Histological and Proteomic Approaches to Assessing the Adrenal Stress Response in Common Dolphins (Delphinus delphis)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Histological Examination
Imaging Technique and Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Protein Analysis
2.4.1. Tissue Preparation
2.4.2. Deparaffinization
2.4.3. Protein Extraction
2.4.4. One Dimensional SDS-PAGE
2.4.5. Preparation of Protein Samples for Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
Filter Aided Sample Preparation (FASP) Method
In-Gel Protein Digestion Method
2.4.6. Protein Identification by LC-MS/MS and Data Analysis
3. Results
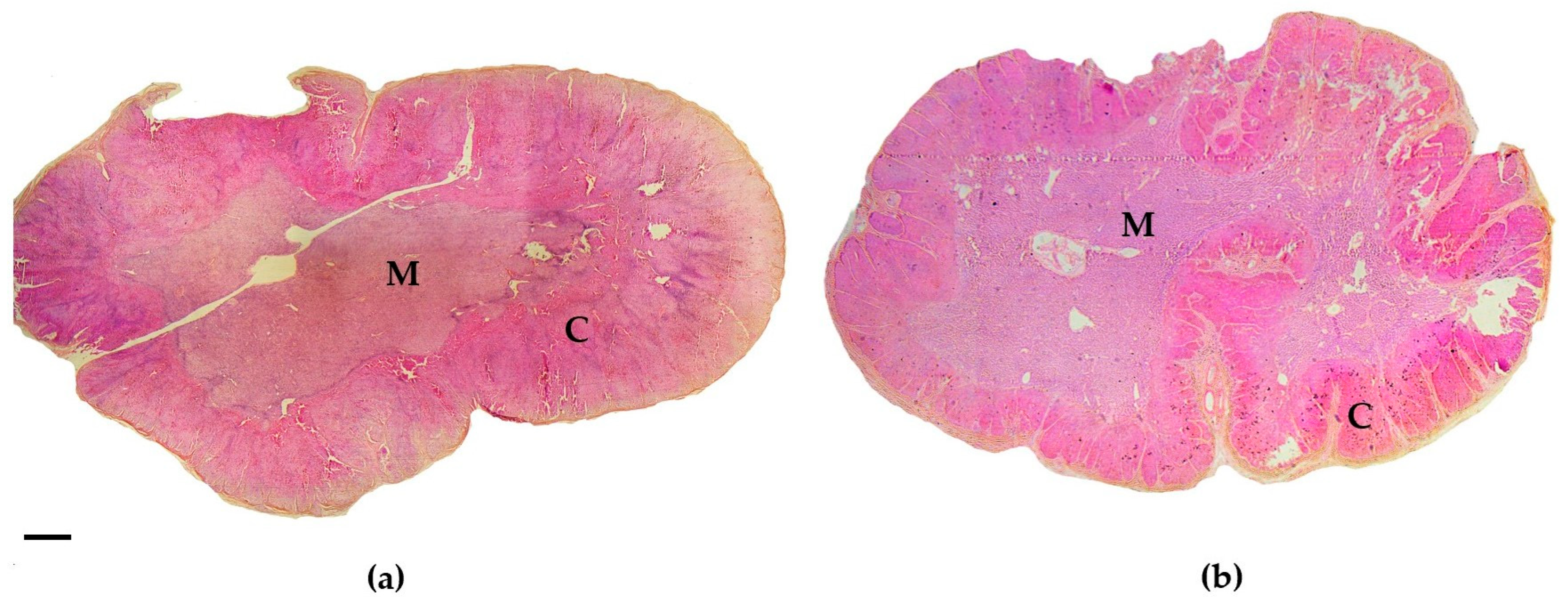
3.1. Histological Examination
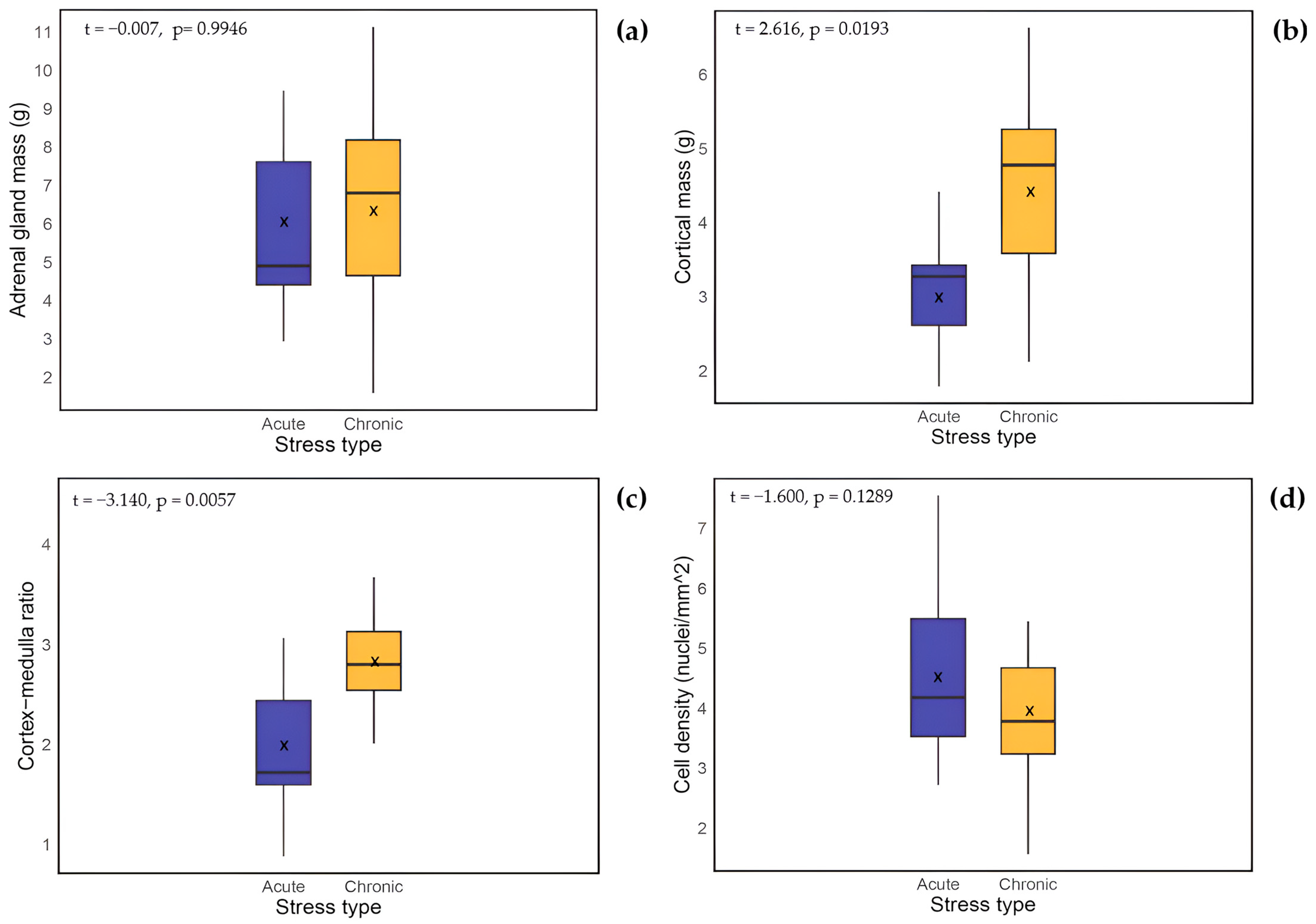
3.1.1. Biological Related Effects on Adrenal Gland Mass
3.1.2. Biologically Related Effects on Cortex-Medulla Proportions
3.1.3. Biologically Related Effects on Cortical Cell Density
3.2. Protein Extraction
3.2.1. Protein Yield and Quality of the Extraction Method
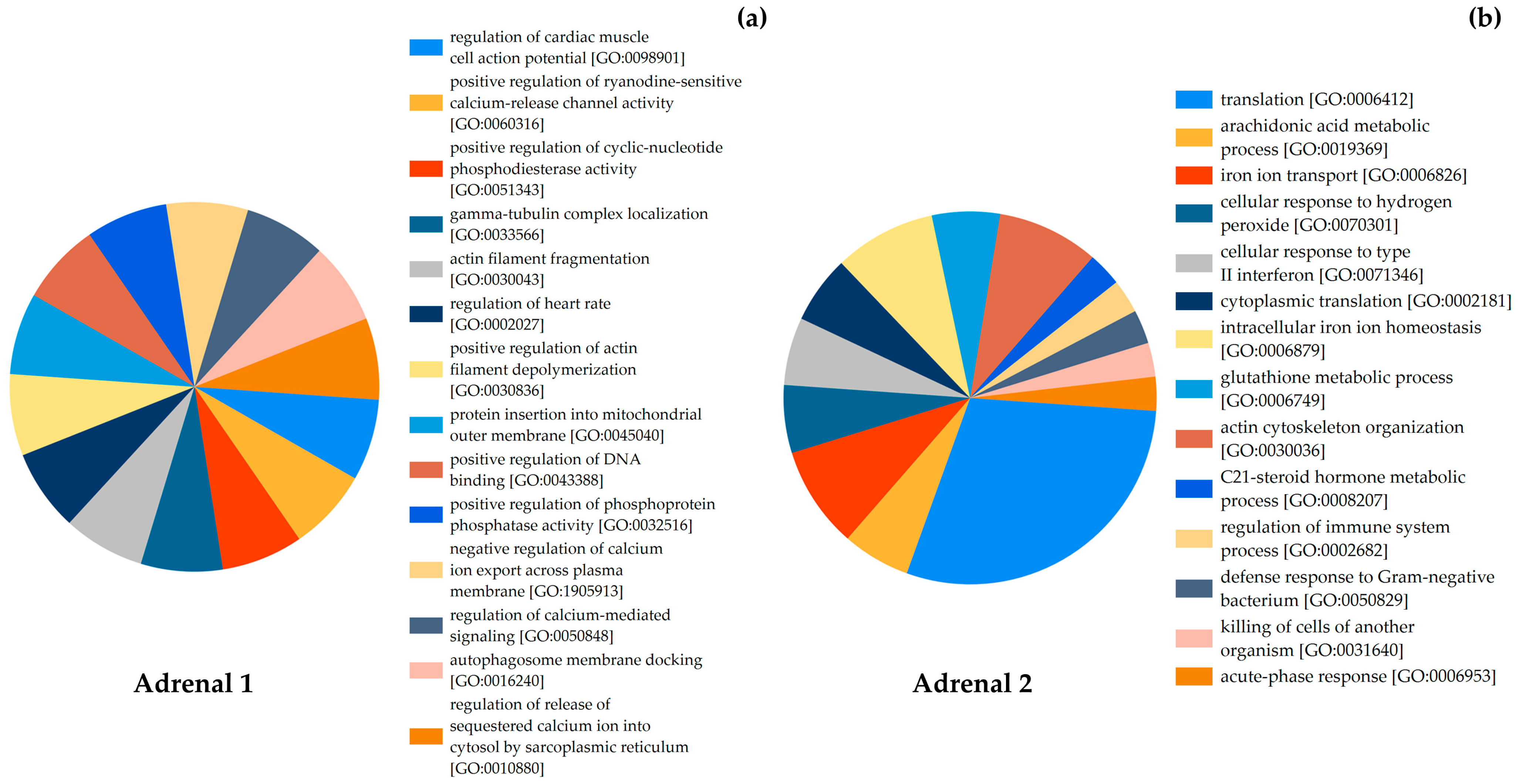
3.2.2. Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Analysis for Protein Identification
4. Discussion
4.1. Histological Examinations
4.2. Protein Extraction and Functional Interpretation
4.3. Broader Implications and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Myrick, A.C.; Perkins, P.C. Adrenocortical Color Darkness and Correlates as Indicators of Continuous Acute Premortem Stress in Chased and Purse-Seine Captured Male Dolphins. Pathophysiology 1995, 2, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.; Marwaha, K.; Sanvictores, T.; Awosika, A.O.; Ayers, D. Physiology, Stress Reaction; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.S.; Pfeiffer, D.C.; Cowan, D.F. Morphology and Histology of the Atlantic Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) Adrenal Gland with Emphasis on the Medulla. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2005, 34, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherlock, M.; Scarsbrook, A.; Abbas, A.; Fraser, S.; Limumpornpetch, P.; Dineen, R.; Stewart, P.M. Adrenal Incidentaloma. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 775–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, M.L.; Butler, L.K. Endocrinology of Stress. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 20, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, D. Potential Synergism between Stress and Contaminants in Free-Ranging Cetaceans. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 2007, 20, 194–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.; Murphy, S.; O’Donovan, J.; Minto, C.; Mirimin, L.; Slattery, O. Assessing Biomarkers in Common Dolphin: Insights from Novel Blubber Cortisol Analysis. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2025, 589, 152112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, C.; Manteca, X.; García-Párraga, D.; Tallo-Parra, O. Validating a Non-Invasive Method for Assessing Cortisol Concentrations in Scraped Epidermal Skin from Common Bottlenose Dolphins and Belugas. Animals 2024, 14, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellar, N.M.; Catelani, K.N.; Robbins, M.N.; Trego, M.L.; Allen, C.D.; Danil, K.; Chivers, S.J. Blubber Cortisol: A Potential Tool for Assessing Stress Response in Free-Ranging Dolphins without Effects Due to Sampling. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laast, V.A.; Larsen, T.; Allison, N.; Hoenerhoff, M.J.; Boorman, G.A. Distinguishing Cystic Degeneration from Other Aging Lesions in the Adrenal Cortex of Sprague-Dawley Rats. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 42, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.Y.; Rotstein, D.S.; McLellan, W.A.; Costidis, A.M.; Lovewell, G.; Schaefer, A.M.; Romero, C.H.; Bossart, G.D. Macroscopic and Histopathologic Findings From a Mass Stranding of Rough-Toothed Dolphins (Steno Bredanensis) in 2005 on Marathon Key, Florida, USA. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.S.; Curnick, D.J.; Baillie, A.; Barber, J.L.; Barnett, J.; Brownlow, A.; Deaville, R.; Davison, N.J.; Ten Doeschate, M.; Jepson, P.D.; et al. Sea Temperature and Pollution Are Associated with Infectious Disease Mortality in Short-Beaked Common Dolphins. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepson, P.D.; Bennett, P.M.; Deaville, R.; Allchin, C.R.; Baker, J.R.; Law, R.J. Relationships between Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Health Status in Harbor Porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) Stranded in the United Kingdom. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.; Law, R.J.; Deaville, R.; Barnett, J.; Perkins, M.W.; Brownlow, A.; Penrose, R.; Davison, N.J.; Barber, J.L.; Jepson, P.D. Organochlorine Contaminants and Reproductive Implication in Cetaceans. In Marine Mammal Ecotoxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 3–38. ISBN 978-0-12-812144-3. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, J.P. Neural Control of Chronic Stress Adaptation. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiken, T.; Höfle, U.; Bennett, P.M.; Allchin, C.R.; Kirkwood, J.K.; Baker, J.R.; Appleby, E.C.; Lockyer, C.H.; Walton, M.J.; Sheldrick, M.C. Adrenocortical Hyperplasia, Disease and Chlorinated Hydrocarbons in the Harbour Porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1993, 26, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, D.S.; Yeates, L.C.; Crocker, D.E. Cold Stress Induces an Adrenocortical Response in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2011, 42, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.S.; Cowan, D.F.; Pfeiffer, D.C. Morphological Changes in the Atlantic Bottlenose Dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) Adrenal Gland Associated with Chronic Stress. J. Comp. Pathol. 2006, 135, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venn-Watson, S.; Colegrove, K.M.; Litz, J.; Kinsel, M.; Terio, K.; Saliki, J.; Fire, S.; Carmichael, R.; Chevis, C.; Hatchett, W.; et al. Adrenal Gland and Lung Lesions in Gulf of Mexico Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Found Dead Following the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möstl, E.; Palme, R. Hormones as Indicators of Stress. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2002, 23, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Herman, J.P. Neural Regulation of Endocrine and Autonomic Stress Responses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Hu, G.; Shan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Gong, T.; Liu, D. Citrate Synthase and OGDH as Potential Biomarkers of Atherosclerosis under Chronic Stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9957908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leathem, J.H.; Stauber, L.A. Adrenal lipid and alkaline phosphatase in hamsters infected with leishmania donovani. Endocrinology 1952, 50, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanczkowski, W.; Sue, M.; Bornstein, S.R. The Adrenal Gland Microenvironment in Health, Disease and during Regeneration. Hormones 2017, 16, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyarmin, J.; Hekman, R.; Champagne, C.; McCormley, M.; Stephan, A.; Crocker, D.; Houser, D.; Khudyakov, J. Blubber Proteome Response to Repeated ACTH Administration in a Wild Marine Mammal. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 33, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolesky, P.; Parry, C.; Boxall, B.; Wells, R.; Venn-Watson, S.; Janech, M.G. Proteomic Analysis of Non-Depleted Serum Proteins from Bottlenose Dolphins Uncovers a High Vanin-1 Phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, J.L.; Botting, C.H.; Brownlow, A.; Hall, A.J. Not Just Fat: Investigating the Proteome of Cetacean Blubber Tissue. Conserv. Physiol. 2018, 6, coy003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.A. Cytochrome P450 1A as a Biomarker of Contaminant Exposure in Free-Ranging Marine Mammals. Master’s Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, M.; Marsili, L. Multi-Trial Ecotoxicological Diagnostic Tool in Cetacean Skin Biopsies. In Skin Biopsy—Perspectives; Khopkar, U., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-290-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K. Expression of Glutathione S-Transferase (GST) Genes in the Marine Copepod Tigriopus Japonicus Exposed to Trace Metals. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 89, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, P.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Robertson, W.D.; Zarrine-Afsar, A.; Deterra, D.; Richter, V.; Schlüter, H. Protein Species as Diagnostic Markers. J. Proteom. 2016, 134, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, M.G.; Caricato, R.; Giordano, M.E. Pollution Biomarkers in the Framework of Marine Biodiversity Conservation: State of Art and Perspectives. Water 2021, 13, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, P.A.; Schaefer, A.M.; Romano, T.A.; Bossart, G.D.; Lamb, S.V.; Reif, J.S. Stress Response of Wild Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) during Capture–Release Health Assessment Studies. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 206, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, I.C.; Kaschner, K.; Dormann, C.F. Current Global Risks to Marine Mammals: Taking Stock of the Threats. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 221, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on the Assessment of the Cumulative Effects of Anthropogenic Stressors on Marine Mammals; Ocean Studies Board; Division on Earth and Life Studies; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Approaches to Understanding the Cumulative Effects of Stressors on Marine Mammals; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 23479. ISBN 978-0-309-44048-6. [Google Scholar]
- Perrin, W.F. Common Dolphins. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 255–259. ISBN 978-0-12-373553-9. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, S.; Evans, P.G.H.; Pinn, E.; Pierce, G.J. Conservation Management of Common Dolphins: Lessons Learned from the North-East Atlantic. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2021, 31, 137–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN Delphinus Delphis; Hammond, P.S.; Bearzi, G.; Bjørge, A.; Forney, K.; Karczmarski, L.; Kasuya, T.; Perrin, W.F.; Scott, M.D.; Wang, J.Y.; et al. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2008; E.T6336A12649851. [Google Scholar]
- ICES. Workshop on Estimation of Mortality of Marine mammals Due to Bycatch; International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES)/Conseil International Pour L’exploration de la Mer(CIEM): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S. 1st Progress Report on Ascobans Species Action Plan for North-East Atlantic Common Dolphin. In Proceedings of the 10th Meeting of the Parties, Odense, Denmark, 10–12 September 2024. ASCOBANS/MOP10/Inf.6.1.4. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, S.; Minto, C.; Rogan, E.; Deaville, R.; O’Donovan, J.; Daly, M.; Levesque, S.; Berrow, S.; Brownlow, A.; Davison, N.J.; et al. Emaciated Enigma: Decline in Body Conditions of Common Dolphins in the Celtic Seas Ecoregion. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e70325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwis, H.A.S.S.; Albrecht, S.; Murphy, S.; O’Donovan, J.; Berrow, S.; Daly, M.; Levesque, S.; O’Dwyer, K. Stomach Parasites and Health Status of Short-Beaked Common Dolphins, Delphinus Delphis, Stranded along the Irish Coastline. Mar. Biol. 2025, 172, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vence, M.; Chantada-Vazquez, M.D.P.; Sosa-Fajardo, A.; Agra, R.; Barcia De La Iglesia, A.; Otero-Glez, A.; García-González, M.; Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.M.; Nuñez, C.; Bravo, J.J.; et al. Protein Extraction From FFPE Kidney Tissue Samples: A Review of the Literature and Characterization of Techniques. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 657313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, S.; O’Donovan, J.; Daly, M.; Murphy, S.; O’Connell, M.; Jepson, P.; Deaville, R.; Barnett, J.; Berrow, S.D. Supply of Verte—Brate Necropsy and Sample Recovery Services 2017–2018 & 2019 Merged Final Reports; Marine Institute Report Series; Marine Institute: Galway, Ireland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, S.; Winship, A.; Dabin, W.; Jepson, P.; Deaville, R.; Reid, R.; Spurrier, C.; Rogan, E.; López, A.; González, A.; et al. Importance of Biological Parameters in Assessing the Status of Delphinus Delphis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 388, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.; Collet, A.; Rogan, E. Mating strategy in the male common dolphin (Delphinus delphis): What gonadal analysis tells us. J. Mammal. 2005, 86, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaville, R.; Jepson, P. CSIP Final Report for the Period 1st January 2005–31st December 2010; UK Cetacean Strandings Investigation Programme: Report to the UK Department for Food and Rural Affairs and the Devolved Administrations; UK Cetacean Strandings Investigation Programme: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Singh, S. A Comparative Analysis of Manual Point-Counting Method and Automated Pixel-Counting Method of Area Percentage Estimation on Placenta. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 2009, 31, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, J.R. Filter-Aided Sample Preparation for Proteome Analysis. In Microbial Proteomics; Becher, D., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1841, pp. 3–10. ISBN 978-1-4939-8693-4. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. Is Proteomics the New Genomics? Cell 2007, 130, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus Computational Platform for Comprehensive Analysis of (Prote)Omics Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathan, M.; Keerthikumar, S.; Ang, C.; Gangoda, L.; Quek, C.Y.J.; Williamson, N.A.; Mouradov, D.; Sieber, O.M.; Simpson, R.J.; Salim, A.; et al. FunRich: An Open Access Standalone Functional Enrichment and Interaction Network Analysis Tool. Proteomics 2015, 15, 2597–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, D.F. Observations on the Pilot Whale Globicephala melaena: Organweight and Growth. Anat. Rec. 1966, 155, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.P.; Clark, L.S.; Haubold, E.M.; Worthy, G.A.J.; Cowan, D.F. Organ Weights and Growth Profiles in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from the Northwestern Gulf of Mexico. Aquat. Mamm. 2006, 32, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.; Rogan, E. External Morphology of the Short-beaked Common Dolphin, Delphinus delphis: Growth, Allometric Relationships and Sexual Dimorphism. Acta Zool. 2006, 87, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lair, S.; Béland, P.; De Guise, S.; Martineau, D. Adrenal hyperplastic and degenerative changes in beluga whales. J. Wildl. Dis. 1997, 33, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.W.; Weisser, J.; Nilse, L.; Costa, F.; Keller, E.; Tholen, M.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N.; Biniossek, M.; Bronsert, P.; Schilling, O. Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissues (FFPE) as a Robust Source for the Profiling of Native and Protease-Generated Protein Amino Termini. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, E.; Broeckx, V.; Mertens, I.; Sagaert, X.; Prenen, H.; Landuyt, B.; Schoofs, L. Analysis of the Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Proteome: Pitfalls, Challenges, and Future Prospectives. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccher, A.; Seminati, D.; L’Imperio, V.; Casati, G.; Pilla, D.; Malapelle, U.; Piga, I.; Bindi, G.; Marando, A.; Bonoldi, E.; et al. Pathology Laboratory Archives: Conservation Quality of Nucleic Acids and Proteins for NSCLC Molecular Testing. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.K.; Brosnahan, C.L.; Pande, A.; Baker, C.F.; Geoghegan, J.L.; Kitson, J.; Gemmell, N.J.; Dowle, E.J. Formalin-fixed Paraffin-embedded (FFPE) Samples Help to Investigate Transcriptomic Responses in Wildlife Disease. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2025, 25, e13805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M.B.; Padula, M.P. Analysis of Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissue Via Proteomic Techniques and Misconceptions of Antigen Retrieval. BioTechniques 2016, 60, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimzadeh, O.; Atkinson, M.J.; Tapio, S. Qualitative and Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissue. In Proteomic Profiling; Posch, A., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1295, pp. 109–115. ISBN 978-1-4939-2549-0. [Google Scholar]
- García, A.G.; García-De-Diego, A.M.; Gandía, L.; Borges, R.; García-Sancho, J. Calcium Signaling and Exocytosis in Adrenal Chromaffin Cells. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 1093–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, C.C.; Ryu, M.-S.; Frey, A.; Patel, S. Cytosolic Iron Chaperones: Proteins Delivering Iron Cofactors in the Cytosol of Mammalian Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 12764–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumakura, K.; Ohara-Imaizumi, M.; Battaini, F.; Sasakawa, N.; Ohkubo, S. Multiple Roles of Actin Cytoskeleton in Catecholamine Release from Chromaffin Cell. In Catecholamine Research; Nagatsu, T., Nabeshima, T., McCarty, R., Goldstein, D.S., Eds.; Advances in Behavioral Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 53, pp. 57–60. ISBN 978-1-4419-3388-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sunwoo, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Bae, S.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, C.S.; Joo, S.Y.; Choi, H.S.; Suh, M.; Kim, S.W.; Choi, Y.J.; et al. Chronic and Acute Stress Monitoring by Electrophysiological Signals from Adrenal Gland. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, D.R.; Abunasef, S.K.; Khalil, S. Role of Adrenal Progenitor Cells in the Structural Response of Adrenal Gland to Various Forms of Acute Stress and Subsequent Recovery in Adult Male Albino Rats. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2025, 13, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehling, P.; Model, K.; Brandner, K.; Kovermann, P.; Sickmann, A.; Meyer, H.E.; Kühlbrandt, W.; Wagner, R.; Truscott, K.N.; Pfanner, N. Protein Insertion into the Mitochondrial Inner Membrane by a Twin-Pore Translocase. Science 2003, 299, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, S.; Chandra, T.S. Oxidative Stress Protection and Glutathione Metabolism in Response to Hydrogen Peroxide and Menadione in Riboflavinogenic Fungus Ashbya Gossypii. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 2307–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nairz, M.; Weiss, G. Iron in Infection and Immunity. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 75, 100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, I.A. The Adrenal Gland. In Handbook of Endocrine Investigations in Children; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 83–109. ISBN 978-0-7236-0719-9. [Google Scholar]
- Carballeira, A.; Brown, J.W.; Fishman, L.M.; Trujillo, D.; Odell, D.K. The Adrenal Gland of Stranded Whales (Kogia Breviceps and Mesoplodon Europaeus): Morphology, Hormonal Contents, and Biosynthesis of Corticosteroids. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1987, 68, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, S.; Crocker, D.; Houser, D.; Mashburn, K. Stress Physiology in Marine Mammals: How Well Do They Fit the Terrestrial Model? J. Comp. Physiol. B 2015, 185, 463–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ser, Z.; Kentsis, A. Three Protein Extraction Methods for Mass Spectrometry Proteomics of Fresh Frozen Mouse Tissue. Res. Sqaure, 2020; preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, L.J.R.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Giese, E.G. Environmental Contaminants and the HPA Axis: Advances in Adrenocortical Hormone Research in Cetaceans. Chemosphere 2025, 385, 144562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, R.L.; Storm, J.; Koger, R.; Thompson, E.; Williams, R.S.; Dagleish, M.P.; Babayan, S.A.; Ten Doeschate, M.T.I.; Davison, N.J.; Brownlow, A.C. The Dead Do Tell Tales: Using Pathology Data From Cetacean Necropsy Reports to Gain Insights Into Animal Health. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 15, e72119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Biological Factor | Biological Level | Chronically Stressed (n) | Acutely Stressed (n) | “Other” (n) | Total (per Level) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 8 | 10 | 13 | 31 |
| Female | 11 | 4 | 10 | 25 | |
| Unkown | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Sexual maturity | Mature | 11 | 6 | 16 | 33 |
| Immature | 8 | 7 | 8 | 23 | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Nutritional status | Poor | 12 | 3 | 10 | 25 |
| Moderate | 5 | 7 | 13 | 25 | |
| Good | 2 | 4 | 2 | 8 | |
| Decomposition state | Fresh | 7 | 8 | 8 | 23 |
| Slight | 5 | 3 | 13 | 21 | |
| Moderate | 7 | 3 | 4 | 14 | |
| Total (per Stress type) | 19 | 14 | 25 | 58 |
| Parameter | Statistics | Acutely Stressed | Chronically Stressed | All Individuals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adrenal gland mass (g) | Mean | 5.925 | 6.700 | 5.881 |
| Median | 4.900 | 6.810 | 5.580 | |
| SEM | 0.677 | 0.760 | 0.391 | |
| IQR | 3.195 | 3.527 | 3.690 | |
| n | 11 | 14 | 43 | |
| Cortex-medulla ratio | Mean | 1.962 | 2.892 | 2.529 |
| Median | 1.720 | 2.801 | 2.573 | |
| SEM | 0.231 | 0.185 | 0.129 | |
| IQR | 0.840 | 0.586 | 1.092 | |
| n | 9 | 17 | 45 | |
| Cortical cell density (nuclei/mm2) | Mean | 5.006 | 4.030 | 4.330 |
| Median | 4.298 | 3.800 | 4.180 | |
| SEM | 0.598 | 0.210 | 0.180 | |
| IQR | 2.494 | 1.348 | 1.260 | |
| n | 11 | 13 | 41 |
| Adrenal Gland | Weight (g) | Protein Concentration (mg/mL) | Cause of Death | Stress Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adrenal 1 | 0.176 | 5.878 | Bycatch | Acute |
| Adrenal 2 | 0.265 | 16.218 | Infectious disease | Chronic |
| Uniprot ID | Protein Name | Biological Process |
|---|---|---|
| P18990 | Hemoglobin subunit beta | Iron ion transport [GO:0006826] |
| A0A2U3V018 | Calmodulin-1 | Regulation of calcium-mediated signaling [GO:0050848] Positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity [GO:0060316] Regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum [GO:0010880] Regulation of cardiac muscle contraction [GO:0055117] Regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential [GO:0098901] |
| A0A6J3S6J4 | Keratin | Regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032465] |
| A0A6J3PXY9 | Actin | Regulation of cytokinesis [GO:0032465] |
| B6VQP8 | Ferritin | Intracellular iron ion homeostasis [GO:0006879] |
| A0A2U3V291 | Cytochrome b5 type B | Positive regulation of phosphoprotein phosphatase activity [GO:0032516] |
| A0A2U4BAL8 | Retinal dehydrogenase 1 | Positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT [GO:0046427] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medina Santana, C.; Slattery, O.; O’Donovan, J.; Murphy, S. Histological and Proteomic Approaches to Assessing the Adrenal Stress Response in Common Dolphins (Delphinus delphis). Animals 2025, 15, 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192924
Medina Santana C, Slattery O, O’Donovan J, Murphy S. Histological and Proteomic Approaches to Assessing the Adrenal Stress Response in Common Dolphins (Delphinus delphis). Animals. 2025; 15(19):2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192924
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedina Santana, Claudia, Orla Slattery, Jim O’Donovan, and Sinéad Murphy. 2025. "Histological and Proteomic Approaches to Assessing the Adrenal Stress Response in Common Dolphins (Delphinus delphis)" Animals 15, no. 19: 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192924
APA StyleMedina Santana, C., Slattery, O., O’Donovan, J., & Murphy, S. (2025). Histological and Proteomic Approaches to Assessing the Adrenal Stress Response in Common Dolphins (Delphinus delphis). Animals, 15(19), 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192924






