T. A., Eynon, B., Emery, M., Rawling, M., & Merrifield, D. L. (2025). In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Autochthonous Probiotics and Their Effects on the Mucosal Health of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Animals, 15(22), 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223296





