Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Extruded Linseed on Growth Performance and Meat Quality of Young Holstein Bulls
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Dietary Treatments
2.2. Slaughtering and Meat Sampling
2.3. Meat Quality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Animal Performance
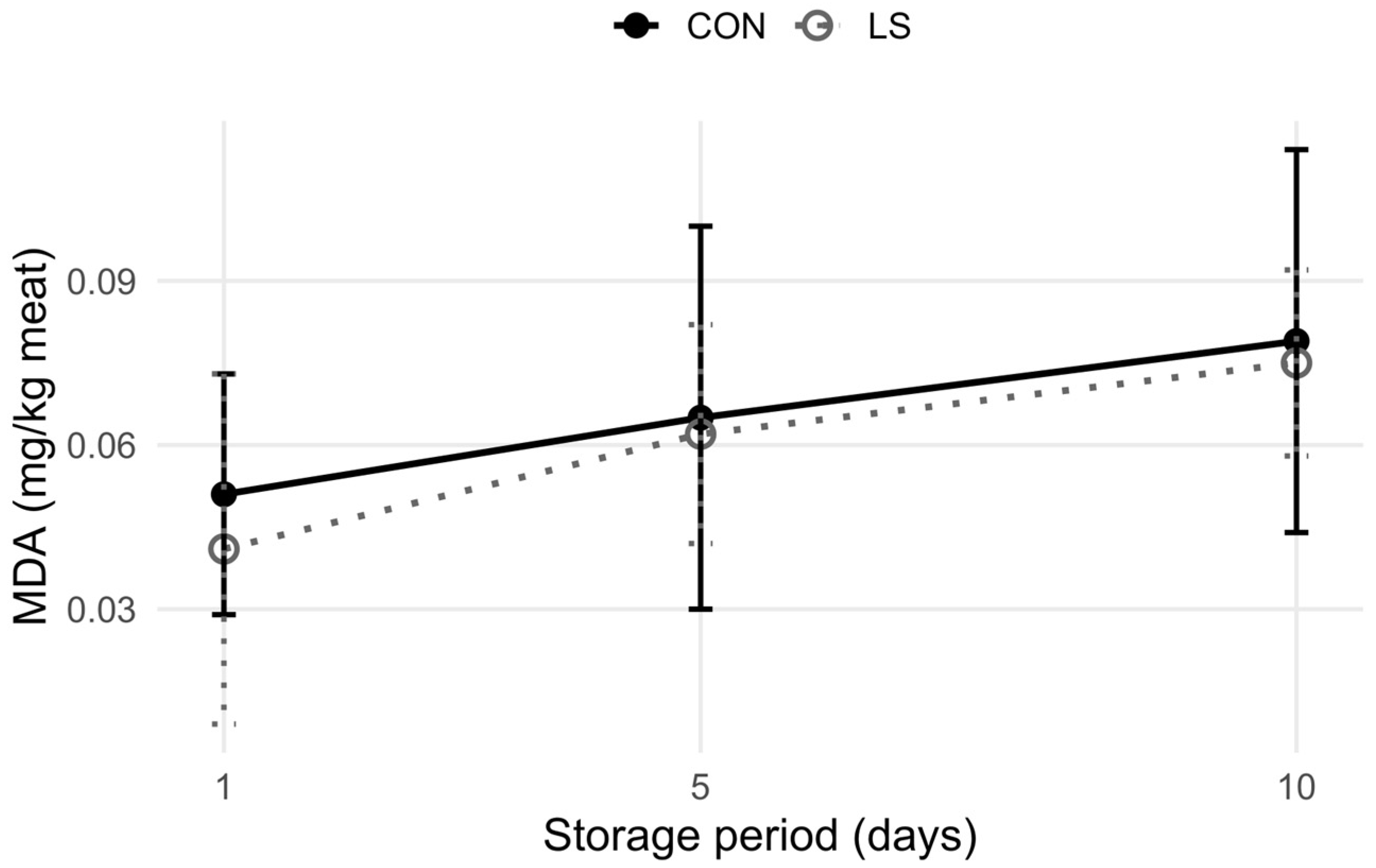
3.2. Meat Quality Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Food Balances (2010–Present); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Eurostat. Milk and Milk Product Statistics; Eurostat: Luxembourg, 2024.
- FAO. Meat Market Review: Emerging Trends and Outlook, December 2020; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bown, M.; Muir, P.; Thomson, B. Dairy and Beef Breed Effects on Beef Yield, Beef Quality and Profitability: A Review. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 59, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouillard, J.S. Current Situation and Future Trends for Beef Production in the United States of America—A Review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, J.W.; Clarke, A.; Byrne, A.W.; Doyle, R.; Blake, M.; Cromie, A.; Barrett, D. Exploring the Opinions of Irish Beef Farmers Regarding Dairy Beef Integration. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 660061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezagholivand, A.; Nikkhah, A.; Khabbazan, M.H.; Mokhtarzadeh, S.; Dehghan, M.; Mokhtabad, Y.; Sadighi, F.; Safari, F.; Rajaee, A. Feedlot Performance, Carcass Characteristics and Economic Profits in Four Holstein-Beef Crosses Compared with Pure-Bred Holstein Cattle. Livest. Sci. 2021, 244, 104358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, S.; Realini, C.E.; Bach, A.; Pérez-Juan, M.; Devant, M. Effect of Castration and Slaughter Age on Performance, Carcass, and Meat Quality Traits of Holstein Calves Fed a High-Concentrate Diet. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsitsos, A.; Dokou, S.; Chatzimanou, T.; Giannenas, I.; Economou, V.; Arsenos, G. Improvement of the Meat Quality of Holstein Bulls Fed a Diet Enriched with Oregano Oil. Animals 2024, 14, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, S.; Pérez, M.; Aris, A.; Bach, A.; Devant, M. Effect of Dietary Energy Density and Meal Size on Growth Performance, Eating Pattern, and Carcass and Meat Quality in Holstein Steers Fed High-Concentrate Diets. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 3515–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scollan, N.; Hocquette, J.-F.; Nuernberg, K.; Dannenberger, D.; Richardson, I.; Moloney, A. Innovations in Beef Production Systems That Enhance the Nutritional and Health Value of Beef Lipids and Their Relationship with Meat Quality. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.K.; Mridula, D.; Rehal, J.; Barnwal, P. Flaxseed: A Potential Source of Food, Feed and Fiber. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaić, A.; Škorput, D.; Luković, Z.; Salajpal, K.; Kljak, K.; Radovčić, N.M.; Karolyi, D. Effect of Linseed Feeding on Carcass and Meat Quality and Intramuscular Fatty Acid Profile of Simmental Bulls Slaughtered at Different Ages. Foods 2025, 14, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renna, M.; Brugiapaglia, A.; Zanardi, E.; Destefanis, G.; Prandini, A.; Moschini, M.; Sigolo, S.; Lussiana, C. Fatty Acid Profile, Meat Quality and Flavour Acceptability of Beef from Double-Muscled Piemontese Young Bulls Fed Ground Flaxseed. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronberg, S.L.; Scholljegerdes, E.J.; Murphy, E.J.; Ward, R.E.; Maddock, T.D.; Schauer, C.S. Treatment of Flaxseed to Reduce Biohydrogenation of α-Linolenic Acid by Ruminal Microbes in Sheep and Cattle, and Increase n-3 Fatty Acid Concentrations in Red Meat1,2. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 4618–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Yue, X.; Li, F.; Li, F.; Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Hou, P. Flax Seed Meal Improved the Meat Tenderness, Nutritional Value of Fatty Acids, and Catalase Activity of Hu Lambs. Meat Sci. 2025, 222, 109750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, A.F.; Gonthier, C.; Ouellet, D.R. Effects of Extrusion of Flaxseed on Ruminal and Postruminal Nutrient Digestibilities. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2003, 57, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP); Villa, R.E.; Azimonti, G.; Bonos, E.; Christensen, H.; Durjava, M.; Dusemund, B.; Gehring, R.; Glandorf, B.; Kouba, M.; et al. Assessment of the Feed Additive Copper Bilysinate for All Animal Species for the Renewal of Its Authorisation (Senzyme GmbH). EFSA J. 2025, 23, e9356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterk, A.; Hovenier, R.; Vlaeminck, B.; Van Vuuren, A.M.; Hendriks, W.H.; Dijkstra, J. Effects of Chemically or Technologically Treated Linseed Products and Docosahexaenoic Acid Addition to Linseed Oil on Biohydrogenation of C18:3n-3 in Vitro. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5286–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauregard, A.; Dallaire, M.-P.; Gervais, R.; Chouinard, P.Y. Lactational Performance of Cows Fed Extruded Flaxseed in Commercial Dairy Herds. Anim.—Open Space 2023, 2, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonthier, C.; Mustafa, A.F.; Ouellet, D.R.; Chouinard, P.Y.; Berthiaume, R.; Petit, H.V. Feeding Micronized and Extruded Flaxseed to Dairy Cows: Effects on Blood Parameters and Milk Fatty Acid Composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moallem, U. The Effects of Extruded Flaxseed Supplementation to High-Yielding Dairy Cows on Milk Production and Milk Fatty Acid Composition. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 152, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neveu, C.; Baurhoo, B.; Mustafa, A. Effect of Feeding Extruded Flaxseed with Different Grains on the Performance of Dairy Cows and Milk Fatty Acid Profile. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INRA. INRA Feeding System for Ruminants; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 90-8686-292-6.
- Albertí, P.; Beriain, M.J.; Ripoll, G.; Sarriés, V.; Panea, B.; Mendizabal, J.A.; Purroy, A.; Olleta, J.L.; Sañudo, C. Effect of Including Linseed in a Concentrate Fed to Young Bulls on Intramuscular Fatty Acids and Beef Color. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premier Nutrition. Premier Atlas 2014. Ingredients Matrix; Premier Nutrition: Brereton, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tsitsos, A.; Economou, V.; Chouliara, E.; Koutouzidou, G.; Arsenos, G.; Ambrosiadis, I. Effect of Chitosan and Alginate-Based Edible Membranes with Oregano Essential Oil and Olive Oil in the Microbiological, Physicochemical and Organoleptic Characteristics of Mutton. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.A.; Hunt, M.C.; Barbut, S.; Claus, J.R.; Cornforth, D.P.; Joseph, P.; Kim, Y.H.B.; Lindahl, G.; Mancini, R.A.; Nair, M.N.; et al. American Meat Science Association Guidelines for Meat Color Measurement. Meat Muscle Biol. 2023, 6, 12473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaperda, Z.; Argyriadou, A.; Nechalioti, P.M.; Alvanou, M.; Makri, S.; Bouroutzika, E.; Kyriazis, I.D.; Tekos, F.; Veskoukis, A.S.; Kallitsis, T.; et al. Redox Biomarker Baseline Levels in Cattle Tissues and Their Relationships with Meat Quality. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg, M. The Instrumental Texture Profile Analysis Revisited. J. Texture Stud. 2019, 50, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, D.U.; Olson, D.G.; Jo, C.; Love, J.; Jin, S.K. Volatiles Production and Lipid Oxidation in Irradiated Cooked Sausage as Related to Packaging and Storage. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M. A Summary of Global Flax Seed Supply Chains. 2022. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365885966_A_Summary_of_Global_Flax_Seed_Supply_Chains (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Greenwood, P.L. Review: An Overview of Beef Production from Pasture and Feedlot Globally, as Demand for Beef and the Need for Sustainable Practices Increase. Animal 2021, 15, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragni, M.; Toteda, F.; Tufarelli, V.; Laudadio, V.; Facciolongo, A.; Dipalo, F.; Vicenti, A. Feeding of Extruded Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) and Pasture in Podolica Young Bulls: Effects on Growth Traits, Meat Quality and Fatty Acid Composition. Pak. J. Zool. 2014, 46, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Albertí, P.; Gómez, I.; Mendizabal, J.A.; Ripoll, G.; Barahona, M.; Sarriés, V.; Insausti, K.; Beriain, M.J.; Purroy, A.; Realini, C. Effect of Whole Linseed and Rumen-Protected Conjugated Linoleic Acid Enriched Diets on Feedlot Performance, Carcass Characteristics, and Adipose Tissue Development in Young Holstein Bulls. Meat Sci. 2013, 94, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazzin, M.; Bovolenta, S.; Sepulcri, A.; Piasentier, E. Effect of Whole Linseed Addition on Meat Production and Quality of Italian Simmental and Holstein Young Bulls. Meat Sci. 2012, 90, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinn, R.A.; Jorquera, A.P. Feed Value of Supplemental Fats Used in Feedlot Cattle Diets. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2007, 23, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, B.W.; Moss, G.E.; Rule, D.C. A Decade of Developments in the Area of Fat Supplementation Research with Beef Cattle and Sheep1. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, E188–E204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertí, P.; Panea, B.; Sañudo, C.; Olleta, J.L.; Ripoll, G.; Ertbjerg, P.; Christensen, M.; Gigli, S.; Failla, S.; Concetti, S.; et al. Live Weight, Body Size and Carcass Characteristics of Young Bulls of Fifteen European Breeds. Livest. Sci. 2008, 114, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaei-Sharifabadi, H.; Seradj, A.R.; Mora, J.; Costa-Roure, S.; Balcells, J.; De La Fuente, G.; Villalba, D. Effects of Energy Level and Presentation Form of Concentrate in Intensive Dairy Calves Fattening System: Impact on Growth Performance and Feeding Behavior of Holstein and Montbeliarde Breeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2024, 318, 116145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, N.; Devant, M.; Díaz, I.; Font-Furnols, M.; Oliver, M.A.; García, J.A.; Bach, A. Increasing the Amount of N-3 Fatty Acid in Meat from Young Holstein Bulls through Nutrition. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, Z. Rheological Property of Extruded and Enzyme Treated Flaxseed Mucilage. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyne, J.M.; Evans, R.D.; Berry, D.P. Dressing Percentage and the Differential between Live Weight and Carcass Weight in Cattle Are Influenced by Both Genetic and Non-Genetic Factors1. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotta, P.P.; Prado, I.N.D.; Prado, R.M.D.; Moletta, J.L.; Silva, R.R.; Perotto, D. Carcass Characteristics and Chemical Composition of the Longissimus Muscle of Nellore, Caracu and Holstein-Friesian Bulls Finished in a Feedlot. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geletu, U.S.; Usmael, M.A.; Mummed, Y.Y.; Ibrahim, A.M. Quality of Cattle Meat and Its Compositional Constituents. Vet. Med. Int. 2021, 2021, 7340495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immonen, K.; Kauffman, R.G.; Schaefer, D.M.; Puolanne, E. Glycogen Concentrations in Bovine Longissimus Dorsi Muscle. Meat Sci. 2000, 54, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immonen, K.; Ruusunen, M.; Hissa, K.; Puolanne, E. Bovine Muscle Glycogen Concentration in Relation to Ænishing Diet, Slaughter and Ultimate pH. Meat Sci. 2000, 55, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicks, J.; Beline, M.; Gomez, J.F.M.; Luzardo, S.; Silva, S.L.; Gerrard, D. Muscle Energy Metabolism, Growth, and Meat Quality in Beef Cattle. Agriculture 2019, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killinger, K.M.; Calkins, C.R.; Umberger, W.J.; Feuz, D.M.; Eskridge, K.M. Consumer Visual Preference and Value for Beef Steaks Differing in Marbling Level and Color. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82, 3288–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abril, M.; Campo, M.M.; Önenç, A.; Sañudo, C.; Albertí, P.; Negueruela, A.I. Beef Colour Evolution as a Function of Ultimate pH. Meat Sci. 2001, 58, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, B.W.B.; van de Ven, R.J.; Mao, Y.; Coombs, C.E.O.; Hopkins, D.L. Using Instrumental (CIE and Reflectance) Measures to Predict Consumers’ Acceptance of Beef Colour. Meat Sci. 2017, 127, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poveda-Arteaga, A.; Krell, J.; Gibis, M.; Heinz, V.; Terjung, N.; Tomasevic, I. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors Affecting the Color of Fresh Beef Meat—Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoň, L.; Marounek, M.; Kudrna, V.; Bureš, D.; Zahrádková, R. Growth Performance and Fatty Acid Profiles of Intramuscular and Subcutaneous Fat from Limousin and Charolais Heifers Fed Extruded Linseed. Meat Sci. 2007, 76, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razminowicz, R.H.; Kreuzer, M.; Leuenberger, H.; Scheeder, M.R.L. Efficiency of Extruded Linseed for the Finishing of Grass-Fed Steers to Counteract a Decline of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Beef. Livest. Sci. 2008, 114, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.H. Handbook of Meat and Meat Processing, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4398-3683-5. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.J.; Beak, S.-H.; Jung, D.J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Jeong, I.H.; Piao, M.Y.; Kang, H.J.; Fassah, D.M.; Na, S.W.; Yoo, S.P.; et al. Genetic, Management, and Nutritional Factors Affecting Intramuscular Fat Deposition in Beef Cattle—A Review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabtay, A.; Shor-Shimoni, E.; Orlov, A.; Agmon, R.; Trofimyuk, O.; Tal, O.; Cohen-Zinder, M. The Meat Quality Characteristics of Holstein Calves: The Story of Israeli “Dairy Beef”. Foods 2021, 10, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Węglarz, A. Meat Quality Defined Based on pH and Colour Depending on Cattle Category and Slaughter Season. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 55, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricardo-Rodrigues, S.; Laranjo, M.; Elias, M.; Potes, M.E.; Agulheiro-Santos, A.C. Establishment of a Tenderness Screening Index for Beef Cuts Using Instrumental and Sensory Texture Evaluations. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2024, 35, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chriki, S.; Renand, G.; Picard, B.; Micol, D.; Journaux, L.; Hocquette, J.F. Meta-Analysis of the Relationships between Beef Tenderness and Muscle Characteristics. Livest. Sci. 2013, 155, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wezemael, L.; De Smet, S.; Ueland, Ø.; Verbeke, W. Relationships between Sensory Evaluations of Beef Tenderness, Shear Force Measurements and Consumer Characteristics. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Huidobro, F.R.; Miguel, E.; Blázquez, B.; Onega, E. A Comparison between Two Methods (Warner–Bratzler and Texture Profile Analysis) for Testing Either Raw Meat or Cooked Meat. Meat Sci. 2005, 69, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, D.; Monteiro, M.J.; Voss, H.-P.; Komora, N.; Teixeira, P.; Pintado, M. The Most Important Attributes of Beef Sensory Quality and Production Variables That Can Affect It: A Review. Livest. Sci. 2021, 250, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.M.; Oiseth, S.K.; Purslow, P.P.; Warner, R.D. A Structural Approach to Understanding the Interactions between Colour, Water-Holding Capacity and Tenderness. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgaru, V.; Popescu, L.; Netreba, N.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A.; Sturza, R. Assessment of Quality Indices and Their Influence on the Texture Profile in the Dry-Aging Process of Beef. Foods 2022, 11, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.B.; Kawachi, H.; Choi, C.B.; Choi, C.W.; Wu, G.; Sawyer, J.E. Cellular Regulation of Bovine Intramuscular Adipose Tissue Development and Composition. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, E72–E82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahmani, P.; Mapiye, C.; Prieto, N.; Rolland, D.C.; McAllister, T.A.; Aalhus, J.L.; Dugan, M.E.R. The Scope for Manipulating the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Content of Beef: A Review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.V.; Malau-Aduli, B.S.; Cavalieri, J.; Nichols, P.D.; Malau-Aduli, A.E.O. Enhancing Omega-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Content of Dairy-Derived Foods for Human Consumption. Nutrients 2019, 11, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molendi-Coste, O.; Legry, V.; Leclercq, I.A. Why and How Meet N-3 PUFA Dietary Recommendations? Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2011, 2011, 364040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, C.; Abodi, M.; D’Oria, V.; Milani, G.P.; Agostoni, C.; Mazzocchi, A. Alpha-Linolenic Acid and Cardiovascular Events: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitznerová, A.; Šuleková, M.; Nagy, J.; Marcinčák, S.; Semjon, B.; Čertík, M.; Klempová, T. Lipid Peroxidation Process in Meat and Meat Products: A Comparison Study of Malondialdehyde Determination between Modified 2-Thiobarbituric Acid Spectrophotometric Method and Reverse-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules 2017, 22, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Barba, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. A Comprehensive Review on Lipid Oxidation in Meat and Meat Products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, A.B.; Silva, M.V.D.; Lannes, S.C.D.S. Lipid Oxidation in Meat: Mechanisms and Protective Factors—A Review. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethra, P.V.; Sunooj, K.V.; Aaliya, B.; Navaf, M.; Akhila, P.P.; Sudheesh, C.; Mir, S.A.; Shijin, A.; George, J. Critical Factors Affecting the Shelf Life of Packaged Fresh Red Meat—A Review. Meas. Food 2023, 10, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | CON | LS |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredient (% DM basis) | ||
| Corn silage | 20.3 | 20.3 |
| Wheat straw | 10.2 | 10.1 |
| Corn grain, ground | 49.1 | 44.1 |
| Soybean meal | 11.9 | 11.9 |
| Cottonseed | 6.2 | 6.2 |
| Whole linseed | 0.0 | 5.1 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Sodium chloride | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Vitamin mineral premix | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| Chemical analysis | ||
| Crude protein, % of DM | 13.94 | 14.65 |
| Crude fiber, % of DM | 12.12 | 12.49 |
| Ether extract, % of DM | 4.19 | 5.88 |
| Starch, % of DM | 39.70 | 36.52 |
| Neutral detergent fiber, % of DM | 26.97 | 27.50 |
| Acid detergent fiber, % of DM | 14.10 | 14.63 |
| UFV 1, kg DM | 1.05 | 1.07 |
| Fatty acid composition 2 (% total fatty acids) | ||
| C16:0 | 9.26 | 7.36 |
| C18:0 | 2.21 | 2.03 |
| C18:1 n-9 | 9.60 | 8.89 |
| C18:2 n-6 | 20.52 | 16.34 |
| C18:3 n-3 | 0.12 | 6.22 |
| Treatments 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | LS | SEM 2 | p-Value | |
| Initial BW, kg | 436.3 | 444.2 | 11.260 | 0.749 |
| Final BW, kg | 625.8 | 641.6 | 11.964 | 0.548 |
| Average daily gain, kg | 1.46 | 1.49 | 0.043 | 0.740 |
| Average daily DMI 3, kg/Days | 14.0 | 13.6 | 0.476 | 0.684 |
| FCR 4 | 10.2 | 9.3 | 0.560 | 0.432 |
| Hot carcass weight 5, kg | 312.4 | 314.9 | 4.60, 6.40 | 0.421 |
| Dressing percentage (%) | 50.8 | 51.0 | 0.155 | 0.593 |
| Treatments 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | LS | SEM 2 | p-Value | |
| pH | 5.7 | 5.6 | 0.014 | 0.011 |
| Lightness-L* | 35.4 | 35.9 | 0.685 | 0.774 |
| Redness-a* | 16.8 | 17.8 | 0.400 | 0.224 |
| Yellowness-b* | 8.6 | 8.9 | 0.476 | 0.310 |
| Chroma | 19.0 | 20.0 | 0.459 | 0.297 |
| Hue angle° | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.021 | 0.800 |
| Hardness1 (g) | 1659.4 | 1630.1 | 198.892 | 0.946 |
| Hardness2 (g) | 1298.7 | 1344.5 | 162.236 | 0.897 |
| Adhesiveness (g) | −7.5 | −7.5 | 0.912 | 0.985 |
| Springiness | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.016 | 0.352 |
| Cohesiveness | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.014 | 0.311 |
| Gumminess 3 (g) | 695.3 | 966.2 | 5.0, 6.0 | 0.690 |
| Chewiness 3 (g) | 519.0 | 695.4 | 4.6, 6.4 | 0.421 |
| Resilience | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.015 | 0.515 |
| Moisture (%) | 74.0 | 74.8 | 0.372 | 0.321 |
| Protein (%) | 22.6 | 21.7 | 0.349 | 0.212 |
| Fat (%) | 3.2 | 3.2 | 0.204 | 0.920 |
| Collagen (%) | 1.7 | 1.7 | 0.057 | 0.780 |
| Salt (%) | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.087 | 0.848 |
| Ash (%) | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.091 | 0.929 |
| Treatments 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty Acid 1 | CON | LS | SEM 3 | p-Value |
| C14:0 | 4.352 | 4.324 | 0.053 | 0.810 |
| C14:1 | 1.110 | 1.138 | 0.021 | 0.534 |
| C15:0 | 0.438 | 0.456 | 0.008 | 0.260 |
| C16:0 | 28.914 | 29.320 | 0.127 | 0.112 |
| C16:1 | 3.622 | 3.716 | 0.114 | 0.705 |
| C17:0 | 0.882 | 0.906 | 0.016 | 0.494 |
| C17:1 | 0.496 | 0.472 | 0.010 | 0.235 |
| C18:0 | 19.022 | 18.472 | 0.276 | 0.349 |
| C18:1 n-9 trans | 0.174 | 0.166 | 0.009 | 0.697 |
| C18:1 n-9 cis | 37.404 | 37.276 | 0.305 | 0.848 |
| C18:2 n-6 trans | 0.340 | 0.292 | 0.017 | 0.179 |
| C18:2 n-6 cis | 2.290 | 2.474 | 0.068 | 0.191 |
| C18:3 n-3 | 0.210 | 0.362 | 0.025 | <0.001 |
| C20:0 | 0.086 | 0.072 | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| C20:1 n-9 cis | 0.118 | 0.098 | 0.006 | 0.066 |
| C21:0 | 0.140 | 0.100 | 0.001 | 0.141 |
| Σn-6 4 | 2.658 | 2.730 | 0.078 | 0.670 |
| Σn-3 5 | 0.230 | 0.390 | 0.027 | <0.001 |
| ΣMUFA 6 | 43.462 | 42.600 | 0.495 | 0.416 |
| ΣPUFA 7 | 2.898 | 3.132 | 0.091 | 0.214 |
| ΣSFA 8 | 53.210 | 54.238 | 0.421 | 0.244 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dokou, S.; Filippitzi, M.E.; Tsitsos, A.; Papanikolopoulou, V.; Priskas, S.; Economou, V.; Bonos, E.; Giannenas, I.; Arsenos, G. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Extruded Linseed on Growth Performance and Meat Quality of Young Holstein Bulls. Animals 2025, 15, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142123
Dokou S, Filippitzi ME, Tsitsos A, Papanikolopoulou V, Priskas S, Economou V, Bonos E, Giannenas I, Arsenos G. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Extruded Linseed on Growth Performance and Meat Quality of Young Holstein Bulls. Animals. 2025; 15(14):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142123
Chicago/Turabian StyleDokou, Stella, Maria Eleni Filippitzi, Anestis Tsitsos, Vasiliki Papanikolopoulou, Stergios Priskas, Vangelis Economou, Eleftherios Bonos, Ilias Giannenas, and Georgios Arsenos. 2025. "Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Extruded Linseed on Growth Performance and Meat Quality of Young Holstein Bulls" Animals 15, no. 14: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142123
APA StyleDokou, S., Filippitzi, M. E., Tsitsos, A., Papanikolopoulou, V., Priskas, S., Economou, V., Bonos, E., Giannenas, I., & Arsenos, G. (2025). Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Extruded Linseed on Growth Performance and Meat Quality of Young Holstein Bulls. Animals, 15(14), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142123











