Simple Summary
Fatness management in late-pregnancy sows is critical for optimizing reproductive performance and subsequent productivity, as it is closely associated with maternal metabolic status. Given the essential roles of gut microbiota in host metabolic pathways, microbiota-related research has received increasing attention over the past few decades. Our previous study demonstrated that protocatechuic acid (PCA) significantly improved glycolipid metabolism in a murine model, but relevant applications of PCA in sows remain largely unexplored. To provide a scientific basis for the rational utilization of PCA and PCA-rich natural resources, this study aims to investigate the effects of dietary supplementation with PCA and PCA-rich Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract (EU) on reproductive performance in late-pregnancy sows. Results in this paper showed that dietary supplementation with PCA and PCA-rich EU enhanced reproductive performance and colostrum immunoglobulin levels in late-pregnancy sows, which were potentially mediated through alteration of maternal gut microbiota linked to inflammation and glucose metabolism. This original manuscript provides scientific references for the rational utilization of PCA, EU, and other PCA-rich natural resources in sow feeding programs.
Abstract
Nutrition during late pregnancy plays a critical role in fetal development. This study was conducted to investigate the effects and underlying mechanisms of protocatechuic acid (PCA) and PCA-rich Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract (EU) on reproductive performance using late-pregnancy sows as a model. A total of 30 sows (Landrace × Yorkshire; average parity: 3–4) with similar body condition (assessed as a score of 4 on a 5-point scale) were randomly assigned to three treatments (n = 10 per group) from day 80 of gestation until farrowing and fed either a basal diet, a basal diet supplemented with 200 g/t of PCA, or 1000 g/t of EU. Results demonstrated that dietary supplementation with PCA and EU, which delivered a negligible amount of PCA but contained other bioactive phytochemicals such as chlorogenic acid, significantly increased litter weight at birth and the number of healthy piglets (p < 0.05), along with elevated levels of colostral immunoglobulins and reduced serum interleukin (IL)-6 concentrations (p < 0.05). Furthermore, PCA supplementation was associated with a decrease in fasting glucose levels and improved insulin sensitivity (p < 0.05), accompanied by an increased relative abundance of Bacteroidetes (p < 0.05). Analysis of gut microbial composition revealed that both PCA and EU reduced the relative abundance of Paraprevotella (p < 0.05), while PCA increased the abundance of the dgA11_gut_group (p < 0.05), and EU enriched Caldicoprobacter (p < 0.05). Correlation analysis indicated that PCA- and EU-modulated genera, such as Lysinibacillus, were positively associated with colostrum lactose and colostrum fat but negatively correlated with the number of somatic cells, colostrum protein, degreased dry matter, total solids, and urea nitrogen (p < 0.05). In conclusion, dietary supplementation with PCA and EU differentially enhanced reproductive performance and colostrum immunoglobulins, at least partially, through the modulation of inflammation and glucose metabolism-related gut microbiota in late-pregnancy sows.
1. Introduction
Late pregnancy represents a critical developmental window for the fetus, particularly in mammalian species [1]. During this period, the maternal physiological status undergoes dynamic biochemical changes that influence fetal development via placental transfer [2]. Maintaining glycolipid metabolic homeostasis during late pregnancy is essential for optimal maternal performance, as multiple tissues compete for plasma glucose to support mammary gland development, fetal growth, milk synthesis, and uterine contractions [3]. Physiological insulin resistance facilitates the redistribution of glucose to support both mammary and fetal development. However, persistent and excessive insulin resistance, referred to as pathological insulin resistance, can have detrimental effects on both mother and fetus [4]. A clinical study involving 2647 women with gestational diabetes mellitus in late pregnancy revealed that increased insulin resistance is predictive of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including cesarean delivery, preterm birth, and macrosomia [5]. Colostrum-derived immunoglobulins are crucial for the establishment of neonatal immunity [6], yet maternal hyperglycemia-induced immunostimulation in colostrum [7] has been associated with unfavorable metabolic profiles in offspring, including elevated biomarkers of insulin resistance [8]. Maternal obesity is linked to systemic inflammation and may expose the developing fetus to inflammatory environments [9]. Research has indicated that obesity in sows promotes placental lipotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammation, potentially through activation of the JNK/NF-κB signaling pathway [10]. As an emerging research focus [11,12,13], gut microbiota play pivotal roles in ameliorating insulin resistance and promoting placental angiogenesis [14], and can profoundly influence maternal and offspring health through vertical transmission [15]. Crusell et al. [16] observed a decline in fecal microbial OTUs (p = 0.0002) and Shannon’s diversity (p = 0.012) from late pregnancy to postpartum in a cohort of 125 pregnant women (43 women with gestational diabetes mellitus and 82 women with normal glucose), suggesting a potential link to heightened inflammatory responses and insulin resistance [17]. Alterations in gut microbiota during late pregnancy are closely associated with the absorption and metabolism of microbiota-derived metabolites such as glucose, thereby contributing to the formation of a specialized metabolic system that supports maternal tissue and fetal development [18].
Although dietary restriction is a commonly used and cost-effective strategy for managing body condition in pregnant sows [19], natural feed additives offer promising alternatives that reduce the need for high-level technical expertise in on-farm management [20]. Polyphenol-rich wild plants are widely consumed globally [21,22]. Anthocyanins, due to their catecholic structure, exhibit potent antioxidant properties and hold promise as therapeutic agents for metabolic disorders, as demonstrated in rodent models and human clinical trials [23]. Our previous studies have demonstrated that anthocyanins, particularly cyanidin-3-glucoside (C3G), derived from blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L. berry), can alleviate inflammation [24] and improve glucose metabolism [25] in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese mice. Protocatechuic acid (PCA), a phenolic metabolite of C3G found in numerous plant species, especially in the endemic Chinese herb Eucommia ulmoides native to Zhangjiajie, Hunan Province, has been shown to improve inflammation and insulin resistance in mice by upregulating fibroblast growth factor 1 (Fgf1), insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (Igfbp2), insulin receptor substrate 1 (Irs1), and insulin receptor substrate 2 (Irs2) [26] and to modulate gut microbiota in piglets (Pig Improvement Company line 337 × C48, 28 d of age, 8.87 kg ± 0.11 kg BW) [27]. Therefore, this study was designed to investigate the effects of dietary supplementation with PCA and PCA-rich Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract (EU) on the reproductive performance, immune status, metabolic parameters, and gut microbiota of sows during late pregnancy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diets and Reagents
The composition of pregnancy feed is shown in Supplemental Table S1. Protocatechuic acid (PCA ≥ 97%, HPLC) was purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract (EU) was provided by Hengxing Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Zhangjiajie, Hunan, China).
2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
The concentration of PCA in EU was detected using an HPLC system with a C18 column (250 × 4.6 mm, JASGC, Tokyo, Japan). Briefly, EU (40 mg/mL) was dissolved in a 100% methanol aqueous solution, followed by shaking and ultrasonic treatment for at least 1 h, and ultimately filtered with a Nylon filter (13 mm × 0.22 μm, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Shanghai, China). To calculate concentration of PCA, the solvent system was a mixture of A (100% CH3CN) and C (0.1% HCOOH in water), and the gradient was as follows: 0–5 min (5% A; 95% C); 5–10 min (7% A; 93% C); 10–20 min (13% A; 87% C); 20–30 min (16% A; 84% C); 30–40 min (25% A; 75% C); 40–41 min (30% A; 70% C); 41–47 min (90% A; 10% C); and 47–52 min (5% A; 95% C), with the flow rate of 1.2 mL/min, 10 μL sample and column temperature of 35 °C. Spectrophotometric detection was performed at 254 nm using an Agilent 1260 Infinity II HPLC system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The concentration of PCA in EU was identified according to retention time with the known compounds as standards (PCA ≥ 97%, HPLC).
2.3. Experimental Design
The experimental procedures were approved by the Hunan Agricultural University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Permission No. 2020034). A total of 30 sows (Landrace × Yorkshire; average parity: 3–4) with similar body condition (assessed as a score of 4 on a 5-point scale) were randomly allocated into 3 treatments (n = 10) on day 80 of pregnancy. The sample size of n = 10 sows per group was determined based on common practice and observed effect sizes in the prior literature investigating dietary interventions in late-pregnancy sows [28,29]. All 3 groups were fed the same basal diet (control group, CTL; for composition, see Table S1). The PCA and EU groups were prepared by top-dressing the basal diet with the respective additive using a feed mixer immediately prior to feeding. The final diets consisted of the basal diet supplemented with 200 g/t of PCA (PCA group), or 1000 g/t of EU (EU group). Sows were housed in an environmentally controlled gestation barn (30 m × 10 m) under a 12 h light/12 h dark cycle, with ambient temperature maintained at 20 ± 2 °C and relative humidity at 60–70%. Each sow was kept in an individual stall (0.6 m × 2.1 m).
On day 110 of gestation, sows were moved to individual farrowing pens (2.2 m × 1.8 m) in a separate, environmentally controlled farrowing room. The farrowing room was maintained under the same light cycle (12 h light/12 h dark) and similar humidity (60–70%). The ambient temperature for the sows was maintained at approximately 20–22 °C, with supplemental localized heat (e.g., heat lamps) provided for the newborn piglets within the creep area of the pen. Before that, the body condition scores of sows approaching farrowing were recorded via a generic sow body condition caliper. Then, fasting auricular venous blood and colostrum samples were collected during the farrowing process (within 2 h of the first piglet being born). Moreover, reproductive performance was accurately recorded.
2.4. Reproductive Performance
Reproductive performance, including average individual weight, total litter size, litter weight at birth, number of healthy piglets (Landrace × Yorkshire), number of weak piglets (≤0.5 kg), number of stillbirths, and stillbirth rate in each sow, was recorded and analyzed.
2.5. Analysis of Colostrum Composition
Seven items in regular analysis of colostrum, including somatic cell number, colostrum fat, colostrum protein, colostrum lactose, degreased dry matter, total solids, and urea nitrogen, were achieved by the Hunan Dairy Cow Production Performance Measurement Center (Changsha, China).
The contents of immunoglobulins (IgG and IgM) in colostrum were tested using commercial swine-specific ELISA kits (Shanghai Enzyme-linked Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The absorbance was read using a porous chemiluminescence instrument (Varioskan flash, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.6. Analysis of Serum Indexes
Serum was obtained with centrifugation at 1500× g for 10 min after standing at room temperature for at least 30 min. Levels of glucose, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and malondialdehyde (MDA) in serum were detected using commercial assay kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Research Institute, Nanjing, China) following the manufacturer’s protocols. Levels of insulin, IL-1β, and IL-6 in serum were detected, according to ELISA kits (Shanghai Enzyme-linked Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). All the above indices were determined with a porous chemiluminescence instrument (Varioskan flash, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
Insulin resistance was reflected with HOMA-IR (homeostasis model assessment-estimated insulin resistance) according to the following formula [30]:
HOMA-IR = fasting insulinemia (mIU/L) × fasting glycemia (mg/dL)/405
2.7. Analysis of Gut Microbiota
Fresh fecal samples were collected from each sow via rectal stimulation on the day of farrowing (within 2 h of the first piglet being born), immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C until DNA extraction. Fecal DNA was extracted using a commercial Stool DNA Isolation Kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China). The quality and concentration of the extracted DNA were verified using a Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA). Amplification of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene V4 region was conducted with barcoded primers 515F (5′-GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′), as detailed in Supplementary Table S3. The PCR mixture (25 µL) contained 12.5 µL of 2× Taq PCR MasterMix, 1 µL of each primer (5 µM), 3 µL of BSA (2 ng/µL), 3 µL of DNA template (30 ng), and 4.5 µL of ddH2O. The thermal cycling conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min; 25 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 45 s, annealing at 50 °C for 50 s, and extension at 72 °C for 45 s, followed by a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. Amplicons were purified, quantified, pooled in equimolar ratios, and sequenced on an Illumina platform by Allwegene Technology Inc. (Beijing, China) [26].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
All data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Statistics (Version 21.0, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Differences among the 3 treatment groups were assessed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). When the ANOVA indicated a significant effect, post hoc comparisons were conducted using Fisher’s Least Significant Difference (LSD) test. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The relationship between gut microbiota and measured indicators was evaluated using Pearson’s correlation analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Calculation of Concentration of PCA in EU
Complex substances in EU were detected at 254 nm. Among these, chlorogenic acid was the most abundant component (see Supplementary Figure S1A). The concentration of PCA in EU was calculated to be 0.18 mg/g by establishing a standard curve based on the standard concentration and peak area (see Supplementary Figure S1B).
3.2. Effect of PCA and EU on the Body Condition Score of Sows
As depicted in Supplementary Figure S2A, PCA showed a non-significant tendency to reduce the body condition score of sows (p = 0.062, 5.06 ± 0.80, 4.37 ± 0.92, and 4.98 ± 0.67 for the CTL, PCA, and EU groups, respectively).
3.3. Supplement of PCA and EU Differentially Enhanced Reproductive Performances, as Reflected by Litter Weight at Birth and the Number of Healthy Piglets
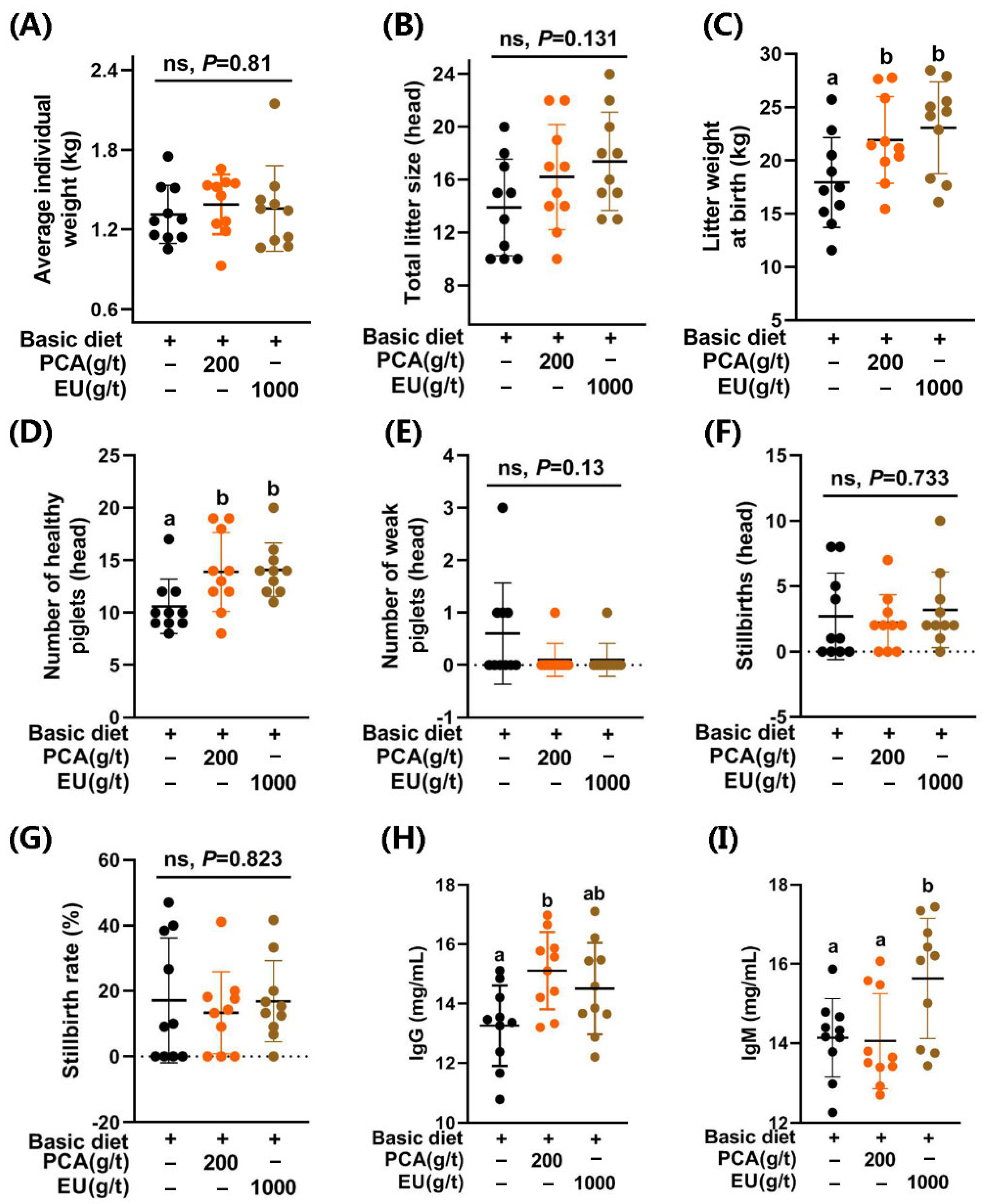
As shown in Figure 1, supplementation with PCA significantly increased the litter weight at birth (p < 0.05, Figure 1C) and the number of healthy piglets (p < 0.05, Figure 1D). A similar improvement was observed in the EU group (p < 0.05). However, they had limited effects (p > 0.05) on the average individual weight (Figure 1A), total litter size (Figure 1B), the number of weak piglets (≤0.5 kg) (Figure 1E), the number of stillbirths (Figure 1F), and the stillbirth rate (Figure 1G).
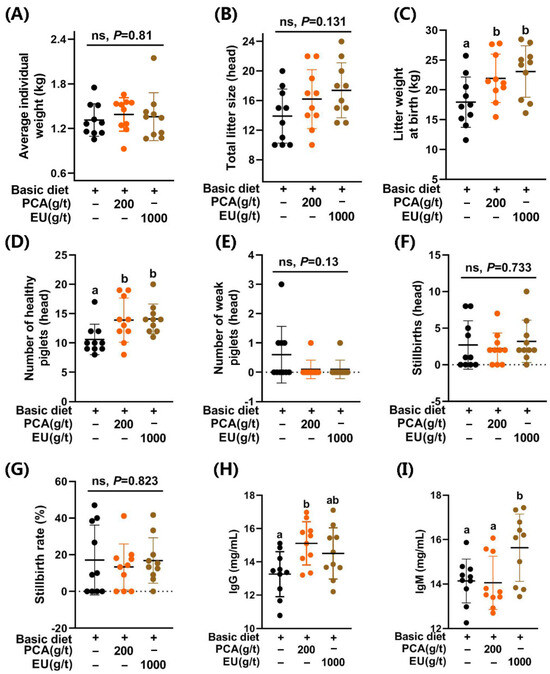
Figure 1.
Effects of PCA and EU on reproductive performance and immunoglobulins in sows during late pregnancy. (A) Average individual weight. (B) Total litter size. (C) Litter weight at birth. (D) Number of healthy piglets. (E) Number of weak piglets. (F) Stillbirths. (G) Stillbirth rate. Contents of IgG (H) and IgM (I) in colostrum. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 10). Bars with different letters differ significantly (p < 0.05). EU, Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract; PCA, protocatechuic acid. Different lowercase letters above the bars indicate statistically significant differences among groups (p < 0.05), ns represents a non-significant difference (p ≥ 0.05).
3.4. Supplementation with PCA and EU Differentially Increased Immunoglobulins in Colostrum
Supplementation with PCA and EU had no significant effects on seven items in the routine analysis of colostrum (p > 0.05, see Supplementary Figure S2B–H). Interestingly, PCA supplementation significantly elevated the levels of IgG in colostrum (p < 0.05, Figure 1H). Differently, EU supplementation significantly increased the levels of IgM in colostrum (p < 0.05, Figure 1I).
3.5. Effects of PCA and EU on the Redox Status, Inflammatory Cytokines, and Glucose Metabolism in Serum
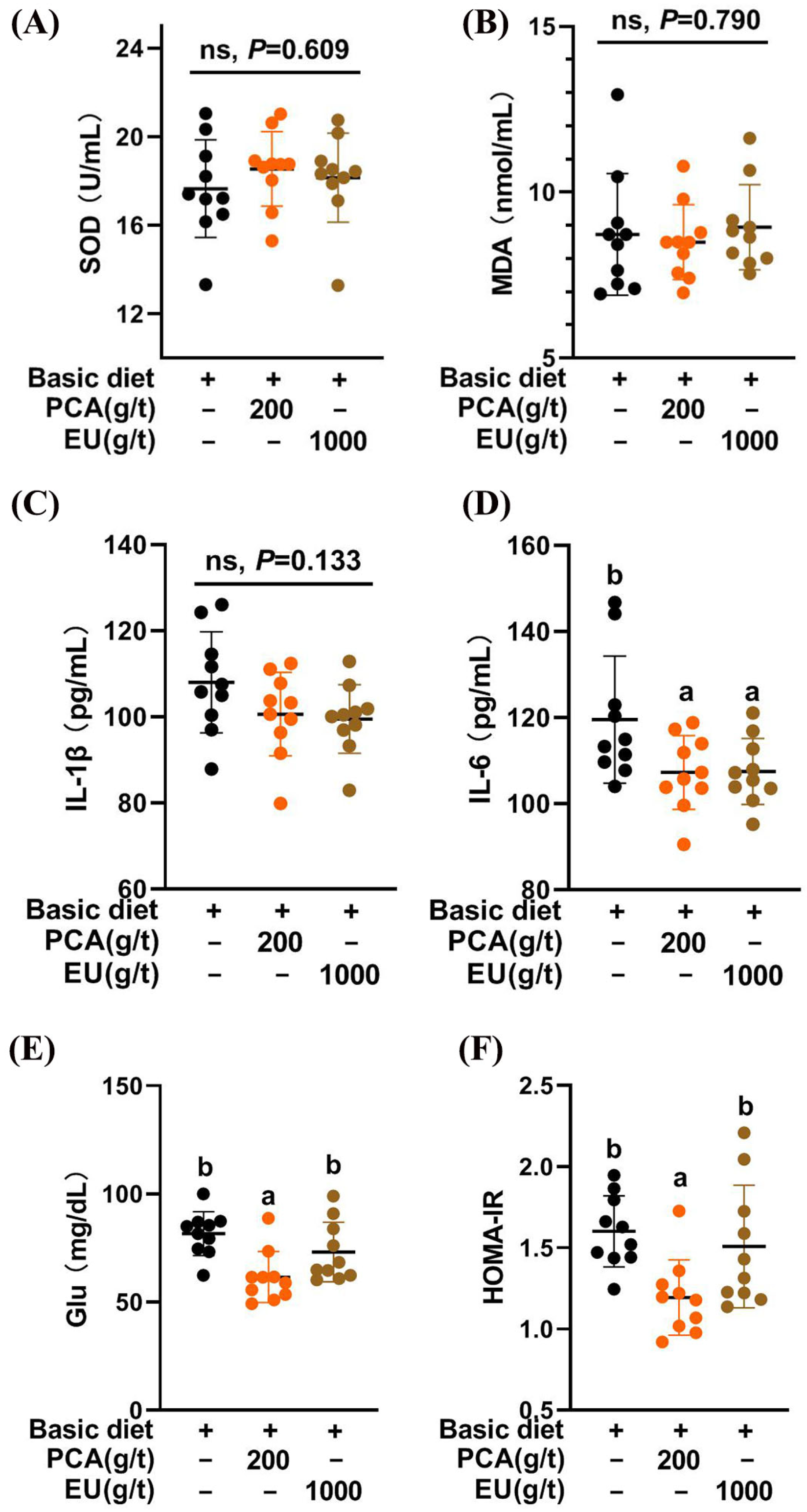
As shown in Figure 2A,B, the CTL, PCA group, and EU group exhibited similar redox statuses (p > 0.05).
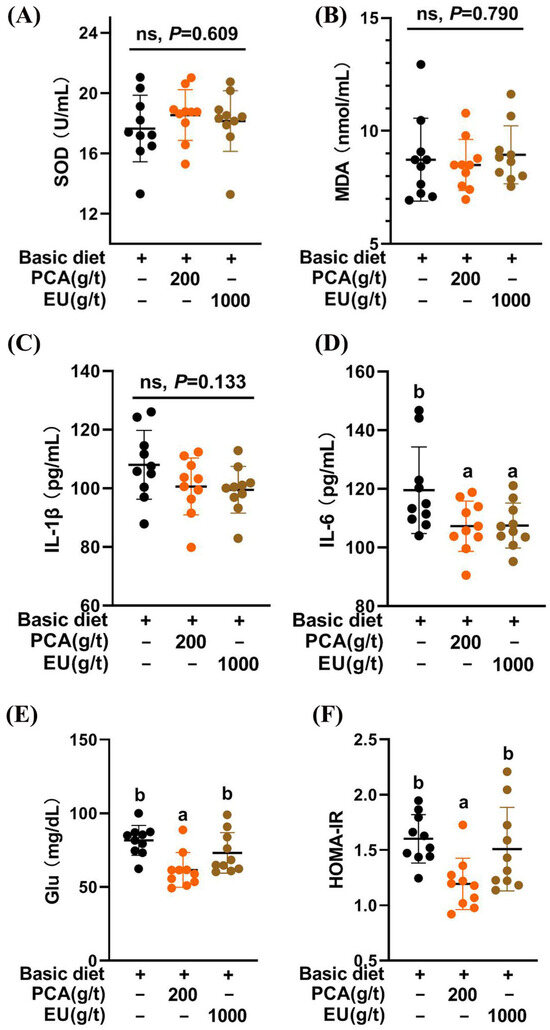
Figure 2.
Effects of PCA and EU on redox status, inflammatory cytokines, and glucose metabolism in sows during late pregnancy. (A) Levels of SOD in serum. (B) Levels of MDA in serum. (C) Levels of IL-1β in serum. (D) Levels of IL-6 in serum. (E) Levels of glucose in serum. (F) Insulin resistance in serum. EU, Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract; Glu, glucose; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment-estimated insulin resistance; MDA, malondialdehyde; PCA, protocatechuic acid; SOD, superoxide dismutase. Different lowercase letters above the bars indicate statistically significant differences among groups (p < 0.05), ns represents a non-significant difference (p ≥ 0.05).
3.6. Effects of PCA and EU on Gut Microbiota
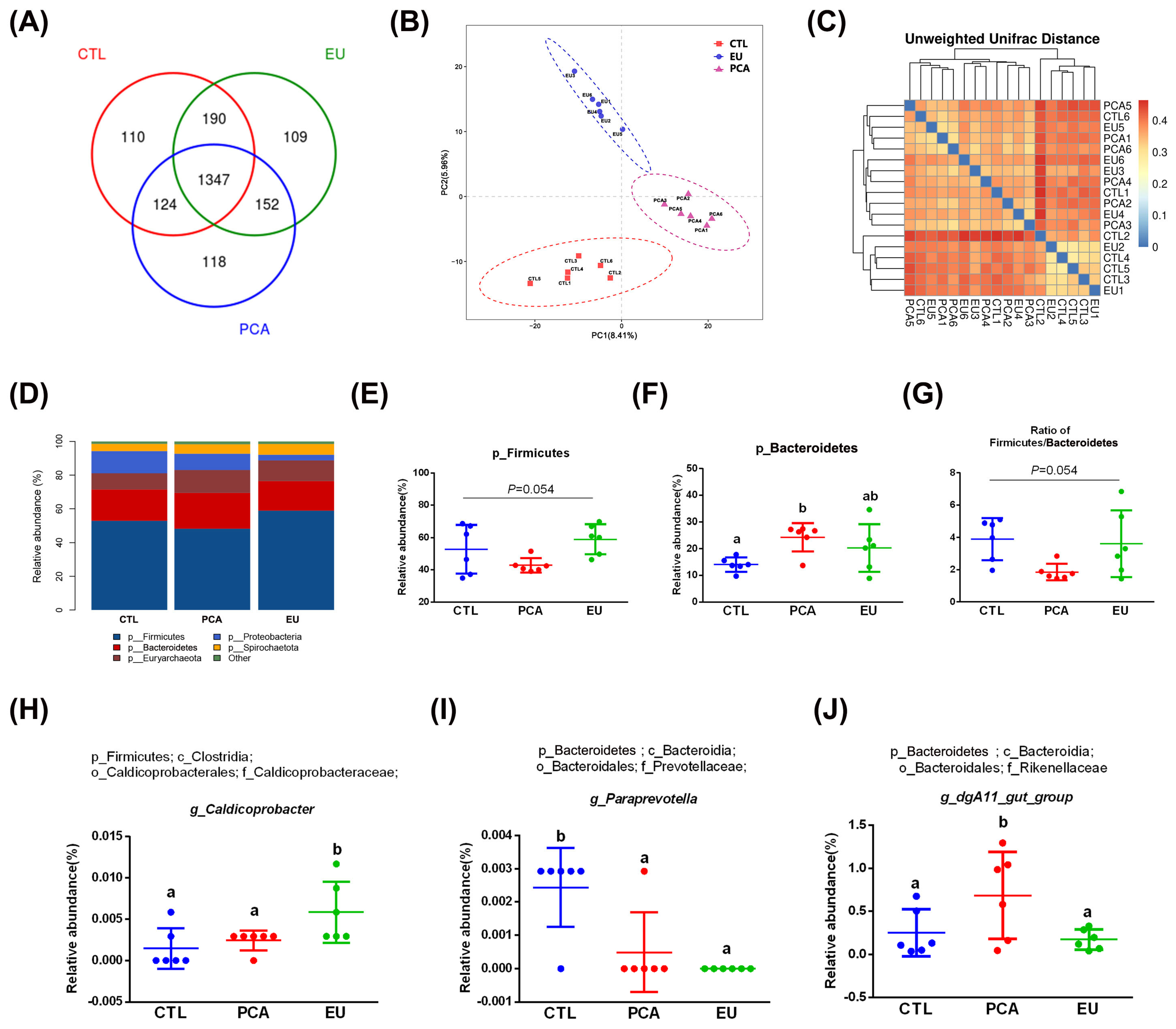
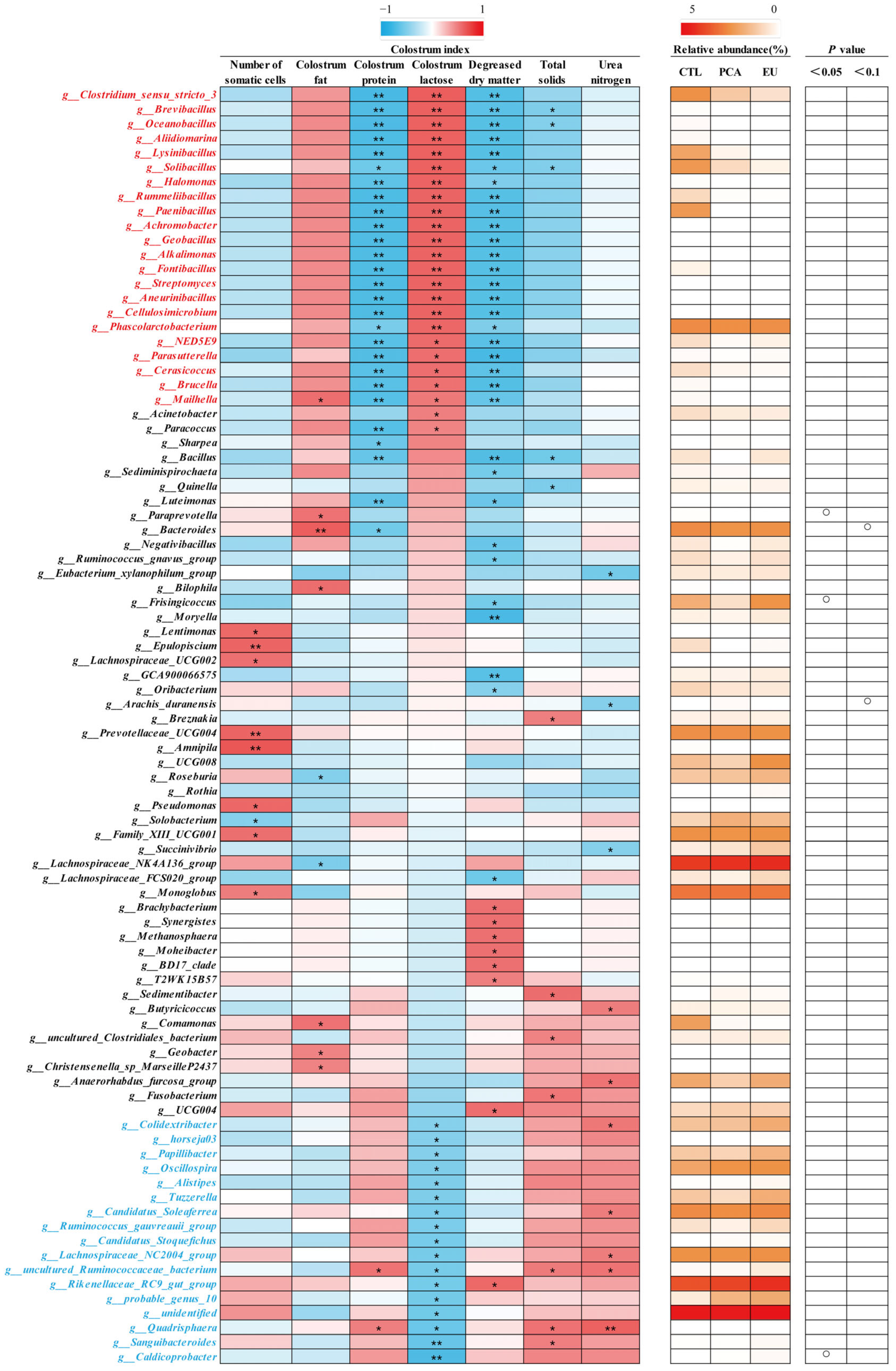
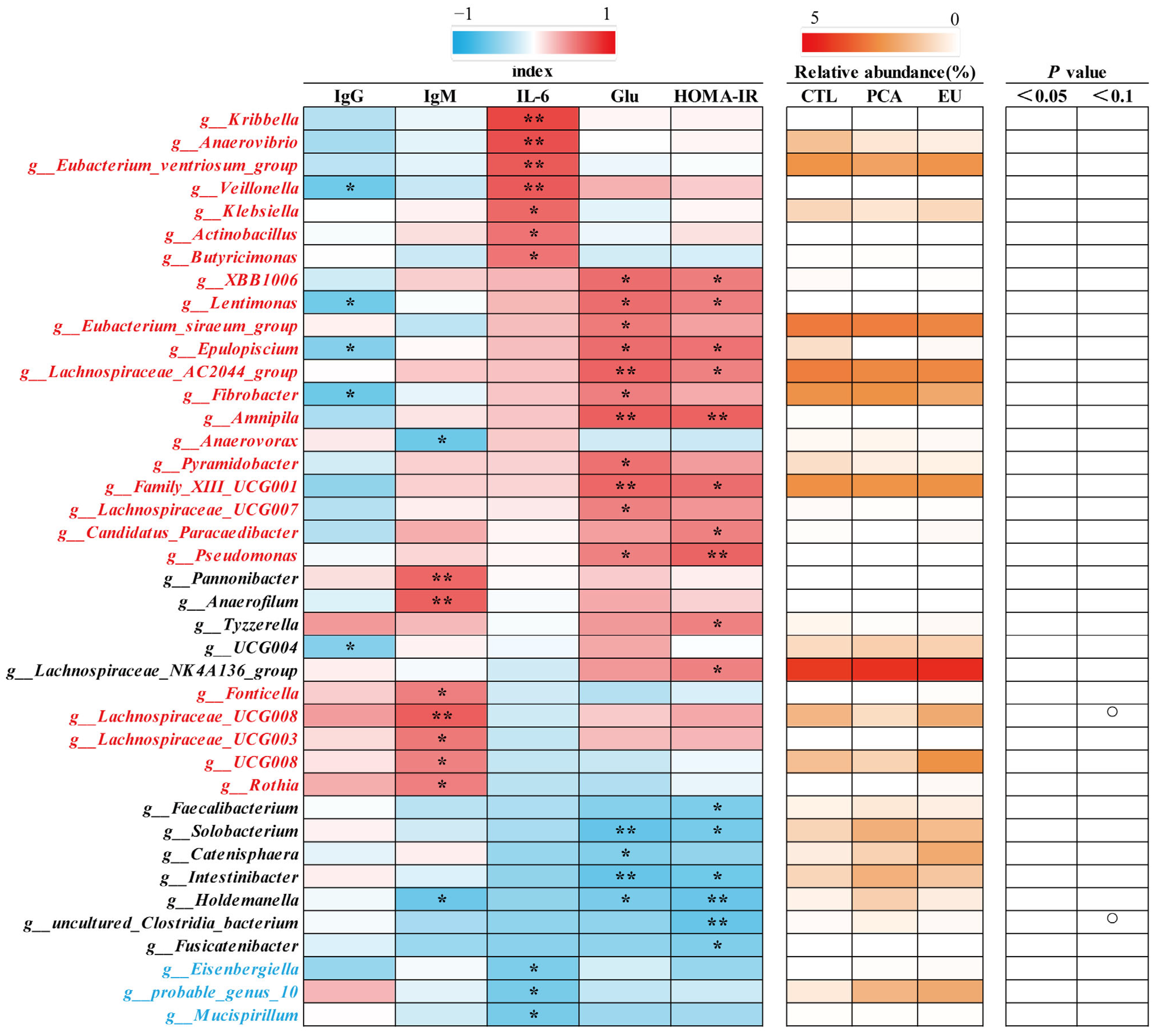
Supplementation with PCA and EU led to greater gut microbiota diversity (see Supplementary Table S2 and Figure 3A). When compared to the CTL group, closer clusters were observed between the PCA and EU groups (Figure 3B,C). Although PCA showed a non-significant trend in the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes (p = 0.054, Figure 3G), it increased the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes (p < 0.05, Figure 3F). However, in the EU group, these changes were not significant (p > 0.05, Figure 3D–G). Further analysis at the genus level revealed that EU increased the relative abundance of Caldicoprobacter (p < 0.05, Figure 3H), while PCA increased the relative abundance of dgA11_gut_group (p < 0.05, Figure 3J). Compared to the CTL group, both EU and PCA decreased the relative abundance of Paraprevotella (p < 0.05, Figure 3I). All genera that were significantly correlated with the indicators were screened. Correlation analysis between gut microbiota and colostrum indicators showed that several genera positively correlated with colostrum lactose or fat had a relative decrease in the PCA and EU groups, such as Clostridium_sensu_stricto_3 and Lysinibacillus. These gut microbiota were negatively correlated with the number of somatic cells, colostrum protein, degreased dry matter, total solids, and urea nitrogen. Conversely, genera that negatively correlated with colostrum lactose, including Caldicoprobacter and Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, had a relative increase in the PCA and EU groups, and these gut microbiota were positively correlated with colostrum protein, degreased dry matter, total solids, and urea nitrogen (Figure 4). Correlation analyses between gut microbiota, immunoglobulins, and serum indicators revealed that genera, such as Anaerovibrio and Veillonella, positively correlated with IL-6 or insulin resistance suppressed in the PCA and EU group. However, these gut microbiota were negatively correlated with IgG or IgM. Additionally, genera, including Rothia, negatively correlated with IL-6 or insulin resistance showed a relative increase in the PCA and EU group, and these gut microbiota were positively correlated with IgG or IgM (Figure 5).
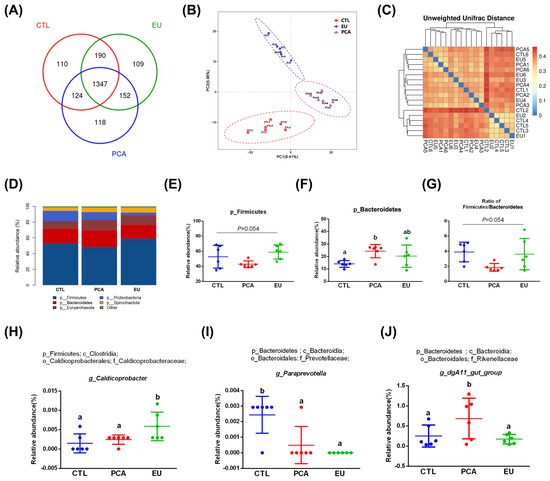
Figure 3.
Effects of PCA and EU on gut microbiota in sows during late pregnancy. (A) Venn plot between the CTL, EU, and PCA groups. (B) PLS-DA. (C) β-diversity indices of unweighted_unifrac_distance. The redder the color, the farther the distance. (D) Relative abundance of gut microbiota at phylum levels. Relative abundance of Firmicutes (E) and Bacteroidetes (F). (G) Ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes. Relative abundance of Caldicoprobacter (H), Paraprevotella (I), and dgA11_gut_group (J). EU, Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract; PCA, protocatechuic acid; PLS-DA, partial least squares discrimination analysis. Different lowercase letters above the bars indicate statistically significant differences among groups (p < 0.05).
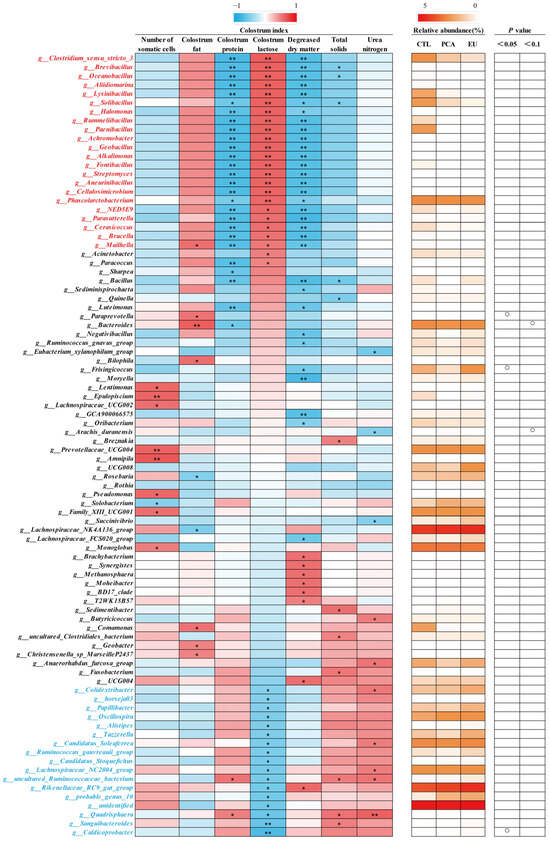
Figure 4.
Correlation of genera and colostrum indicators. The intensity of the colors represents the degree of association (red, positive correlation; blue, negative correlation) or represents the relative abundance of a specific genus in CTL, PCA, and EU groups from 0–5% (from white to red). Significant correlations were found at * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, which represent in the form of a circle. EU, Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract; PCA, protocatechuic acid.
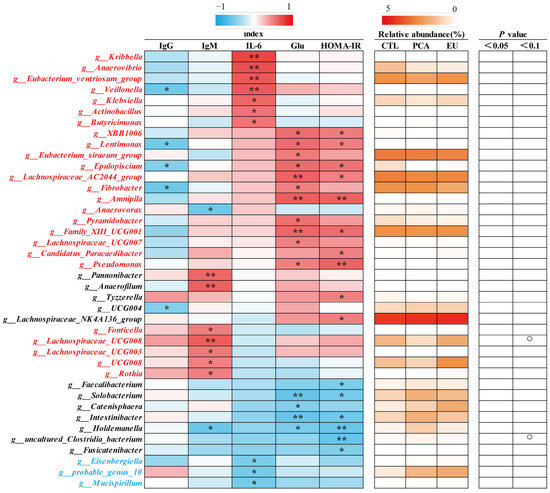
Figure 5.
Correlation of genera and immunoglobulins together with serum indicators. The intensity of the colors represents the degree of association (red, positive correlation; blue, negative correlation) or represents the relative abundance of a specific genus in CTL, PCA, and EU groups from 0–5% (from white to red). Significant correlations were found at * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, which represent in the form of a circle. EU, Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract; Glu, glucose; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment-estimated insulin resistance; PCA, protocatechuic acid.
4. Discussion
An undesirable lighter weight at birth results in reduced viability of the offspring, leading to increased pre-weaning mortality rates [31]. It has been noted that the genetics-selected hyperprolific profiles of sows are a major contributing factor to the occurrence of low-viability piglets (Duroc × Landrace × Yorkshire) and neonatal mortality [32]. In comparison to the control group (CTL), supplementation with PCA and EU significantly enhanced litter weight at birth (21.93 ± 4.05 vs. 23.08 ± 4.31 vs. 17.94 ± 4.22; PCA vs. EU vs. CTL) and the number of healthy piglets (13.9 ± 3.75 vs. 14.1 ± 2.56 vs. 10.6 ± 2.59; PCA vs. EU vs. CTL) but with modest effects on average individual weight (1.39 ± 0.23 vs. 1.36 ± 0.32 vs. 1.31 ± 0.22; PCA vs. EU vs. CTL) or total litter size (16.2 ± 3.99 vs. 17.4 ± 3.72 vs. 13.9 ± 3.67; PCA vs. EU vs. CTL), suggesting that normal individual weights can be maintained even with larger litter sizes [33]. Appropriate interventions during late pregnancy can enhance the survival rates of low-birthweight piglets. Otherwise, an increase in total litter size may prove detrimental to their health outcomes. Notably, collaborative efforts aimed at improving both birthweights and colostrum quality play a crucial role in ensuring piglet survival from birth through weaning [34]. Supporting this notion, the addition of PCA significantly elevated IgG levels in colostrum, while supplementation with EU notably increased IgM concentrations in colostrum.
The results of improvements in birth weight, the number of healthy piglets, and colostrum immunoglobulin content following the addition of PCA and EU were consistent with the effects observed from supplementation with other bioactive substances, such as conjugated linoleic acids [35,36] and various polyphenols [37]. This suggests a potential influence of PCA and EU on the immunity-related status of sows that is transmitted to their offspring [15]. Given that chronic low-grade inflammation contributes to insulin resistance [38], our findings strongly support that the inclusion of PCA improved glucose metabolism and reduced inflammatory cytokine production in sows during late pregnancy. This aligns with our recent research indicating that PCA enhanced the expression of genes associated with insulin action, particularly Fgf1, Igfbp2, Irs1, and Irs2 [26]. Unexpectedly, EU did not demonstrate significant improvement in glucose metabolism within this study. This might be attributed to its lower PCA content (0.018%), which was less than reported concentrations in other studies (0.04–0.05%) [39]. It is critical to note that the physiological effects observed in the PCA and EU groups likely stem from distinct mechanisms, given the vast difference in the delivered dose of protocatechuic acid. The effects of the high-dose, pure PCA are directly attributable to this compound. In contrast, the benefits of the EU extract, which delivered a negligible amount of PCA, are most likely mediated by other bioactive constituents (e.g., chlorogenic acid, a well-documented polyphenol known for its bioactive regulatory effects on inflammation [40,41,42].) present in the complex phytochemical matrix or through synergistic effects among them.
Higher levels of IgG coupled with lower levels of IgM or IgA constitute critical components of colostrum immune substances [43]. As an immunity-enhancing substance transmitted prenatally to offspring via either the placenta or yolk sac in sows [44], colostrum IgG levels can increase even at lower systemic inflammation levels [45] when supplemented with PCA. This finding was further supported by correlations observed between gut microbiota and immunoglobulins alongside serum indicators. Consequently, our previous study demonstrated that PCA mitigated inflammation in LPS-induced piglets (Pig Improvement Company line 337 × C48) [27]. Additionally, this study confirmed that both PCA and EU significantly decreased serum IL-6 levels. Another investigation also indicated that PCA inhibited IgG leakage in ischemia-induced rats [46]. The dietary EU utilized in this study demonstrated a significant enhancement in reproductive performance, alongside an increase in colostrum IgM.
Gut microbiota play crucial roles in maintaining metabolic balance during pregnancy in sows. This notion is supported by studies demonstrating that dietary interventions, such as liquid whey-enriched diets, can significantly reshape the gut microbial community and improve intestinal health in pigs [47,48]. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio has been proposed as a potential biomarker for an imbalanced microbial community, which is often associated with inflammatory and metabolic disorders [49]. Evidence indicates that Firmicutes are more effective than Bacteroidetes as an energy source, promoting more efficient caloric absorption [27]. In the current study, although PCA rather than EU supplementation significantly increased the abundance of Bacteroidetes, the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio only exhibited a non-significant trend towards a decrease, which may be attributed to concurrent, non-significant variations within the Firmicutes phylum. This finding might elucidate their differing impacts on glucose metabolism. Furthermore, three genera were found to be significantly influenced by EU and PCA. For instance, Caldicoprobacter, identified as a primary candidate responsible for enhanced production of hydrolytic enzymes [50], was elevated by EU. dgA11_gut_group, a genus with limited research, showed increased levels due to PCA. Conversely, Paraprevotella, recognized as an opportunistic pathogen [51], was reduced by both EU and PCA.
Although the composition of colostrum is critical for piglets to obtain energy and maintain body temperature, sow-derived colostrum is characterized by a high content of protein but a relatively low content of lactose and fat [52]. In the present study, EU and PCA had limited effects on the number of somatic cells, fat, protein, lactose, degreased dry matter, total solids, and urea nitrogen in colostrum. However, several genera, including Clostridium_sensu_stricto_3 and Lysinibacillus, decreased in the PCA and EU groups and were positively correlated with colostrum lactose and colostrum fat rather than the number of somatic cells, colostrum protein, degreased dry matter, total solids, and urea nitrogen, while genera, such as Caldicoprobacter and Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, exhibited a reversed relevance. These results might offer an explanation that PCA and EU improved maternal immunostimulatory response in colostrum, potentially through modulating gut microbiota, thus improving the metabolic status of sows during late pregnancy. These genera belonged to different phyla and occupied a relatively considerable quantity, even though most of them had no statistical significance in the EU and PCA groups.
5. Conclusions
Dietary supplementation of PCA (200 g/t) and complex EU (1000 g/t) in sows during late pregnancy can differentially and effectively improve reproductive performance and colostrum immunoglobulin contents, at least partly by regulating inflammation and glucose metabolism-related microbial community structure.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani15213166/s1. Figure S1: Quantification of protocatechuic acid (PCA) in Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract (EU) with HPLC; Figure S2: Effects of PCA or EU on body condition scores and colostrum composition of sows; Table S1: Composition and nutrient levels of basal diet during pregnancy; Table S2: The effects of PCA and EU on the α-diversity of gut microbiota; Table S3: Primer sequences used in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.H., H.Z. and S.W.; Validation, S.W.; Formal analysis, J.T.; Investigation, J.T.; Resources, J.T.; Data curation, J.T.; Writing—original draft, J.T. and S.W.; Writing—review and editing, J.H., H.Z. and S.W.; Visualization, J.T.; Supervision, J.H., H.Z. and S.W.; Project administration, J.T.; Funding acquisition, S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U22A20515).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The experimental procedures were approved by the Hunan Agricultural University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Permission No. 2020034) on 15 March 2020.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable. This study did not involve human subjects. The animals were sourced from the university-owned experimental farm of Hunan Agricultural University.
Data Availability Statement
The 16S rRNA sequencing data generated in this study are openly available in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/, accessed on 15 October 2025, under the BioProject accession number PRJNA1345594. All other data supporting the findings are available within the article and its Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Cao, M.; Lin, Y.; Xu, S.; Che, L.; Fang, Z.; Feng, B.; et al. Improvement of insulin sensitivity by dietary fiber consumption during late pregnant sows is associated with gut microbiota regulation of tryptophan metabolism. Anim. Microbiome 2024, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yan, P. Effects of backfat thickness on oxidative stress and inflammation of placenta in large white pigs. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, P.K.; Farmer, C.; Feyera, T. Physiology and nutrition of late gestating and transition sows. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.M.; Shah, N.M.; Lillycrop, K.A.; Cui, W.; Johnson, M.R.; Singh, N. Multigenerational diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1245899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Juan, J.; Xu, Q.; Su, R.; Hirst, J.; Yang, H. Increasing insulin resistance predicts adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes 2020, 12, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, R.; Tsukahara, T. Composition and physiological functions of the porcine colostrum. Anim. Sci. J. 2021, 92, e13618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes Fagundes, D.L.; Franca, E.L.; da Silva Fernandes, R.T.; Hara Cde, C.; Morceli, G.; Honorio-Franca, A.C.; Calderon Ide, M. Changes in T-cell phenotype and cytokines profile in maternal blood, cord blood and colostrum of diabetic mothers. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Renner, S.; Martins, A.; Streckel, E.; Braun-Reichhart, C.; Backman, M.; Prehn, C.; Klymiuk, N.; Bahr, A.; Blutke, A.; Landbrecht-Schessl, C. Mild maternal hyperglycemia in INS (C93S) transgenic pigs causes impaired glucose tolerance and metabolic alterations in neonatal offspring. Dis. Model. Mech. 2019, 12, dmm039156. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimori, M.; Franca, E.L.; Morais, T.C.; Fiorin, V.; de Abreu, L.C.; Honorio-Franca, A.C. Cytokine and adipokine are biofactors can act in blood and colostrum of obese mothers. Biofactors 2017, 43, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Jinglong, X.; Shusheng, D.; Aiyou, W. Maternal obesity stimulates lipotoxicity and up-regulates inflammatory signaling pathways in the full-term swine placenta. Anim. Sci. J. = Nihon Chikusan Gakkaiho 2018, 89, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Gou, W.; Wu, P.; Lai, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, K.; Shuai, M.; Tang, J.; Miao, Z.; Chen, J. Landscape of the gut mycobiome dynamics during pregnancy and its relationship with host metabolism and pregnancy health. Gut 2024, 73, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, S.; He, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Feng, B.; Che, L. A Gestational Pectin Diet Could Improve the Health of Multiparous Sows by Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Cytokine Level during Late Pregnancy. Animals 2024, 14, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Chang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Maternal malic acid may ameliorate oxidative stress and inflammation in sows through modulating gut microbiota and host metabolic profiles during late pregnancy. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Xiong, W.; Ma, S.; Luo, J.; Ye, H.; Huang, S.; Li, F.; Xiang, X.e.; Chen, Q.; Gao, B. Konjac flour-mediated gut microbiota alleviates insulin resistance and improves placental angiogenesis of obese sows. Amb. Express 2023, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Ma, S.; Li, D.; Wang, C. Consumption of dietary fiber from different sources during pregnancy alters sow gut microbiota and improves performance and reduces inflammation in sows and piglets. mSystems 2021, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crusell, M.K.W.; Hansen, T.H.; Nielsen, T.; Allin, K.H.; Rühlemann, M.C.; Damm, P.; Vestergaard, H.; Rørbye, C.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Christiansen, O.B.; et al. Gestational diabetes is associated with change in the gut microbiota composition in third trimester of pregnancy and postpartum. Microbiome 2018, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, R.; Luo, H.; Liao, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiao, X.; Li, L. The interplay between the gut microbiota and metabolism during the third trimester of pregnancy. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1059227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión-López, M.; Madrid, J.; Martínez, S.; Hernández, F.; Orengo, J. Effects of the feeding level in early gestation on body reserves and the productive and reproductive performance of primiparous and multiparous sows. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 148, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, S.; Huang, W.; Yang, M.; He, Y.; Li, Z. Allicin in pregnancy diets modulates steroid metabolism in pregnant sows and placental sulphate metabolism promoting placental angiogenesis and foetal development. Animal 2024, 18, 101224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monari, S.; Ferri, M.; Salinitro, M.; Tassoni, A. New insights on primary and secondary metabolite contents of seven italian wild food plants with medicinal applications: A comparative study. Plants 2023, 12, 3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Casar, R.; González-Jaramillo, N.; Bailon-Moscoso, N.; Rojas-Le-Fort, M.; Romero-Benavides, J.C. Five underutilized Ecuadorian fruits and their bioactive potential as functional foods and in metabolic syndrome: A review. Molecules 2024, 29, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godyla-Jabłoński, M.; Raczkowska, E.; Jodkowska, A.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Sozański, T.; Bronkowska, M. Effects of anthocyanins on components of metabolic syndrome—A review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Yano, S.; Hisanaga, A.; He, X.; He, J.; Sakao, K.; Hou, D.X. Polyphenols from Lonicera caerulea L. berry attenuate experimental nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines productions and lipid peroxidation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tan, J.; He, Z.; He, X.; Hou, D.X.; He, J.; Wu, S. Inhibitory effect of blue honeysuckle extract on high-fat-diet-induced fatty liver in mice. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Hu, R.; Gong, J.; Fang, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; He, Z.; Hou, D.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; et al. Protection against Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease by Protocatechuic Acid. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2238959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; He, Z.; Liu, M.; Tan, J.; Zhang, H.; Hou, D.-X.; He, J.; Wu, S. Dietary protocatechuic acid ameliorates inflammation and up-regulates intestinal tight junction proteins by modulating gut microbiota in LPS-challenged piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanglei, C.; Shuangshuang, X.; Chunxue, L.; Junbo, L.; Ifen, H.; Lili, Z.; Shuaipeng, G.; Bo, Z. Effects of silymarin supplementation in late pregnancy and lactation on reproductive performance, colostrum quality, blood biochemistry and inflammation levels of sows. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2025, 57, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Tianle, G.; Ran, L.; Liang, H.; Quanfang, H.; Hongmei, W.; Rui, Z.; Peiqiang, Y.; Xiaoling, Z.; Lingjie, H.; Yong, Z.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG improves insulin sensitivity and offspring survival via modulation of gut microbiota and serum metabolite in a sow model. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D. Homeostasis model assessment : Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoos, A.; Muro, B.B.D.; Carnevale, R.F.; Chantziaras, I.; Biebaut, E.; Janssens, G.P.J.; Maes, D. Relationship between piglets’ survivability and farrowing kinetics in hyper-prolific sows. Porc. Health Manag. 2023, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddersholm, K.V.; Bahnsen, I.; Bruun, T.S.; de Knegt, L.V.; Amdi, C. Identifying risk factors for low piglet birth weight, high within-litter variation and occurrence of intrauterine growth-restricted piglets in hyperprolific sows. Animals 2021, 11, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Gómez, M.; Garcia-Contreras, C.; Pesantez-Pacheco, J.L.; Torres-Rovira, L.; Heras-Molina, A.; Astiz, S.; Óvilo, C.; Isabel, B.; Gonzalez-Bulnes, A. Differential effects of litter size and within-litter birthweight on postnatal traits of fatty pigs. Animals 2020, 10, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourley, K.M.; Calderon, H.I.; Woodworth, J.C.; DeRouchey, J.M.; Tokach, M.D.; Dritz, S.S.; Goodband, R.D. Sow and piglet traits associated with piglet survival at birth and to weaning. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bee, G. Dietary Conjugated Linoleic Acids Alter Adipose Tissue and Milk Lipids of Pregnant and Lactating Sows. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2292–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Li, P.L.; Bai, L.L.; Liu, H.; Lai, C.H.; Thacker, P.A.; Wang, F.L. Responses in colostrum production and immunoglobulin concentrations to conjugated linoleic acid fed to multiparous sows during late gestation. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 210, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, G.; Kebreab, E.; Yu, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; He, H.; Fang, R.; Dai, Q. Effects of dietary grape seed polyphenols supplementation during late gestation and lactation on antioxidant status in serum and immunoglobulin content in colostrum of multiparous sows1. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 2515–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Jung, B.C.; Villivalam, S.D.; Lim, H.-W.; Kang, S. JMJD8 is a novel molecular nexus between adipocyte-intrinsic inflammation and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2022, 71, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Xiao, H.; Bao, H.; Li, M.; Xue, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, L. Tissue distribution comparison of six active ingredients from an Eucommiae cortex extract between normal and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 2049059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Meng, H.; Du, M.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K. Chlorogenic acid ameliorates intestinal inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB and endoplasmic reticulum stress in lipopolysaccharide-challenged broilers. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.-C.; Ji, X.-Y.; Che, H.-Y.; Meng, Y.; Wu, H.-Y.; Zhang, J.-B.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Yuan, B. CGA alleviates LPS-induced inflammation and milk fat reduction in BMECs through the NF-κB signaling pathway. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, M.; Wu, J.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, X.; Tian, C.; Hou, J.; Wang, L.; Gao, K.; Yang, X. Chlorogenic Acid Enhances the Intestinal Health of Weaned Piglets by Inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway and Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klobasa, F.; Werhahn, E.; Butler, J.E. Regulation of humoral immunity in the piglet by immunoglobulins of maternal origin. Res. Vet. Sci. 1981, 31, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socha-Banasiak, A.; Pierzynowski, S.; Woliński, J.; Grujic, D.; Goncharova, K. The pig as a model for premature infants—The importance of immunoglobulin supplementation for growth and development. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2017, 31, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo Sureda, E.; Zhao, X.; Artuso-Ponte, V.; Wall, S.-C.; Li, B.; Fang, W.; Uerlings, J.; Zhang, Y.; Schroyen, M.; Grelet, C. Isoquinoline alkaloids in sows’ diet reduce body weight loss during lactation and increase igg in colostrum. Animals 2021, 11, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kho, A.R.; Choi, B.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, D.K.; Lee, S.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, K.-H.; Song, H.K.; Choi, H.C.; Suh, S.W. Effects of protocatechuic acid (PCA) on global cerebral ischemia-induced hippocampal neuronal death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, M.; Mauro, C.; Lidia, P.; Leyanis Herrera, L.; Maria, L.; Antonino, G.; Anna Maria, S.; Giuseppe, T.; Alessandro, Z.; Marialuisa, A.; et al. Histological Assessment of Intestinal Changes Induced by Liquid Whey-Enriched Diets in Pigs. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 716. [Google Scholar]
- Anna Maria, S.; Francesca, A.; Giuseppe, T.; Valentina, R.; Francesco, F.; Riccardo, A.C.; Andreu, P.; Giuseppe, P.; Alessandro, Z. Effect of a Co-Feed Liquid Whey-Integrated Diet on Crossbred Pigs’ Fecal Microbiota. Animals 2023, 13, 1750. [Google Scholar]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio: A relevant marker of gut dysbiosis in obese patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Johnson, Z.; Gu, X.; Bohutskyi, P.; Chen, S. Dairy manure acidogenic fermentation at hyperthermophilic temperature enabled superior activity of thermostable hydrolytic enzymes linked to the genus Caldicoprobacter. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 391, 129978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Du, L.; Cao, Q.; Tang, J.; Zhou, C.; et al. A metagenomic study of the gut microbiome in Behcet’s disease. Microbiome 2018, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Declerck, I.; Sarrazin, S.; Dewulf, J.; Maes, D. Sow and piglet factors determining variation of colostrum intake between and within litters. Animal 2017, 11, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).