Seroprevalence of 16 Leptospira Serovars in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) Hunted in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
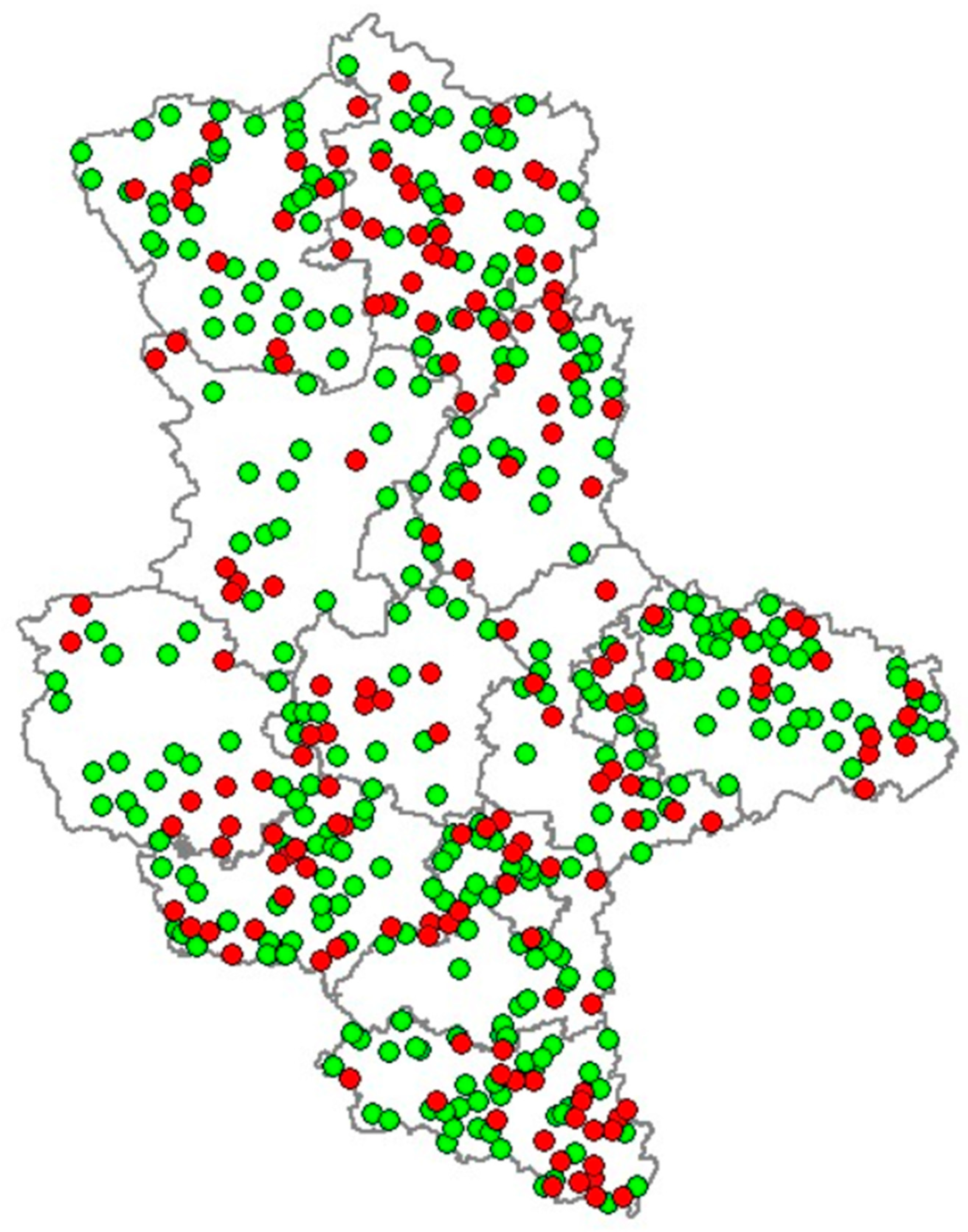
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Microscopic Agglutination Test (MAT)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
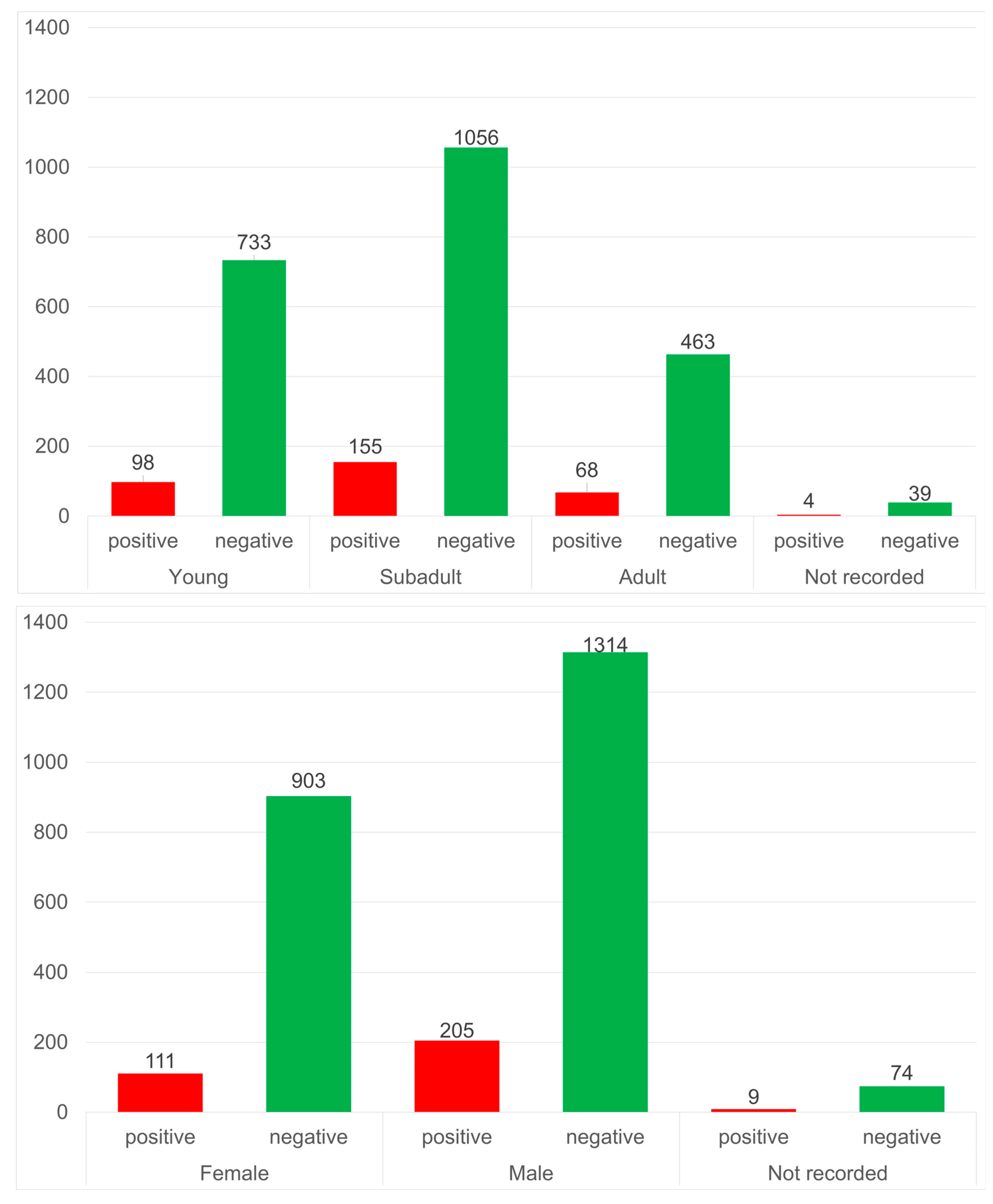
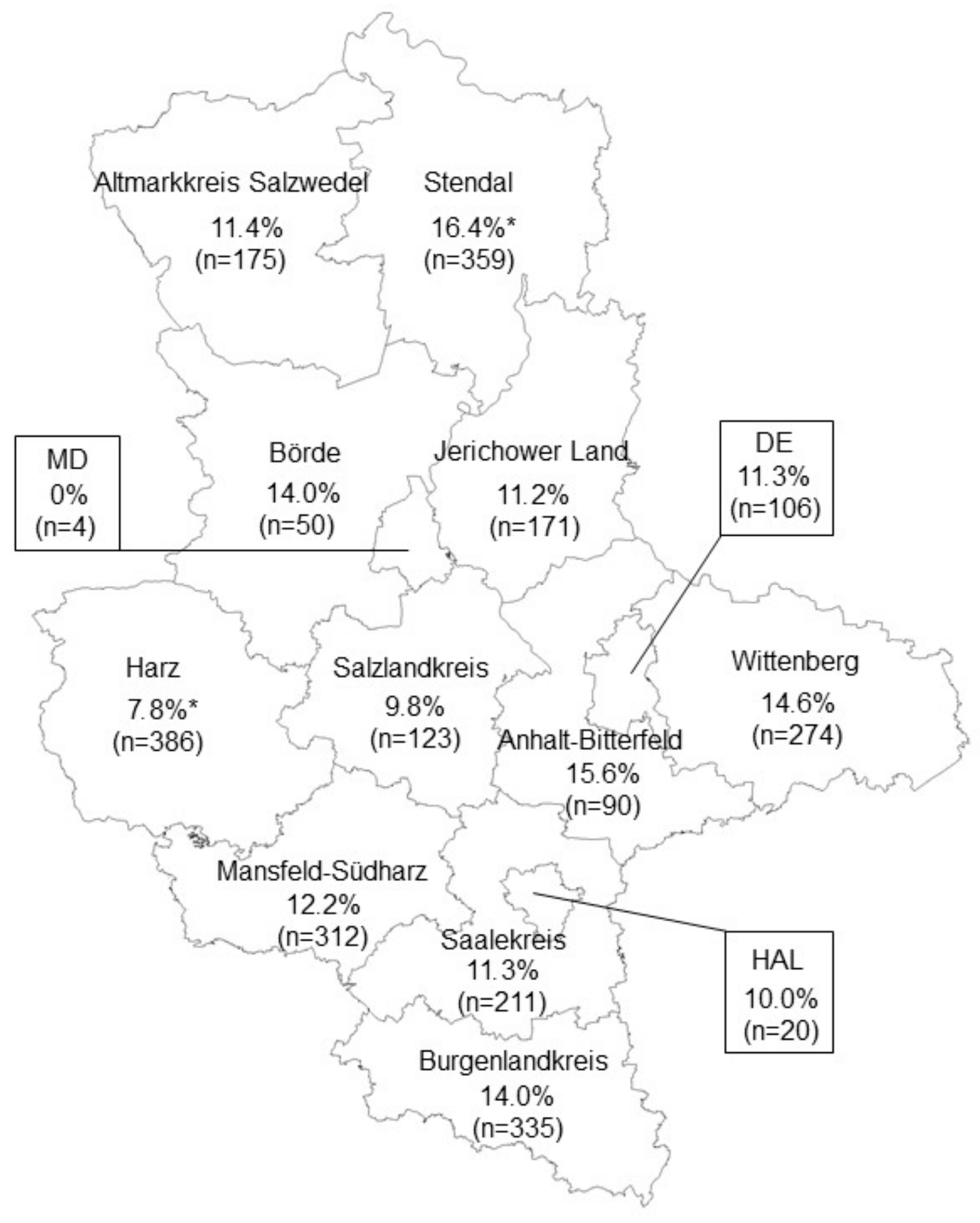
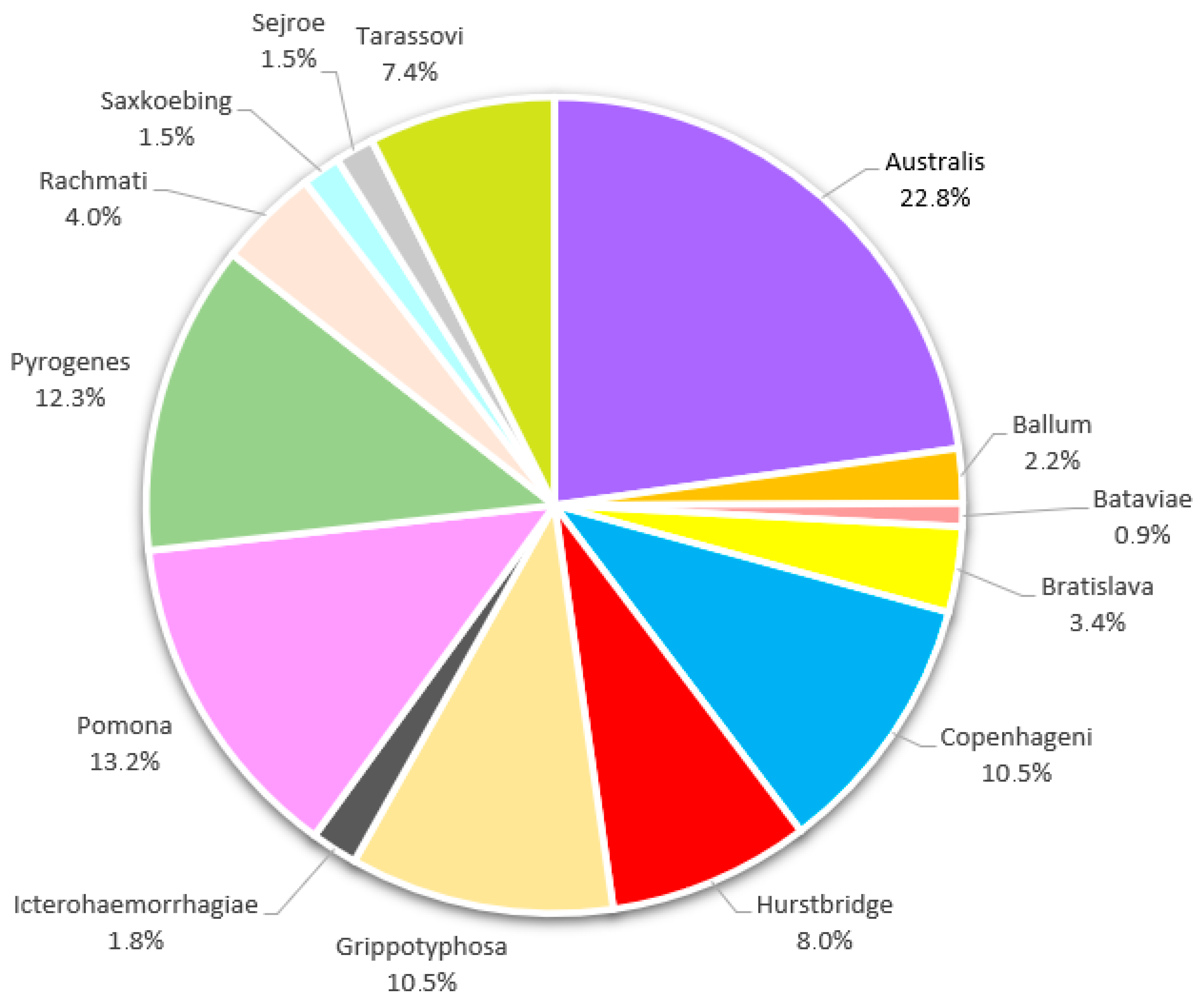
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, F.; Hagan, J.E.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Torgerston, P.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Stein, C.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Ko, A.I. Global Morbidity and Mortality of Leptospirosis: A Systematic Review. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Available online: https://survstat.rki.de/ (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Nau, L.H.; Emirhar, D.; Obiegala, A.; Mylius, M.; Runge, M.; Jacob, J.; Bier, N.; Nöckler, K.; Imholt, C.; Below, D.; et al. Leptospirose in Deutschland: Aktuelle Erkenntnisse zu Erregerspezies, Reservoirwirten und Erkrankungen bei Mensch und Tier [Leptospirosis in Germany: Current knowledge on pathogen species, reservoir hosts, and disease in human and animals]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2019, 62, 1510–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, A.; Luge, E.; Guerra, B.; Wittschen, P.; Gruber, A.D.; Loddenkemper, C.; Schneider, T.; Lierz, M.; Ehlert, D.; Appel, B.; et al. Leptospirosis in urban wild boars, Berlin, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vengust, G.; Lindtner-Knific, R.; Zele, D.; Bidovec, A. Leptospira antibodies in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Slovenia. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2008, 54, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavica, A.; Cvetnić, Ž.; Konjević, D.; Janicki, Z.; Severin, K.; Deždek, D.; Starešina, V.; Sindičić, M.; Antić, J. Detection of Leptospira spp. serovars in wild boars (Sus scrofa) from continental Croatia. Vet. Archiv. 2010, 80, 247–80257. [Google Scholar]
- Boqvist, S.; Bergström, K.; Magnusson, U. Prevalence of antibody to six Leptospira serovars in Swedish wild boars. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Żmudzki, J.; Jabłoński, A.; Nowak, A.; Zębek, S.; Arent, Z.; Bocian, Ł.; Pejsak, Z. First overall report of Leptospira infections in wild boars in Poland. Acta Vet. Scand. 2016, 58, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilia, G.; Bertelloni, F.; Angelini, M.; Cerri, D.; Fratini, F. Leptospira Survey in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) Hunted in Tuscany, central Italy. Pathogens 2020, 9, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roquelo, C.; Kodjo, A.; Marié, J.L.; Davoust, B. Serological and molecular survey of Leptospira spp. infections in wild boars and red foxes from Southeastern France. Vet. World 2021, 14, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thaipadungpanit, J.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Chierakul, W.; Smythe, L.D.; Petkanchanapong, W.; Limpaiboon, R.; Apiwatanaporn, A.; Slack, A.T.; Suputtamongkol, Y.; White, N.J.; et al. A dominant clone of Leptospira interrogans associated with an outbreak of human leptospirosis in Thailand. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2007, 1, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arent, Z.; Pardyak, L.; Dubniewicz, K.; Płachno, B.J.; Kotula-Balak, M. Leptospira taxonomy: Then and now. Med. Weter. 2022, 78, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 296–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Faine, S.; Adler, B.; Bolin, C.A.; Perolat, P. Leptospira and Leptospirosis; Medisci Press: Melbourne, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH). Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, 13th ed.; Paris Chapter 3.1.12 Leptospirosis (version adopted in May 2021); WOAH: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Human Leptospirosis: Guidance for Diagnosis, Surveillance and Control; WHO Library in Publication Data; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cilia, G.; Bertelloni, F.; Cerri, D.; Fratini, F. Leptospira fainei Detected in Testicles and Epididymis of Wild Boar (Sus scrofa). Biology 2021, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chiriboga, J.; Barragan, V.; Arroyo, G.; Sosa, A.; Birdsell, D.N.; España, K.; Mora, A.; Espín, E.; Mejía, M.E.; Morales, M.; et al. High Prevalence of Intermediate Leptospira spp. DNA in Febrile Humans from Urban and Rural Ecuador. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abd Rahman, A.N.; Hasnul Hadi, N.H.; Sun, Z.; Thilakavathy, K.; Joseph, N. Regional Prevalence of Intermediate Leptospira spp. in Humans: A Meta-Analysis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Piscopo, N.; Tamburis, O.; Bonavolontà, F.; Verde, M.; Manno, M.; Mancusi, M.; Esposito, L. Assessing wild boar presence and activity in a monitoring specific area of Campania region using camera traps. Acta Imeko 2023, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscopo, N.; Costanzo, M.; Gelzo, M.; Sacchettino, L.; Vitiello, C.; Balestrieri, A.; Napolitano, F.; Esposito, L. Effect of the 7sarcoptic mange upon metabolome profiling in wild boar. Res. Vet. Sci. 2025, 183, 105505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, G.; Piscopo, N.; Pagnini, U.; Esposito, L.; Montagnaro, S. Detection of selected pathogens in reproductive tissues of wild boars in the Campania region, southern Italy. Acta Vet. Scand. 2024, 66, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, K.; Martano, M.; Piscopo, N.; Viola, P.; Altamura, G.; Veneziano, V.; Carvajal Urueña, A.; Esposito, L. Prevalence of Eucoleus garfiai in Wild Boars Hunted at Different Altitudes in the Campania and Latium Regions (Italy). Animals 2023, 13, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Denzin, N.; Borgwardt, J.; Freuling, C.; Müller, T. Spatio-temporal analysis of the progression of Aujeszky’s disease virus infection in wild boar of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Geospat. Health 2013, 8, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denzin, N.; Borgwardt, J. Vorkommen und geografische Verbreitung von Antikörpern gegen Hepatitis E-virus beim Wildschwein in Sachsen-Anhalt (2011). [Occurrence and geographical distribution of antibodies to hepatitis E virus in wild boars of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany (2011)]. Berl. Und Münchener Tierärztliche Wochenschr. 2013, 126, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Otto, P.; Chaignat, V.; Klimpel, D.; Diller, R.; Melzer, F.; Müller, W.; Tomaso, H. Serological investigation of wild boars (Sus scrofa) and red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) as indicator animals for circulation of Francisella tularensis in Germany. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schweinepest-Monitoring-Verordnung. Verordnungzur Durchführung Eines Monitorings Auf Das Virus Der Klassischen Und Afrikanischen Schweinepest bei Wild- und Hausschweinen; Bundesgesetzblatt Teil I, Nr.51, S.2518; Bundesministerium der Justiz und für Verbraucherschutz: Berlin, Germany, 2016.
- R Development Core Team. Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; The R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, F.P.; Kmetiuk, L.B.; Pellizzaro, M.; Yamakawa, A.C.; Martins, C.M.; Morikawa, V.M.; de Barros-Filho, I.R.; Langoni, H.; Dos Santos, A.P.; Biondo, A.W. Leptospira spp. Antibody in Wild Boars (Sus scrofa), Hunting Dogs (Canis lupus familiaris), and Hunters of Brazil. J. Wildl. Dis. 2021, 57, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neis, L.Z.; Kuhn, R.; Cruz, J.C.; Rosa, T.D.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Bertagnolli, A.C.; Loiko, M.R.; Reck, J.; Mayer, F.Q. Assessing leptospirosis and toxoplasmosis seropositivity in wild boars (Sus scrofa): Implications for public and animal health in Southern Brazil. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 113, 102231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espí, A.; Prieto, J.M.; Alzaga, V. Leptospiral antibodies in Iberian red deer (Cervus elaphus hispanicus), fallow deer (Dama dama) and European wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Asturias, Northen Spain. Vet. J. 2010, 183, 226–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Treml, F.; Pikula, J.; Holešovska, Z. Prevalence of antibodies against leptospires in the wild boar (Sus scrofa L., 1758). Vet. Med.–Czech. 2003, 48, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetnic, Z.; Margaletic, J.; Tončić, J.; Turk, N.; Milas, Z.; Špičić, S.; Lojkić, M.; Terzić, M.; Jemeršić, L.; Humski, A.; et al. A serological survey and isolation of leptospires from small rodents and wild boars in the Republic of Croatia. Vet. Med. 2003, 48, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale-Goncalves, H.M.; Cabral, J.A.; Faria, M.C.; Nunes-Pereira, M.; Faria, A.S.; Veloso, O.; Vieira, M.L.; Paiva-Cardoso, N. Prevalence of Leptospira antibodies in wild boars (Sus scrofa) from Northern Portugal: Risk factor analysis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 143, 2126–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebani, V.V.; Cerri, D.; Poli, A.; Andreani, E. Prevalence of Leptospira and Brucella antibodies in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Tuscany, Italy. J. Wildl. Dis. 2003, 39, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kravelienė, B.; Stadalienė, I.; Rudejevienė, J.; Burbaitė, E.; Juodžentė, D.; Masiulis, M.; Buitkuvienė, J.; Šakalienė, J.; Zamokas, G. Prevalence of Leptospira spp. in Lithuanian Wild Boars (Sus scrofa). Pathogens 2025, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Petersen, A.M.; Boye, K.; Blom, J.; Schlichting, P.; Krogfelt, K.A. First isolation of Leptospira fainei serovar Hurstbridge from two human patients with Weil’s syndrome. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzouni, J.P.; Parola, P.; La Scola, B.; Postic, D.; Brouqui, P.; Raoult, D. Human infection caused by Leptospira fainei. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chappel, R.J.; Khalik, D.A.; Adler, B.; Bulach, D.M.; Faine, S.; Perolat, P.; Vallance, V. Serological titres of Leptospira fainei serovar hurstbridge in human sera in Australia. Epidemiol. Infect. 1998, 121, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Perolat, P.; Chappel, R.J.; Adler, B.; Baranton, G.; Bulach, D.M.; Billinghurst, M.L.; Letocart, M.; Merien, F.; Serrano, M.S. Leptospira fainei sp. nov., isolated from pigs in Australia. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48 Pt 3, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Species | Serovar | Serogroup | Strain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leptospira interrogans | Australis | Australis | Ballico |
| Bataviae | Bataviae | Swart | |
| Bratislava | Bratislava | Jez Bratislava | |
| Canicola | Canicola | Hond Utrecht IV | |
| Copenhageni | Icterohaemorrhagiae | M20 | |
| Hardjo type Prajitno | Sejroe | Hardjoprajitno | |
| Icterohaemorrhagiae | Icterohaemorrhagiae | RGA | |
| Pomona | Pomona | Pomona | |
| Pyrogenes | Pyrogenes | Salinem | |
| Rachmati | Autumnalis | Rachmat | |
| Leptospira borgpetersenii | Ballum | Ballum | MUS127 |
| Saxkoebing | Sejroe | MUS24 | |
| Sejroe | Sejroe | M84 | |
| Tarassovi | Tarassovi | Perepelitsin | |
| Leptospira kirschneri | Grippotyphosa type Moskva | Grippotyphosa | Moskva V |
| Leptospira fainei | Hurstbridge | Hurstbridge | BUT6 |
| Leptospira Serovar | Titer | Total (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 200 | 400 | 800 | 1600 | ||
| Australis | 47 | 18 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 74 (22.8%) |
| Ballum | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 (2.2%) |
| Bataviae | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (0.9%) |
| Bratislava | 9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 11 (3.4%) |
| Copenhageni | 21 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 34 (10.5%) |
| Hurstbridge | 20 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 26 (8.0%) |
| Grippotyphosa | 29 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 34 (10.5%) |
| Icterohaemorrhagiae | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 (1.8%) |
| Pomona | 32 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 43 (13.2%) |
| Pyrogenes | 35 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 (12.3%) |
| Rachmati | 11 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 (4.0%) |
| Saxkoebing | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (1.5%) |
| Sejroe | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 (1.5%) |
| Tarassovi | 16 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 24 (7.4%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stagnoli, A.; House, R.V.; Hagemann, J.; Dohmann, K.; Pfeffer, M.; Albrecht, C. Seroprevalence of 16 Leptospira Serovars in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) Hunted in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Animals 2025, 15, 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182725
Stagnoli A, House RV, Hagemann J, Dohmann K, Pfeffer M, Albrecht C. Seroprevalence of 16 Leptospira Serovars in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) Hunted in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Animals. 2025; 15(18):2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182725
Chicago/Turabian StyleStagnoli, Alice, Robert Valerio House, Juliane Hagemann, Karen Dohmann, Martin Pfeffer, and Catrin Albrecht. 2025. "Seroprevalence of 16 Leptospira Serovars in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) Hunted in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany" Animals 15, no. 18: 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182725
APA StyleStagnoli, A., House, R. V., Hagemann, J., Dohmann, K., Pfeffer, M., & Albrecht, C. (2025). Seroprevalence of 16 Leptospira Serovars in Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) Hunted in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Animals, 15(18), 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182725








