Analysis of the Biochemical Effect of Enrofloxacin on American Shad (Alosa sapidissima) Infected with Aeromonas hydrophila
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup and Sampling
2.2. Hepatic Histopathological Alterations, ENR Determination in Muscle, Hepatic Enzymatic Activities
2.3. RNA-Seq
2.4. Metabolome and Combined Analysis
2.5. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
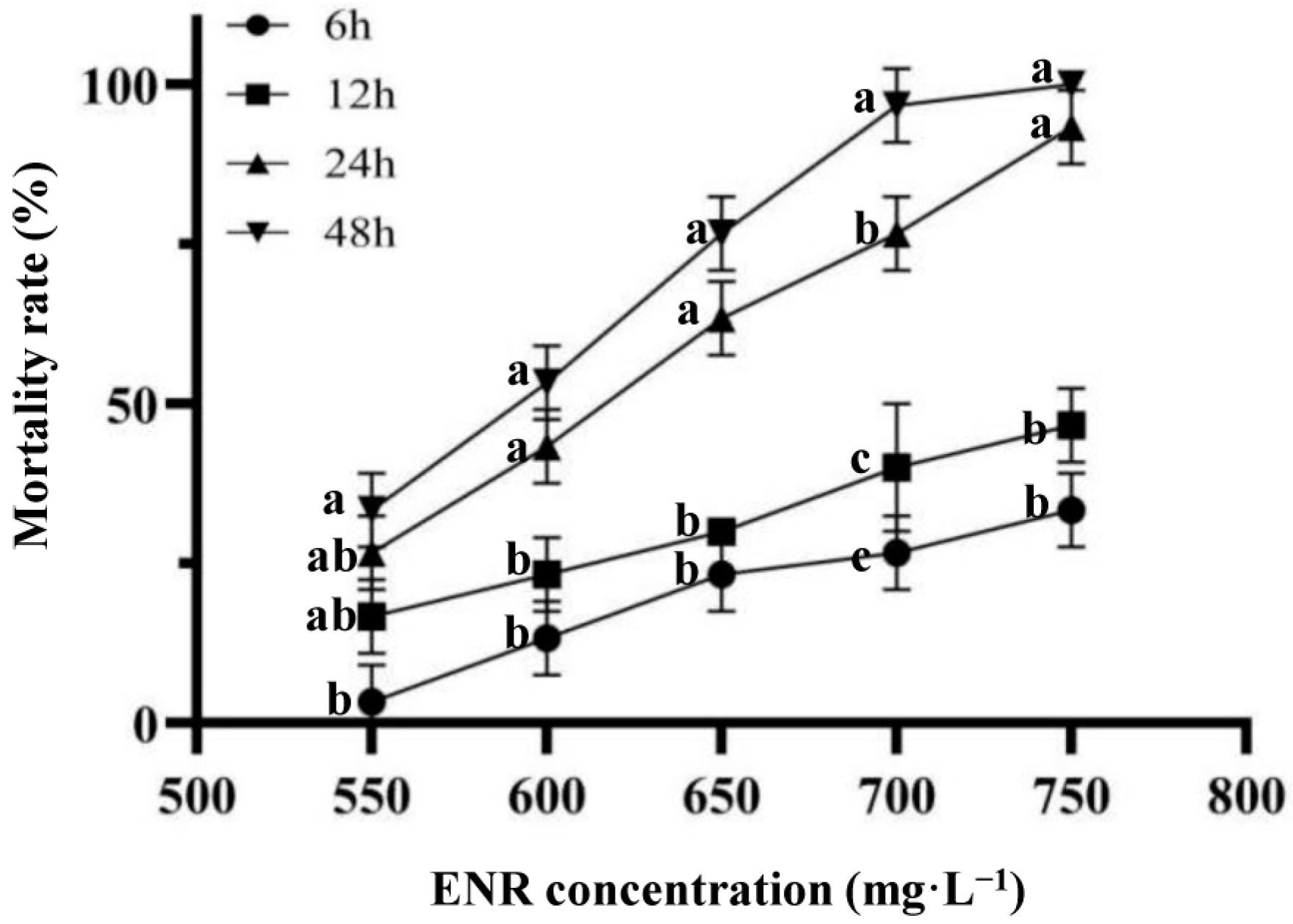
3.1. LC50 for ENR on Juvenile American Shad
3.2. Histopathological Alterations Induced by A. hydrophila and Normal and Excessive Concentrations of the Therapeutic Drug ENR
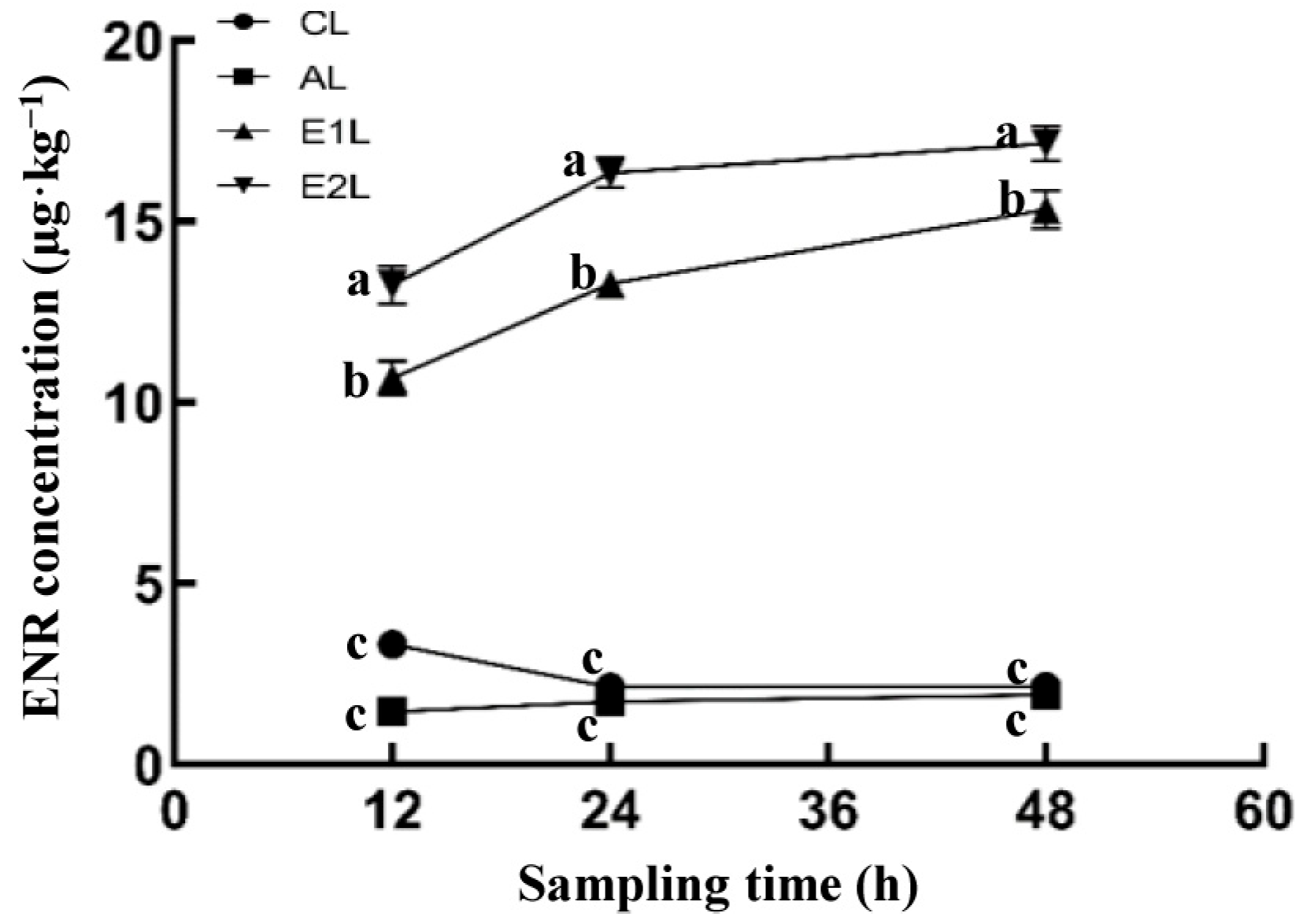
3.3. ENR Residues in Shad Muscle at 12~48 h
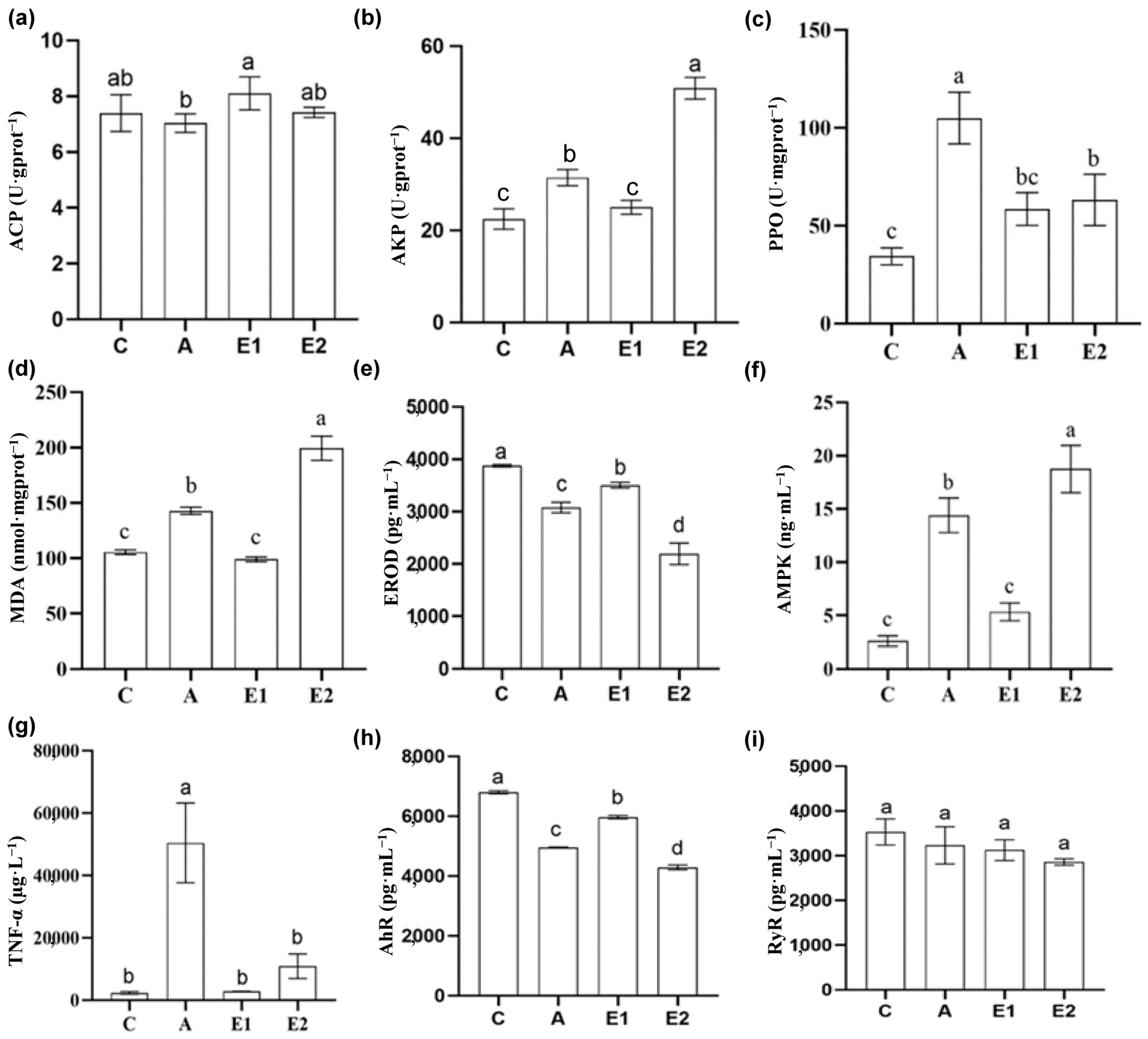
3.4. Hepatic Enzymatic Activities at 48 h
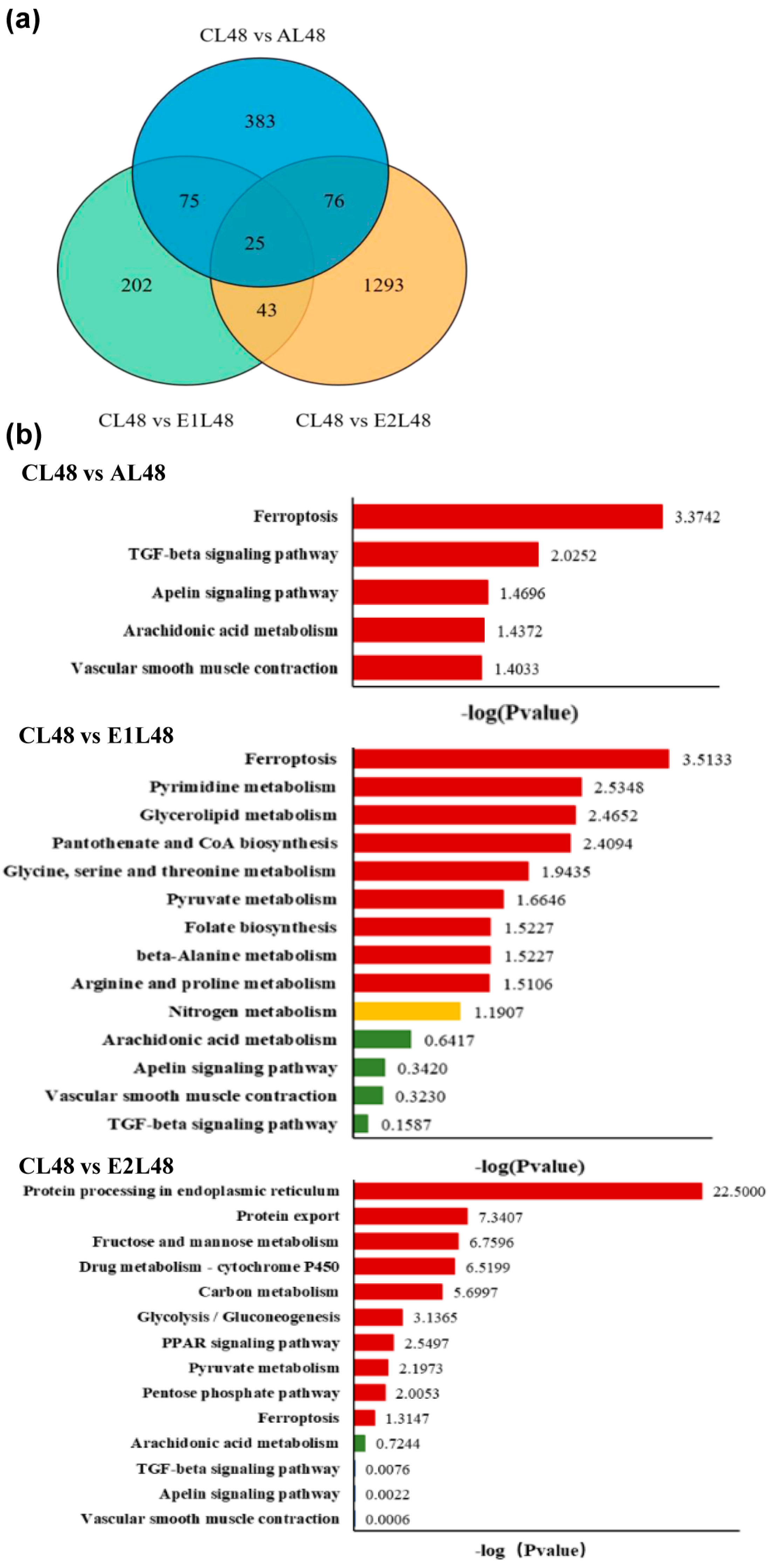
3.5. RNA-Seq After ENR Exposure
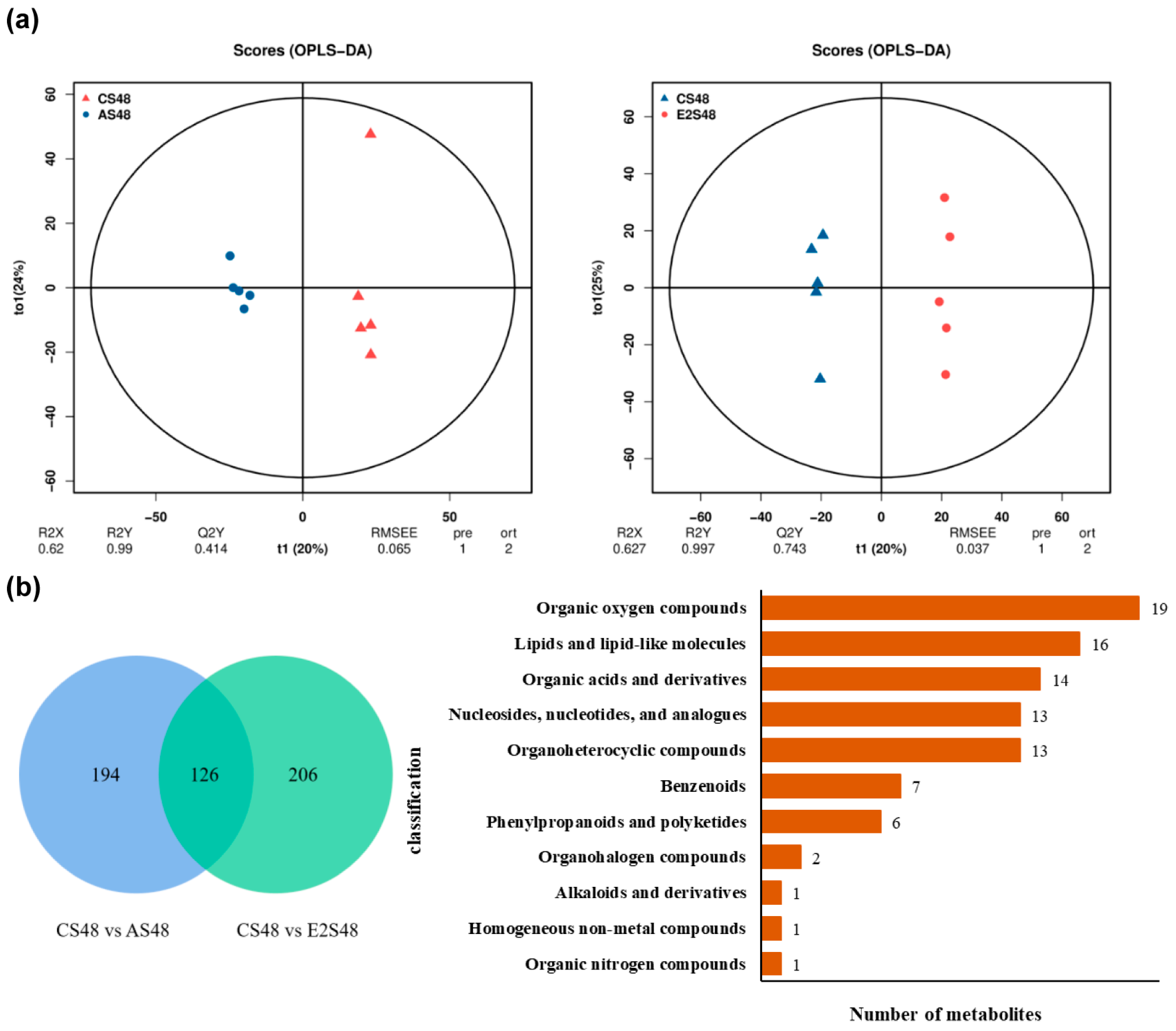
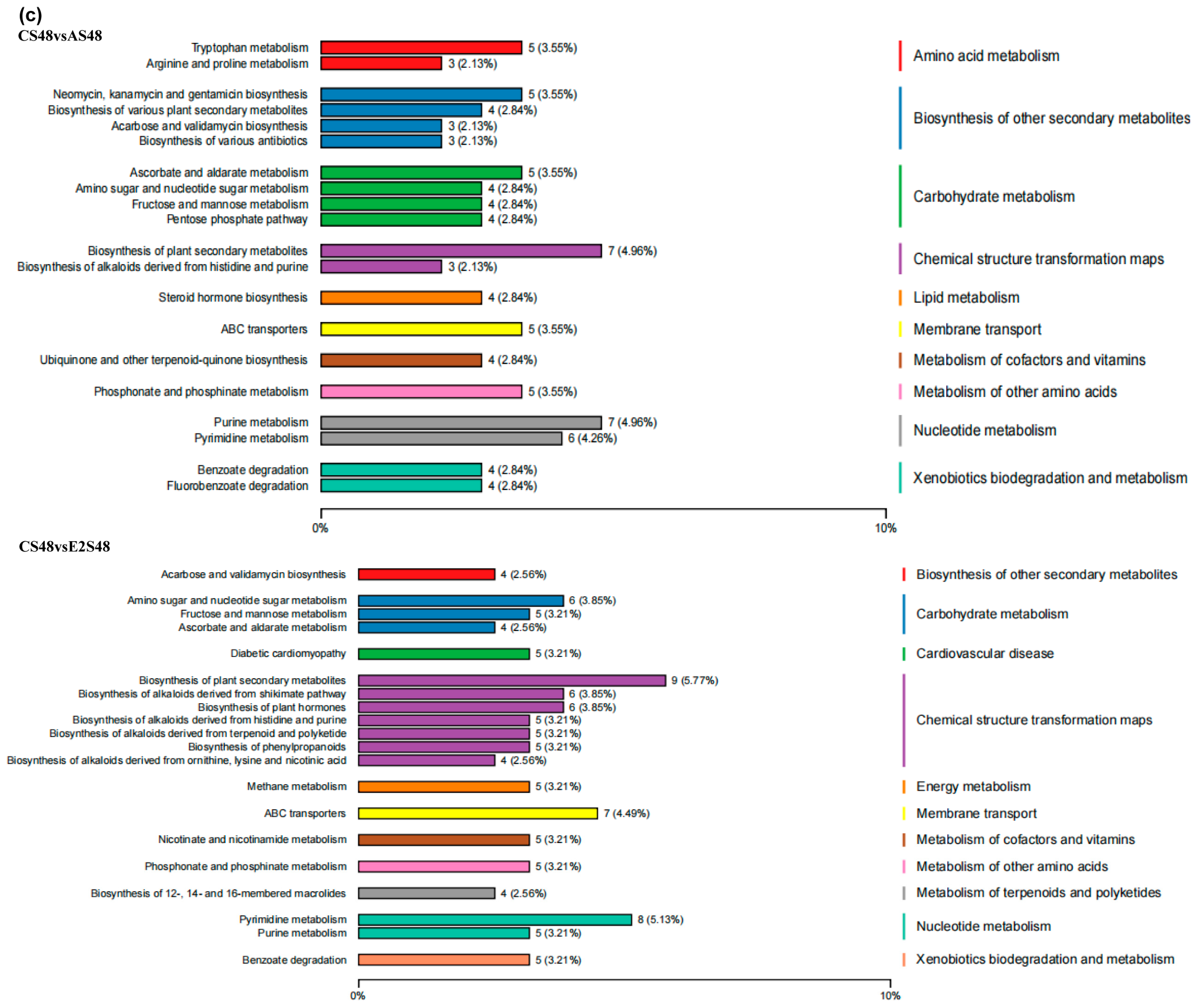
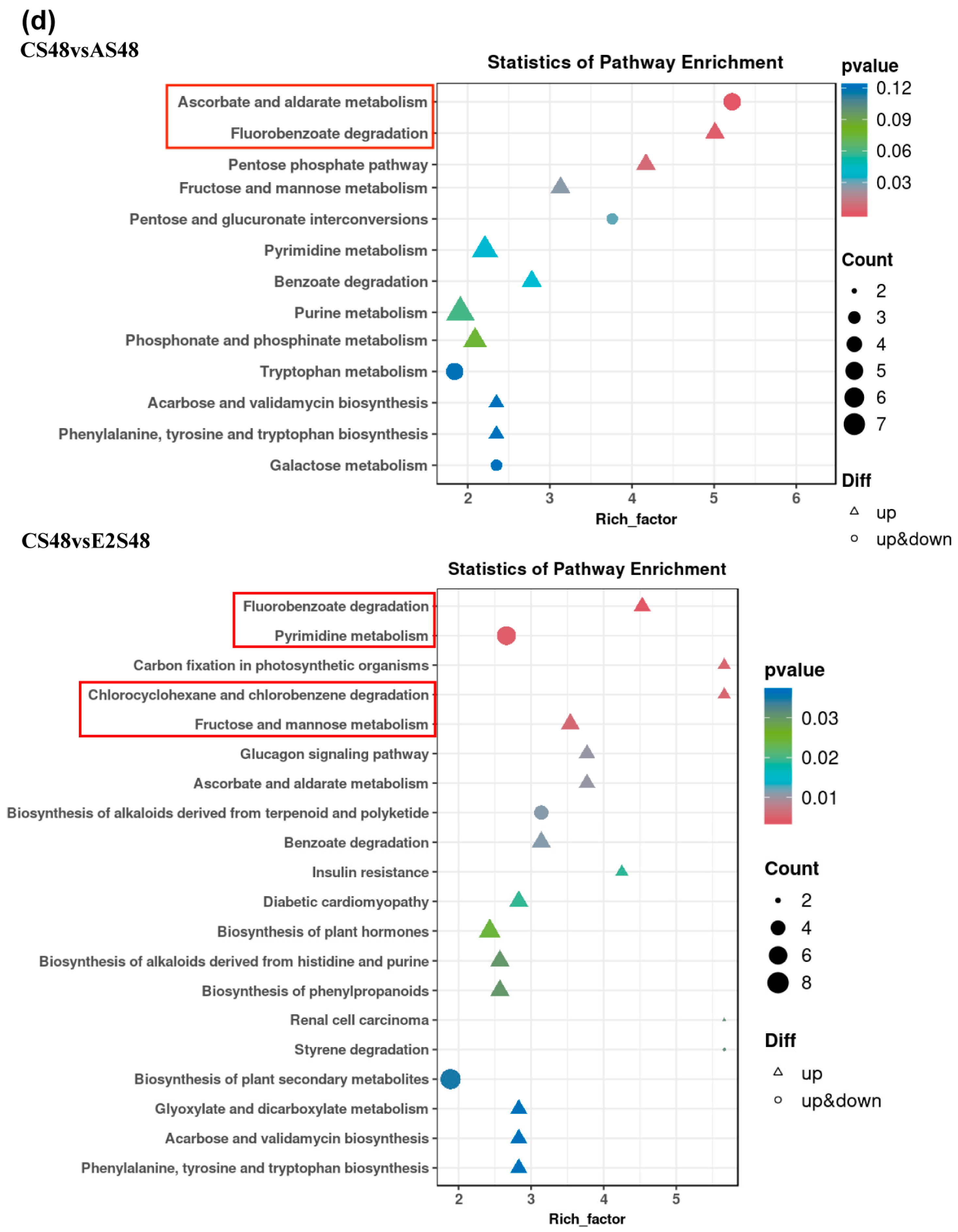
3.6. Metabolome
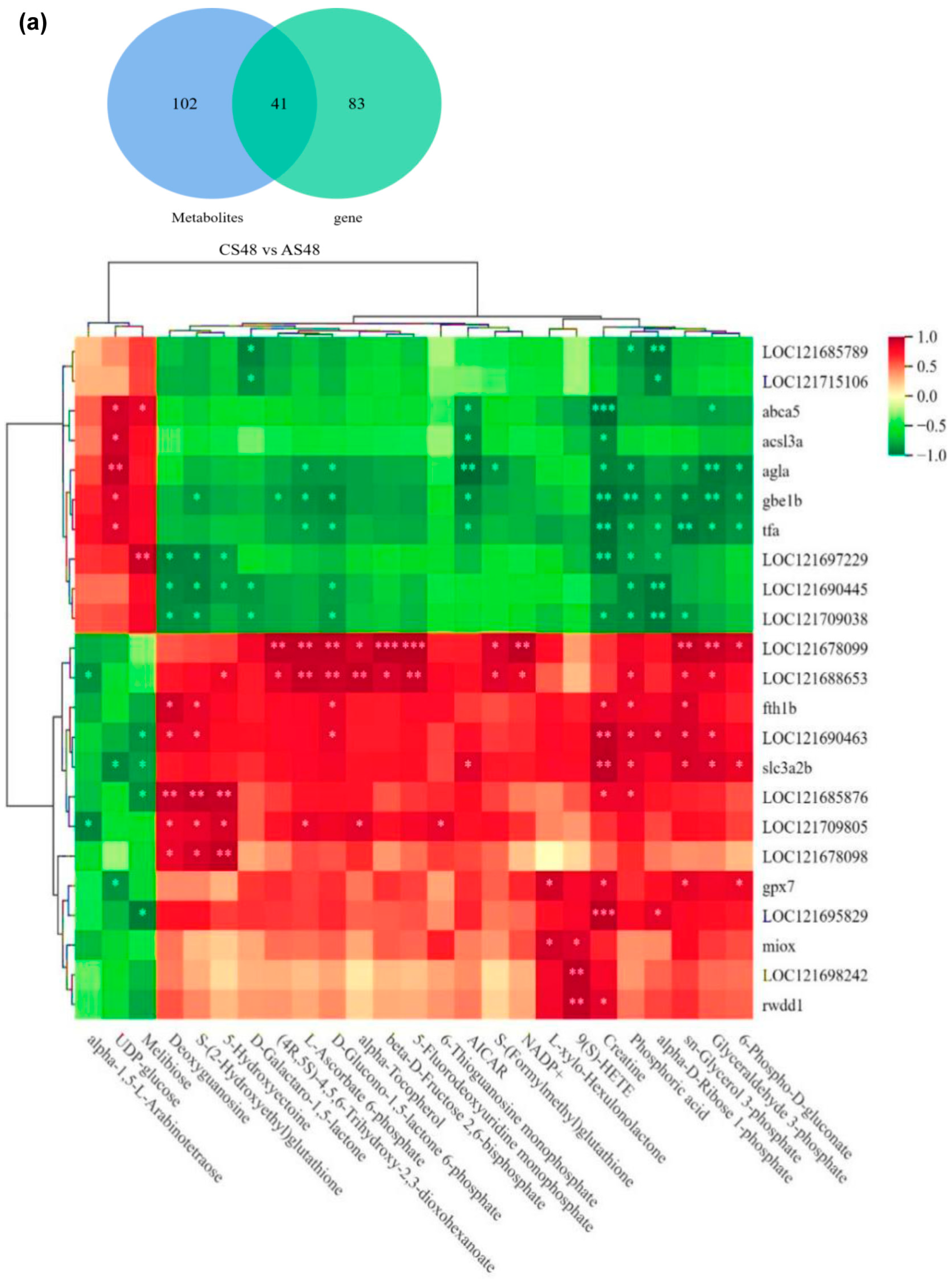
3.7. The Combined Analysis Under ENR Exposure
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental Antibiotics in American Shad Culture
4.2. Mode of Action After ENR Exposure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Gene Names | Primers | Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | F: GACAAGTACAGTTGTGCGCC R: TGGCCCATACCAACCATCAC | 194 |
| loc121678099 | F: GGATTGGGCAAGAGAAGCCT R: GTACTCAAAGCGGTCCCCAA | 165 |
| loc121684913 | F: AGAGCACCTGAAACGAAGGG R: ATGCTGCTCGACAAAGTGGA | 201 |
| loc121698291 | F: TCTGGCAGATTGTGAACGCT R: GTTTTGGGCCCTCATAGGCT | 225 |
| loc121699800 | F: AAGTCTGTGGTTGCGGGTAG R: AGCACCGCAATGTCAGAAGA | 263 |
| loc121700164 | F: ACGCCGTCAAATAGCCAAGA R: CTTGCACTTGAGAGGGGGAG | 243 |
| loc121707498 | F: GGCACGTCTTCACAGGGTAA R: GTTCTGTGTGCTGCACCTTG | 160 |
| loc121709038 | F: GCACATACGCTGGGGTTTTC R: GCACGTTGTTGAATCCCTCG | 206 |
| loc121709129 | F: GTCAACGGGTTCGGTGTTTG R: GTCGGGGTCCACCATTTCAT | 247 |
| chka | F: AGCCTTGGAGATGAACCACG R: GCCACTTTGGCTCCTTGTTG | 286 |
| dnajb6b | F: AGCGACATAGGCTGCATACC R: TCACCAGAAACCCCGCTTAC | 250 |
| dnajc3a | F: TAAAGGCCACCTCCAAGCTG R: TGAGGCACGTTTGGTTCAGT | 277 |
| efr3ba | F: AGGGCAGTCGCATGATTCAA R: TCCTGACGGGAGCATTTGTC | 277 |
| igfbp1a | F: CGGTGGATCCCAGTTGTGAA R: AGCATTGGTGTTTTCGGTGC | 203 |
| klf10 | F: TTCCATCCCTCGCCTTGTTC R: CAGTGTCCACGCTTGTTGTG | 217 |
| nfil3-5 | F: CGCATCATCAGCAAGTGAGC R: CCGTCACTGGAGGAAGTGTC | 250 |
| sept4b | F: AGTCGAGAGAGTGCCGTTTG R: CAGATTTGCGATGCACCTGG | 291 |
| sfxn1 | F: ACCAATAAGCTCCCTTGGGC R: ATCTGTCGGGCCTTTTCCAG | 230 |
| si_dkey-34d22.1 | F: CAAGCGCTGACATCATCACG R: AGGCTCACAGAAGCAGCAAT | 271 |
| slc10a4 | F: TTGGAGCGTAACAGGGACAC R: TGCTTGTGAGCAGAATCGGT | 219 |
| slc3a2b | F: GTGGACCTTCTTCTGTCGGG R: CGATCTCGTCCCCGTAGTTG | 235 |
| sptb | F: GCATGCCTTCAATGTAGCCG R: CCAACTTGCGGTTGTTCAGG | 287 |
| tfa | F: TGCGCCTTATGAAGGCAAGA R: CCTGCTTGCGCATGATCTTC | 296 |
| tgfb2 | F: AAGCTACGGTGTGTTCTGGG R: CCGACTAGGTCGCAATCTCC | 221 |
| vkorc1 | F: GCCCTACACGTCGAGCTATC R: TGCAAGATACACAGAGCCCG | 288 |
References
- Shardo, J.D. Comparative embryology of teleostean fishes. I. Development and staging of the american shad, Alosa sapidissima (Wilson, 1811). J. Morphol. 1995, 225, 125–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tang, Z.; Li, W.; Chu, Z.; Hong, X.; Zhu, X.; Xu, H. Identifying the germ cells during embryogenesis and gametogenesis by germ-line gene vasa in an anadromous fish, American shad Alosa sapidissima. J. Fish Biol. 2018, 92, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayse, S.M.; Regish, A.M.; McCormick, S.D. Survival and spawning success of American shad (Alosa sapidissima) in varying temperatures and levels of glochidia infection. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 1821–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Guan, C.; Huang, B.; Lei, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hong, L. Developmental changes in digestive enzyme activity in American shad, Alosa sapidissima, during early ontogeny. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, N.; Xi, B.; Xie, J. A study on bacterial etiology and histopathology associated with hemorrhagic disease in American shad Alosa sapidissima. Aquac. Res. 2024, 2024, 8869167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, N. A review on pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and their mitigation through medicinal herbs in aquaculture. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, Q.; Fu, L. Metabolic and transcriptional disruption of American shad (Alosa sapidissima) by enrofloxacin in commercial aquaculture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res Int. 2022, 29, 2052–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, K. Exposure to enrofloxacin affects the early development and metabolic system of juvenile American shad, as indicated by host metabolism and the environmental microbiome. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 76, ovac037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Z.; Xiong, X.; Hu, H.; Jia, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, G. Occurrence, distribution, and ecological risks of antibiotics in Honghu Lake and surrounding aquaculture ponds, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 50732–50742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, H.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z. Antibiotics in aquaculture ponds from Guilin, South of China: Occurrence, distribution, and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Shi, P.; Pan, Y.; Li, A. Occurrence, distribution and potential environmental risks of pollutants in aquaculture ponds during pond cleaning in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 939, 173610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Zeng, Z. Antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes, and bacterial community composition in fresh water aquaculture environment in China. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Yuan, X.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S. Antibiotics in marine aquaculture farms surrounding Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea: Distribution characteristics considering various culture modes and organism species. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Diao, Z.; Sun, K.; Hao, Q.; Liu, S.; Ying, G. Tissue distribution, bioaccumulation characteristics and health risk of antibiotics in cultured fish from a typical aquaculture area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, L.; Tang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Xu, M.; Zhou, Z.; Bai, H.; Zhang, M.; Ying, G. Deciphering spread of quinolone resistance in mariculture ponds: Cross-species and cross-environment transmission of resistome. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Liu, X.; Lee, S.; Kho, Y.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, P.; Choi, K. Ecological risk assessment of amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, and neomycin: Are their current levels in the freshwater environment safe? Toxics 2021, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhang, L.; Gan, J.; Peng, J.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Lu, X.; He, L.; Cheng, B. Effect of flowing water on the pharmacokinetic properties of norfloxacin in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) after single-dose oral administration. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Xu, G. Multi-omics platforms reveal the synergistic effect in tilapia intestine under microplastics and sulfamethoxazole, BDE153 acute co-exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2025, 26, 8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tang, H.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xu, G. Integrated transcriptomics and proteomics analyses reveal the ameliorative effect of hepatic damage in tilapia caused by microplastics with chlorella addition. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2024, 285, 117076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Yona, A.; Wang, X.; Xu, G. Multi-omics insights into copper sulfate toxicity in American shad (Alosa sapidissima): Impacts on oxidative stress, cytoskeletal integrity, immune regulation, and gut–metabolism balance. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2025, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, T.; Xi, B.; Chen, K.; Pan, L.; Xie, J.; Xu, P. Comparative transcriptomic and proteomic analyses reveal upregulated expression of virulence and iron transport factors of Aeromonas hydrophila under iron limitation. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, J.; Xu, F.; Xu, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, L. Ecotoxicological effects of sulfonamides and fluoroquinolones and their removal by a green alga (Chlorella vulgaris) and a cyanobacterium (Chrysosporum ovalisporum). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, Z.; Wang, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Toxicological effects of enrofloxacin and its removal by freshwater micro-green algae Dictyosphaerium sp. Huan Jing Ke Xue. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2020, 41, 2688–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrabi, M.; Alexandrino, D.A.M.; Aloulou, F.; Elleuch, B.; Liu, B.; Jia, Z.; Almeida, C.M.R.; Mucha, A.P.; Carvalho, M.F. Biodegradation of oxytetracycline and enrofloxacin by autochthonous microbial communities from estuarine sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corum, O.; Terzi, E.; Durna Corum, D.; Tastan, Y.; Gonzales, R.C.; Kenanoglu, O.N.; Arriesgado, D.M.; Navarro, V.R.; Bilen, S.; Sonmez, A.Y.; et al. Plasma and muscle tissue disposition of enrofloxacin in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) after intravascular, intraperitoneal, and oral administrations. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2022, 39, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.R.; Sergio, A.J.A.; Bate, C.S.; Koopman, N.; Roland, J.B.; Notman-Grobler, O.D.P.; Mastrodimitropoulos, P.M.B.; Piczak, M.L.; Lennox, R.J. A review of migratory Alosidae marine ecology in the northwest Atlantic. J. Fish Biol. 2025, 106, 677–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, K.K.; Lu, L.; Huang, J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Naher, H.; Baki, M.A.; Sarker, A.; et al. First report of de novo assembly and annotation from brain and blood transcriptome of an anadromous shad, Alosa sapidissima. BMC Genom. Data 2022, 23, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Shi, Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, Z. Impact of probiotics on enzyme activities, intestinal microbial remodeling, and metabolic pathways in American shad (Alosa sapidissima) at high temperatures. Mar. Biotechnol. 2025, 27, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhu, W.; Liang, Z.; Feng, B.; Xie, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Fu, J.; Miao, L.; et al. High-temperature stress response: Insights into the molecular regulation of American shad (Alosa sapidissima) using a multi-omics approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, K.; Huang, W. Structural and functional comparisons of the environmental microbiota of pond and tank environments at different locations for the commercial aquaculture of American shad. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Gao, C.; Deng, P.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Shi, Y. Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism by which probiotic alleviate the response of juvenile American shad (Alosa sapidissima) to high temperatures. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xue, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Xie, H. Transformation pathways of enrofloxacin chlorination disinfection by-products in constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Paredes, J.G.; Thompson, K.D.; Metselaar, M.; Shahin, K.; Soto, E.; Richards, R.H.; Penman, D.J.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Adams, A. A polyphasic approach for phenotypic and genetic characterization of the fastidious aquatic pathogen Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Xiong, D. Semicarbazide conferred developmental toxicity in Oryzias melastigma embryos by oxidative stress and energy metabolism disorder. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 287, 107531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Tian, S.; Guo, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, B. α-Ketoglutarate downregulates thiosulphate metabolism to enhance antibiotic killing. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 64, 107214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Lin, H.; Yuan, S.; Peng, X.; Li, H. Aspartate potentiates tobramycin against multidrug-resistant Edwardsiella tarda through enhancing proton motive force and membrane permeability. mSystems 2025, 10, e0079425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, N.; Hess, C.; Hess, M. GWAS and comparative genomics reveal candidate antibiotic resistance genes in the avian pathogen Gallibacterium anatis for six widespread antibiotics. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 290, 109995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, Y. Biotransformation of enrofloxacin-copper combined pollutant in aqueous environments by fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides (CGMCC 40504). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, H.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Hu, B.; Lu, L.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Hu, W. Characteristics of tylosin and enrofloxacin degradation in swine manure digested by black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lv, P.; Yang, J.; Xu, G. Characterization and adsorption capacity of modified biochar for sulfamethylimidine and methylene blue in water. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 29966–29978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, H.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, G. Endocytosis, endoplasmic reticulum, actin cytoskeleton affected in tilapia liver under microplastics and BDE153 co-exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 289, 110117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Jin, W.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xu, G. Apoptosis, MAPK signaling pathway affected in tilapia liver following microplastics and sulfamethoxazole co-exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2025, 53, 101370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

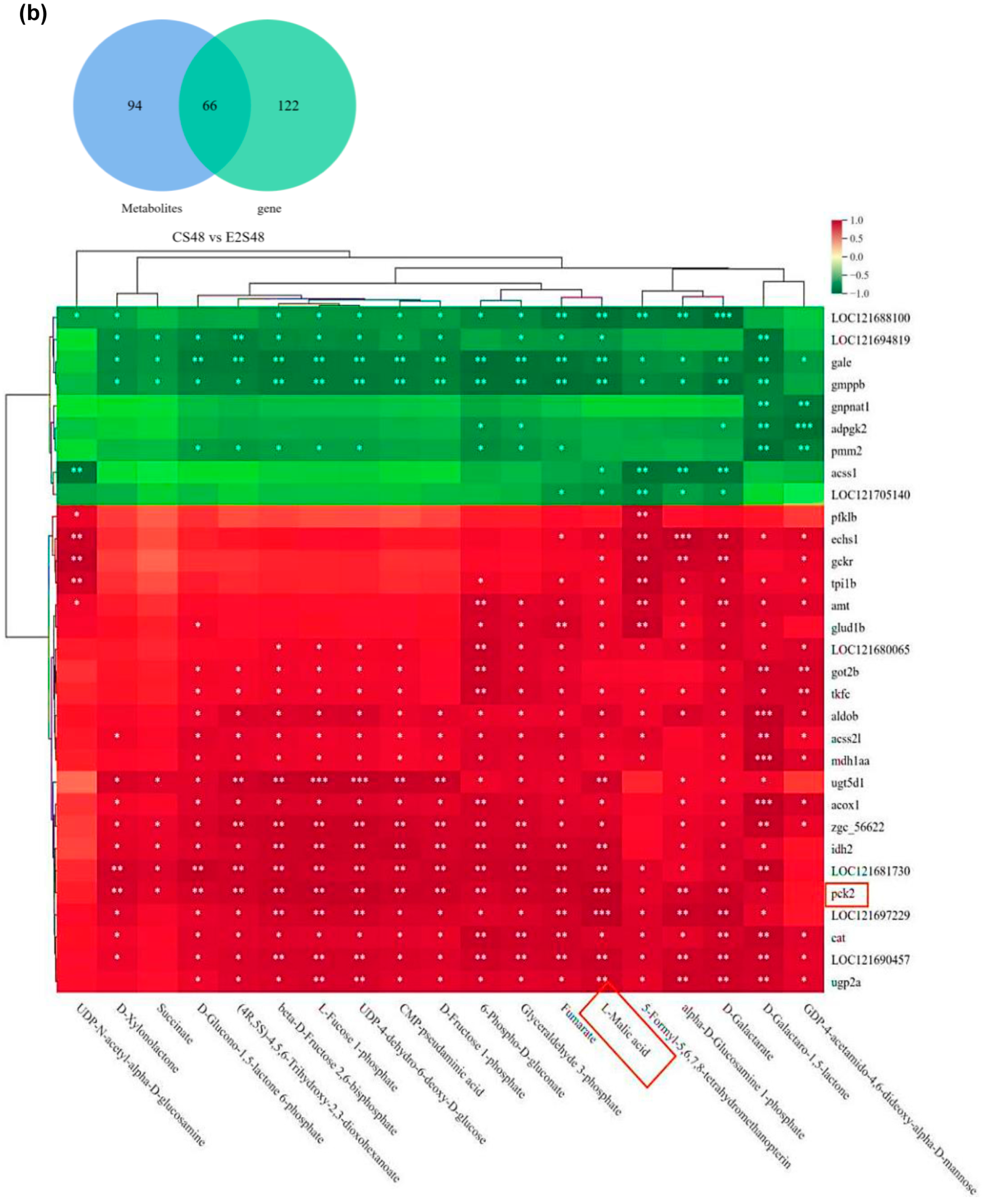
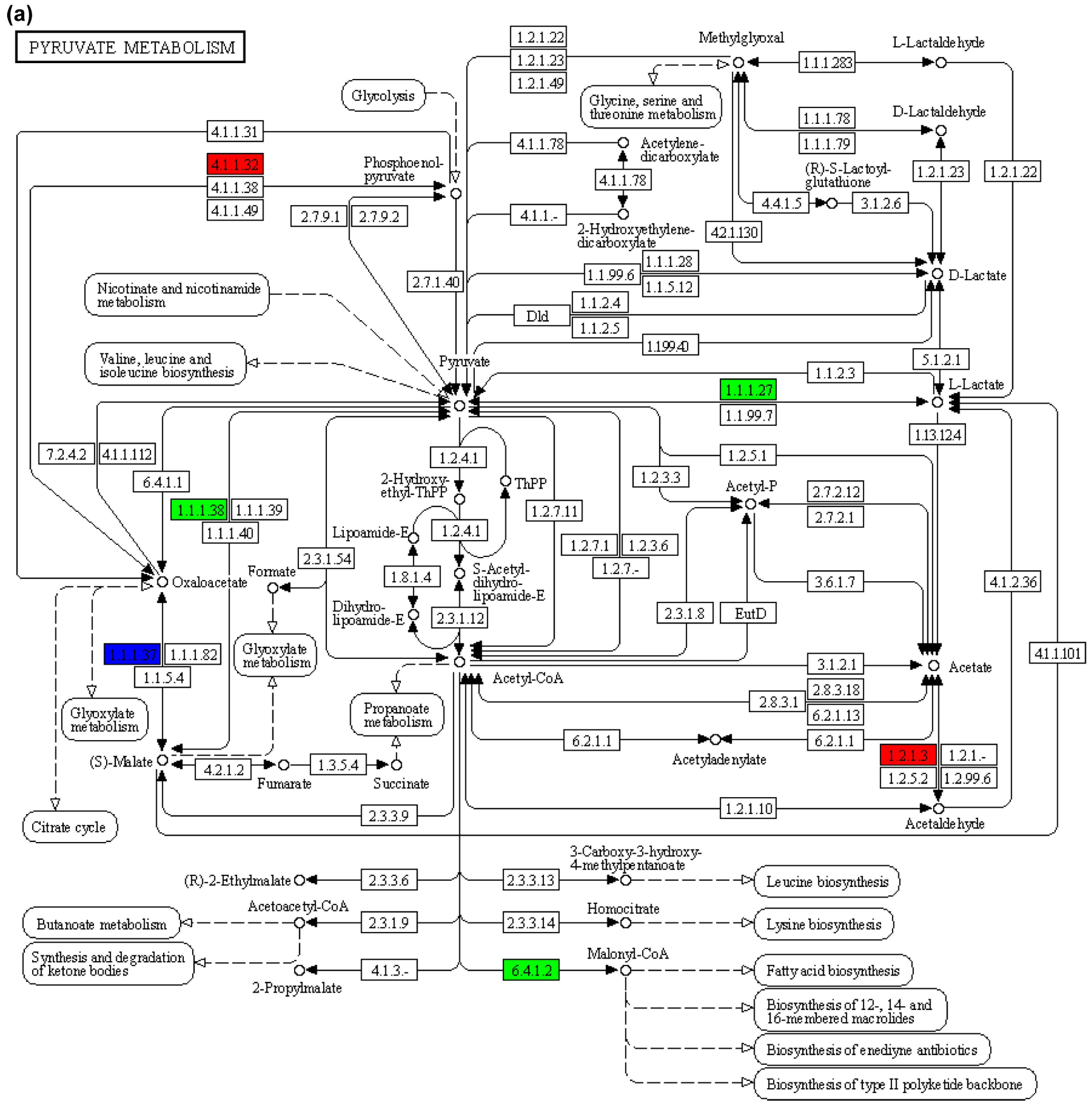

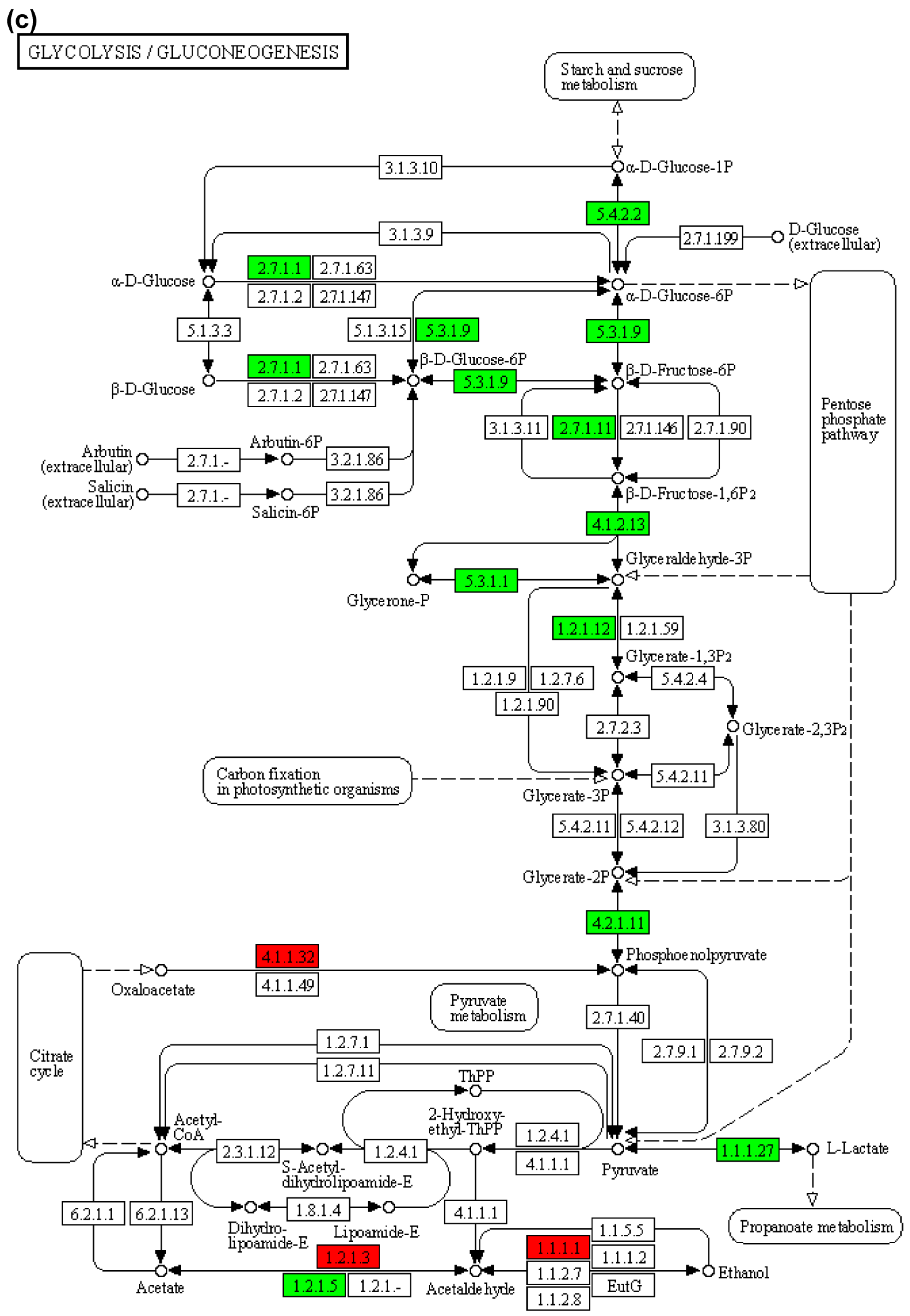
| Name | CL48 vs. AL48 | CL48 vs. E1L48 | CL48 vs. E2L48 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log2FC | p Value | qPCR | Log2FC | p Value | qPCR | Log2FC | p Value | qPCR | |
| loc121678099 | 3.14 | 1.91 × 10−7 | 2.78 | 3.01 | 2.67 × 10−5 | 3.16 | 2.34 | 0.0002 | 2.55 |
| loc121684913 | −1.20 | 0.0041 | −1.14 | −1.19 | 0.0038 | −1.28 | 1.25 | 0.0006 | 1.17 |
| loc121698291 | −1.54 | 8.78 × 10−5 | −1.36 | −3.86 | 7.08 × 10−16 | −4.05 | −1.88 | 0.0002 | −2.02 |
| loc121699800 | −3.04 | 2.49 × 10−5 | −2.96 | −2.14 | 0.0061 | −2.29 | −2.79 | 4.92 × 10−6 | −3.05 |
| loc121700164 | 1.45 | 0.0029 | 1.33 | 2.74 | 0.0023 | 2.86 | −1.34 | 0.0001 | −1.36 |
| loc121707498 | −1.51 | 8.76 × 10−7 | −1.53 | −1.08 | 0.0088 | −1.09 | −3.80 | 2.99 × 10−28 | −3.94 |
| loc121709038 | −2.18 | 4.66 × 10−6 | −2.34 | −1.34 | 0.0001 | −1.47 | −1.49 | 0.0033 | −1.52 |
| loc121709129 | −0.74 | 0.0039 | −0.86 | −0.70 | 0.0017 | −0.82 | −0.59 | 0.0089 | −0.63 |
| chka | 1.10 | 8.60 × 10−5 | 1.21 | 1.21 | 0.0068 | 1.30 | −0.83 | 0.0040 | −0.92 |
| dnajb6b | −0.83 | 0.0008 | −0.96 | −0.90 | 0.0005 | −0.92 | −0.77 | 0.0081 | −0.82 |
| dnajc3a | −0.83 | 0.0055 | −0.78 | −0.83 | 0.0091 | −0.84 | −2.00 | 1.36 × 10−13 | −2.31 |
| efr3ba | −1.24 | 0.0008 | −1.34 | −0.98 | 0.0053 | −1.03 | −0.90 | 0.0065 | −1.06 |
| igfbp1a | 1.99 | 0.0007 | 2.01 | 2.35 | 0.0049 | 2.34 | −2.04 | 4.91 × 10−5 | −2.37 |
| klf10 | 1.55 | 0.0028 | 1.62 | 2.47 | 0.0035 | 2.58 | −2.06 | 6.08 × 10−7 | −2.18 |
| nfil3-5 | −1.46 | 0.0001 | −1.54 | −0.89 | 0.0016 | −0.94 | −0.84 | 0.0037 | −0.92 |
| sept4b | 1.56 | 0.0003 | 1.63 | 1.19 | 0.0001 | 1.23 | 1.70 | 1.05 × 10−8 | 1.77 |
| sfxn1 | −0.84 | 0.0010 | −0.88 | −1.19 | 0.0073 | −1.17 | −0.66 | 0.0052 | −0.67 |
| si_dkey-34d22.1 | 1.36 | 0.0007 | 1.34 | 1.63 | 0.0060 | 1.72 | −1.04 | 0.0012 | −1.19 |
| slc10a4 | 1.60 | 0.0006 | 1.62 | 2.22 | 0.0059 | 2.27 | −1.60 | 0.0035 | −1.74 |
| slc3a2b | 1.00 | 4.67 × 10−6 | 1.17 | 1.16 | 0.0005 | 1.25 | −1.15 | 5.99 × 10−5 | −1.23 |
| sptb | −1.01 | 0.0001 | −1.09 | −1.09 | 0.0048 | −1.18 | 0.66 | 0.0074 | 0.67 |
| tfa | −0.79 | 0.0004 | −0.84 | −0.74 | 0.0092 | −0.86 | −0.73 | 4.60 × 10−5 | −0.82 |
| tgfb2 | −1.38 | 1.06 × 10−5 | −1.34 | −1.14 | 3.08 × 10−5 | −1.27 | −1.45 | 9.88 × 10−6 | −1.55 |
| vkorc1 | −0.74 | 0.0064 | −0.82 | −1.10 | 0.0021 | −1.16 | −1.31 | 1.62 × 10−6 | −1.39 |
| KEGG Pathway | Gene Number | Metabolite Number | Ko ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fructose and mannose metabolism | 16 | 5 | ko00051 |
| Carbon metabolism | 31 | 7 | ko01200 |
| Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 10 | 4 | ko00053 |
| Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | 11 | 4 | ko00630 |
| Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 13 | 3 | ko00040 |
| Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) | 10 | 3 | ko00020 |
| Pyruvate metabolism | 11 | 3 | ko00620 |
| Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 17 | 6 | ko00520 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Xi, B.; Yuan, J.; Xu, G. Analysis of the Biochemical Effect of Enrofloxacin on American Shad (Alosa sapidissima) Infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Animals 2025, 15, 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202962
Zheng Y, Li J, Wang X, Chen K, Xi B, Yuan J, Xu G. Analysis of the Biochemical Effect of Enrofloxacin on American Shad (Alosa sapidissima) Infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Animals. 2025; 15(20):2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202962
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yao, Jiajia Li, Xiaofei Wang, Kai Chen, Bingwen Xi, Julin Yuan, and Gangchun Xu. 2025. "Analysis of the Biochemical Effect of Enrofloxacin on American Shad (Alosa sapidissima) Infected with Aeromonas hydrophila" Animals 15, no. 20: 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202962
APA StyleZheng, Y., Li, J., Wang, X., Chen, K., Xi, B., Yuan, J., & Xu, G. (2025). Analysis of the Biochemical Effect of Enrofloxacin on American Shad (Alosa sapidissima) Infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Animals, 15(20), 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15202962





