Multi-Niche Microbiota of a Desert-Adapted Lizard: 16S rRNA Profiling of Teratoscincus roborowskii Endemic to the Turpan Depression in Northwest China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. 16S rRNA Amplification and Sequencing
2.4. Microbial Community Analysis Pipeline
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Function Prediction
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Microbial 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
3.2. Microbial Diversity Analysis
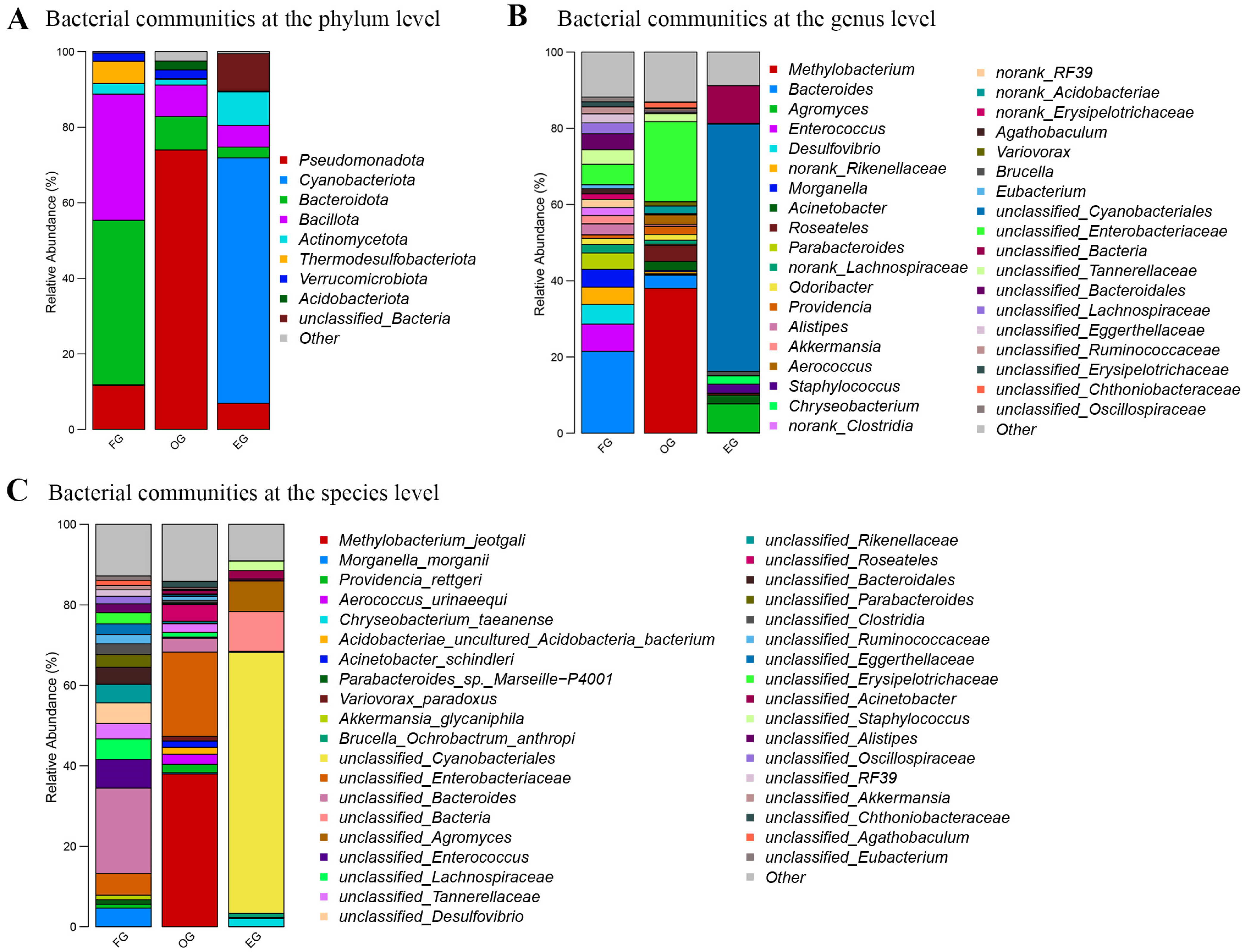
3.3. Microbial Composition Across Habitats
3.4. LEfSe Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Wei, Q.; Shi, L.; Zhang, H. Characteristics of flora in different segments of the digestive tract of Lycodon rufozonatus. Animals 2023, 13, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharyya, S.; Majumder, S.; Nandi, S.; Ghosh, A.; Saha, S.; Bhattacharya, M. Uncovering mercury accumulation and the potential for bacterial bioremediation in response to contamination in the Singalila National Park. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.E.; Godwin, C.M.; Cardinale, B.J. Biodiversity effects in the wild are common and as strong as key drivers of productivity. Nature 2017, 549, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.K.; Dao, C.J.; Ma, P.X.; Li, B.; Yan, K. Characteristics of nitrogen cycle-related bacterial community and its response to soil in the main lead-zinc mine reclamation area of Lanping. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2025, 46, 399–408, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, S.; Duffy, J.E.; Zavaleta, E. The functions of biological diversity in an age of extinction. Science 2012, 336, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Yan, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Z. Comparison of gut flora diversity between captive and wild Tokay gecko (Gekko gecko). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 897923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Qi, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Chang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, J. Multi-omics approaches revealed the associations of host metabolism and gut microbiome with phylogeny and environmental adaptation in mountain dragons. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 913700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetz, P.; Freed, P.; Aguilar, R.; Reyes, F.; Kudera, J.; Hošek, J. The Reptile Database. Available online: https://reptile-database.reptarium.cz/search (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Fung, T.C.; Olson, C.A.; Hsiao, E.Y. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.S.; Shin, N.R.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, M.S.; Whon, T.W.; Hyun, D.W.; Yun, J.H.; Jung, M.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Bae, J.W. Host habitat is the major determinant of the gut microbiome of fish. Microbiome 2021, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zhu, W.; Yu, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, B.; Wang, C.; Shu, L.; Li, X.; Yin, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Host development overwhelms environmental dispersal in governing the ecological succession of zebrafish gut flora. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.Y.; Ma, J.E.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, L.M.; He, N.; Liu, H.Y.; Luo, S.Y.; Wu, Z.J.; Han, R.C.; et al. Diets alter the gut microbiome of crocodile lizards. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.M.; Chen, J.Q.; Du, Y.; Lin, C.X.; Qu, Y.F.; Lin, L.H.; Ji, X. Microbial communities are thermally more sensitive in warm-climate lizards compared with their cold-climate counterparts. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1374209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, N.; Tang, X.; Liu, N.; Zhao, W. Changes in intestinal flora across an altitudinal gradient in the lizard Phrynocephalus vlangalii. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 4695–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Li, N.; Dayananda, B. Environment-dependent variation in gut flora of an oviparous lizard (Calotes versicolor). Animals 2021, 11, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.M.; Zhao, K.T.; Zhou, K.Y. Fauna Sinica, Reptilia, Vol. 2, Squamata, Lacertilia; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1999. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.R.; Song, Y.C.; Shi, L. Home range of Teratoscincus roborowskii (Gekkonidae): Influence of sex, season, and body size. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 395–401, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macey, J.R.; Wang, Y.; Ananjeva, N.B.; Larson, A.; Papenfuss, T.J. Vicariant patterns of fragmentation among gekkonid lizards of the genus Teratoscincus produced by the Indian collision: A molecular phylogenetic perspective and an area cladogram for Central Asia. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1999, 12, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, D.; Ma, R.; Guo, X.; Li, J. Comparative mitogenomics of wonder geckos (Sphaerodactylidae: Teratoscincus Strauch, 1863): Uncovering evolutionary insights into protein-coding genes. Genes 2025, 16, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.Z.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L. Seasonal dietary shifts alter the gut flora of a frugivorous lizard T. roborowskii (Squamata, Sphaerodactylidae). Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, 10363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.H.; Li, H.Y.; Xie, L.J.; Fan, J.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Yu, W.Q.; Xu, Y.T.; He, M.L.; Jiang, Y.; Bai, X.; et al. Intestinal flora was associated with occurrence risk of chronic non-communicable diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 31, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, R.; Edwards, R. Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kõljalg, U.; Nilsson, R.H.; Abarenkov, K.; Tedersoo, L.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bahram, M.; Larsson, K.-H. Towards a unified paradigm for sequence-based identification of Fungi. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5271–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 9 November 2025).
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, G.F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package, Version 2.6-2; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 9 November 2025).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org/ (accessed on 9 November 2025).
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Alm, E.J. Inferring correlation networks from genomic survey data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleros, L.; Barcellos, M.; Grecco, S.; Garzón, J.P.; Lozano, J.; Urioste, V.; Gastal, G. Longitudinal study of the bovine cervico-vaginal bacterial microbiota throughout pregnancy using 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2024, 124, 105657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, T.L. ggraph: An Implementation of Grammar of Graphics for Graphs and Networks. R Package, Version 2.2.1.9000; The Comprehensive R Archive Network: Vienna, Austria, 2024. Available online: https://github.com/thomasp85/ggraph (accessed on 9 November 2025).
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleford-Colquhoun, B.L.; Clemente, C.; Whiting, M.J.; Ortiz-Barrientos, D.; Frère, C.H. Archipelagos of the Anthropocene: Rapid and extensive differentiation of native terrestrial vertebrates in a single metropolis. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 2466–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberdi, A.; Aizpurua, O.; Bohmann, K.; Zepeda-Mendoza, M.L.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Do Vertebrate Gut Metagenomes Confer Rapid Ecological Adaptation? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littleford-Colquhoun, B.L.; Weyrich, L.S.; Kent, N.; Frere, C.H. City life alters the gut microbiome and stable isotope profiling of the eastern water dragon (Intellagama lesueurii). Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 4592–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, B.D.; Funabashi, M.; Adame, M.D.; Wang, Z.; Boktor, J.C.; Haney, J.; Wu, W.L.; Rabut, C.; Ladinsky, M.S.; Hwang, S.J.; et al. A gut-derived metabolite alters brain activity and anxiety behaviour in mice. Nature 2022, 602, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.T.; Dai, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.J.; Lin, L.H.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Qu, Y.F.; Ji, X. Captivity affects diversity, abundance, and functional pathways of gut flora in the northern grass lizard Takydromus septentrionalis. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.Y.; Wheeler, E.; Cann, I.K.; Mackie, R.I. Phylogenetic analysis of the fecal microbial community in herbivorous land and marine iguanas of the Galápagos Islands using 16S rRNA-based pyrosequencing. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Pu, H.; Cai, D.; Luo, G.; Zhao, L.; Li, K.; Zou, J.; Zhao, X.; Yu, M.; Wu, Y.; et al. Characterization of the bacterial microbiota in different gut and oral compartments of splendid japalure (Japalura sensu lato). BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colston, T.J.; Jackson, C.R. Microbiome evolution along divergent branches of the vertebrate tree of life: What is known and unknown. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3776–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichert, A.; Corzett, C.H.; Schechter, M.S.; Unfried, F.; Markert, S.; Becher, D.; Fernandez-Guerra, A.; Liebeke, M.; Schweder, T.; Polz, M.F.; et al. Verrucomicrobia use hundreds of enzymes to digest the algal polysaccharide fucoidan. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, K.D.; Amaya, J.; Passement, C.A.; Dearing, M.D.; McCue, M.D. Unique and shared responses of the gut flora to prolonged fasting: A comparative study across five classes of vertebrate hosts. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahman, N.; Parks, D.H.; Vanwonterghem, I.; Morrison, M.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P. A phylogenomic analysis of the bacterial phylum Fibrobacteres. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, N.M.; Addison, S.L.; Macdonald, L.J.; Lloyd-Jones, G. Biodiversity of active and inactive bacteria in the gut flora of wood-feeding huhu beetle larvae (Prionoplus reticularis). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7000–7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The controversial role of human gut Lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutschei, T.; Beidler, I.; Bartosik, D.; Seeßelberg, J.M.; Teune, M.; Bäumgen, M.; Ferreira, S.Q.; Heldmann, J.; Nagel, F.; Krull, J.; et al. Marine Bacteroidetes enzymatically digest xylans from terrestrial plants. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 25, 1713–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Robb, C.S.; Unfried, F.; Kappelmann, L.; Markert, S.; Song, T.; Harder, J.; Avcı, B.; Becher, D.; Xie, P.; et al. Alpha- and beta-mannan utilization by marine Bacteroidetes. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 4127–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.; Hehemann, J.H.; Rebuffet, E.; Czjzek, M.; Michel, G. Environmental and gut bacteroidetes: The food connection. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, K.D.; Brun, A.; Magallanes, M.; Brinkerhoff, J.; Laspiur, A.; Acosta, J.C.; Caviedes-Vidal, E.; Bordenstein, S.R. Gut microbial ecology of lizards: Insights into diversity in the wild, effects of captivity, variation across gut regions and transmission. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pei, H.; Xing, T.; Chen, D.; Chen, Y.; Hao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Ding, J. Gut bacteria and host metabolism: The keys to sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) quality traits. Food Chem. 2025, 482, 144178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Luo, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhao, D.; Bi, X.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Xiang, H.; Hu, S. Global marine cold seep metagenomes reveal diversity of taxonomy, metabolic function, and natural products. Genom. Proteom. Bionf. 2024, 22, qzad006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, G.A.; Albarrak, H.; McColl, C.J.; Pizarro, A.; Sanaka, H.; Gomez-Nguyen, A.; Cominelli, F.; Paes Batista da Silva, A. The oral-gut axis: Periodontal diseases and gastrointestinal disorders. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2023, 29, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matějková, T.; Hájková, P.; Stopková, R.; Stanko, M.; Martin, J.F.; Kreisinger, J.; Stopka, P. Oral and vaginal microbiota in selected field mice of the genus Apodemus: A wild population study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.; Schwarzkopf, S.; Kinoshita, A.; Tröscher-Mußotter, J.; Dänicke, S.; Camarinha-Silva, A.; Huber, K.; Frahm, J.; Seifert, J. Evolution of rumen and oral microbiota in calves is influenced by age and time of weaning. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Older, C.E.; Diesel, A.B.; Lawhon, S.D.; Queiroz, C.R.R.; Henker, L.C.; Rodrigues Hoffmann, A. The feline cutaneous and oral microbiota are influenced by breed and environment. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larréché, S.; Bousquet, A.; da Silva, L.; Planelles, A.; Ksas, R.; Mérens, A.; Chippaux, J.P. Antibiotic susceptibility of cultivable microbiota from the oral cavity of captive Bothrops atrox and Bothrops lanceolatus: Implications for the treatment of snakebite-associated infections in the French departments of America. Infect. Dis. Now 2023, 53, 104721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, J.; Fan, Y.; Guo, P.; Tian, Z. Fecal and oral microbiome analysis of snakes from China reveals a novel natural emerging disease reservoir. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1339188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, L.H.; Francis, T.B.; Ferraro, M.; Hehemann, J.H.; Fuchs, B.M.; Amann, R.I. Verrucomicrobiota are specialist consumers of sulfated methyl pentoses during diatom blooms. ISME J. 2022, 16, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podosokorskaya, O.A.; Elcheninov, A.G.; Novikov, A.A.; Merkel, A.Y.; Kublanov, I.V. Fontisphaera persica gen. nov., sp. nov., a thermophilic hydrolytic bacterium from a hot spring of Baikallake region, and proposal of Fontisphaeraceae fam. nov., and Limisphaeraceae fam. nov. within the Limisphaerales ord. nov. (Verrucomicrobiota). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 46, 126438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, C.; Cao, P.; Xu, C.; Hou, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L. Flora in the throat and risk factors for Laryngeal Carcinoma. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7356–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumoff, D.G.; Dedysh, S.N. Bacteria from poorly studied phyla as a potential source of new enzymes: β-galactosidases from planctomycetes and verrucomicrobia. Microbiology 2018, 87, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.-Y.; Liu, X.-J.; Lu, D.-C.; Ye, Y.-Q.; Liu, X.-Y.; Yu, F.; Yang, H.; Li, F.; Du, Z.-J.; Ye, M.-Q. Insights into the physiological and metabolic features of Thalassobacterium, a novel genus of Verrucomicrobiota with the potential to drive the carbon cycle. MBio 2025, 16, e0030525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, C.A.; Vuong, H.E.; Yano, J.M.; Liang, Q.Y.; Nusbaum, D.J.; Hsiao, E.Y. The Gut Microbiota mediates the anti-seizure effects of the ketogenic diet. Cell 2018, 173, 1728–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwerkerk, J.P.; van der Ark, K.C.H.; Davids, M.; Claassens, N.J.; Finestra, T.R.; de Vos, W.M.; Belzer, C. Adaptation of Akkermansia muciniphila to the oxic-anoxic interface of the mucus layer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6983–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, P.M.; Bay, S.K.; Meier, D.V.; Chiri, E.; Cowan, D.A.; Gillor, O.; Woebken, D.; Greening, C. Energetic basis of microbial growth and persistence in desert ecosystems. MSystems 2020, 5, e00495-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demergasso, C.; Neilson, J.W.; Tebes-Cayo, C.; Véliz, R.; Ayma, D.; Laubitz, D.; Barberán, A.; Chong-Díaz, G.; Maier, R.M. Hyperarid soil microbial community response to simulated rainfall. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1202266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Bray–Curtis | Unweighted UniFrac | Weighted UniFrac | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | F | p | F | p | F | p | |||
| FG vs. OG | 6.916091 | 0.301801 | 0.001 | 15.87053 | 0.497969 | 0.001 | 14.08823 | 0.468231 | 0.001 |
| FG vs. EG | 5.171305 | 0.319783 | 0.002 | 7.654786 | 0.410339 | 0.003 | 14.88895 | 0.575108 | 0.002 |
| OG vs. EG | 4.384139 | 0.284978 | 0.001 | 4.578687 | 0.293907 | 0.005 | 9.050716 | 0.451391 | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; He, J.; Luo, J.; Xiong, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, D. Multi-Niche Microbiota of a Desert-Adapted Lizard: 16S rRNA Profiling of Teratoscincus roborowskii Endemic to the Turpan Depression in Northwest China. Animals 2025, 15, 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223273
Luo X, He J, Luo J, Xiong H, Xiao Y, Zhao Y, Guo X, Chen D. Multi-Niche Microbiota of a Desert-Adapted Lizard: 16S rRNA Profiling of Teratoscincus roborowskii Endemic to the Turpan Depression in Northwest China. Animals. 2025; 15(22):3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223273
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xing, Jinlei He, Jie Luo, Hang Xiong, Yuying Xiao, Yanqin Zhao, Xianguang Guo, and Dali Chen. 2025. "Multi-Niche Microbiota of a Desert-Adapted Lizard: 16S rRNA Profiling of Teratoscincus roborowskii Endemic to the Turpan Depression in Northwest China" Animals 15, no. 22: 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223273
APA StyleLuo, X., He, J., Luo, J., Xiong, H., Xiao, Y., Zhao, Y., Guo, X., & Chen, D. (2025). Multi-Niche Microbiota of a Desert-Adapted Lizard: 16S rRNA Profiling of Teratoscincus roborowskii Endemic to the Turpan Depression in Northwest China. Animals, 15(22), 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223273






