Whole-Genome Resequencing Identifies Candidate Genes for Tail Fat Deposition in Sheep
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing Library Construction
2.3. Quality Control and Comparison
2.4. Selection Signal Analysis
2.5. Detection and Annotation of Candidate Genes
2.6. Candidate Gene Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Sequencing Data
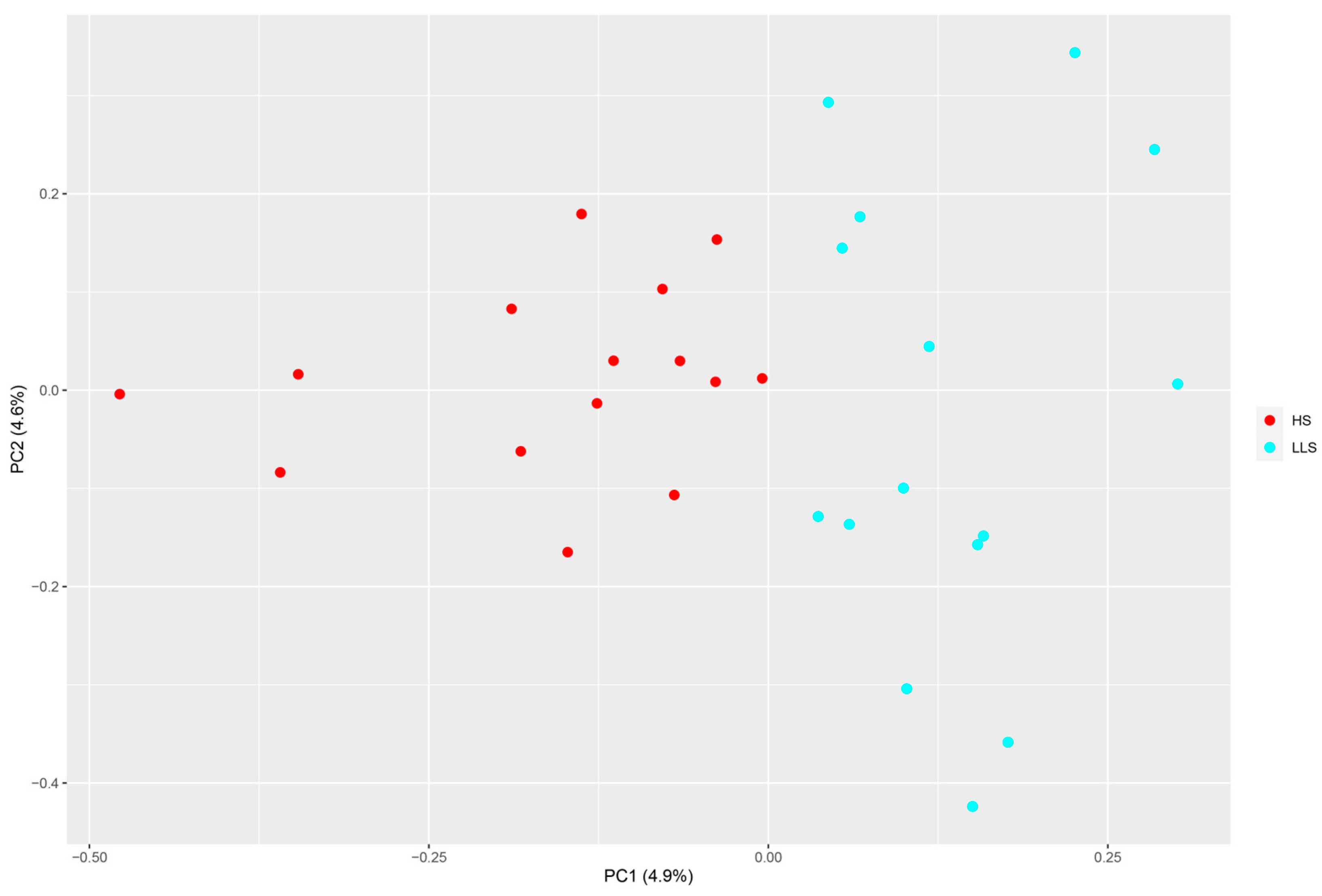
3.2. Population Genetic Analysis
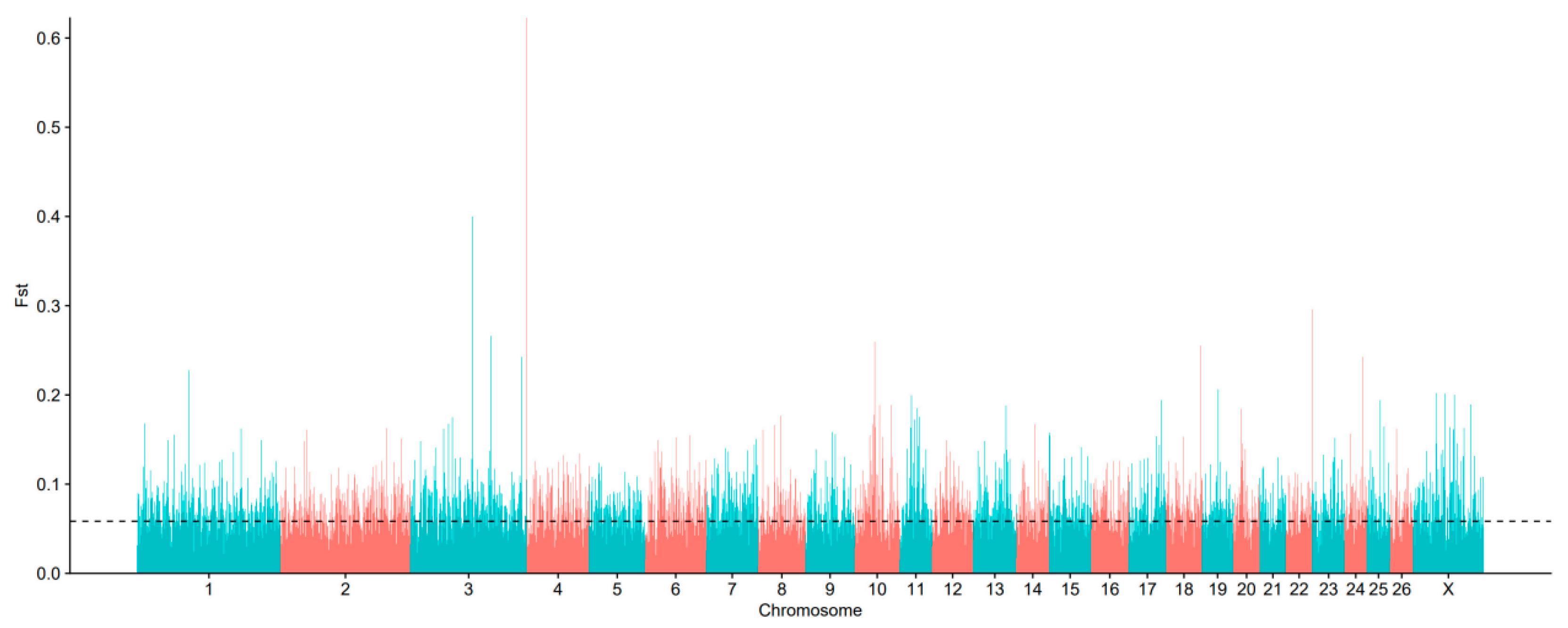
3.3. Identification of Signatures of Selection Between Long-Fat-Tailed and Short-Fat-Tailed Sheep Breeds Using FST Analysis
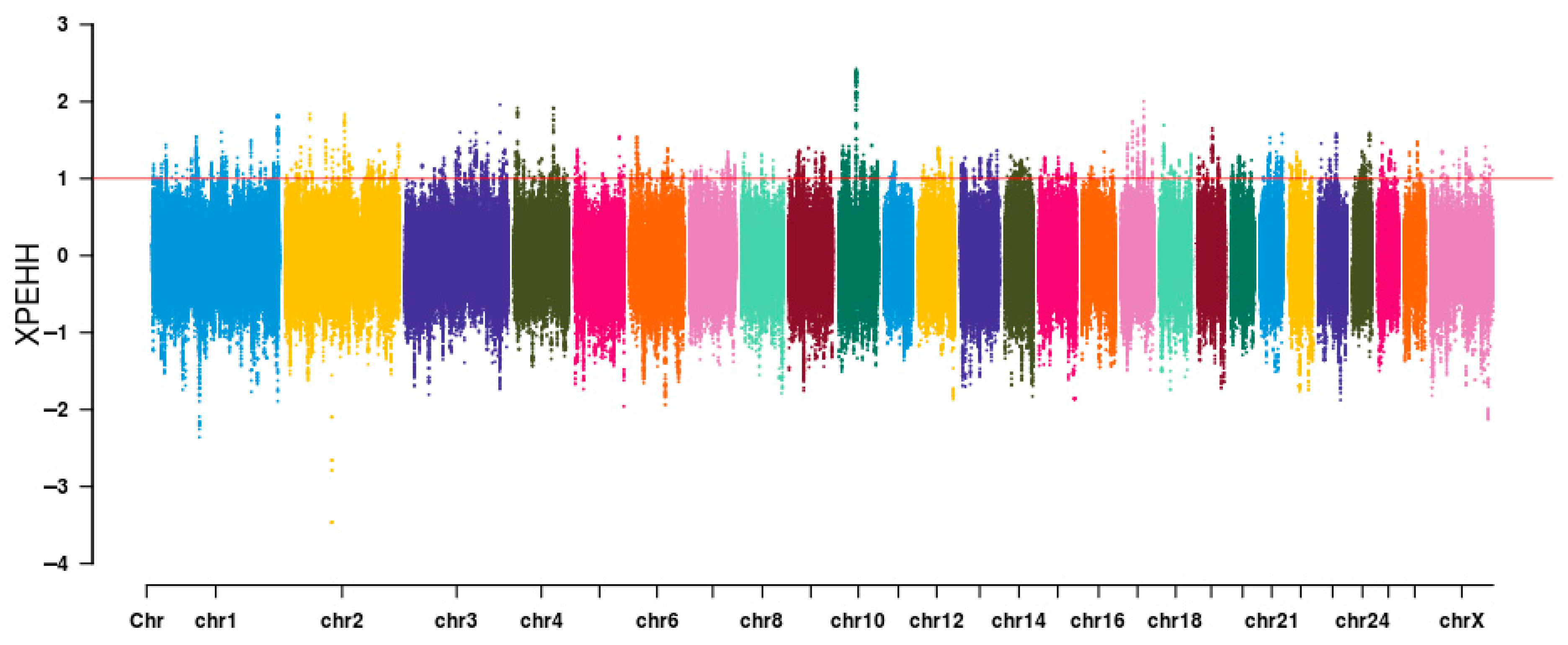
3.4. Identification of Signatures of Selection Between Long-Fat-Tailed and Short-Fat-Tailed Sheep Breeds Using XP-EHH Analysis
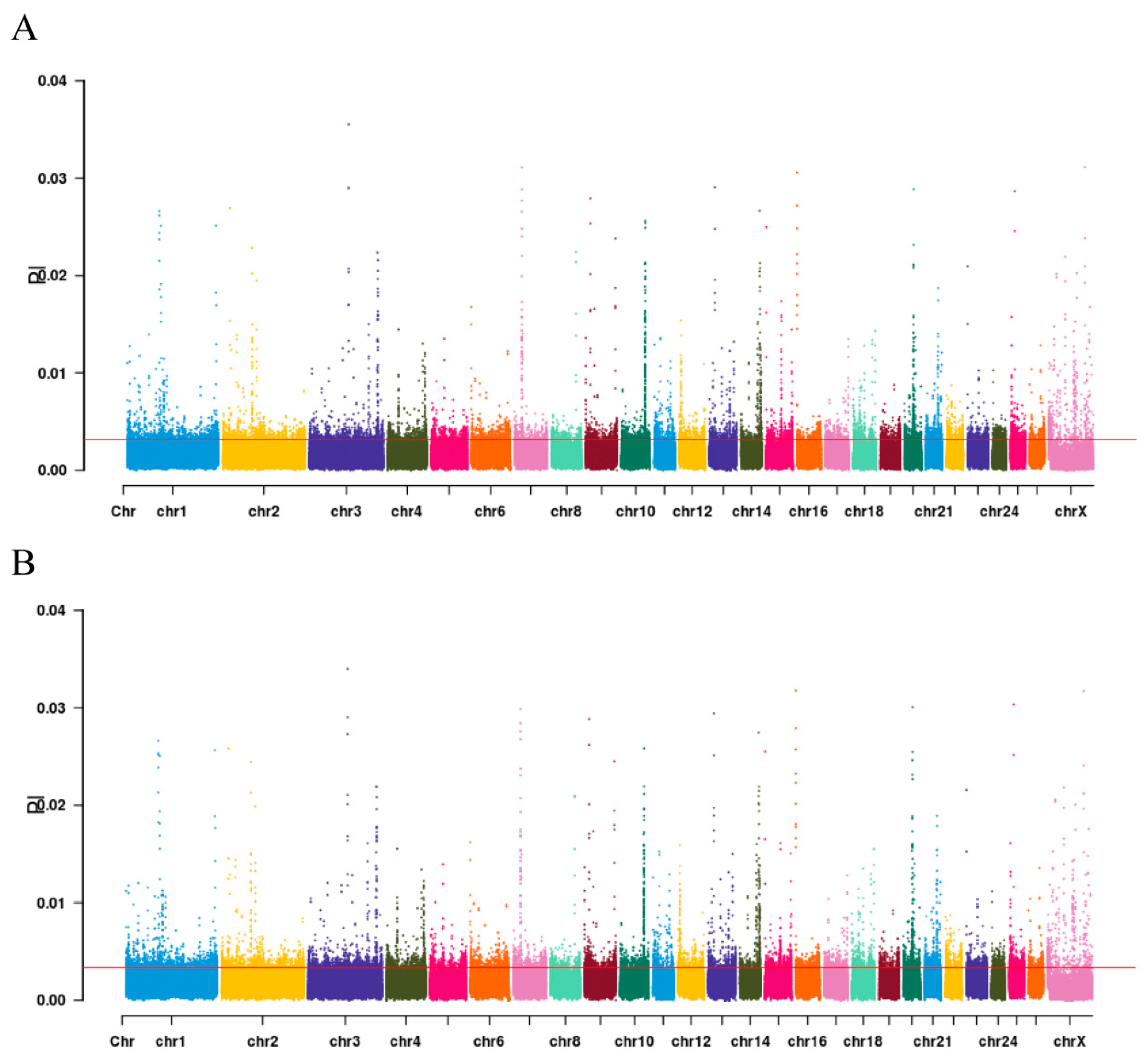
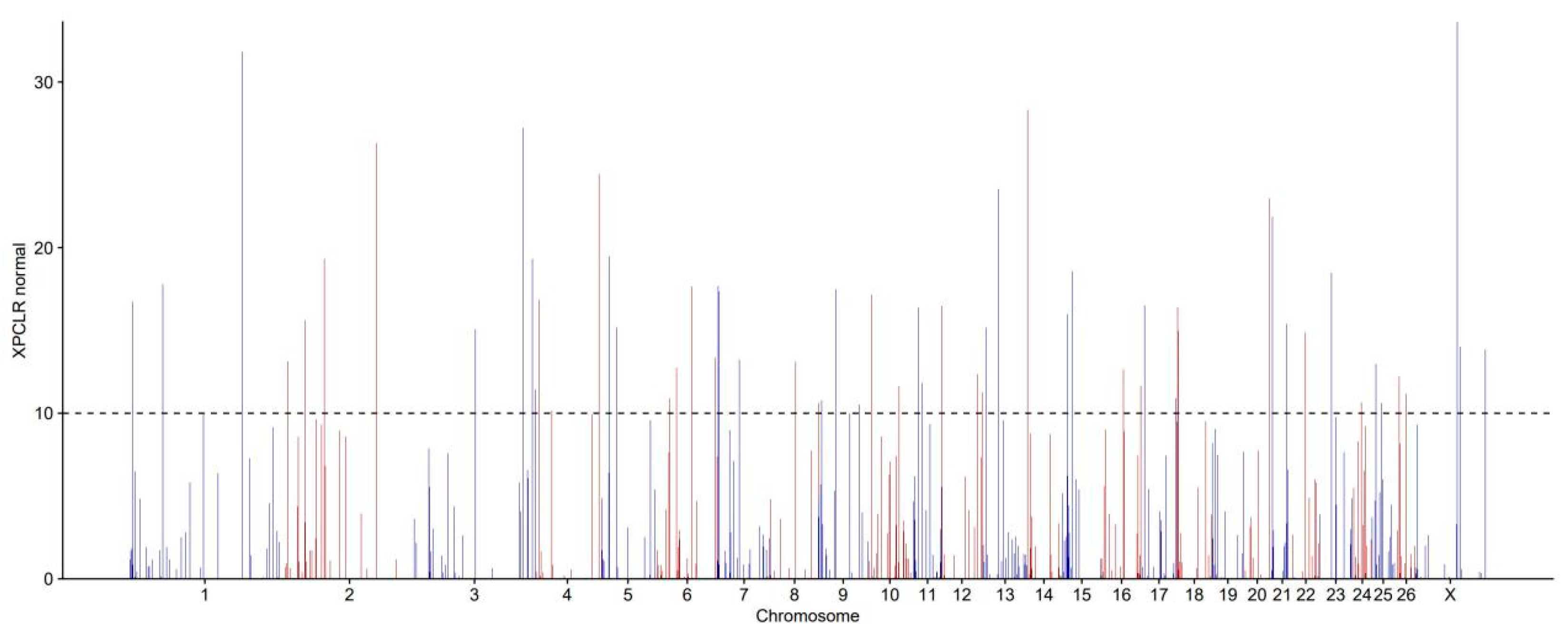
3.5. Identification of Signatures of Selection Between Long-Fat-Tailed and Short-Fat-Tailed Sheep Breeds Using XP-CLR Analysis
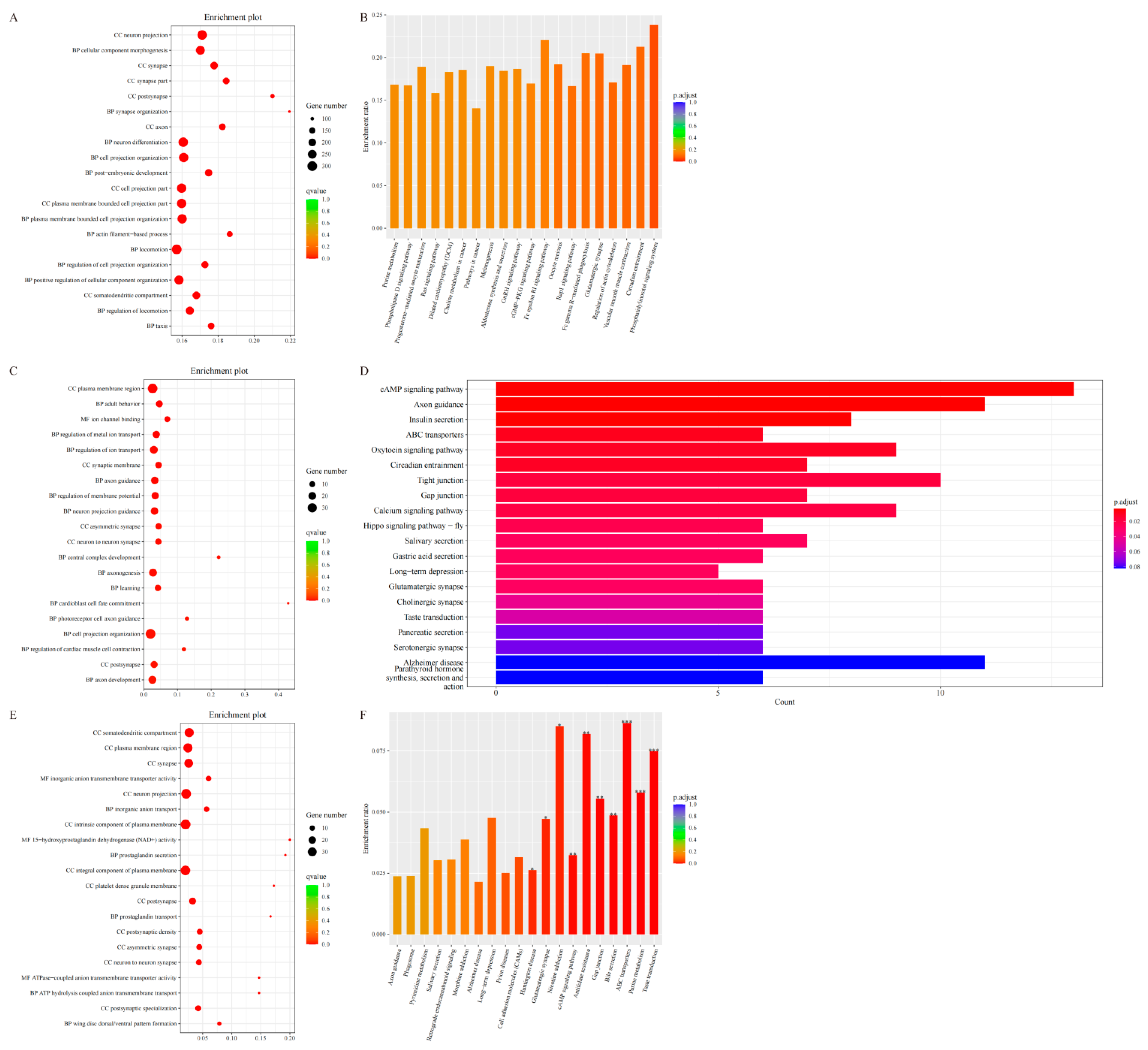
3.6. Enrichment Analysis
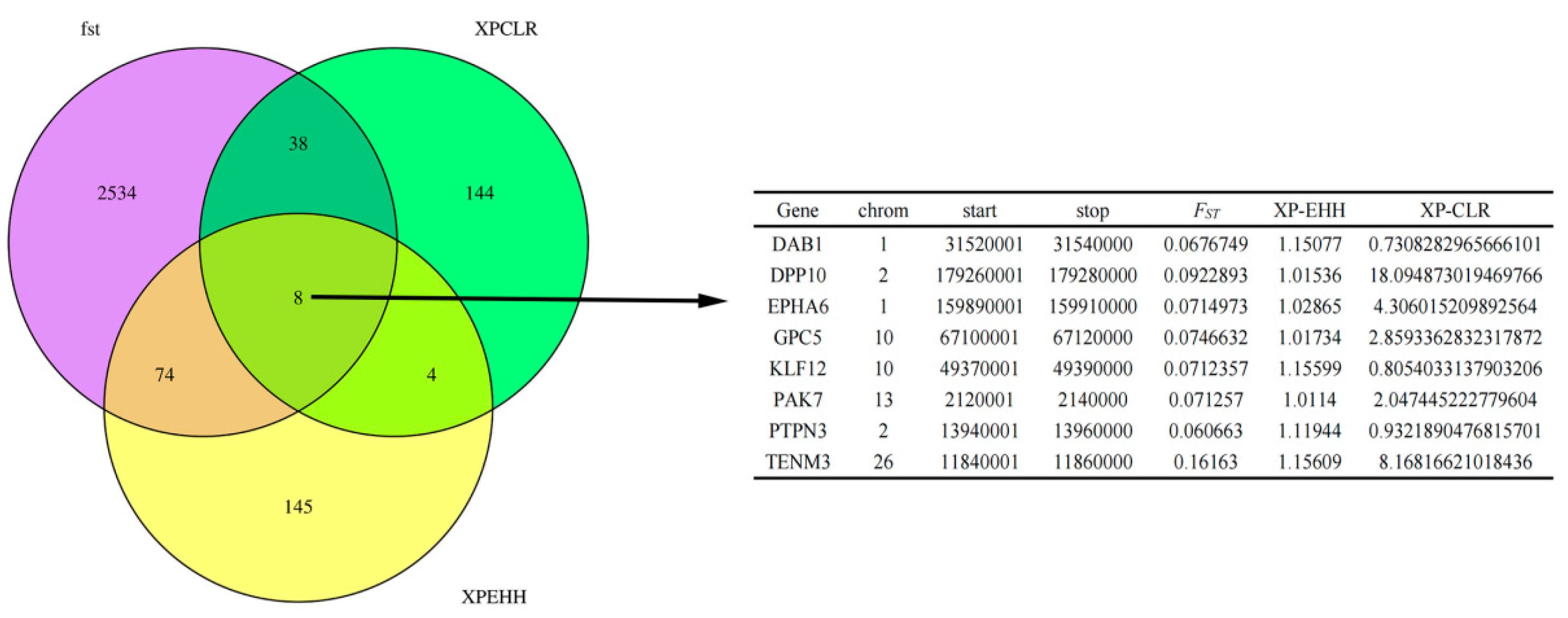
3.7. Shared Gene
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Lu, Z.; Jin, M.; Fei, X.; Quan, K.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Chu, M.; Wang, H.; Wei, C. Verification and Analysis of Sheep Tail Type-Associated PDGF-D Gene Polymorphisms. Animals 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, J.; Han, J.; Yang, B. Association Between BMP2 Functional Polymorphisms and Sheep Tail Type. Animals 2020, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Lu, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, H.; Lu, J.; Quan, K.; Di, R.; et al. Transcriptome reveals key microRNAs involved in fat deposition between different tail sheep breeds. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Bakhtiarizadeh, M.R.; Salehi, A. Meta-analysis of RNA-Seq datasets highlights novel genes/pathways involved in fat deposition in fat-tail of sheep. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shao, J.; He, S.; Guo, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.; Nanaei, H.A.; Chen, L.; Li, R.; Xu, H.; et al. Allele-specific expression and splicing provide insight into the phenotypic differences between thin- and fat-tailed sheep breeds. J. Genet. Genom. 2022, 49, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Qiao, L.; An, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Ren, Y.; Pan, Y.; Jing, J.; Liu, W. Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissues from two fat-tailed sheep breeds reveals key genes involved in fat deposition. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Gao, L.; Gan, S. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Key Genes and Pathways Activated in Response to Fat Deposition in Two Sheep Breeds With Distinct Tail Phenotype. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 639030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalds, P.; Zhou, S.; Gao, Y.; Cai, B.; Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Genetics of the phenotypic evolution in sheep: A molecular look at diversity-driving genes. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2022, 54, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deribe, B.; Beyene, D.; Dagne, K.; Getachew, T.; Gizaw, S.; Abebe, A. Morphological diversity of northeastern fat-tailed and northwestern thin-tailed indigenous sheep breeds of Ethiopia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, S.; Bahbahani, H.; Moioli, B.; Ahbara, A.; Al Abri, M.; Almathen, F.; Da Silva, A.; Belabdi, I.; Portolano, B.; Mwacharo, J.M.; et al. Novel and known signals of selection for fat deposition in domestic sheep breeds from Africa and Eurasia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amane, A.; Belay, G.; Nasser, Y.; Kyalo, M.; Dessie, T.; Kebede, A.; Getachew, T.; Entfellner, J.-B.D.; Edea, Z.; Hanotte, O.; et al. Genome-wide insights of Ethiopian indigenous sheep populations reveal the population structure related to tail morphology and phylogeography. Genes Genom. 2020, 42, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, S.; Ghias, J.S.; Hasanpur, K.; Mohammadi, S.A.; Ebrahimie, E. Molecular mechanisms of fat deposition: IL-6 is a hub gene in fat lipolysis, comparing thin-tailed with fat-tailed sheep breeds. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2021, 64, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Guo, T.; Yue, Y.; Lu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yuan, C.; Niu, C.; Yang, M.; Yang, B. Quantitative proteomic analysis identified differentially expressed proteins with tail/rump fat deposition in Chinese thin- and fat-tailed lambs. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Y.; Erdenee, S.; Hu, L.; Chen, H.; Cai, Y.; Lan, X. Comparative Transcriptome Profiling of mRNA and lncRNA Related to Tail Adipose Tissues of Sheep. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiye, Z.; Song, S.; Li, M.; Huang, X.; Luo, Y.; Fang, S. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis reveals different methylation patterns in Chinese indigenous sheep with different type of tail. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1125262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhao, H.; Tang, X.; Li, Q.; Yi, X.; Liu, S.; Sun, X. Novel InDels of GHR, GHRH, GHRHR and Their Association with Growth Traits in Seven Chinese Sheep Breeds. Animals 2020, 10, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Liu, Q.; Tang, J.; Di, R.; Chu, M. TGIF1 and SF1 polymorphisms are associated with litter size in Small Tail Han sheep. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2020, 55, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitti, J.J.; Grossman, S.R.; Sabeti, P.C. Detecting natural selection in genomic data. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2013, 47, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Guo, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.E.; Emu, Q.; Zhang, H. Whole-Genome Resequencing Reveals Genetic Diversity and Wool Trait-Related Genes in Liangshan Semi-Fine-Wool Sheep. Animals 2024, 14, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-X.; Wang, B.; Jing, J.-N.; Ma, R.; Luo, Y.-H.; Li, X.; Yan, Z.; Liu, Y.-J.; Gao, L.; Ren, Y.-L.; et al. Whole-body adipose tissue multi-omic analyses in sheep reveal molecular mechanisms underlying local adaptation to extreme environments. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Sun, W.; Guo, T.; Li, J.; Zhu, S.; Lu, Z.; Qiao, G.; Han, M.; Zhao, H.; Yang, B.; et al. Genome-Wide Selective Signatures Reveal Candidate Genes Associated with Hair Follicle Development and Wool Shedding in Sheep. Genes 2021, 12, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cheng, J.; Li, X.; Huang, K.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yang, X.; et al. Comprehensive multi-tissue epigenome atlas in sheep: A resource for complex traits, domestication, and breeding. Imeta 2024, 3, e254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balfourier, F.; Bouchet, S.; Robert, S.; De Oliveira, R.; Rimbert, H.; Kitt, J.; Choulet, F. Worldwide phylogeography and history of wheat genetic diversity. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav0536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Mo, D.; Luo, L.; Xu, S.; Lv, F. The goat pan-genome reveals patterns of gene loss during domestication. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, I.; de la Rosa, R.; Rallo, L.; Belaj, A. Selection of RAPD markers for olive (Olea europaea L.) cultivars identification. Acta Hortic. 1999, 474, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzelsoy, G.; Akkaya, C.; Atak, D.; Dunn, C.D.; Kabakcioglu, A.; Ozlu, N.; Ince-Dunn, G. Terminal neuron localization to the upper cortical plate is controlled by the transcription factor NEUROD2. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerng, H.H.; Qian, Y.; Pfaffinger, P.J. Modulation of Kv4.2 channel expression and gating by dipeptidyl peptidase 10 (DPP10). Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 2380–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.W.; Herrick, T.M.; Cooper, J.A. Reelin-induced tyrosine [corrected] phosphorylation of disabled 1 during neuronal positioning. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.Y.; Riviere, P.J.; Trojnar, J.; Junien, J.-L.; Akinsanya, K.O. Cloning and characterization of dipeptidyl peptidase 10, a new member of an emerging subgroup of serine proteases. Biochem. J. 2003, 373 Pt 1, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-L.; Qu, Y.-J.; Lu, Y.C.; Bondarenko, V.E.; Wang, S.; Skerrett, I.M.; Morales, M.J. DPP10 is an inactivation modulatory protein of Kv4.3 and Kv1.4. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 291, C966–C976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Arnaud, L.; Cooper, J.A. Both the phosphoinositide and receptor binding activities of Dab1 are required for Reelin-stimulated Dab1 tyrosine phosphorylation. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 139, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolt, P.C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Bock, H.H.; Blacklow, S.C.; Herz, J. Phosphoinositide binding by the disabled-1 PTB domain is necessary for membrane localization and Reelin signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9671–9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shah, V.; Keshvara, L. The role of the PTB domain in regulation of DAB1 phosphorylation. Biochemistry 2007, 21, A241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zhao, B.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, K.; Pan, Y.; Liu, W. TPT1 promotes the adipogenic differentiation of stromal vascular fractions via the PI3K/AKT pathway and FOXO1 in sheep. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2023, 51, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, H.H.; Jossin, Y.; Liu, P.; Förster, E.; May, P.; Goffinet, A.M.; Herz, J. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase interacts with the adaptor protein Dab1 in response to Reelin signaling and is required for normal cortical lamination. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38772–38779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Wei, D.; Tang, L.; Wang, S.; Pan, C.; Ma, Y.; Ma, Y. SGK1 Affects the Phosphorylation of FOXO1/FOXO3 Promoting Bovine Fat Deposition via the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolt, P.C.; Jeon, H.; Song, H.K.; Herz, J.; Eck, M.J.; Blacklow, S.C. Origins of peptide selectivity and phosphoinositide binding revealed by structures of disabled-1 PTB domain complexes. Structure 2003, 11, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, M.; Xia, W.; Xu, Y.; Mao, Q.; Wang, J.; Dong, G.; Xu, L.; Yang, X.; Yin, R. Glypican-5 suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of the lung adenocarcinoma by competitively binding to Wnt3a. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 79736–79746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, N.; Wu, L.; Hu, Z.; Xu, B.; Cai, T.; et al. GPC5, a novel epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor, inhibits tumor growth by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6120–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, G.; Xu, X.; Geng, R.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y. Transcriptome profile analysis of adipose tissues from fat and short-tailed sheep. Gene 2014, 549, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Bakhtiarizadeh, M.R.; Salehi, A. Meta-analysis of RNA-Seq datasets highlights novel genes/pathways involved in fat deposition in fat-tail of sheep. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1159921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, L.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Hu, P.; Zhang, X.; et al. Perilipin 5 improves hepatic lipotoxicity by inhibiting lipolysis. Hepatology 2015, 61, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Bell, M.; Sreenevasan, U.; Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Dalen, K.; Londos, C.; Yamaguchi, T.; Rizzo, M.A.; Coleman, R.; et al. Unique regulation of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) by perilipin 5, a lipid droplet-associated protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 15707–15715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Chen, A. Perilipin 5 restores the formation of lipid droplets in activated hepatic stellate cells and inhibits their activation. Lab. Investig. 2016, 96, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, W.; Willis-Owen, S.A.; Jiang, L.; Ma, Y.; Tian, X.; Moffatt, M.; Cookson, W.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y. Polymorphisms of PHF11 and DPP10 are associated with asthma and related traits in a Chinese population. Respiration 2010, 79, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | Abbreviation | Size | Type | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lanzhou fat-tailed sheep | LLS | 15 | blood |  |
| Hu sheep | HS | 15 | blood |  |
| Chromosomes | N_Variants | Bin_Start | Bin_End | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| chr1 | 234 | 99950001 | 99970000 | LOC101114737 |
| chr3 | 337 | 119610001 | 119630000 | |
| chr3 | 153 | 119650001 | 119670000 | |
| chr3 | 128 | 119660001 | 119680000 | |
| chr3 | 248 | 119670001 | 119690000 | |
| chr3 | 212 | 154030001 | 154050000 | |
| chr3 | 206 | 213100001 | 213120000 | |
| chr3 | 206 | 213110001 | 213130000 | |
| chr4 | 195 | 160001 | 180000 | |
| chr4 | 121 | 170001 | 190000 | |
| chr4 | 84 | 180001 | 200000 | |
| chr4 | 63 | 190001 | 210000 | |
| chr4 | 42 | 200001 | 220000 | |
| chr10 | 323 | 38570001 | 38590000 | |
| chr10 | 355 | 38580001 | 38600000 | |
| chr10 | 334 | 38590001 | 38610000 | |
| chr10 | 290 | 38600001 | 38620000 | |
| chr10 | 328 | 38610001 | 38630000 | |
| chr10 | 398 | 38620001 | 38640000 | |
| chr18 | 149 | 66460001 | 66480000 | TRNAE-UUC-84, LOC101104530 |
| chr18 | 212 | 66470001 | 66490000 | LOC105603275, LOC105603310 |
| chr18 | 241 | 66480001 | 66500000 | LOC105603275, LOC105603310, LOC106990142 |
| chr18 | 188 | 66490001 | 66510000 | LOC105603275, LOC106990142 |
| chr19 | 242 | 31750001 | 31770000 | MITF |
| chr22 | 1 | 50780001 | 50800000 | |
| chr24 | 324 | 35120001 | 35140000 | COL26A1 |
| chr24 | 225 | 35130001 | 35150000 | COL26A1 |
| chrX | 145 | 43220001 | 43240000 | ZNF674 |
| chrX | 147 | 60010001 | 60030000 | TEX11 |
| chrX | 152 | 79200001 | 79220000 | FATE1, CNGA2 |
| Chromosomes | Start | Stop | XP-CLR | Chromosomes | Start | Stop | XP-CLR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 205504001 | 205506000 | 21.286 | 12 | 595001 | 597000 | 14.876 |
| 1 | 1205503001 | 205505000 | 12.206 | 12 | 65394001 | 65396000 | 11.191 |
| 1 | 59281001 | 59283000 | 11.906 | 12 | 594001 | 596000 | 10.862 |
| 1 | 3687001 | 3689000 | 11.216 | 12 | 74271001 | 74273000 | 10.209 |
| 2 | 179123001 | 179125000 | 18.095 | 13 | 29303001 | 29305000 | 19.179 |
| 2 | 82793001 | 82795000 | 13.294 | 13 | 7107001 | 7109000 | 12.393 |
| 3 | 200422001 | 200424000 | 15.017 | 16 | 38115001 | 38117000 | 10.056 |
| 3 | 217141001 | 217143000 | 10.660 | 18 | 3797001 | 3799000 | 19.272 |
| 6 | 67238001 | 67240000 | 24.500 | 18 | 4993001 | 4995000 | 17.599 |
| 6 | 110111001 | 110113000 | 18.562 | 18 | 3556001 | 3558000 | 11.217 |
| 6 | 40289001 | 40291000 | 17.723 | 18 | 55897001 | 55899000 | 11.204 |
| 6 | 27372001 | 27374000 | 15.127 | 20 | 47588001 | 47590000 | 16.284 |
| 6 | 25664001 | 25666000 | 10.685 | 21 | 6528001 | 6530000 | 12.379 |
| 6 | 113967001 | 113969000 | 10.321 | 22 | 23001001 | 23003000 | 14.462 |
| 7 | 2631001 | 2633000 | 16.668 | 22 | 23005001 | 23007000 | 12.506 |
| 7 | 4248001 | 4250000 | 16.384 | 23 | 24097001 | 24099000 | 11.478 |
| 7 | 41107001 | 41109000 | 12.502 | 25 | 8859001 | 8861000 | 11.271 |
| 8 | 46959001 | 46961000 | 12.301 | 26 | 8807001 | 8809000 | 12.374 |
| 10 | 7466001 | 7468000 | 14.839 | 26 | 21757001 | 21759000 | 11.324 |
| 10 | 57489001 | 57491000 | 10.097 | X | 76736001 | 76738000 | 21.189 |
| 11 | 15145001 | 15147000 | 11.448 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, P.; Cai, Y.; Xu, H.; Cao, X.; Li, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhang, D.; et al. Whole-Genome Resequencing Identifies Candidate Genes for Tail Fat Deposition in Sheep. Animals 2025, 15, 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203046
Zhang X, Li Y, Zhao Y, Guo P, Cai Y, Xu H, Cao X, Li Q, Ma X, Zhang D, et al. Whole-Genome Resequencing Identifies Candidate Genes for Tail Fat Deposition in Sheep. Animals. 2025; 15(20):3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203046
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaowen, Yufei Li, Yongqing Zhao, Penghui Guo, Yong Cai, Hongwei Xu, Xin Cao, Qiongyi Li, Xiaoxia Ma, Derong Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Whole-Genome Resequencing Identifies Candidate Genes for Tail Fat Deposition in Sheep" Animals 15, no. 20: 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203046
APA StyleZhang, X., Li, Y., Zhao, Y., Guo, P., Cai, Y., Xu, H., Cao, X., Li, Q., Ma, X., Zhang, D., & Bai, J. (2025). Whole-Genome Resequencing Identifies Candidate Genes for Tail Fat Deposition in Sheep. Animals, 15(20), 3046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15203046





