Construction and Characterization of Immortalized Skin Fibroblasts from Milu Deer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Collection
2.2. Primary Culture and Subculture
2.3. Lentivirus Production and Target Cell Transduction
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Karyotyping
2.7. Growth Curve Analysis
2.8. Cell-Cycle Detection
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
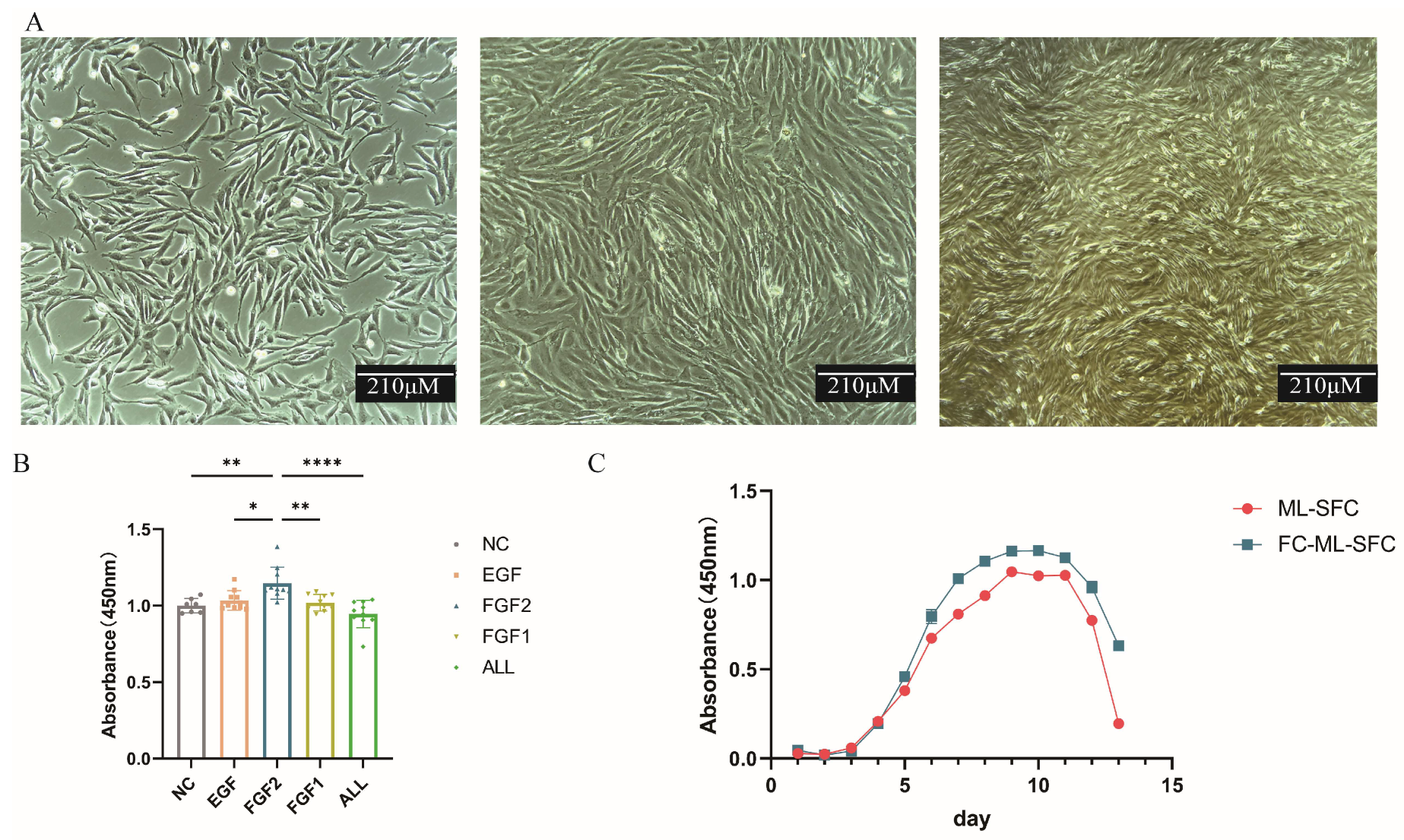
3.1. Culture and Cryopreservation of Primary Milu Skin Fibroblast Cells (ML-SFC)
3.2. Identification of ML-SFC
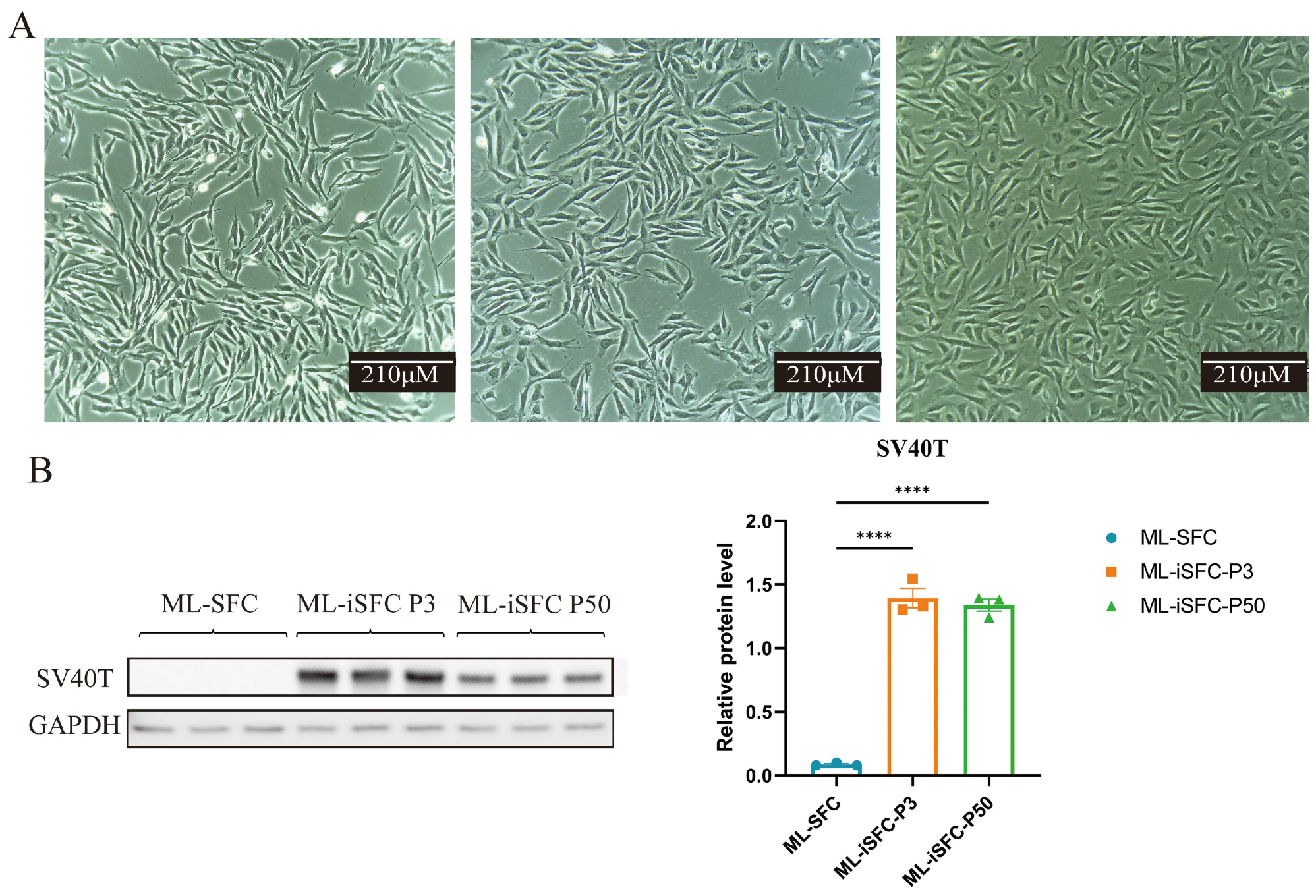
3.3. Establishment of Immortalized Milu Skin Fibroblasts (ML-iSFC)
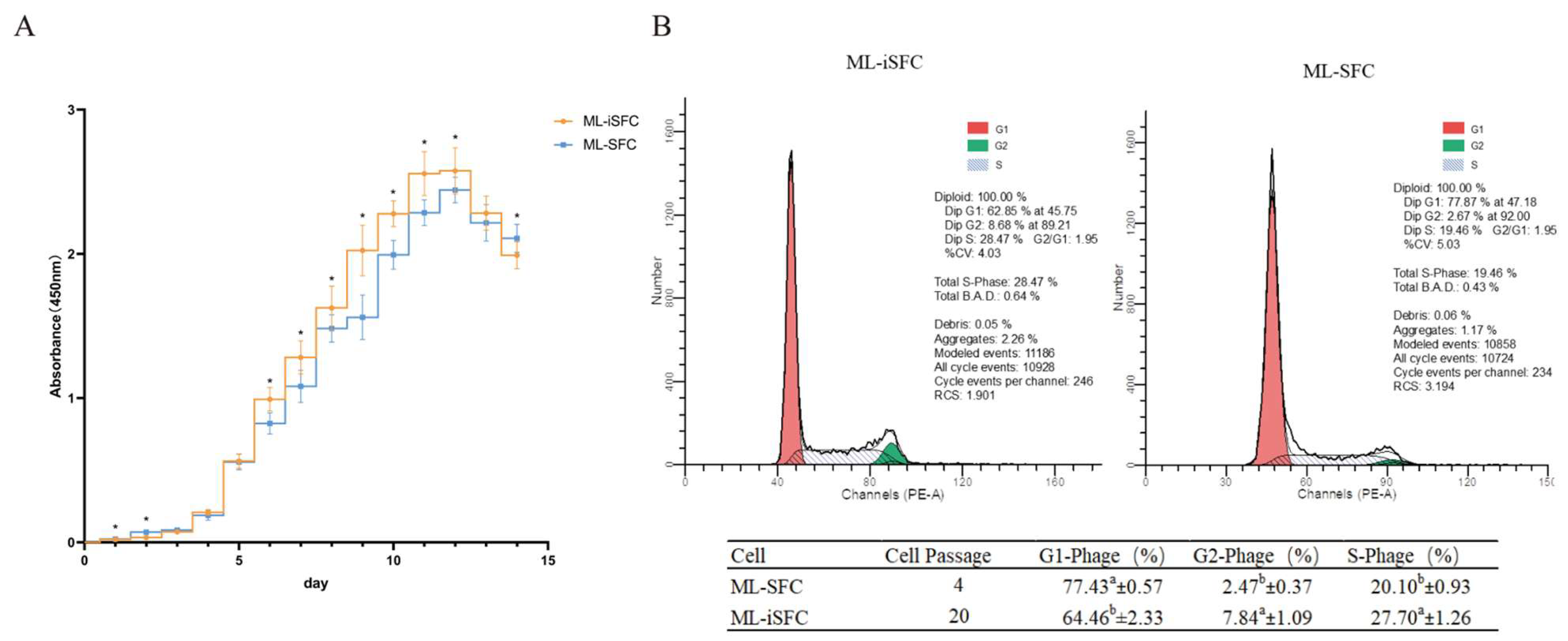
3.4. Growth Characteristics Analysis of ML-iSFC Cell Lines
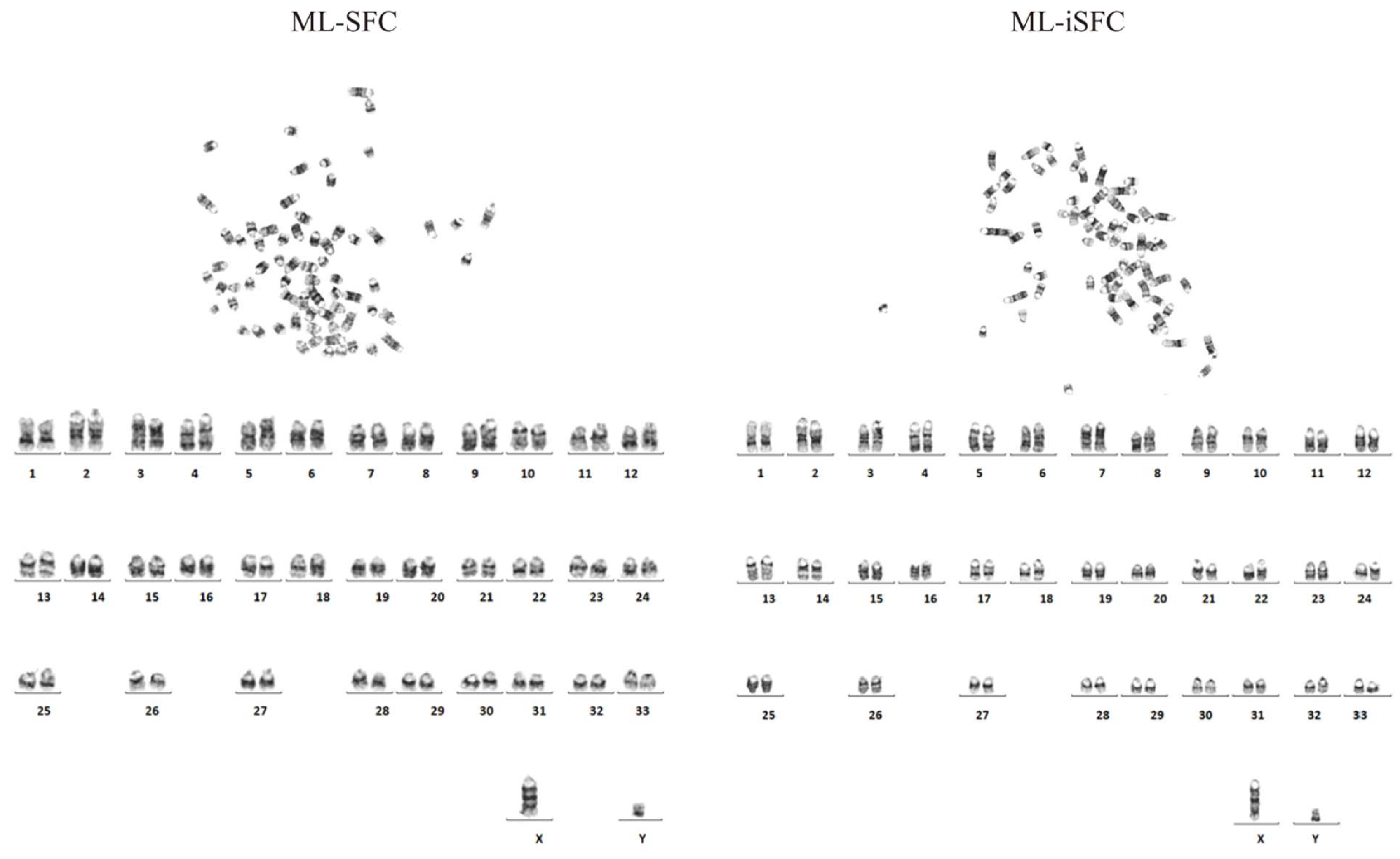
3.5. Karyotype Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simon, D. Conservation of animal genetic resources. Reviewing the problem. Ann. Genet. Sel. Anim. 1982, 14, 557–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.J.; Kim, M.K.; Jang, G.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, S.G.; Park, J.E.; Park, K.; Park, C.; Sohn, S.H.; Kim, D.Y.; et al. Cloning endangered gray wolves (Canis lupus) from somatic cells collected postmortem. Theriogenology 2008, 70, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, B.; Xiao, K.; Tan, C.; Du, H. Establishment and characterization of a cell line derived from fin of the endangered Yangtze sturgeon (Acipenser dabryanus). Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2020, 56, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Li, C.J.; Yue, H.M.; Du, H.; Yang, X.G.; Yoshino, T.; Hayashida, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Wei, Q.W. Establishment of intraperitoneal germ cell transplantation for critically endangered Chinese sturgeon Acipenser sinensis. Theriogenology 2017, 94, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cui, M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, G.; Feng, J.; Lian, Z. Transgenic cloned sheep overexpressing ovine toll-like receptor 4. Theriogenology 2013, 80, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.R.; Zhong, B.S.; Jia, R.X.; Wan, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Fan, Y.X.; Wang, L.Z.; You, J.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, F. Production of myostatin-targeted goat by nuclear transfer from cultured adult somatic cells. Theriogenology 2013, 79, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lan, H.; Shao, M.; Yu, Y.; Quan, F.; Zhang, Y. Production of transgenic cattle highly expressing human serum albumin in milk by phiC31 integrase-mediated gene delivery. Transgenic Res. 2015, 24, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.J.; Kim, D.H.; Hwang, I.S.; Kim, D.E.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, K.; Im, G.S.; Lee, J.W.; Hwang, S. Generation of alpha-1,3-galactosyltransferase knocked-out transgenic cloned pigs with knocked-in five human genes. Transgenic Res. 2017, 26, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.S.; Smith, T.J.; Blieden, T.M.; Phipps, R.P. Fibroblasts as sentinel cells—Synthesis of chemokines and regulation of inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, I.A.; Hewitson, T.D. Fibroblast differentiation in wound healing and fibrosis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2007, 257, 143–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.S.; Zhu, F.F.; Yong, J.; Zhang, P.B.; Hou, P.P.; Li, H.G.; Jiang, W.; Cai, J.; Liu, M.; Cui, K.; et al. Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Adult Rhesus Monkey Fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, L.; Fan, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.Q.; Kaback, D.; Oudiz, J.; Patrick, T.; Yee, S.P.; Tian, X.C.; et al. Establishment of Bovine-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Zhang, S.H.; Zou, G.Y.; An, J.H.; Li, Y.; Lin, D.N.; Wang, D.H.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.S.; Feng, T.Y.; et al. Generation and characterization of giant panda induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadn7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.W.; Go, R.E.; Lee, G.A.; Kim, C.D.; Chun, Y.J.; Choi, K.C. Immortalization of human corneal epithelial cells using simian virus 40 large T antigen and cell characterization. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2016, 78, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seridi, N.; Hamidouche, M.; Belmessabih, N.; El Kennani, S.; Gagnon, J.; Martinez, G.; Coutton, C.; Marchal, T.; Chebloune, Y. Immortalization of primary sheep embryo kidney cells. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2021, 57, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Cassar, L.; Pinto, A.; Li, H. Mechanisms of cell immortalization mediated by EB viral activation of telomerase in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, T.B.; Hermes, R.; Goeritz, F.; Appeltant, R.; Colleoni, S.; de Mori, B.; Diecke, S.; Drukker, M.; Galli, C.; Hayashi, K.; et al. The ART of bringing extinction to a freeze—History and future of species conservation, exemplified by rhinos. Theriogenology 2021, 169, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, R.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S.; Zou, H.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, Y. Establishment of Immortalized Yak Ruminal Epithelial Cell Lines by Lentivirus-Mediated SV40T and hTERT Gene Transduction. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8128028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.A.; O’Hare, M.J.; Reiser, J.; Coward, R.J.; Inward, C.D.; Farren, T.; Xing, C.Y.; Ni, L.; Mathieson, P.W.; Mundel, P. A conditionally immortalized human podocyte cell line demonstrating nephrin and podocin expression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Cui, L.; Dong, J.; Meng, X.; Qian, C.; Wang, H. Immortalization effect of SV40T lentiviral vectors on canine corneal epithelial cells. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, H.L.; Banga, S.S.; Dasgupta, T.; Houghton, J.; Hubbard, K.; Jha, K.K.; Kim, S.H.; Lenahan, M.; Pang, Z.; Pardinas, J.R.; et al. SV40-mediated immortalization of human fibroblasts. Exp. Gerontol. 1996, 31, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, G.J.; Green, H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J. Cell Biol. 1963, 17, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipas, J.M. SV40: Cell transformation and tumorigenesis. Virology 2009, 384, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.Q.; Szekely, L.; Klein, G.; Ringertz, N. Intranuclear redistribution of SV40T, p53, and PML in a conditionally SV40T-immortalized cell line. Exp. Cell Res. 1996, 229, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butel, J.S.; Lednicky, J.A. Response to more about: Cell and molecular biology of simian virus 40: Implications for human infections and disease. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butel, J.S.; Lednicky, J.A. Cell and molecular biology of simian virus 40: Implications for human infections and disease. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, R.; Franke, W.W.; Schiller, D.L.; Geiger, B.; Krepler, R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: Patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell 1982, 31, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulbecco, R.; Allen, R.; Okada, S.; Bowman, M. Functional changes of intermediate filaments in fibroblastic cells revealed by a monoclonal antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1915–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Liu, R.; Zhong, Z.; Shan, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hailer, F.; Bai, J. Construction and Characterization of Immortalized Skin Fibroblasts from Milu Deer. Animals 2025, 15, 2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192889
Zhang P, Liu R, Zhong Z, Shan Y, Cheng Z, Guo Q, Zhang H, Hailer F, Bai J. Construction and Characterization of Immortalized Skin Fibroblasts from Milu Deer. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192889
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Pan, Riujia Liu, Zhenyu Zhong, Yunfang Shan, Zhibin Cheng, Qingyun Guo, Hao Zhang, Frank Hailer, and Jiade Bai. 2025. "Construction and Characterization of Immortalized Skin Fibroblasts from Milu Deer" Animals 15, no. 19: 2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192889
APA StyleZhang, P., Liu, R., Zhong, Z., Shan, Y., Cheng, Z., Guo, Q., Zhang, H., Hailer, F., & Bai, J. (2025). Construction and Characterization of Immortalized Skin Fibroblasts from Milu Deer. Animals, 15(19), 2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192889





