Phase Angle as a Non-Invasive Biomarker of Fluid Overload in Canine Right Heart Failure: A Bioelectrical Impedance Approach
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Heart Failure Definition
2.3. Cardiac Disease Classification Criteria
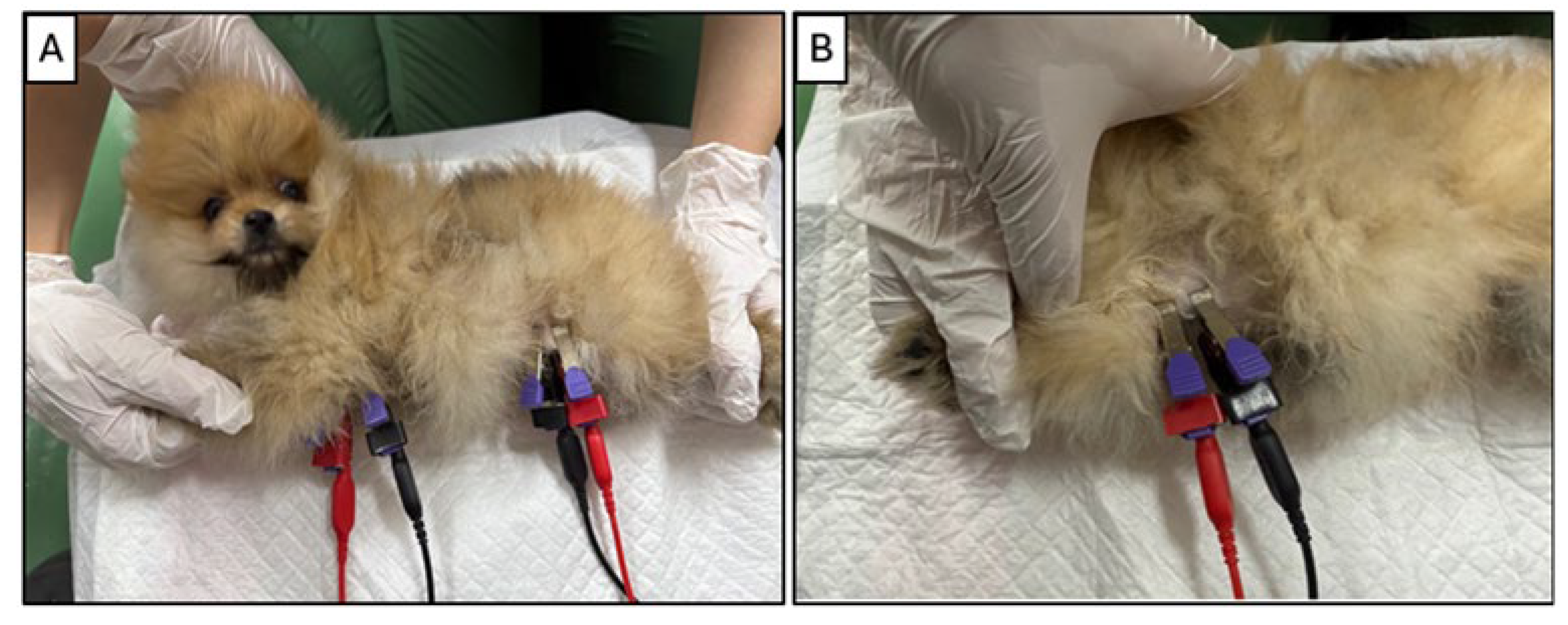
2.4. Bioelectrical Impedance Monitoring
2.5. Plasma Osmolality Assessment
2.6. Echocardiographic Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Patient Characteristics and Data Availability
- A subset of RHF and LHF cases demonstrated overlapping biventricular dysfunction and were excluded from strictly categorized comparisons.
- Several dogs exhibited systemic comorbidities not directly related to cardiac dysfunction, which could have confounded bioimpedance and biochemical results.
- Incomplete datasets were present in some individuals while PhA measurements were available, corresponding plasma biochemical parameters required to calculate osmolality (OSM) were missing.
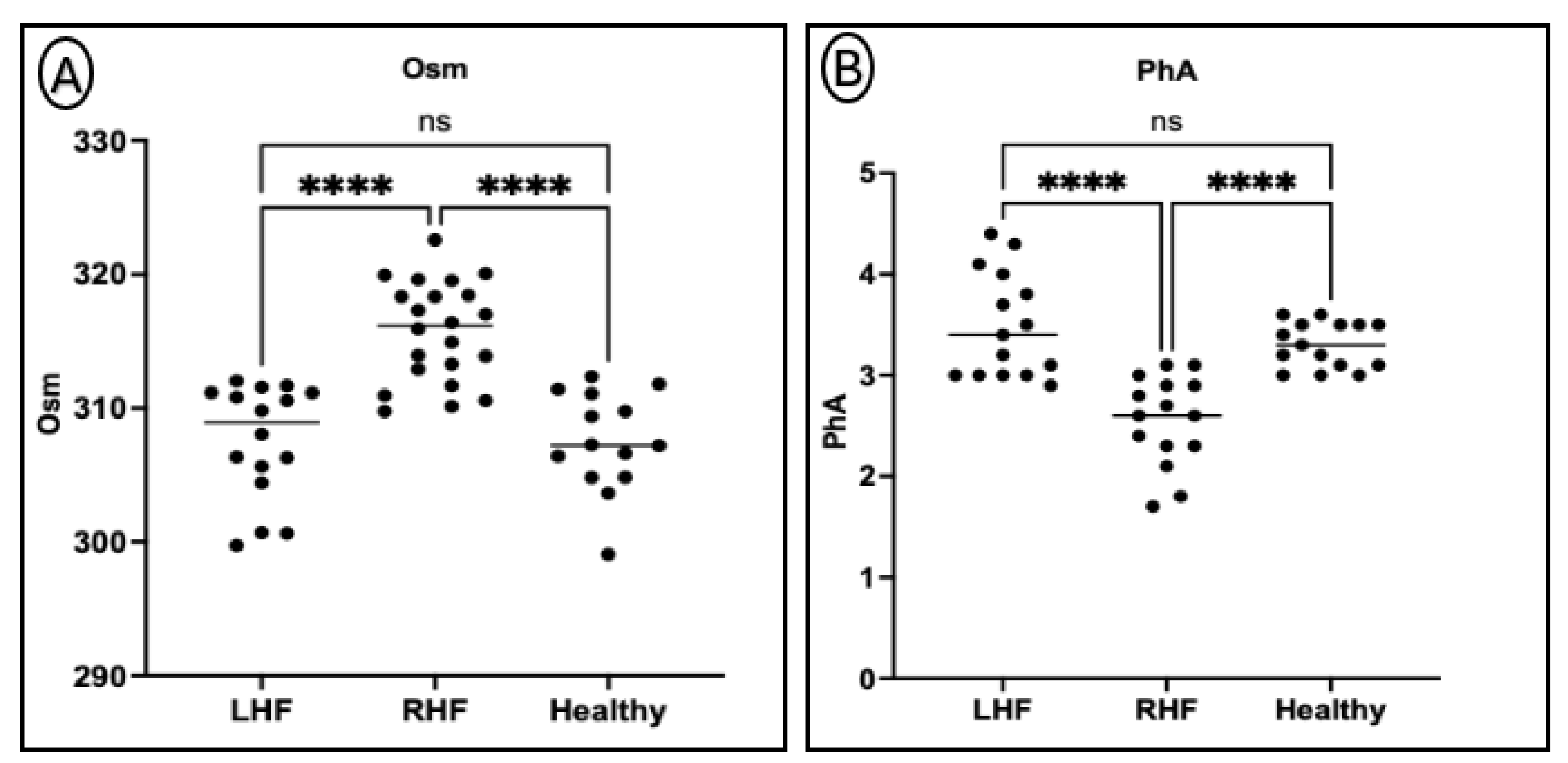
3.3. Differences in Plasma Osmolality and Phase Angle Between Groups
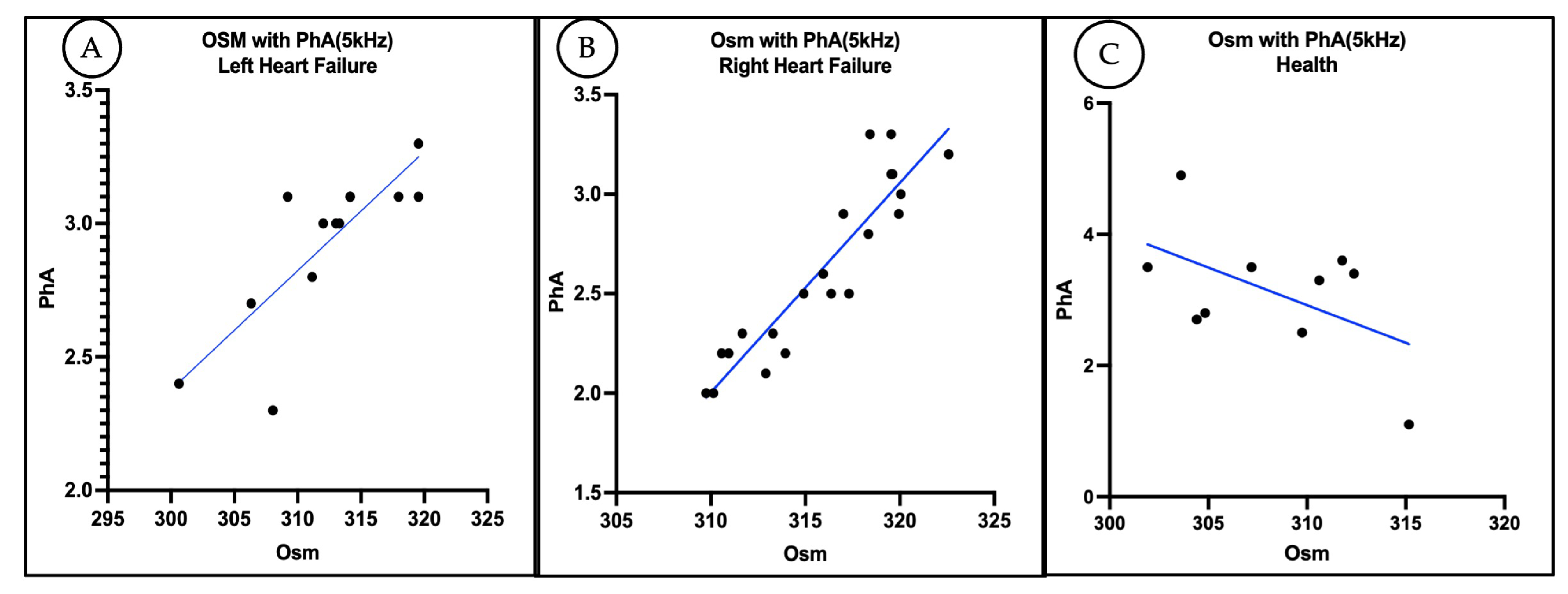
3.4. Correlation Between Plasma Osmolality and Phase Angle
3.5. Relationship Between Body Weight and Phase Angle
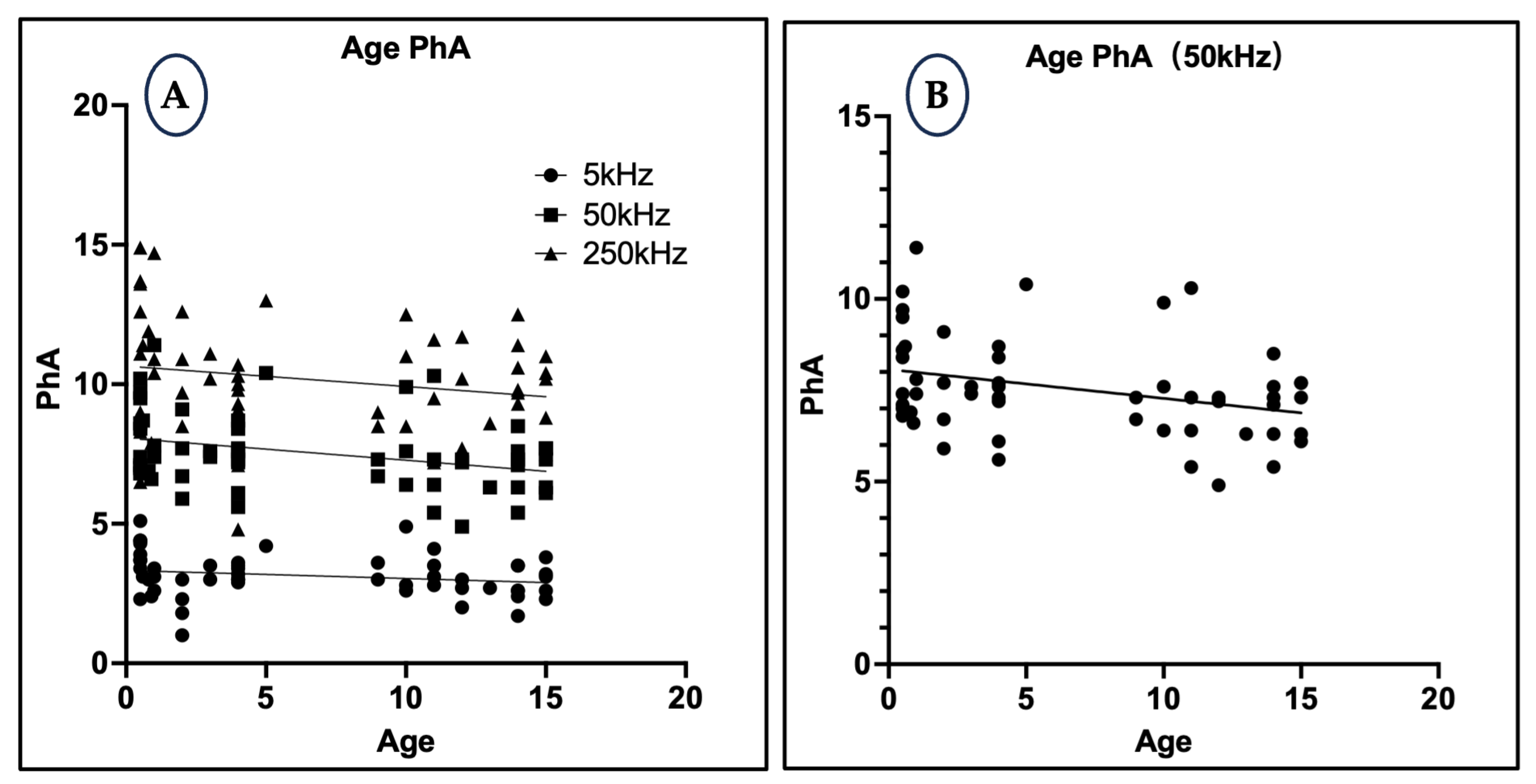
3.6. Relationship Between Age and Phase Angle
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PhA | Phase Angle |
| BIA | Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis |
| RHF | Right Heart Failure |
| LHF | Left Heart Failure |
| OSM | Osmolality |
| ECF | Extracellular Fluid |
| ICW | Intracellular Fluid |
| RAAS | Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System |
| ADH | Antidiuretic Hormone |
References
- Mialich, M.S.; Sicchieri, J.M.F.; Junior, A.A.J. Analysis of Body Composition: A Critical Review of the Use of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, K.; Wirth, R.; Neubauer, M.; Eckardt, R.; Stobäus, N. The Bioimpedance Phase Angle Predicts Low Muscle Strength, Impaired Quality of Life, and Increased Mortality in Old Patients with Cancer. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, 173.e17–173.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, S.F.; Mohktar, M.S.; Ibrahim, F. The Theory and Fundamentals of Bioimpedance Analysis in Clinical Status Monitoring and Diagnosis of Diseases. Sensors 2014, 14, 10895–10928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, G.; Paterna, S.; Di Pasquale, P.; Torres, D.; Fatta, A.; Mezzero, M.; Scaglione, R.; Licata, G. The Usefulness of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Differentiating Dyspnea Due to Decompensated Heart Failure. J. Card. Fail. 2008, 14, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Chung, H.C.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.-J.; Chang, J.W.; Lee, J.S. Relationship between Extracellular Water Fraction of Total Body Water Estimated by Bioimpedance Spectroscopy and Cardiac Troponin T in Chronic Haemodialysis Patients. Blood Purif. 2009, 28, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; Avelar, A.; dos Santos, L.; Silva, A.M.; Gobbo, L.A.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Sardinha, L.B.; Cyrino, E.S. Hypertrophy-Type Resistance Training Improves Phase Angle in Young Adult Men and Women. Int. J. Sports Med. 2017, 38, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm-Leen, E.R.; Hall, Y.N.; Horwitz, R.I.; Chertow, G.M. Phase Angle, Frailty and Mortality in Older Adults. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2014, 29, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmar, M. Reliability and Variability of Bioimpedance Measures in Normal Adults: Effects of Age, Gender, and Body Mass. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Phys. Anthropol. 2003, 122, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, R.D.; Silva, A.M.; Borges, J.H.; Cirolini, V.X.; Páscoa, M.A.; Guerra-Júnior, G.; Gonçalves, E.M. Physical Training over 6 Months Is Associated with Improved Changes in Phase Angle, Body Composition, and Blood Glucose in Healthy Young Males. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2019, 31, e23275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.A.N.; Jorge, A.J.L.; de Andrade Martins, W.; Cardoso, G.P.; Dos Santos, M.M.; Rosa, M.L.G.; Lima, G.A.B.; de Moraes, R.Q.; da Cruz Filho, R.A. Phase Angle Measured by Electrical Bioimpedance and Global Cardiovascular Risk in Older Adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisini, N.; Corda, A.; Birettoni, F.; Miglio, A.; Antognoni, M.T. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) Detects Body Resistance Increase in Dogs Undergoing Blood Donation. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 3889–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D.A.; Backus, R.C.; Rogers, Q.R.; Van Loan, M.D. Evaluation of Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for the Assessment of Extracellular and Total Body Water in Healthy Cats. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 1757S–1759S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswood, A.; Gordon, S.G.; Häggström, J.; Wess, G.; Stepien, R.L.; Oyama, M.A.; Keene, B.W.; Bonagura, J.; MacDonald, K.A.; Patteson, M.; et al. Longitudinal Analysis of Quality of Life, Clinical, Radiographic, Echocardiographic, and Laboratory Variables in Dogs with Preclinical Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease Receiving Pimobendan or Placebo: The EPIC Study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, J.A. Manual of Veterinary Echocardiography; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1998; ISBN 0683009389. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, C.; Bonagura, J.; Ettinger, S.; Fox, P.; Gordon, S.; Haggstrom, J.; Hamlin, R.; Keene, B.; Luis-Fuentes, V.; Stepien, R. Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Canine Chronic Valvular Heart Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2009, 23, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.R. Canine and Feline Cardiology; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Doiguchi, O.; Takahashi, T. Examination of Quantitative Analysis and Measurement of the Regurgitation Rate in Mitral Valve Regurgitation by the “Proximal Isovelocity Surface Area” Method. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2000, 62, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidholm, A.; Ljungvall, I.; Michal, J.; Häggström, J.; Höglund, K. Congenital Heart Defects in Cats: A Retrospective Study of 162 Cats (1996–2013). J. Vet. Cardiol. 2015, 17, S215–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittleson, M.D. Small Animal Cardiovascular Medicine; Congenit. Pulmonic Stenosis; Mosby: London, UK, 1998; pp. 248–259. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, S. Japanese Society of Veterinary Cardiology, Veterinary Cardiology Certification Program, Lecture (25) Valvular heart disease in dogs and cats: Treatment of mitral regurgitation. Vet. Circ. Small Anim. Cardiol. J. 2014, 3, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Orton, E.C.; Herndon, G.D.; Boon, J.A.; Gaynor, J.S.; Hackett, T.B.; Monnet, E. Influence of Open Surgical Correction on Intermediate-Term Outcome in Dogs with Subvalvular Aortic Stenosis: 44 Cases (1991–1998). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 216, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimura, S. Japanese Society of Veterinary Cardiology, Veterinary Cardiology Certification Program, Lecture 5, Congenital Heart Disease: Left-to-Right Shunt Disease. Vet. Circ. Small Anim. Cardiol. J. 2015, 4, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bosy-Westphal, A.; Danielzik, S.; Dörhöfer, R.; Later, W.; Wiese, S.; Müller, M.J. Phase Angle from Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis: Population Reference Values by Age, Sex, and Body Mass Index. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2006, 30, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinger, R.H.G. Pathophysiology of Heart Failure. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2021, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegger, A.J.; Liebau, G. The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System, Antidiuretic Hormone and Sympathetic Nerve Activity in an Experimental Model of Congestive Heart Failure in the Dog. Clin. Sci. 1982, 62, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S.; Funayama, H. Hyponatremia Associated with Congestive Heart Failure: Involvement of Vasopressin and Efficacy of Vasopressin Receptor Antagonists. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adin, D.; Atkins, C.; Londoño, L.; Del Nero, B. Correction of serum chloride concentration in dogs with congestive heart failure. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adin, D.; Kurtz, K.; Atkins, C.; Papich, M.G.; Vaden, S. Role of electrolyte concentrations and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone activation in the staging of canine heart disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Nakamoto, T.; Iizuka, M. Early Diagnosis and Estimation of Pulmonary Congestion and Edema in Patients with Left-Sided Heart Diseases from Histogram of Pulmonary CT Number. Chest 1996, 109, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, e263–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abassi, Z.; Khoury, E.E.; Karram, T.; Aronson, D. Edema Formation in Congestive Heart Failure and the Underlying Mechanisms. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 933215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicchitano, P.; Massari, F. The Role of Bioelectrical Phase Angle in Patients with Heart Failure. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Piccoli, A.; Pichard, C. Body Composition Measurements: Interpretation Finally Made Easy for Clinical Use. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2003, 6, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, S.; Acquaro, M.; Agostoni, P.; Ambrosio, G.; Carluccio, E.; Castiglione, V.; Colombo, D.; D’Alto, M.; Delle Grottaglie, S.; Dini, F.L.; et al. Right Heart Failure in Left Heart Disease: Imaging, Functional, and Biochemical Aspects of Right Ventricular Dysfunction. Heart Fail. Rev. 2023, 28, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.C.; Brantlov, S. Bioimpedance Basics and Phase Angle Fundamentals. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellido, D.; García-García, C.; Talluri, A.; Lukaski, H.C.; García-Almeida, J.M. Future Lines of Research on Phase Angle: Strengths and Limitations. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K.C.; Goldstein, S. Congestive Heart Failure and Pulmonary Edema. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Heymsfield, S. Human Body Composition; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2005; Volume 918, ISBN 0736046550. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, L.A.; Rettori, O.; Mejia, R.H. Correlation between Body Fluid Volumes and Body Weight in the Rat. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1966, 210, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa-Silva, M.C.G.; Barros, A.J.D.; Wang, J.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Pierson, R.N., Jr. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis: Population Reference Values for Phase Angle by Age and Sex. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeusette, I.; Greco, D.; Aquino, F.; Detilleux, J.; Peterson, M.; Romano, V.; Torre, C. Effect of Breed on Body Composition and Comparison between Various Methods to Estimate Body Composition in Dogs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 88, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, J.M. Pleural Effusions from Congestive Heart Failure. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 31, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, L.; Rand, J.; Ward, L. Measuring body composition in dogs using bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy. Vet. J. 2024, 304, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauten, S.D.; Cox, N.R.; Brawner, W.R.; Baker, H.J. Use of dual energy x-ray absorptiometry for noninvasive body composition measurements in clinically normal dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lark, R.K.; Henderson, R.C.; Renner, J.B.; Fung, E.B.; Stallings, V.A.; Conaway, M.; Stevenson, R.D. Dual X-ray absorptiometry assessment of body composition in children with altered body posture. J. Clin. Densitom. 2001, 4, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, L.; Vankan, D.; Rand, J.; Flickinger, E.; Ward, L. Measuring body composition in dogs using multifrequency bioelectrical impedance analysis and dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Vet. J. 2016, 212, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
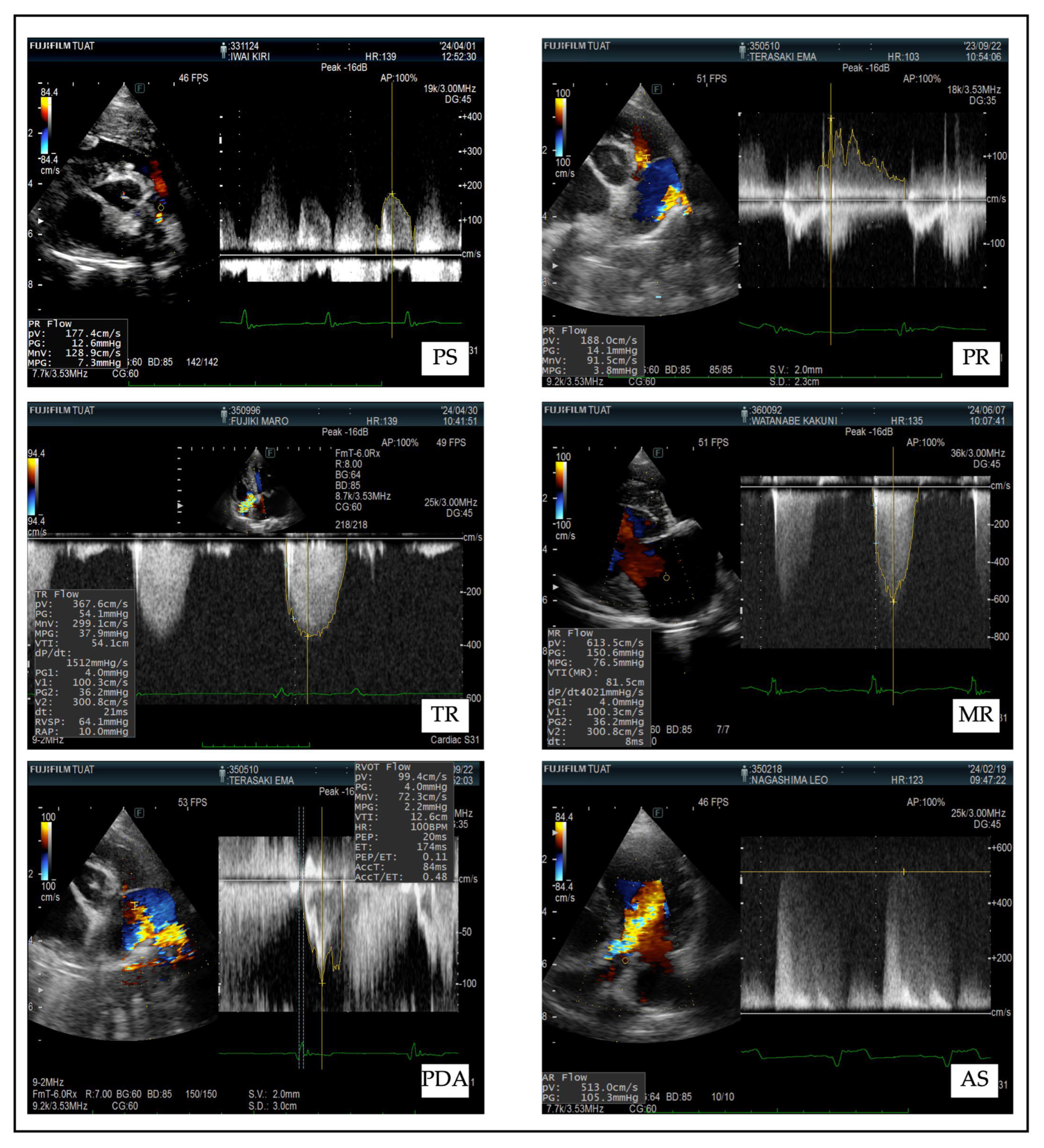

| Disease | Diagnostic Features | Doppler Parameters | Clinical Signs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pulmonary Stenosis (PS) |
|
|
|
| Pulmonary Regurgitation (PR) |
|
|
|
| Tricuspid Regurgitation (TR) |
|
|
|
| Mitral Regurgitation (MR) |
|
|
|
| Aortic Stenosis (AS) |
|
|
|
| Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) |
|
|
|
| Group | Total Cases | Used for PhA Analysis | Used for OSM Analysis | Used for Statistical Tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHF | 35 | 15 | 16 | 28 |
| LHF | 35 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| Control | 40 | 25 | 14 | 25 |
| Total | 110 | 62 | 52 | 75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Mandour, A.S.; Farag, A.; Xu, T.; Terai, K.; Shimada, K.; Hamabe, L.; Yokoi, A.; Tanaka, R. Phase Angle as a Non-Invasive Biomarker of Fluid Overload in Canine Right Heart Failure: A Bioelectrical Impedance Approach. Animals 2025, 15, 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192877
Li Z, Mandour AS, Farag A, Xu T, Terai K, Shimada K, Hamabe L, Yokoi A, Tanaka R. Phase Angle as a Non-Invasive Biomarker of Fluid Overload in Canine Right Heart Failure: A Bioelectrical Impedance Approach. Animals. 2025; 15(19):2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192877
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zongru, Ahmed S. Mandour, Ahmed Farag, Tingfeng Xu, Kazuyuki Terai, Kazumi Shimada, Lina Hamabe, Aimi Yokoi, and Ryou Tanaka. 2025. "Phase Angle as a Non-Invasive Biomarker of Fluid Overload in Canine Right Heart Failure: A Bioelectrical Impedance Approach" Animals 15, no. 19: 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192877
APA StyleLi, Z., Mandour, A. S., Farag, A., Xu, T., Terai, K., Shimada, K., Hamabe, L., Yokoi, A., & Tanaka, R. (2025). Phase Angle as a Non-Invasive Biomarker of Fluid Overload in Canine Right Heart Failure: A Bioelectrical Impedance Approach. Animals, 15(19), 2877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15192877








