Unlocking Immune Signatures: Surrogate Markers for Assessing VHSV Vaccine Efficacy in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement and Experimental Animals
2.2. Virus Culture and Inactivation
2.3. Vaccination and Sampling
2.4. Challenge
2.5. Antigen-Specific Antibodies
2.6. Gene Expression After Vaccination
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
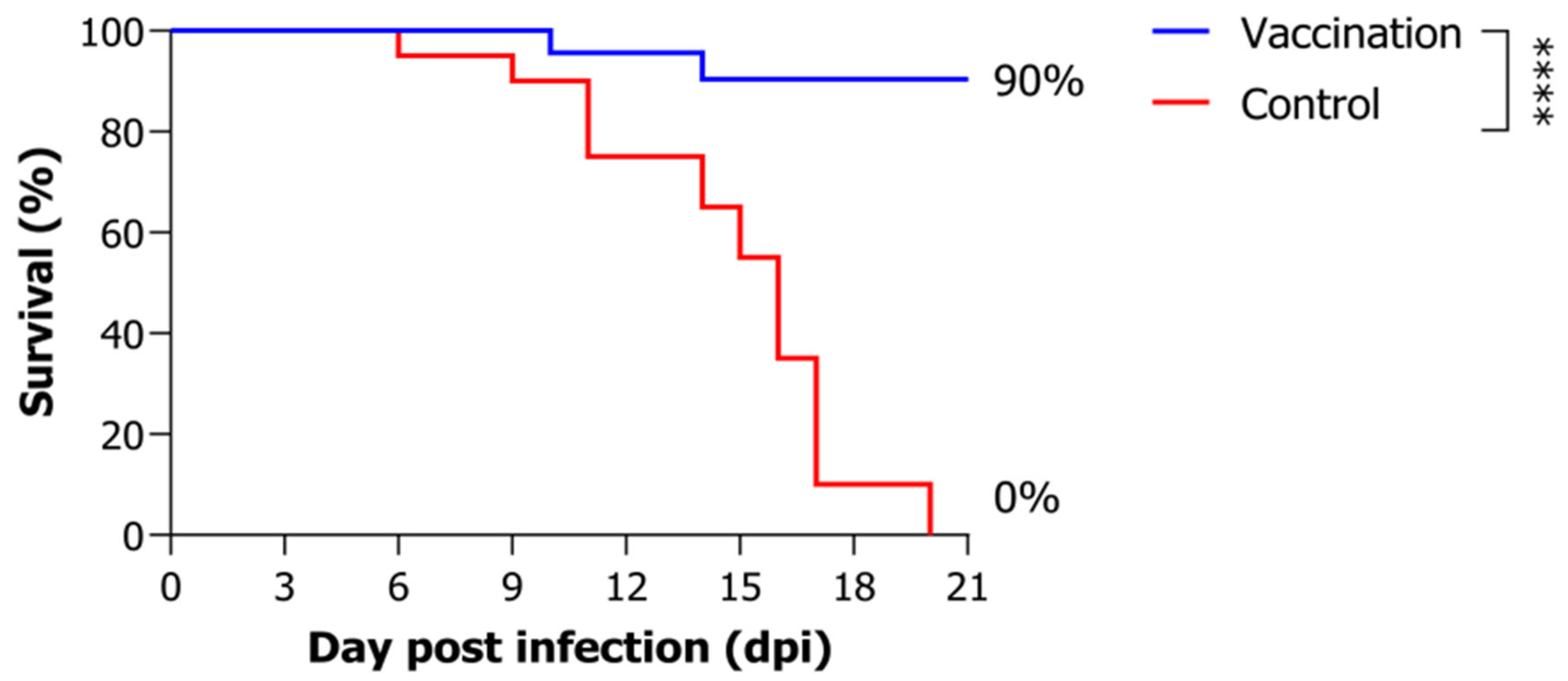
3.1. Artificial Infection Experiment
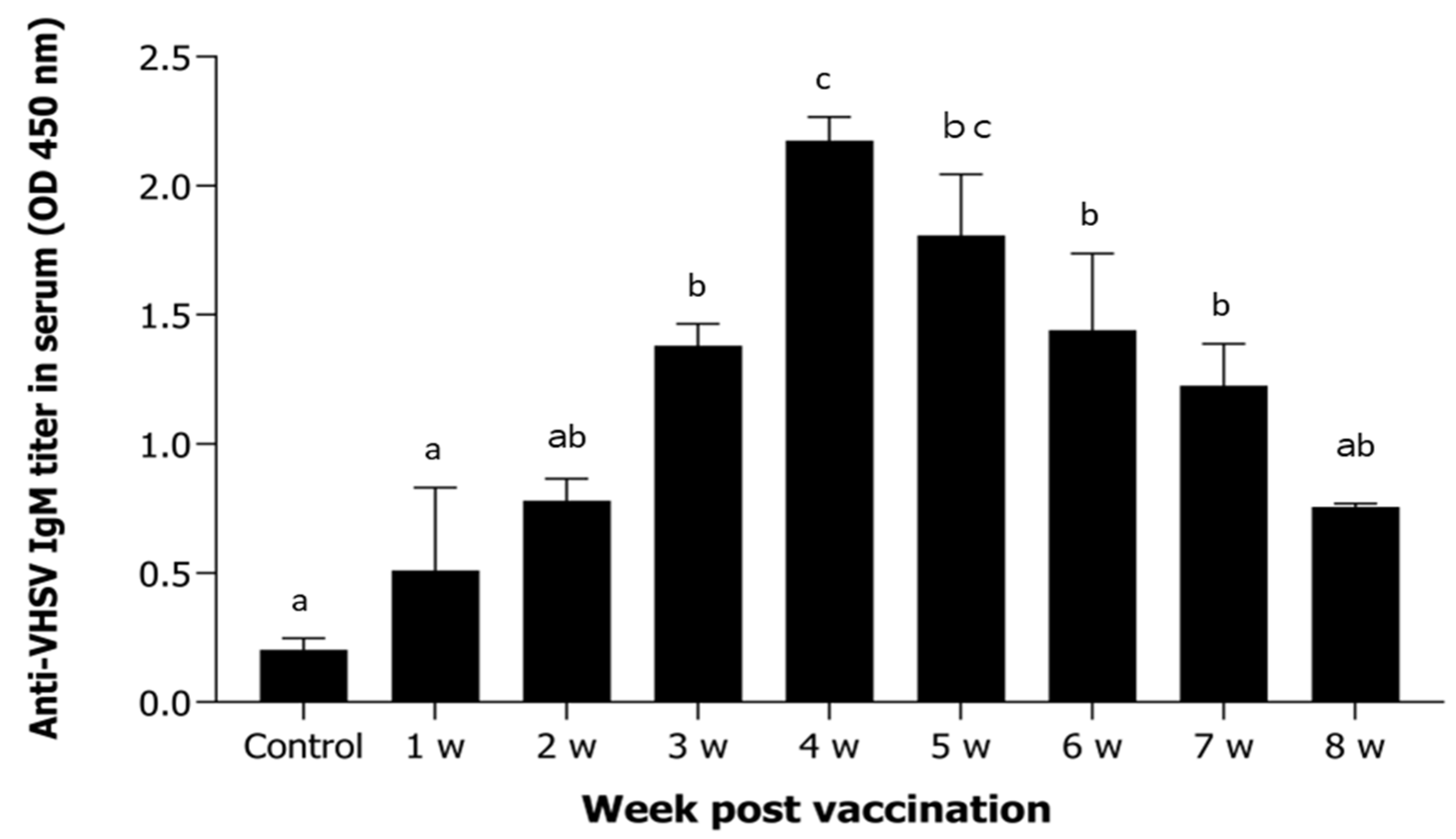
3.2. Antigen-Specific Antibodies After Vaccination
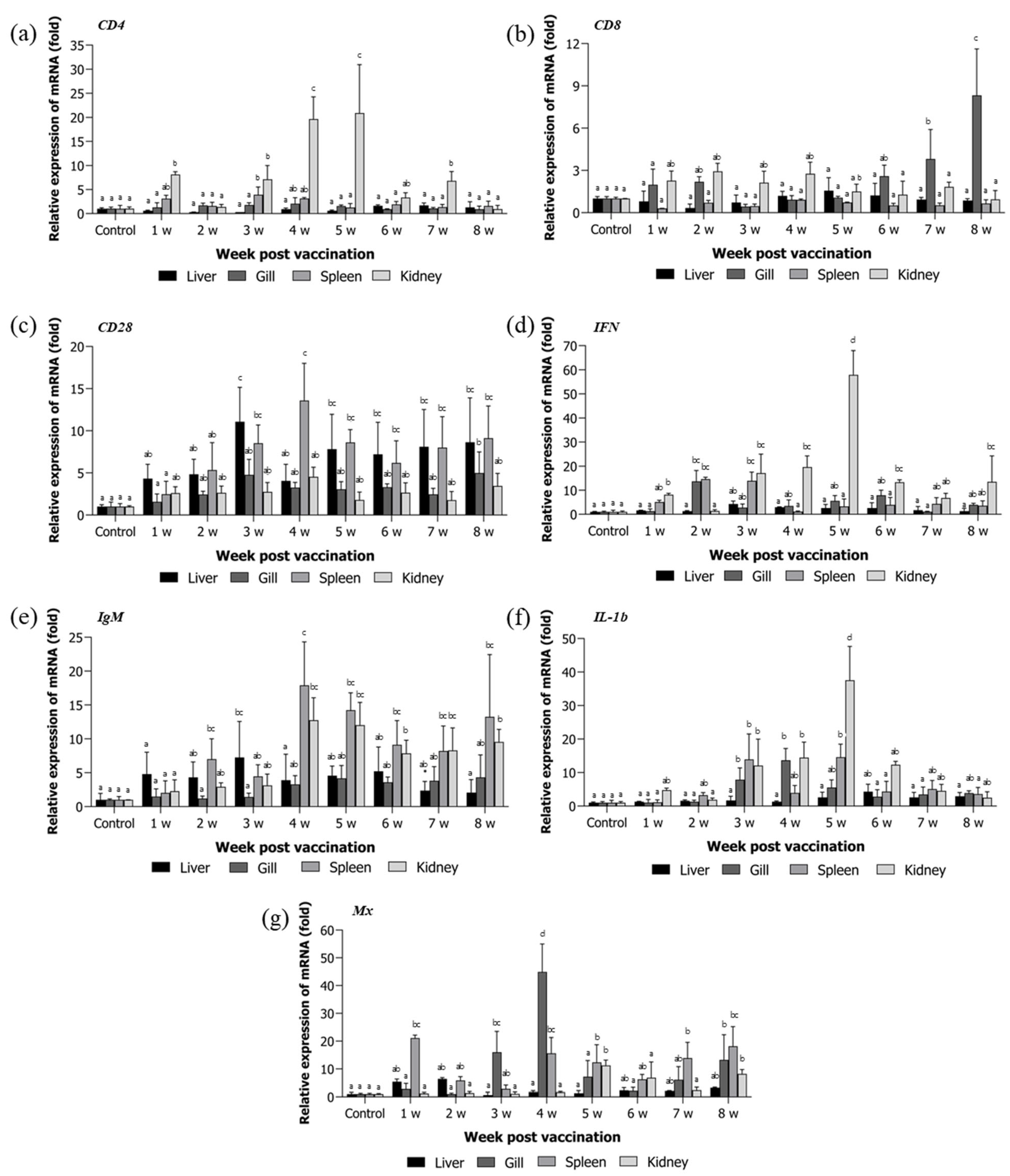
3.3. Immune Gene Expression Analysis
3.4. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD4 | cluster of differentiation 4 |
| CD8 | cluster of differentiation 8 |
| CD28 | cluster of differentiation 28 |
| CPE | cytopathic effect |
| EF-1α | elongation factor 1-alpha |
| FHM | fathead minnow |
| IFN | interferon |
| IgM | immunoglobulin M |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1 beta |
| MOI | multiplicity of infection |
| MS-222 | tricaine methanesulfonate (anesthetic) |
| Mx | myxovirus-resistance protein |
| NV | non-virion protein (VHSV gene product) |
| OIE | World Organisation for Animal Health |
| RPS | relative percent survival |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| TCID50 | 50% tissue-culture infectious dose |
| VHSV | viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus |
References
- Tordo, N.; Benmansour, A.; Calisher, C.H.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Fang, R.X.; Jackson, A.O.; Kurath, G.; Leong, J.C.; Nadin-Davis, S.; Tesh, R.B.; et al. Family Rhabdoviridae. In Virus Taxonomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 623–640. [Google Scholar]
- Egusa, S.; Inouye, K. Fish Pathology, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, K. Fish Viruses and Fish Viral Diseases; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Winton, J.R.; Batts, W.N.; Deering, R.E.; Brunson, R.; Hopper, K.; Nishizawa, T. Characteristics of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus isolated from Pacific salmon in North America. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1989, 1, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Batts, W.N.; Arakawa, C.K.; Winton, J.R. Detection of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus and other fish viruses by using the polymerase chain reaction. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- WOAH (World Organisation for Animal Health). Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals; WOAH: Paris, France, 2024; Available online: https://www.oie.int (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Kim, W.S.; Nishizawa, T.; Yoshimizu, M.; Park, J.W.; Kim, J.D. Isolation of VHSV (viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus) from wild olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) in Korea. Fish Pathol. 2003, 38, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Small, H.J.; Snow, M. Changes in the virus carrier state of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) after exposure to VHSV. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 93, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Oidtmann, B.; Dixon, P.; Way, K.; Joiner, C.; Bayley, A. Detection of VHSV in marine waters using passive samplers. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1781–1793. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, O.B.; Ørpetveit, I.; Lyngstad, T.M.; Kahns, S.; Skall, H.F.; Olesen, N.J.; Dannevig, B.H. Outbreak of viral hemorrhagic septicemia (VHS) in seawater-farmed rainbow trout in Norway caused by VHS virus genotype III. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 85, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.; Zahra, A. Advancements in vaccination strategies for aquaculture: Protecting fish health and sustainability. In Complementary and Alternative Medicine: Immunization/Vaccinology; Unique Scientific Publishers: Faisalabad, Pakistan, 2024; Available online: https://uniquescientificpublishers.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/immunization-vaccinology/332-341.pdf (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Del-Pozo, J.; Collet, B. Non-lethal sequential individual monitoring of viremia in relation to DNA vaccination in fish. Vaccines 2021, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Kole, S.; Qadiri, S.S.N.; Shin, S.M.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, J.; Jung, S.J. Inactivated-viral vaccine: Formulation and evaluation of its protective efficacy against viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus (VHSV) infection in olive flounder. Vaccine 2019, 37, 7032–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.H.; Park, C.S.; Kole, S.; Ryu, J.W.; Jung, S.J. Water temperature and immunization period required to establish immunity against the viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus vaccine in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2024, 591, 741118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, M.Y.; Jeong, J.M.; Kang, G.; Woo, W.S.; Kim, K.H.; Son, H.J.; Park, C.I. Identification and characterization of CD83 and CD276 as markers of dendritic cells in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 158, 110149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avunje, S.; Kim, W.S.; Park, C.S.; Oh, M.J.; Jung, S.J. Toll-like receptors and interferon associated immune factors in viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus-infected olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kole, S.; Dar, S.A.; Shin, S.M.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, S.J. Potential efficacy of chitosan-PLGA-encapsulated trivalent immersion vaccine in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) against viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV). Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 761130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendis, W.R.H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, G.W.; Kang, S.Y. Antiviral activity of the coumarin derivative scoparone against viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus in vitro and in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2024, 571, 740968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Y.; Nie, L.; Zhu, G.; Xiang, L.X.; Shao, J.Z. B cells in teleost fish act as pivotal initiating APCs in priming adaptive immunity: An evolutionary perspective on the origin of the B-1 cell subset and B7 molecules. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 2699–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Ryu, J.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.E.; Park, C.H.; Oh, M.J.; Jung, S.J. Elucidating the functional roles of helper and cytotoxic T cells in the cell-mediated immune responses of olive flounder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Liu, W.; Tang, X.; Sheng, X.; Chi, H. The expression of CD28 and its synergism on the immune response of flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) to thymus-dependent antigen. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 765036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, C.; Esteban, M.A. Molecular Characterization of the T Cell Costimulatory Receptors CD28 and CTLA4 in the European Sea Bass. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 109, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randelli, E.; Buonocore, F.; Scapigliati, G. Cell Markers and Determinants in Fish Immunology. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, N.O.; Costa, M.M.; Secombes, C.J.; Wang, T. Gene expression profiling in vaccinated rainbow trout against Yersinia ruckeri reveals differential immune responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, M.K.; Laing, K.J.; Winton, J.R. Early transcriptional responses in rainbow trout leukocytes upon exposure to the DNA vaccine for infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoloki, S.; Munang’andu, H.M.; Evensen, Ø. Oral administration of vaccines: The future of fish vaccination? Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 52, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monir, M.S.; Yusoff, M.S.M.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Amal, M.N.A. Effect of an oral bivalent vaccine on immune response and immune gene profiling in vaccinated red tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) during infections with Streptococcus agalactiae and Aeromonas hydrophila. Biology 2022, 11, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, H.; Bakke, A.F.; Sommerset, I.; Afanasyev, S. A time-course study of gene expression and antibody repertoire at early time post vaccination of Atlantic salmon. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somamoto, T.; Yoshiura, Y.; Sato, A.; Nakao, M.; Nakanishi, T. Expression profiles of TCRβ and CD8α mRNA correlate with virus-specific cell-mediated cytotoxic activity in ginbuna crucian carp. Virology 2006, 346, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somamoto, T.; Koppang, E.O.; Fischer, U. Antiviral functions of CD8⁺ cytotoxic T cells in teleost fish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 44, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.S.; Kim, S.J.; Yoon, S.Y.; Krishnan, R.; Oh, M.J. Comparison of survival efficacy by rearing time after challenged with viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) immersion-treated with live VHSV vaccine. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, S.; Shin, S.M.; Kwak, I.S.; Cho, S.H.; Jung, S.J. Chitosan-PLGA encapsulated trivalent oral vaccine against viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus, Streptococcus parauberis, and Miamiensis avidus in olive flounder. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 128, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Bruce, T.J.; Jones, E.M.; Cain, K.D. A review of fish vaccine development strategies: Conventional methods and modern biotechnological approaches. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailone, R.L.; Fukushima, H.C.S.; Ventura Fernandes, B.H.; De Aguiar, L.K.; Corrêa, T.; Janke, H.; Grejo Setti, P.; Roça, R.D.O.; Borra, R.C. Zebrafish as an alternative animal model in human and animal vaccination research. Lab. Anim. Res. 2020, 36, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miccoli, A.; Manni, M.; Picchietti, S.; Scapigliati, G. State-of-the-art vaccine research for aquaculture use: The case of three economically relevant fish species. Vaccines 2021, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, M.-Y.; Jeong, J.-M.; Kang, G.; Woo, W.-S.; Kim, K.-H.; Son, H.-J.; Joo, M.-S.; Park, C.-I. Oral administration enhances directly mucosal immune system in intestine of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2025, 162, 105262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, J.-M.; Kwon, M.-G.; Park, C.-I. Unlocking Immune Signatures: Surrogate Markers for Assessing VHSV Vaccine Efficacy in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Animals 2025, 15, 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121728
Jeong J-M, Kwon M-G, Park C-I. Unlocking Immune Signatures: Surrogate Markers for Assessing VHSV Vaccine Efficacy in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Animals. 2025; 15(12):1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121728
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Ji-Min, Mun-Gyeong Kwon, and Chan-Il Park. 2025. "Unlocking Immune Signatures: Surrogate Markers for Assessing VHSV Vaccine Efficacy in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)" Animals 15, no. 12: 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121728
APA StyleJeong, J.-M., Kwon, M.-G., & Park, C.-I. (2025). Unlocking Immune Signatures: Surrogate Markers for Assessing VHSV Vaccine Efficacy in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Animals, 15(12), 1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121728




