Technologies in Biomarker Discovery for Animal Diseases: Mechanisms, Classification, and Diagnostic Applications
Simple Summary
Abstract
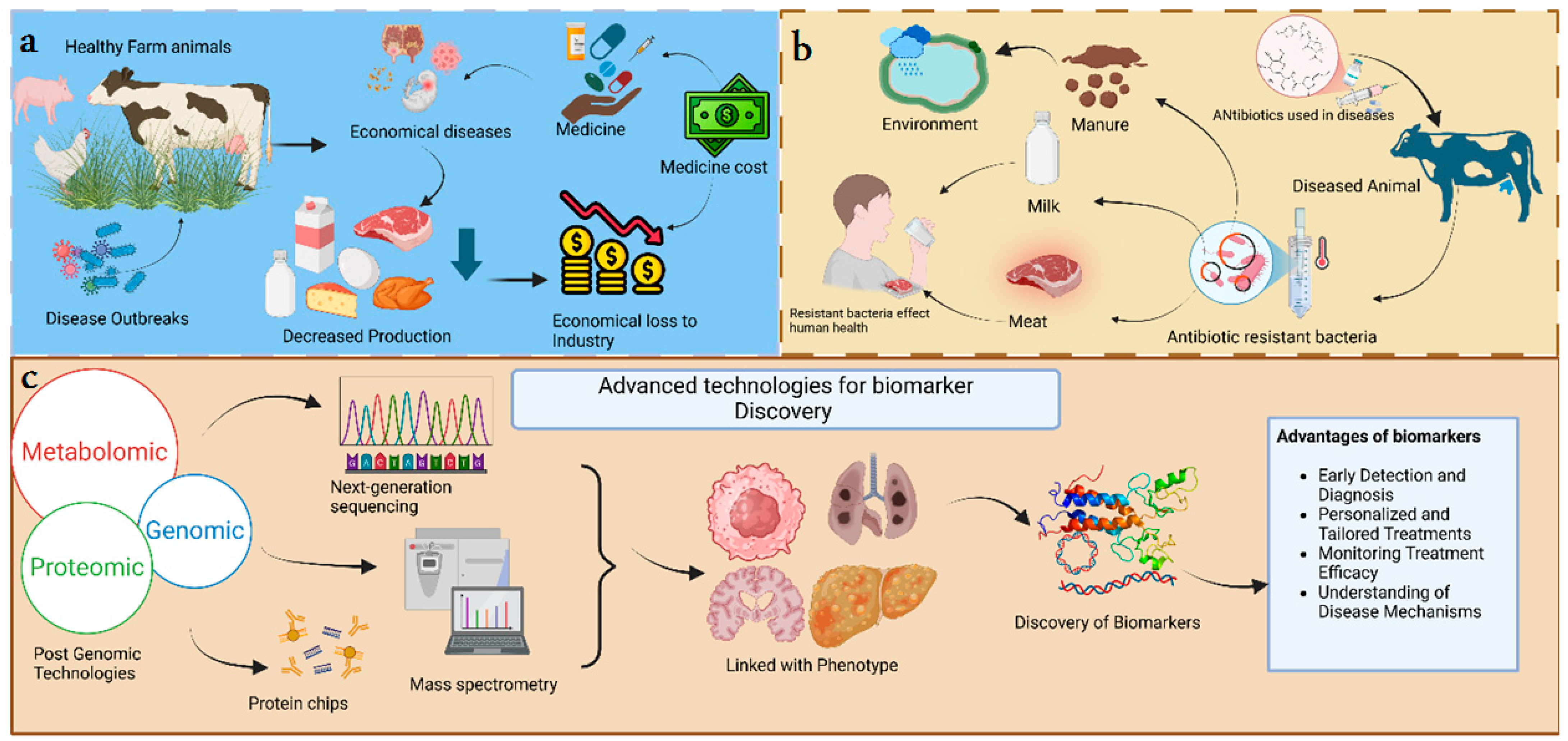
1. Introduction
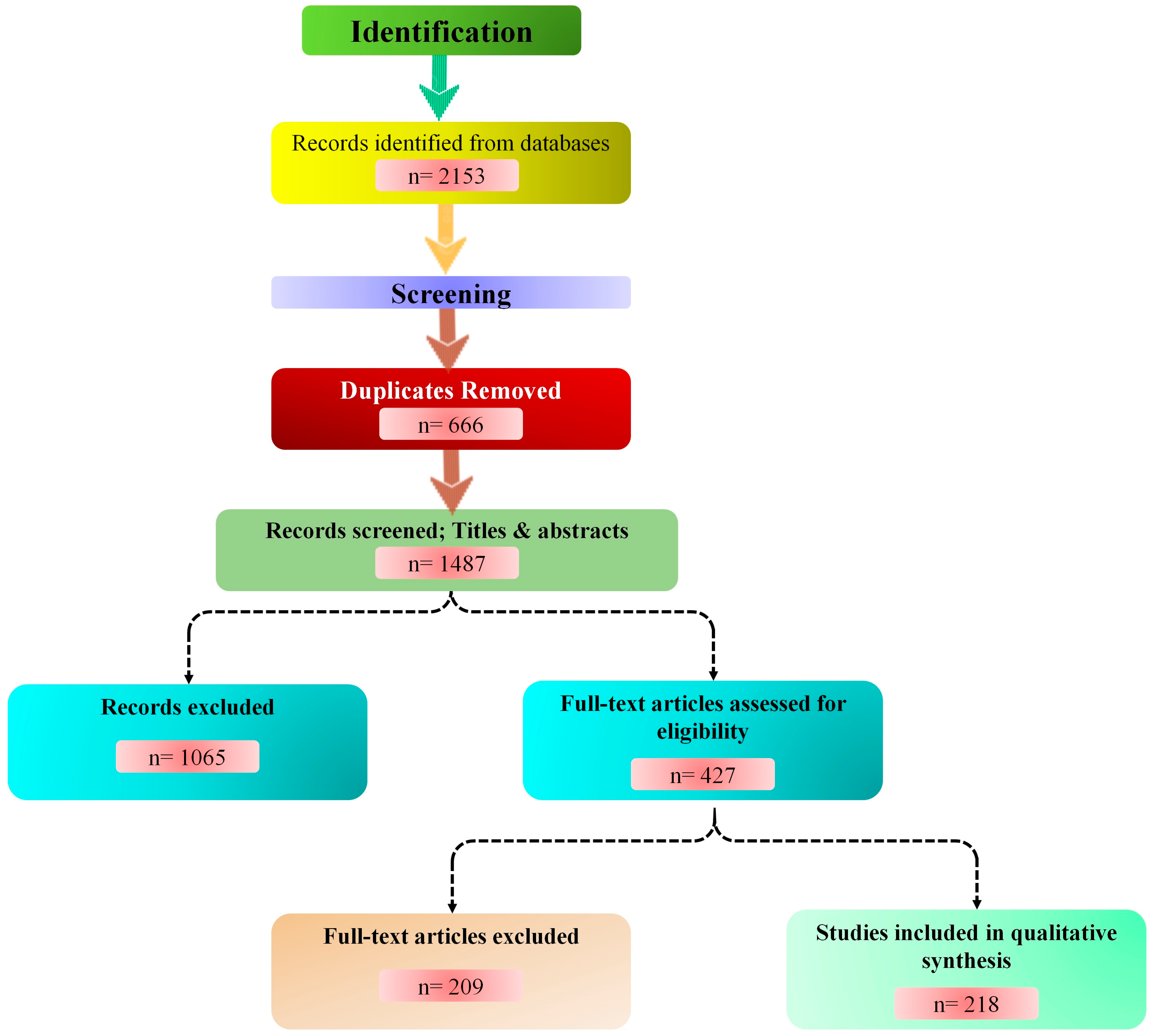
2. Methodology
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
- PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) (accessed on 12 April 2025);
- Web of Science (https://www.webofscience.com) (accessed on 19 April 2025);
- Scopus (https://www.scopus.com) (accessed on 21 April 2025);
- CAB Abstracts (https://www.cabi.org/cab-abstracts) (accessed on 3 May 2025);
- IEEE Xplore (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org) (accessed on 25 April 2025);
- Google Scholar (https://scholar.google.com) (accessed on 8 April 2025).
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Screening and Data Extraction
2.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
3. Technological Innovations Revolutionizing Veterinary Diagnostics
Clinical Translation Assessment Framework
| Technology Name | Primary Function/Mechanism | Key Advantages of Early Diagnosis | Relevant Animal Disease Applications (If General) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI-enhanced Imaging | Computer-based image analysis to detect abnormalities | Quicker, smarter, more accurate, consistent tumor identification, accessible portable options | Veterinary oncology (tumor identification), hematology, urinalysis, lymph node/skin masses | [19] |
| Liquid Biopsies | Non-invasive analysis of circulating biomarkers (e.g., cfDNA) | Non-invasive/minimally invasive, facilitates earlier detection and treatment planning | Veterinary oncology (cancer-associated genomic alterations) | [19] |
| Molecular Diagnostics | Analysis of DNA/RNA molecules for disease markers | Precision medicine, earlier detection, personalized treatments, and monitoring disease progression | Infectious diseases, cancer | [19] |
| Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | High-throughput DNA/RNA sequencing for genomic alterations | Rapid turnaround, single-base resolution, cost-effective, de novo analysis | Infectious animal diseases, cancer (cfDNA), and host susceptibility | [33] |
| Mass Spectrometry (MS) | Sensitive and specific detection/quantification of proteins/metabolites | High accuracy, specificity, detects disease-specific signatures, analyzes PTMs, identifies low-abundance proteins | Protein biomarker discovery (cancer, neurodegenerative), metabolomics (liver fibrosis, gastric injury) | [34,35] |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy | Exploits the magnetic properties of nuclei for metabolite detection | Non-destructive, comprehensive metabolic profiling, structural elucidation, high reproducibility, in vivo analysis | Cattle metabolism, disease biomarker discovery (cancer, cardiovascular), metabolomics | [36,37,38] |
| CRISPR/Cas9 Technology | Precise gene editing and modulation of gene function | Creates disease models, identifies therapeutic targets, elucidates molecular underpinnings of disease | Central nervous system diseases, host susceptibility to viral infections | [39] |
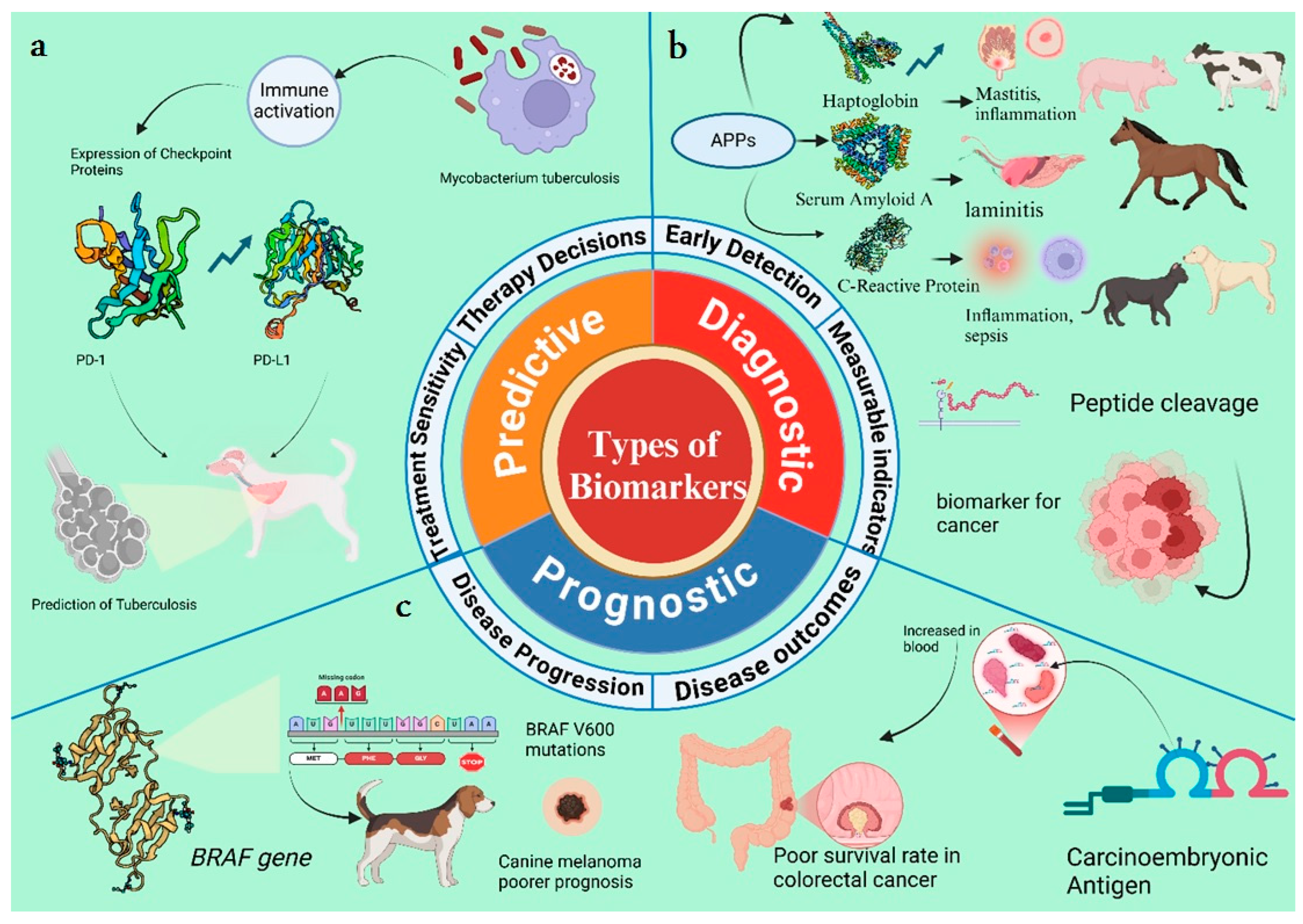
4. Types of Biomarkers
4.1. Diagnostic Biomarkers
4.2. Prognostic Biomarkers
4.3. Predictive Biomarkers
5. Advanced Technologies
5.1. Genomic Approaches
5.2. Proteomic Technology
| Disease/Condition | Animal Species | Biological Sample | Selected Protein Biomarkers | Proteomic Technology Used | Key Findings/Significance | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canine Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease (MMVD) with Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) | Dog | Serum | Myosin heavy chain 1 (MYOM1), Histone deacetylasw7 (HDAC7) (upregulated); Pleckstrin homology domain-containing family M member 3 (PLEKHM3), Diacylglycerol lipase alpha (DAGLA), Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like protein 6 (TTLL6) (downregulated) | LC-MS/MS, Label-free quantification | Potential diagnostic/prognostic markers for MMVD progression and PH development | [106] |
| Feline Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD) | Cat | Serum | ANTXR1, DUSP2, VTN, CNOT3, PSMA5 (upregulated in DJD); CFHR3 (downregulated in DJD) | LC-MS/MS, Label-free quantification | Identified novel biomarkers for DJD and chronic pain in cats, useful for diagnosis and monitoring | [34] |
| Bovine Mastitis (Clinical and Subclinical) | Cattle | Milk, Serum | Serum Amyloid A (SAA), Haptoglobin, Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein, Lactoferrin, Caseins, Serum albumin | 2DE, LC-MS/MS, Label-free, iTRAQ | Acute phase proteins and milk proteins altered during inflammation, useful for early detection | [107] |
| Equine Plasma Proteome Characterization | Horse | Plasma | Albumin, Alpha 2 macroglobulin, Fibrinogen (alpha/gamma/beta chain), Serotransferrin | LC-MS/MS, DIA/SWATH-MS | Provides baseline for healthy equine plasma, crucial for identifying disease-specific changes | [108] |
5.3. Metabolomics
5.4. Integrative Approaches
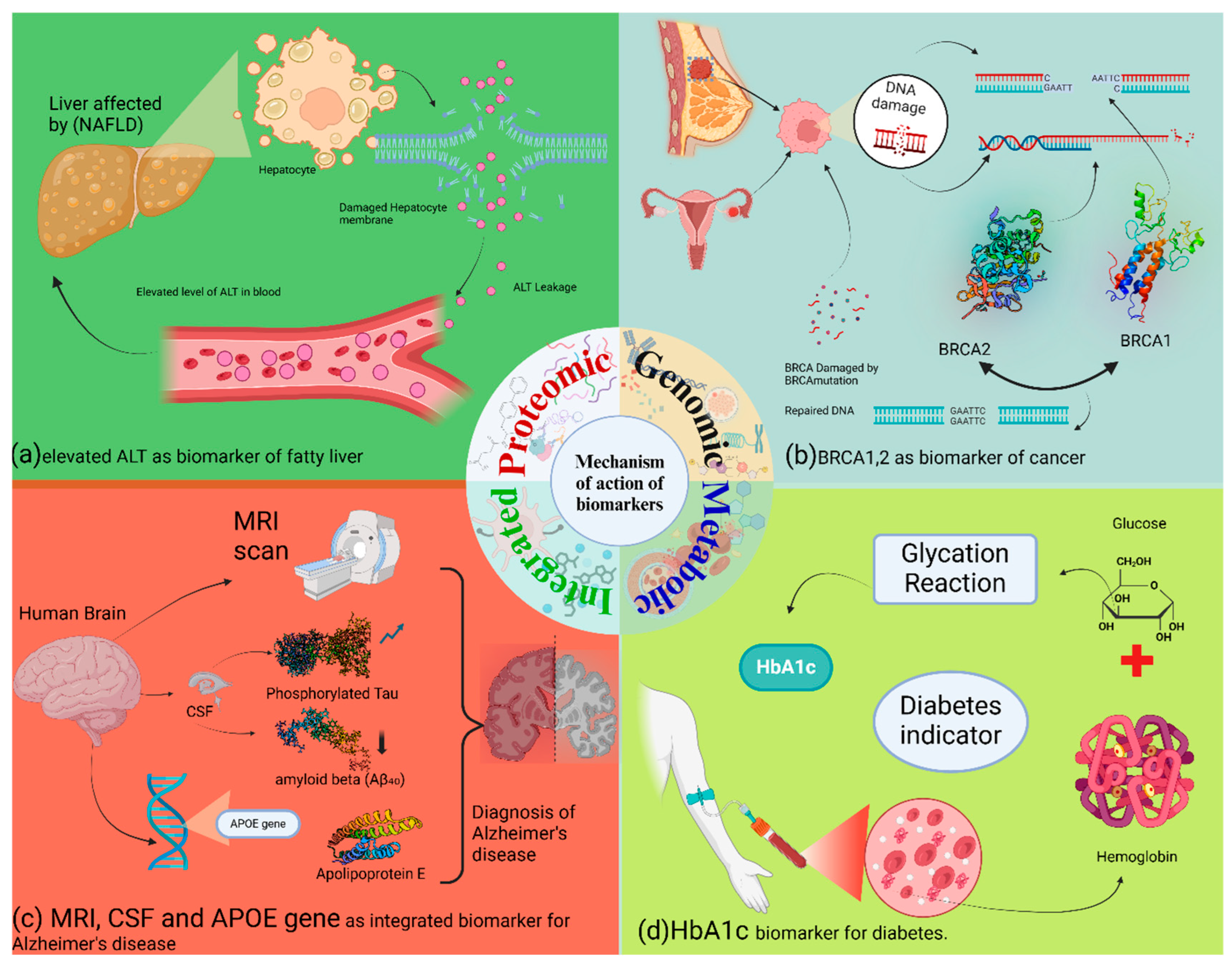
6. Mode of Action of Biomarkers
7. Case Studies of Biomarker Application in Serious Animal Diseases
8. Challenges and Future Perspectives
9. Practical Constraints in Resource-Limited Settings
9.1. Artificial Intelligence Implementation Barriers
9.2. CRISPR Diagnostic Challenge
9.3. Liquid Biopsy Viability Gaps
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tadesse, B.; Tesfahun, A.; Molla, W.; Demisse, E.; Jemberu, W.T. Foot and mouth disease outbreak investigation and estimation of its economic impact in selected districts in northwest Ethiopia. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 6, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; Ren, F.; Bian, T.; Sun, L.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, L.; Qu, X. The economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome outbreak in four Chinese farms: Based on cost and revenue analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1024720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.; Mamphweli, S.; Meyer, E.; Okoh, A. Antibiotic Use in Agriculture and Its Consequential Resistance in Environmental Sources: Potential Public Health Implications. Molecules 2018, 23, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, K.M.; Reinke, S.N.; Kelly, R.S.; Chen, Q.; Su, M.; McGeachie, M.; Weiss, S.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Lasky-Su, J.A. A roadmap to precision medicine through post-genomic electronic medical records. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappes, A.; Tozooneyi, T.; Shakil, G.; Railey, A.F.; McIntyre, K.M.; Mayberry, D.E.; Rushton, J.; Pendell, D.L.; Marsh, T.L. Livestock health and disease economics: A scoping review of selected literature. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1168649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, J.K.; Kelly, T.; Bird, B.; Chenais, E.; Roug, A.; Vidal, G.; Gallardo, R.; Zhou, H.; VanHoy, G.; Smith, W. A One Health Approach to Reducing Livestock Disease Prevalence in Developing Countries: Advances, Challenges, and Prospects. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 13, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmed, I.; Akhtar, T.; Amir, M.; Parveen, S.; Narayan, E.; Iqbal, H.M.; Rehman, S.U. Strategies and innovations for combatting diseases in animals. World Acad. Sci. J. 2024, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemi, J.K.; Lehtonen, H. Livestock Product Trade and Highly Contagious Animal Diseases. 2014. Available online: https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/169759/?v=pdf (accessed on 11 April 2014).
- McElwain, T.F.; Thumbi, S. Animal pathogens and their impact on animal health, the economy, food security, food safety and public health. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2017, 36, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meade, E.; Slattery, M.A.; Garvey, M. Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Zoonotic Clinically Relevant WHO Priority Pathogens. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bava, R.; Castagna, F.; Lupia, C.; Poerio, G.; Liguori, G.; Lombardi, R.; Naturale, M.D.; Mercuri, C.; Bulotta, R.M.; Britti, D. Antimicrobial Resistance in Livestock: A Serious Threat to Public Health. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devleesschauwer, B.; Martins, S.B.; di Bari, C.; Fastl, C.; Venkateswaran, N.; Pigott, D. Linking animal and human health burden: Challenges and opportunities. Sci. Tech. Rev. 2024, 43, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, B.M.; Levy, S.B. Food animals and antimicrobials: Impacts on human health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corella, D.; Ordovas, J.M. Biomarkers: Background, classification and guidelines for applications in nutritional epidemiology. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31 (Suppl. S3), 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Ijaz, M.; Farooqi, S.H.; Ali, M.M.; Ali, A.; Umar, A.; Shahid, R. Use of Genomics in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Livestock and Animal Diseases. In Recent Trends in Livestock Innovative Technologies; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2023; pp. 188–213. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, R.E.; Kirwan, J.; Doherty, M.K.; Whitfield, P.D. Biomarker discovery in animal health and disease: The application of post-genomic technologies. Biomark. Insights 2007, 2, 117727190700200040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, H.C.; McCrindle, C.M.; Du Toit, D. Veterinary extension on sampling techniques related to heartwater research. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2010, 81, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, A.H.; Oshiro, T.; Ungkulpasvich, U.; Yamaguchi, J.; Morishita, M.; Khdair, S.A.; Hatakeyama, H.; Hirotsu, T.; di Luccio, E. Advancing Veterinary Oncology: Next-Generation Diagnostics for Early Cancer Detection and Clinical Implementation. Animals 2025, 15, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odenkirk, M.T.; Reif, D.M.; Baker, E.S. Multiomic Big Data Analysis Challenges: Increasing Confidence in the Interpretation of Artificial Intelligence Assessments. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7763–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglio, A.; Cremonini, V.; Leonardi, L.; Manuali, E.; Coliolo, P.; Barbato, O.; Dall’Aglio, C.; Antognoni, M.T. Omics Technologies in Veterinary Medicine: Literature Review and Perspectives in Transfusion Medicine. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2023, 50, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanamala, J.K.P.; Sivaramakrishnan, V.; Mummidi, S. Editorial: Integrated multi-omic studies of metabolic syndrome, diabetes and insulin-related disorders: Mechanisms, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1537554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melak, A.; Aseged, T.; Shitaw, T. The Influence of Artificial Intelligence Technology on the Management of Livestock Farms. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2024, 2024, 8929748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasiou, M.C. Vet informatics and the future of drug discovery in veterinary medicine. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1494242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavipanje, N.; Nasri, M.H.F.; Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E. Trends and future directions of artificial intelligence applications in Iranian livestock production systems. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2024, 25, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrick, B.A.; London, R.E.; Bushel, P.R.; Grissom, S.F.; Paules, R.S. Platforms for biomarker analysis using high-throughput approaches in genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and bioinformatics. IARC Sci. Publ. 2011, 163, 121–142. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, J.N.; Meredith, G.L.; Montelongo, M.; Gill, D.R.; Krehbiel, C.R.; Payton, M.E.; Confer, A.W. Relationship of vitamin E supplementation and antimicrobial treatment with acute-phase protein responses in cattle affected by naturally acquired respiratory tract disease. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2002, 63, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Annan, R.S.; Carr, S.A.; Neubert, T.A. Overview of peptide and protein analysis by mass spectrometry. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2010, 62, 16.1.1–16.1.30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ophoff, A. Metabolomics in Veterinary Medicine: Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus and Targeted Metabolomic Analysis of Salmonella Enteritidis. Master’s Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://iowa7-test.atmire.com/entities/publication/0ac08385-6986-4abd-818e-844f5897d1bd (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Kabay, G.; DeCastro, J.; Altay, A.; Smith, K.; Lu, H.W.; Capossela, A.M.; Moarefian, M.; Aran, K.; Dincer, C. Emerging Biosensing Technologies for the Diagnostics of Viral Infectious Diseases. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2201085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Su, D.; Jiang, F.; Wu, W. Development of a direct competitive ELISA for the detection of Mycoplasma bovis infection based on a monoclonal antibody of P48 protein. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S. Artificial Intelligence and Sensor Innovations: Enhancing Livestock Welfare with a Human-Centric Approach. Hum.-Centric Intell. Syst. 2024, 4, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.J.; Jenkins, T.L. Management and analysis of high-throughput sequence data for infectious animal diseases. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2023, 42, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascelles, B.D.X.; Ponnala, R.; Kamerling, S.G.; Williams, T. Proteomic profiling of serum in cats with naturally occurring degenerative joint disease and co-morbid conditions. Front. Pain Res. 2025, 6, 1501932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, A.; Kim, W.; Park, J.; Park, Y.; Lee, W.; Lee, S.; Kim, H. Mass Spectrometry Advancements and Applications for Biomarker Discovery, Diagnostic Innovations, and Personalized Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essawi, T.; Hammoudeh, W.; Sabri, I.; Sweidan, W.; Farraj, M.A. Determination of Helicobacter pylori virulence genes in gastric biopsies by PCR. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 606258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Chehelgerdi, M. Genotyping and antibiotic resistance properties of Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from human and animal gastric biopsies. Infect Drug Resist 2018, 11, 2545–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Allam, A.A.; Aldhalmi, A.K.; Kamal, M.; Arif, M.; Alawam, A.S.; Rudayni, H.A.; Taha, A.E.; Swelum, A.A.; Elolimy, A.A. Integrating metabolomics for precision nutrition in poultry: Optimizing growth, feed efficiency, and health. Front. Veter-Sci. 2025, 12, 1594749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Qureshi, N.; Khan, R.; Son, Y.-O.; Maqbool, T. CRISPR/Cas9-Based therapeutics as a promising strategy for management of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and prospects. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1578138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, T.R.W.; Skerrett-Byrne, D.A.; Gibb, Z.; Nixon, B.; Swegen, A. The Future of Biomarkers in Veterinary Medicine: Emerging Approaches and Associated Challenges. Animals 2022, 12, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aupperle-Lellbach, H.; Kehl, A.; de Brot, S.; van der Weyden, L. Clinical Use of Molecular Biomarkers in Canine and Feline Oncology: Current and Future. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califf, R.M. Biomarker definitions and their applications. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.H.; Ladame, S. Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers for cancer. In Bioengineering Innovative Solutions for Cancer; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, W.T.; Parra Vello, T.; Lelis, G.C.; Ferreira Deleigo, A.V.; Takahira, R.K.; Martinez, D.S.T.; de Oliveira, R.F. Chemical Sensors and Biosensors for Point-of-Care Testing of Pets: Opportunities for Individualized Diagnostics of Companion Animals. ACS Sens. 2025, 10, 3222–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Kit, A.; Nielsen, H.M.; Tost, J. DNA methylation based biomarkers: Practical considerations and applications. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2314–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiao, H.; Wong, D.T. Salivary biomarkers for clinical applications. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2009, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, S.; Kushner, I.; Samols, D. C-reactive Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48487–48490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koho, N.; Rajamäki, M.M.; Viitanen, S.J. Serum procalcitonin as a diagnostic biomarker in dogs with bacterial respiratory diseases. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2024, 53, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Rubić, I.; Rešetar Maslov, D.; González-Sánchez, J.C.; Mrljak, V.; Cerón, J.J.; Hansen, S. Towards the Identification of New Biomarkers in Saliva and Serum for Treatment Monitoring of Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndrome: A Liquid Proteomic Approach. Animals 2024, 14, 3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckersall, P.D.; Bell, R. Acute phase proteins: Biomarkers of infection and inflammation in veterinary medicine. Vet. J. 2010, 185, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharwat, M.; Alkhedhairi, S.; El Tigani-Asil, E.T.A. Clinical predictive significance of biomarker molecules elevation during the transition period in cattle suffering from different pathological states: A review. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llibre, A.; Duffy, D. Immune response biomarkers in human and veterinary research. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 59, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.E.; Yoo, H.S. Biomarkers as diagnostic tools for mycobacterial infections in cattle. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2021, 22, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, L.G.D.; Ali, S.; de Oliveira, C.A.F. Evaluation of Adsorbent’s Efficiency by Using Biomarker Approaches in Farm Animals: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godara, B.; Kaur, R. Diagnostic Significance of Biochemical Markers In Veterinary Clinical Biochemistry. In Futuristic Trends in Agriculture Engineering & Food Sciences; IIP Series: Karnataka, India, 2024; pp. 191–206. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Bae, H.; Ahn, S.; Shin, S.; Cho, A.; Cho, K.W.; Jung, D.I.; Yu, D. Cell-Free DNA as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Dogs With Tumors. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 735682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombe, P.; Béguin, J.; Benchekroun, G.; Le Roux, D. Blood biomarkers for canine cancer, from human to veterinary oncology. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2022, 20, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasheri, A.; Cassidy, J.P. Biomarkers in veterinary medicine: Towards targeted, individualised therapies for companion animals. Vet. J. 2010, 185, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardana, K.; Schramm, S.J.; Tembe, V.; Mueller, S.; Thompson, J.F.; Scolyer, R.A.; Mann, G.J.; Yang, J. Identification, Review, and Systematic Cross-Validation of microRNA Prognostic Signatures in Metastatic Melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, N.G.; Vergara, I.A.; Long, G.V.; Scolyer, R.A. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers in melanoma. Pathology 2024, 56, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurzba, S.; Salo, T.A.; Coletta, R.D. Editorial: Prognostic biomarkers for oral cancer. Front. Oral Health 2022, 3, 994387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.; Cai, L.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, E.; Huang, C.; et al. Proteomics-driven noninvasive screening of circulating serum protein panels for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takabe, K.; Benesch, M.G.K. Biomarker Research in World Journal of Oncology. World J. Oncol. 2023, 14, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez Hernández, R.; Ramasco Rueda, F. Biomarkers as Prognostic Predictors and Therapeutic Guide in Critically Ill Patients: Clinical Evidence. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Klein, L.; Petersen, J.; Vollmuth, P.; Jaeger, P.; Maier-Hein, K. Enhancing predictive imaging biomarker discovery through treatment effect analysis. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Gonzalez-Juarbe, N.; Pieper, R.; Yu, Y.; Vashee, S. Predictive biomarkers for latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Tuberculosis 2024, 147, 102399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.T.; Westergaard, N. Predictive biomarkers and personalized pharmacotherapy. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2022, 22, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westergaard, N.; Vermehren, C.; Jørgensen, J.T. [Predictive biomarkers in medical treatment]. Ugeskr. Laeger 2022, 184, V05220300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zachut, M.; Šperanda, M.; de Almeida, A.M.; Gabai, G.; Mobasheri, A.; Hernández-Castellano, L.E. Biomarkers of fitness and welfare in dairy cattle: Healthy productivity. J. Dairy Res. 2020, 87, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oetzel, G. Subacute Ruminal Acidosis in Dairy Herds: Physiology, Pathophysiology, Milk Fat Responses, and Nutritional Management. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Conference, American Association of Bovine Practitioners, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hailemariam, D.; Mandal, R.; Saleem, F.; Dunn, S.M.; Wishart, D.S.; Ametaj, B.N. Identification of predictive biomarkers of disease state in transition dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 2680–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Chester, N.; Xiong, A.; Radaelli, E.; Wang, H.; Brillantes, M.; Gulendran, G.; Glassman, P.; Siegel, D.L.; Mason, N.J. Development and pharmacokinetic assessment of a fully canine anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody for comparative translational research in dogs with spontaneous tumors. mAbs 2023, 15, 2287250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, W.; Ghosh, S. C-reactive protein and the biology of disease. Immunol. Res. 2013, 56, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melus, C.; Rossin, B.; Aure, M.; Mahler, M. Biomarker and data science as integral part of precision medicine. In Precision Medicine and Artificial Intelligence; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Satam, H.; Joshi, K.; Mangrolia, U.; Waghoo, S.; Zaidi, G.; Rawool, S.; Thakare, R.P.; Banday, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Das, G.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Technology: Current Trends and Advancements. Biology 2023, 12, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husien, H.M.; Saleh, A.A.; Hassanine, N.; Rashad, A.M.A.; Sharaby, M.A.; Mohamed, A.Z.; Abdelhalim, H.; Hafez, E.E.; Essa, M.O.A.; Adam, S.Y.; et al. The Evolution and Role of Molecular Tools in Measuring Diversity and Genomic Selection in Livestock Populations (Traditional and Up-to-Date Insights): A Comprehensive Exploration. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slatko, B.E.; Gardner, A.F.; Ausubel, F.M. Overview of Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2018, 122, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Khedher, M.; Ghedira, K.; Rolain, J.M.; Ruimy, R.; Croce, O. Application and Challenge of 3rd Generation Sequencing for Clinical Bacterial Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.M.; Chiu, S.F.; Akbarpour, M.; Bharat, A.; Ridge, K.M.; Bartom, E.T.; Winter, D.R. A Beginner’s Guide to Analysis of RNA Sequencing Data. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 59, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, D.; Chhugani, K.; Chang, Y.; Karlsberg, A.; Loeffler, C.; Zhang, J.; Muszyńska, A.; Munteanu, V.; Yang, H.; Rotman, J.; et al. RNA-seq data science: From raw data to effective interpretation. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 997383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanova, M.; Yahya, D.; Hachmeriyan, M.; Levkova, M. Diagnostic Yield of Next-Generation Sequencing for Rare Pediatric Genetic Disorders: A Single-Center Experience. Med. Sci. 2025, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S.; Tomiyasu, H.; Tsuboi, M.; Inoue, A.; Ishihara, G.; Uchikai, T.; Chambers, J.K.; Uchida, K.; Yonezawa, T.; Matsuki, N. Comprehensive gene expression analysis of canine invasive urothelial bladder carcinoma by RNA-Seq. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattner, C. Regulation of p53: The next generation. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3149–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowles, J.S.; Denton, C.L.; Gustafson, D.L. Comparative analysis of MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathway activation and inhibition in human and canine melanoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2015, 13, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.F.; Diers, A.R.; Hogg, N. Cancer cell metabolism and the modulating effects of nitric oxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 79, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Gao, Y.; Lan, Y.; Jia, S.; Jiang, R. Pax9 regulates a molecular network involving Bmp4, Fgf10, Shh signaling and the Osr2 transcription factor to control palate morphogenesis. Development 2013, 140, 4709–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smail, C.; Montgomery, S.B. RNA Sequencing in Disease Diagnosis. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2024, 25, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, H.G.; Harris, A.C.; Plassais, J.; Dhawan, D.; Kim, E.M.; Knapp, D.W.; Ostrander, E.A. Genome-wide analyses reveals an association between invasive urothelial carcinoma in the Shetland sheepdog and NIPAL1. npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammons, D.T.; Hopkins, L.S.; Cronise, K.E.; Kurihara, J.; Regan, D.P.; Dow, S. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the cellular and molecular heterogeneity of treatment-naïve primary osteosarcoma in dogs. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrashedy, A.; Mousa, W.; Nayel, M.; Salama, A.; Zaghawa, A.; Elsify, A.; Hasan, M.E. Advances in bioinformatics and multi-omics integration: Transforming viral infectious disease research in veterinary medicine. Virol. J. 2025, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Nam, M.-W.; Lee, H.K.; Choi, K.-C. Use of cutting-edge RNA-sequencing technology to identify biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets in canine and feline cancers and other diseases. J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 24, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, R.; Tonges, S.; Bohl, F.; Lyko, F. Epigenetic biomarkers for animal welfare monitoring. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Gulfishan, M.; Kim, M.S.; Kashyap, M.K. Deciphering Cancer Complexity: Integrative Proteogenomics and Proteomics Approaches for Biomarker Discovery. Methods Mol. Biol. 2025, 2859, 211–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadonte, R.; Caprioli, R.M. Proteomic analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue by MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.P.; Brown, J.M.; Campuzano, I.; Sadler, P.J. Identifying drug metallation sites on peptides using electron transfer dissociation (ETD), collision induced dissociation (CID) and ion mobility-mass spectrometry (IM-MS). Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5458–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.C.; Chan, C.M.; Ma, B.B.; Lam, M.Y.; Choi, G.C.; Au, T.C.; Chan, A.S.; Chan, A.T. Advanced proteomic technologies for cancer biomarker discovery. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2009, 6, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.E.; Borchers, C.H. Mass spectrometry based biomarker discovery, verification, and validation--quality assurance and control of protein biomarker assays. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 840–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcu, C.-M.; Kempenaers, B. Proteomics in behavioral ecology. Behav. Ecol. 2014, 26, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleady, P. Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis and 2D-DIGE. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1664, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilm, M. Principles of electrospray ionization. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2011, 10, M111.009407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Rahman, R.; Rashid, M.; Islam, M.S. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics for biomarker discovery in the Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroprotection 2024, 2, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hober, A.; Rekanovic, M.; Forsström, B.; Hansson, S.; Kotol, D.; Percy, A.J.; Uhlén, M.; Oscarsson, J.; Edfors, F.; Miliotis, T. Targeted proteomics using stable isotope labeled protein fragments enables precise and robust determination of total apolipoprotein(a) in human plasma. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva Raisman, A.; Kotol, D.; Altay, O.; Mardinoglu, A.; Atak, D.; Yurdaydin, C.; Akyildiz, M.; Dayangac, M.; Kirimlioglu, H.; Zeybel, M.; et al. Advancing Chronic Liver Disease Diagnoses: Targeted Proteomics for the Non-Invasive Detection of Fibrosis. Livers 2025, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipka, A.; Wagner, B. Fluorescent bead-based multiplex assays improve serological disease diagnostics and have potential of identifying sensitive immune biomarkers for maintaining health and performance. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2025, 263, S33–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, B.; Schnabel, C.L.; Rollins, A. Increase in Virus-Specific Mucosal Antibodies in the Upper Respiratory Tract Following Intramuscular Vaccination of Previously Exposed Horses Against Equine Herpesvirus Type-1/4. Vaccines 2025, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakarin, S.; Rungsipipat, A.; Roytrakul, S.; Jaresitthikunchai, J.; Phaonakrop, N.; Charoenlappanit, S.; Thaisakun, S.; Surachetpong, S.D. Proteomic analysis of the serum in dogs with pulmonary hypertension secondary to myxomatous mitral valve disease: The preliminary study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1327453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajin, F.; Šmit, I.; Stevanović, V.; Rešetar Maslov, D.; Rubić, I.; Mrljak, V.; Kuleš, J. Current application of proteomics in the veterinary field–a short summary and literature review. Vet. Stanica 2025, 56, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortved, K.F.; Alward, L.; Cowles, B.; Linardi, R.; Barot, D.; Usimaki, A.; Fedie, J.R.; Amodie, D.; Goodrich, L.R. Use of quantitative mass spectrometry-based proteomics and ELISA to compare the alpha 2 macroglobulin concentration in equine blood-based products processed by three different orthobiologic devices. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1335972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Metabolomics for Biomarker Discovery: Moving to the Clinic. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 354671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujak, R.; Struck-Lewicka, W.; Markuszewski, M.J.; Kaliszan, R. Metabolomics for laboratory diagnostics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Raftery, D. NMR-Based Metabolomics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1280, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; McConville, M.; Loukopoulos, P. Metabolomics in the study of spontaneous animal diseases. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basoglu, A.; Bicici, R.O.; Di Cesare, F.; Baspinar, N.; Tenori, L.; Ider, M.; Gulersoy, E. NMR-based-Metabolomics Evaluation in Dogs Infected with Canine Parvovirus: A New Approach for Biomarker/s. Vet. Ital. 2025, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Chen, H.H.; Lung, C.W.; Chen, H.J. Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Activities of Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f.) Lindau. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Gao, G.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Bian, C.; Su, G.; Yang, L. Identification of candidate blood biomarkers through metabolomics analysis in bovine superovulation. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1552045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goertzen, A.; Kidane, B.; Ahmed, N.; Aliani, M. Potential urinary volatile organic compounds as screening markers in cancer—A review. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1448760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajo-Fernández, M.; Souza-Silva, É.A.; Barbas, C.; Rey-Stolle, M.F.; García, A. GC-MS-based metabolomics of volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath: Applications in health and disease. A review. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1295955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.G.; Choi, R.; Gwak, S.; Choi, I.; Jang, G.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, G.A. A Novel Sample Preparation Method for GC-MS Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds in Whole Blood for Veterinary Use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S. Development and Application of Methodologies for Non-Targeted Metabolomics in Animal Models of Lung Injury. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad CEU San Pablo, Madrid, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ressom, H.W. MOTA: Multi-omic integrative analysis for biomarker discovery. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Sanches, P.H.G.; de Melo, N.C.; Porcari, A.M.; de Carvalho, L.M. Integrating molecular perspectives: Strategies for comprehensive multi-omics integrative data analysis and machine learning applications in transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. Biology 2024, 13, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-H.; Li, J.; Cho, W.C. Integrative analysis for complex disease biomarker discovery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1273084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, C.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Chi, H.; Wu, Q.; Yang, G. Integrative biomarker discovery and immune profiling for ulcerative colitis: A multi-methodological approach. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DÉJEAN, S.; LÊ CAO, K.-A. Multivariate Models for Data Integration and Biomarker Selection in ‘Omics Data. In Biological Data Integration: Computer and Statistical Approaches; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 195–250. [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod, M.; Nersessian, N.J. Interdisciplinary problem-solving: Emerging modes in integrative systems biology. Eur. J. Philos. Sci. 2016, 6, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Jin, H.; Bu, X.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q. Recent advances in dual-emission ratiometric fluorescence probes for chemo/biosensing and bioimaging of biomarkers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 383, 82–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, S.T.; Fu, G.; Dou, M.; Xu, F.; Liu, R.; Qi, H.; Li, X. Biomarker detection for disease diagnosis using cost-effective microfluidic platforms. Analyst 2015, 140, 7062–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, M.; Marty, J.L. Recent advances in electrochemical aptasensors for detection of biomarkers. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghayegh, F.; Norouziazad, A.; Haghani, E.; Feygin, A.A.; Rahimi, R.H.; Ghavamabadi, H.A.; Sadighbayan, D.; Madhoun, F.; Papagelis, M.; Felfeli, T. Revolutionary point-of-care wearable diagnostics for early disease detection and biomarker discovery through intelligent technologies. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2400595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Song, S.-Y. Genomic and transcriptomic approaches advance the diagnosis and prognosis of neurodegenerative diseases. Genes 2025, 16, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhanwar-Uniyal, M. BRCA1 in cancer, cell cycle and genomic stability. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, s1107–s1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, P.; Melin, M.; Biagi, T.; Fall, T.; Häggström, J.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; von Euler, H. Mammary tumor development in dogs is associated with BRCA1 and BRCA2. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8770–8774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, P.; Von Euler, H. Molecular biological aspects on canine and human mammary tumors. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasaol, J.C.; Śmieszek, A.; Pawlak, A. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of BRCA1 and BRCA2 as Targets in Canine Oncology: A Comprehensive Review of Their Role in Cancer Development and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Ochiai, K.; Morimatsu, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Wada, S.; Taoda, T.; Iwai, S.; Chikazawa, S.; Orino, K.; Watanabe, K. Effects of the missense mutations in canine BRCA2 on BRC repeat 3 functions and comparative analyses between canine and human BRC repeat 3. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Kitano, T.; Morimatsu, M.; Ochiai, K.; Ishiguro-Oonuma, T.; Oosumi, K.; Lin, X.; Orino, K.; Yoshikawa, Y. A Highly Conserved Region in BRCA2 Suppresses the RAD51-Interaction Activity of BRC Repeats. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enginler, S.O.; Akış, I.; Toydemir, T.S.; Oztabak, K.; Haktanir, D.; Gündüz, M.C.; Kırşan, I.; Fırat, I. Genetic variations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes in dogs with mammary tumours. Vet. Res. Commun. 2014, 38, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govoni, V.M.; Da Silva, T.C.; Guerra, J.M.; Pereira, I.V.A.; Queiroga, F.L.; Cogliati, B. Genetic variants of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes in cats with mammary gland carcinoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2021, 19, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, L.; Dobromylskyj, M.; Wood, G.A.; van der Weyden, L. Feline Oncogenomics: What Do We Know about the Genetics of Cancer in Domestic Cats? Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Z.; Blaileanu, G.; Hansen, B.C.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Gong, D.W. cDNA cloning, genomic structure, chromosomal mapping, and functional expression of a novel human alanine aminotransferase. Genomics 2002, 79, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadizadeh, F.; Faghihimani, E.; Adibi, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Diagnostic biomarkers. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2017, 8, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, A.; May, S.C.; Anderson, R.M.; Samala, N.; Mirmira, R.G. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Translating Disease Mechanisms into Therapeutics Using Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, J.R.; Anthony, S.; Johanssen, V.A.; Yeo, T.; Sealey, M.; Yates, A.G.; Smith, C.F.; Claridge, T.D.W.; Nicholson, B.D.; Moreland, J.A.; et al. Metabolomic Biomarkers in Blood Samples Identify Cancers in a Mixed Population of Patients with Nonspecific Symptoms. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Yokoi, A.; Inoue, H.; Suzuki, H.; Kido, N.; Kanno, A.; Kimura-Koyanagi, M.; Kido, Y.; Asahara, S.I. The usefulness of HbA1c measurement in diabetic mouse models using various devices. Exp. Anim. 2025, 74, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Gautam, V.; Naseem, S. Acute-phase proteins: As diagnostic tool. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Garlanda, C. Humoral Innate Immunity and Acute-Phase Proteins. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godson, D.L.; Campos, M.; Attah-Poku, S.K.; Redmond, M.J.; Cordeiro, D.M.; Sethi, M.S.; Harland, R.J.; Babiuk, L.A. Serum haptoglobin as an indicator of the acute phase response in bovine respiratory disease. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 51, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.K.; Blake, A.B.; Tivers, M.S.; Chan, A.; Ishii, P.E.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M.; Lidbury, J.A. Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Dogs with a Congenital Portosystemic Shunt. Metabolites 2025, 15, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidic, J.; Manzano, M.; Chang, C.M.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Advanced biosensors for detection of pathogens related to livestock and poultry. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.J. Biomarkers in veterinary cancer screening: Applications, limitations and expectations. Vet. J. 2010, 185, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medhora, M.; Gao, F.; Gasperetti, T.; Narayanan, J.; Himburg, H.; Jacobs, E.R.; Clough, A.V.; Fish, B.L.; Szabo, A. Biomarkers to Predict Lethal Radiation Injury to the Rat Lung. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkowski, K.; Pepin, K.M.; Lavelle, M.J.; Miller, R.S.; Fischer, J.; Brown, V.R.; Glow, M.; Smith, B.; Cook, S.; Kohen, K.; et al. Operational lessons learned from simulating an elimination response to a transboundary animal disease in wild animals. Prev. Vet. Med. 2025, 234, 106365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskoueian, E.; Eckersall, P.D.; Bencurova, E.; Dandekar, T. Application of proteomic biomarkers in livestock disease management. In Agricultural Proteomics; Salekdeh, G.H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 299–310. ISBN 9783319432786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miretti, S.; Lecchi, C.; Ceciliani, F.; Baratta, M. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Animal Health and Welfare in Livestock. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 578193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viguier, C.; Arora, S.; Gilmartin, N.; Welbeck, K.; O’Kennedy, R. Mastitis detection: Current trends and future perspectives. Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, H. Breeding Against Infectious Diseases in Animals; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, K.; Plain, K.; Purdie, A.; Saunders, B.M.; de Silva, K. Biomarkers for Detecting Resilience against Mycobacterial Disease in Animals. Infect. Immun. 2019, 88, e00401-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Merodio, L.; Williams, J.A.; Gkoutos, G.V.; Acharjee, A. -Omics biomarker identification pipeline for translational medicine. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabortty, T.; Murthy, C.; Varma, M. Fundamental Limitations in Biomarker Based Early Disease Diagnosis. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, R.D.; Roberts, E.K.; Worsham, A.E.; Ashton, M.N.; Wright, E.A.; Saleh, N.; Hardy, D.M. A Non-invasive, Biomarker Assay for Detecting Chronic Wasting Disease Pathology in White-tailed Deer. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckersall, P.D.; Slater, K.; Mobasheri, A. Biomarkers in veterinary medicine: Establishing a new international forum for veterinary biomarker research. Biomarkers 2009, 14, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.E., Jr.; Foley, P.L.; Clough, N.E.; Ludemann, L.R.; Murtle, D.C. Translating research into licensed vaccines and validated and licensed diagnostic tests. Dev. Biol. 2013, 135, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plou, J.; Valera, P.S.; García, I.; de Albuquerque, C.D.L.; Carracedo, A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Prospects of Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy for Biomarker Monitoring toward Precision Medicine. ACS Photonics 2022, 9, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Sánchez, L.; Peña-Bautista, C.; Baquero, M.; Cháfer-Pericás, C. Novel Ultrasensitive Detection Technologies for the Identification of Early and Minimally Invasive Alzheimer’s Disease Blood Biomarkers. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 86, 1337–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Hu, C.; Wu, G.; Xu, S.; Li, Y. Nanomaterial-based microfluidic systems for cancer biomarker detection: Recent applications and future perspectives. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 158, 116835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Paek, S.-H.; Choi, D.-Y.; Lee, M.-K.; Park, J.-N.; Cho, H.-M.; Paek, S.-H. Real-time Monitoring of Biomarkers in Serum for Early Diagnosis of Target Disease. BioChip J. 2020, 14, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Technology/Method | Key Principle | Applications in Animal Diseases | Recent Examples | Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGS | Simultaneous reading of millions of DNA fragments for rapid, cost-effective genome sequencing; platforms include Illumina, PacBio, Ion Torrent; bioinformatics tools assemble reads into complete genomes | Comprehensive genomic profiling, viral research (mutation tracking, vaccine development), rare genetic conditions diagnosis | Canine Rare Genetic Disorders: Diagnosis of suspected genetic disorders in pediatric patients identifying novel variants (35.9%) | Viral Diseases: Tracking mutations in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus (FMDV), and monitoring Avian Influenza, and African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) for vaccine effectiveness and outbreak control | [89,90] | |
| RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) | Analysis of entire RNA molecules (transcripts) to provide insights into gene expression, alternative splicing, and regulatory mechanisms; RNA extracted, converted to cDNA, then sequenced by NGS | Gene expression profiling, understanding disease progression, identifying therapeutic targets, rare disease diagnosis, drug repurposing | Canine Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma (iUC): Identified 2531 differentially expressed genes; downregulation of TP53, upregulation of ERBB2; mutations in FGFR3; increased PD-L1 expression | Canine Melanoma: Downregulation of MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways; upregulation of NOS2; overexpression of miR-450b leading to increased MMP9 expression | Canine Osteosarcoma (OS): Single-cell RNA-Seq revealed 41 distinct cell types, including novel tumor cell clusters with interferon response gene signatures and specific mregDCs; high cross-species similarity with human OS | [90,91] |
| Epigenomics (DNA Methylation, Histone Modifications) | Study of heritable changes in gene function without DNA sequence alteration; involves marks like DNA methylation and histone modifications; analyzed by ChIP-seq (protein-DNA interactions) and ATAC-seq (chromatin accessibility) | Animal health and welfare monitoring, disease resistance, origin tracing, aging research, breeding programs | Broiler Chickens: DNA methylation clock showed accelerated aging with induced systemic inflammation (2023), predicting health/performance | Livestock/Aquaculture: Location-specific DNA methylation signatures identified in shrimp, salmon, and chickens for origin tracing and assessing practices like antibiotic usage | Mice (Aging): Breakdown in epigenetic information drives aging, restoration reverses signs of aging; increased aging biomarkers with epigenetic disorganization | [92] |
| Single-Cell Genomics (scRNA-seq, scATAC-seq) | Analysis of genetic sequences at individual cell level to resolve cellular heterogeneity; scRNA-seq for gene expression, and scATAC-seq for chromatin accessibility | Uncovering rare cell populations, understanding cellular differentiation/lineage, high-resolution disease insights, biomarker development | Canine Osteosarcoma (OS): Revealed 41 distinct cell types in TME, including novel tumor cell and immune cell populations; identified transcriptional heterogeneity within malignant osteoblasts | Chickens (Pimpled Eggs): Integrated scRNA-seq and scATAC-seq identified ionocytes, TFs (ATF3, ATF4, JUN, FOS), regulating uterine activity, and ion pump downregulation linked to egg formation | Bovine Genomics: Comprehensive catalog of cis-regulatory elements (CREs) in cattle using scATAC-seq (2023); insights into chromatin accessibility in oocytes/embryos and muscle growth in Tianzhu | [89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eman, S.; Mohai Ud Din, R.; Zafar, M.H.; Zhang, M.; Wen, X.; Ma, J.; Saleh, A.A.; Husien, H.M.; Wang, M.; Guo, X. Technologies in Biomarker Discovery for Animal Diseases: Mechanisms, Classification, and Diagnostic Applications. Animals 2025, 15, 3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213132
Eman S, Mohai Ud Din R, Zafar MH, Zhang M, Wen X, Ma J, Saleh AA, Husien HM, Wang M, Guo X. Technologies in Biomarker Discovery for Animal Diseases: Mechanisms, Classification, and Diagnostic Applications. Animals. 2025; 15(21):3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213132
Chicago/Turabian StyleEman, Salwa, Raza Mohai Ud Din, Muhammad Hammad Zafar, Mengke Zhang, Xin Wen, Jiayu Ma, Ahmed A. Saleh, Hosameldeen Mohamed Husien, Mengzhi Wang, and Xiaodong Guo. 2025. "Technologies in Biomarker Discovery for Animal Diseases: Mechanisms, Classification, and Diagnostic Applications" Animals 15, no. 21: 3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213132
APA StyleEman, S., Mohai Ud Din, R., Zafar, M. H., Zhang, M., Wen, X., Ma, J., Saleh, A. A., Husien, H. M., Wang, M., & Guo, X. (2025). Technologies in Biomarker Discovery for Animal Diseases: Mechanisms, Classification, and Diagnostic Applications. Animals, 15(21), 3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213132








