Natural Infection by Fasciola hepatica in Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) from NW Spain: The Usefulness of Necropsy, Coprology, and Three Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for the Diagnosis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
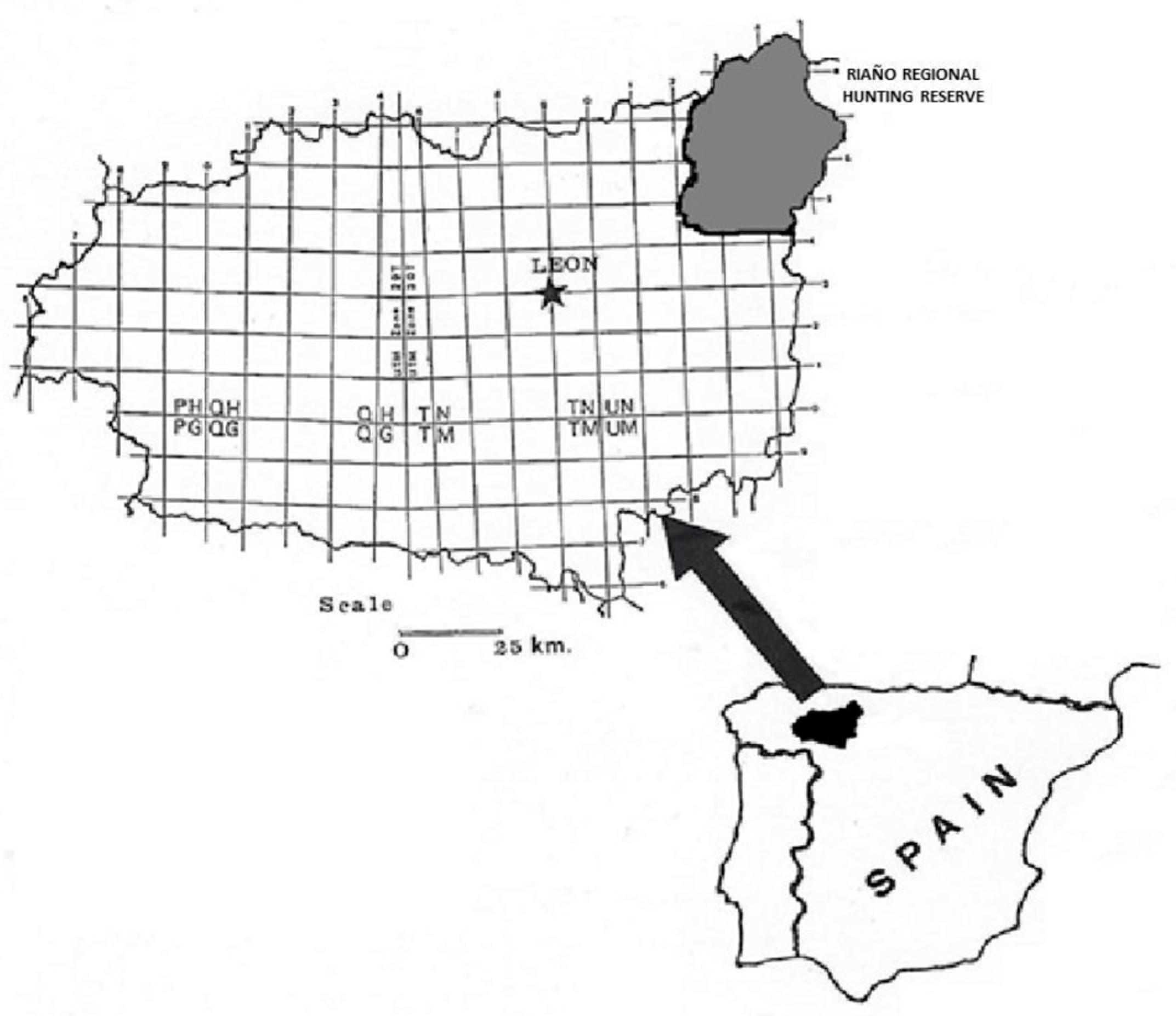
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Animal Sampling
2.3. Parasitological Examination
2.4. Serological Procedures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
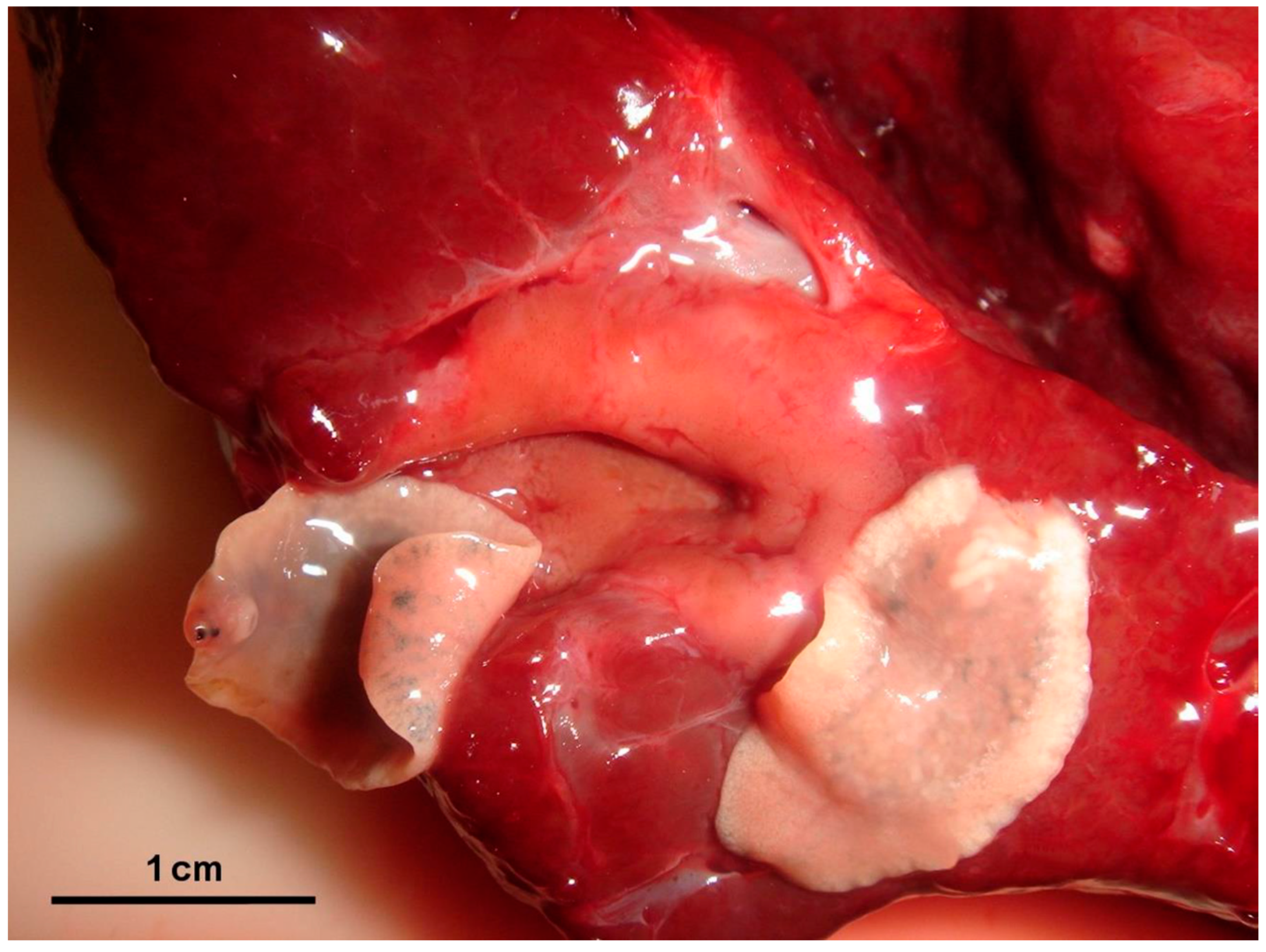
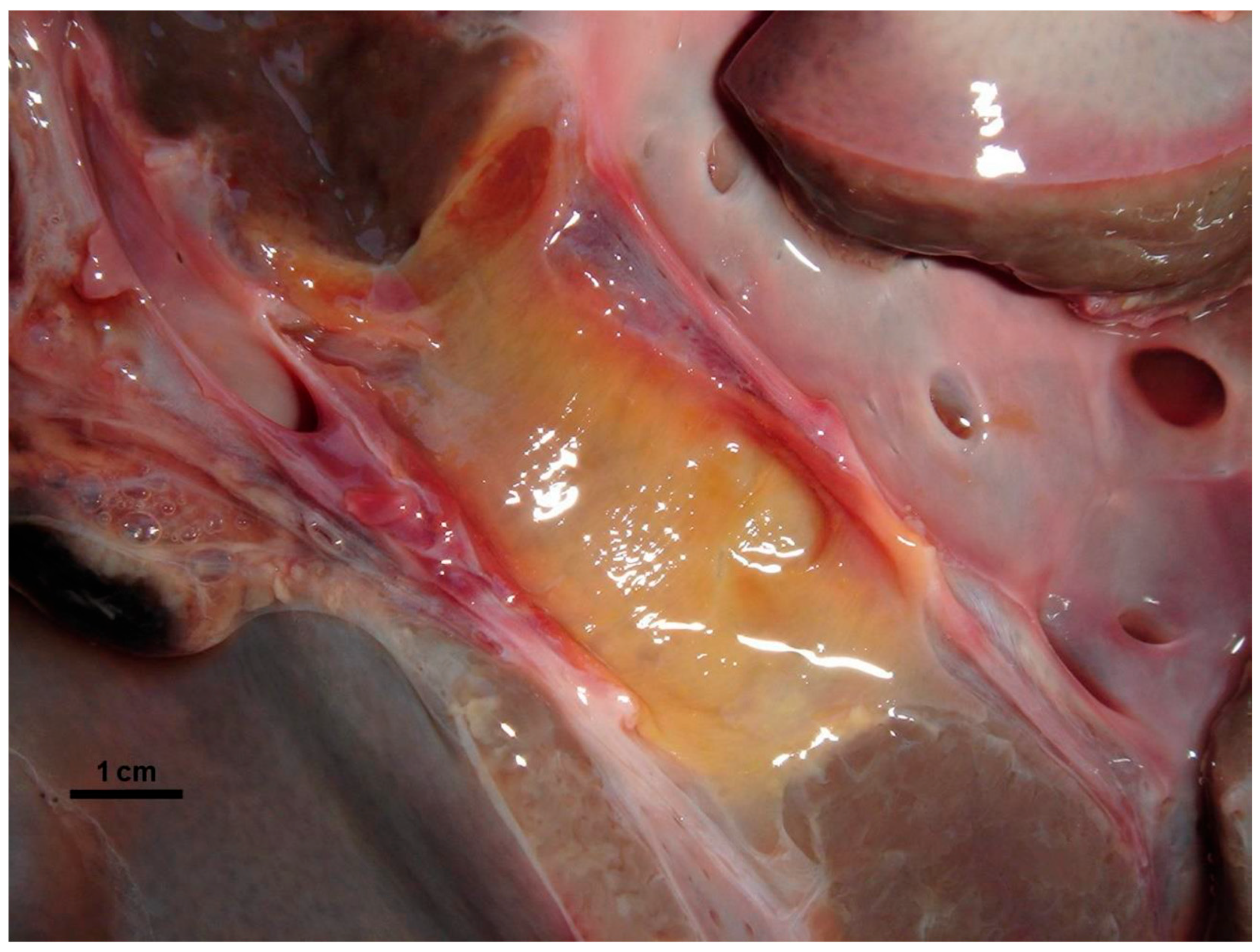
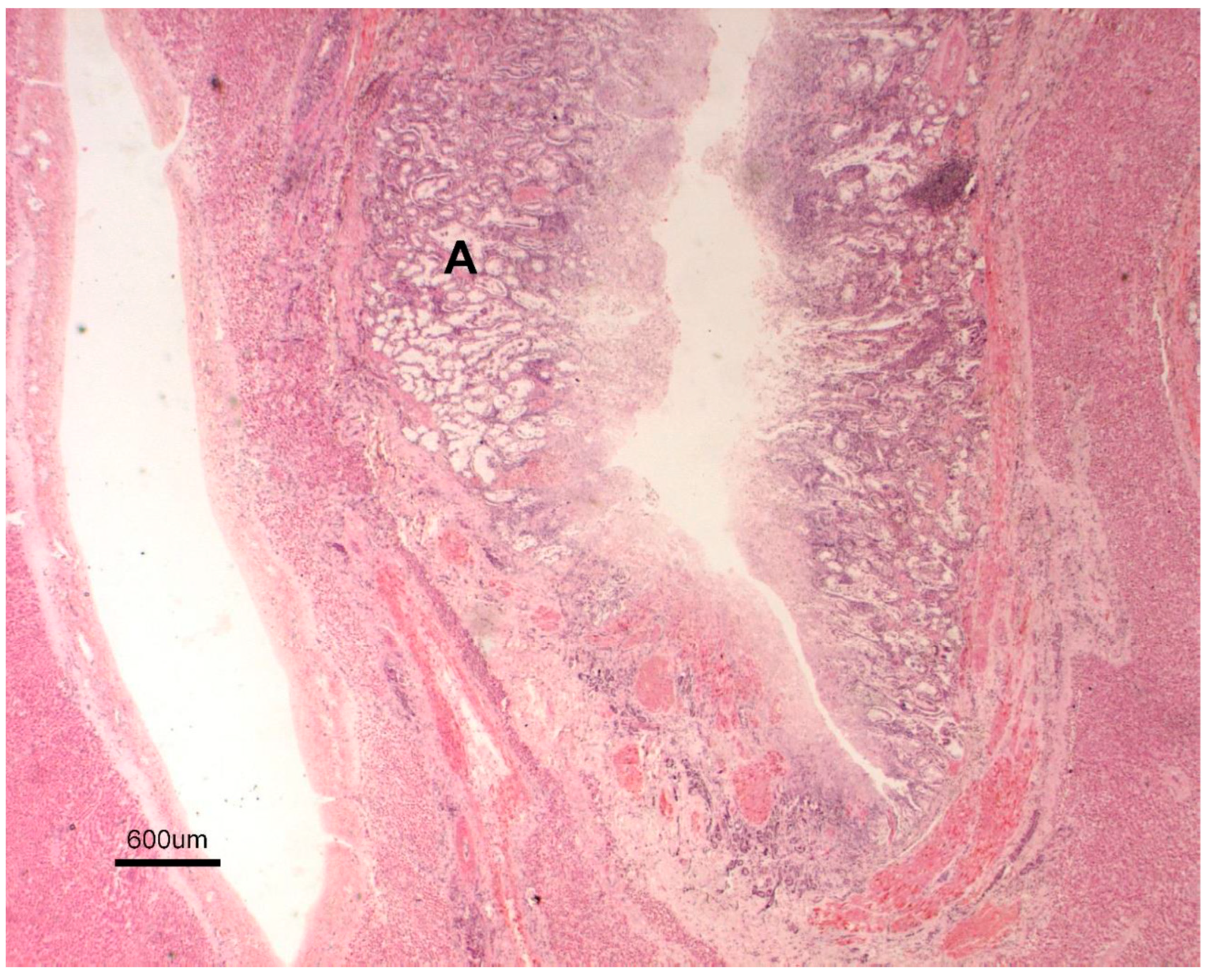
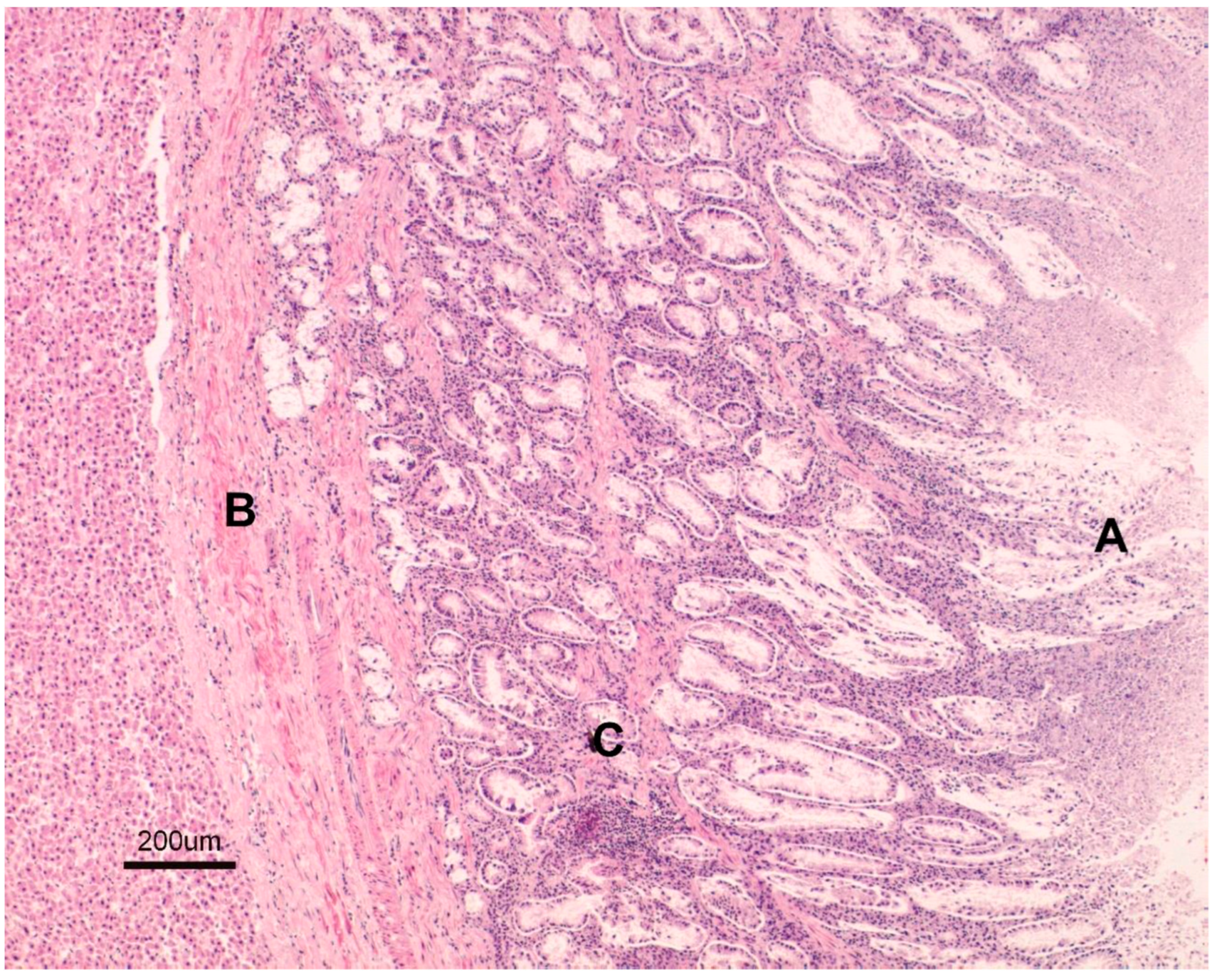
3.1. Necropsy
3.2. Coprology
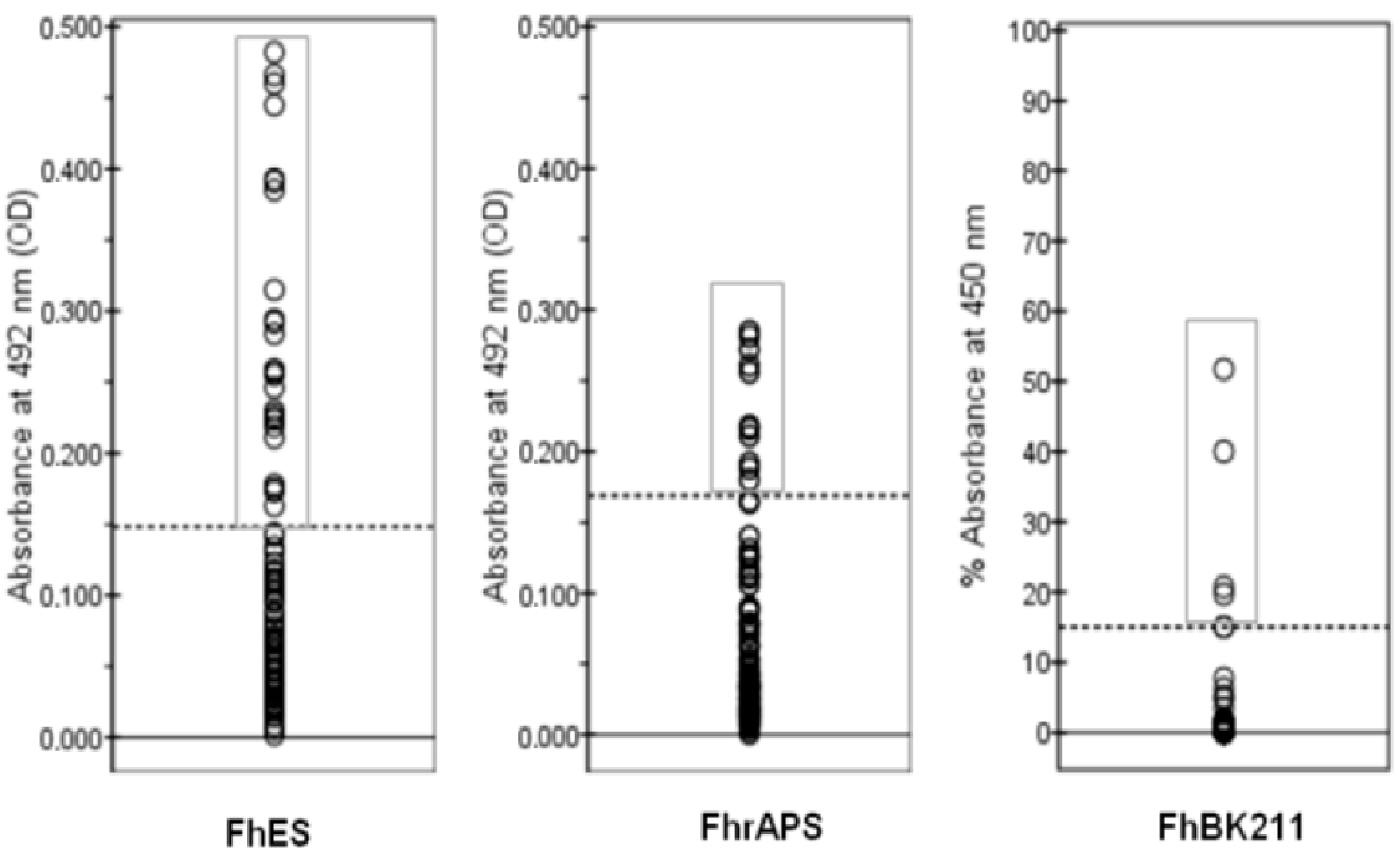
3.3. Serology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schols, R.; Carolus, H.; Hammoud, C.; Muzarabani, K.C.; Barson, M.; Huyse, T. Invasive snails, parasite spillback, and potential parasite spillover drive parasitic diseases of Hippopotamus amphibius in artificial lakes of Zimbabwe. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 160–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Fasciola, Lymnaeids and Human Fascioliasis, with a Global Overview on Disease Transmission, Epidemiology, Evolutionary Genetics, Molecular Epidemiology and Control. Adv. Parasitol. 2009, 69, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.G.; Mott, K.E. Progress in assessment of morbidity due to Fasciola hepatica infection, a review of recent literature. Trop. Dis. Bull. 1990, 87, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Foodborne Trematode Infections, World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/foodborne-trematode-infections (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Alasaad, S.; Li, Q.Y.; Lin, R.Q.; Martín-Atance, P.; Granados, J.E.; Díez-Baños, P.; Pérez, J.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Genetic variability among Fasciola hepatica samples from different host species and geographical localities in Spain revealed by the novel SRAP marker. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 103, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barges, M.D.; Artiga, P.; Khoubbane, M.; Ortiz, P.; Naquira, C.; Mas-Coma, S. Molecular characterisation of Galba truncatula, Lymnae neotrofica and L. schirazensis from Cajamarca, Peru and their potential role in transmission of human and animal fascioliasis. Parasi. Vectors 2012, 5, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manga-González, M.Y.; González-Lanza, C.; González-Warleta, M.; Miñambres, B.; Carro-Corral, C.; Iglesias, J.; Castillejo, J.; Mezo, M. Infection kinetic of Galba truncatula (Mollusca, Basommatophora) by Fasciola hepatica and Calicophoron daubneyi (Trematoda, Digenea) in Galicia (Spain). Acta Parasitol. Portuguesa. 2009, 16, 118–119. [Google Scholar]
- Correa, A.C.; Escobar, J.S.; Durand, P.; Renaud, F.; David, P.; Jarne, P.; Pointier, J.P.; Hurtrez-Boussés, S. Bridging gaps in the molecular phylogeny of the Lymnaeidae (Gastropoda: Pulmonata), vectors of Fascioliasis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.P.; Carneiro, M.B.; Martins, I.V.F.; Bernardo, C.C.; Donatele, D.M.; Pereira Junior, O.S.; Almeida, B.R.; Avelar, B.R.; Leao, A.G.G. Distribution and factors associated with Fasciola hepatica infection in cattle in the south of Espirito Santo State, Brasil. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 17, 271–276. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, A.K.; Williams, D.J.L. The epidemiology and control of liver flukes in cattle and sheep. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuen, S.; Ersdal, C. Fasciolosis-An increasing challenge in the sheep industry. Animals 2022, 12, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquart, G.M.; Armour, J.; Duncan, J.L.; Dunn, A.M.; Jennings, F.W. Veterinary Parasitology, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Beesley, N.J.; Caminade, C.; Charlier, J.; Flynn, R.J.; Hodkinson, J.E.; Martinez-Moreno, A.M.; Martinez-Valladares, M.; Perez, J.; Rinaldi, L.; Williams, D.J.L. Fasciola and fasciolosis in ruminants in Europe: Identifying research needs. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, A.; Baylis, M.; Smith, R.; Pinchbeck, G.; Williams, D. Epidemiology and impact of Fasciola hepatica exposure in high-yielding dairy herds. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 121, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazeri, S.; Rydevik, G.; Handel, I.; Bronsvoort, B.M.d.C.; Sargison, N. Estimation of the impact of Fasciola hepatica infection on time taken for UK beef cattle to reach slaughter weight. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlier, J.; Rinaldi, L.; Musella, V.; Ploeger, H.W.; Chartier, C.; Vineer, H.R.; Hinney, B.; Von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Băcescu, B.; Mickiewicz, M.; et al. Initial assessment of the economic burden of major parasitic helminth infections to the ruminant livestock industry in Europe. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 182, 105103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, J.; Vercruysse, J.; Morgan, E.; Van Dijk, J.; Williams, D.J.L. Recent advances in the diagnosis, impact on production and prediction of Fasciola hepatica in cattle. Parasitology 2014, 141, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeri, S.; Sargison, N.; Kelly, R.F.; Bronsvoort, B.M.d.C.; Handel, I. Evaluation of the performance of five diagnostic tests for Fasciola hepatica infection in naturally infected cattle using a bayesian no gold standard approach. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.S.; Martínez-Carrasco, C.; León-Vizcaíno, L.; Paz-Silva, A.; Díez-Baños, P.; Morrondo, P.; Alonso, F. Detection of antibodies in wild ruminants to evaluate exposure to liver trematodes. J. Parasitol. 2012, 98, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales Santana, B.; Dalton, J.P.; Vasquez Camargo, F.; Parkinson, M.; Ndao, M. The diagnosis of human fascioliasis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using recombinant Cathepsin L protease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sernández, V.; Perteguer, M.J.; Hernández-González, A.; Mezo, M.; González-Warleta, M.; Orbegozo-Medina, R.A.; Romarís, F.; Paniagua, E.; Gárate, T.; Ubeira, F.M. Comparison of recombinant cathepsins L1, L2, and L5 as ELISA targets for serodiagnosis of bovine and ovine fascioliasis. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 1521–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles-Lucas, M.; Becerro-Recio, D.; Serrat, J.; González-Miguel, J. Fascioliasis and fasciolopsiasis: Current knowledge and future trends. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 124, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezo, M.; González-Warleta, M.; Carro, C.; Ubeira, F.M. An ultrasensitive capture ELISA for detection of Fasciola hepatica coproantigens in sheep and cattle using a new monoclonal antibody (MM3). J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezo, M.; Gonzalez-Warleta, M.; Ubeira, F.M. The use of MM3 monoclonal antibodies for the early immunodiagnosis of ovine fascioliasis. J. Parasitol. 2007, 93, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezo, M.; González-Warleta, M.; Castro-Hermida, J.A.; Martínez-Sernández, V.; Ubeira, F.M. Field evaluation of the enhanced MM3-COPRO ELISA test for the diagnosis of Fasciola hepatica infection in sheep. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilla, A.; Bargues, M.D.; Mas-Coma, S. A PCR–RFLP assay for the distinction between Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica. Mol. Cell. Probes 2002, 16, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pérez, J.M.; Robles-Pérez, D.; Rojo-Vázquez, F.A.; Martínez-Valladares, M. Comparation of three different techniques to diagnose Fasciola hepatica infection in experimentally and naturally infected sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Dong, S.J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Mahmmod, Y.S.; Lin, R.Q.; Yuan, Z.G.; Shi, Y.L.; Huang, W.Y.; Zhu, X.Q. Specific PCR-based assays for the identification of Fasciola species: Their development, evaluation and potential usefulness in prevalence surveys. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2013, 104, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, E63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, K.; Hase, T.; Notomi, T. Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol. Cell. Probes 2002, 16, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, A.S.; Zadoks, R.N.; Skuce, P.J.; Mitchell, G.; Gordon-Gibbs, D.K.; Craine, A.; Shaw, D.; Gibb, S.W.; Taggart, M.A. Prevalence of liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) in wild red deer (Cervus elaphus): Coproantigen ELISA is a practicable alternative to faecal egg counting for surveillance in remote populations. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AEMET, State Meteorology Station. Ministry of the Environment and Rural and Marine Management. 2024. Available online: https://www.aemet.es/es/portada (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- MAFF, Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food. Manual of Veterinary Parasitological Laboratory Techniques; H. M. Stationery Office: London, UK, 1986; p. 160.
- Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Paz-Silva, A.; Suárez, J.L.; Panadero, R.; Díez-Baños, P.; Morrondo, P. Use of a sandwich-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (SEA) for the diagnosis of natural Fasciola hepatica infection in cattle from Galicia (NW Spain). Vet. Parasitol. 2000, 93, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Paz-Silva, A.; Suárez, J.L.; Panadero, R.; Pedreira, J.; López, C.; Díez-Baños, P.; Morrondo, P. Influence of age and breed on natural bovine fasciolosis in an endemic area (Galicia, NW Spain). Vet. Res. Commun. 2002, 26, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.; Morrondo, P.; Hillyer, G.V.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Suárez, J.L.; Lomba, C.; Pedreira, J.; Díaz, P.; Díez-Baños, P.; Paz-Silva, A. Immunodiagnosis of current fasciolosis in sheep naturally exposed to Fasciola hepatica by using a 2.9 kDa recombinant protein. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 146, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, M.S.; Piñeiro, P.; Hillyer, G.V.; Suárez, J.L.; Francisco, I.; Cortiñas, F.J.; Díez-Baños, P.; Morrondo, P.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Paz-Silva, A. An approach of the laboratory to the field: Assessment of the influence of cattle management on the seroprevalence of fascioliasis by using polyclonal- and recombinant-based ELISAs. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Silva, A.; Hillyer, G.V.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Rodríguez Medina, J.R.; Arias, M.S.; Morrondo, P.; Díez-Baños, P. Isolation, identification and expression of a Fasciola hepatica cDNA encoding a 2.9-kDa recombinant protein for the diagnosis of ovine fasciolosis. Parasitol. Res. 2005, 95, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.S.; Piñeiro, P.; Sanchez-Andrade, R.; Suárez, J.L.; Hillyer, G.V.; Díez-Baños, P.; Paz-Silva, A.; Morrondo, P. Relationship between exposure to Fasciola hepatica in roe deer (Capreolous capreolous) and cattle extensively reared in an endemic area. Res. Vet. Sci. 2013, 95, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Silva, A.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Suárez, J.L.; Pedreira, J.; Arias, M.S.; López, C.; Panadero, R.; Díaz, P.; Díez-Baños, P.; Morrondo, P. Prevalence of natural ovine fasciolosis shown by demonstrating the presence of serum circulating antigens. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 91, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrusfield, M. Diagnosting Testing in Veterinary Epidemiology; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 305–330. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, A.O.; Lafferty, K.D.; Lotz, J.M.; Shostak, A.W. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. J. Parasitol. 1997, 83, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.W.; Meek, A.H.; Willeberg, P. Veterinary Epidemiology: Principles and Methods; Iowa State University Pres: Ames, IA, USA, 1988; p. 343. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo-Argüello, M.R.; Díez-Baños, M.N.; Martínez-Delgado, A. Parasitic infections in red deer and their repercussions on animal and human health: A study in the north of the province of León. In Parasitic Diseases of Wild Animals and Sustainable Environment: The Wild/Domestic Animal Interface; Hernández-Rodríguez, S., Hidalgo-Argüello, M.R., De la Fuente-López, C., Eds.; Universidad Complutense de Madrid: Madrid, Spain, 2010; pp. 63–95. [Google Scholar]
- Valcárcel, F. Hepatic helminths in red deer in two climatic regions in Spain. Res. Rev. Parasitol. 2003, 63, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rehbein, S.; Lutz, W.; Visser, M.; Winter, R. Investigation of the parasite fauna of wildlife in North Rhine-Westfalia. 2. Endoparasites of red deer. Z. Jagdwiss. 2002, 48, 69–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sleeman, D.P. Parasites of deer in Ireland. J. Life Sci. 1983, 4, 203–210. [Google Scholar]
- Shimalov, V.V.; Shimalov, V.T. Findings of Fasciola hepatica Linnaeus 1758, in wild animals in Belorussia Polesye. Parasitol. Res. 2000, 86, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennema, S.C.; Ducheyne, E.; Vercruysse, J.; Claerebout, E.; Hendrickx, G.; Charlier, J. Relative importance of management, meteorological and environmental factors in the spatial distribution of Fasciola hepatica in dairy cattle in a temperate climate zone. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Baños, N.; Martínez-Delgado, A.; Hidalgo-Argüello, M.R. Comparative survey of hepatic parasites in wild ruminants from three regional hunting reserves in the north of León province (Spain). Acta Parasitol. Portuguesa. 2009, 16, 138–139. [Google Scholar]
- Roldán, C.; Begovoeva, M.; López-Olvera, J.R.; Velarde, R.; Cabezón, O.; Molinar Min, A.R.; Pizzato, F.; Pasquetti, M.; Fernández Aguilar, X.; Mentaberre, G.; et al. Endemic occurrence of Fasciola hepatica in an alpine ecosystem, Pyrenees, Northeastern Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2589–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manga-González, Y.; González-Lanza, C.; Lavín, P. Encuesta parasitológica y ensayos con netobimim frente a Dicrocoelium dendriticum y Fasciola hepatica en ganado vacuno mantenido en pastoreo. Acta Parasitol. Portuguesa. 2001, 8, 348. [Google Scholar]
- Rapsch, C.; Schweizer, G.; Grimm, F.; Kohler, I.; Bauer, C.; Deplazes, P.; Braun, U.; Torgerson, P.R. Estimating the true prevalence of Fasciola hepatica in cattle slaughtered in Switzerland in the absence of an absolute diagnostic test. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.; Lomba, C.; Dacal, V.; Vázquez, L.; Pedreira, J.; Francisco, I.; Piñeiro, P.; Cazapal-Monteiro, C.; Suárez, J.L.; Díez-Baños, P.; et al. Prevalence of mixed trematode infections in an abattoir receiving cattle from northern Portugal and north-west Spain. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Zhang, H.; Sabir, A.J.; Abbas, R.Z.; Ijaz, M.; Durrani, A.Z.; Saleem, M.H.; Ur Rehman, M.; Iqbal, M.K.; Wang, Y.; et al. A review on epidemiology, global prevalence and economical losses of fasciolosis in ruminants. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 109, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Delgado, A. Contribución al Conocimiento del Estado Sanitario del Ciervo (Cervus elaphus) en el Norte de España: Procesos Parasitarios. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de León, León, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- González, S.; Del Rio, M.L.; Díez-Baños, N.; Martínez, A.; Hidalgo, M.R. Contribution to the knowledge of gastrointestinal nematodes in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) from the Province of León, Spain: An epidemiological and molecular study. Animals 2023, 13, 3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, M.; Rojo, F.A.; Martínez, A.R.; Sánchez, M.C.; Hernández, S.; Navarrete, I.; Díez, P.; Quiroz, H.; Carvahlo, M. Parasitología Veterinaria; Mc Graw Hill Interamericana de España, S.A.U.: Madrid, Spain, 1999; p. 968. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M.A. Emerging parasitic diseases of sheep. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 189, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, J.; Doyle, E.; Barwick, J.; Chambers, M.; Kahn, L. Prevalence and pathology of liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) in fallow deer (Dama dama). Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 293, 109427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalor, R.; Cwiklinski, K.; Eliza, N.; Calvani, D.; Dorey, A.; Hamon, S.; López Corrales, J.; Dalton, J.P.; De Marco Verissimo, C. Pathogenicity and virulence of the liver flukes Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica that cause the zoonosis Fasciolosis. Virulence 2021, 12, 2839–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezo, M.; González-Warleta, M.; Castro-Hermida, J.A.; Muino, L.; Ubeira, F.M. Association between anti-F. hepatica antibody levels in milk and production losses in dairy cows. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 180, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenberger, K.; Tichy, A.; Bauer, K.; Pless, P.; Wittek, T. Associations between fasciolosis and milk production, and the impact of anthelmintic treatment in dairy herds. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorchies, P. Comparison of methods for the veterinary diagnosis of liver flukes (Fasciola hepatica) in cattle. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. Cluj-Napoca. Vet. Med. 2007, 64, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Charlier, J.; De Meulemeester, L.; Claerebout, E.; Williams, D.; Vercruysse, J. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation of coprological and serological techniques for the diagnosis of fasciolosis in cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 153, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockwell, Y.; Spithill, T.; Anderson, G.; Grillo, V.; Sangster, N. Comparative kinetics of serological and coproantigen ELISA and faecal egg count in cattle experimentally infected with Fasciola hepatica and following treatment with triclabendazole. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, D.; Schaich, K. Untersuchungen zur experimentellen Fasciolose bei Reh-(Capreolus capreolus) und Rotwild (Cervus elaphus). Z. Jagdwiss. 1973, 19, 183–197. [Google Scholar]
- Pybus, M.J. Liver flukes. In Parasitic Diseases of Wild Mammals, 2nd ed.; Samuel, W.M., Pybus, M.J., Kocan, A.A., Eds.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2001; pp. 121–149. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, G.C.; Forbes, A.B.; Williams, D.J.L.; Salimi-Bejestani, M.R.; Daniel, R.G. Emergence of fasciolosis in cattle in East Anglia. Vet. Rec. 2005, 157, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.; Hillyer, G.V.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Suárez, J.L.; Pedreira, J.; Lomba, C.; Díaz, P.; Morrondo, P.; Díez-Baños, P.; Paz-Silva, A. A 2.9-kDa Fasciola hepatica-recombinant protein based ELISA test for the detection of current-ovine fasciolosis trickle infected. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 137, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, M.A.; Ubeira, F.M.; Khoubbane, M.; Artigas, P.; Muiño, L.; Mezo, M.; Pérez-Crespo, I.; Periago, V.; Mas-Coma, S. MM3-ELISA evaluation of coproantigen release and serum antibody production in sheep experimentally infected with Fasciola hepatica and F. gigantica. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 159, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K.; Bjørnstad, O.N.; Dobson, A.P.; Merler, S.; Poglayen, G.; Randolph, S.E.; Read, A.F.; Skorping, A. Heterogeneities in macroparasite infections: Patterns and processes. In The Ecology of Wildlife Diseases; Hudson, P.J., Rizzoli, A., Grenfell, B.T., Heesterbeek, H., Dobson, A.P., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 6–44. [Google Scholar]
- Revilla-Nuín, B.; Manga-González, M.Y.; Miñambres, B.; González-Lanza, C. Partial characterization and isolation of 130 kDa antigenic protein of Dicrocoelium dendriticum adults. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 134, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.K.; Roberts, L.C.P.; Lean, N.; Zadoks, R.N.; Sargison, N.D.; Skuce, P.J. Identification of the rumen fluke, Calicophoron daubneyi, in GB livestock: Possible implications for liver fluke diagnosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 195, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchís, J.; Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Macchi, M.I.; Piñeiro, P.; Suárez, J.L.; Cazapal-Monteiro, C.; Maldini, G.; Venzal, J.M.; Paz-Silva, A.; Arias, M.S. Infection by Paramphistomidae trematodes in cattle from two agricultural regions in NW Uruguay and NW Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 191, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, J.M.; Stevenson, M.A.; Rathinasamy, V.; Rawlin, G.; Beddoe, T.; Spithill, T.W. Analysis of daily variation in the release of faecal eggs and coproantigen of Fasciola hepatica in naturally infected dairy cattle and the impact on diagnostic test sensitivity. Vet. Parasitol. 2021, 298, 109504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espino, A.M.; Díaz, A.; Pérez, A.; Finlay, C.M. Dynamics of antigenemia and coproantigens during a human Fasciola hepatica outbreak. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 2723–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Andrade, R.; Paz-Silva, A.; Suárez, J.L.; Panadero, R.; Pedreira, J.; Díez-Baños, P.; Morrondo, P. Effect of fasciolicides on the antigenaemia in sheep naturally infected with Fasciola hepatica. Parasitol. Res. 2001, 87, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Host Age | Sex | Seasons | Total n = 100 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤2 Years n = 20 | >2 Years n = 80 | Males n = 26 | Females n = 74 | Autum n = 27 | Winter n = 38 | Spring n = 35 | ||
| Necropsy % | 20 | 10 | 15.4 | 10.8 | 3.7 | 7.9 | 22.8 | 12 |
| ± SD | 2.7 ± 1.7 | 2.6 ± 1.6 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 3.1 ± 1.6 | 1 | 1.7 ± 1.5 | 3.2 ± 1.5 | 2.7 ± 1.5 |
| Range | 1–5 | 1–6 | 1–3 | 1–6 | 1 | 1–3 | 2–6 | 1–6 |
| Egg output (epg) % | 10 | 5 | 7.7 | 5.4 | 7.4 | 2.6 | 8.6 | 6 |
| ± SD | 17 ± 18.4 | 32.5 ± 22.2 | 25 ± 21.2 | 28.5 ± 23.6 | 20 ± 14.1 | 40 | 28 ± 28.8 | 27.3 ± 20.6 |
| Range | 4–30 | 10–60 | 10–40 | 4–60 | 10–30 | 40 | 4–60 | 4–60 |
| FhES-ELISA % | 15 | 36.3 | 42.3 | 28.4 | 37 | 23.7 | 37.1 | 32 |
| FhrAPS-ELISA % | 5 | 15 | 23.1 | 9.5 | 3.7 | 13.2 | 20 | 13 |
| BIO K 211-ELISA % | 0 | 11.3 | 15.4 | 6.9 | 11.1 | 5.3 | 11.4 | 9 |
| FhES-ELISA | FhrAPS-ELISA | BIO K 211-ELISA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infected animals (n = 12) | 7 | 2 | 3 |
| Uninfected animals (n = 88) | 63 | 77 | 82 |
| Sensitivity % | 58.33 | 16.67 | 25 |
| Specificity % | 71.60 | 87.50 | 93.18 |
| PPV % | 21.88 | 15.38 | 33.33 |
| NPV % | 92.65 | 88.51 | 90.11 |
| PLR | 2.053 | 1.333 | 3.700 |
| NLR | 0.582 | 0.952 | 0.805 |
| κ-value | 0.174 | 0.040 | 0.184 |
| p-value | 0.037 | 0.687 | 0.065 |
| Seroprevalence (95% CI) | 32 (23–41) | 13 (6–20) | 9 (3–15) |
| FhES-ELISA | FhrAPS-ELISA | BIO K 211-ELISA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infected animals (n = 6) | 4 | 1 | 2 |
| Uninfected animals (n = 94) | 66 | 82 | 87 |
| Specificity % | 66.67 | 16.67 | 33.33 |
| Specificity % | 70.21 | 87.23 | 92.55 |
| PPV % | 12.50 | 3.12 | 6.25 |
| NPV % | 97.06 | 92.64 | 94.12 |
| PLR | 2.238 | 1.305 | 4.474 |
| NLR | 0.475 | 0.955 | 0.720 |
| κ-value | 0.122 | −0.054 | 0.005 |
| Seroprevalence (95% CI) | 32 (23–41) | 13 (6–20) | 9 (3–15) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González Hidalgo, S.; Diez Baños, N.; Hidalgo Argüello, M.d.R.; Martínez-Delgado, A. Natural Infection by Fasciola hepatica in Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) from NW Spain: The Usefulness of Necropsy, Coprology, and Three Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for the Diagnosis. Animals 2025, 15, 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182649
González Hidalgo S, Diez Baños N, Hidalgo Argüello MdR, Martínez-Delgado A. Natural Infection by Fasciola hepatica in Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) from NW Spain: The Usefulness of Necropsy, Coprology, and Three Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for the Diagnosis. Animals. 2025; 15(18):2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182649
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález Hidalgo, Sara, Natividad Diez Baños, María del Rosario Hidalgo Argüello, and Angelica Martínez-Delgado. 2025. "Natural Infection by Fasciola hepatica in Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) from NW Spain: The Usefulness of Necropsy, Coprology, and Three Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for the Diagnosis" Animals 15, no. 18: 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182649
APA StyleGonzález Hidalgo, S., Diez Baños, N., Hidalgo Argüello, M. d. R., & Martínez-Delgado, A. (2025). Natural Infection by Fasciola hepatica in Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) from NW Spain: The Usefulness of Necropsy, Coprology, and Three Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays for the Diagnosis. Animals, 15(18), 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15182649






