Establishment and Validation of Sensitive Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Aldosterone Quantification in Feline Serum with Reference Interval Determination
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Serum Samples
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Instrumentation and Analytical Conditions
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. Method Validation
2.5.1. Standard Solutions and Calibration Curve
2.5.2. Limit of Quantification, Linearity, and Carryover
2.5.3. Precision, Accuracy, Recovery, Selectivity and Matrix Effect
2.5.4. Stability
2.5.5. Reference Interval
2.5.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Method Validation
3.1.1. Selectivity
3.1.2. Stability
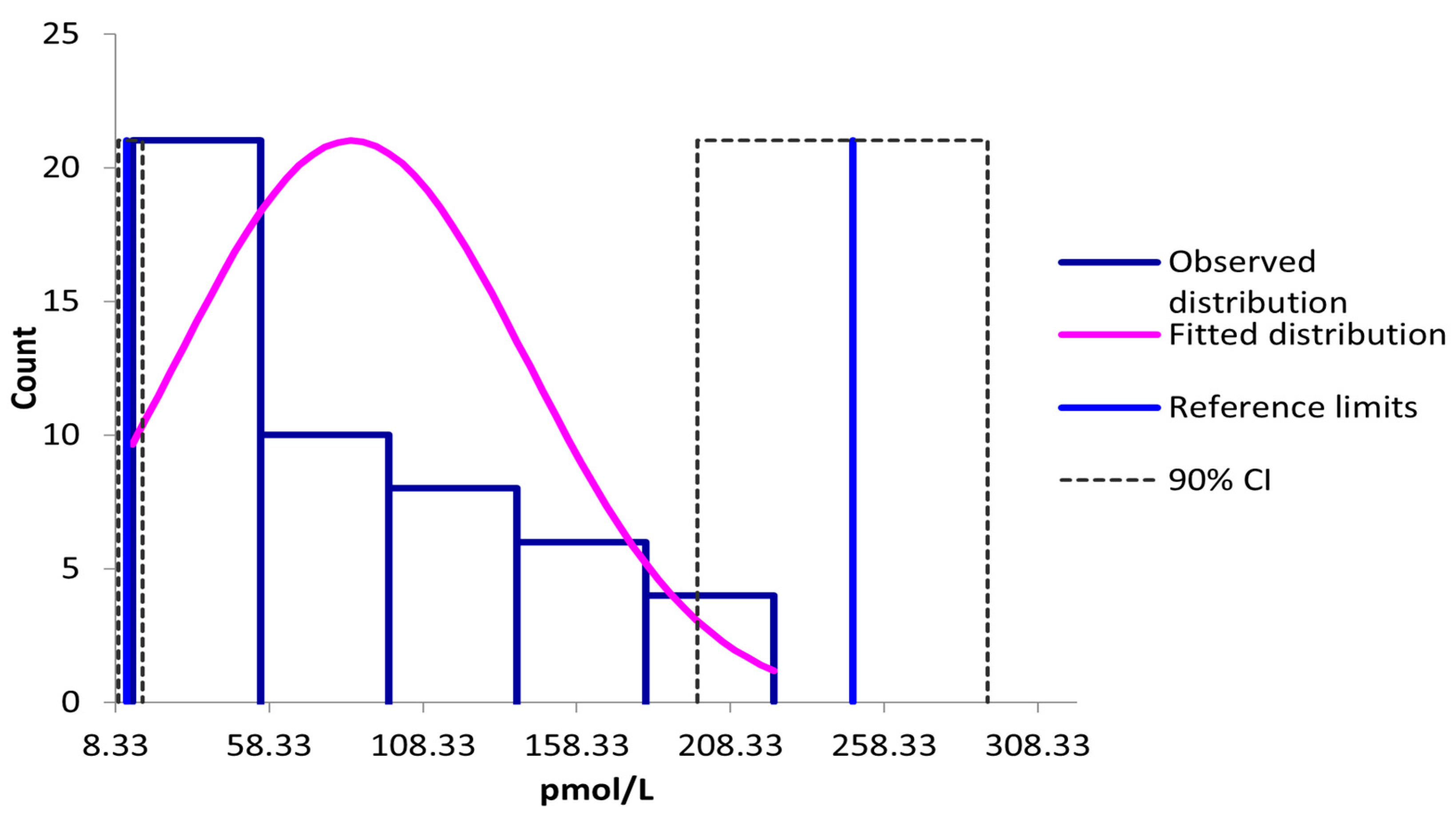
3.2. Reference Interval
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Epstein, M.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Clase, C.M.; Sood, M.M.; Pecoits-Filho, R. Aldosterone, Mineralocorticoid Receptor Activation, and CKD: A Review of Evolving Treatment Paradigms. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 80, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman Ramos, P.; Schiel, R. Hyperaldosteronism (Conn’s Syndrome) in Cats. InPractice 2025, 47, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.F. Regulation of Potassium Homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.A.; Vanchina, M.A.; Ogleby, B.; Jewell, D.E. Increased Water Viscosity Enhances Water Intake and Reduces Risk of Calcium Oxalate Stone Formation in Cats. Animals 2021, 11, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syme, H.M.; Fletcher, M.G.R.; Bailey, S.R.; Elliott, J. Measurement of Aldosterone in Feline, Canine and Human Urine. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2007, 48, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowlie, S.; Ramsey, I.K. Feline Hypoadrenocorticism. In BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Endocrinology; Mooney, C.T., Peterson, M.E., Shiel, R.E., Eds.; British Small Animal Veterinary Association: Chorley, UK, 2023; pp. 303–308. ISBN 978-1-910443-85-9. [Google Scholar]
- Del Magno, S.; Foglia, A.; Rossanese, M.; Montinaro, V.; Cola, V.; Pisoni, L.; Rossetti, D.; Cantatore, M.; De La Puerta, B.; Nicoli, S.; et al. Surgical Findings and Outcomes after Unilateral Adrenalectomy for Primary Hyperaldosteronism in Cats: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Study. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2023, 25, 1098612X221135124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooistra, H.S. Primary Hyperaldosteronism in Cats. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 50, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, M.; Fabrès, V.; Dumont, R.; Chetboul, V.; Chahory, S.; Saponaro, V.; Trehiou, E.; Poissonnier, C.; Passavin, P.; Jondeau, C.; et al. Prospective Evaluation of a Telmisartan Suppression Test as a Diagnostic Tool for Primary Hyperaldosteronism in Cats. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.P.; Lawrence, J.; Andersen, P.; Leathers, V.; Workman, E. Immunoassay Applications in Veterinary Diagnostics. In The Immunoassay Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 623–645. ISBN 978-0-08-097037-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Morris, J.G. Plasma Aldosterone Concentration of Cats. Vet. J. 1998, 155, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetti, M.; Burrello, J.; Goi, J.; Parasiliti-Caprino, M.; Gioiello, G.; Settanni, F.; Monticone, S.; Mulatero, P.; Mengozzi, G. Diagnostic Accuracy of Aldosterone and Renin Measurement by Chemiluminescence for Screening of Patients with Primary Aldosteronism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, Y.; Kono, T.; Teruyama, K.; Ichijo, T.; Sakuma, I.; Nagano, H.; Miyagawa, H.; Kono, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Hashimoto, N.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Aldosterone and Renin Assays for Primary Aldosteronism Screening. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, D.K.; Mazaki-Tovi, M.; Harro, C.C.; Refsal, K.R. Multiple Corticosteroid Abnormalities in Cats with Hyperaldosteronism. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 2152–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, D. Clinical Utility of Laboratory Developed Mass Spectrometry Assays for Steroid Hormone Testing. J. Mass Spectrom. Adv. Clin. Lab 2023, 28, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnir, M.M.; Rockwood, A.L.; Roberts, W.L.; Yue, B.; Bergquist, J.; Meikle, A.W. Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Analysis of Steroids in Clinical Laboratories. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 44, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yucel, K.; Abusoglu, S.; Unlu, A. Comparison of Immunoassay and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Methods in the Measurement of Serum Androstenedione Levels. Clin. Lab. 2018, 64, 170612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffré, A.; Concordet, D.; Braun, J.; Trumel, C. Reference Value Advisor: A New Freeware Set of Macroinstructions to Calculate Reference Intervals with Microsoft Excel. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 40, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaschitz, A.; Maerz, W.; Pilz, S.; Ritz, E.; Scharnagl, H.; Renner, W.; Boehm, B.O.; Fahrleitner-Pammer, A.; Weihrauch, G.; Dobnig, H. Aldosterone/Renin Ratio Determines Peripheral and Central Blood Pressure Values Over a Broad Range. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djajadiningrat-Laanen, S.C.; Galac, S.; Kooistra, H. Primary Hyperaldosteronism: Expanding the Diagnostic Net. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2011, 13, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, R.; Harvey, A.M.; Tasker, S. Primary Hyperaldosteronism in the Cat: A Series of 13 Cases. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2005, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Bai, Y.; Li, C.; Li, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T. CT and MRI of Adrenal Gland Pathologies. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2018, 8, 853–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchekroun, G. Feline Hyperaldosteronism. In BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Endocrinology; Mooney, C.T., Peterson, M.E., Shiel, R.E., Eds.; British Small Animal Veterinary Association: Chorley, UK, 2023; pp. 309–317. ISBN 978-1-910443-85-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, C.; Cicalini, I.; Verrocchio, S.; Di Dalmazi, G.; Federici, L.; Bucci, I. The Potential of Steroid Profiling by Mass Spectrometry in the Management of Adrenocortical Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, G.; Marinova, M.; Artusi, C.; Plebani, M. Mass Spectrometry or Immunoassay: Est Modus in Rebus. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2017, 55, 1243–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinescu, G.; Bidlingmaier, M.; Gruber, M.; Peitzsch, M.; Poitz, D.M.; Van Herwaarden, A.E.; Langton, K.; Kunath, C.; Reincke, M.; Deinum, J.; et al. Mass Spectrometry Reveals Misdiagnosis of Primary Aldosteronism with Scheduling for Adrenalectomy Due to Immunoassay Interference. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 507, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Gugten, J.G.; Holmes, D.T. Quantitation of Aldosterone in Serum or Plasma Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). In Clinical Applications of Mass Spectrometry in Biomolecular Analysis; Garg, U., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1378, pp. 37–46. ISBN 978-1-4939-3181-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, J.A.; Kushnir, M.M.; Palmer, J.; Sadjadi, S.; Rockwood, A.L.; Meikle, A.W. Enhancement of Specificity of Aldosterone Measurement in Human Serum and Plasma Using 2D-LC–MS/MS and Comparison with Commercial Immunoassays. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 970, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpeinen, U.; Hämäläinen, E.; Stenman, U.-H. Determination of Aldosterone in Serum by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 862, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuld, S.; Constantinescu, G.; Pamporaki, C.; Peitzsch, M.; Schulze, M.; Yang, J.; Müller, L.; Prejbisz, A.; Januszewicz, A.; Remde, H.; et al. Screening for Primary Aldosteronism by Mass Spectrometry Versus Immunoassay Measurements of Aldosterone: A Prospective Within-Patient Study. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2024, 9, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Okuyama, M.; Nakagawa, R.; Honma, S.; Satoh, F.; Morimoto, R.; Ito, S.; Takahashi, M.; Numazawa, M. Development of Sensitive Derivatization Method for Aldosterone in Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Corticosteroids. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1200, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adin, D.; Atkins, C.; Domenig, O.; Glahn, C.; DeFrancesco, T.; Meurs, K. Evaluation of Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System Components and Enzymes in Systemically Hypertensive Cats Receiving Amlodipine. Animals 2023, 13, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remane, D.; Meyer, M.R.; Wissenbach, D.K.; Maurer, H.H. Ion Suppression and Enhancement Effects of Co-Eluting Analytes in Multi-Analyte Approaches: Systematic Investigation Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry with Atmospheric-Pressure Chemical Ionization or Electrospray Ionizat. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 3103–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, S.; Djajadiningrat-Laanen, S.C.; Kooistra, H.S.; Van Dongen, A.M.; Voorhout, G.; Van Sluijs, F.J.; Van Den Ingh, T.S.G.A.M.; Boer, W.H.; Rijnberk, A. Primary Hyperaldosteronism, a Mediator of Progressive Renal Disease in Cats. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2005, 28, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepson, R.E.; Syme, H.M.; Elliott, J. Plasma Renin Activity and Aldosterone Concentrations in Hypertensive Cats with and without Azotemia and in Response to Treatment with Amlodipine Besylate. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kley, H.K.; Rick, W. The effect of storage and temperature on the analysis of steroids in plasma and blood. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1984, 22, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stroud, L.R.; Solomon, C.; Shenassa, E.; Papandonatos, G.; Niaura, R.; Lipsitt, L.P.; Lewinn, K.; Buka, S.L. Long-Term Stability of Maternal Prenatal Steroid Hormones from the National Collaborative Perinatal Project: Still Valid After All These Years. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007, 32, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
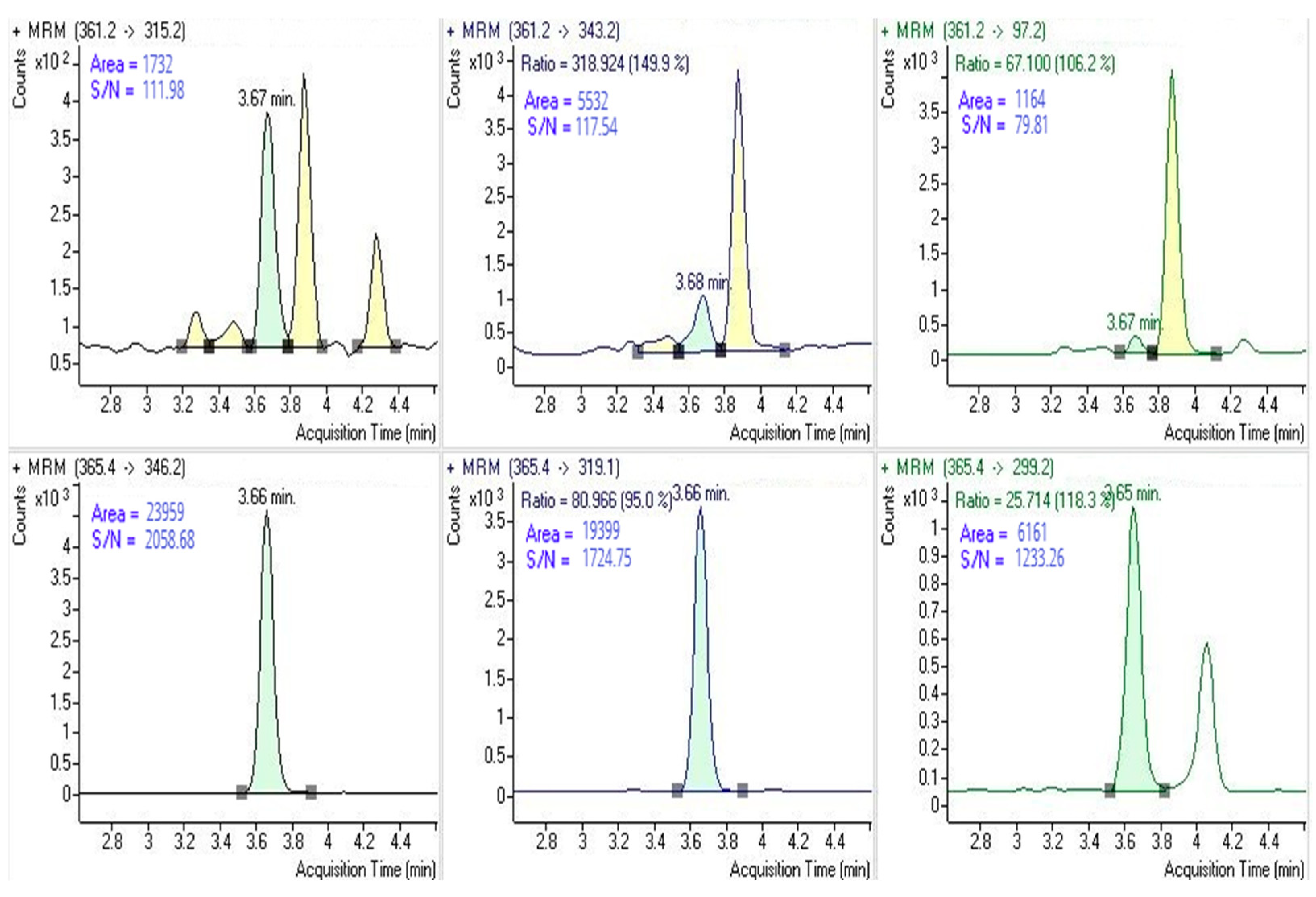
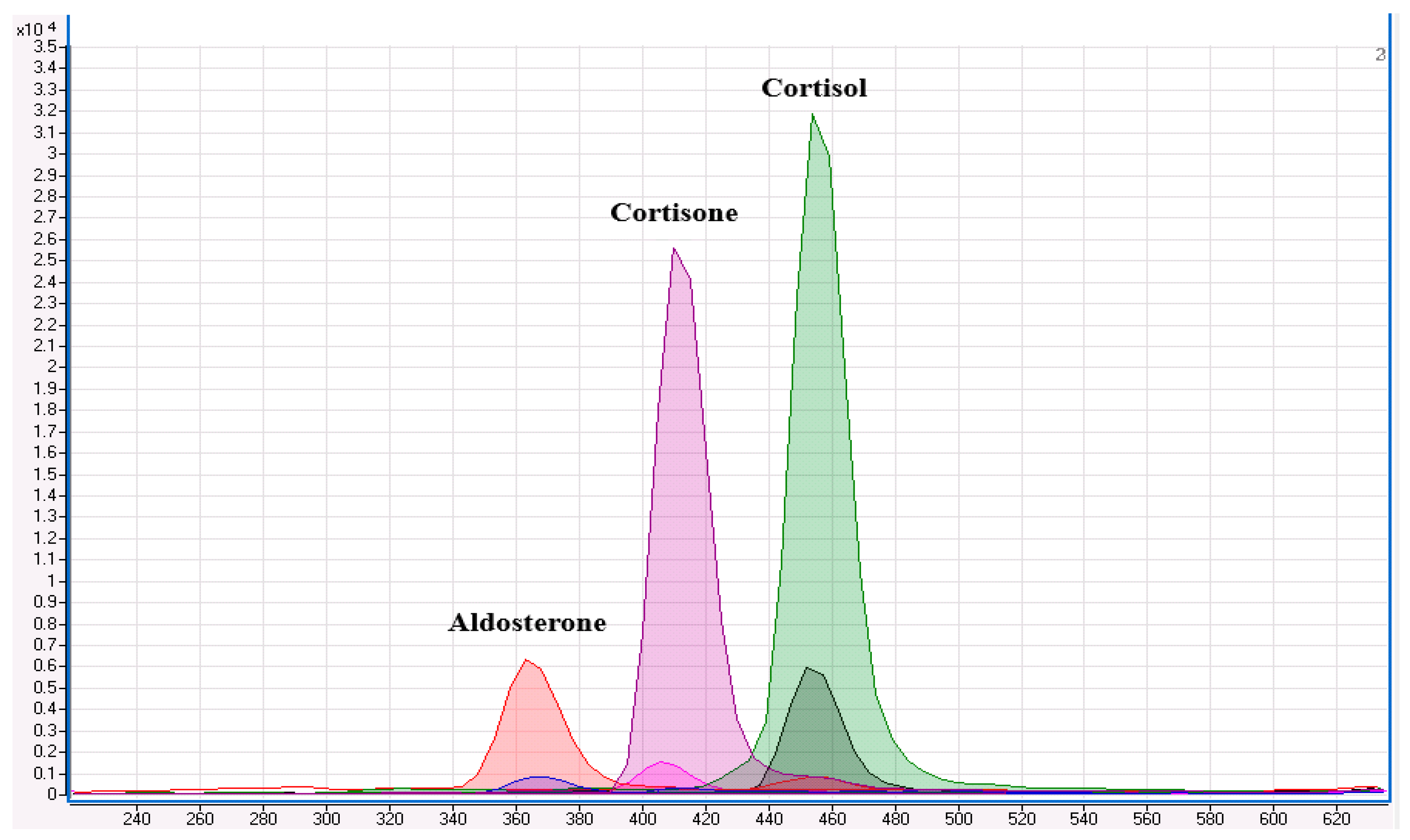
| Spike Level | Intra-Assay Bias 1 | Intra-Assay Bias 2 | Intra-Assay Bias 3 | Inter-Assay Bias | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOQ (5 pg/mL) | Mean (pg/mL) | 4.51 | 5.41 | 5.33 | 5.10 |
| CV | 7.31 | 6.52 | 5.70 | 6.47 | |
| Accuracy | 90.2 | 108.4 | 106.5 | 101.7 | |
| Low (15 pg/mL) | Mean (pg/mL) | 14.1 | 13.9 | 14.6 | 14.2 |
| CV | 3.68 | 6.27 | 10.8 | 6.97 | |
| Accuracy | 94.0 | 92.7 | 96.8 | 94.5 | |
| Medium (500 pg/mL) | Mean (pg/mL) | 524.3 | 511.6 | 497.1 | 511.0 |
| CV | 2.14 | 2.26 | 3.16 | 2.51 | |
| Accuracy | 104.9 | 102.3 | 99.6 | 102.2 | |
| High (1000 pg/mL) | Mean (pg/mL) | 1061.8 | 1003.7 | 991.6 | 1019.0 |
| CV | 2.89 | 4.63 | 4.51 | 3.99 | |
| Accuracy | 106.2 | 100.4 | 99.2 | 101.9 | |
| EM % | Mean | 99.1 | - | - | - |
| CV | 1.72 | - | - | - |
| Stability Type | Nominal Concentration, pg/mL | Mean, pg/mL | Standard Deviation, pg/mL | Percentage Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short term | 10 | 10.4 | 1.42 | 4.20 |
| 500 | 467.3 | 10.1 | −6.54 | |
| 1000 | 929.7 | 21.0 | −7.03 | |
| Long-term refrigerated (5 days) | 10 | 9.09 | 0.81 | −9.10 |
| 500 | 545.8 | 6.13 | 9.16 | |
| 1000 | 1066.7 | 30.4 | 6.67 | |
| Long-term freezing (5 days) | 10 | 9.01 | 0.13 | −9.90 |
| 500 | 545.8 | 20.3 | 9.16 | |
| 1000 | 979.1 | 12.2 | −2.09 | |
| Long-term refrigerated (7 days) | 10 | 10.8 | 1.68 | 8.03 |
| 500 | 546.5 | 59.16 | 9.29 | |
| 1000 | 1119.6 | 53.3 | 12.0 | |
| Long-term freezing (7 days) | 10 | 10.54 | 0.99 | 5.39 |
| 500 | 555.5 | 41.2 | 11.1 | |
| 1000 | 1043.7 | 22.7 | 4.37 | |
| Freeze–thaw | 10 | 9.16 | 0.21 | −8.39 |
| 500 | 539.5 | 12.1 | 7.90 | |
| 1000 | 1044.8 | 27.6 | 4.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furlanello, T.; Bertolini, F.M.; Zoia, A.; Sanchez del Pulgar, J.; Masti, R. Establishment and Validation of Sensitive Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Aldosterone Quantification in Feline Serum with Reference Interval Determination. Animals 2025, 15, 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121687
Furlanello T, Bertolini FM, Zoia A, Sanchez del Pulgar J, Masti R. Establishment and Validation of Sensitive Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Aldosterone Quantification in Feline Serum with Reference Interval Determination. Animals. 2025; 15(12):1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121687
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurlanello, Tommaso, Francesca Maria Bertolini, Andrea Zoia, Jose Sanchez del Pulgar, and Riccardo Masti. 2025. "Establishment and Validation of Sensitive Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Aldosterone Quantification in Feline Serum with Reference Interval Determination" Animals 15, no. 12: 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121687
APA StyleFurlanello, T., Bertolini, F. M., Zoia, A., Sanchez del Pulgar, J., & Masti, R. (2025). Establishment and Validation of Sensitive Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for Aldosterone Quantification in Feline Serum with Reference Interval Determination. Animals, 15(12), 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15121687








