Fish Health Enhancement and Intestinal Microbiota Benefits of Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer Bloch, 1790) on Dietary Sea Lettuce (Ulva rigida C. Agardh, 1823) Extract Supplementation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction, Phytochemical Compositions, and Antioxidant Activity of U. rigida
2.1.1. Preparation and Extraction of U. rigida
2.1.2. Chemical and Structural Analyses of Sulfated Polysaccharides (SPs)
2.1.3. Nutritional Profiles and Fatty Acid Analysis
2.1.4. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.1.5. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
2.1.6. Total Tannins
2.1.7. Total Saponins
2.1.8. Total Antioxidant Assay (TAA)
2.1.9. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
2.1.10. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.1.11. Total Iron Reducing Power Assay
2.1.12. Anti-Lipid Peroxidation Assay
2.1.13. Nitric Oxide Scavenging Activity
2.1.14. Hydrogen Peroxide Scavenging Activity
2.1.15. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
2.1.16. Superoxide Radical Scavenging Activity
2.2. Effects of Ur-HWCE Supplemented Feed on Health Benefits in Asian Seabass
2.2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2.2. Animal Husbandry
2.2.3. Experimental Design
2.2.4. Growth Performance Analysis
2.2.5. Serum and Peripheral Blood Leukocyte (PBL) Isolation
2.2.6. qRT-PCR Analysis of Growth and Immune-Related Genes
2.2.7. Measurement of Oxidative Stress Biochemical Markers in Serum
2.2.8. Cellular and Humoral Immune Response Assays
2.2.9. Blood Biochemical Analysis
2.2.10. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.2.11. Histological Analysis
2.2.12. Disease Resistance and Relative Percent Survival (RPS) to Vibrio vulnificus
2.2.13. Statistical and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Proximate Composition, Chemical and Phytochemical Contents, and Antioxidant Activity of Ur-HWCE
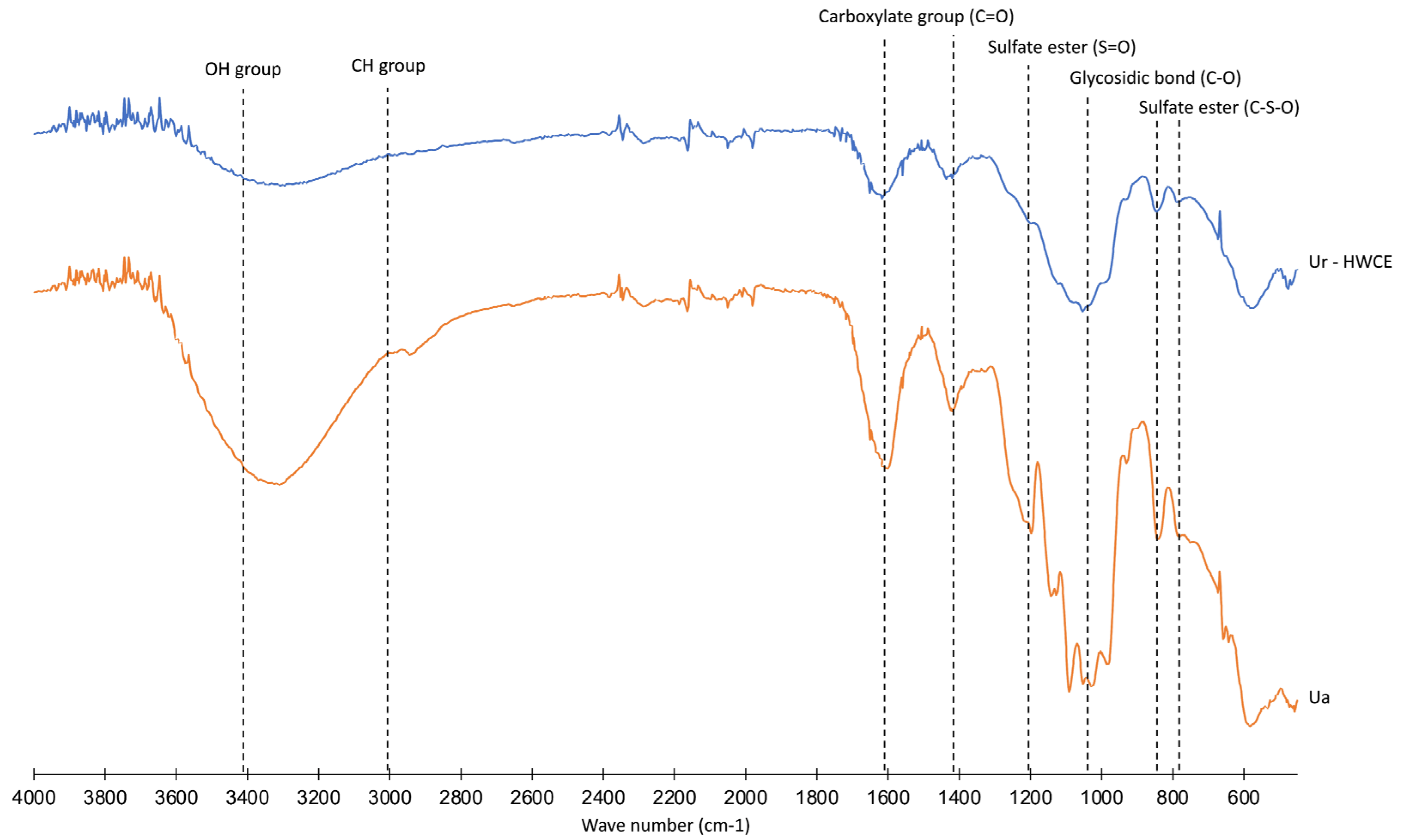
3.2. Structural Analyses of Crude Polysaccharides from Ur-HWCE
3.3. Effects of Ur-HWCE Dietary Supplement on Health Benefits in Asian Seabass
3.3.1. Growth Performance and Survival
3.3.2. Growth-Related Gene Expression
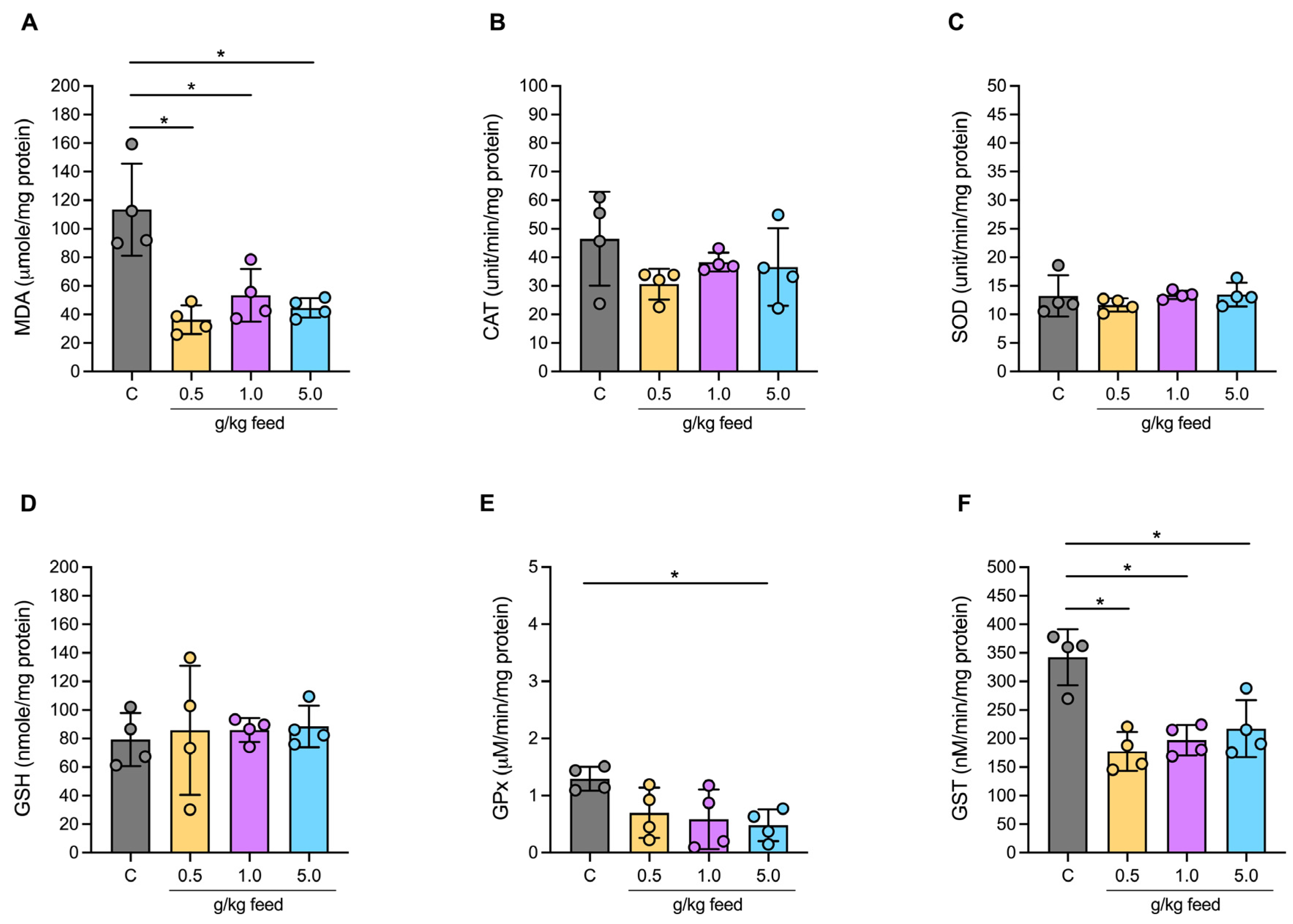
3.3.3. Oxidative Stress Biochemical Markers in Serum
3.3.4. Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses
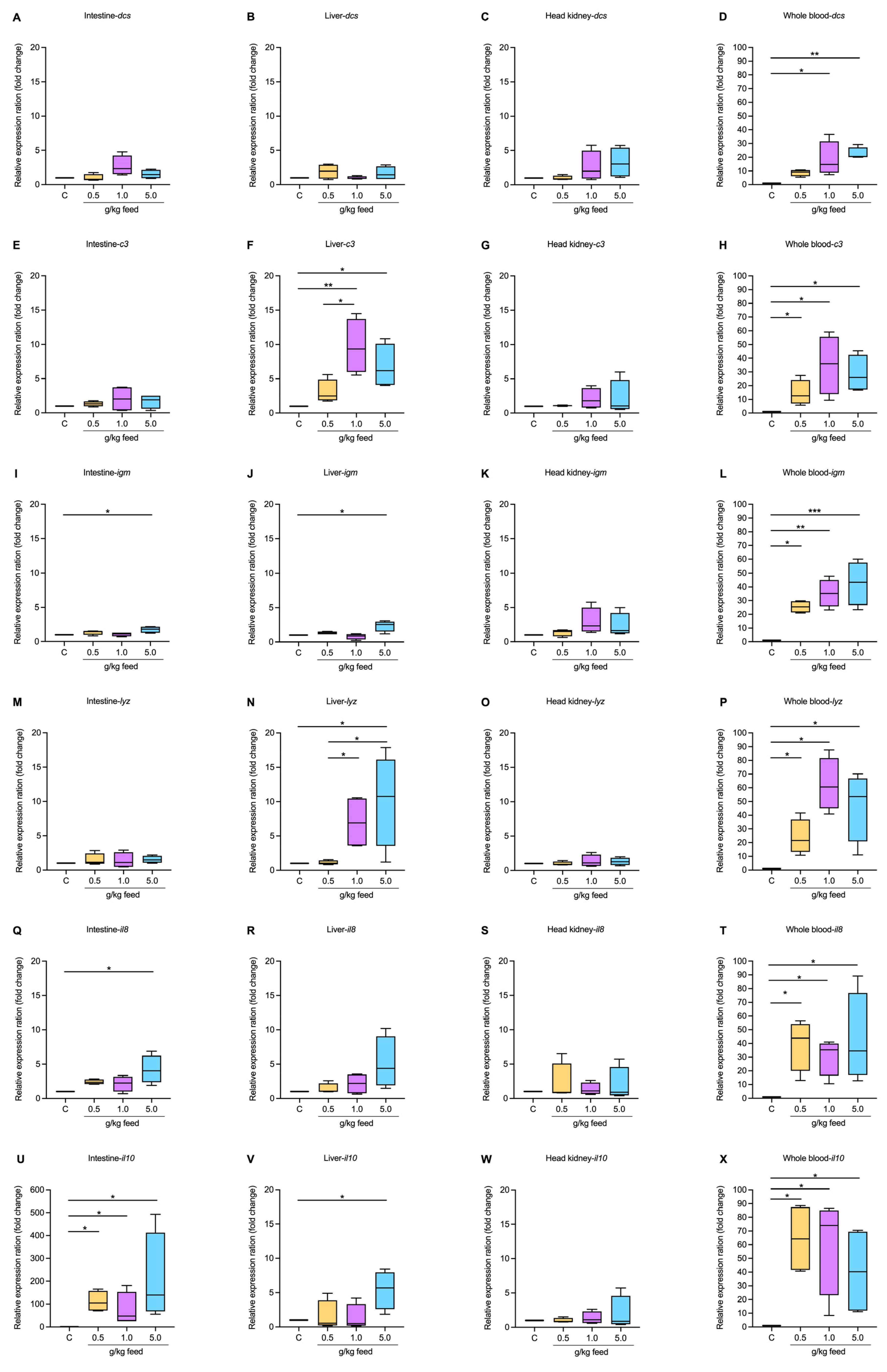
3.3.5. Immune-Related Gene Expression
3.3.6. Blood Biochemical Analysis
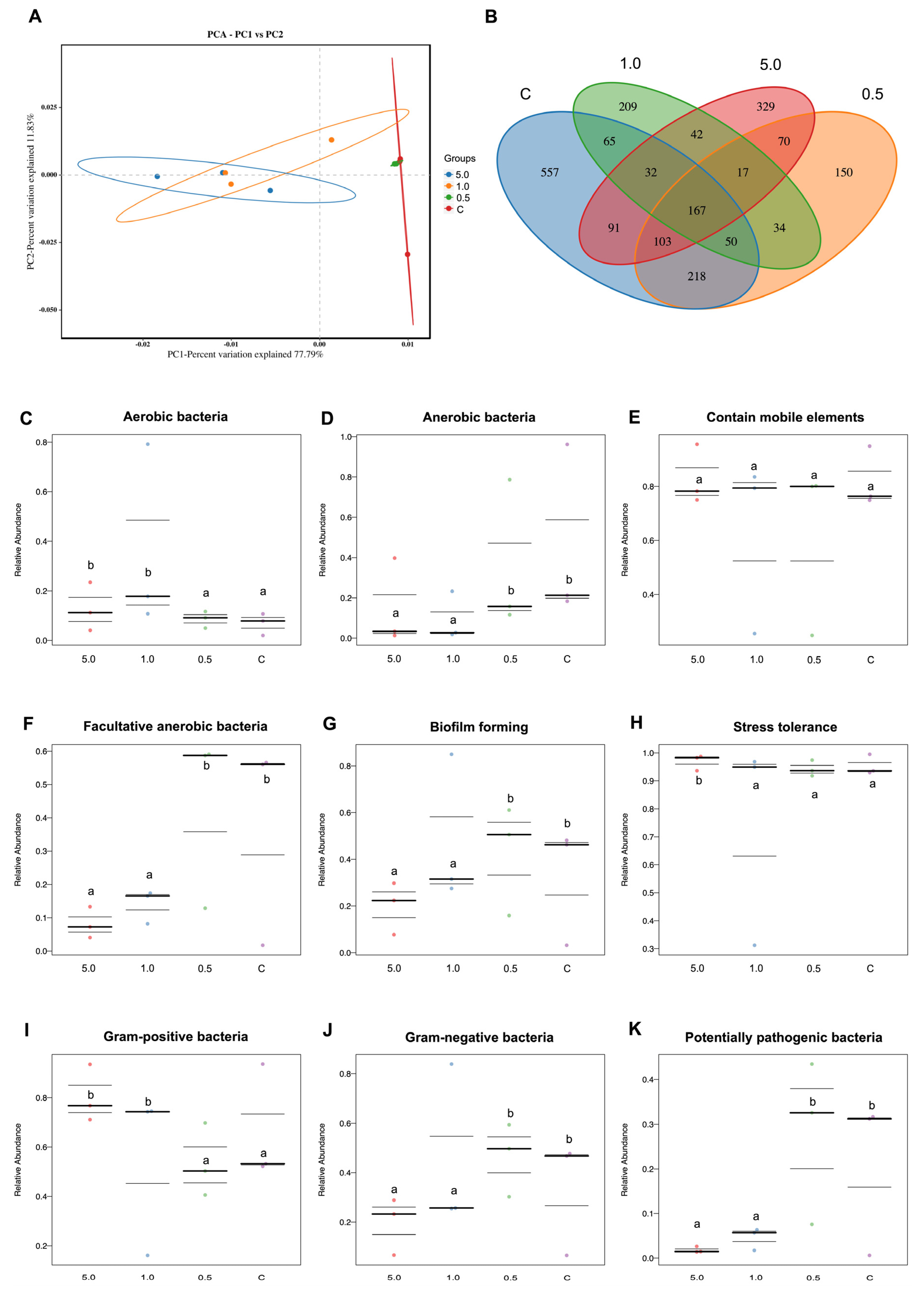
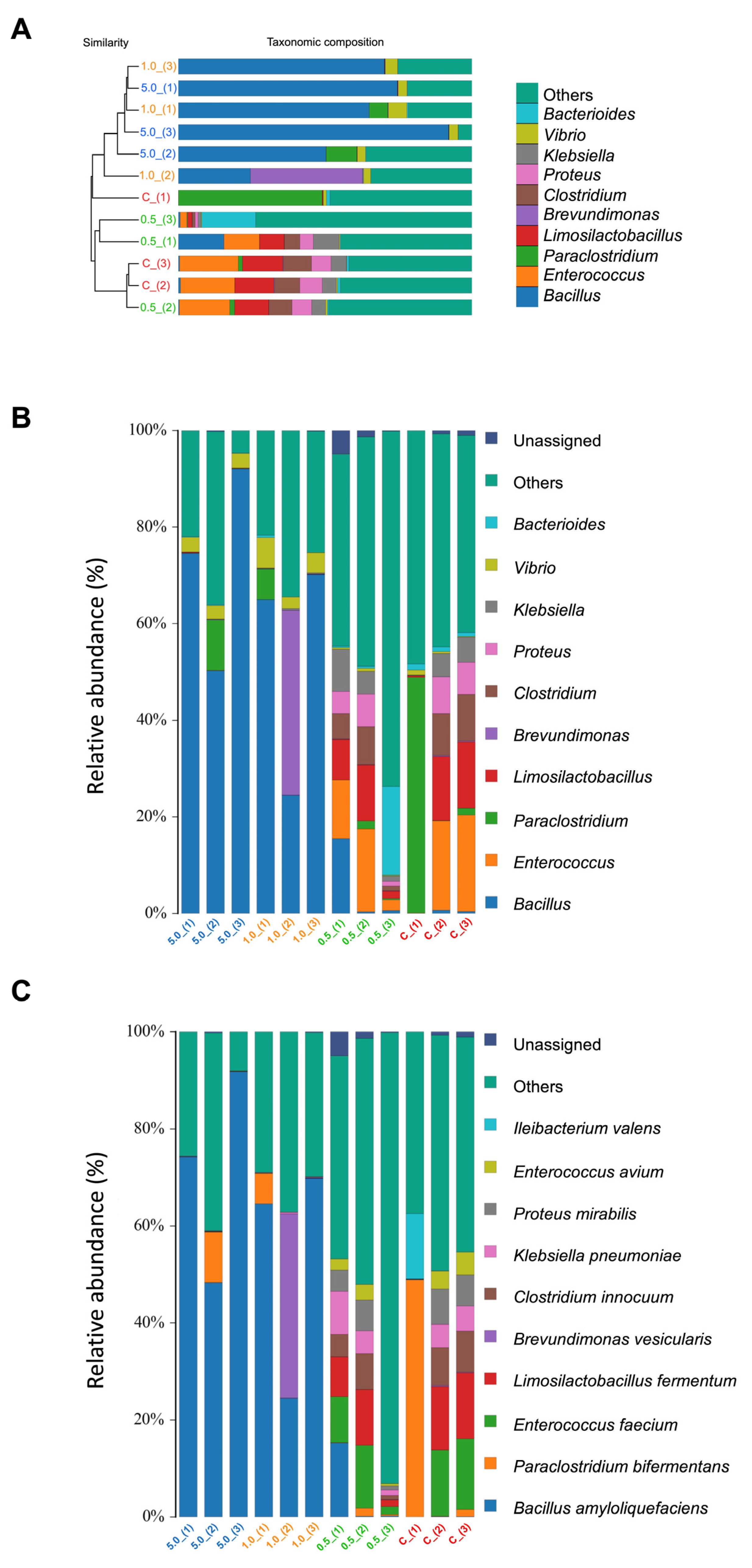
3.3.7. Gut Microbiota Analysis
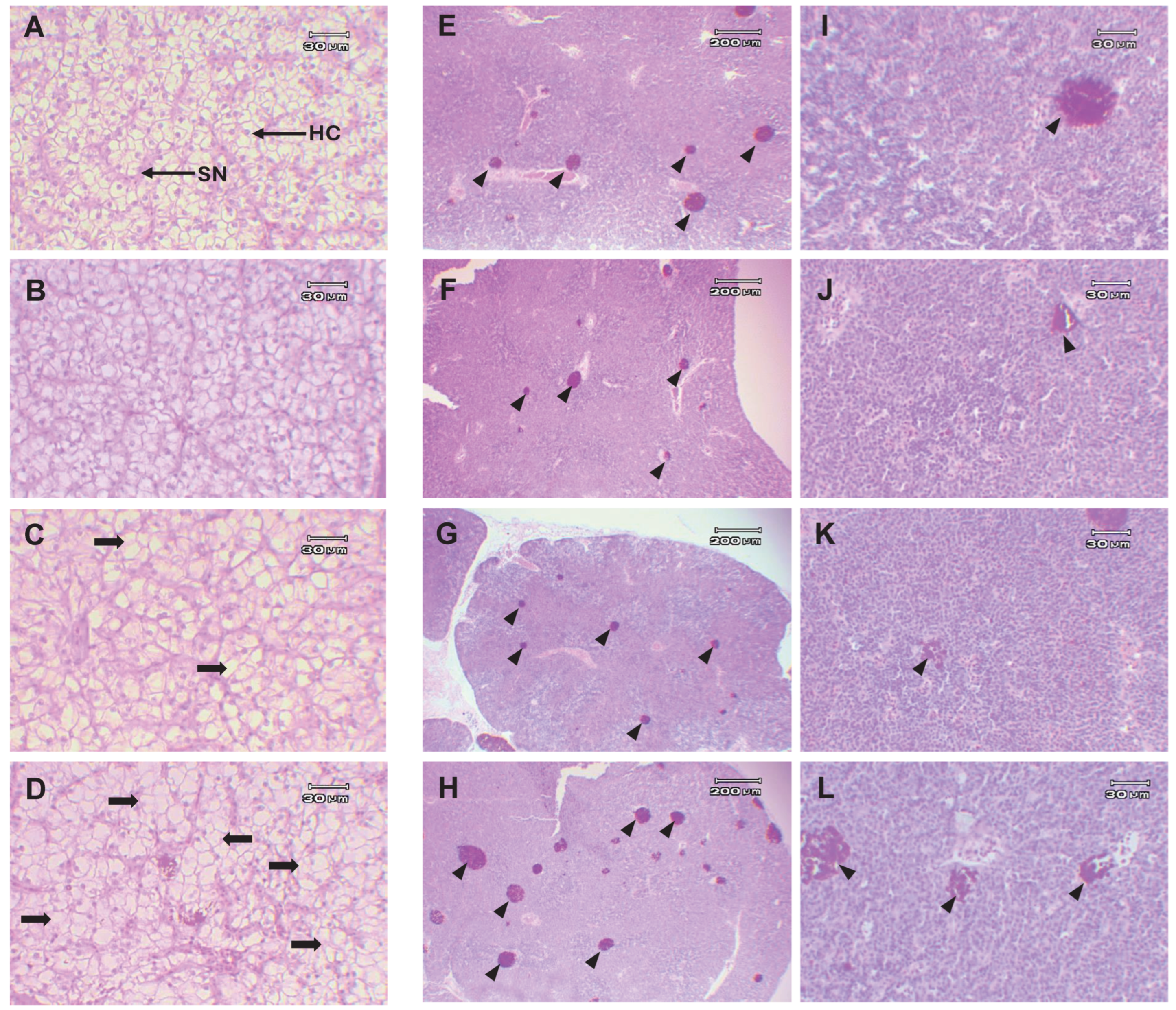
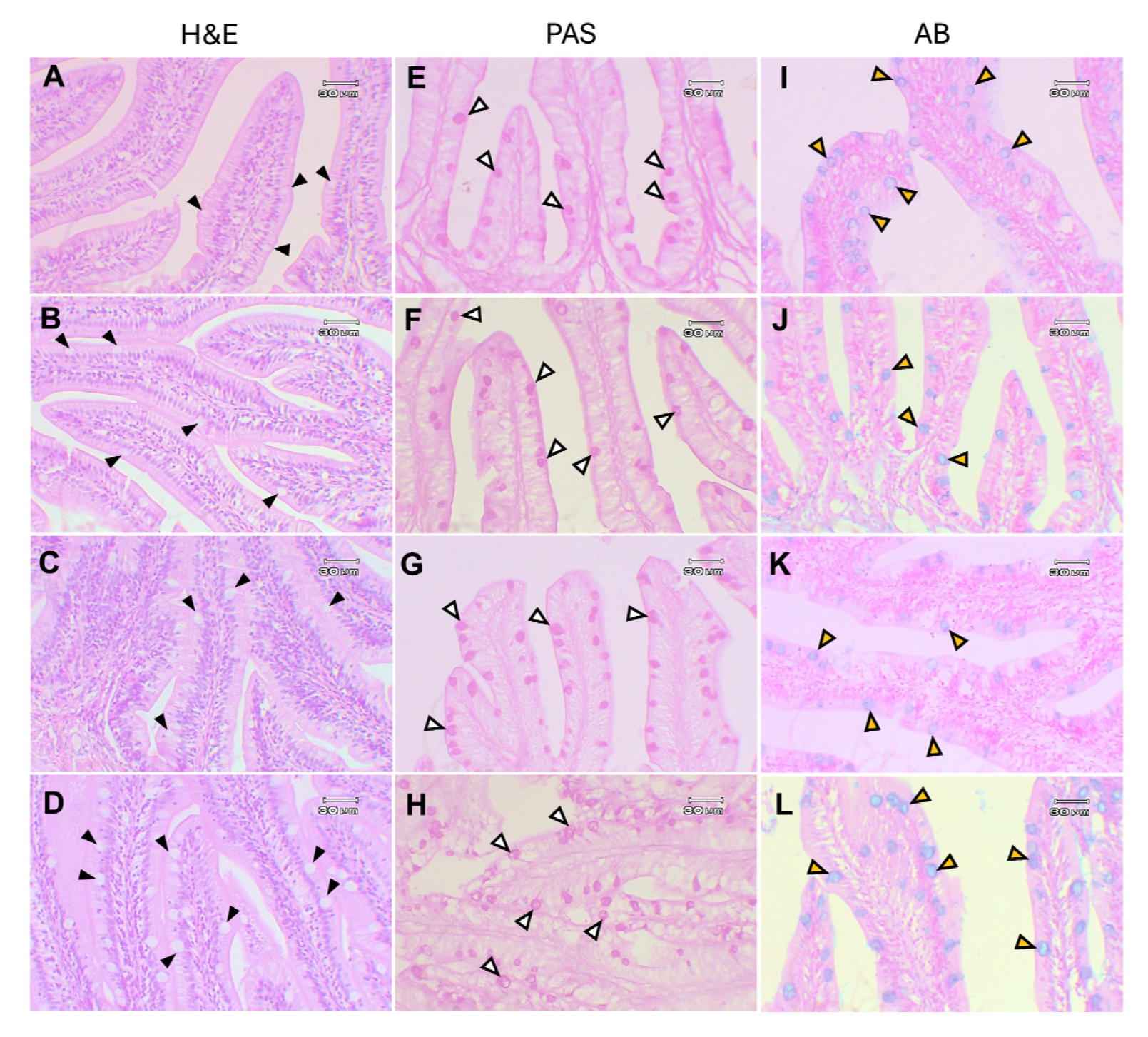
3.3.8. Histological Analysis
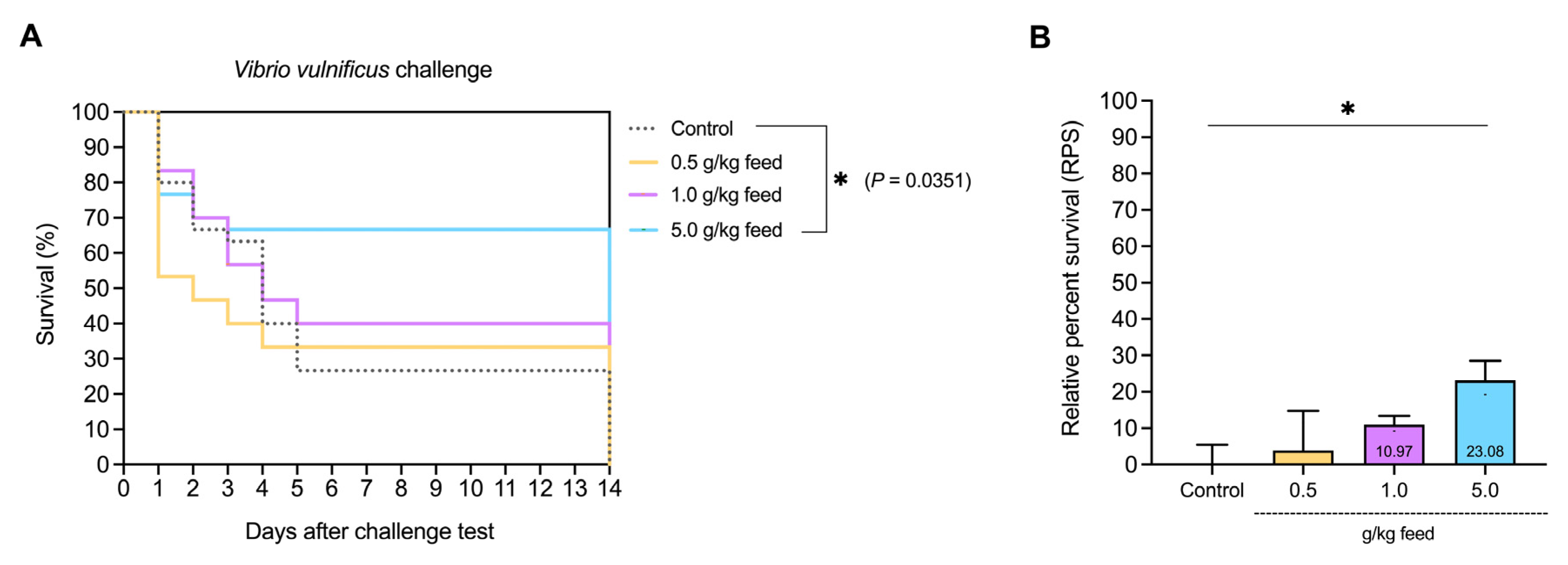
3.3.9. Survival Rate and Relative Percent Survival (RPS) to V. vulnificus Challenge
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meachasompop, P.; Bunnoy, A.; Keaswejjareansuk, W.; Dechbumroong, P.; Namdee, K.; Srisapoome, P. Development of immersion and oral bivalent nanovaccines for streptococcosis and columnaris disease prevention in fry and fingerling Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) nursery farms. Vaccines 2024, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumree, P.; Bunnoy, A.; Tang, X.; Srisapoome, P. Efficacy of whole-cell-based monovalent and bivalent vaccines against Streptococcus iniae and Flavobacterium covae in fingerling Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 144, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Global Aquaculture Production. In Fishery Statistical Collections; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.K.; Dutta, J.; Ahmad, I.; Rather, M.A. Nanotechnology in aquaculture: Transforming the future of food security. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendencia, E.A. Vibrio harveyi isolated from cage-cultured seabass Lates calcarifer Bloch in the Philippines. Aquac. Res. 2002, 33, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupesha Sharma, S.R.; Rathore, G.; Verma, D.K.; Sadhu, N.; Philipose, K.K. Vibrio alginolyticus infection in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch) reared in open sea floating cages in India. Aqua. Res. 2012, 44, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Amal, M.N.A.; Yasin, I.S.M.; Saad, M.Z.; Nasruddin, N.S.; Al-saari, N.; Mino, S.; Sawabe, T. Vibriosis in cultured marine fishes: A review. Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchimuthu, M.; Rosalind George, M.; Riji John, K.; Santhana Kumar, V. Pathogenicity potential of antimicrobial-resistant Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae isolated from maricultured and wild-caught fish of the southeast coast of India. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 4505–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-Y.; Huang, X.; Cheong, K.-L. Recent advances in marine algae polysaccharides: Isolation, structure, and activities. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, K.; Ravichandran, S.; Muralisankar, T.; Uthayakumar, V.; Chandirasekar, R.; Seedevi, P.; Abirami, R.G.; Rajan, D.K. Application of marine-derived polysaccharides as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review of current knowledge and further perspectives. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 1177–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahaye, M.; Robic, A. Structure and functional properties of Ulvan, a polysaccharide from green seaweeds. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated seaweed polysaccharides as multifunctional materials in drug delivery applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, E.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Antibacterial derivatives of marine algae: An overview of pharmacological mechanisms and applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klongklaew, N.; Praiboon, J.; Tamtin, M.; Srisapoome, P. Antibacterial and antiviral activities of local Thai green macroalgae crude extracts in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansemir, A.; Blume, M.; Schröder, S.; Lindequist, U. Screening of cultivated seaweeds for antibacterial activity against fish pathogenic bacteria. Aquaculture 2006, 252, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craigie, J.; Wen, Z.; Van der Meer, J. Interspecific, intraspecific and nutritionally-determined variations in the composition of agars from Gracilaria spp. De Gruyter Brill 1984, XXVII, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Latimer, G.W., Jr. (Ed.) Official Methods of Analysis. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 22nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, K.; Wu, X.; Liu, R.H. Antioxidant activity of apple peels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez, A.A.L.; Gomez, J.D.; Vattuone, M.A.; Lsla, M.I. Antioxidant activities of Sechium edule (Jacq.) Swartz extracts. Food Chem. 2006, 97, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamilselvi, N.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Dhamotharan, R.; Arumugam, P.; Sagadevan, E. Analysis of total phenols, total tannins and screening of phytocomponents in Indigofera aspalathoides (Shivanar Vembu) Vahl EX DC. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2012, 4, 3259–3265. [Google Scholar]
- Anhwange, B.A.; Ajibola, V.O.; Oniye, S.J. Chemical studies of the seeds of Moringa oleifera (Lam) and Detarium microcarpum (Guill ans Sperr). J. Biol. Sci. 2004, 4, 711–715. [Google Scholar]
- Umamaheswari, M.; Chatterjee, T.K. In vitro antioxidant activities of the fractions of Coccinia grandis L. leaf extract. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2007, 5, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susanti, D.; Sirat, H.M.; Ahmad, F.; Ali, R.M.; Aimi, N.; Kitajima, M. Antioxidant and cytotoxic flavonoids from the flowers of Melastoma malabathricum L. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülçin, İ. Antioxidant activity of caffeic acid (3, 4-dihydroxycinnamic acid). Toxicology 2006, 217, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.Y.; Yen, C.L. Reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxidation product-scagenging ability of yogurt organism. J. Diary Sci. 1999, 82, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, H.; Malli, F.; Rammal, H.; Hijazi, A.; Bassal, A.; Ajouz, N.; Badran, B. Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of Lebanes Eryngium creticum L. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, S1217–S1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruch, R.J.; Cheng, S.J.; Klauning, J.E. Prevention of cytotoxicity and inhibition of intracellular communication by antioxidant catechins isolated from Chinese green tea. Carcinogenesis 1989, 10, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J. Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease. Biochem. J. 1984, 219, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha, S.N.; Latha, B.V. In vitro antioxidant and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of Ruta graveolens methanol extract. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2012, 5, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hazra, B.; Biswas, S.; Mandal, N. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of Spondias pinnata. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2008, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; p. 1000. [Google Scholar]
- Paankhao, N.; Sangsawang, A.; Kantha, P.; Paankhao, S.; Promsee, K.; Soontara, C.; Kongsriprapan, S.; Srisapoome, P.; Kumwan, B.; Meachasompop, P.; et al. Antioxidant and antibacterial efficiency of the ethanolic leaf extract of Kratom (Mitragyna speciosa (Korth.) Havil) and its effects on growth, health, and disease resistance against Edwardsiella tarda infection in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 152, 109771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnoy, A.; Thompson, K.D.; Thangsunan, P.; Chokmangmeepisarn, P.; Yata, T.; Pirarat, N.; Kitiyodom, S.; Thangsunan, P.; Sukkarun, P.; Prukbenjakul, P.; et al. Development of a bivalent mucoadhesive nanovaccine to prevent francisellosis and columnaris diseases in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 138, 108813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnoy, A.; Thangsunan, P.; Chokmangmeepisarn, P.; Yata, T.; Klongklaew, N.; Pirarat, N.; Kitiyodom, S.; Srisapoome, P.; Rodkhum, C. Mucoadhesive cationic lipid-based Flavobacterium oreochromis nanoencapsulation enhanced the efficacy of mucoadhesive immersion vaccination against columnaris disease and strengthened immunity in Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 127, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saengrung, J.; Bunnoy, A.; Du, X.; Huang, L.; An, R.; Liang, X.; Srisapoome, P. Effects of ribonucleotide supplementation in modulating the growth of probiotic Bacillus subtilis and the synergistic benefits for improving the health performance of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 140, 108983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanichavetin, K.; Uchuwittayakul, A.; Namdee, K.; Srisapoome, P. Oral booster effects of bivalent nanovaccine-primed fingerlings of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer, Bloch 1790) to prevent streptococcosis and columnaris diseases. Aquaculture 2024, 592, 741165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangrerk, C.; Uchuwittayakul, A.; Srisapoome, P. Identification, expression and antimicrobial functional analysis of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in response to Streptococcus iniae and Flavobacterium covae in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer Bloch, 1790). Animals 2024, 14, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchuwittayakul, A.; Thangsunan, P.; Thangsunan, P.; Rodkhum, C.; Srisapoome, P. Molecular structure and functional responses of IgM, IgT and IgD to Flavobacterium covae and Streptococcus iniae infection in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer Bloch, 1790). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 153, 109823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paria, A.; Dong, J.; Babu, P.P.S.; Makesh, M.; Chaudhari, A.; Thirunavukkarasu, A.R.; Purushothaman, C.S.; Rajendran, K.V. Evaluation of candidate reference genes for quantitative expression studies in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) during ontogenesis and in tissues of healthy and infected fishes. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 54, 597–605. [Google Scholar]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehly, A.C. The Assay of Catalases and Peroxidases. In Methods of Biochemical Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 357–424. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, Y.; Noguchi, T.; Okabe, T.; Kajiyama, M. Superoxide dismutase in various tissues from rabbits bearing the Vx-2 carcinoma in the maxillary sinus. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 4233–4235. [Google Scholar]
- Jollow, D.J.; Mitchell, J.R.; Zampaglione, N.; Gillette, J.R. Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 1974, 11, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandas, J.; Marshall, J.J.; Duggin, G.G.; Horvath, J.S.; Tiller, D.J. Differential distribution of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes in rabbit kidney: Possible implications in analgesic nephropathy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1984, 33, 1801–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habig, W.H.; Pabst, M.J.; Jakoby, W.B. Glutathione S-transferases. The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnoy, A.; Na-Nakorn, U.; Srisapoome, P. Probiotic effects of a novel strain, Acinetobacter KU011TH, on the growth performance, immune responses, and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila of bighead catfish (Clarias macrocephalus Gunther, 1864). Microorganisms 2019, 7, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnoy, A.; Na-Nakorn, U.; Srisapoome, P. Development of a monoclonal antibody specific to the IgM heavy chain of bighead catfish (Clarias macrocephalus): A biomolecular tool for the detection and quantification of IgM molecules and IgM(+) cells in clarias catfish. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchuwittayakul, A.; Rodkhum, C.; Srisapoome, P. Production of a monoclonal antibody specific to the IgM heavy chain of Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer Bloch, 1790) and its application in assessing health status following vaccination and challenges with Flavobacterium covae and Streptococcus iniae. Aquaculture 2025, 594, 741445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feranchuk, S.; Belkova, N.; Potapova, U.; Kuzmin, D.; Belikov, S. Evaluating the use of diversity indices to distinguish between microbial communities with different traits. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokmangmeepisarn, P.; Senapin, S.; Taengphu, S.; Thompson, K.D.; Srisapoome, P.; Uchuwittayakul, A.; Rodkhum, C. Protective efficiency and immune responses to single and booster doses of formalin-inactivated scale drop disease virus (SDDV) vaccine in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, K.; Kadirvel, V.; Subramaniyan, T. Seaweeds, an aquatic plant-based protein for sustainable nutrition—A review. Future Foods 2022, 5, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardhana, N.; Kim, K.N.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, S.H.; Ha, J.H.; Song, C.B.; Lee, J.B.; Jeon, Y.J. Optimisation of hydrophilic antioxidant extraction from Hizikiafusiformis by integrating treatments of enzymes, heat and pH control. Int. J. Food Sci. 2008, 43, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdt, S.L.; Kraan, S. Bioactive compounds in seaweed: Functional food applications and legislation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 543–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, A.H.L.; Davies, S.J.; Soler-Vila, A.; Fitzgerald, R.; Johnson, M.P. Macroalgae as a sustainable aquafeed ingredient. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 458–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, E.M.; Al-Souti, A.S.; Sharawy, Z.Z.; El-Haroun, E.; Ashour, M. Impact of dietary ddministration of seaweed polysaccharide on growth, microbial abundance, and growth and immune-related genes expression of the Pacific whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Life 2023, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, N.A.; Ibrahim, D.; Sulaiman, S.F.; Supardy, A. Assessment of antioxidant activity, total phenolic content and in-vitro toxicity of Malaysian red seaweed, Acanthophora spicifera. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2011, 3, 182–191. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, A.H.L.; Soler-Vila, A.; O’Keeffe, D.; Casburn, P.; Fitzgerald, R.; Johnson, M.P. The inclusion of Palmaria palmata macroalgae in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) diets: Effects on growth, haematology, immunity and liver function. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3091–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersin, T.V.; Mapes, H.M.; Journey, M.L.; Beckman, B.R.; Lema, S.C. Insulin-like growth factor-1 (Igf1) signaling responses to food consumption after fasting in the Pacific rockfish Sebastes carnatus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2023, 282, 111444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breves, J.P.; Phipps-Costin, S.K.; Fujimoto, C.K.; Einarsdottir, I.E.; Regish, A.M.; Björnsson, B.T.; McCormick, S.D. Hepatic insulin-like growth-factor binding protein (igfbp) responses to food restriction in Atlantic salmon smolts. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 233, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Xu, Q. Roles of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins in regulating IGF actions. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 142, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbary, P.; Aminikhoei, Z. Effect of water-soluble polysaccharide extract from the green alga Ulva rigida on growth performance, antioxidant enzyme activity, and immune stimulation of grey mullet Mugil cephalus. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, M.A.B.; Francis, P.; Rohani, M.F.; Azam, M.S.; Mock, T.S.; Francis, D.S. Seaweed and seaweed-based functional metabolites as potential modulators of growth, immune and antioxidant responses, and gut microbiota in fish. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-Y.; Chen, W.-D.; Liu, Y.-J.; Niu, J.; Chen, M.; Tian, L.-X. Effect of different dietary levels of Gracilaria lemaneiformis dry power on growth performance, hematological parameters and intestinal structure of juvenile Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2016, 450, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.; Mabrouk, M.M.; Ayoub, H.F.; El-Feky, M.M.; Zaki, S.Z.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Rossi, W.; Van Doan, H.; El-Haroun, E.; Goda, A.M.-S. Effect of dietary seaweed extract supplementation on growth, feed utilization, hematological indices, and non-specific immunity of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus challenged with Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 3467–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashoof, S.; Criscitiello, M.F. Fish Immunoglobulins. Biology 2016, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.B.; Jane-Wit, D.; Pober, J.S. Complement membrane attack complex: New roles, mechanisms of action, and therapeutic targets. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.M.; An, J. Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2007, 45, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedalhosseini, S.H.; Salati, A.P.; Torfi Mozanzadeh, M.; Parrish, C.C.; Shahriari, A.; Ahangarzadeh, M. Effect of dietary seaweed (Gracilaria pulvinata and Sargassum ilicifolium) on serum and mucosal immunity, some growth and immune-related genes expression, antioxidant status, and fatty acid profile in Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer). Aquac. Nutr. 2024, 2024, 3683163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhzadeh, N.; Ahmadifar, E.; Soltani, M.; Tayefi-Nasrabadi, H.; Mousavi, S.; Naiel, M.A.E. Brown seaweed (Padina australis) extract can promote performance, innate immune responses, digestive enzyme activities, intestinal gene expression and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Animals 2022, 12, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Harikrishnan, R.; Devi, G.; Bhat, E.A.; Paray, B.A. Stimulatory effects of seaweed Laminaria digitata polysaccharides additives on growth, immune-antioxidant potency and related genes induction in Rohu carp (Labeo rohita) during Flavobacterium columnare infection. Aquaculture 2024, 579, 740253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, E.; Conlon, M.; Hayes, M. Seaweed components as potential modulators of the gut microbiota. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.T.; Simões, M.; Costa, C.; Passos, R.; Baptista, T. Modulatory effect of Gracilaria gracilis on European seabass gut microbiota community and its functionality. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrhman, A.; Ashour, M.; Al-Zahaby, M.; Sharawy, Z.; Nazmi, H.; Zaki, M.; Ahmed, N.H.; Ahmed, S.; El-Haroun, E.; Doan, H. Effect of polysaccharides derived from brown macroalgae Sargassum dentifolium on growth performance, serum biochemical, digestive histology and enzyme activity of hybrid red tilapia. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Genes | Gene group | Primer Names | Nucleotide Sequences (5′→3′) | Tm (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin-like growth factors (igf1) | Growth-related gene | Lc_Igf1 | F: ACGCTGCAGTTTGTATGTGG R: CCTTAGTCTTGGGAGGTGCA | 60 | XM_018697285.1 |
| Dendritic cells (dcs) | Immune-related gene | Lc_Dcs | F: AAGACAGTAGACCTCTCCCACA R: CAAACAGGGGAAGGACTGAGAG | 60 | [35] |
| Complement C3 (c3) | Lc_C3 | F: CATCACCAAAGAAATGCTGCCA R: CTCATAAGACGGAGCAGGTCTC | 60 | [36] | |
| Immunoglobulin m (ighm) | Lc_IgM | F: TGTCAAGGTAAACGAGGGAGC R: TCCCCTGGATCCATTCGTCA | 60 | [37] | |
| Lysozyme (lyz) | Lc_Lyz | F: TGCATCACACACCATGGCAA R: CATCCACGTTGTCATAGGAG | 60 | [36] | |
| Interleukin-8 (il8) | Lc_IL8 | F: GCATCATCAAGGAGAGAAAGCC R: GTGTCTGCTCAGCTTGTTTCTT | 60 | [38] | |
| Interleukin-10 (il10) | Lc_IL10 | F: GCTAGATCAGACCGTCGAAGAC R: TGACATCACTCTTGAGCTCGTC | 60 | [36] | |
| Actin beta (actb) | References/housekeeping gene | Lc_B-actin | F: TACCACCGGTATCGTCATGGA R: CCACGCTCTGTCAGGATCTTC | 60 | [39] |
| Elongation factor 1-alpha (ef1a) | Lc_ef1a | F: GTTGCCTTTGTCCCCATCTC R: CTTCCAGCAGTGTGGTTCCA | 60 | [40] | |
| Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gapdh) | Lc_gapdh | F: CGCTTCCTGCACAACCAACT R: GTGGCAGTGATGGCATGAAC | 60 | [40] |
| Analysis Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Proximate composition | |
| Total protein (%) | 6.75 |
| Total carbohydrate (%) | 57.63 |
| Fat (%) | 0.26 |
| Ash (%) | 31.96 |
| Moisture (%) | 3.40 |
| Sulfate polysaccharide (%) | 6.01 |
| Fatty acids (%) | |
| Saturated fatty acid: Lauric acid (C12:0) | 0.01 |
| Saturated fatty acid: Palmitic acid (C16:0) | 0.14 |
| Unsaturated fatty acid: Stearic acid (C18:0) | 0.04 |
| Unsaturated fatty acid: Oleic acid (C18:1n9c) | 0.04 |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2n6C) | 0.01 |
| Bioactive compounds | |
| Total phenolic content (mg GAE/g extract) | 2.33 ± 0.28 |
| Total flavonoid content (mg QE/g extract) | 2.41 ± 0.25 |
| Total tannins (mg TAE/g extract) | 1.05 ± 0.18 |
| Total saponins (mg/g extract) | 0.37 ± 0.06 |
| Antioxidant activities | |
| Total antioxidants (µg GAE/g extract) | 11.86 ± 1.76 |
| ABTS radical scavenging (IC50, mg/mL) | 18.23 ± 0.32 |
| DPPH radical scavenging (IC50, mg/mL) | 112.24 ± 10.75 |
| Reducing power (EC50, mg/mL) | 108.33 ± 13.29 |
| Anti-lipid peroxidation (IC50, mg/mL) | 92.7 ± 2.1 |
| Nitric oxide scavenging activity (IC50, mg/mL) | 88.5 ± 1.6 |
| Hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity (IC50, mg/mL) | 91.2 ± 1.8 |
| Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity (IC50, mg/mL) | 85.6 ± 2.0 |
| Superoxide radical scavenging activity (IC50, mg/mL) | 89.8 ± 1.9 |
| Groups | WG (g) | ADG (g) | SGR (%) | FCR | Survival Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 31.38 ± 2.30 | 1.05 ± 0.08 | 4.04 ± 0.20 | 1.54 ± 0.09 | 100% |
| 0.5 g/kg feed | 32.38 ± 1.59 | 1.08 ± 0.05 | 4.90 ± 0.50 | 1.48 ± 0.07 | 100% |
| 1.0 g/kg feed | 30.13 ± 1.94 | 1.00 ± 0.06 | 4.71 ± 0.53 | 1.60 ± 0.10 | 100% |
| 5.0 g/kg feed | 31.5 ± 3.18 | 1.05 ± 0.11 | 4.82 ± 0.63 | 1.53 ± 0.15 | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klongklaew, N.; Tansutaphanit, S.; Tiewpair, P.; Buncharoen, W.; Phaksopa, J.; Srisapoome, P.; Uchuwittayakul, A. Fish Health Enhancement and Intestinal Microbiota Benefits of Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer Bloch, 1790) on Dietary Sea Lettuce (Ulva rigida C. Agardh, 1823) Extract Supplementation. Animals 2025, 15, 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121714
Klongklaew N, Tansutaphanit S, Tiewpair P, Buncharoen W, Phaksopa J, Srisapoome P, Uchuwittayakul A. Fish Health Enhancement and Intestinal Microbiota Benefits of Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer Bloch, 1790) on Dietary Sea Lettuce (Ulva rigida C. Agardh, 1823) Extract Supplementation. Animals. 2025; 15(12):1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121714
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlongklaew, Nawanith, Sanikan Tansutaphanit, Pornphimon Tiewpair, Wararut Buncharoen, Jitraporn Phaksopa, Prapansak Srisapoome, and Anurak Uchuwittayakul. 2025. "Fish Health Enhancement and Intestinal Microbiota Benefits of Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer Bloch, 1790) on Dietary Sea Lettuce (Ulva rigida C. Agardh, 1823) Extract Supplementation" Animals 15, no. 12: 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121714
APA StyleKlongklaew, N., Tansutaphanit, S., Tiewpair, P., Buncharoen, W., Phaksopa, J., Srisapoome, P., & Uchuwittayakul, A. (2025). Fish Health Enhancement and Intestinal Microbiota Benefits of Asian Seabass (Lates calcarifer Bloch, 1790) on Dietary Sea Lettuce (Ulva rigida C. Agardh, 1823) Extract Supplementation. Animals, 15(12), 1714. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121714









