Effects of Replacing Fishmeal with Soybean Meal on Intestinal Histology, Antioxidation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Inflammation, Tight Junction, and Microbiota in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Experimental Diets and Design
2.3. Feeding Trial and Sample Collection
2.4. Serum Biochemical Parameters and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities Analyses
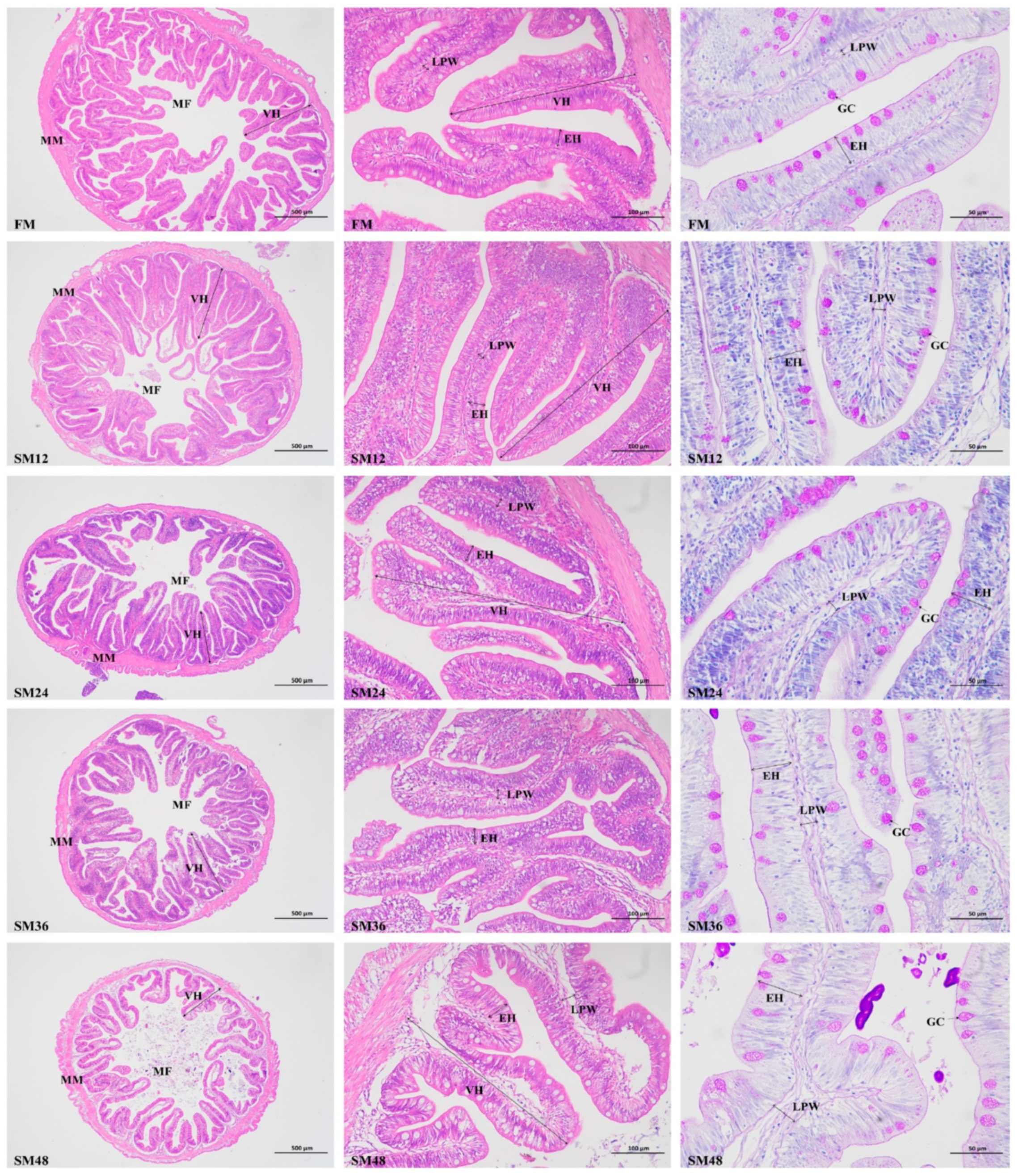
2.5. Intestinal Histological Analysis
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
| Target Genes | Primer Sequence Forward (5′-3′) | Primer Sequence Reverse (5′-3′) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endoplasmic reticulum stress | |||
| chop | CGGCCAAAAAGAGTCGCAAA | TCTCCGCTTTCAATCGCTCA | XM020096956 |
| perk | CTACCACCTACATCGTCCGC | ACCGGCTCAAAGTCAGTCAG | XM020105998 |
| grp78 | GTCGTGAGGTTGAGAAGGCA | TCATGGTGGAACGGAACAGG | DQ662232 |
| Inflammatory response | |||
| il-10 | TTTCAAAAGCCCGTTTGCGT | TTGGTTTCCTCCGTCACTCC | KF025663 |
| tgf-β1 | CAGCGAACACGAGCCAAACAC | TGTTCTGAGGGATGGACATGGTG | [27] |
| tnf-α | AGGGTATGGCTCTTCACGG | AAAGGCCCCCCAGCACCTTACACAT | AB040449 |
| il-6 | AATACGAGCCCACCGACAG | TGACCAGGGTTCCTCATCTTT | DQ884914 |
| Apoptosis | |||
| bax | GAGACACGGAGACAGCAAT | TTAGTGGGACTGAGTGAGGA | XM_020094597 |
| casp3 | CTGACTTCCTCTACGCCTTCT | AAACTCTACCGCCACCTTG | JQ394697 |
| casp6 | AACCTAACGGAGACAGATGC | CTGTGATGTCCTGAATAGCG | XM_020101241 |
| casp9 | CAAGCCTTTCCATTATTCCT | CAGTGGGTGTAGCAGGTTGTA | XM_020089046 |
| Tight junction | |||
| zo-1 | GGCACCAGGGTTTGGCTTCG | CGTCCGCTCCGTGTCTCAT | XM_020078978 |
| zo-2 | CGCAGTGGTATCCCATCGT | AGTGTAAGTCCCGCCCTCAT | XM_020105133 |
| claudin-5 | GTCTGTTTGTGCTGGTGCCTCT | CTCTTGGTCGGTGCGTATGTT | XM _020099317 |
| claudin-15 | TTCCCTTCACTACTCGCTTTAA | CATACCAGGACACTGAGACCAT | XM_020095475 |
| ocln | TCTTTGCTCTGAAGACCCGC | ATTGTTCACCCATGCCTCCA | [27] |
| muc-13 | ATGCGTCGCTTGTCCCACT | CATAAGGTTTCCCGATGTCT | XM_020106590 |
| muc-15 | GTCCAGTAGCGAAGTGAGTGA | GTTGTTGCGTAGCGTTGAT | XM_020099418 |
| Reference gene | |||
| β-actin | GGAAATCGTGCGTGACATTAAG | CCTCTGGACAACGGAACCTCT | HQ386788 |
2.7. Intestinal Microbiota Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth and Feed Performance
3.2. Serum Biochemical Parameters
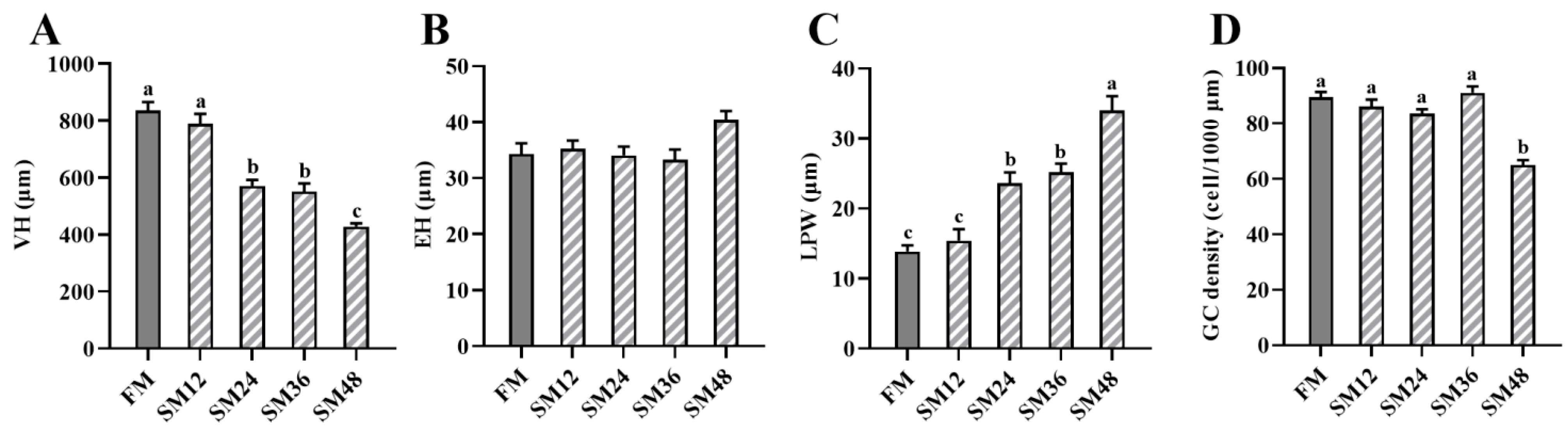
3.3. Intestinal Morphology
3.4. Intestinal Antioxidant Enzymes Activities
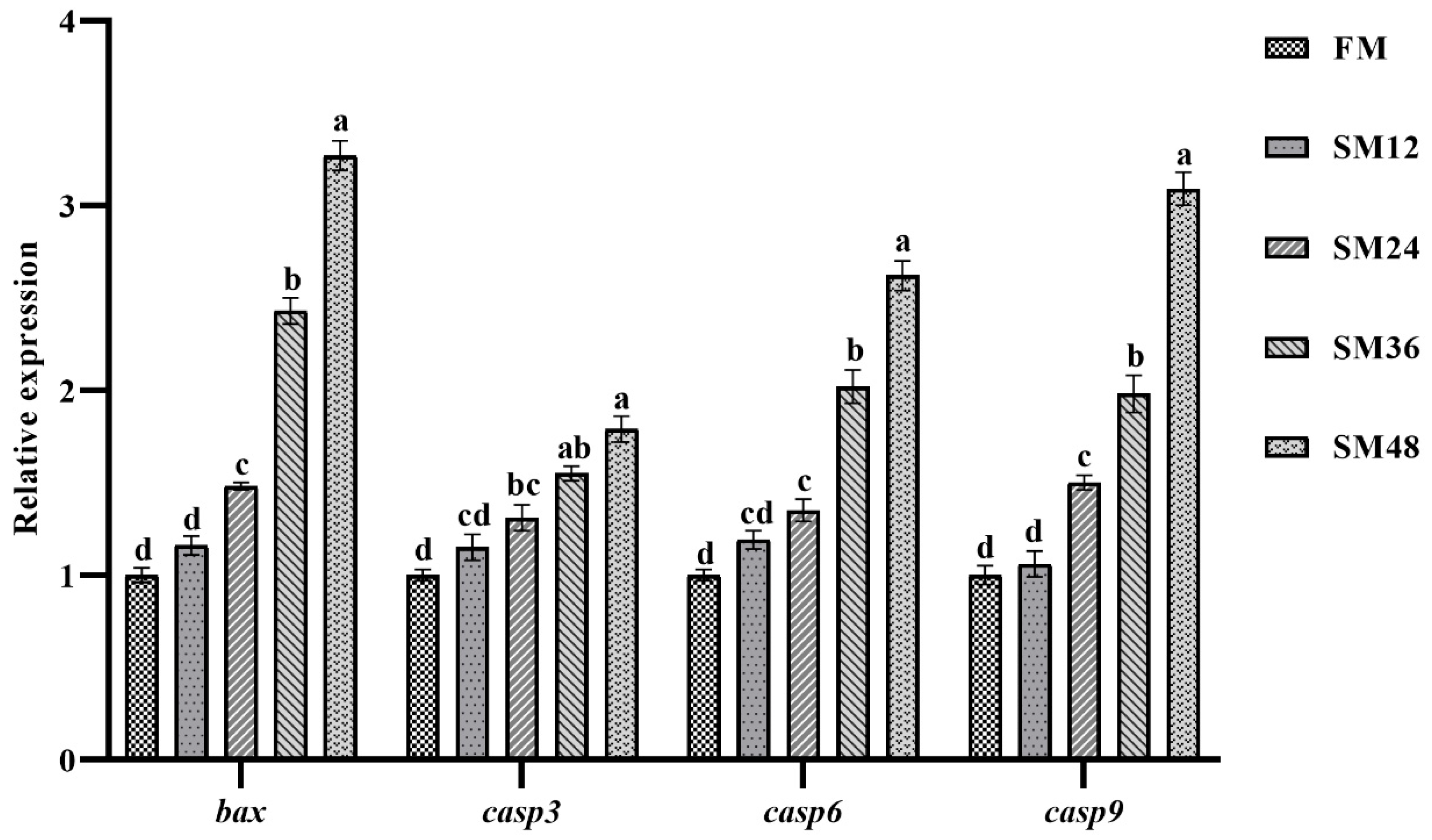
3.5. The Expression of Genes Related to ERS and Inflammation in Intestine
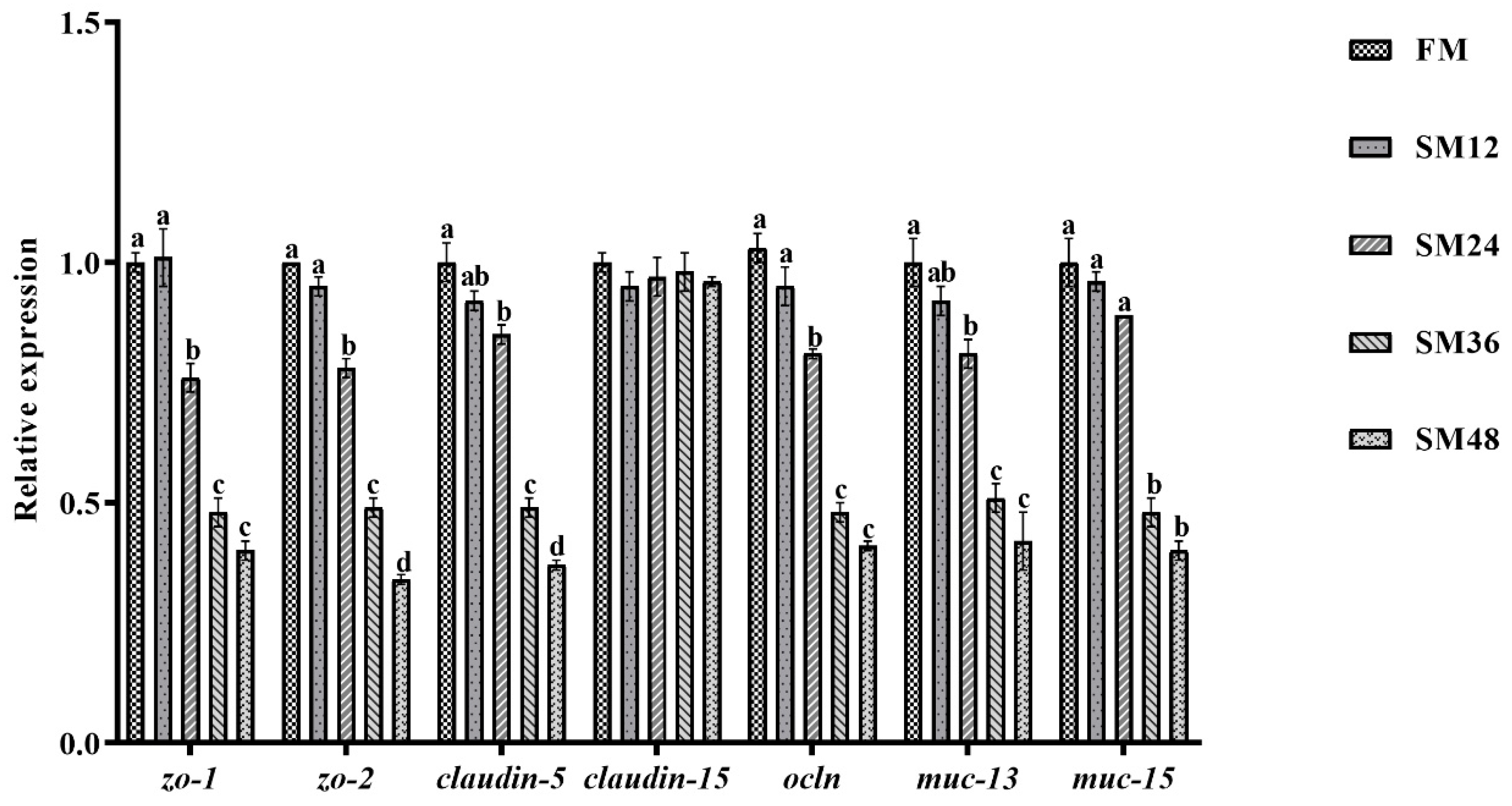
3.6. The Expression of Genes Related to Apoptosis and Tight Junction in Intestine
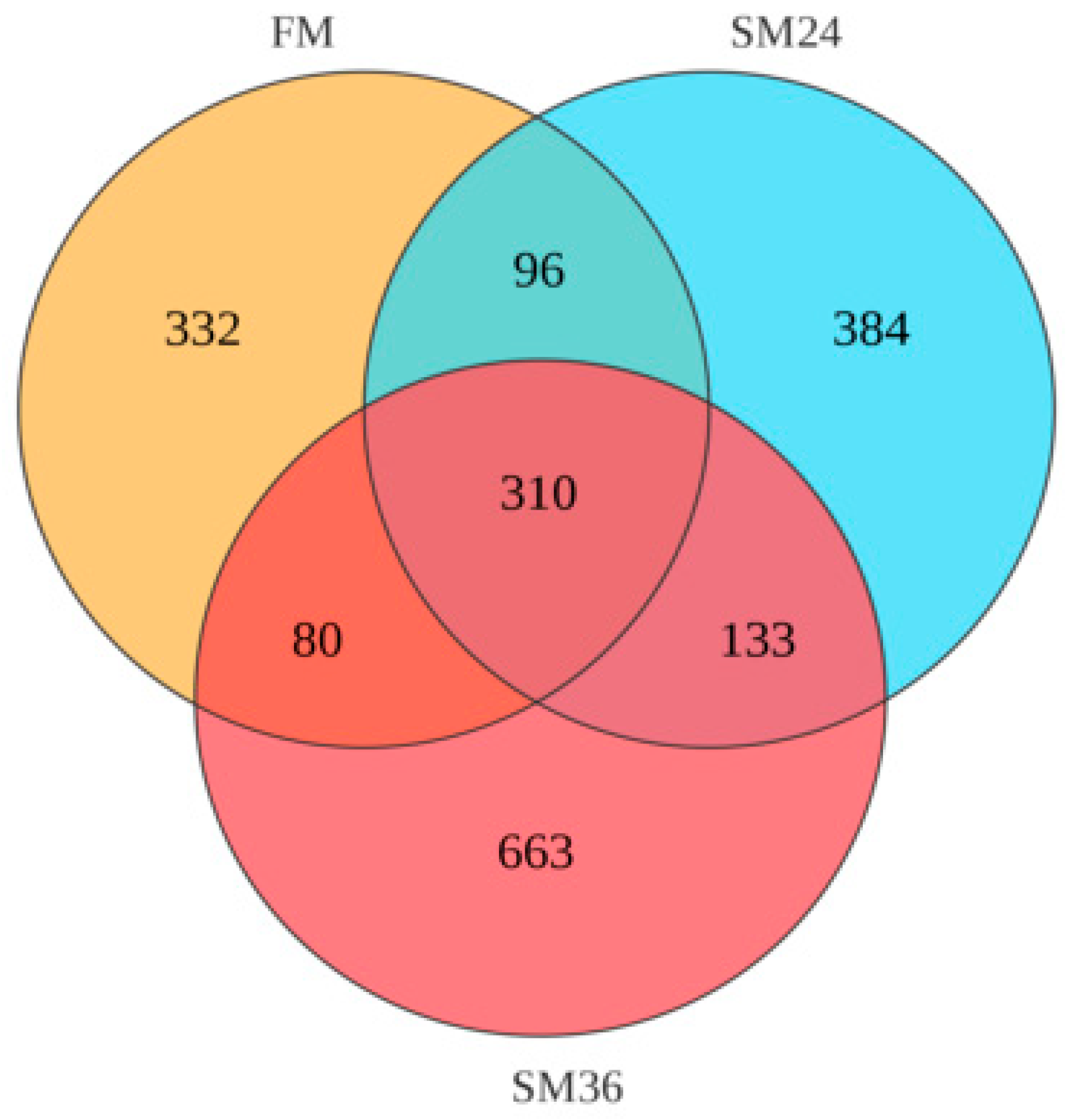
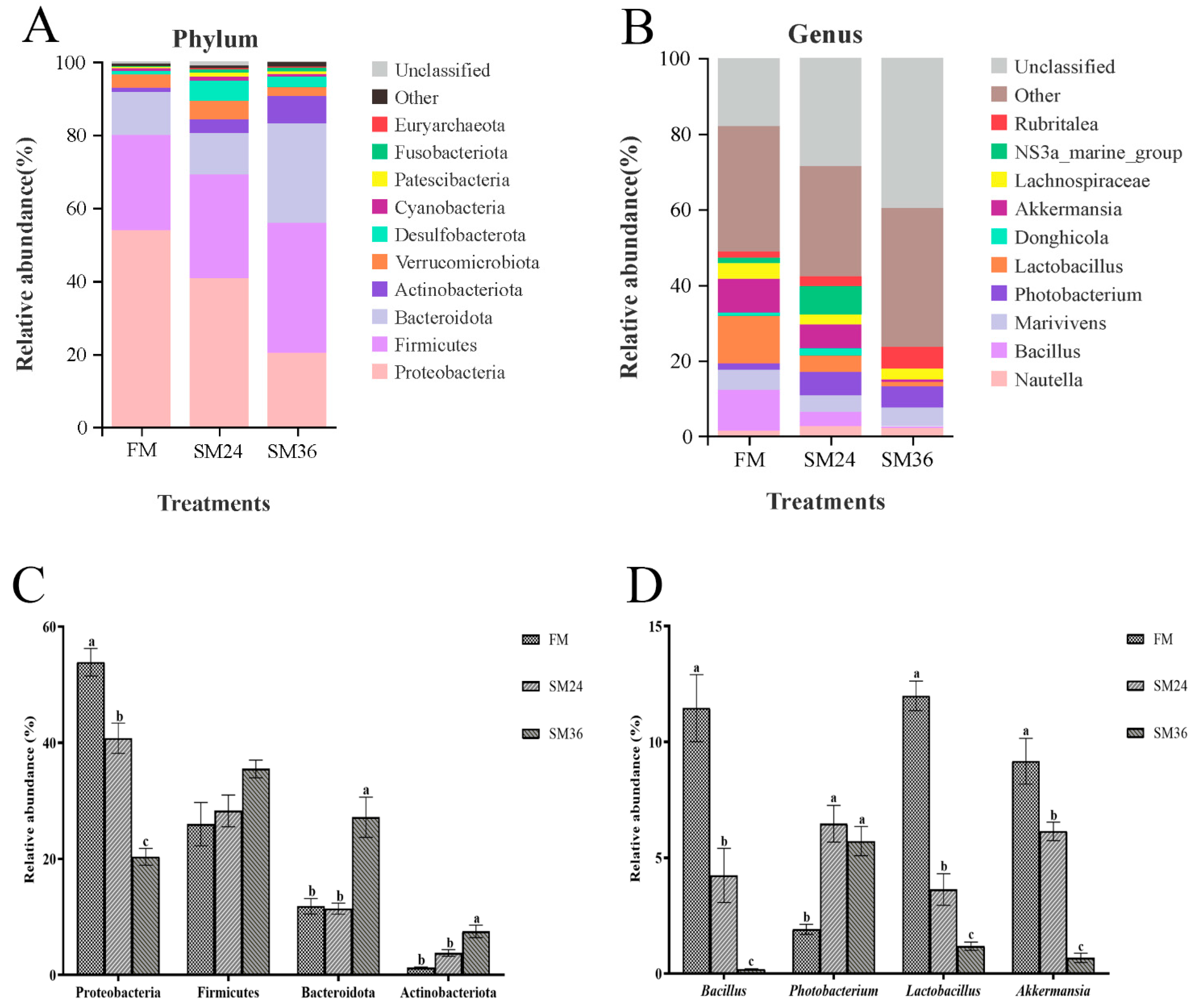
3.7. Intestinal Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyd, C.E.; D’Abramo, L.R.; Glencross, B.D.; Huyben, D.C.; Juarez, L.M.; Lockwood, G.S.; McNevin, A.A.; Tacon, A.G.; Teletchea, F.; Tomasso, J.R., Jr. Achieving sustainable aquaculture: Historical and current perspectives and future needs and challenges. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2020, 51, 578–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Xu, J.; Ma, S.; Liang, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, D.; Xue, M. C1 gas protein: A potential protein substitute for advancing aquaculture sustainability. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 1179–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.E. The ethics and sustainability of capture fisheries and aquaculture. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2016, 29, 35–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorakis, K. Ethical issues in aquaculture production. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2010, 23, 345–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriaga-Hernández, D.; Hernández, C.; Martínez-Montaño, E.; Ibarra-Castro, L.; Lizárraga-Velázquez, E.; Leyva-López, N.; Chávez-Sánchez, M.C. Fish meal replacement by soybean products in aquaculture feeds for white snook, Centropomus viridis: Effect on growth, diet digestibility, and digestive capacity. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Han, B.; Xu, J.; Zhu, J.; Hu, J.; Wan, W.; Miao, S. Replacement of fishmeal with soybean meal affects the growth performance, digestive enzymes, intestinal microbiota and immunity of Carassius auratus gibelio♀ × Cyprinus carpio♂. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Rahimnejad, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, K.; Song, K.; Wang, L.; Mai, K. Substituting fish meal with soybean meal in diets for Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus): Effects on growth, digestive enzymes activity, gut histology, and expression of gut inflammatory and transporter genes. Aquaculture 2018, 483, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Quesada, J.P.; Viana, M.T.; Rombenso, A.N.; Guerrero-Rentería, Y.; Nomura-Solís, M.; Gomez-Calle, V.; Lazo, J.P.; Mata-Sotres, J.A. Enteritis induction by soybean meal in Totoaba macdonaldi diets: Effects on growth performance, digestive capacity, immune response and distal intestine integrity. Aquaculture 2018, 495, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Wang, B.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y. Integrative transcriptomic and microRNAomic profiling reveals immune mechanism for the resilience to soybean meal stress in fish gut and liver. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhong, L.; Chi, S.; Chu, W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y. Sodium butyrate supplementation in high-soybean meal diets for juvenile rice field eel (Monopterus albus): Effects on growth, immune response and intestinal health. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volatiana, J.A.; Sagada, G.; Xu, B.; Zhang, J.; Ng, W.K.; Shao, Q. Effects of butyrate glycerides supplementation in high soybean meal diet on growth performance, intestinal morphology and antioxidative status of juvenile black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, N.; Xu, X.; Xu, B. Soya-saponins induce intestinal inflammation and barrier dysfunction in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 77, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Dai, J.; Yang, P.; Hu, H.; Ai, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mai, K. The protective role of glutamine on enteropathy induced by high dose of soybean meal in turbot, Scophthalmus maximus L. Aquaculture 2018, 497, 510–519. Aquaculture 2018, 497, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, X.; Feng, L.; Jiang, W.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, S.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X. Soybean glycinin disrupted intestinal structural integrity related to aggravation of apoptosis and downregulated transcription of tight junction proteins in the intestine of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A.; Xu, W.; Chen, K.; He, Z.; Hu, Y. Effects of replacing fishmeal with soybean meal on the immune and antioxidant capacity, and intestinal metabolic functions of red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 149, 109600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Morón, E.; Abad-Jiménez, Z.; Martinez de Maranon, A.; Iannantuoni, F.; Escribano-López, I.; López-Domènech, S.; Salom, C.; Jover, A.; Mora, V.; Roldan, I. Relationship between oxidative stress, ER stress, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes: The battle continues. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, N.; Talwar, P.; Parimisetty, A.; Lefebvre d’Hellencourt, C.; Ravanan, P. A molecular web: Endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhang, M.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sui, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, C. Comparison of the performance of raw and Lactobacillus paracasei fermented soybean meal in diets for turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.): Growth, intestinal morphology, apoptosis, tight junction, and microbiota. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Shao, C.; He, Z.; Chang, R.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y. Soybean meal-refined treatment mitigated high soybean meal diet-induced oxidative damage in the gut of crayfish via microbial metabolic function remodeling. Aquaculture 2025, 601, 742286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, A.; Peng, C.; Xie, R.; Wang, Z.; Tan, B.; Wang, T.; Zhang, W. Effects of fermented soybean meal substitution for fish meal on intestinal flora and intestinal health in pearl gentian grouper. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1194071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Zeng, C.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Shao, J.; Zhao, W. TLR2/TLR5 signaling and gut microbiota mediate soybean-meal-induced enteritis and declined growth and antioxidant capabilities in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton, S.; Wan, A.; Murphy, K.; Collins, F.; Ahern, G.; Sugrue, I.; Busca, K.; Egan, F.; Muller, N.; Whooley, J. Replacing fishmeal with plant protein in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) diets by supplementation with fish protein hydrolysate. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Song, Z.; Xia, C.; Mu, H.; Chen, X.; Cheng, H.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhang, L. Comparative evaluation of soybean meal vs. extruded soybean meal as a replacer for fishmeal in diets of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus): Effects on growth performance and muscle quality. Aquaculture 2024, 578, 740136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Su, Z.; Xia, C.; Li, L.; Song, Z.; Mu, H.; Cheng, H.; Xu, J.; Dong, Z.; Yan, B. Effects of β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate inclusion on growth performance and fillet quality of olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus fed low fishmeal based diets. Aquaculture 2025, 609, 742790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, B.R.; Song, J.H.; Park, B.S.; Kim, D.; Kwak, J.H.; Do, H.K.; Kim, A.R.; Kim, W.J.; Song, S.K. Distinct immune tones are established by Lactococcus lactis BFE920 and Lactobacillus plantarum FGL0001 in the gut of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 55, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Bai, N.; Zhang, Y.; Krogdahl, Å. Soybean meal induces enteritis in turbot Scophthalmus maximus at high supplementation levels. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Dai, J.; Yang, P.; Xu, W.; Ai, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mai, K. Sodium butyrate supplementation in high-soybean meal diets for turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.): Effects on inflammatory status, mucosal barriers and microbiota in the intestine. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; He, R.; Xu, W.; Mai, K.; He, G. Effects of soybean meal fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum P8 on growth, immune responses, and intestinal morphology in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 2016, 464, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimnejad, S.; Lu, K.; Wang, L.; Song, K.; Mai, K.; Davis, D.A.; Zhang, C. Replacement of fish meal with Bacillus pumillus SE5 and Pseudozyma aphidis ZR1 fermented soybean meal in diets for Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokou, F.; Sarropoulou, E.; Cotou, E.; Rigos, G.; Henry, M.; Alexis, M.; Kentouri, M. Effects of fish meal replacement by a soybean protein on growth, histology, selected immune and oxidative status markers of gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2015, 46, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; El Basuini, M.F.; Hossain, M.S.; Nhu, T.H.; Dossou, S.; Moss, A.S. Effects of dietary supplementation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus or/and Lactococcus lactis on the growth, gut microbiota and immune responses of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 49, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doan, H.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Dawood, M.A.; Chitmanat, C.; Tayyamath, K. Effects of Cordyceps militaris spent mushroom substrate and Lactobacillus plantarum on mucosal, serum immunology and growth performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Luo, D. Application of haematology parameters for health management in fish farms. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 704–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunji, J.; Kloas, W.; Wirth, M.; Neumann, N.; Pietsch, C. Effect of housefly maggot meal (magmeal) diets on the performance, concentration of plasma glucose, cortisol and blood characteristics of Oreochromis niloticus fingerlings. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zan, S.; Meng, X.; Zhang, F. Probiotic-fermented blueberry pomace alleviates obesity and hyperlipidemia in high-fat diet C57BL/6J mice. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Meng, X.; Duan, P.; Sun, L.; Sun, Y. Effect of dietary lipid level on the growth performance, feed utilization, body composition and blood chemistry of juvenile starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus). Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; He, J.; Zhan, T.; Li, Y.; Yan, M.; Huang, Y. Effects of antimicrobial peptides on serum biochemical parameters, antioxidant activity and non-specific immune responses in Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Ruan, G.; Fan, W.; Wang, Q.; Fang, L.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y. Immune response to acute heat stress in the intestine of the red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 100, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Qian, P.; Wu, C.; Xie, Y.; Yang, W.; Song, R.; Wu, J.; Ye, J. Effects of dietary pantothenic acid on growth, antioxidant ability and innate immune response in juvenile black carp. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrells, C.; Williams, P.; Southgate, P.; Crampton, V. Immunological, physiological and pathological responses of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to increasing dietary concentrations of soybean proteins. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1999, 72, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravi, S.; Rahimnejad, S.; Herault, M.; Fournier, V.; Lee, C.R.; Bui, H.T.D.; Jeong, J.B.; Lee, K.J. Effects of protein hydrolysates supplementation in low fish meal diets on growth performance, innate immunity and disease resistance of red sea bream Pagrus major. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 45, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rašković, B.; Stanković, M.; Marković, Z.; Poleksić, V. Histological methods in the assessment of different feed effects on liver and intestine of fish. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 56, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Krogdahl, Å.; Penn, M.; Thorsen, J.; Refstie, S.; Bakke, A.M. Important antinutrients in plant feedstuffs for aquaculture: An update on recent findings regarding responses in salmonids. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yuan, X.; Luo, H.; Shao, J.; Chen, X. High percentage of dietary soybean meal inhibited growth, impaired intestine healthy and induced inflammation by TLR-MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogdahl, Å.; Gajardo, K.; Kortner, T.M.; Penn, M.; Gu, M.; Berge, G.M.; Bakke, A.M. Soya saponins induce enteritis in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3887–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Song, K. Effects of substituting fishmeal with soybean meal on growth performance and intestinal morphology in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Aquac. Rep. 2017, 5, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tian, Y.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, B. Dietary gamma-aminobutyric acid ameliorates growth impairment and intestinal dysfunction in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) fed a high soybean meal diet. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornick, S.; Tawiah, A.; Chadee, K. Roles and regulation of the mucus barrier in the gut. Tissue Barriers 2015, 3, e982426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Bhavan, P.S.; Seenivasan, C.; Shanthi, R.; Muralisankar, T. Replacement of fishmeal with Spirulina platensis, Chlorella vulgaris and Azolla pinnata on non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidant activities of Macrobrachium rosenbergii. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2014, 67, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, J.; Du, Z.; Kong, Y. An evaluation of replacing fish meal with fermented soybean meal in the diet of Macrobrachium nipponense: Growth, nonspecific immunity, and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 44, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Liu, C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Mai, K.; He, G. Effects of dietary raw or Enterococcus faecium fermented soybean meal on growth, antioxidant status, intestinal microbiota, morphology, and inflammatory responses in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 100, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmer, I.L.; Willemsen, N.; Hilal, N.; Bartelt, A. A guide to understanding endoplasmic reticulum stress in metabolic disorders. Mol. Metab. 2021, 47, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yang, M.; Liu, D.; Pan, M.; Wu, C.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Dietary taurine modulates hepatic oxidative status, ER stress and inflammation in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) fed high carbohydrate diets. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 109, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liang, J.; Chen, F.; Tang, X.; Liao, L.; Liu, Q.; Luo, J.; Du, Z.; Li, Z.; Luo, W. High carbohydrate diet induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress, promoted inflammation and apoptosis, impaired intestinal barrier of juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 119, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, N.; He, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhou, C.; Du, Y.; Du, Z.; Su, X.; Zhang, M. Xylanase improves the intestinal barrier function of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed with soybean (Glycine max) meal. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, J. Growth performance, plasma components, and intestinal barrier in grouper (Epinephelus coioides) are altered by dietary fish meal replacement with extruded soybean meal. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrera, M.I.; Galdames, J.A.; Jimenez-Reyes, M.F.; Reyes, A.E.; Avendaño-Herrera, R.; Romero, J.; Feijóo, C.G. Soybean meal induces intestinal inflammation in zebrafish larvae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urán, P.; Gonçalves, A.; Taverne-Thiele, J.; Schrama, J.; Verreth, J.; Rombout, J. Soybean meal induces intestinal inflammation in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 25, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Liu, Y.; Ou, W.; Dai, J.; Ai, Q.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K.; Zhang, Y. The protective role of daidzein in intestinal health of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) fed soybean meal-based diets. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Yu, H.; Liang, X.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, M. Dietary butylated hydroxytoluene improves lipid metabolism, antioxidant and anti-apoptotic response of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 72, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadi, A.; Banan, A.; Fields, J.; Keshavarzian, A. Intestinal barrier: An interface between health and disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 18, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.; Turner, J.R. Cell biology of tight junction barrier regulation and mucosal disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a029314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, T.; Furuse, M. Tight junction structure and function revisited. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T. Regulation of the intestinal barrier by nutrients: The role of tight junctions. Anim. Sci. J. 2020, 91, e13357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Shi, F.; Zhu, J.; Shao, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhou, G.; Wu, H.; She, J.; Shi, W. Piperine, a functional food alkaloid, exhibits inhibitory potential against TNBS-induced colitis via the inhibition of IκB-α/NF-κB and induces tight junction protein (claudin-1, occludin, and ZO-1) signaling pathway in experimental mice. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2020, 39, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Deng, J.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Wu, J.; Xiao, D.; Darko, K.O.; Huang, Y.; Tao, T.; Peng, M. Vitamin A inhibits the action of LPS on the intestinal epithelial barrier function and tight junction proteins. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempstock, W.; Nagata, N.; Ishizuka, N.; Hayashi, H. The effect of claudin-15 deletion on cationic selectivity and transport in paracellular pathways of the cecum and large intestine. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.; DeCoffe, D.; Molcan, E.; Gibson, D.L. Diet-induced dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota and the effects on immunity and disease. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1095–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celi, P.; Cowieson, A.; Fru-Nji, F.; Steinert, R.; Kluenter, A.M.; Verlhac, V. Gastrointestinal functionality in animal nutrition and health: New opportunities for sustainable animal production. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 234, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, H.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Qi, M.; Ji, H. Dietary nano-selenium alleviated intestinal damage of juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) induced by high-fat diet: Insight from intestinal morphology, tight junction, inflammation, anti-oxidization and intestinal microbiota. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 8, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Tan, K.; Gong, Q.; Peng, Y.; Liang, M.; Xu, P.; Liang, X.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Cai, X. Positive effects of Lithospermum erythrorhizon extract added to high soybean meal diet on growth, intestinal antioxidant capacity, intestinal microbiota, and metabolism of pearl gentian grouper. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 39, 102500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, D.Y. Microbial diversity in the intestine of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2013, 414, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammes, F.; Reveco, F.E.; Romarheim, O.H.; Landsverk, T.; Mydland, L.T.; Øverland, M. Candida utilis and Chlorella vulgaris counteract intestinal inflammation in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, J.; Hu, J.; Dong, X.; Sun, L. Dietary soybean meal affects intestinal homoeostasis by altering the microbiota, morphology and inflammatory cytokine gene expression in northern snakehead. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijs, Y.; Bech, P.K.; Vazquez-Albacete, D.; Bentzon-Tilia, M.; Sonnenschein, E.C.; Gram, L.; Zhang, S.D. Marine Proteobacteria as a source of natural products: Advances in molecular tools and strategies. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 1333–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalm, N.D.; Groisman, E.A. Navigating the gut buffet: Control of polysaccharide utilization in Bacteroides spp. Trends Microbiol. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, S.; Veltman, K.; Cichon, C.; Sonnenborn, U.; Schmidt, M.A. Differential targeting of the E-Cadherin/β-Catenin complex by gram-positive probiotic lactobacilli improves epithelial barrier function. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujio-Vejar, S.; Vasquez, Y.; Morales, P.; Magne, F.; Vera-Wolf, P.; Ugalde, J.A.; Navarrete, P.; Gotteland, M. The gut microbiota of healthy Chilean subjects reveals a high abundance of the phylum Verrucomicrobia. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, N.; Amal, M.N.A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Saad, M.Z.; Nasruddin, N.S.; Al-saari, N.; Mino, S.; Sawabe, T. Vibriosis in cultured marine fishes: A review. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Long, Z.; Qin, H.; Lin, H.; Zhou, S.; Kong, L.; Ma, J.; Lin, Y. Dietary supplementation of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides alleviates soybean meal-induced enteritis in spotted sea bass Lateolabrax maculatus. Anim. Nutr. 2025, 20, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Mai, K.; He, G. Resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress and inflammatory response in turbot fed with soybean meal based diet. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 91, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredients | FM | SM12 | SM24 | SM36 | SM48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fishmeal | 60.00 | 52.80 | 45.60 | 38.40 | 31.20 |
| Soybean meal | 0.00 | 10.38 | 20.77 | 31.15 | 41.54 |
| Wheat meal | 24.10 | 18.02 | 13.25 | 8.48 | 3.70 |
| Wheat gluten | 3.50 | 4.50 | 5.50 | 6.50 | 7.50 |
| α-Starch | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Fish oil | 2.00 | 3.70 | 4.10 | 4.50 | 4.90 |
| Soybean lecithin | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| Premix 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Attractant 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Methionine | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.32 |
| Lysine | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 0.44 |
| Others 3 | 1.90 | 1.90 | 1.90 | 1.90 | 1.90 |
| Proximate composition | |||||
| Crude protein | 50.24 | 50.35 | 50.28 | 50.13 | 50.18 |
| Crude lipid | 9.93 | 9.91 | 9.91 | 9.91 | 9.90 |
| Ash | 14.83 | 13.69 | 13.87 | 12.71 | 12.45 |
| Item | FM | SM12 | SM24 | SM36 | SM48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP (g/L) | 67.57 ± 0.72 a | 61.42 ± 1.00 b | 55.52 ± 0.63 c | 51.53 ± 1.15 c | 49.27 ± 0.86 d |
| ALB (g/L) | 14.06 ± 0.47 | 14.58 ± 0.31 | 14.15 ± 0.32 | 14.12 ± 0.60 | 14.51 ± 0.45 |
| GLU (mmol/L) | 3.06 ± 0.07 c | 2.93 ± 0.12 c | 3.11 ± 0.18 c | 4.13 ± 0.12 b | 6.03 ± 0.10 a |
| TG (mmol/L) | 3.03 ± 0.11 c | 3.27 ± 0.16 c | 4.29 ± 0.11 b | 4.75 ± 0.12 b | 5.42 ± 0.17 a |
| TC (mmol/L) | 6.52 ± 0.03 | 6.42 ± 0.13 | 6.31 ± 0.13 | 6.29 ± 0.20 | 6.35 ± 0.16 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 2.06 ± 0.05 a | 2.05 ± 0.09 a | 1.66 ± 0.04 b | 1.54 ± 0.07 b | 1.22 ± 0.03 c |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.67 ± 0.16 b | 3.49 ± 0.25 b | 3.63 ± 0.21 b | 3.50 ± 0.08 b | 4.76 ± 0.13 a |
| LZM (U/mL) | 207.06 ± 11.69 a | 188.30 ± 11.41 a | 146.75 ± 3.25 b | 130.10 ± 5.45 b | 127.50 ± 6.29 b |
| Item | FM | SM12 | SM24 | SM36 | SM48 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-AOC (U/mg prot) | 4.99 ± 0.09 a | 4.70 ± 0.09 ab | 4.59 ± 0.03 b | 3.37 ± 0.12 c | 2.52 ± 0.06 d |
| CAT (U/mg prot) | 4.39 ± 0.39 | 4.74 ± 0.33 | 4.78 ± 0.15 | 4.78 ± 0.26 | 4.88 ± 0.10 |
| SOD (U/mg prot) | 125.05 ± 2.79 a | 122.79 ± 2.30 ab | 121.91 ± 1.77 ab | 112.13 ± 2.16 bc | 103.22 ± 3.74 c |
| MDA (nmol/mg prot) | 1.74 ± 0.10 c | 1.69 ± 0.07 c | 2.09 ± 0.12 c | 2.76 ± 0.07 b | 3.61 ± 0.12 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Dong, Z.; Mu, H. Effects of Replacing Fishmeal with Soybean Meal on Intestinal Histology, Antioxidation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Inflammation, Tight Junction, and Microbiota in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Animals 2025, 15, 2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192895
Su Z, Zhang Y, Wei C, Zhang F, Wang L, Li Y, Zhang Z, Xu J, Dong Z, Mu H. Effects of Replacing Fishmeal with Soybean Meal on Intestinal Histology, Antioxidation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Inflammation, Tight Junction, and Microbiota in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Animals. 2025; 15(19):2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192895
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Zhenxia, Yanjie Zhang, Chaoqing Wei, Fengxiang Zhang, Lei Wang, Yaxuan Li, Zhengqiu Zhang, Jianhe Xu, Zhiguo Dong, and Hua Mu. 2025. "Effects of Replacing Fishmeal with Soybean Meal on Intestinal Histology, Antioxidation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Inflammation, Tight Junction, and Microbiota in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)" Animals 15, no. 19: 2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192895
APA StyleSu, Z., Zhang, Y., Wei, C., Zhang, F., Wang, L., Li, Y., Zhang, Z., Xu, J., Dong, Z., & Mu, H. (2025). Effects of Replacing Fishmeal with Soybean Meal on Intestinal Histology, Antioxidation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Inflammation, Tight Junction, and Microbiota in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Animals, 15(19), 2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192895






