Synthetic Feed Attractants in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Culture: Effects on Growth, Health, and Appetite Stimulation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Synthetic Flavors and Production of Experimental Diets
2.3. Experimental Design and Zootechnical Parameters
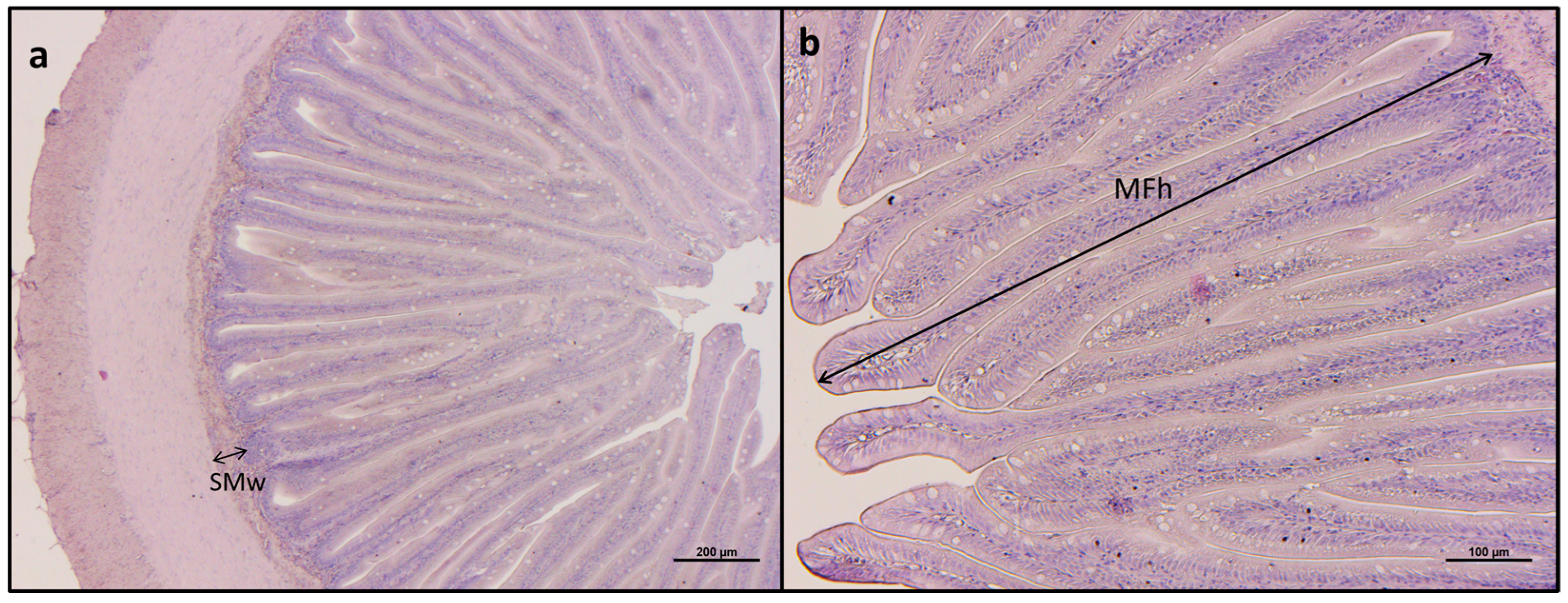
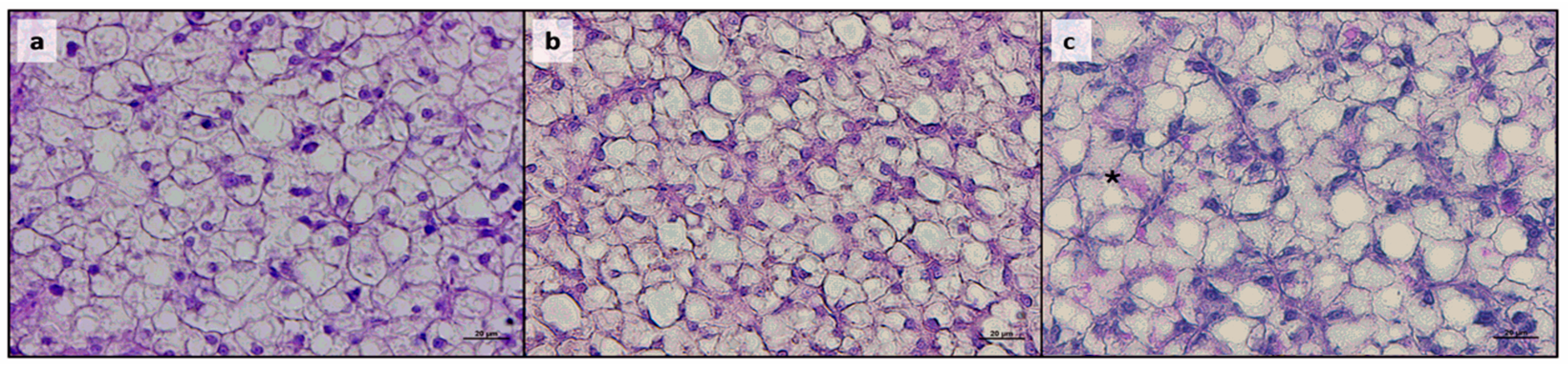
2.4. Histological Analysis
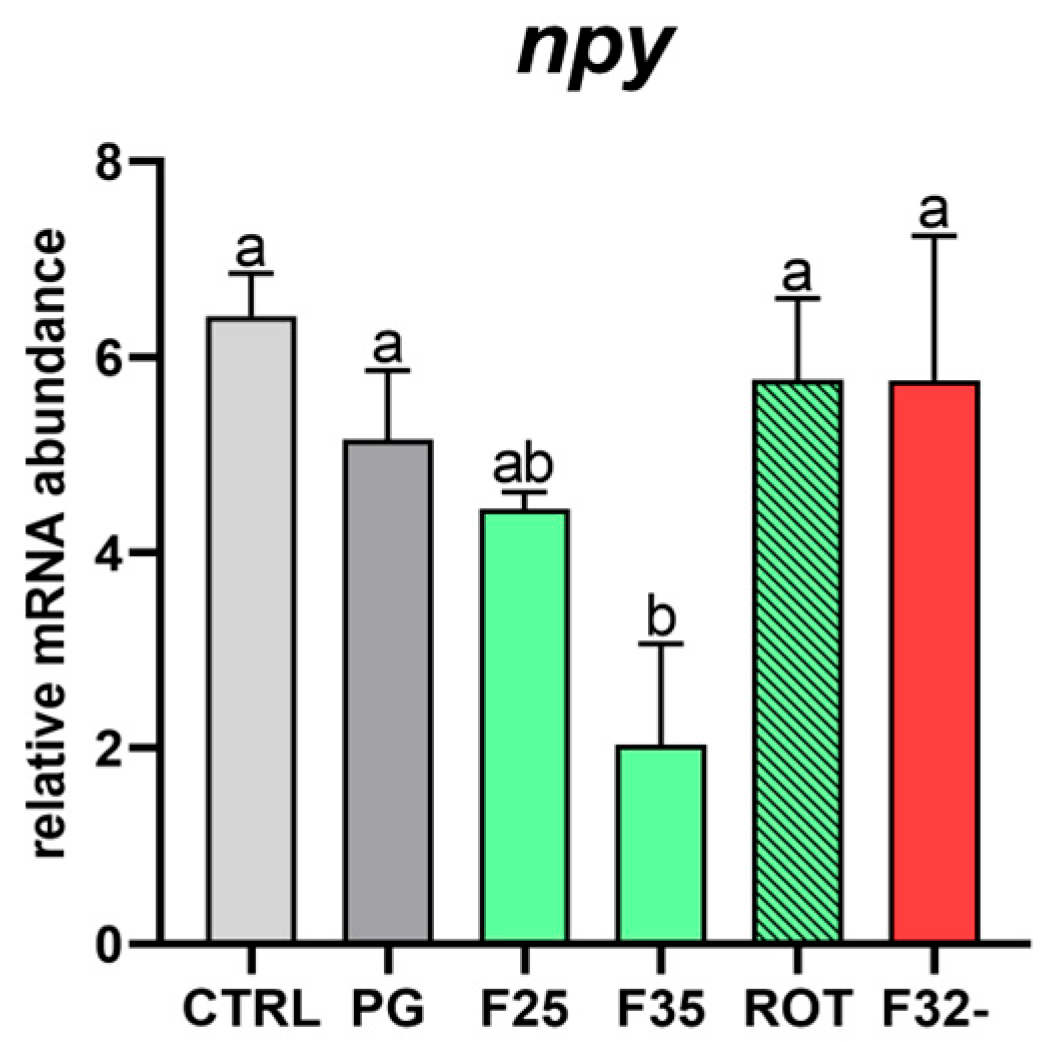
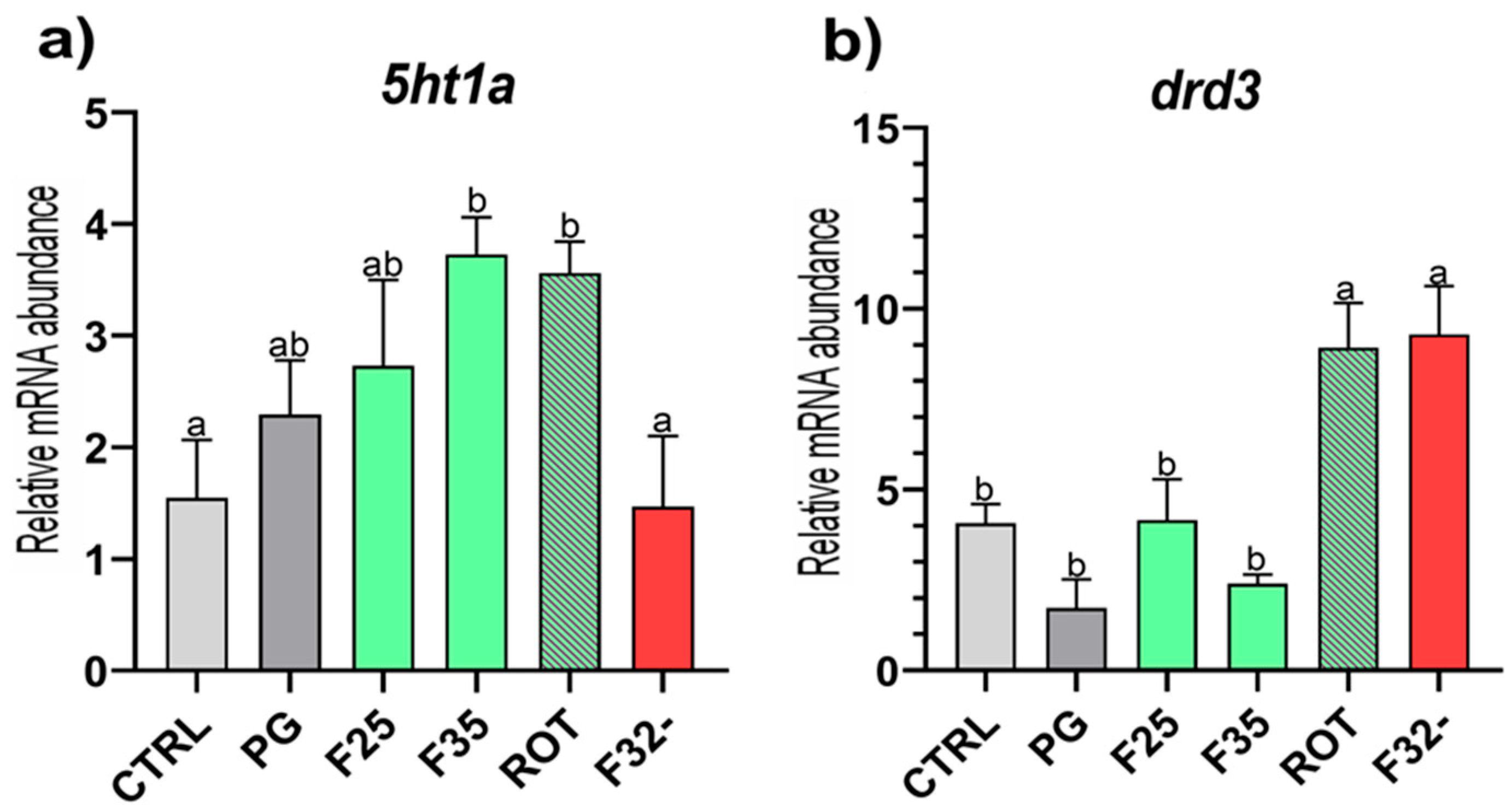
2.5. Molecular Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Zootechnical Performance
3.2. Histological Analyses
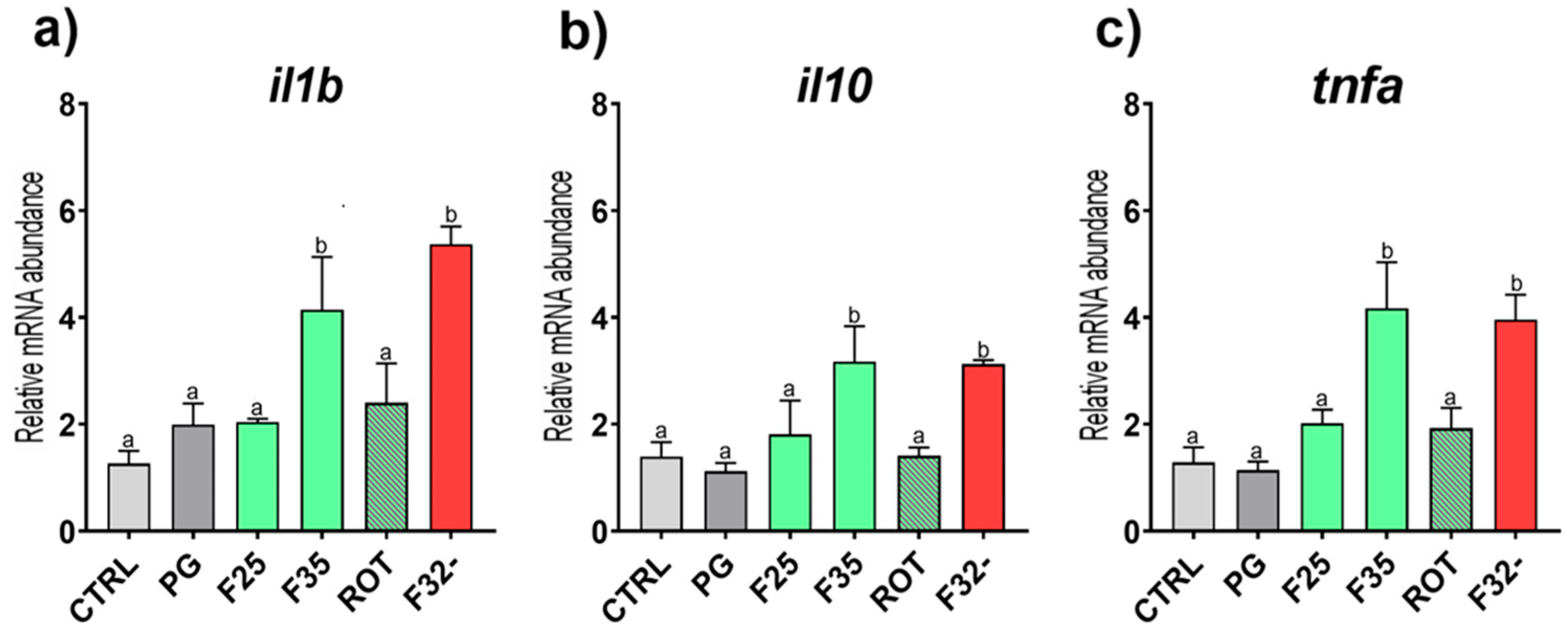
3.3. Real-Time qPCR Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024—Blue Transformation in Action; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sapkota, A.; Sapkota, A.R.; Kucharski, M.; Burke, J.; McKenzie, S.; Walker, P.; Lawrence, R. Aquaculture Practices and Potential Human Health Risks: Current Knowledge and Future Priorities. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goda, A.M.; El-Haroun, E.R.; Kabir Chowdhury, M.A. Effect of Totally or Partially Replacing Fish Meal by Alternative Protein Sources on Growth of African Catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822) Reared in Concrete Tanks. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashion, T.; Le Manach, F.; Zeller, D.; Pauly, D. Most Fish Destined for Fishmeal Production Are Food-Grade Fish. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macusi, E.D.; Cayacay, M.A.; Borazon, E.Q.; Sales, A.C.; Habib, A.; Fadli, N.; Santos, M.D. Protein Fishmeal Replacement in Aquaculture: A Systematic Review and Implications on Growth and Adoption Viability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, S.; Peres, H.; Serra, C.; Martínez-Llorens, S.; Tomás-Vidal, A.; Jover-Cerdá, M.; Oliva-Teles, A. Meat and Bone Meal as Partial Replacement of Fishmeal in Diets for Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) Juveniles: Diets Digestibility, Digestive Function, and Microbiota Modulation. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randazzo, B.; Di Marco, P.; Zarantoniello, M.; Daniso, E.; Cerri, R.; Finoia, M.G.; Capoccioni, F.; Tibaldi, E.; Olivotto, I.; Cardinaletti, G. Effects of Supplementing a Plant Protein-Rich Diet with Insect, Crayfish or Microalgae Meals on Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) and European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Growth, Physiological Status and Gut Health. Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.W.; Karpol, A.; Friedman, S.; Maru, B.T.; Tracy, B.P. Recent Advances in Single Cell Protein Use as a Feed Ingredient in Aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantoniello, M.; Pulido Rodriguez, L.F.; Randazzo, B.; Cardinaletti, G.; Giorgini, E.; Belloni, A.; Secci, G.; Faccenda, F.; Pulcini, D.; Parisi, G.; et al. Conventional Feed Additives or Red Claw Crayfish Meal and Dried Microbial Biomass as Feed Supplement in Fish Meal-Free Diets for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Possible Ameliorative Effects on Growth and Gut Health Status. Aquaculture 2022, 554, 738137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, G.; Collado, M.C.; Monge-Ortiz, R.; Tomás-Vidal, A.; Jover-Cerdá, M.; Peñaranda, D.S.; Pérez Martínez, G.; Martínez-Llorens, S. Long-Term Feeding with High Plant Protein Based Diets in Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata, L.) Leads to Changes in the Inflammatory and Immune Related Gene Expression at Intestinal Level. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulu, S.; Langi, S.; Hasimuna, O.J.; Missinhoun, D.; Munganga, B.P.; Hampuwo, B.M.; Gabriel, N.N.; Elsabagh, M.; Van Doan, H.; Abdul Kari, Z.; et al. Recent Advances in the Utilization of Insects as an Ingredient in Aquafeeds: A Review. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 11, 334–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santigosa, E.; García-Meilán, I.; Valentin, J.M.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Médale, F.; Kaushik, S.; Gallardo, M.A. Modifications of Intestinal Nutrient Absorption in Response to Dietary Fish Meal Replacement by Plant Protein Sources in Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) and Rainbow Trout (Onchorynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2011, 317, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlaugotne, B.; Pubule, J.; Blumberga, D. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using More Sustainable Ingredients in Fish Feed. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatlin, D.M.; Barrows, F.T.; Brown, P.; Dabrowski, K.; Gaylord, T.G.; Hardy, R.W.; Herman, E.; Hu, G.; Krogdahl, Å.; Nelson, R.; et al. Expanding the Utilization of Sustainable Plant Products in Aquafeeds: A Review. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 551–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Pan, Q. Effects of Four Feeding Stimulants in High Plant-Based Diets on Feed Intake, Growth Performance, Serum Biochemical Parameters, Digestive Enzyme Activities and Appetite-Related Genes Expression of Juvenile GIFT Tilapia (Oreochromis sp.). Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 23, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirkolaie, A.K. Reduction in the Environmental Impact of Waste Discharged by Fish Farms through Feed and Feeding. Rev. Aquac. 2011, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Huang, S.; Yang, Z.; Shi, F.; Feng, Y.; Khatoon, Z. Fish Feed Quality Is a Key Factor in Impacting Aquaculture Water Environment: Evidence from Incubator Experiments. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeşilayer, N.; Kaymak, I.E. Effect of Partial Replacement of Dietary Fish Meal by Soybean Meal with Betaine Attractant Supplementation on Growth Performance and Fatty Acid Profiles of Juvenile Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, D.; D’Agaro, E. Alternative Plant Protein Sources in Sea Bass Diets. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 4, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecillas, S.; Robaina, L.; Caballero, M.J.; Montero, D.; Calandra, G.; Mompel, D.; Karalazos, V.; Kaushik, S.; Izquierdo, M.S. Combined Replacement of Fishmeal and Fish Oil in European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax): Production Performance, Tissue Composition and Liver Morphology. Aquaculture 2017, 474, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, D.; Velasco, C.; Pereira, M.J.; Sá, T.; Rocha, C.; Cunha, L.M.; Lima, R.C.; Brazinha, C.; Pintado, M.; Valente, L.M.P. Incorporating Sardine Cooking Water Aromas into Plant-Based Diets for European Seabass: Effects on Appetite Regulation, Growth and Sensory Properties of Fish Flesh. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2024, 314, 116017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.S.; Kim, J.; Olowe, O.S.; Cho, S.H. Dietary Optimum Inclusion Level of Jack Mackerel Meal for Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus, Temminck & Schlegel, 1846). Aquaculture 2022, 559, 738432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt-Chabbert, J.A.; Skalli, A.; Young, O.A.; Gisbert, E. Effects of Feeding Stimulants on the Feed Consumption, Growth and Survival at Glass Eel and Elver Stages in the European Eel (Anguilla anguilla). Aquac. Nutr. 2012, 18, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasumyan, A.O. The Taste System in Fishes and the Effects of Environmental Variables. J. Fish. Biol. 2019, 95, 155–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, S. The Physiology of Taste in Fish: Potential Implications for Feeding Stimulation and Gut Chemical Sensing. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2017, 25, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magni, P.; Dozio, E.; Ruscica, M.; Celotti, F.; Masini, M.A.; Prato, P.; Broccoli, M.; Mambro, A.; Morè, M.; Strollo, F. Feeding Behavior in Mammals Including Humans. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1163, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkoff, H. The Neuroendocrine Regulation of Food Intake in Fish: A Review of Current Knowledge. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pedro, N.; Björnsson, B.T. Regulation of Food Intake by Neuropeptides and Hormones. Food Intake Fish. 2001, 269–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Macedo, I.C.; De Freitas, J.S.; Da Silva Torres, I.L. The Influence of Palatable Diets in Reward System Activation: A Mini Review. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 2016, 7238679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soengas, J.L.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M.; Delgado, M.J. Central Regulation of Food Intake in Fish: An Evolutionary Perspective. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 60, R171–R199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Peng, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H.; Xiao, Q.; Tang, S.; Liang, X.F. Effects of Three Feed Attractants on the Growth, Biochemical Indicators, Lipid Metabolism and Appetite of Chinese Perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 23, 101075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusche, K.; Berends, K.; Wuertz, S.; Susenbeth, A.; Schulz, C. Evaluation of Feed Attractants in Potato Protein Concentrate Based Diets for Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2011, 321, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakuwa, F.; Masumoto, T.; Fukada, H. Identification of Feeding Stimulants for Greater Amberjack Seriola dumerili in Muscle Tissue of Jack Mackerel Trachurus japonicus. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.W.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y.; Skura, B.J.; Higgs, D.A.; Dosanjh, B. Pacific Hake (Merluccius productus Ayres, 1855) Hydrolysates as Feed Attractants for Juvenile Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha Walbaum, 1792). Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.A.; Bulbul, M.; Koshio, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Nguyen, B.T.; Komilus, C.F. Effect of Complete Replacement of Fishmeal by Dehulled Soybean Meal with Crude Attractants Supplementation in Diets for Red Sea Bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 2012, 350–353, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytrestøyl, T.; Aas, T.S.; Åsgård, T. Utilisation of Feed Resources in Production of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) in Norway. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, D.P.; Harris, A.M.; Bevan, D.J.; Simmons, L.A.; Azevedo, P.A.; Cho, C.Y. Feather Meals and Meat and Bone Meals from Different Origins as Protein Sources in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Diets. Aquaculture 2000, 181, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fang, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Guan, D.; Sun, H.; Yun, X.; Zhou, J. The Efficiency of Adding Amino Acid Mixtures to a Diet Free of Fishmeal and Soybean Meal as an Attractant in Yellow River Carp (Cyprinus carpio Var. ). Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, R.W.; Maiolo, S.; Malcorps, W.; Little, D.C. Life Cycle Inventories of Marine Ingredients. Aquaculture 2023, 565, 739096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.; Olivotto, I.; Cattaneo, N.; Pavanello, M.; Şener, İ.; Antonucci, M.; Chemello, G.; Gioacchini, G.; Zarantoniello, M. The Promising Role of Synthetic Flavors in Advancing Fish Feeding Strategies: A Focus on Adult Female Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Growth, Welfare, Appetite, and Reproductive Performances. Animals 2024, 14, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.; Zarantoniello, M.; Antonucci, M.; Cattaneo, N.; Rattin, M.; De Russi, G.; Secci, G.; Lucon-Xiccato, T.; Lira de Medeiros, A.C.; Olivotto, I. The Application of Synthetic Flavors in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Rearing with Emphasis on Attractive Ones: Effects on Fish Development, Welfare, and Appetite. Animals 2023, 13, 3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Beltrán, J.M.; Esteban, M.Á. Nature-Identical Compounds as Feed Additives in Aquaculture. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 123, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, L.; Piferrer, F. The Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a Model Organism, with Emphasis on Applications for Finfish Aquaculture Research. Rev. Aquac. 2014, 6, 209–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferrer, F.; Ribas, L. The Use of the Zebrafish as a Model in Fish Aquaculture Research. Fish. Physiol. 2020, 38, 273–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Vázquez, F.J.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A. Biology of European Sea Bass; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 1–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.J. Morphology of the Olfactory (Smell) System in Fishes. Encycl. Fish. Physiol. 2011, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermen, F.; Franco, L.M.; Wyatt, C.; Yaksi, E. Neural Circuits Mediating Olfactory-Driven Behavior in Fish. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsching, S.I. Taste and Smell in Zebrafish. In The Senses: A Comprehensive Reference; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 3, pp. 466–492. ISBN 9780128054093. [Google Scholar]
- Kasumyan, A.O.; Marusov, E.A. Selective Feeding in Fish: Effect of Feeding and Defensive Motivations Evoked by Natural Odors. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2016, 6, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassef, E.A.; Saleh, N.E.; Abdel-Latif, H.M. Beneficial Effects of Some Selected Feed Additives for European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.): A Review. Int. Aquat. Res. 2023, 15, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon-Xiccato, T.; De Russi, G.; Bertolucci, C. A Novel-Odour Exploration Test for Measuring Anxiety in Adult and Larval Zebrafish. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 335, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zufall, F.; Leinders-Zufall, T. The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Odor Adaptation. Chem. Senses 2000, 25, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berejikian, B.A.; Tezak, E.P.; LaRae, A.L. Innate and Enhanced Predator Recognition in Hatchery-Reared Chinook Salmon. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2003, 67, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Sims, V.C.; Atema, J.; Gerlach, G.; Kingsford, M.J. How Stable Are the Reef Odor Preferences of Settling Reef Fish Larvae? Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2011, 44, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroldoǧan, O.T.; Kumlu, M.; Aktaş, M. Optimum Feeding Rates for European Sea Bass Dicentrarchus labrax L. Rear. Seawater Freshw. Aquac. 2004, 231, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchini, G.M.; Hardy, R.W. Research in Aquaculture Nutrition: What Makes an Experimental Feeding Trial Successful? Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2025, 33, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.R.S.; De Oliveira, S.R.; Luczinski, T.G.; Paulo, I.G.P.; Boscolo, W.R.; Bittencourt, F.; Signor, A. Palatability of Protein Hydrolysates from Industrial Byproducts for Nile Tilapia Juveniles. Animals 2019, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarantoniello, M.; de Oliveira, A.A.; Sahin, T.; Freddi, L.; Torregiani, M.; Tucciarone, I.; Chemello, G.; Cardinaletti, G.; Gatto, E.; Parisi, G.; et al. Enhancing Rearing of European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in Aquaponic Systems: Investigating the Effects of Enriched Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Prepupae Meal on Fish Welfare and Quality Traits. Animals 2023, 13, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cionna, C.; Maradonna, F.; Olivotto, I.; Pizzonia, G.; Carnevali, O. Effects of Nonylphenol on Juveniles and Adults in the Grey Mullet, Liza aurata. Reprod. Toxicol. 2006, 22, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randazzo, B.; Zarantoniello, M.; Gioacchini, G.; Giorgini, E.; Truzzi, C.; Notarstefano, V.; Cardinaletti, G.; Huyen, K.T.; Carnevali, O.; Olivotto, I. Can Insect-Based Diets Affect Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Reproduction? A Multidisciplinary Study. Zebrafish 2020, 17, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Sousa, V.; Oliveira, B.; Canadas-Sousa, A.; Abreu, H.; Dias, J.; Kiron, V.; Valente, L.M.P. An In-Depth Characterisation of European Seabass Intestinal Segments for Assessing the Impact of an Algae-Based Functional Diet on Intestinal Health. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, R.; Gerlach, G.; Lawrence, C.; Smith, C. The Behaviour and Ecology of the Zebrafish, Danio rerio. Biol. Rev. 2008, 83, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xu, H.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Z. Regulatory Roles of Cytokines in T and B Lymphocytes-Mediated Immunity in Teleost Fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 144, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, I.E.; Wadsworth, S.; Secombes, C.J. Cytokine Expression in the Intestine of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) during Infection with Aeromonas Salmonicida. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Secombes, C.J. The Function of Fish Cytokines. Biology 2016, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busti, S.; Rossi, B.; Volpe, E.; Ciulli, S.; Piva, A.; D’Amico, F.; Soverini, M.; Candela, M.; Gatta, P.P.; Bonaldo, A.; et al. Effects of Dietary Organic Acids and Nature Identical Compounds on Growth, Immune Parameters and Gut Microbiota of European Sea Bass. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Cao, L.-P.; Du, J.-L.; He, Q.; Gu, Z.-Y.; Jeney, G.; Xu, P.; Yin, G.-J. Effects of High-Fat Diet on Steatosis, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Autophagy in Liver of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusche, K.; Nagel, F.; Arning, S.; Wuertz, S.; Susenbeth, A.; Schulz, C. Effect of Different Dietary Levels of Potato Protein Concentrate Supplemented with Feed Attractants on Growth Performance of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2013, 183, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.A.; Stuber, G.D. Overlapping Brain Circuits for Homeostatic and Hedonic Feeding. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniganti, T.; Deogade, A.; Maduskar, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Guru, A.; Subhedar, N.; Ghose, A. Sensitivity of Olfactory Sensory Neurons to Food Cues Is Tuned to Nutritional States by Neuropeptide Y Signaling. J. Neurochem. 2021, 159, 1028–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwasek, K.; Wojno, M.; Iannini, F.; McCracken, V.J.; Molinari, G.S.; Terova, G. Nutritional Programming Improves Dietary Plant Protein Utilization in Zebrafish Danio rerio. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Maceira, J.J.; Otero-Rodiño, C.; Mancebo, M.J.; Soengas, J.L.; Aldegunde, M. Food Intake Inhibition in Rainbow Trout Induced by Activation of Serotonin 5-HT2C Receptors Is Associated with Increases in POMC, CART and CRF MRNA Abundance in Hypothalamus. J. Comp. Physiol. B Biochem. Syst. Environ. Physiol. 2016, 186, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Maceira, J.J.; Mancebo, M.J.; Aldegunde, M. The Involvement of 5-HT-like Receptors in the Regulation of Food Intake in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 161, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, I.M.; Sartori, B.M.; Castro, T.F.D.; Lunkes, L.C.; Virote, B.d.C.R.; Murgas, L.D.S.; de Souza, R.P.; Brunialti-Godard, A.L. Behavioral Plasticity and Gene Regulation in the Brain during an Intermittent Ethanol Exposure in Adult Zebrafish Population. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 192, 172909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.M.; Kenny, P.J. Dopamine D2 Receptors in Addiction-like Reward Dysfunction and Compulsive Eating in Obese Rats. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, J.H. Dopamine Signaling in Reward-Related Behaviors. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CTRL Diet | |
|---|---|
| Proximate composition (%) | |
| Crude protein % | 48.00 |
| Crude fat % | 24.00 |
| Crude fiber % | 0.85 |
| Crude ash % | 8.60 |
| Total carbohydrates % | 9.55 |
| P % | 1.30 |
| Vit C mg/kg | 400 |
| Vit E mg/kg | 300 |
| Parameter | Score | Description |
|---|---|---|
| + | 0–5 observations per section | |
| Mucosal fold fusion | ++ | 5–15 observations per section |
| +++ | >15 observations per section | |
| + | Scarce lymphocyte infiltration | |
| Basal inflammatory influx | ++ | Moderated infiltration |
| +++ | Diffused infiltration | |
| − | Absent | |
| Supranuclear vacuoles | + | Scattered |
| ++ | Diffused | |
| +++ | Highly abundant |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) | A.T. (°C) | NCBI ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| npy | AACTCCAACAGCGCAGTACA | CGTGGGTTGTTGGTATGAGA | 59 | XM_051391215.1 |
| 5ht1a | GGGTTGTTTTCAGGACCAAG | CGCAGAAAGGAGAAGAGCAA | 58 | XM_051426243 |
| drd3 | GAATGAGCTGCGAGGTGAA | CGTGGGTTGTTGGTATGAGA | 58 | XM_051411236 |
| il1b | AACTCCAACAGCGCAGTACA | AGACTGGCTTTGTCCACCAC | 58 | AJ_311925 |
| il10 | GCAGTCCCATGTGCAACAAC | TGCTACTGAACCTACGTCGC | 59 | AM_268529 |
| tnfa | GACTGGCGAACAACCAGATT | GTCCGCTTCTGTAGCTGTCC | 59 | DQ_070246 |
| b-actin (hk) | GGTACCCATCTCCTGCTCCAA | GACGTCGCACTTCATGATGCT | 60 | AJ_537421 |
| 18s (hk) | AGGGTGTTGGCAGACGTTAC | CTTCTGCCTGTTGAGGAACC | 60 | XM_051390998 |
| CTRL | PG | F25 | F35 | ROT | F32- | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | - |
| IBW (g/fish) | 67.8 ± 6.3 | 71.5 ± 8.9 | 72.6 ± 8.1 | 75.3 ± 7.8 | 71.6 ± 7.8 | 75.9 ± 8.3 | 0.8291 |
| FBW (g/fish) | 196.0 ± 35.4 a | 180.1 ± 17.6 a | 194.1 ± 15.1 a | 256.1 ± 16.1 b | 219.9 ± 19.7 ab | 176.2 ± 10.8 a | 0.0043 |
| WG (g/fish) | 120.9 ± 25.8 a | 108.1 ± 17.6 a | 122.2 ± 15.2 a | 194.1 ± 26.1 b | 167.9 ± 32.7 ab | 110.4 ± 13.9 a | 0.0026 |
| RGR (%) | 181.6 ± 22.7 a | 160.1 ± 24.5 a | 169.7 ± 21.0 a | 251.9 ± 20.2 b | 210.3 ± 27.2 ab | 176.6 ± 19.3 a | 0.0034 |
| SGR (%) | 1.7 ± 0.1 ab | 1.5 ± 0.2 ab | 1.6 ± 0.1 ab | 2.2 ± 0.2 c | 1.8 ± 0.2 bc | 1.3 ± 0.1 a | 0.0003 |
| FCR | 0.96 ± 0.08 | 1.17 ± 0.09 | 1.17 ± 0.09 | 0.96 ± 0.10 | 1.04 ± 0.09 | 1.20 ± 0.15 | 0.0359 |
| Daily FI (%) | 75.4 ± 2.7 a | 74.1 ± 2.2 a | 80.4 ± 3.2 ab | 90.1 ± 5.6 b | 87.6 ± 2.5 b | 73.9 ± 6.1 a | 0.0008 |
| CTRL | PG | F25 | F35 | ROT | F32- | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distal intestine | |||||||
| Mucosal fold height | 1023.0 ± 73.9 | 969.4 ± 52.0 | 977.7 ± 71.9 | 942.2 ± 75.2 | 1097.0 ± 40.2 | 918.0 ± 30.1 | <0.05 |
| Submucosa width | 38.98 ± 0.04 | 40.92 ± 2.50 | 45.03 ± 2.64 | 40.31 ± 2.05 | 42.34 ± 1.54 | 45.86 ± 2.04 | <0.05 |
| Mucosal fold fusion | + | + | + | + | + | + | − |
| Basal inflammatory influx | + | + | + | + | + | + | − |
| Supranuclear vacuoles | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Hepatic parenchyma | |||||||
| Fat fraction (%) | 48.9 ± 3.5 a | 50.7 ± 4.5 a | 49.7 ± 6.5 a | 60.5 ± 3.9 b | 58.5 ± 2.6 b | 47.8 ± 7.3 a | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conti, F.; Zarantoniello, M.; Cattaneo, N.; Antonucci, M.; Belfiore, E.A.; Olivotto, I. Synthetic Feed Attractants in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Culture: Effects on Growth, Health, and Appetite Stimulation. Animals 2025, 15, 2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142060
Conti F, Zarantoniello M, Cattaneo N, Antonucci M, Belfiore EA, Olivotto I. Synthetic Feed Attractants in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Culture: Effects on Growth, Health, and Appetite Stimulation. Animals. 2025; 15(14):2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142060
Chicago/Turabian StyleConti, Federico, Matteo Zarantoniello, Nico Cattaneo, Matteo Antonucci, Elena Antonia Belfiore, and Ike Olivotto. 2025. "Synthetic Feed Attractants in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Culture: Effects on Growth, Health, and Appetite Stimulation" Animals 15, no. 14: 2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142060
APA StyleConti, F., Zarantoniello, M., Cattaneo, N., Antonucci, M., Belfiore, E. A., & Olivotto, I. (2025). Synthetic Feed Attractants in European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Culture: Effects on Growth, Health, and Appetite Stimulation. Animals, 15(14), 2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15142060






