Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Protective Effects of Selenomethionine Against Liver Oxidative Injury in Piglets
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals, Diets, and Sample Collection
2.3. Diet, Serum, and Liver Selenium Content Analysis
2.4. Histological Analysis
2.5. Antioxidant Capacity Analysis
2.6. Determination of mRNA Expression Levels by RT-qPCR
2.7. Proteomic Analysis
2.8. Validation of Proteomics Results Using Commercial Assay Kits
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
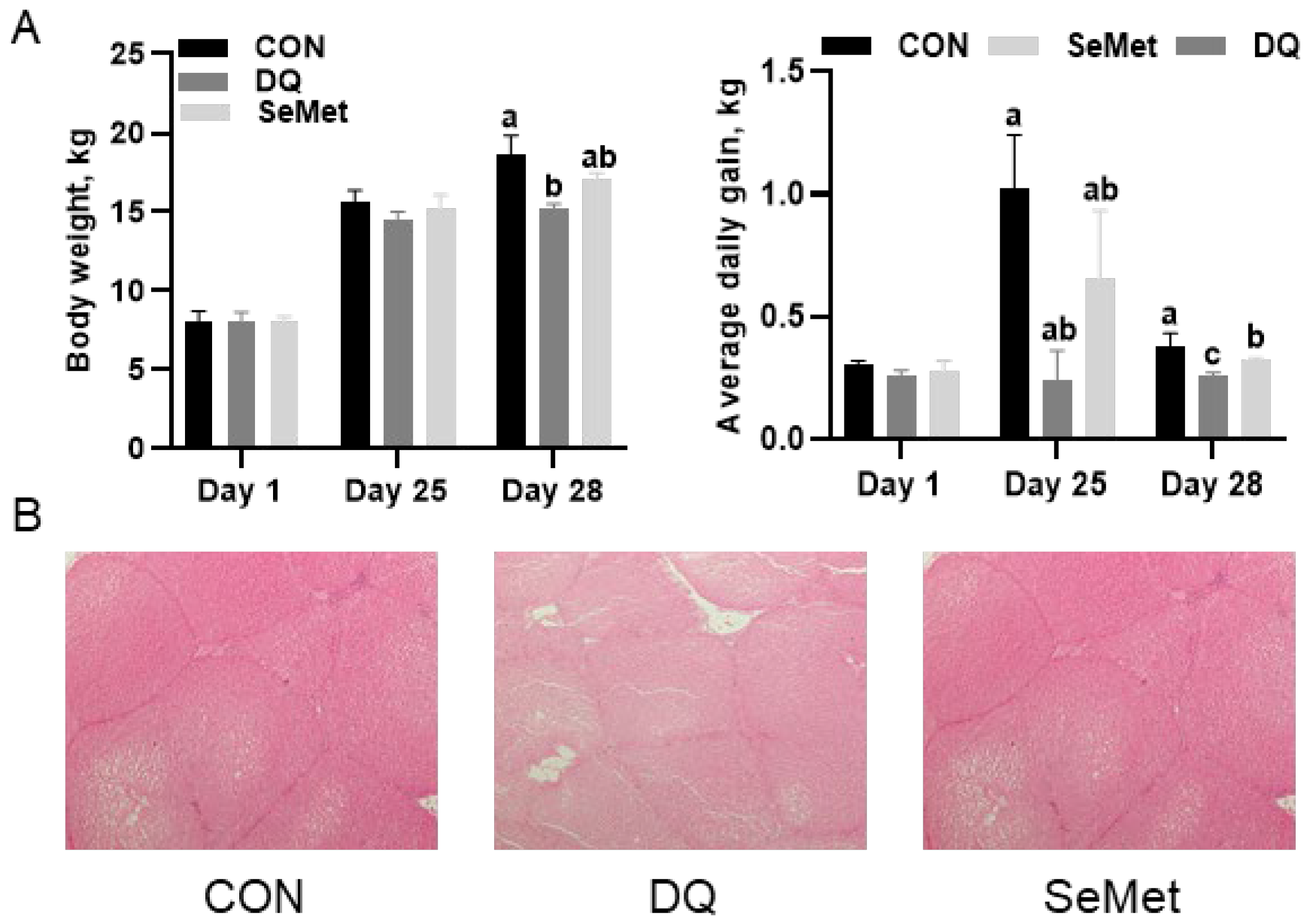
3.1. Growth Performance and Liver Morphology
3.2. Serum and Liver Antioxidant Capacity
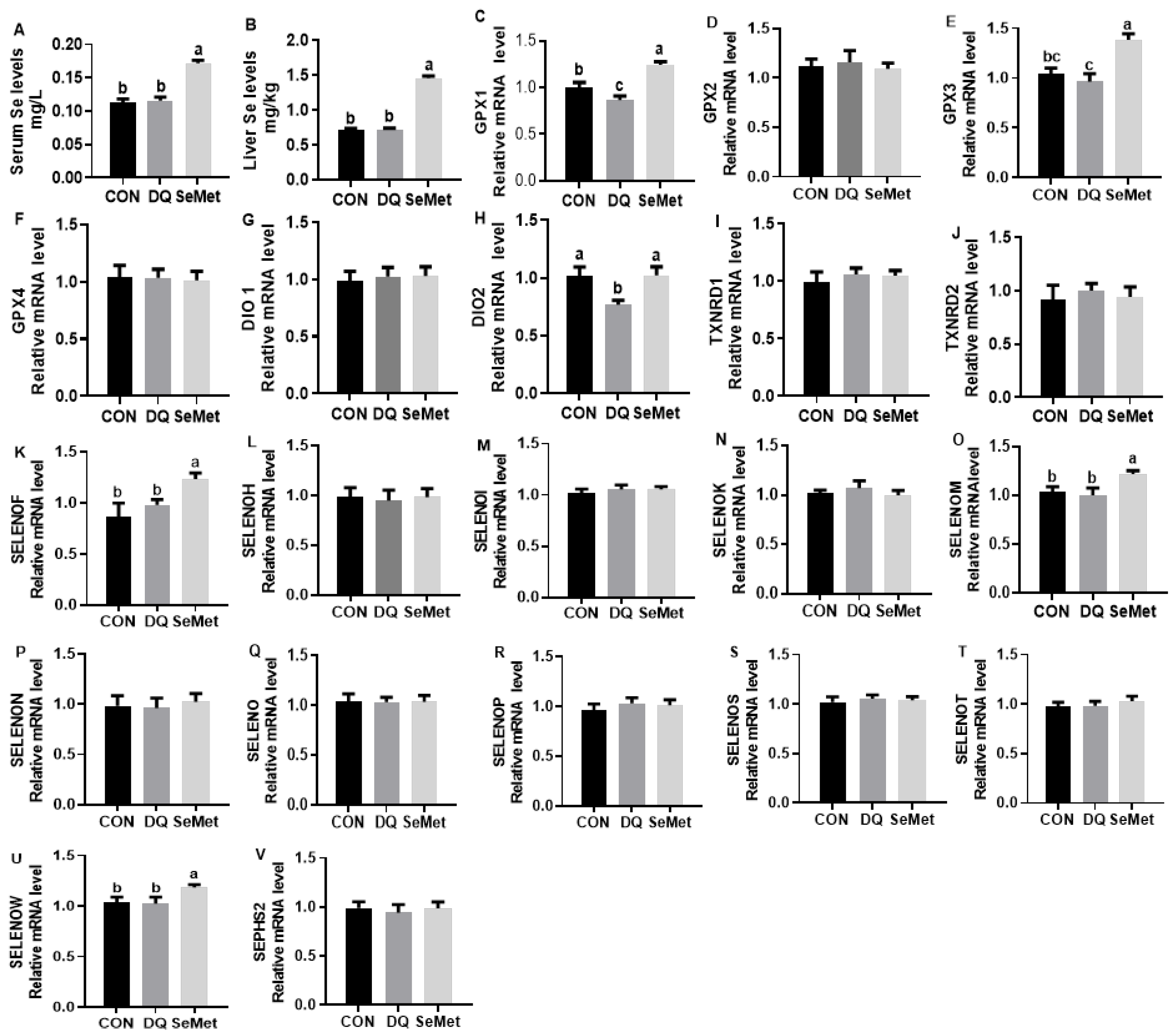
3.3. Selenium Status and Liver Selenoprotein Transcriptome
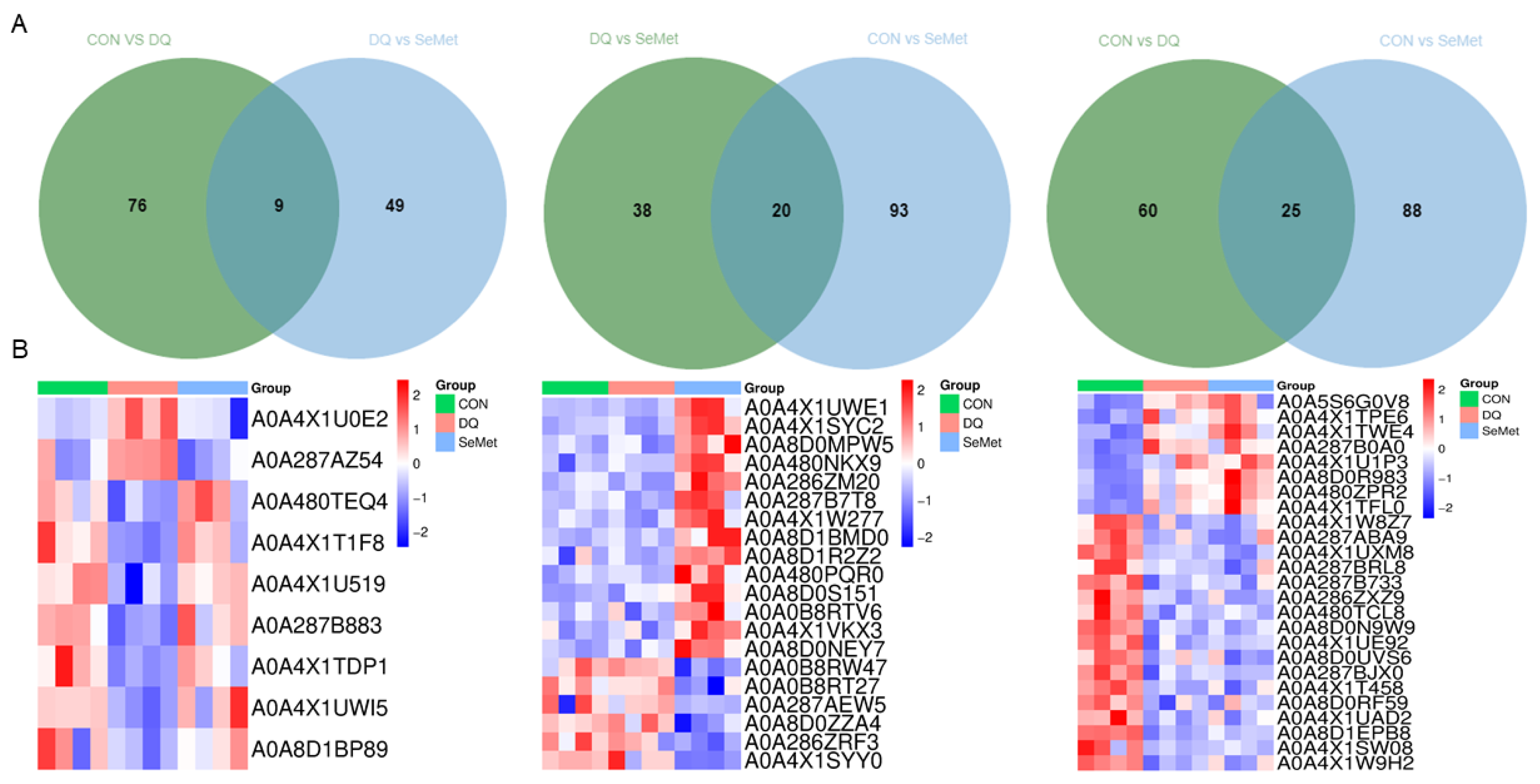
3.4. Protein Identification and DEPs Analysis
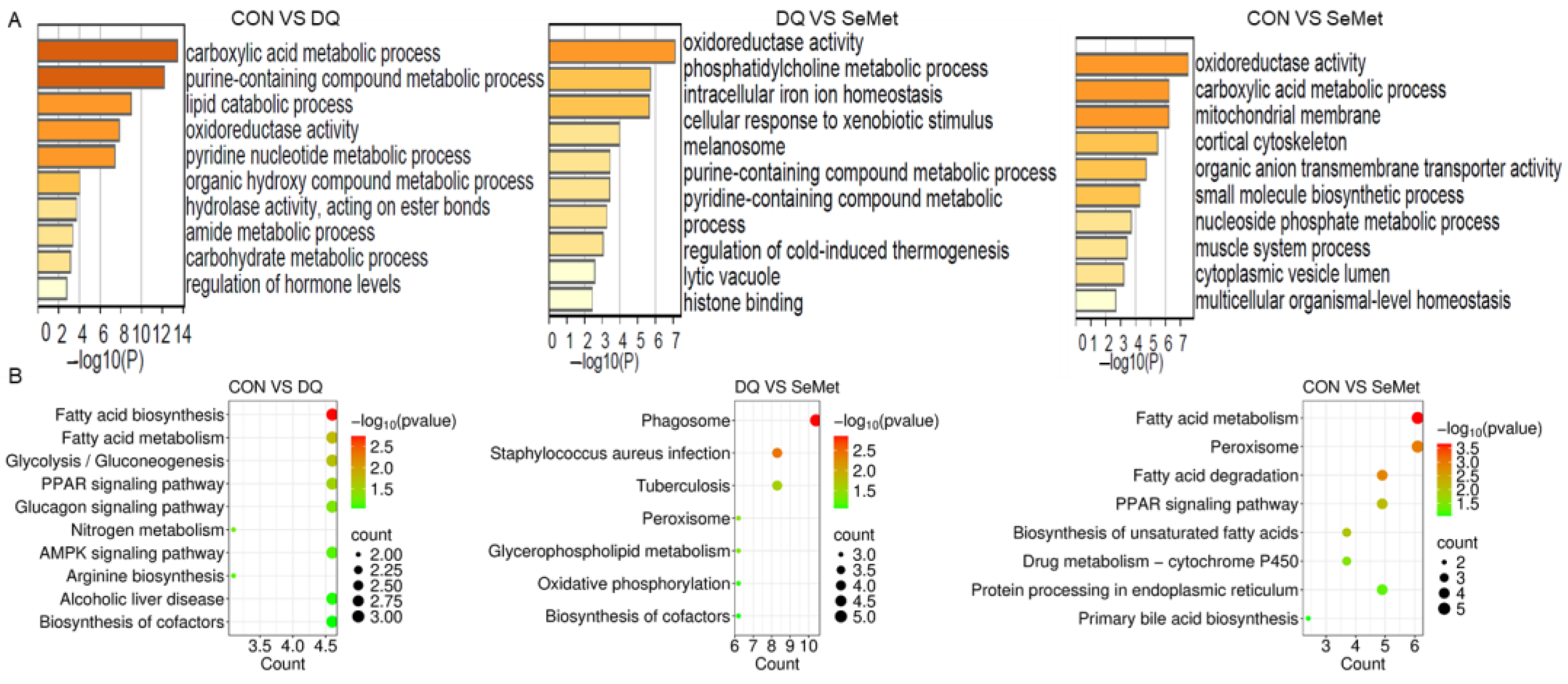
3.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis of DEPs
3.6. Validation of Proteomics Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bacou, E.; Walk, C.; Rider, S.; Litta, G.; Perez-Calvo, E. Dietary Oxidative Distress: A Review of Nutritional Challenges as Models for Poultry, Swine and Fish. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, D.; Collin, A.; Merlot, E.; Baeza, E.; Guilloteau, L.A.; Le Floc’h, N.; Thomas, A.; Fontagne-Dicharry, S.; Gondret, F. Review: Implication of redox imbalance in animal health and performance at critical periods, insights from different farm species. Animal 2022, 16, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Xing, M.; Gu, X. Research Progress on Oxidative Stress and Its Nutritional Regulation Strategies in Pigs. Animals 2021, 11, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Valle, V.; Chavez-Tapia, N.C.; Uribe, M.; Mendez-Sanchez, N. Role of oxidative stress and molecular changes in liver fibrosis: A review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4850–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Roh, Y.J.; Han, S.J.; Park, I.; Lee, H.M.; Ok, Y.S.; Lee, B.C.; Lee, S.R. Role of Selenoproteins in Redox Regulation of Signaling and the Antioxidant System: A Review. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrenner, H.; Speckmann, B.; Klotz, L.O. Selenoproteins: Antioxidant selenoenzymes and beyond. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 595, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, T.; Han, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J. Effect of Different Selenium Sources on Growth Performance, Tissue Selenium Content, Meat Quality, and Selenoprotein Gene Expression in Finishing Pigs. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 196, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhan, T.; Li, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J. Development and application of a HPLC-ICP-MS method to determine selenium speciation in muscle of pigs treated with different selenium supplements. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrup, N.; Ravn-Haren, G. Toxicity of repeated oral intake of organic selenium, inorganic selenium, and selenium nanoparticles: A review. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 79, 127235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Yin, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, J.; Jia, G.; Liu, G.; Tian, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Hydroxy Selenomethionine Alleviates Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Disorder of Pigs Induced by Dietary Oxidative Stress via Relieving the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jia, G.; Liu, G.; Tian, G.; Chen, X.; Cai, J.; Kang, B.; et al. Hydroxy Selenomethionine Improves Meat Quality through Optimal Skeletal Metabolism and Functions of Selenoproteins of Pigs under Chronic Heat Stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, J.; Xiang, X.; Tang, J.; Wang, L.; Jia, G.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Tian, G.; Cai, J.; Kang, B.; et al. Hydroxy Selenomethionine Exert Different Protective Effects Against Dietary Oxidative Stress-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Spleen and Thymus of Pigs. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 3107–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Ji, W.; Liu, H. The use of selenomethionine to reduce ammonia toxicity in porcine spleen by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy mediated by oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, L.; Jia, G.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Tian, G.; Cai, J.; et al. Selenoproteins synergistically protect porcine skeletal muscle from oxidative damage via relieving mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; He, Y.; Jia, G.; Liu, G.; Tian, G.; Chen, X.; Cai, J.; Kang, B.; Zhao, H. Selenogenome and AMPK signal insight into the protective effect of dietary selenium on chronic heat stress-induced hepatic metabolic disorder in growing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zhang, X.; Pi, S.; Chang, J.; Dou, X.; Yan, S.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhu, L.; et al. Dietary supplementation with biogenic selenium nanoparticles alleviate oxidative stress-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction. NPJ Sci. Food 2022, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Zeng, H.; Shao, Q.; Tang, J.; Wang, L.; Jia, G.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Tian, G.; Cai, J.; et al. Selenomethionine alleviates environmental heat stress induced hepatic lipid accumulation and glycogen infiltration of broilers via maintaining mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis. Redox Biol. 2023, 67, 102912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, S.; Sun, D.; Si, X.; Yu, X.; et al. Targeted Metabolomics Analysis Reveals that Dietary Supranutritional Selenium Regulates Sugar and Acylcarnitine Metabolism Homeostasis in Pig Liver. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanek, L. Proteomics to study adaptations in marine organisms to environmental stress. J. Proteom. 2014, 105, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, T.; Fang, B.; Liu, X.; Yu, Z.; Ma, X.; Gooneratne, R.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Ju, X. Overexpression of heat shock protein 70 induces apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells in heat-stressed pigs: A proteomics approach. J. Therm. Biol. 2022, 108, 103289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C. Multi-Omics Profiling Reveals Se Deficiency-Induced Redox Imbalance, Metabolic Reprogramming, and Inflammation in Pig Muscle. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, X.; Qin, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J. Selenium Deficiency Induces Pathological Cardiac Lipid Metabolic Remodeling and Inflammation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, e2100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 39235-2020; Nutrient Requirements of Swine. China Agricultural University Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jia, P.; Ji, S.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, T. Comparison of the effects of resveratrol and its derivative pterostilbene on hepatic oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in piglets challenged with diquat. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4202–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, M.; Yu, B.; Mao, X.B.; Zheng, P.; He, J.; Chen, D.W. Responses of growth performance and tryptophan metabolism to oxidative stress induced by diquat in weaned pigs. Animal 2012, 6, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Lv, M.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, D. The effect of dietary tryptophan levels on oxidative stress of liver induced by diquat in weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Liu, M.; Ren, W.; Duan, J.; Yang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, R.; Chen, L.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Effects of dietary supplementation with glutamate and aspartate on diquat-induced oxidative stress in piglets. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagawa, M. Protein carbonylation: Molecular mechanisms, biological implications, and analytical approaches. Free Radic. Res. 2021, 55, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Ji, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T. Piceatannol Ameliorates Hepatic Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Dysfunction of Weaned Piglets Challenged with Diquat. Animals 2020, 10, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Cao, L.; Jia, G.; Liu, G.; Chen, X.; Tian, G.; Cai, J.; Shang, H.; Zhao, H. The protective effect of selenium from heat stress-induced porcine small intestinal epithelial cell line (IPEC-J2) injury is associated with regulation expression of selenoproteins. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 122, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, N.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, X.; Kim, K.; Wu, Z.; Bravo, D.M.; Blanchard, A.; Ji, P. Organic selenium supplement partially alleviated diquat-induced oxidative insults and hepatic metabolic stress in nursery pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Jia, G.; Liu, G.; Tian, G.; Chen, X.; Cai, J.; Kang, B.; Zhao, H. Selenium exerts protective effects against heat stress-induced barrier disruption and inflammation response in jejunum of growing pigs. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryukov, G.V.; Castellano, S.; Novoselov, S.V.; Lobanov, A.V.; Zehtab, O.; Guigo, R.; Gladyshev, V.N. Characterization of mammalian selenoproteomes. Science 2003, 300, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Guan, P.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, L.; Peng, C.; Kong, X.; Zhou, X. Age-Dependent Developmental Changes of Selenium Content and Selenoprotein Expression and Content in Longissimus Dorsi Muscle and Liver of Duroc Pigs. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevet, J.R. The antioxidant glutathione peroxidase family and spermatozoa: A complex story. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2006, 250, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, M.W.; Hoffmann, P.R. Endoplasmic reticulum-resident selenoproteins as regulators of calcium signaling and homeostasis. Cell Calcium 2018, 70, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yao, H.D.; Li, S.; Xu, S.W. Antioxidative role of selenoprotein W in oxidant-induced chicken splenic lymphocyte death. Biometals 2014, 27, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, B.; Liu, M.; Ni, J.; Tian, J. Role of Selenoprotein F in Protein Folding and Secretion: Potential Involvement in Human Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Hashimoto, A.C.; Sasuclark, A.R.; Khadka, V.S.; Gurary, A.; Pitts, M.W. Selenoprotein M Promotes Hypothalamic Leptin Signaling and Thioredoxin Antioxidant Activity. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 35, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Shang, Y. Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase aggravates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in asthma by suppressing the Nrf2 pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 5001–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Dou, X.; Song, X.; Chang, J.; Pi, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zeng, X.; Xu, C. Protective effect of biogenic selenium nanoparticles against diquat-induced acute toxicity via regulation of gut microbiota and its metabolites. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 170, 113480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouzzine, M.; Gulberti, S.; Ramalanjaona, N.; Magdalou, J.; Fournel-Gigleux, S. The UDP-glucuronosyltransferases of the blood-brain barrier: Their role in drug metabolism and detoxication. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Barcus, M.; Kim, J.; Lum, K.L.; Mills, C.; Lei, X.G. High Dietary Selenium Intake Alters Lipid Metabolism and Protein Synthesis in Liver and Muscle of Pigs. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, D.; Liu, J.; Blaszczak, A.; Wright, V.; Jalilvand, A.; Needleman, B.; Noria, S.; Renton, D.; Hsueh, W. Adipocyte DIO2 Expression Increases in Human Obesity but Is Not Related to Systemic Insulin Sensitivity. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 2464652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Han, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.C. Endoplasmic reticulum-resident selenoproteins and their roles in glucose and lipid metabolic disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Accession | Gene Symbol | Protein Name | Molecular Function | Biological Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0A4X1U0E2 | QPRT | nicotinate-nucleotide pyrophosphorylase | nicotinate-nucleotide diphosphorylase (carboxylating) activity | NAD biosynthetic process |
| A0A287AZ54 | PDXP | pyridoxal phosphatase | pyridoxal phosphatase activity | pyridoxal phosphate catabolic process |
| A0A480TEQ4 | apolipoprotein A2 | lipid binding | lipid transport | |
| A0A4X1T1F8 | apolipoprotein A1 | |||
| A0A4X1U519 | C1q domain-containing protein | - | - | |
| A0A287B883 | PTMS | parathymosin | histone binding | negative regulation of apoptotic process |
| A0A4X1TDP1 | PTMSA | prothymosin alpha | - | - |
| A0A4X1UWI5 | ETNPPL | ethanolamine-phosphate phospho-lyase | transaminase activity | - |
| A0A8D1BP89 | FASN | fatty acid synthase | hydrolase | fatty acid biosynthesis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Yan, S.; Miao, J.; Li, W.; Li, Z. Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Protective Effects of Selenomethionine Against Liver Oxidative Injury in Piglets. Animals 2025, 15, 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131989
Zhang K, Yan S, Miao J, Li W, Li Z. Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Protective Effects of Selenomethionine Against Liver Oxidative Injury in Piglets. Animals. 2025; 15(13):1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131989
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kai, Shuhui Yan, Junhong Miao, Wen Li, and Zhenxu Li. 2025. "Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Protective Effects of Selenomethionine Against Liver Oxidative Injury in Piglets" Animals 15, no. 13: 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131989
APA StyleZhang, K., Yan, S., Miao, J., Li, W., & Li, Z. (2025). Proteomic Analysis Reveals the Protective Effects of Selenomethionine Against Liver Oxidative Injury in Piglets. Animals, 15(13), 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15131989





