Novel Insight into Dugong Mortality: First Report of Systemic Achromobacter xylosoxidans Infection, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation, and Associated Pathogenesis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Signalment and History
2.2. Necropsy
2.3. Bacteriological Examination
2.4. Histopathology
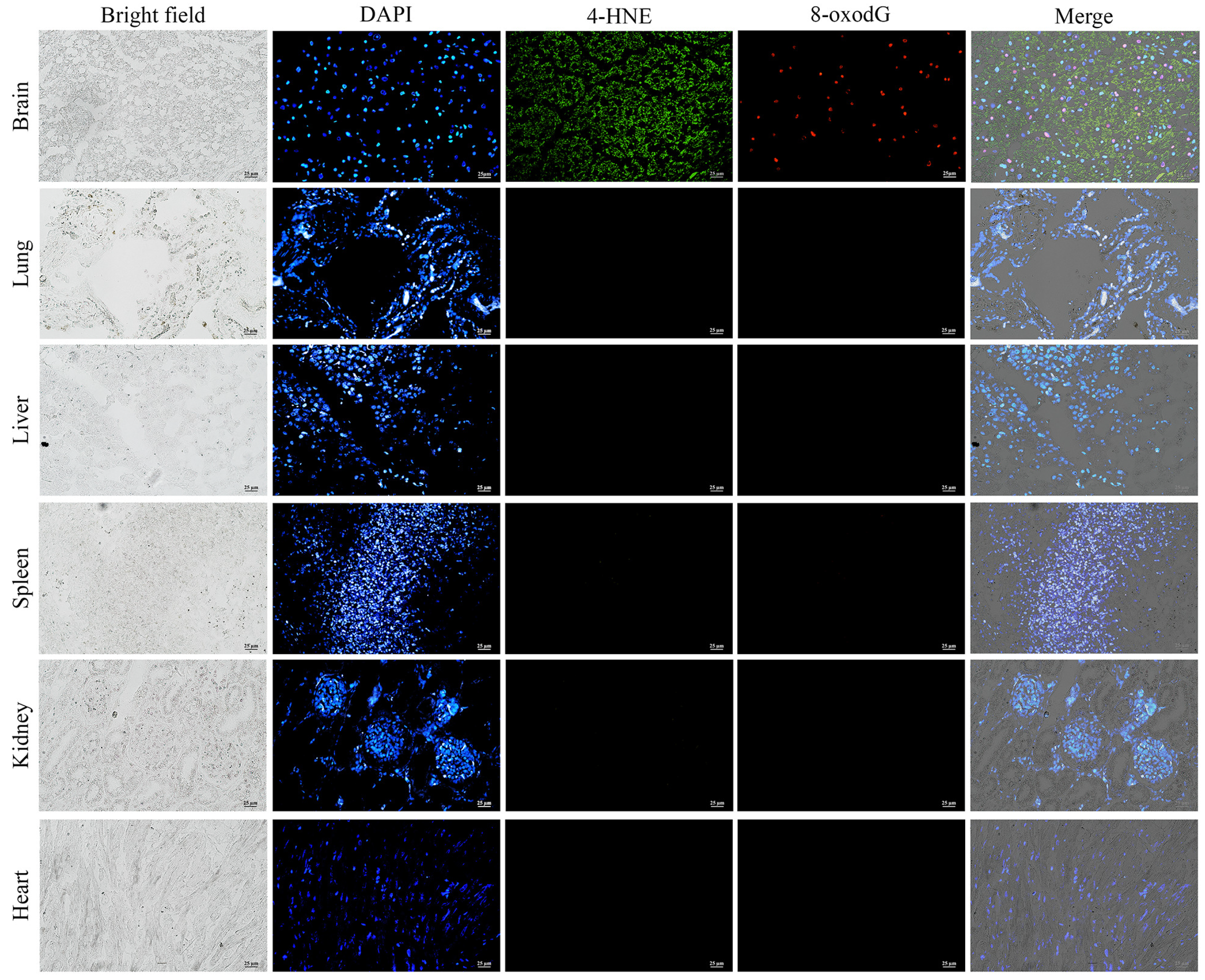
2.5. Biomarker of Oxidative Damage
2.6. AI Tools Statement
3. Results
3.1. Anamnesis, Clinical Examination, and Treatment
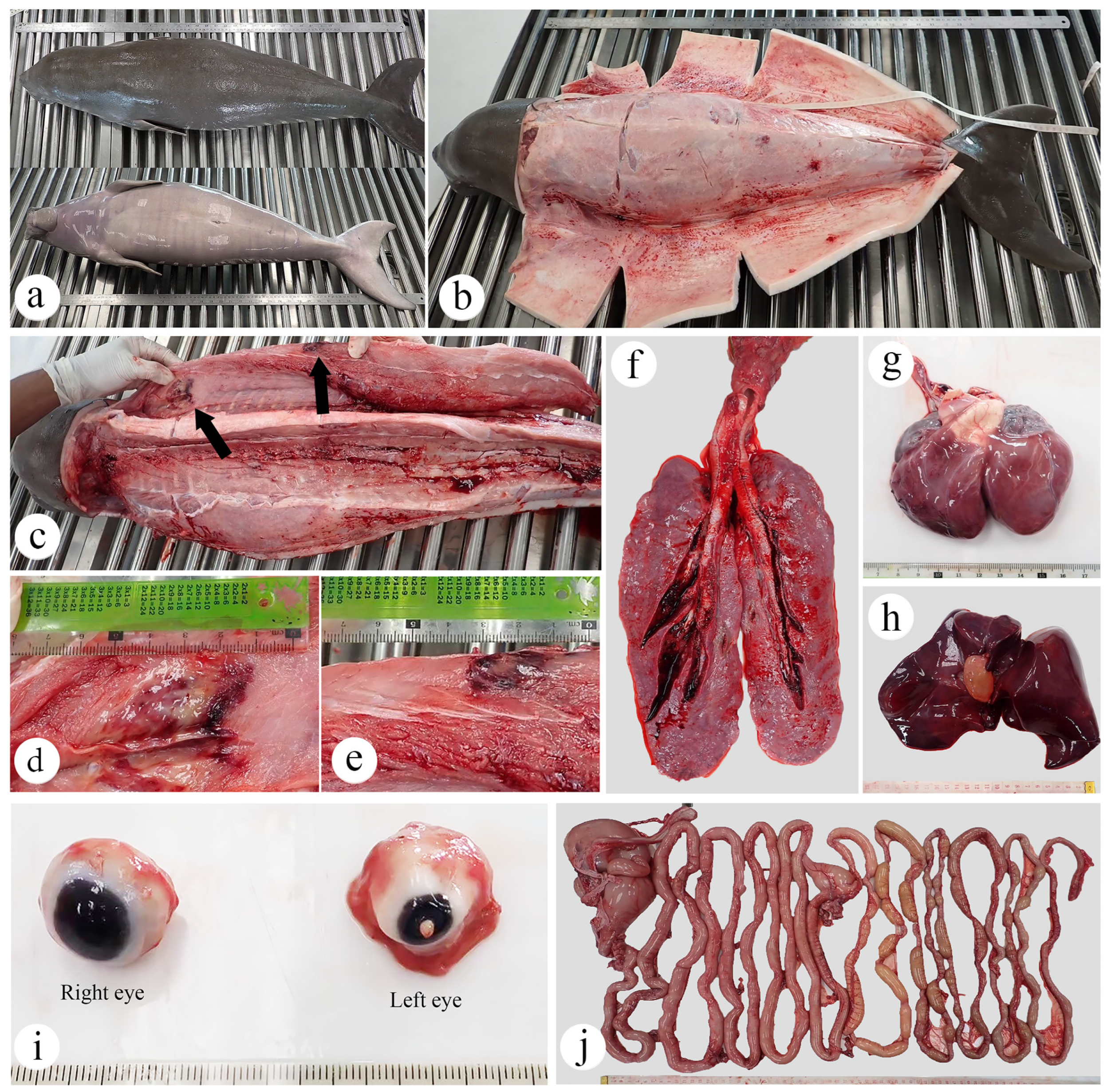
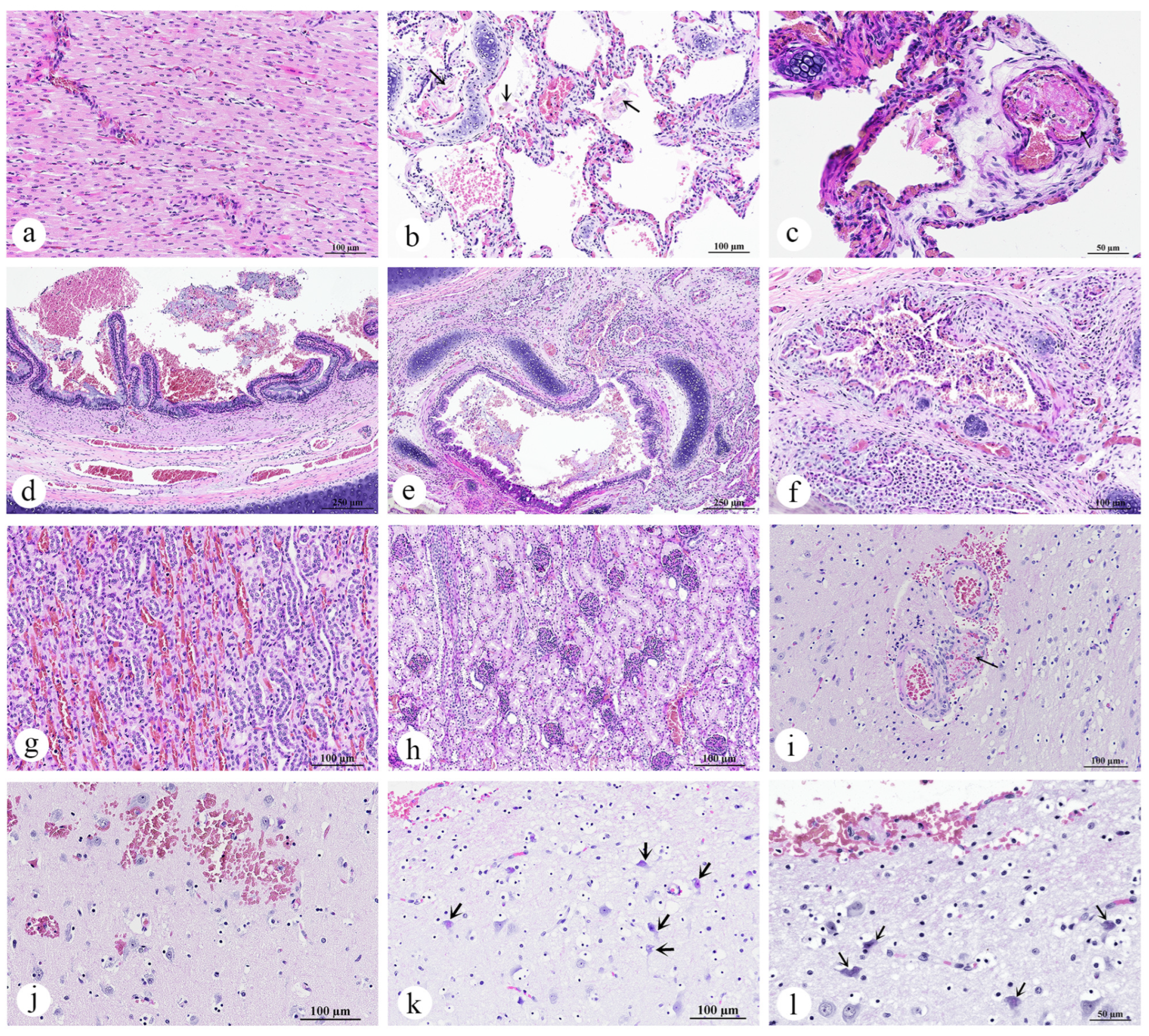
3.2. Necropsy and Histopathology Investigations
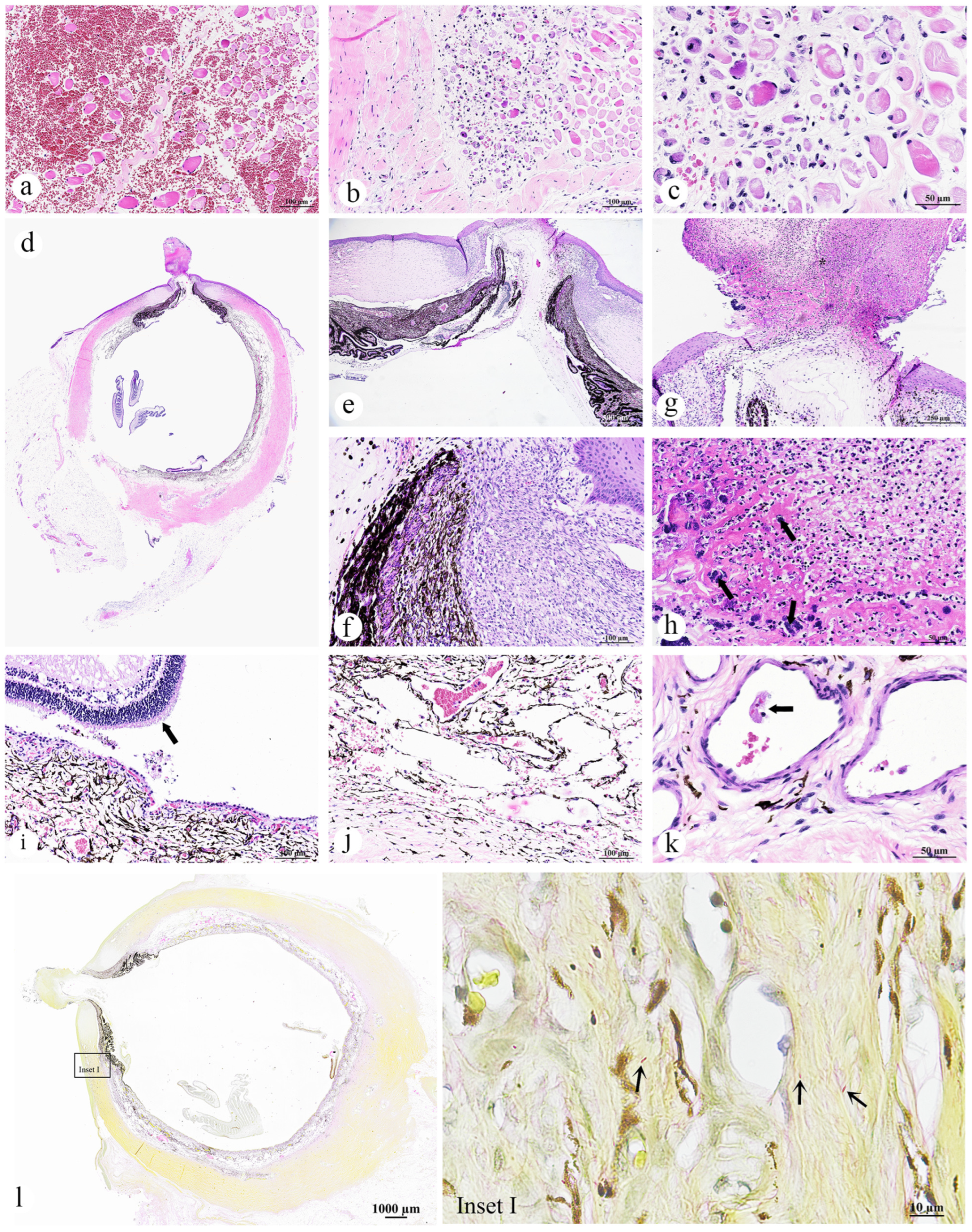
3.2.1. Skin and Muscle
- Skeletal muscle: Myositis and myonecrosis, multifocal, chronic-active, with myofiber degeneration and atrophy, myocyte regeneration, and histiocytic infiltration.
3.2.2. Eye
- Left eye: Kerato-uveitis, chronic-active, suppurative and necrotizing, with corneal perforation, anterior synechia, retinal detachment, fibrin thrombi, and bacterial colonization (Gram-negative bacilli);
- Right eye: No significant lesions.
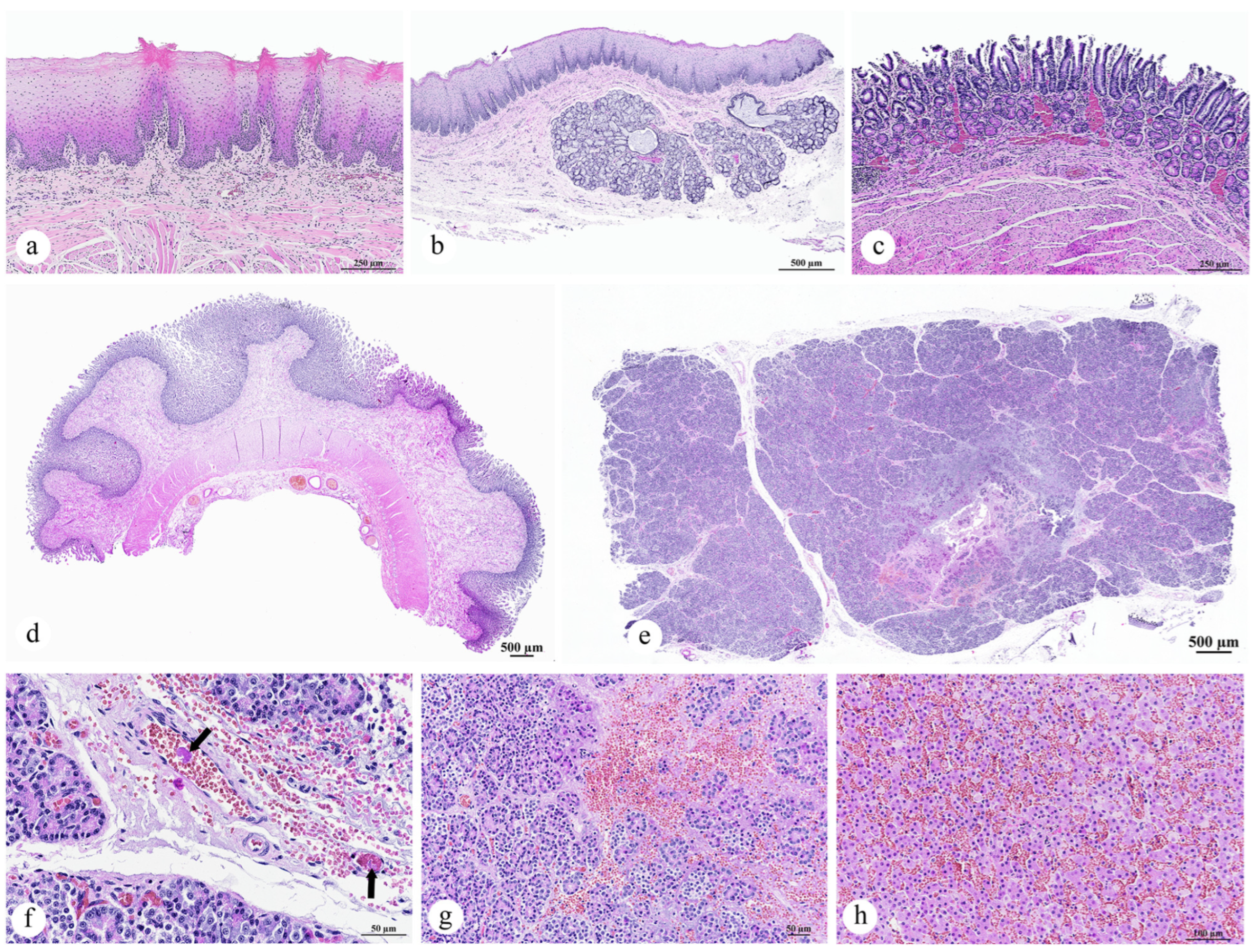
3.2.3. Gastrointestinal Organ and the Accessory Digestive Structures
- Pancreas: Pancreatic necrosis, lytic, multifocal to coalescing, peracute, with fibrin thrombi and vascular necrosis;
- Liver: Congestion, multifocal to coalescing, moderate to severe, with hepatocellular degeneration;
- Esophagus: Parakeratotic hyperkeratosis, mild;
- Stomach and intestine: Congestion, mild;
- Tongue: No significant lesions.
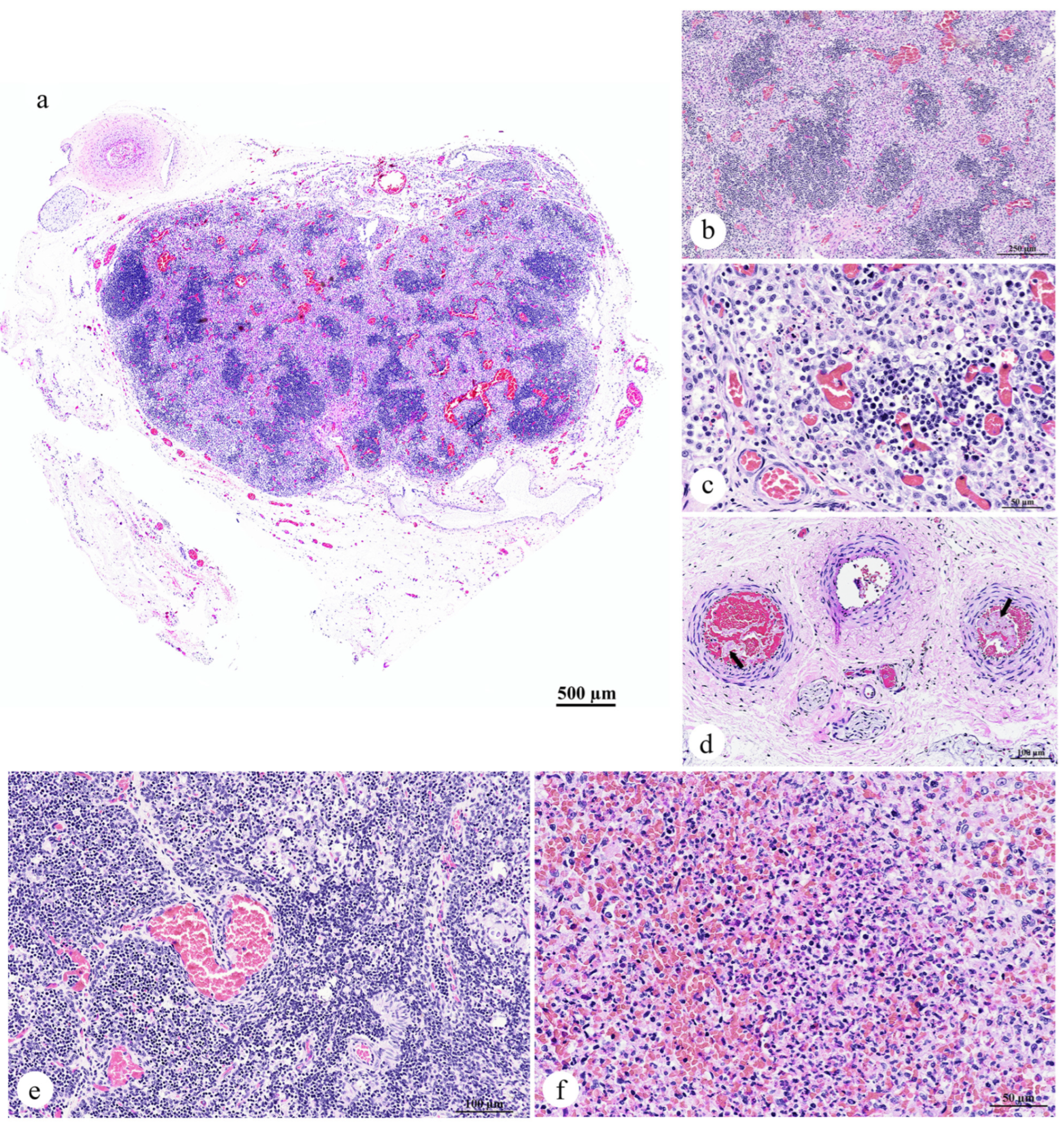
3.2.4. Lymph Node, Thymus, and Spleen
- Lymph node: Lymphadenitis, neutrophilic and histiocytic, acute, multifocal to coalescing, with paracortical hyperplasia, vascular congestion, and fibrin thrombi;
- Spleen: Splenitis, neutrophilic and necrotizing, acute, multifocal, severe, with red pulp hypercellularity and white pulp depletion;
- Thymus: No significant lesions.
3.2.5. Cardiorespiratory System
- Lung: Pulmonary congestion and edema, acute, multifocal to coalescing, with pulmonary hemorrhage, intra-aveolar squames (aspiration), and fibrin thrombi;
- Trachea: Intraluminal mucus and epithelial debris;
- Bronchi/bronchioles: Bronchopneumonia, lymphohistiocytic and neutrophilic, mild to moderate, with mucosal and submucosal inflammation;
- Heart: Congestion, no significant lesions.
3.2.6. Adrenal Glands, Kidneys, and Urinary Bladder
- Kidneys: Congestion, multifocal, mild to moderate;
- Urinary bladder: No significant lesions;
- Adrenal glands: No significant lesions.
3.2.7. Brain
- Cerebrum, brainstem, and cerebellum: Thromboembolic vasculopathy with fibrinoid necrosis and microhemorrhages, multifocal, with neuronal degeneration and necrosis.
3.3. Bacteriological Analysis and Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
3.4. Immunofluorescence Analysis of Oxidative Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4-HNE | 4-hydroxynonenal |
| 8-oxodG | 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine |
| DIC | Disseminated intravascular coagulation |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| IM | Intramuscular |
| IUCN | International Union for Conservation of Nature |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SID | Semel in die, which is Latin for “once a day” or “once daily” |
| °C | Degrees Celsius |
References
- IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Dugong Dugon. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/6909/160756767 (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- Hines, E.; Adulyanukosol, K.; Poochaviranon, S.; Somany, P.; Ath, L.; Cox, N.; Symington, K.; Tun, T.; Ilangakoon, A.; Iongh, H.; et al. Conserv . Dugongs Asia Pac. 2012, 58, 58–76. [Google Scholar]
- Panyawai, J.; Prathep, A. A systematic review of the status, knowledge, and research gaps of dugong in Southeast Asia. Aquat. Mamm. 2022, 48, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharat, A.; Lee, Y. Measuring the nonuse value of the dugong (Dugong dugon) in Thailand. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2020, 13, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.Z.H.; Ow, Y.X.; Jaafar, Z. Dugongs (Dugong dugon) along hyper-urbanized coastlines. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 945123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daochai, C.; Sornying, P.; Keawchana, N.; Manmoo, S.; Khumraksa, P.; Kaewmong, P.; Ninwat, S.; Upanoi, T.; Sukkarun, P.; Suyapoh, W. Investigation into the causes of mortality in cetaceans and sirenian populations in the Andaman Sea, Thailand: A retrospective analysis spanning 2018–2023. Vet. World 2024, 17, 2889–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalone, C.; Mazzariol, S.; Pautasso, A.; Di Guardo, G.; Di Nocera, F.; Lucifora, G.; Ligios, C.; Franco, A.; Fichi, G.; Cocumelli, C.; et al. Cetacean strandings in Italy: An unusual mortality event along the Tyrrhenian Sea coast in 2013. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2014, 109, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Sarmiento, A.M.; Carvalho, V.L.; Díaz-Delgado, J.; Ressio, R.A.; Fernandes, N.C.C.A.; Guerra, J.M.; Sacristán, C.; Groch, K.R.; Silvestre-Perez, N.; Ferreira-Machado, E.; et al. Molecular, serological, pathological, immunohistochemical and microbiological investigation of Brucella spp. in marine mammals of Brazil reveals new cetacean hosts. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1674–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Delgado, J.; Fernández, A.; Sierra, E.; Sacchini, S.; Andrada, M.; Vela, A.I.; Quesada-Canales, Ó.; Paz, Y.; Zucca, D.; Groch, K.; et al. Pathologic findings and causes of death of stranded cetaceans in the Canary Islands (2006–2012). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leguia, M.; Garcia-Glaessner, A.; Muñoz-Saavedra, B.; Juarez, D.; Barrera, P.; Calvo-Mac, C.; Jara, J.; Silva, W.; Ploog, K.; Amaro, L.; et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) in marine mammals and seabirds in Peru. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.E.; Read, A.J. A Bayesian uncertainty analysis of cetacean demography and bycatch mortality using age-at-death data. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 1914–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IJsseldijk, L.L.; Camphuysen, K.C.; Keijl, G.O.; Troost, G.; Aarts, G. Predicting harbor porpoise strandings based on near-shore sightings indicates elevated temporal mortality rates. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 668038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obusan, M.C.M.; Caras, J.A.A.; Lumang, L.S.L.; Calderon, E.J.S.; Villanueva, R.M.D.; Salibay, C.C.; Siringan, M.A.T.; Rivera, W.L.; Masangkay, J.S.; Aragones, L.V. Bacteriological and histopathological findings in cetaceans that stranded in the Philippines from 2017 to 2018. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0243691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, J.D.; Wells, R.S.; Rhinehart, H.L.; Hansen, L.J. Aerobic microorganisms associated with free-ranging bottlenose dolphins in coastal Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic Ocean waters. J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, P.J.; Johnson, W.R.; Pisani, J.; Bossart, G.D.; Adams, J.; Reif, J.S.; Fair, P.A. Isolation of culturable microorganisms from free-ranging bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from the southeastern United States. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 148, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obusan, M.C.M.; Villanueva, R.M.D.; Siringan, M.A.T.; Rivera, W.L.; Aragones, L.V. Leptospira spp. and Toxoplasma gondii in stranded representatives of wild cetaceans in the Philippines. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obusan, M.C.M.; Aragones, L.V.; Salibay, C.C.; Siringan, M.A.T.; Rivera, W.L. Occurrence of human pathogenic bacteria and Toxoplasma gondii in cetaceans stranded in the Philippines: Providing clues on ocean health status. Aquat. Mamm. 2015, 41, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukkarun, P.; Arnuphapprasert, A.; Khumraksa, P.; Daochai, C.; Jantrakajorn, S.; Keawchana, N.; Sornying, P.; Suyapoh, W. Identification and Pathological Assessment of Mycobacterium spp. Infections in Wild Marine Mammals from the Andaman Sea, Thailand. In Proceedings of the 26th Khon Kaen Veterinary Annual International Conference (KVAC), Khon Kaen, Thailand, 16–17 July 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, P.; Baker, J.; Kuiken, T.; Simpson, V.; Kennedy, S.; Bennett, P. Pulmonary pathology of harbour porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) stranded in England and Wales between 1990 and 1996. Vet. Rec. 2000, 146, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, E.; Fernández, A.; Felipe-Jiménez, I.; Zucca, D.; Díaz-Delgado, J.; Puig-Lozano, R.; Câmara, N.; Consoli, F.; Díaz-Santana, P.; Suárez-Santana, C. Histopathological differential diagnosis of meningoencephalitis in cetaceans. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerba, C.P. Environmentally transmitted pathogens. In Environmental Microbiology, 3rd ed.; Pepper, I.L., Gerba, C.P., Gentry, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 10, pp. 509–550. [Google Scholar]
- Semeraro, N.; Ammollo, C.T.; Semeraro, F.; Colucci, M. Sepsis-associated disseminated intravascular coagulation and thromboembolic disease. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 2, e2010024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, W.; Rogers, L.; Pinpimai, K.; Dittmer, K.; Marshall, J.; Chilvers, B. Septicaemia and meningitis in sea lion pups with hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 176, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, S.; Johnson, S.; Rios, C.; Fletcher, D.J. Coagulation and fibrinolysis in northern elephant seals. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 46, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H. Age determination of the dugong (Dugong dugon) in northern Australia and its biological implications. Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. Spec. Iss. 1980, 3, 181–201. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Marine and Coastal Resources (DMCR). Dugong Necropsy Manual in Thailand; Department of Marine and Coastal Resources: Bangkok, Thailand, 2013. (In Thai) [Google Scholar]
- Abutarbush, S.M. Veterinary Medicine—A Textbook of the Diseases of Cattle, Horses, Sheep, Pigs and Goats, 10th ed.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1830–1903. [Google Scholar]
- Goudalier, C.; Mouillot, D.; Bernagou, L.; Boksmati, T.; Bristol, C.; Clark, H.; Herandarudewi, S.M.C.; Hocdé, R.; Koester, A.; McIvor, A.J.; et al. Drone photogrammetry reveals contrasting body conditions of dugongs across the Indo-Pacific. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliares, K.R.; Bogomolni, A.; Touhey, K.M.; Herzig, S.M.; Harry, C.T. Marine Mammal Necropsy: An Introductory Guide; NOAA Fisheries: Woods Hole, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Eros, C.; Marsh, H.; Bonde, R.; O’Shea, T.; Beck, C.; Recchia, C.; Dobbs, K.; Turner, M.; Lemm, S.; Pears, R. Procedures for the Salvage and Necropsy of the Dugong; GBRMPA Research Publication No. 85; Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority: Townsville, QLD, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Suyapoh, W.; Nilake, C.; Sriamad, A.; Assawakulkamneard, T.; Prasertsee, T.; Jantrakajorn, S. First report of Streptococcus iniae infection in cultured spotted scat (Scatophagus argus) in Thailand. J. Fish Dis. 2025, e70031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasone, I.; Kinjo, T.; Yamane, N.; Kisanuki, K.; Shiohira, C.M. Laboratory-based evaluation of the colorimetric VITEK-2 Compact system for species identification and of the advanced expert system for detection of antimicrobial resistances: VITEK-2 Compact system identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 58, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.; Kirby, W.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suyapoh, W.; Keawchana, N.; Sornying, P.; Tangkawattana, S.; Khirilak, P.; Jantrakajorn, S. Mixed Eimeria and Cryptosporidium infection and its effects on pathology and clinical outcomes in juvenile Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) cultured in Thailand. J. Fish Dis. 2024, 47, e13914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyapoh, W.; Thaweechart, B.; Wae-asae, P.; Keawchana, N.; Sornying, P.; Manmoo, S.; Rakwong, P.; Jantrakajorn, S. Detection and pathological effects of intestinal parasites in spotted scat Scatophagus argus: Filisoma spp. and Cryptosporidium spp. as infective agents and their roles in fish inflammatory response. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2025, vsaf009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantrakajorn, S.; Keawchana, N.; Sornying, P.; Khirilak, P.; Suyapoh, W. Intestinal inflammation, oxidative damage, and pathogenesis of intestinal Cryptosporidium in juvenile Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer). J. World Aquacult. Soc. 2024, 56, e13114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, V.; McMichael, L.; Hunter, M.E.; Takoukam Kamla, A.; Lanyon, J.M. A new DNA extraction method (HV-CTAB-PCI) for amplification of nuclear markers from open ocean-retrieved faeces of an herbivorous marine mammal, the dugong. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0278792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanyon, J.M.; Wong, A.; Long, T.; Woolford, L. Serum biochemistry reference intervals of live wild dugongs (Dugong dugon) from urban coastal Australia. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 44, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, J.P.; Burd, E.M. Other gram-negative and gram-variable bacilli. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 8th ed.; Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 2667–2683.e2664. [Google Scholar]
- Turel, O.; Kavuncuoglu, S.; Hosaf, E.; Ozbek, S.; Aldemir, E.; Uygur, T.; Hatipoğlu, N.; Siraneci, R. Bacteremia due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans in neonates: Clinical features and outcome. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Barragán, E.; Sandino Pérez, J.; Corbella, L.; Orellana, M.A.; Fernández-Ruiz, M. Achromobacter xylosoxidans bacteremia: Clinical and microbiological features in a 10-year case series. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2018, 31, 268–273. [Google Scholar]
- Rajni, E.; Kataria, S.; Sarna, M.K.; Garg, V.K. A case of bacteremia by Achromobacter xylosoxidans in an immunocompromised host and review of literature. Arch. Med. Health Sci. 2023, 11, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, V.; Rosel, A.C.; Ruppitsch, W.; Allerberger, F.; Carranza Valencia, A.; Markovic, M.; Luckschander-Zeller, N.; Szostak, M.P.; Spergser, J.; Loncaric, I.; et al. The first bacterial endocarditis due to Achromobacter xylosoxidans in a dog. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girling, S.L.; Innes, J.F. Infection of a total hip prosthesis in a dog caused by Achromobacter (Alcaligenes) xylosoxidans. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2006, 47, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorbach, B.S.; Rotstein, D.S.; Stacy, N.I.; Mavian, C.; Salemi, M.; Waltzek, T.B.; de Wit, M. Fatal systemic salmonellosis in a Florida manatee (Trichechus manatus latirostris). J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, J.H.; Tabuchi, M.; Rotstein, D.S.; Subramaniam, K.; Rodrigues, T.C.S.; Waltzek, T.B.; Stacy, N.I.; Wilson, P.W.; Kiryu, Y.; Uzal, F.A.; et al. Novel lethal clostridial infection in Florida manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris): Cause of the 2013 unusual mortality event in the Indian River Lagoon. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 841857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Shibuya, H.; Ohba, S.; Nojiri, T.; Shirai, W. Mycobacteriosis in two captive Florida manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2003, 34, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trancassini, M.; Iebba, V.; Citerà, N.; Tuccio, V.; Magni, A.; Varesi, P.; Biase, R.; Totino, V.; Santangelo, F.; Gagliardi, A.; et al. Outbreak of Achromobacter xylosoxidans in an Italian cystic fibrosis center: Genome variability, biofilm production, antibiotic resistance, and motility in isolated strains. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, B.; Kidd, T.J.; Stewart, A.G.; Harris, P.; Paterson, D.L. Achromobacter infections and treatment options. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01025-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalhoub, H.; Kampmeier, S.; Kahl, B.C.; Van Bambeke, F. Role of efflux in antibiotic resistance of Achromobacter xylosoxidans and Achromobacter insuavis isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 895389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.M.; Penstoft, L.N.; Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. Motility, biofilm formation and antimicrobial efflux of sessile and planktonic cells of Achromobacter xylosoxidans. Pathogens 2019, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, H.; Zaman, A.; Rafiq, W.; Murtaza, M.H.; Ullah, I. Immunosuppression in infectious diseases: Causes and effects. In Innate Immunity—New Perspectives and Therapeutic Opportunities; Lasfar, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.S.; da Silva, V.P.; Bracarense, A.P.F.R.L.; Domit, C. Environmental aspects and diseases related to immunosuppression in cetaceans: A concise review. Semina: Ciênc. Agrár. 2018, 39, 2897–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsili, L.; Di Guardo, G.; Mazzariol, S.; Casini, S. Insights into cetacean immunology: Do ecological and biological factors make the difference? Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Jiang, F.; Ma, J.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Zhu, Y.; Yong, J.W.H. Intersecting planetary health: Exploring the impacts of environmental stressors on wildlife and human health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 283, 116848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoureux, L.; Bador, J.; Fardeheb, S.; Mabille, C.; Couchot, C.; Massip, C.; Salignon, A.L.; Berlie, G.; Varin, V.; Neuwirth, C. Detection of Achromobacter xylosoxidans in hospital, domestic, and outdoor environmental samples and comparison with human clinical isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7142–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.H.; Kim, H.; Lim, S.M.; Kang, J.M. Nosocomial outbreak of Achromobacter spp. bacteremia due to germicide contamination: A systematic review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 6374–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, T.H.; Hansen, M.A.; Jensen, P.O.; Hansen, L.; Riber, L.; Cockburn, A.; Kolpen, M.; Hansen, C.R.; Ridderberg, W.; Eickhardt, S.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the cystic fibrosis pathogen Achromobacter xylosoxidans NH44784-1996 complies with important pathogenic phenotypes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gando, S.; Levi, M.; Toh, C.H. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. J. Intensive Care 2025, 13, 32–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, C.; Jourdi, G.; Adjambri, E.; Walborn, A.; Patel, P.; Fareed, J.; Elalamy, I.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Gerotziafas, G.T. Disseminated intravascular coagulation: An update on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic strategies. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2018, 24 (Suppl. S9), S8–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepthi, K.G.; Prabagaran, S.R. Ocular bacterial infections: Pathogenesis and diagnosis. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 145, 104206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, C.Y.; Ho, M.; Iu, L.P.-l.; Sin, H.P.-y.; Chen, L.J.; Lui, G.; Brelen, M.E.; Young, A.L. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of endogenous Klebsiella endophthalmitis: A 12-year review. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 13, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedermann, C.J. Hypoalbuminemia as surrogate and culprit of infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, J.S. Gut health, stress, and immunity in neonatal dairy calves: The host side of host-pathogen interactions. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedney, C.J.; Harvill, E.T. The neonatal immune system and respiratory pathogens. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, S.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, C.; Wan, J.; Yang, J.; Xing, X. Oxidative stress in acute pulmonary embolism: Emerging roles and therapeutic implications. Thromb. J. 2024, 22, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zennadi, R. Oxidative stress and thrombosis during aging: The roles of oxidative stress in RBCs in venous thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Tissue/Organ | Congestion | Hemorrhage | Necrosis | Cellular Infiltration | Fibrin Thrombi in Capillary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal system | |||||
| Skeletal muscle | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Nervous and sensory system | |||||
| Brain | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Eye | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Digestive system | |||||
| Tongue | ✓ | ||||
| Esophagus | ✓ | ||||
| Stomach | ✓ | ||||
| Intestine | ✓ | ||||
| Pancreas | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Liver | ✓ | ||||
| Lymphatic system | |||||
| Lymph node | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Spleen | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Thymus | ✓ | ||||
| Urinary system | |||||
| Kidney | ✓ | ||||
| Urinary bladder | ✓ | ||||
| Endocrine system | |||||
| Adrenal gland | ✓ | ||||
| Cardiorespiratory system | |||||
| Heart | ✓ | ||||
| Trachea | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Bronchi/bronchioles | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Alveolar | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Antibiotic | Concentration (µg) of the Antibiotic in Disc | Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant | Intermediate | Sensitive | ||
| Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid | 20/10 | - | - | 23 |
| Amikacin | 30 | 12 | - | - |
| Cefazolin | 30 | 13 | - | - |
| Ceftriaxone | 30 | 12 | - | - |
| Doxycycline | 30 | - | - | 20 |
| Enrofloxacin | 5 | - | 19 | - |
| Imipenem | 10 | - | - | 27 |
| Marbofloxacin | 5 | - | 17 | - |
| Oxytetracycline | 30 | 13 | - | - |
| Sulfa-trimethoprim | 1.25/23.7 | - | - | 26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eiamcharoen, P.; Khumraksa, P.; Ninwat, S.; Suttiboon, T.; Keawchana, N.; Sornying, P.; Suyapoh, W. Novel Insight into Dugong Mortality: First Report of Systemic Achromobacter xylosoxidans Infection, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation, and Associated Pathogenesis. Animals 2025, 15, 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162441
Eiamcharoen P, Khumraksa P, Ninwat S, Suttiboon T, Keawchana N, Sornying P, Suyapoh W. Novel Insight into Dugong Mortality: First Report of Systemic Achromobacter xylosoxidans Infection, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation, and Associated Pathogenesis. Animals. 2025; 15(16):2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162441
Chicago/Turabian StyleEiamcharoen, Piyaporn, Piyarat Khumraksa, Santi Ninwat, Tatsawan Suttiboon, Narissara Keawchana, Peerapon Sornying, and Watcharapol Suyapoh. 2025. "Novel Insight into Dugong Mortality: First Report of Systemic Achromobacter xylosoxidans Infection, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation, and Associated Pathogenesis" Animals 15, no. 16: 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162441
APA StyleEiamcharoen, P., Khumraksa, P., Ninwat, S., Suttiboon, T., Keawchana, N., Sornying, P., & Suyapoh, W. (2025). Novel Insight into Dugong Mortality: First Report of Systemic Achromobacter xylosoxidans Infection, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation, and Associated Pathogenesis. Animals, 15(16), 2441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15162441






