Microbiota–Metabolite–Host Crosstalk Mediates the Impact of Dietary Energy Levels on Colonic Homeostasis in High-Altitude Ruminants
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiment
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.4. Colon Immune Index Determination
2.5. Total RNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.6. Microbial DNA Extraction
2.7. PCR Amplification and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.8. Untargeted Metabolomics and Targeted Short-Chain Fatty Acid Profiling
2.9. Validation of Differentially Expressed Genes Using qPCR Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
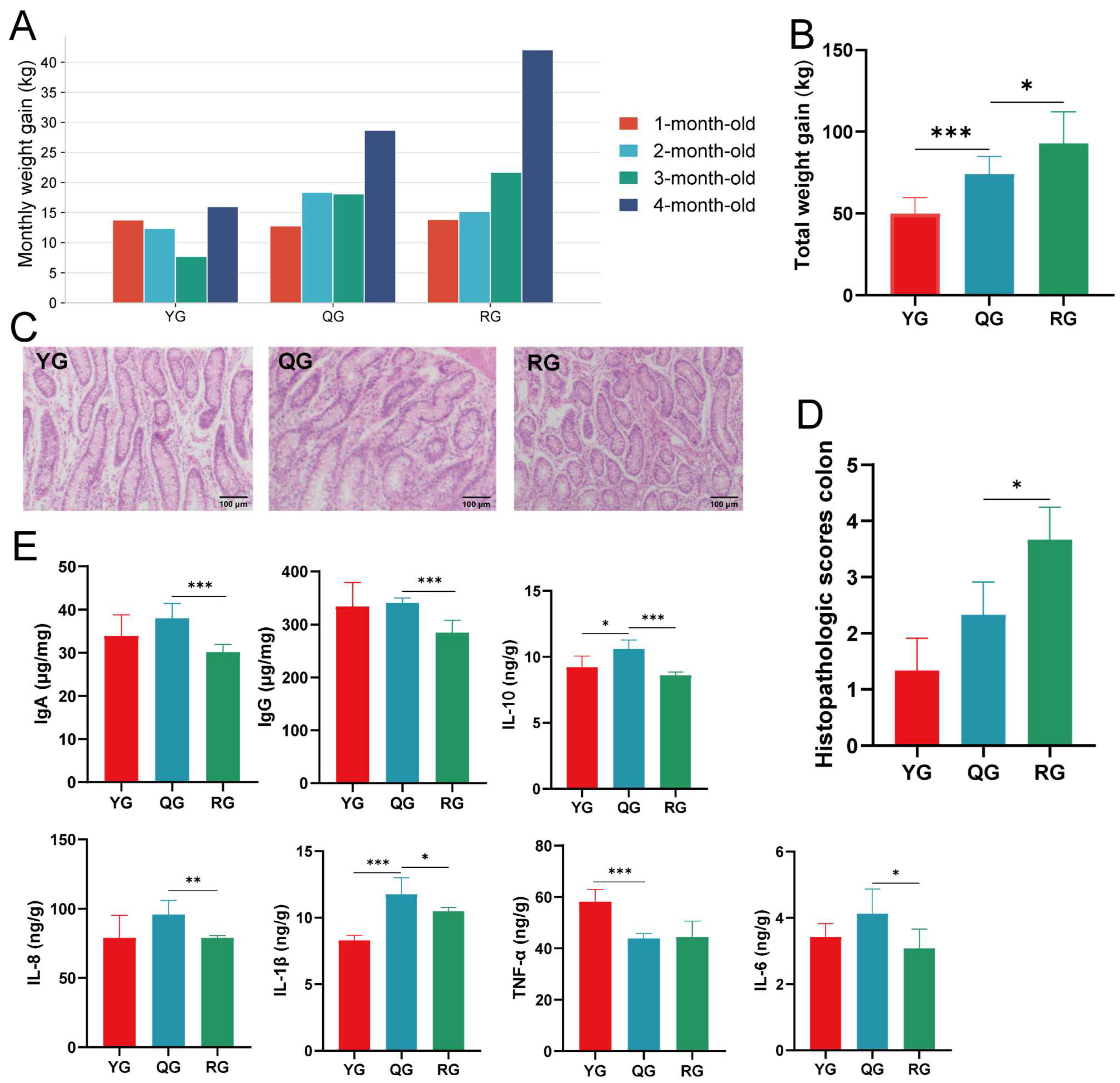
3.1. Growth Performance, Colonic Pathology, and Immune Responses
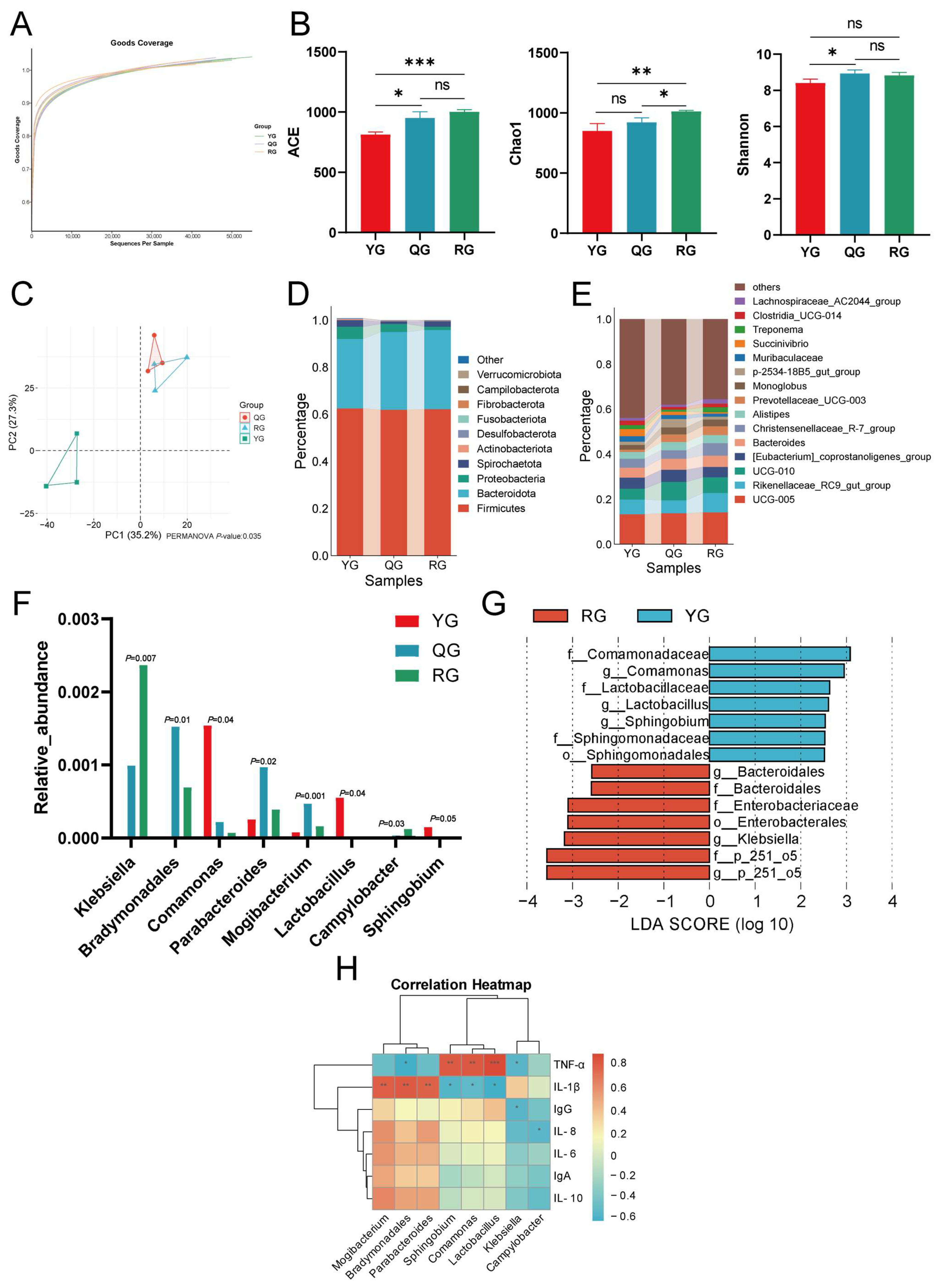
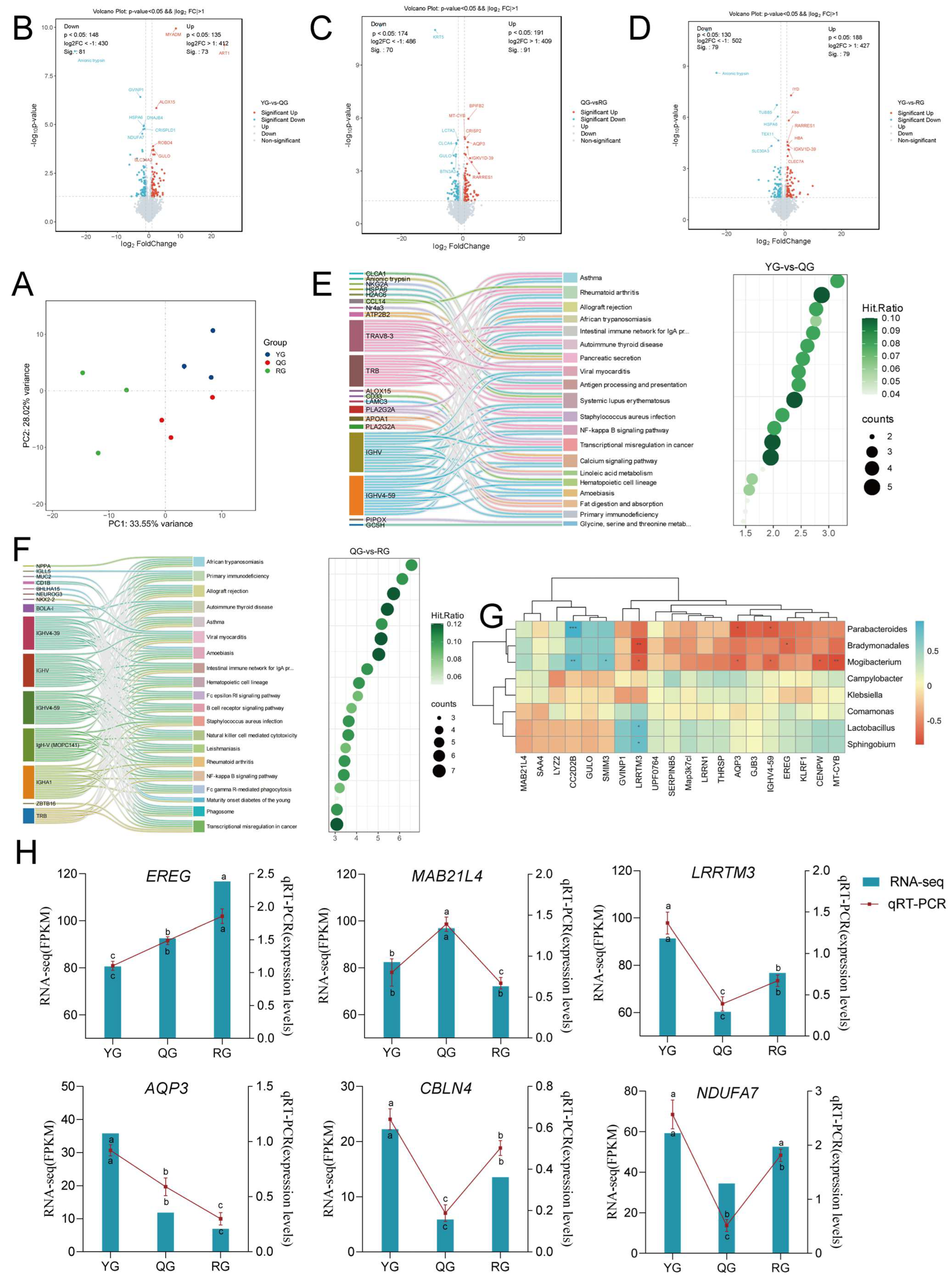
3.2. 16S rRNA Analysis Revealed That Energy Levels Alter the Colonic Microbiome
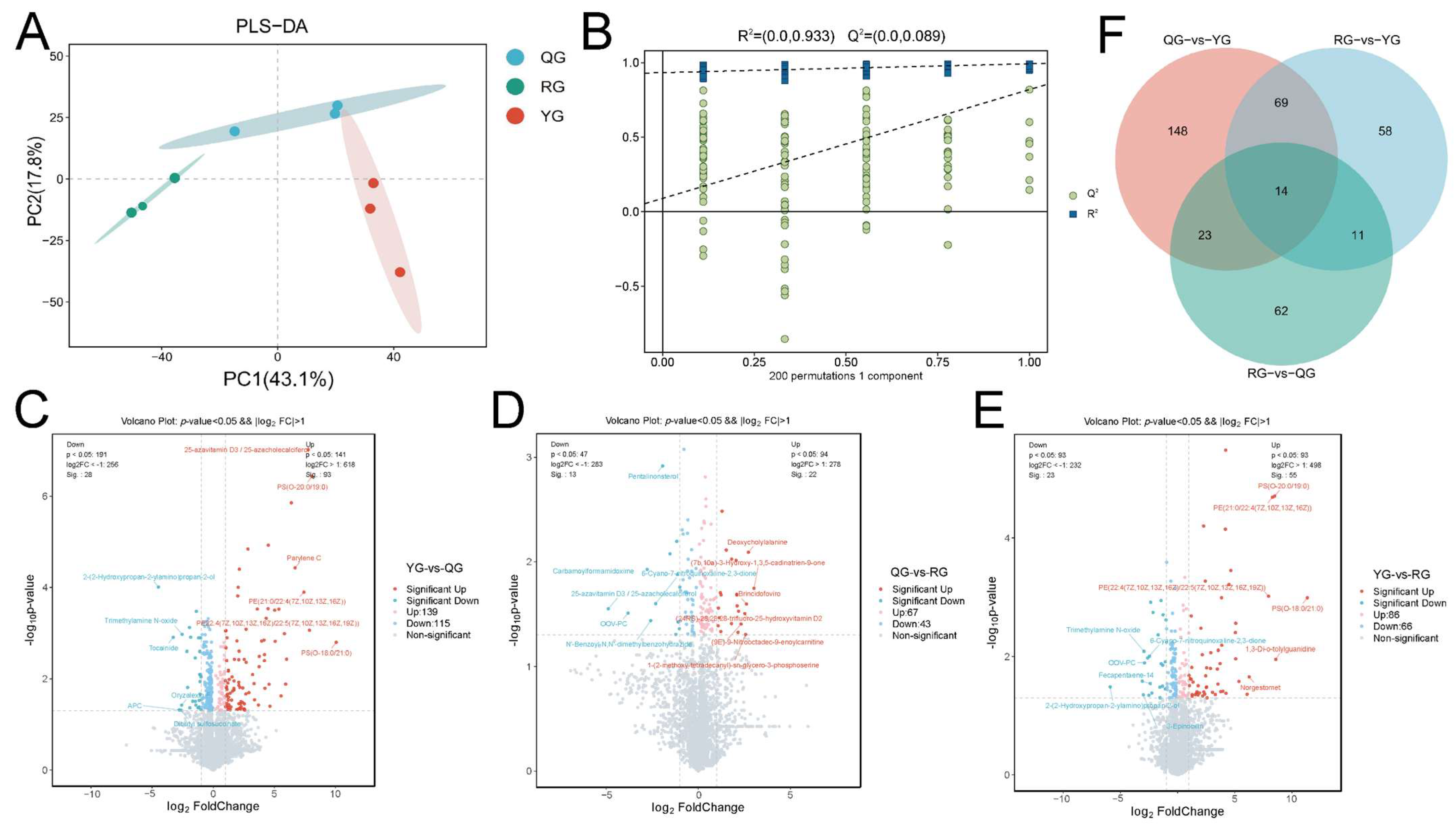
3.3. Responses of Serum Metabolic Profiles to Energy Levels
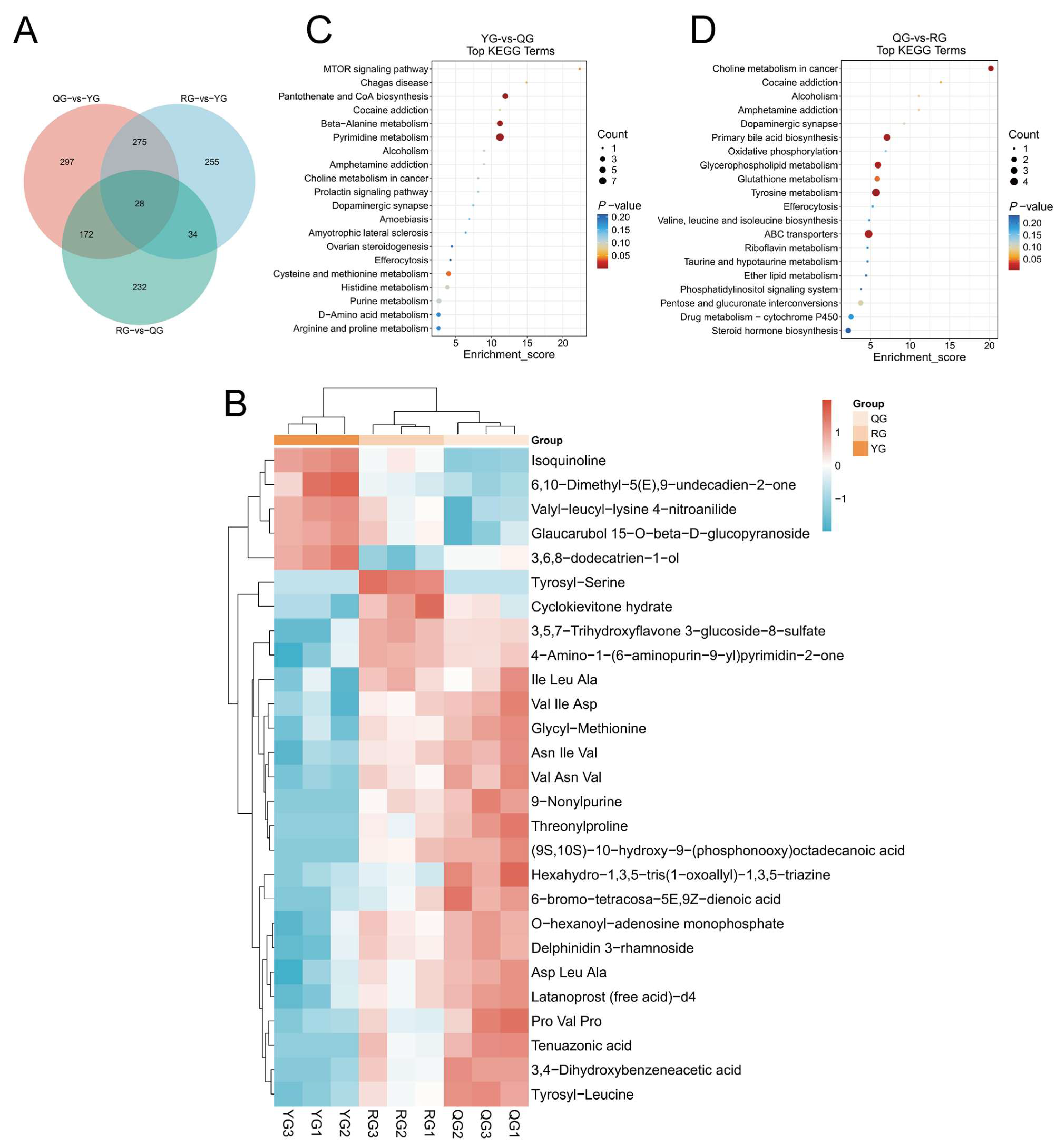
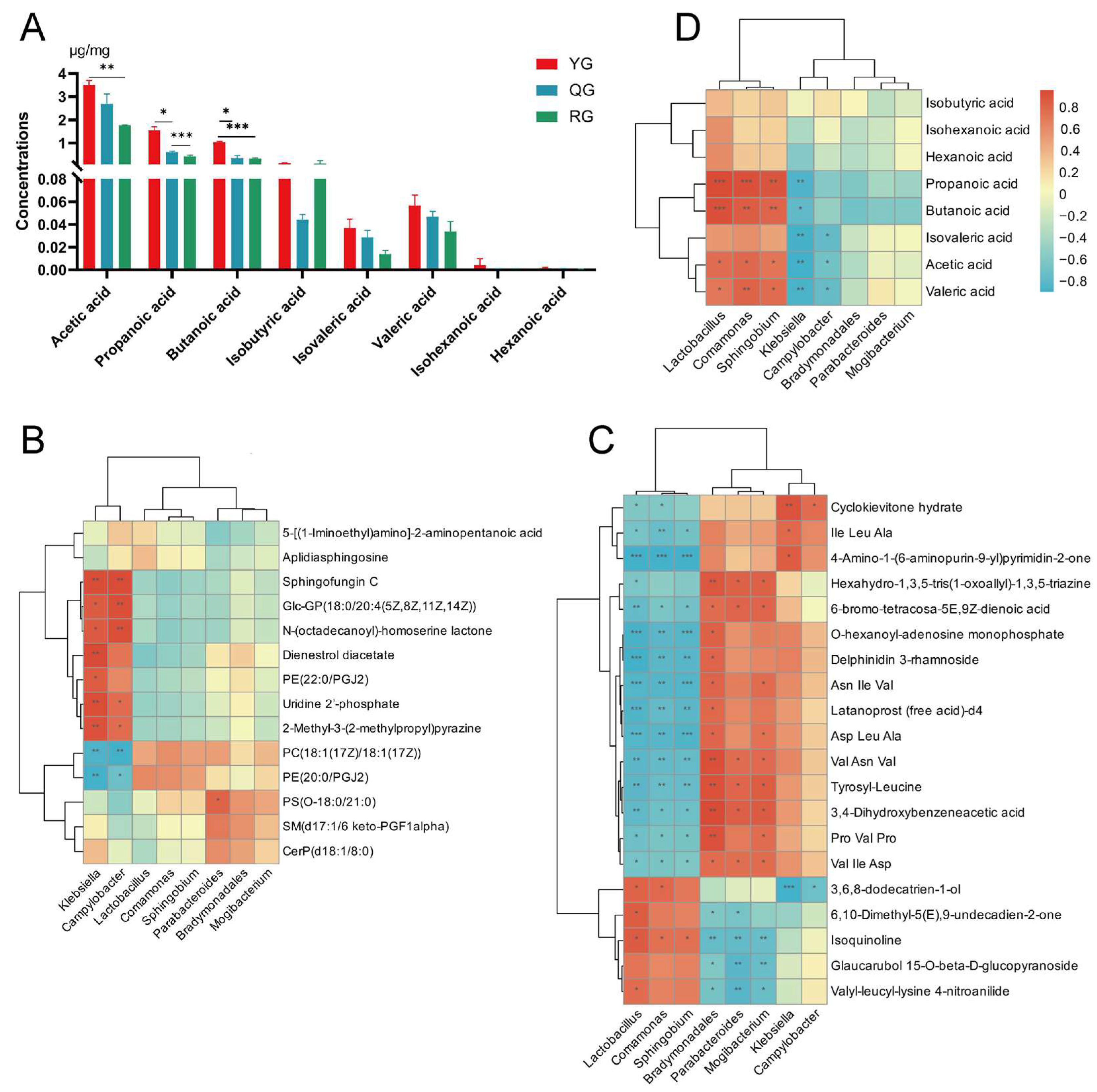
3.4. Analysis of Local Metabolic Differences and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in the Colon Under Different Energy Treatments
3.5. Response of Colon Transcriptomics to Diets with Different Energy Levels
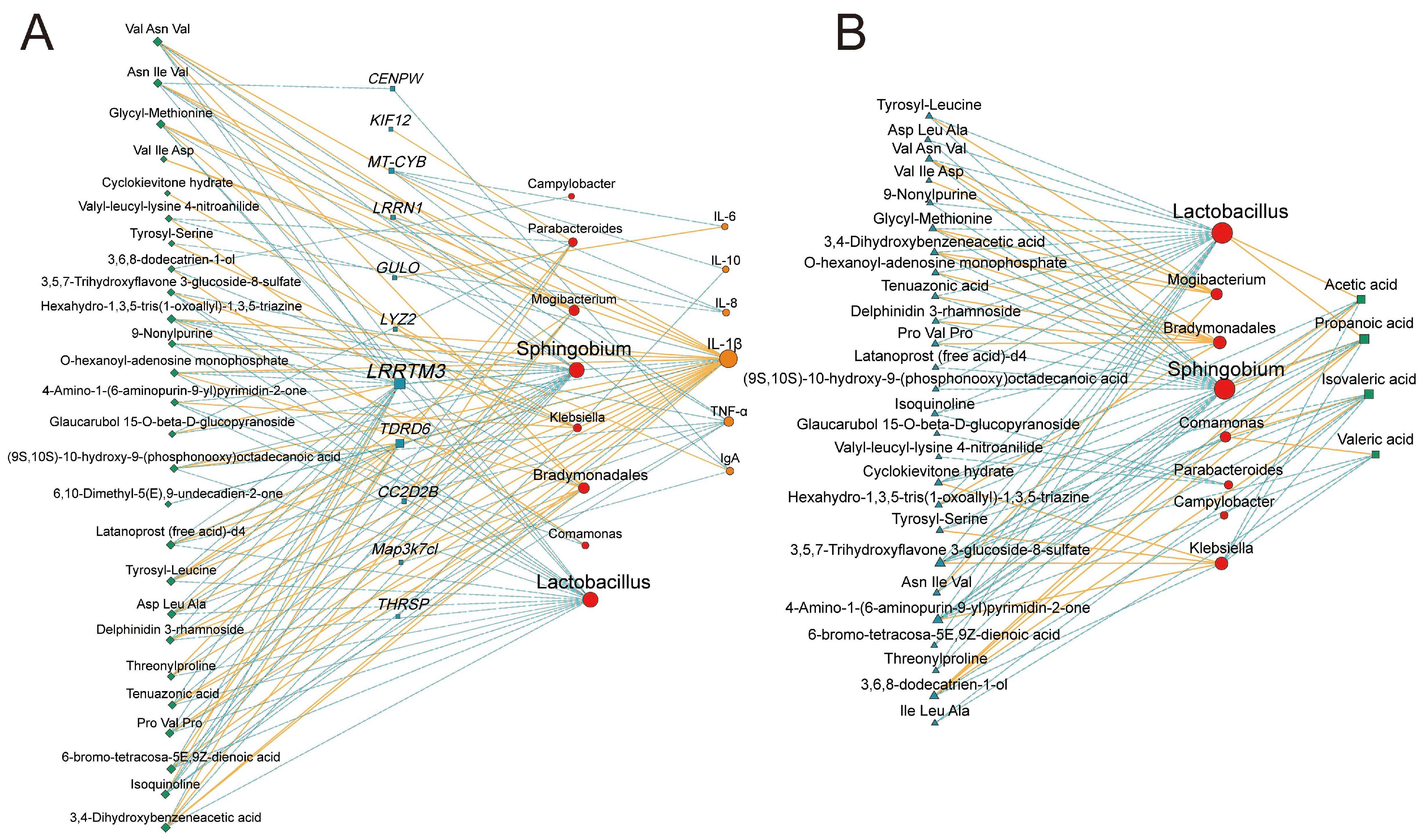
3.6. Multi-Omics Integration Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayes, J.P. Altitudinal and seasonal effects on aerobic metabolism of deer mice. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1989, 159, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochachka, P.W. Exercise limitations at high altitude: The metabolic problem and search for its solution. In Circulation, Respiration, and Metabolism: Current Comparative Approaches; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; pp. 240–249. [Google Scholar]
- McClelland, G.B.; Scott, G.R. Evolved mechanisms of aerobic performance and hypoxia resistance in high-altitude natives. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 561–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, E.C.; Metcalfe, N.B.; Llewellyn, M.S. The potential role of the gut microbiota in shaping host energetics and metabolic rate. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yang, J.; Yuan, H. Recent progress in research on the gut microbiota and highland adaptation on the Qinghai—Tibet plateau. J. Evol. Biol. 2021, 34, 1514–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Xu, B.; Song, P.; Jiang, F.; Gao, H.; Cai, Z.; Gu, H.; Zhang, T. Comparative macrogenomics reveal plateau adaptation of gut microbiome in cervids. BMC Biol. 2025, 23, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X. Fecal microbiota reveal adaptation of herbivores to the extreme environment of the qinghai–tibet plateau. Grassl. Res. 2024, 3, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Tian, J.; Tian, P.; Cong, R.; Luo, Y.; Geng, Y.; Tao, S.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, R. Feeding a high concentration diet induces unhealthy alterations in the composition and metabolism of ruminal microbiota and host response in a goat model. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, R.J.; Sasson, G.; Garnsworthy, P.C.; Tapio, I.; Gregson, E.; Bani, P.; Huhtanen, P.; Bayat, A.R.; Strozzi, F.; Biscarini, F. A heritable subset of the core rumen microbiome dictates dairy cow productivity and emissions. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Cao, C.; Zhang, M.; Kwok, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. Lactobacillus casei zhang exerts probiotic effects to antibiotic-treated rats. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 5888–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, M.M.; Chourasia, R.; Phukon, L.C.; Sarkar, P.; Ray, R.C.; Singh, S.P.; Rai, A.K. Lactic acid bacteria in the functional food industry: Biotechnological properties and potential applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 10730–10748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjana, A.; Tiwari, S.K. Bacteriocin-producing probiotic lactic acid bacteria in controlling dysbiosis of the gut microbiota. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 851140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Pi, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, P.; Zhou, T.; Gu, Q. Effects of exopolysaccharide from lactobacillus rhamnosus on human gut microbiota in in vitro fermentation model. LWT 2021, 139, 110524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoman, C.J.; White, B.A. Gastrointestinal tract microbiota and probiotics in production animals. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2014, 2, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Chai, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Yao, J. Effect of alfalfa hay and starter feeding intervention on gastrointestinal microbial community, growth and immune performance of yak calves. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Wu, S.; Liang, Z. Multi-omics reveal mechanisms of high enteral starch diet mediated colonic dysbiosis via microbiome-host interactions in young ruminant. Microbiome 2024, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Sun, H.; He, Z.; Fischer-Tlustos, A.; Ma, T.; Steele, M.; Guan, L.L. Transcriptome analysis revealed that delaying first colostrum feeding postponed ileum immune system development of neonatal calves. Genomics 2021, 113, 4116–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, M.A.; Hassan, F.; Rehman, M.S.; Huws, S.A.; Cheng, Y.; Din, A.U. Gut microbiome colonization and development in neonatal ruminants: Strategies, prospects, and opportunities. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, D.; Zheng, A.; Ma, Q. Glutathione metabolism-mediated ferroptosis reduces water-holding capacity in beef during cold storage. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Brosh, A.; Chen, J.Q.; Gibb, M.J.; Shang, Z.H.; Guo, X.S.; Mi, J.D.; Zhou, J.W.; Wang, H.C.; et al. Seasonal heat production and energy balance of grazing yaks on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 198, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 815-2004. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF/English.aspx/NYT815-2004 (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Shen, J.; Han, X.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S.; Jin, C.; Liu, T.; Cao, Y.; Lei, X.; Yao, J. High rumen-degradable starch diet promotes hepatic lipolysis and disrupts enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in dairy goats. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2755–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Han, X.; Cao, Y.; Yao, J. Metagenomic analyses of microbial and carbohydrate-active enzymes in the rumen of dairy goats fed different rumen degradable starch. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F.; Fuss, I.; Kelsall, B.L.; Stüber, E.; Strober, W. Antibodies to interleukin-12 abrogate established experimental colitis in mice. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; Trapnell, C.; Donaghey, J.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Improving RNA-Seq expression estimates by correcting for fragment bias. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T.; et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36 (Suppl. S1), D480–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossa, C.W.; Oberdorf, W.E.; Yang, L.; Aas, J.A.; Paster, B.J.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Brodie, E.L.; Malamud, D.; Poles, M.A.; Pei, Z. Design of 16S rRNA gene primers for 454 pyrosequencing of the human foregut microbiome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 4135–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kechin, A.; Boyarskikh, U.; Kel, A.; Filipenko, M. Cutprimers: A new tool for accurate cutting of primers from reads of targeted next generation sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2017, 24, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. Dada2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative pcr and the 2− δδct method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccard, J.; Rutledge, D.N. A consensus orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (opls-da) strategy for multiblock omics data fusion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 769, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W.; Mao, S. A high grain diet dynamically shifted the composition of mucosa-associated microbiota and induced mucosal injuries in the colon of sheep. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, P.; Combes, S.; Pascal, G.; Cauquil, L.; Julliand, V. Dietary composition and yeast/microalgae combination supplementation modulate the microbial ecosystem in the caecum, colon and faeces of horses. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 123, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, M.; Luo, S.; Zhang, R.; Han, P.; Hu, W. Metabolic responses to ethanol in saccharomyces cerevisiae using a gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approach. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmuthuge, N.; Guan, L.L. Gut microbiome and omics: A new definition to ruminant production and health. Anim. Front. 2016, 6, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wu, X.; Chu, M.; Bao, P.; Xiong, L.; Liang, C.; Ding, X.; Pei, J.; Yan, P. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of the pamir yak (bos grunniens). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 3165–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chida, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Takino, T.; Kawamoto, S.; Hagiwara, K. Changes in immune system and intestinal bacteria of cows during the transition period. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2021, 14, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Xie, W.; Zhou, S.; Ma, N.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Shen, X.; Chang, G. A high-concentrate diet induces colonic inflammation and barrier damage in hu sheep. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 9644–9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, N.; Fariñas, F.; Cabrera-Gómez, C.G.; Pallarès, F.J.; Ramis, G. Weaning causes a prolonged but transient change in immune gene expression in the intestine of piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, E.L.; Pearce, E.J. Metabolic pathways in immune cell activation and quiescence. Immunity 2013, 38, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; Curtis, A.M.; Goel, G.; Lauterbach, M.A.; Sheedy, F.J.; Gleeson, L.E.; van den Bosch, M.W.; Quinn, S.R.; Domingo-Fernandez, R.; Johnston, D.G.; et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates Hif-1a activity and IL-1b induction and is a critical determinant of the Warburg effect in LPS-activated macrophages. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachut, M.; Tam, J.; Contreras, G.A. Modulating immunometabolism in transition dairy cows: The role of inflammatory lipid mediators. Anim. Front. 2022, 12, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhang, K.; Xu, T.; Chang, G.; Loor, J.J.; Shen, X. Disturbances of ruminal microbiota and liver inflammation, mediated by lps and histamine, in dairy cows fed a high-concentrate diet. Animals 2024, 14, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, D. Molecular pathogenesis of klebsiella pneumoniae. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Poirel, L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Schwaber, M.J.; Daikos, G.L.; Cormican, M.; Cornaglia, G.; Garau, J.; Gniadkowski, M.; Hayden, M.K. Clinical epidemiology of the global expansion of klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.M. The clinical importance of emerging campylobacter species. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Global epidemiology of campylobacter infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virili, C.; Centanni, M. “With a little help from my friends”—The role of microbiota in thyroid hormone metabolism and enterohepatic recycling. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 458, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E.; Wahl, R. Microbiota and thyroid interaction in health and disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Lu, G.; Gao, D.; Lv, Z.; Li, D. The relationships between the gut microbiota and its metabolites with thyroid diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 943408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, P.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Lan, J.; Chen, D. An association of gut microbiota with different phenotypes in chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, I.; Maslennikov, R.; Kudryavtseva, A.; Avdeeva, A.; Krasnov, G.; Diatroptov, M.; Bakhitov, V.; Aliev, S.; Sedova, N.; Fedorova, M. Gut microbiota and cytokine profile in cirrhosis. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2024, 12, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.; Wang, S.; Liang, Q.; Du, Z.; Tian, R.; Ouyang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, A.; Gong, Y.; Chen, G. Bradymonabacteria, a novel bacterial predator group with versatile survival strategies in saline environments. Microbiome 2020, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezeji, J.C.; Sarikonda, D.K.; Hopperton, A.; Erkkila, H.L.; Cohen, D.E.; Martinez, S.P.; Cominelli, F.; Kuwahara, T.; Dichosa, A.E.; Good, C.E. Parabacteroides distasonis: Intriguing aerotolerant gut anaerobe with emerging antimicrobial resistance and pathogenic and probiotic roles in human health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1922241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Tang, L.; Liu, S.; Hu, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, S.; Tang, X.; Tang, T. Parabacteroides produces acetate to alleviate heparanase-exacerbated acute pancreatitis through reducing neutrophil infiltration. Microbiome 2021, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahara, H.; Yanamoto, S.; Takahashi, M.; Hamada, Y.; Asaka, T.; Kitagawa, Y.; Moridera, K.; Noguchi, K.; Maruoka, Y.; Yahara, K. Shotgun metagenomic analysis of saliva microbiome suggests mogibacterium as a factor associated with chronic bacterial osteomyelitis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e302569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaka, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Tobe, K. The gut microbiome: A core regulator of metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 256, e220111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Xiang, J.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Pan, W. Gut microbial response to host metabolic phenotypes. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1019430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Gebeyew, K.; Wu, Z.; Chen, B.; Jiao, J.; Tan, Z.; Tian, D.; He, Z. Fat-rich diet promotes microbiome-dependent atp synthesis in sheep model. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2025, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliphant, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Macronutrient metabolism by the human gut microbiome: Major fermentation by-products and their impact on host health. Microbiome 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogal, A.; Valdes, A.M.; Menni, C. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between gut microbiota and diet in cardio-metabolic health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1897212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducker, G.S.; Rabinowitz, J.D. One-carbon metabolism in health and disease. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.M.; Ye, J. Reprogramming of serine, glycine and one-carbon metabolism in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zou, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Xiang, J.; Wang, B. Amino acid metabolism in immune cells: Essential regulators of the effector functions, and promising opportunities to enhance cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnúsdóttir, S.; Ravcheev, D.; de Crécy-Lagard, V.; Thiele, I. Systematic genome assessment of b-vitamin biosynthesis suggests co-operation among gut microbes. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; van der Zwaag, M.; Wedman, J.J.; Permentier, H.; Plomp, N.; Jia, X.; Kanon, B.; Eggens-Meijer, E.; Buist, G.; Harmsen, H. Coenzyme a precursors flow from mother to zygote and from microbiome to host. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2650–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razak, M.A.; Begum, P.S.; Viswanath, B.; Rajagopal, S. Multifarious beneficial effect of nonessential amino acid, glycine: A review. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1716701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.; Xiong, M.; Chen, J.; Jian, C.; Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Zeng, F.; Huang, Q. The change of plasma metabolic profile and gut microbiome dysbiosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 931431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada Venegas, D.; De la Fuente, M.K.; Landskron, G.; González, M.J.; Quera, R.; Dijkstra, G.; Harmsen, H.J.; Faber, K.N.; Hermoso, M.A. Corrigendum: Short chain fatty acids (scfas)-mediated gut epithelial and immune regulation and its relevance for inflammatory bowel diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cong, Y. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites in the regulation of host immune responses and immune-related inflammatory diseases. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardamagna, M.; Berciano-Guerrero, M.; Lavado-Valenzuela, R.; Auclin, É.; Onieva-Zafra, J.L.; Plaza-Andrades, I.; Oliver, J.; Garrido-Aranda, A.; Perez-Ruiz, E.; Álvarez, M. Association of gut microbiota and immune gene expression with response to targeted therapy in braf mutated melanoma. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 25430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Q.; Li, N.; Bao, P.; Huang, C.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, T.; Ma, C.; Deng, J.; Jiang, F.; Jia, J.; et al. Microbiota–Metabolite–Host Crosstalk Mediates the Impact of Dietary Energy Levels on Colonic Homeostasis in High-Altitude Ruminants. Animals 2025, 15, 2929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192929
Yu Q, Li N, Bao P, Huang C, Zheng Q, Wang T, Ma C, Deng J, Jiang F, Jia J, et al. Microbiota–Metabolite–Host Crosstalk Mediates the Impact of Dietary Energy Levels on Colonic Homeostasis in High-Altitude Ruminants. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192929
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Qinran, Ning Li, Pengjia Bao, Chun Huang, Qingbo Zheng, Tong Wang, Chaofan Ma, Jingying Deng, Fengtao Jiang, Jianlei Jia, and et al. 2025. "Microbiota–Metabolite–Host Crosstalk Mediates the Impact of Dietary Energy Levels on Colonic Homeostasis in High-Altitude Ruminants" Animals 15, no. 19: 2929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192929
APA StyleYu, Q., Li, N., Bao, P., Huang, C., Zheng, Q., Wang, T., Ma, C., Deng, J., Jiang, F., Jia, J., & Yan, P. (2025). Microbiota–Metabolite–Host Crosstalk Mediates the Impact of Dietary Energy Levels on Colonic Homeostasis in High-Altitude Ruminants. Animals, 15(19), 2929. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192929




