Effect of Polygain™ Supplementation on Growth Performance, Lesion Severity, and Oocyst Shedding in Eimeria-Challenged Broiler Chickens
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coccidia Preparation
2.2. Compound Preparation
2.3. Birds and Housing
2.4. Treatments
2.5. Eimeria Challenge
2.6. Data Collection
2.7. Percent Optimum Anticoccidial Activity (POAA)
2.8. Reduction Lesion Score (RLS)
2.9. Oocyst per Gram (OPG)
2.10. Relative Oocyst Production (ROP)
2.11. The Anticoccidial Index (ACI)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
2.13. Safety and Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight Gain (BWG) and Growth Performance
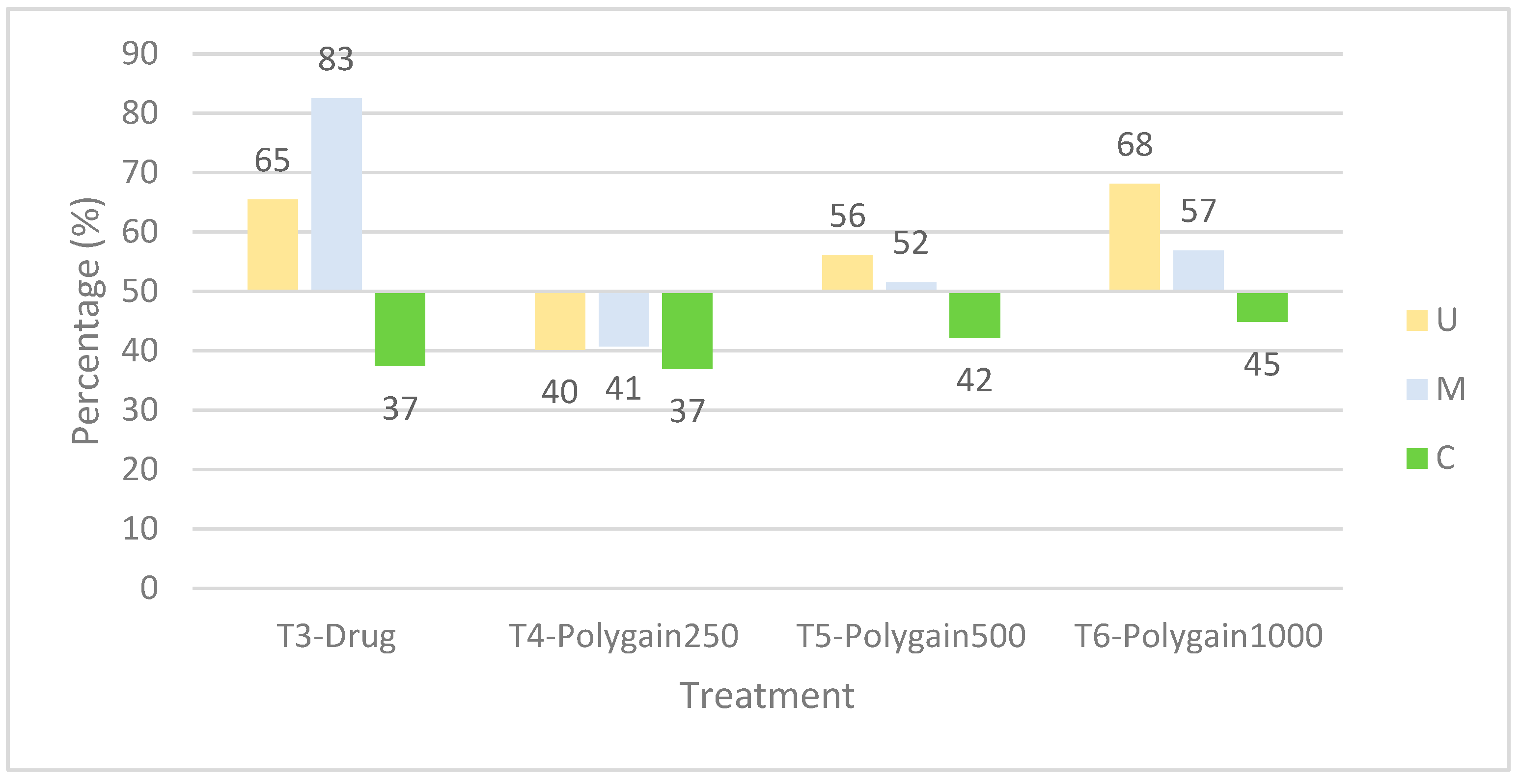
3.2. Lesion Scores
3.3. Oocyst per Gram and Relative Oocyst Production
3.4. Anticoccidial Index
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ROP | Relative Oocyst Production |
| RLS | Reduction Lesion Score |
| POAA | Percent Optimal Anticoccidial Activity |
| ACI | Anticoccidial Index |
| PRSE | Polyphenol-Rich Sugarcane Extract |
| GC-MS | Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometer |
| CP | Charoen Pokphand |
| FCR | Feed Conversion Ratio |
| GSR | Growth Survival Ratio |
| OPG | Oocyst per Gram |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| CRD | Completely Randomized Design |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| PPE | Protective Personal Equipment |
| DPI | Day Post-Infection |
| BWG | Body Weight Gain |
| U | Upper Intestine |
| M | Mid-Intestine |
| C | Caecum |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid–Related Factor 2 |
| AMR | Antimicrobial Multiple Resistance |
References
- Blake, D.P.; Knox, J.; Dehaeck, B.; Huntington, B.; Rathinam, T.; Ravipati, V.; Ayoade, S.; Gilbert, W.; Adebambo, A.O.; Jatau, I.D.; et al. Re-calculating the cost of coccidiosis in chickens. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, W.; Bellet, C.; Blake, D.P.; Tomley, F.M.; Rushton, J. Revisiting the Economic Impacts of Eimeria and Its Control in European Intensive Broiler Systems with a Recursive Modeling Approach. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 558182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Osorio, S.; Chaparro-Gutiérrez, J.J.; Gómez-Osorio, L.M. Overview of Poultry Eimeria Life Cycle and Host-Parasite Interactions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.R.; Silva, L.J.G.; Pereira, A.; Esteves, A.; Duarte, S.C.; Pena, A. Coccidiostats and Poultry: A Comprehensive Review and Current Legislation. Foods 2022, 11, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, P.; Hu, D.; Tang, X.; Zhang, S.; Shi, F.; Yan, X.; Yan, W.; Shi, T.; Wang, S.; et al. Advancements in understanding chicken coccidiosis: From Eimeria biology to innovative control strategies. One Health Adv. 2024, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadykalo, S.; Roberts, T.; Thompson, M.; Wilson, J.; Lang, M.; Espeisse, O. The value of anticoccidials for sustainable global poultry production. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beber, C.L.; Aragrande, M.; Canali, M. Policies and strategies to control antimicrobial resistance in livestock production: A comparative analysis of national action plans in European Union Member States. Health Policy 2025, 152, 105238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, A.; van Klinken, R.D.; Jones, D.; Wang, J. Consumers’ perspectives on antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance in food animals: A systematic review. NPJ Sci. Food. 2025, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillehoj, H.; Liu, Y.; Calsamiglia, S.; Fernandez-Miyakawa, M.E.; Chi, F.; Cravens, R.L.; Oh, S.; Gay, C.G. Phytochemicals as antibiotic alternatives to promote growth and enhance host health. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiti-Asli, M.; Ghanaatparast-Rashti, M. Dietary oregano essential oil alleviates experimentally induced coccidiosis in broilers. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 120, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-y.; Di, K.-q.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.-f.; Xi, J.-z.; Wang, D.-H.; Hao, E.-Y.; Xu, L.-J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, R.-Y. Effect of natural garlic essential oil on chickens with artificially infected Eimeria tenella. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 300, 109614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dkhil, M.A.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Abdel Moneim, A.E.; Delic, D. Protective effect of Azadirachta indica extract against Eimeria papillata-induced coccidiosis. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.M.H.; Zayeda, R.; Elakany, H.; Badr, S.; Abou-Rawash, A.; Abd-Ellatieff, H. Anticoccidial activity of Aloe Vera Leafs’ aqueous extract and vaccination against Eimeria tenella: Pathological study in broilers. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.; Iqbal, Z.; Khan, M.; Zafar, M.; Zia, M. Anticoccidial Activity of Curcuma longa L. in Broilers. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2010, 53, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, F.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Steinbrenner, H.; Sies, H.; Dkhil, M.A. Towards identifying novel anti-Eimeria agents: Trace elements, vitamins, and plant-based natural products. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3547–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikusato, M.; Namai, F.; Yamada, K. Effect of Feeding Sugarcane Bagasse-Extracted Polyphenolic Mixture on the Growth Performance, Meat Quality, and Oxidative and Inflammatory Status of Chronic Heat-Stressed Broiler Chickens. Animals 2024, 14, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshmand, A.; Young, P.; Campbell, B.; Kheravii, S.K.; Sharma, N.K.; Afshari, R.; Dias, D.A.; Flavel, M.; Kitchen, B.; Wu, S.-B. In vitro inhibitory activities of sugarcane extract on avian Eimeria sporozoites. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2021, 17, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penglase, S.; Ackery, T.; Kitchen, B.; Flavel, M.; Condon, K. The Effects of a Natural Polyphenol Extract from Sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) on the Growth, Survival, and Feed Conversion Efficiency of Juvenile Black Tiger Shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathap, P.; Chauhan, S.S.; Flavel, M.; Mitchell, S.; Cottrell, J.J.; Leury, B.J.; Dunshea, F.R. Effects of Sugarcane-Derived Polyphenol Supplementation on Methane Production and Rumen Microbial Diversity of Second-Cross Lambs. Animals 2024, 14, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edirisinghe, N.; Flavel, M.; Pouniotis, D.; Zakaria, R.; Lim, K.F.; Dias, D. From feed to fork: Immunity, performance and quality of products from farm animals fed sugarcane products. Front. Anim. Sci. 2024, 5, 1352961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.M.; Chasser, K.M.; Duff, A.F.; Briggs, W.N.; Latorre, J.D.; Barta, J.R.; Bielke, L. Comparison of multiple methods for induction of necrotic enteritis in broilers. I. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2018, 27, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, A.; Thebo, P.; Mattsson, J.G. A simplified protocol for molecular identification of Eimeria species in field samples. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 146, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tongkamsai, S.; Boobphahom, S.; Apphaicha, R.; Chansiripornchai, N. Prevalence and anticoccidial drug sensitivity of Eimeria tenella isolated from commercial broiler farms in Thailand. Vet. World. 2025, 18, 1561–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.; Reid, W.M. Anticoccidial drugs: Lesion scoring techniques in battery and floor-pen experiments with chickens. Exp. Parasitol. 1970, 28, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais, M.M.; Akhtar, M.; Muhammad, F.; Haq Au Anwar, M.I. Immunotherapeutic effects of some sugar cane (Saccharum officinarum L.) extracts against coccidiosis in industrial broiler chickens. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 128, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabkhazaeli, F.; Modrisanei, M.; Nabian, S.; Mansoori, B.; Madani, A. Evaluating the resistance of Eimeria spp. Field isolates to anticoccidial drugs using three different indices. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2013, 8, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, D.P.; Sasai, K.; Gaafar, S.M.; Smothers, C.D. Effects of different levels of oocyst inocula of Eimeria acervulina, E. tenella, and E. maxima on plasma constituents, packed cell volume, lesion scores, and performance in chickens. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougald, L.R.; Da Silva, J.M.L.; Solis, J.; Braga, M. A survey of sensitivity to anticoccidial drugs in 60 isolates of coccidia from broiler chickens in Brazil and Argentina. Avian Dis. 1987, 31, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.P.; Mckenzie, M.E. Poultry Coccidiosis and Effect of Coccidiosis Diagnostic and Testing Procedures, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson, J.N. Coccidiosis: Oocyst counting technique for coccidiostat evaluation. Exp. Parasitol. 1970, 28, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.H.; Sun, B.B.; Zuo, B.X.Z.; Chen, X.Q.; Du, A.F. Prevalence and drug resistance of avian Eimeria species in broiler chicken farms of Zhejiang province, China. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2104–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, E.C.; Campbell, W.C.; Cuckler, A.C. Development of Resistance to Quinoline Coccidiostats under Field and Laboratory Conditions. J. Parasitol. 1968, 54, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Liu, G.; White, D.L.; Tompkins, Y.H.; Kim, W.K. Effects of mixed Eimeria challenge on performance, body composition, intestinal health, and expression of nutrient transporter genes of Hy-Line W-36 pullets (0–6 wks of age). Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Han, B.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Si, H.; Hu, D. Effects of Six Natural Compounds and Their Derivatives on the Control of Coccidiosis in Chickens. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Aziza, F.A.M.; El-Metenawy, T.M.; Rabie, N.S.; Hassan, E.R.; Elbayoumi, K.M.; Mekky, H.M.; Girh, Z.M.S.A.; Bosila, M.A. Comparative study between chemical anticoccidial medication and natural prepared products on experimentally infected broiler chickens. J. Parasit. Dis. 2023, 47, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.M.; Miska, K.B.; Kahl, S.; Jenkins, M.C.; Shao, J.; Proszkowiec-Weglarz, M. Effects of Eimeria tenella on Cecal Luminal and Mucosal Microbiota in Broiler Chickens. Avian Dis. 2022, 66, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, D.E.; Stephens, J.F. Upper Intestinal Tract Infection Produced by E. acervulina and Absorption of 65Zn and 131I-labeled Oleic Acid. J. Nutr. 1967, 93, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, Y.; Cottrell, J.J.; Suleria, H.A.R.; Dunshea, F.R. Gut Microbiota-Polyphenol Interactions in Chicken: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-C.; Steiner, T.; Aufy, A.; Lien, T.-F. Effects of supplemental essential oil on growth performance, lipid metabolites and immunity, intestinal characteristics, microbiota and carcass traits in broilers. Livest. Sci. 2012, 144, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Rehman, M.U.; He, Y.; Li, A.; Jian, F.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S. Exploring the interplay between Eimeria spp. infection and the host: Understanding the dynamics of gut barrier function. Vet. Q. 2025, 45, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attree, E.; Sanchez-Arsuaga, G.; Jones, M.; Xia, D.; Marugan-Hernandez, V.; Blake, D.; Tomley, F. Controlling the causative agents of coccidiosis in domestic chickens; an eye on the past and considerations for the future. CABI Agric. Biosci. 2021, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, Z.; Alkheraije, K.A. Botanicals: A promising approach for controlling cecal coccidiosis in poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1157633. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, D.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, Y.; Feng, W.; Peng, C. Interactions between gut microbiota and polyphenols: A mechanistic and metabolomic review. Phytomedicine 2023, 119, 154979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Jha, R. Oxidative Stress in the Poultry Gut: Potential Challenges and Interventions. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peek, H.W.; Landman, W.J.M. Coccidiosis in poultry: Anticoccidial products, vaccines and other prevention strategies. Vet. Q. 2011, 31, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, P.; Wei, L.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y. Effects of dietary supplementation with chlorogenic acid on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and hepatic inflammation in broiler chickens subjected to diquat-induced oxidative stress. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Xu, Y.-L.; Zhu, Z.-Q. Chlorogenic Acid on the In Vitro Germination, Invasion and Intracellular Proliferation of Ameson portunus (Microsporidia). Research Square. 2025. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-6226867/v1 (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Gao, S.; Wang, K.; Xiong, K.; Xiao, S.; Wu, C.; Zhou, M.; Li, L.; Yuan, G.; Jiang, L.; Xiong, Q.; et al. Unraveling the Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway in the DF-1 Chicken Fibroblast Cell Line: Insights into T-2 Toxin-Induced Oxidative Stress Regulation. Toxins 2023, 15, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolathingal-Thodika, N.; Elayadeth-Meethal, M.; Dunshea, F.R.; Eckard, R.; Flavel, M.; Chauhan, S.S. Is early life programming a promising strategy for methane mitigation and sustainable intensification in ruminants? Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 982, 179654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlaźlak, S.; Pietrzak, E.; Biesek, J.; Dunislawska, A. Modulation of the immune system of chickens a key factor in maintaining poultry production—A review. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismiraj, M.R.; Arts, J.A.J.; Parmentier, H.K. Maternal Transfer of Natural (Auto-) Antibodies in Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2380–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, L.A. Possibilities of early life programming in broiler chickens via intestinal microbiota modulation. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Aguilar, G.R.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Research Agenda for Antimicrobial Resistance in Human Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.; Krogh, K.A.; Björklund, E.; Halling-Sørensen, B.; Brandt, A. Environmental risk assessment of ionophores. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuspa, M.A.M.; Soares, I.; Belote, B.L.; Kawazoe, U.; Santin, E. Comparing performance and resistance of two broilers breeds challenged by Eimeria acervulina. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 287, 109235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, E.; Arabkhazaeli, F.; Madani, S.A. Intraspecific Variations in Biology and Pathogenesis of Two Eimeria maxima Isolates from Distinct Geographic Locations. Vet. Med. Sci. 2025, 11, e70235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengat Prakashbabu, B.; Thenmozhi, V.; Limon, G.; Kundu, K.; Kumar, S.; Garg, R.; Clark, E.L.; Rao, A.S.R.S.; Raj, D.G.; Raman, M.; et al. Eimeria species occurrence varies between geographic regions and poultry production systems and may influence parasite genetic diversity. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 233, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, L.F.V.B.; Sakomura, N.K.; Reis, M.d.P.; Mariani, A.B.; Lambert, W.; Andretta, I.; Létourneau-Montminy, M.-P. Coccidiosis infection and growth performance of broilers in experimental trials: Insights from a meta-analysis including modulating factors. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 103021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.L.; Barreto, F.; Rau, R.B.; Silva, G.R.D.; Lara, L.J.C.; Figueiredo, T.C.; de Assis, D.C.S.; de Vasconcelos Cançado, S. Determination of the residue levels of nicarbazin and combination nicarbazin-narasin in broiler chickens after oral administration. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jones, J.E.; Solis, J.; Hughes, B.L.; Castaldo, D.J.; Toler, J.E. Production and Egg-Quality Responses of White Leghorn Layers to Anticoccidial Agents. Poult. Sci. 1990, 69, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannavan, A.; Ball, G.; Kennedy, D.G. Nicarbazin contamination in feeds as a cause of residues in eggs. Food Addit. Contam. 2000, 17, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunaratne, N.; Silva, S.; Herath, M.; Liyanage, R.; Weththasinghe, P.; Jayawardana, B.; De Seram, E.; Pushpakumara, A.; Flavel, M. Effects of supplementing a polyphenol-rich sugarcane extract through drinking water on egg production and quality of laying hens. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0317292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
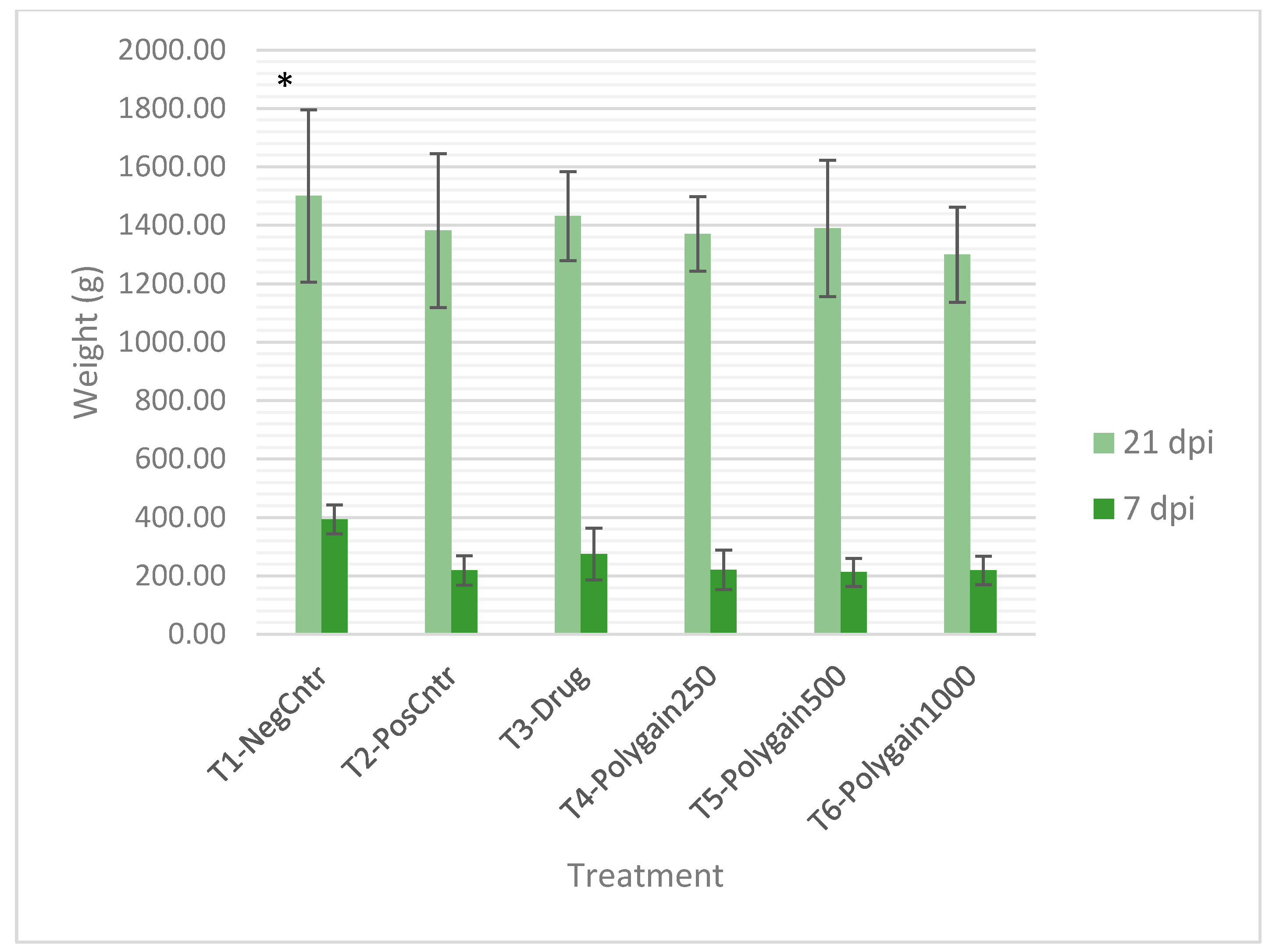
| Treatment | GSR | POAA |
|---|---|---|
| T1-NegCntr | 1.86 | N.A |
| T2-PosCntr | 1.46 | N.A |
| T3-Drug | 1.59 | 31.80 |
| T4-Polygain250 | 1.47 | 4.09 |
| T5-Polygain500 | 1.46 | 0.98 |
| T6-Polygain1000 | 1.46 | 1.68 |
| Treatment | Lesion Scores | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 dpi | 21 dpi | |||||||
| U | M | C | TLS | U | M | C | TLS | |
| T1-NegCntr | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A | 0 A |
| T2-PosCntr | 1.9 ± 0.9 B | 1.4 ± 1.8 B | 2.9 ± 0.9 B | 6.3 ± 2.7 B | 1.7 ± 0.6 B | 1.3 ± 0.6 B | 0 A | 3.0 ± 1.1 B |
| T3-Drug | 0.6 ± 0.4 C | 0.2 ± 0.4 C | 1.8 ± 1.0 C | 2.8 ± 0.8 BC | 0.6 ± 1.5 CD | 0.5 ± 1.1 CD | 0.3 ± 1.1 B | 1.6 ± 0.8 AB |
| T4-Polygain250 | 1.1 ± 1.0 BC | 0.8 ± 1.0 B | 1.8 ± 1.2 C | 3.9 ± 0.5 C | 0.9 ± 0.8 CD | 0.7 ± 0.6 CD | 0.1 ± 0.3 AB | 1.7 ± 0.4 B |
| T5-Polygain500 | 0.8 ± 1.0 C | 0.6 ± 1.1 B | 1.6 ± 0.9 C | 3.2 ± 0.5 C | 1.0 ± 0.7 D | 0.7 ± 0.6 CD | 0.3 ± 0.6 B | 2.1 ± 0.3 B |
| T6-Polygain1000 | 0.6 ± 1.1 C | 0.6 ± 1.1 B | 1.6 ± 0.9 C | 2.9 ± 06 C | 0.5 ± 0.6 C | 0.4 ± 0.6 C | 0 A | 1.0 ± 0.3 AB |
| Treatment | Oocyst Per Gram | |
|---|---|---|
| 6 dpi | 20 dpi | |
| NegCntr, T1 | 0 a | 0 A |
| PosCntr, T2 | 15,264,608 b | 777 B |
| T3, drug | 435,308 c | 79 B |
| T4, Polygain™250 | 254,667 c | 407 B |
| T5, Polygain™500 | 479,917 c | 472 B |
| T6, Polygain™1000 | 476,408 c | 914 B |
| Treatment | rBWGR | Mortality % | Survival Rate (%) | Lesion Score | ROP | ACI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1-NegCntr | N.A | 0.00% A | 100 | N.A | N.A | N.A |
| T2-PosCntr | 55.63 | 13.30% A | 91.66 | N.A | N.A | N.A |
| T3-Drug | 69.90 | 8.30% A | 95.83 | 2.75 AB | 2.85 | 160.13 |
| T4-Polygain250 | 56.22 | 7.70% A | 95.83 | 3.85 B | 1.67 | 146.54 |
| T5-Polygain500 | 54.00 | 7.70% A | 95.83 | 3.23 B | 3.14 | 143.46 |
| T6-Polygain1000 | 55.67 | 7.70% A | 95.83 | 2.85 B | 3.12 | 145.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Llalla Vidal, T.M.; Boobphahom, S.; Tongkamsai, S.; Flavel, M. Effect of Polygain™ Supplementation on Growth Performance, Lesion Severity, and Oocyst Shedding in Eimeria-Challenged Broiler Chickens. Animals 2025, 15, 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213130
Llalla Vidal TM, Boobphahom S, Tongkamsai S, Flavel M. Effect of Polygain™ Supplementation on Growth Performance, Lesion Severity, and Oocyst Shedding in Eimeria-Challenged Broiler Chickens. Animals. 2025; 15(21):3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213130
Chicago/Turabian StyleLlalla Vidal, Thalia Marina, Siraprapa Boobphahom, Suttitas Tongkamsai, and Matthew Flavel. 2025. "Effect of Polygain™ Supplementation on Growth Performance, Lesion Severity, and Oocyst Shedding in Eimeria-Challenged Broiler Chickens" Animals 15, no. 21: 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213130
APA StyleLlalla Vidal, T. M., Boobphahom, S., Tongkamsai, S., & Flavel, M. (2025). Effect of Polygain™ Supplementation on Growth Performance, Lesion Severity, and Oocyst Shedding in Eimeria-Challenged Broiler Chickens. Animals, 15(21), 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15213130








