Simple Summary
Handling fish in aquaculture disrupts the natural balance of skin bacteria, which play a crucial role in disease prevention. Anesthetic baths, used to reduce stress during handling, may further disturb this balance. This study revealed that benzocaine, used as an anesthetic bath, alters the skin mucus bacterial community structure of Atlantic salmon, potentially leading to dysbiosis (an imbalance in bacterial composition). Such disruptions could impair host–microbe interactions and increase susceptibility to opportunistic pathogens. These findings highlight the importance of understanding the impacts of anesthetics on fish microbiomes to improve aquaculture practices, promote fish health, and support more sustainable farming systems.
Abstract
Routine aquaculture practices such as capture, transportation, and handling can disrupt the relationship between commensal and opportunistic bacteria in the fish skin microbiome. Anesthetic baths are a common welfare practice in aquaculture to reduce stress during handling. However, to date, no studies assessed the effect of anesthetics on bacterial communities in fish skin mucus. This study is the first to evaluate the influence of benzocaine, a widely used anesthetic, on the skin mucus bacterial microbiome of Atlantic salmon reared in a recirculating aquaculture system (RAS). Using Illumina high-throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing, we found that bacterial richness and diversity were significantly reduced in skin mucus samples from fish with anesthesia (ANE) when compared with those without anesthesia (CTR). The predominant bacterial classes in both groups were Gammaproteobacteria (54.1–62.6%) and Betaproteobacteria (22.6–22.9%). However, significant dissimilarities in beta diversity were observed between the bacterial community structure of salmon skin mucus samples from ANE and CTR. These findings demonstrate that benzocaine exposure alters skin mucus microbiome of Atlantic salmon potentially leading to dysbiosis. This study also provides baseline information on the bacterial communities of Atlantic salmon skin mucus microbiome in an RAS. As no temporal resampling was performed, the duration and persistence of these changes remain unknown and warrant further investigation.
1. Introduction
Sustainable aquaculture relies heavily on maintaining the health and welfare of farmed fish. One critical yet often overlooked aspect of fish health is the role of microbial communities inhabiting their skin. Fish skin microbiome plays a vital role in maintaining host health, immunity, and ecological interactions within aquatic environments [1]. Fishes are always in close contact with their surrounding water, which naturally host a wide diversity of microorganisms [2,3]. As the fish skin is the interface between the organism and its surrounding environment, it plays a paramount role in its protection. In fact, the fish skin mucus is a primary physical and biochemical barrier, which acts as a first line of defence against pathogens that naturally occur in aquatic environments [4,5]. Overall fish health largely depends on the maintenance of a suitable balance between commensal and opportunistic bacteria in fish skin mucus [6,7]. However, in aquaculture, fish are subjected to various stressors and handling practices which may, at times, disrupt the balance of these microbial communities. Therefore, comprehending the dynamics of the fish skin microbiome and its response to environmental perturbations is essential to promote fish welfare, manage disease, and ensure a sustainable production of healthy high-quality fish [8,9].
Anesthetic baths are commonly employed in aquaculture to safely handle fish during multiple procedures, such as grading, tagging, transportation, and when performing medical treatments. These baths require target fish to be immersed in a diluted solution of anesthetic agent(s) for a given time frame, in order to induce a state of sedation or anesthesia that may minimize stress and facilitate the target procedure that needs to be performed with the fish [10,11]. Stress in fish can lead to multiple physiological responses, such as elevated levels of cortisol, compromised immune function, and decreased growth rates [12,13]. Several studies have already focused on the physiological effects of anesthetic baths in fish, such as stress responses [14], shifts in metabolic parameters [15], and impacts on respiratory function [16]. While these studies provide valuable insights into the safety and efficacy of anesthetic agents, the potential impact of these chemicals on the skin microbiome of cultured fish, particularly economically important species such as Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), remains poorly understood.
Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) represent a cornerstone species in global aquaculture, contributing significantly to seafood production and economic livelihoods. This species is among the most intensively farmed in aquaculture, with a global production surpassing 27,000 thousand tonnes in 2020 [17]. Farmed Atlantic salmon accounts for over 32% of all marine and coastal finfish farming, making it one of the most lucrative and technologically advanced sectors within the global fish production industry [17,18]. As aquaculture intensifies to meet growing demand, the use of anesthetic baths becomes increasingly prevalent for routine tasks in fish farms and when performing therapeutic interventions. Yet, the consequences of anesthetic agents on the fish skin microbiome composition and function remain largely unexplored, raising concerns about potential disruptions of host–microbe interactions and susceptibility to opportunistic pathogens.
Traditional culture-based methods and low-resolution molecular techniques often provided an incomplete and potentially biased perspective on microbial diversity, limiting our understanding of microbial interactions and their functional roles. In contrast, advances in high-throughput sequencing technologies have revolutionized our ability to characterize microbial communities and untangle their roles in host physiology and disease susceptibility, particularly within aquaculture [6,19,20,21].
In this study, we addressed the impact of benzocaine on the skin mucus bacterial microbiome of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar), using a high-throughput sequencing approach. Additionally, we characterized the bacterial communities inhabiting the skin mucus microbiome of Atlantic salmon cultured in a recirculating aquaculture system (RAS) located in the southernmost location of this species natural distribution in the Atlantic. The characterization of Atlantic salmon core skin microbiome was performed using salmon skin mucus samples without anesthesia, which we considered as our control group. Given the intimate association between the skin microbiome and its fish host health, establishing baseline information on bacterial communities is crucial for optimizing aquaculture practices and mitigating potential risks to the health of farmed Atlantic salmon.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site, Animals and Feeding
The present study was performed using an RAS located in northern Portugal (40°38′21.1″ N, 8°43′42.2″ W), the southernmost limit of the natural distribution of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Briefly, 1236 post-smolts (average fresh weight: 190 ± 30 g) were purchased from a Norwegian hatchery and live shipped by truck in 4 separated tanks (each one with a 2 m3 volume) equipped with individual life-support systems. No mortality was recorded during transportation and fish were stocked at a density of ca. 3.1 kg/m3 for approximately 5 months in a 320 m3 concrete rectangular tank (14 m × 8 m × 2.5 m). Saltwater was pumped from a coastal lagoon (Mira channel in Ria de Aveiro), being sand-filtered before entering the RAS. The RAS was equipped with two sand-filters (ASTRAL Pool, each one with Ø2 m, 1050 kg of 1–2 mm gravel and 3800 kg of 0.4–0.8 mm sand) and microbiological disinfection was secured by two UV filters with three 300 W lamps in each. Biological filtration was performed using a protein skimmer (volume: 2.5 m3; filtration rate 40 m3/h) and a fluidized biofilter (volume: 3.5 m3; filtration rate 40 m3/h) (Figure S1). The recirculation water flow was ~120 m3/h and a 10% partial water change was performed each week. Fish were fed ad-libitum, three times a day, using two different standard commercial diets (Prime 200 and Prime 500, Skretting) adjusted to different fish weights. Daily feed uptake varied from 1.6 to 1.3% of the total biomass. Atlantic salmon fish feed Prime 200 was firstly used until the specimens reached ~450 g fresh weight and Prime 500 was used subsequently, until the sampling moment. The analytical composition of fish feed varied from 25 to 32% for lipids, from 45.2 to 41.6% for crude protein, from 5.7 to 4.9% for crude ashes and from 2.1 to 4.5% for crude fiber. Manual feeding was always performed to better assess overall fish health and welfare. No antibiotics or probiotics were used during this trial.
2.2. Salmon Skin Mucus Sampling and DNA Extraction
Twenty Atlantic salmon post-smolts (average weight: 595 g) stoked during approximately 5 months under the culture conditions described above, were randomly collected using hand nets. All fish were visually inspected and showed no external signs of disease or abnormalities and thus, were considered healthy. Ten specimens were immersed up to 10 min in an anesthetic bath (~100 L) using 30–40 mg of benzocaine (commercially sold as Aquacen, 200 mg/mL), while the other ten specimens were exposed to the same procedure but using a saltwater bath alone with no anesthetic. The temperature of the bath was approximately 15 °C for both treatments and matched the temperature of the aquaculture system to minimize thermal stress. Benzocaine was chosen as the anesthetic bath due to its wide use by the aquaculture industry, availability and easiness of acquisition, in accordance with Regulation (EU) No 37/2010). Each sampled fish was placed individually in a separate sterile plastic bag (310 × 500 mm) for approximately 60 s, the time strictly necessary to collect enough skin mucus for further analysis. Following this procedure, all sampled fish were released alive to the production tank, with no mortality being recorded post sampling. All procedures employed are considered ethically accepted and safeguard welfare and best practices during fish handling.
Plastic bags containing samples of skin mucus from fish exposed to anesthesia (ANE) and control fish that were not exposed to anesthesia (CTR) were sealed and immediately transported to the laboratory using a refrigerated polystyrene box. Mucus samples (500 mg each) were collected from the mucus released by the sampled fish that accumulated in the sterilized plastic bags. The mucus was carefully retrieved using a micropipette and transferred into microcentrifuge tubes containing 1 mL of PBS (Phosphate-Saline Solution at pH 7.4) [22]. Samples were centrifuged at 16,000× g at 4 °C for 16 min to pellet microbial biomass. After decanting the supernatant, microbial biomass pellets were stored immediately at −20 °C until DNA extraction. Total community DNA (TC) was extracted from skin mucus samples of fish without anesthesia (10 replicates) and from skin mucus samples of fish exposed to anesthesia (10 replicates) using the FastDNA® SPIN soil Kit (MPbiomedicals, Solon, OH, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.3. Water Sampling and DNA Extraction
Water samples (five replicates) were also collected from two sampling compartments: (1) the supply pipeline of inflowing water (collecting water from the coastal lagoon) (Sup) and (2) the biofilter tank (Bio). Ammonium (NH3–N), nitrites (NO2− N), nitrates (N NO3−), and phosphates (PO4–P) were determined following the 8507, 8016, and 8155 methods described in the Hach Spectrophotometer DR 2800 (Hach, Loveland, CO, USA) standard analytical procedures and according to EPA Method 300.1 and 351.2. Conventional physical-chemical parameters such as, temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), oxi-redox potential, and salinity were recorded daily at approximately 11 a.m. using specific probes (Hanna HI8424 and HI9147, Hanna Instruments—Woonsocket, RI, USA), which were calibrated regularly following the manufacturer’s instructions.
For bacterial community analysis, water samples were filtered (250 mL) through 0.2 µm pore polycarbonate membranes (Poretics, Livermore, CA, USA) and total community (TC) DNA extraction was performed directly on the filter using an E.Z.N.A Soil DNA Extraction kit (Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.4. Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis
The V4 hypervariable region of the 16S rRNA gene amplicons were amplified using PCR primers 515F (5′-GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVHHHTWTCTAAT-3′) [23] with a barcode on the forward primer [24].
A 30 cycle PCR assay using the HotStarTaq Plus Master Mix Kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA) was performed under the following conditions: 94 °C for 3 min, followed by 30 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 53 °C for 40 s and 72 °C for 1 min, and a final elongation step at 72 °C for 5 min. After amplification, PCR products were checked in 2% agarose gel to determine the success of amplification and the relative intensity of bands.
Multiple samples were pooled together in equal proportions based on their molecular weight and DNA concentrations, which were quantified using a Qubit fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Pooled samples were purified using calibrated Ampure XP beads AMPure XP beads (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA), with pooled samples and purified PCR product being used to prepare an Illumina DNA library. Sequencing was performed at MR DNA (www.mrdnalab.com, Shallowater, TX, USA) using Illumina MiSeq (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Sequence data were processed using MR DNA analysis pipeline (MR DNA, Shallowater, TX, USA). Briefly, sequences were joined, depleted of barcodes and then sequences < 150 bp or with ambiguous base calls were removed. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were generated after denoising sequences and filtering chimeras. OTUs were defined by clustering at 3% divergence (97% similarity) and final OTUs were taxonomically classified using BLASTn v2.10.1 against a curated database derived from the Ribosomal Database Project (RDPII) [25] and NCBI (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, accessed on 5 July 2020); see Supplementary Table S1 for the complete OTU dataset. The reference database was curated by integrating high-quality 16S rRNA gene sequences from both the NCBI nucleotide database and the RDP. NCBI-derived sequences were further filtered for quality and trimmed to match the target amplicon region, ensuring consistency and accuracy in taxonomic classification via BLASTn.
2.5. Data Analyses
An OTU table containing the raw abundance of all operational taxonomic units (OTUs) of skin mucus samples with anesthesia (ANE) and without anesthesia (CTR) was imported to R. Singletons were removed from the analysis to minimize possible problems with sequencing errors associated with Illumina. The table was log10(x + 1) transformed and a distance matrix was constructed with the Bray Curtis similarity coefficient using the vegdist() function in the vegan package in R (version 2.11.1; http://www.r-project.org/).
Beta diversity analysis was calculated based on Bray Curtis similarity distances and visualised using principal coordinates analysis (PCO) with the cmdscale() function in R.
Alpha bacterial diversity was assessed by calculating the OTUs recorded, Chao1 index, and Pielou’s evenness index. Both indexes were calculated with the diversity() function in the vegan package in R. Differences in microbial alpha diversity were assessed using the Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney after rejecting normality using the Shapiro’s test and homogeneity of variance using the Bartlett’s test. Variation in microbial beta diversity and taxa composition were assessed using PRIMER v6 with the PERMANOVA+ add-on software.
To determine the distribution of OTUs in salmon skin mucus samples of fish exposed and not exposed to anesthesia, a Venn diagram was assembled using the venn() function in the gplots package in R. OTUs with more than 50,000 sequence reads were selected and used to assess the most dominant taxonomic groups.
Similarity percentage analysis (SIMPER) was used to reveal the percentage contributions of each OTU to the average dissimilarity between salmon skin mucus samples with and without anesthesia. SIMPER was constructed based on Bray–Curtis distance metrics using PRIMER v6.
To assess the Atlantic salmon core microbiome, we used the skin mucus samples collected from fish that were not exposed to anesthesia, which we considered as our control group. This choice aimed to prevent any potential shifts in the natural bacterial composition of the skin mucus caused by the anesthetic bath. Therefore, whenever we mention skin mucus samples without specifying exposure to anesthesia, we are always referring to samples obtained from fish not exposed to the anesthetic bath.
The microbiome of salmon skin mucus samples (without anesthesia) was compared with the water samples collected from the RAS. Data were assembled into an OTU table and uploaded to R. Variation in OTU composition was visualized using principal coordinates analysis (PCO) following the same method mentioned above. Differences in the bacterial composition of salmon skin mucus associated bacteria and water samples were tested using PERMANOVA. Alpha and beta diversity analysis were assessed using the same methods described above. To investigate the most dominant taxonomic groups, only OTUs with more than 20,000 sequence reads were used. Variation in the relative abundance of the most abundant bacterial OTUs was assessed using bar plot graphs and generated with the barplot2() function in the R.
The core microbiome of salmon skin mucus was assessed using skin mucus samples without anesthesia by selecting the OTUs that were present simultaneously in all individuals.
To assess the presence of potential pathogenic species, OTUs assigned to genera known to be pathogens of Atlantic salmon [26] were selected and investigated. A BLAST search (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) was used to obtain the closest relatives of selected OTUs (pathogens and abundant taxa).
All DNA sequences generated in this study were submitted to the NCBI SRA: Accession number PRJNA1102691.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Anesthesia in the Skin Mucus Microbiome of Atlantic salmon
3.1.1. Diversity and Community Structure of Bacterial Composition
After quality filtering, 2,831,388 sequence reads were detected and assigned to 1962 OTUs. Fish skin mucus samples of specimens exposed to anesthesia displayed 949,138 reads, while those from fish that were not exposed to anesthesia presented 1,882,250 reads. There was a significant variation in the number of reads between skin mucus samples originating from fish exposed (ANE) or non-exposed to anesthesia (CTR) (PERMANOVA: Pseudo-F = 9.458, p = 0.007). The number of OTUs varied from 1581 OTUs in skin mucus samples from fish with anesthesia and 1690 OTUs in fish without anesthesia (Table S1).
Shared and unique OTUs between skin mucus samples of both treatments can be observed in the Venn diagram (Figure 1). Skin mucus samples without anesthesia displayed the highest number of unique OTUs, 381 OTUs, while mucus samples with anesthesia displayed the lowest number, only 272 OTUs. Concerning shared OTUs, skin mucus samples of Atlantic salmon shared a total of 1309 OTUs.
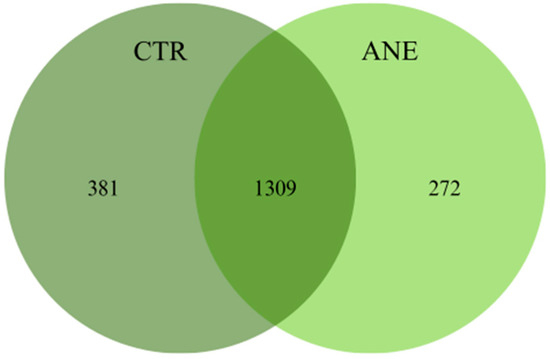
Figure 1.
Venn diagram showing the number of bacterial OTUs shared between salmon skin mucus with (ANE) and without anesthesia (CTR).
In terms of bacterial community diversity, our results revealed that richness (Observed OTUs) and diversity (Chao1) were lower in skin mucus samples from fish with anesthesia. Bacterial communities in skin mucus samples of fish with anesthesia were more even (Figure 2). Significant differences were found in Chao1 index (Wilcoxon: p = 0.019) and Pielou’s evenness (Wilcoxon: p = 0.004) (Figure 2). The observed reduction in richness (Chao1), alongside the increase in evennessevenness, in salmon skin mucus samples from fish exposed to anesthesia suggests that additional taxa were present, but their relative abundances were unevenly distributed. These shifts in evenness could be attributed to stress-induced microbial shifts, where certain taxa proliferate while others decline, or even disappear from the community, as a response to exposure to anesthesia. The PCO ordination analysis showed a pronounced separation between bacterial communities from skin mucus samples from fish with anesthesia and those without anesthesia (Figure S2). Significant dissimilarities were also found in the community structure (beta diversity) between salmon skin mucus samples from fish with (ANE) or without anesthesia (CTR) (PERMANOVA: Pseudo-F = 1.847, p = 0.036). These results suggested that the use of anesthesia somehow disturbs bacterial communities associated with salmon skin mucus.
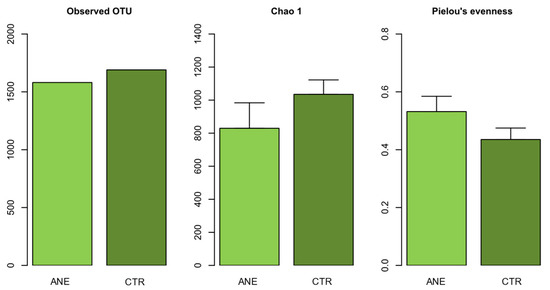
Figure 2.
Bacterial α-diversity (Observed OTUs, Chao1 index and Pielou’s evenness index) in the salmon skin samples with (ANE) and without (CTR).
3.1.2. Taxonomic Profiling of Bacterial Composition
The overall taxonomic analyses grouped bacterial sequences into twenty phyla, forty classes, and ninety-six orders.
Figure 3 highlights the relative abundance of the most dominant bacterial groups (≥50,000 reads) found in fish skin mucus samples. Proteobacteria was the most abundant phylum, presenting a relative abundance ranging between 86 and 91%. Phylum Proteobacteria consists of a diverse group of bacteria recovered from different hosts and environments. This phylum is also the most common one reported in fish skin mucus microbiome [27,28,29].
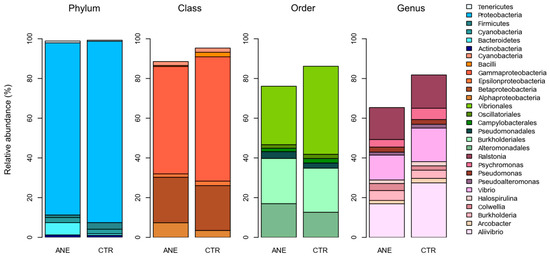
Figure 3.
Relative abundance of the most dominant bacterial groups (6 phyla, 6 classes, 6 orders, and 10 genera) identified in the salmon skin mucus samples with (ANE) and without anesthesia (CTR).
The most dominant classes detected in skin mucus communities from fish with or without anesthesia, respectively, were Gammaproteobacteria (ranging between 54.1 and 62.6%) and Betaproteobacteria (ranging between 22.9 and 22.6%). Concerning orders, the most dominant ones in skin mucus communities from fish with or without anesthesia, respectively, were Vibrionales (ranging between 29.4 and 44.3%), Burkholderiales (ranging between 22.8 and 22.2%), and Alteromonadales (raging between 17.0 and 12.7%). Order Burkholderiales had already been previously reported in the skin microbiome of other fish species [30,31]. At genus level, skin mucus communities from fish with or without anesthesia, respectively, were mainly composed by Ralstonia (ranging between 16.1 and 16.7%), Vibrio (ranging between 12.5 and 16.9%), and Aliivibrio (ranging between 16.9 and 27.5%); it is worth highlighting that Aliivibrio was the most abundant bacterial genus recorded.
Overall, while salmon skin mucus with and without anesthesia shared common genera, the structure of bacterial communities from skin mucus of fish exposed to anesthesia (ANE) was significantly different from that of conspecifics that were not anesthetized (CTR) (PERMANOVA: Pseudo-F = 6.647, p = 0.018). The structure of bacterial communities is known to shift as a response to a given stimulus [32,33], thus suggesting that the microbiome of salmon skin mucus can be affected by benzocaine when an anesthetic bath is applied to a fish being handled.
An in-depth bacterial composition analysis of the skin mucus samples detected six dominant OTUs (≥50,000 reads): OTUs 1 (Vibrio), 3097 (Aliivibrio), 3110 (Vibrio), 2 (Ralstonia), 4 (Burkholderia), and 427 (Psychromonas). Significant differences were detected in the relative abundance of the majority of the most abundant OTUs, except for OTUs 4 and 3110 (Table S2). OTU 3097 was the most abundant OTU with 721,685 sequence reads. According to BLAST this OTU was related to Aliivibrio wodanis [GenBank accession number (acc.) JQ361731] isolated from Oncorhynchus mykiss (Table S3). This Aliivibrio species is considered as a potential pathogen because it is often associated with “winter ulcer” disease in Atlantic salmon [34,35]. However, Klakegg et al. (2020) reported the use of Aliivibrio strains as potential probiotic agents to improve the health of farmed fish strains [36].
OTU 2, assigned to the genus Ralstonia, was also highly abundant, with a total of 308,514 sequence reads, accounting for 90,921 reads in salmon skin mucus with anesthesia and 217,593 reads in salmon skin mucus without anesthesia. Members of this genus are commonly associated with fish and have been reported as part of the healthy microbiome of Atlantic salmon [37,38]. It has been suggested that these organisms may exhibit antimicrobial activity or contribute to the biosynthesis of bioactive compounds, which could confer beneficial effects on the host [39].
OTU 427, assigned to the genus Psychromonas, exhibited a similar trend to OTU 2, with higher abundances in salmon skin mucus samples without anesthesia. Although the ecological role of Psychromonas in the marine environment remains not fully understood, it has been reported as a prevalent bacterial genus in the microbiomes of various fish species [40,41].
In order to assess the contribution of each OTU to the dissimilarities recorded in the skin mucus of fish with or without anesthesia, similarity percentages (SIMPER) were determined, with these highlighting five OTUs: 1, 2, 427, 3097, and 3110 (Table 1). OTU 3097 was the OTU that contributed the most (23.7%) for the differences recorded. This OTU was the most dominant one detected in our data and according to BLAST, was related to Vibrio wodanis. SIMPER also revealed that OTUs 3110 and 2 contributed with 10.54% and 9.64%, respectively, to the average dissimilarity between skin mucus samples of fish with and without anesthesia. These OTUs were identified as Vibrio and Ralstonia, respectively, and were also dominant OTUs. Together, OTUs 3097, 3110, and 2 contributed with nearly 44% of all differences recorded between the bacterial communities present in salmon skin mucus samples.

Table 1.
Similarity percentage analysis (SIMPER) identifying which OTU contribute to the differences detected in the skin microbiome of samples with (ANE) and without anesthesia (CTR).
It is important to acknowledge that our study design did not include temporal resampling to evaluate the persistence or reversibility of the observed microbiome shifts following anesthesia. As such, it remains unclear whether the changes in taxonomic composition and diversity represent transient fluctuations or longer-term dysbiosis. Despite these limitations, our findings contribute novel insights into a relatively unexplored area. To the authors best knowledge, to date, there is no information on the potential effect of benzocaine anesthetic baths on fish skin mucus associated microbial communities. However, there are several studies addressing the role of local anesthetics as antimicrobial agents, but always framed under a human health perspective and mostly focusing in lidocaine [42]. Morrow and Berry (1988) studied the antimicrobial properties of benzocaine as a liquid topical anesthetic used in dentistry [43]. In this study, the authors assessed the antimicrobial activity of benzocaine (20%) against several microorganisms commonly found within the oral cavity for 1 min and 2 h [43]. A significant reduction was observed in the growth of all the species investigated when compared with a negative control, for the two-time frames investigated. The results reported by Morrow and Berry (1988) are in line with our data, suggesting that the use of an anesthetic bath does change bacterial communities, with our study showcasing those changes associated with the skin mucus of Atlantic salmon [43].
In fish, skin mucus represents the first barrier against pathogenic organisms, preventing the development of diseases [44]. Fish skin microbiome is colonized by different bacterial species, with their capacity to maintain a healthy balance between commensal and opportunistic bacteria being paramount to ensure synergistic relationships and overall fish health [45]. Nonetheless, it is well documented that aquaculture practices (such as netting, grading, sorting, and transport) can affect the balance of fish skin microbial communities [28]. Therefore, if one highlights that some of these practices commonly require the use of anesthesia, it is important to carefully evaluate the potential effects of using an anesthetic bath on the fish skin microbiome, in order to avoid disturbances on their bacterial communities beyond those already promoted by netting, grading, sorting, or transporting fish. It is important to determine beforehand if the use of anesthesia can induce significant microbial unbalances, to the hypothetical point of even causing dysbiosis in the skin microbiome of fish and/or allow the proliferation of opportunistic bacteria.
Moreover, it is important to mention that most studies assessing the skin or gut microbiome of several fish species, employ anesthesia prior to sampling and, in many cases, fish are even euthanized using an anaesthetic overdose [27,28,46,47,48]. Thus, in light of our findings, previous studies should now be interpreted with further caution, as significant shifts in the microbiome reported for fish in these studies may have been involuntarily shaped through anesthesia.
3.2. Comparison of Skin Mucus Microbiome of Atlantic salmon and Rearing Water
3.2.1. Overall Assessment of Bacterial Composition
Physical and chemical parameters recorded during sampling are summarized in Table S4. Temperature, salinity, pH, and nitrites were similar in both water compartments. Salinity remained close to 35, and pH varied between 7.6 and 8.2. On the other hand, and as expected, ammonia, nitrate, and phosphate concentrations were lower in samples from inflowing water being pumped from the coastal lagoon.
The PCO ordination analysis (Figure 4) shows a clear separation of two main groups in the ordination representing the water samples and the salmon skin mucus samples. Here, and for all subsequent analyses, skin mucus samples not exposed to anesthesia (CTR) will be used to characterize the bacterial communities associated with Atlantic salmon skin mucus and to compare it with that of surrounding water. The primary axis of variation in the PCO in Figure 4 revealed that bacterial communities present in the water samples and salmon skin mucus samples are clearly different.
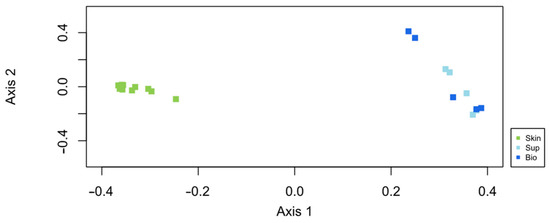
Figure 4.
Ordination showing the first two axes of PCO analysis of the bacterial community present: in the salmon skin microbiome (Skin) and in two compartments of the water samples (Sup—Supply water, Bio—Biofilter water).
Statistically, highly significant differences (PERMANOVA: Pseudo-F = 13.118, p < 0.001) were detected in the bacterial composition among groups (water and skin mucus samples). Although we have found differences in some physical and chemical parameters between the water compartments, our results did not reveal distinct microbial communities. In line with these results, the PCO did not show pronounced separation between bacterial communities from different water compartments (biofilter water samples and supply water samples), and statistically no significant differences were observed among the water samples, from a compositional perspective (PERMANOVA: t = 1.209, p = 0.188). As such, subsequent statistical analysis performed did not consider the two water compartments individually (5 replicates of water supply + 5 replicates of biofilter water), using instead the 10 water samples as replicates.
Approximately 2,213,372 sequences were recorded and clustered into 1843 bacterial OTUs (after quality filtering) (Table S5). A total of 1522 OTUs were detected in salmon skin mucus samples, while only 727 OTUs were detected in the water samples (Figure S3). Analysis of microbial alpha diversity (Figure S3) showed that the water samples presented a higher diversity when compared to salmon skin mucus samples. Statistically, there are significant differences in alpha diversity between salmon skin samples and the water samples (Chao1 index: Wilcoxon: p < 0.001; Pielou’s evenness index: Wilcoxon: p = 0.010). Previous studies have also reported highest microbial alfa diversity in the water samples when compared salmon skin mucus and the gut [49].
Although the water samples showed lower microbial richness, OTU abundances were more evenly distributed. The low richness in the water samples is in fact related to the low rare OTUs (OTUs with only 1 or 2 reads) recorded on these samples. On the other hand, beta diversity analysis, calculated based on the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity index and visualized through the PCO ordination analysis (Figure 4), revealed a clear separation of two main groups in the ordination, representing the water samples and the salmon skin mucus samples. As aforementioned, significant differences were detected between the salmon skin mucus microbiome and that of the water samples.
3.2.2. Taxonomic Bacterial Composition
The overall taxonomic analyses grouped bacterial sequences into 35 phyla, 84 classes, and 171 orders. Figure 5 highlights the relative abundance of the most dominant bacterial groups. Proteobacteria was the most abundant phylum (ranging between 58.1 and 89.2%), followed by Actinobacteria (ranging between 1 and 12.7%), Firmicutes (ranging between 3.3 and 11.3%), and Bacteroidetes (ranging between 0.8 and 11.2%). Phylum Proteobacteria was the most dominant in salmon skin mucus samples, while phyla Actinobacteria, Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes were the most dominant in the water samples. A predominance of the phyla Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes has also been previously reported on the skin mucus microbiome of Atlantic salmon, in a study assessing the skin associated microbiota during the transition of individuals of this species from freshwater to seawater [27].
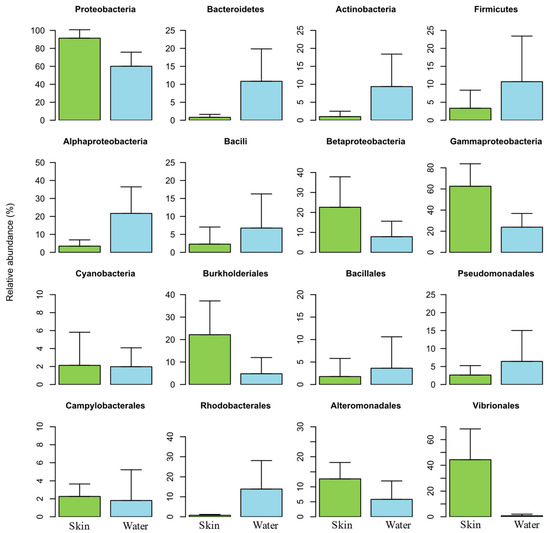
Figure 5.
Relative abundance of the most dominant bacterial groups (4 phyla, 5 classes, and 7 orders) in the salmon skin microbiome (Skin) and in the water samples (Water).
The majority of OTUs classified within the class Gammaproteobacteria were classified into the orders Vibrionales, Alteromonadales, and Pseudomonadales (Figure 5). While the orders Vibrionales e Alteromonadales were dominant in salmon skin mucus samples, the order Pseudomonadales was dominant in the water samples. The high abundances of this order in the water samples are related to the family Moraxellaceae and specifically the genus Acinetobacter. Members of this genus had been already identified as emerging fish pathogens [50].
3.2.3. Composition Analysis of Dominant OTUs in Salmon Skin Mucus
The dominance analysis revealed nine OTUs (≥20,000 sequence reads) in the salmon skin mucus microbiome: OTU 3097 (Aliivibrio wodanis), OTU 3110 (Vibrio), OTU 2 (Ralstonia solanacearum), OTU 427 (Psychromonas), OTU 1 (Vibrio), OTU 4 (Burkholderia), OTU 7 (Pseudoalteromonas), OTU 14 (Paenibacillus), and OTU 8 (Pseudomonas) (Figure S4 and Table S3).
The genera Vibrio, Ralstonia, Burkholderia, Pseudoalteromonas, Psychromonas, and Pseudomonas were previously reported as the most abundant groups in the skin associated microbiome of Atlantic salmon [27,28,51].
Aliivibrio wodanis, the most abundant OTU, is frequently isolated (concurrently with Moritella viscosa) from farmed Atlantic salmon with winter-ulcer disease [35,52]. However, Karlsen et al. (2014) observed that A. wodanis alone can also cause infection in Atlantic salmon, although its colonization requires a predisposed damage in the host area of colonization, a feature which suggests a low virulence [34]. As already referenced, Klakegg et al. (2020) described A. wodanis as a potential probiotic, namely against M. viscosa [36]. The authors revealed an increase in growth and resistance of cultured lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) against bacterial diseases after they were exposed to probiotic A. wodanis. Likewise, members of the genera Paenibacillus and Pseudoalteromonas have also shown potential probiotic properties against several aquaculture bacterial pathogens [53,54]. According to Aranda et al. (2012), Pseudoalteromonas sp. strains can be used as Vibrio-biocontrol agents, as they are able to produce a putatively novel class of bacteriostatic compounds [53].
3.2.4. Core Microbiome Composition of Atlantic salmon
Of the 1522 OTUs found in salmon skin mucus samples, only 143 were common to all individuals sampled, thus forming the core microbiome (Table S6). The core skin mucus microbiome was formed by 14 classes, 27 orders, and 28 families that enclosed a total of 65 different bacterial genera. The core skin mucus microbiome of Atlantic salmon is predominantly composed by proteobacterial OTUs. Proteobacteria was the most representative phylum in the core microbiome of Atlantic salmon, displaying a relative abundance of 95%. Gammaproteobacteria and Betaproteobacteria were the most dominant classes featuring a relative abundance of 66% and 24%, respectively. Proteobacteria has been reported as the most predominant bacterial phylum in the skin-associated communities of the core microbiome of Atlantic salmon, highlighting their key role in the microbiome of this fish species [49,55].
Although Vibrionales (47%) was the most dominant order at the core of salmon skin mucus bacterial composition, orders Burkholderiales (24%) and Alteromonodales (13%) also showed high relative abundances. At family level, Vibrionaceae (47%), Burkholderiaceae (23%), and Psychromonadaceae (6%) were the ones featuring higher relative abundances in the skin mucus of Atlantic salmon core microbiome. From the 66 genera identified in the core microbiome of Atlantic salmon skin mucus, the most abundant ones were Aliivibrio (28%), Vibrio (19%), Ralstonia (18%), Psychromonas (6%), and Burkholderia (4%). Genus Aliivibrio was established in 2007, with the reclassification of several Vibrio species [56]. Vibrio spp. are Gram-negative bacteria, that are ubiquitous in marine, estuarine, and freshwater environments. Both genera, Aliivibrio and Vibrio are considered pathogenic, as they are frequently associated with diseased animals. Several members of Vibrio and Aliivibrio (V. anguillarum, V. parahaemolyticus, V. vulnificus, Aliivibrio salmonicida) are responsible for Vibriosis, one of the most common bacterial diseases in aquaculture systems [57,58,59]. The high pathogenicity of these genera is related to its adhesive capacity to mucosal surfaces, which could explain the high abundance of these taxa in the skin mucus of Atlantic salmon [60,61]. Minniti et al. (2019), in a study assessing the skin–mucus proteome of farmed Atlantic salmon, also recorded genus Vibrio as the most abundant bacterial genera in this biological matrix [51]. Other authors have described genus Vibrio and Ralstonia as the most abundant in the skin mucus microbiome of Atlantic salmon [28,51], findings that are certainly aligned with the ones reported in the present study.
From the ten dominant OTUs found in the skin mucus microbiome of Atlantic salmon, nine were detected in the core microbiome. This finding points out the importance of identifying and understanding the most dominant taxa present on fish skin mucus microbiome, in order to allow the establishment of baseline information (in terms of microbiome composition and structure) that can later be helpful to monitoring the overall health of cultured fish.
Overall, our study recorded several similarities in the core skin mucus microbiome of Atlantic salmon with that reported in previous studies, although it is worth highlighting that despite Atlantic salmon being one of the most important aquaculture species worldwide, there still is a generalized lack of information concerning the skin mucus microbiome of this species.
3.2.5. Bacterial Community Profile of Rearing Water
Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes were the main dominating phyla in the water samples analyzed, although Firmicutes and Actinobacteria also presented high relative abundances (Figure 5). Salmon skin mucus and water samples had similar bacterial compositions at phylum-level, although these displayed different abundances.
Orders Pseudomonadales, Actinomycetales and Alteromonadales were the most abundant ones detected in the water samples (Figure S5).
As above mentioned, Acinetobacter was the most abundant genus in the water samples, displaying a relative abundance of 4.8%. Nonetheless, it is worth highlighting that genera Roseobacter and Streptococcus were also abundant in the water samples analyzed, with a relative abundance of 4.6% and 3%, respectively (Figure S5).
The dominance of genus Acinetobacter in the water samples is mostly explained by OTU 34, as this was the most abundant OTU found in the water samples processed, with 12,865 sequence reads. BLAST (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ results related this OTU to Acinetobacter junii [GenBank accession number (acc.) MT613873] isolated from a water surface in India. This bacterium was recorded as a nosocomial pathogen and can be found colonizing human and environmental samples [62]. Members of genus Acinetobacter had already been identified as emerging fish pathogens, with Malick et al. (2020) having identified Acinetobacter junii as the causative agent of a fish disease outbreak in India [50].
Genus Roseobacter belongs to the Roseobacter clade, one of the major marine bacterial groups, comprising up to 20% of all bacterioplankton communities in the ocean [63], thus it was not a surprise to find that this is also one of the main dominating bacteria detected in the bacterioplankton communities of several aquaculture systems [19,29]. Furthermore, previous studies suggest that the Roseobacter clade may play an important role against the development of fish pathogens in aquaculture systems [64,65]. In fact, Martins et al. (2018) suggested that the high abundance of members of the Roseobacter clade may play a role in suppressing the development of Vibrio lineages in aquaculture systems [66].
OTUs 63 and 169 were the most abundant OTUs in the water samples, being allocated to genus Streptococcus (8450 sequence reads) and having been identified as S. parasanguinis and S. thermophillus, respectively. Although genus Streptococcus is mostly associated with fish diseases [67], there are evidence that some species, such as S. thermophillus, may also be used as probiotic agent in aquaculture [68].
All of the most abundant genera of bacteria detected in the water samples were also detected in the skin mucus samples of Atlantic salmon, in line with previous reported by Minniti et al. (2017) [28]. Overall, while we have found some differences in the microbial composition between the samples of fish skin mucus and water that were analyzed in our study, our data suggest that culture water shapes the diversity and structure of Atlantic salmon skin mucus microbiome. Approximately 55% (406 OTUs) of the OTUs found in the water samples analyzed were also detected in the skin mucus of sampled fish. These results agree with previous studies that suggest that fish skin has specialized microbial communities that are influenced by surrounding water but are still able to feature distinct bacterial taxa [28,49].
3.2.6. Potential Pathogens Detected in the Skin Mucus Microbiome of Atlantic salmon and in Rearing Water
To understand the presence of potential pathogenic bacteria in the skin mucus microbiome of Atlantic salmon and surrounding water, the relative abundance of OTUs belonging to genera known to be potential fish pathogens was investigated. From the 16 potential pathogenic genera listed in the scientific literature [69], 11 were detected in our samples (Figure 6).
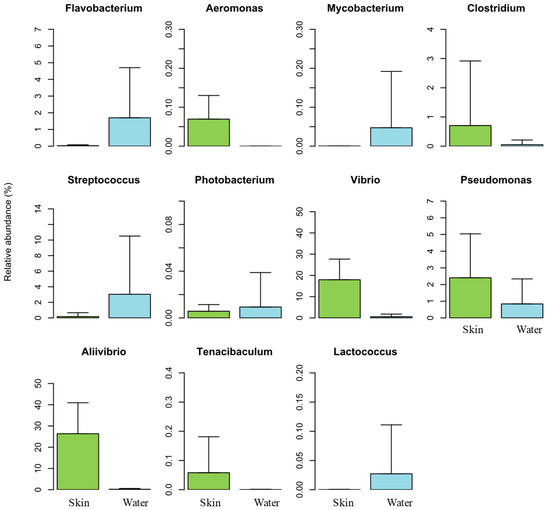
Figure 6.
Relative abundance of potential pathogenic genera detected in the salmon skin microbiome (Skin) and in the water samples (Water).
Aliivibrio and Vibrio were the most abundant potential pathogenic genera found in our samples, with a relative abundance of 26% and 17% (552,762 and 374,145 sequence reads) in fish skin mucus samples and only 0.2% and 0.5% (591 and 1660 sequence reads) in the water samples, respectively. As already mentioned, the most abundant OTU detected in our data was OTU 3097 (Aliivibrio wodanis) with 552,593 sequence reads. This OTU alone accounts for almost the total abundance of genus Aliivibrio in our work. Despite species within this genus being considered as potential pathogens, there are evidence that Aliivibrio strains, specifically A. wodanis, can also be used as probiotic agents in aquaculture [36]. Genera Aliivibrio and Vibrio were significantly more abundant in samples from salmon skin mucus than in those from culturing seawater, most likely because of their high adhesive ability to mucosal surfaces [60,61].
Genera Aliivibrio (26%), Vibrio (17%), Pseudomonas (2.4%), Clostridium (0.7%), and Aeromonas (0.07%) showed higher abundances in Atlantic salmon skin mucus samples, while Streptococcus (3%), Flavobacteria (1.7%), Mycobacterium (0.05%), Lactococcus (0.02%), and Photobacterium (0.009%) presented higher abundances in the water samples (Figure 6). Furthermore, genera Vibrio, Aliivibrio, Flavobacterium, Mycobacterium, Streptococcus, Photobacterium, and Lactococcus were significantly more abundant in Atlantic salmon skin mucus samples. These results suggest that this biological matrix in fish is an important reservoir for many of the potential bacterial pathogens surveyed in aquaculture, both in terms of abundance and pathogenic species diversity.
Genera Renibacterium, Nocardia, Aerococcus, Enterobacterium, and Edwardsiella, which are well known for their pathogenicity in aquaculture, were not detected in any of the samples surveyed in the present work.
Genus Aeromonas was the only one detected exclusively in salmon skin mucus samples (3 OTUs), although we did not detect A. salmonicida, one of the most important primary pathogens impacting salmonid fish [70]. Likewise, despite the high abundance of Vibrio and Aliivibrio recorded in our samples, the species Aliivibrio salmonicida (former Vibrio salmonicida) was not recorded. This bacterium is the causative agent of cold-water vibriosis that causes hemorrhagic septicemia and occurs mostly in farmed Atlantic salmon [71,72].
Apart from Aliivibrio and Vibrio, all the other potential pathogenic bacterial genera detected were present at a very low abundance. In fact, genera Photobacterium, Mycobacterium, Aeromonas, Tenacibaculum, Lactococcus, and Clostridium all together accounted for less than 1% of the total bacterial community detected both in fish skin mucus and seawater. Despite the presence of potential pathogenic bacterial genera, no diseased fish were registered during the study period.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, we assessed the influence of a benzocaine anesthetic bath on the skin mucus microbiome of cultured Atlantic salmon. While previous studies have reported the antimicrobial properties of anesthetic agents, to date this issue has been mostly addressed in the context of human health. Our results revealed that the use of benzocaine as an anesthetic bath impacts the skin mucus microbiome of Atlantic salmon. However, further investigation is certainly needed to better understand the mechanisms behind these shifts, whether the pre-anesthesia fish skin mucus microbiome is re-established post-anesthesia, and what the timeframe for such recovery might be. It is important to note that this study did not include temporal resampling to evaluate the duration or persistence of microbiome changes following anesthesia. Therefore, future research should explore these temporal dynamics and assess the effects of different anesthetic agents and exposure conditions. Moreover, it is also important to determine if similar results to the ones reported in the present study are also observed under different experimental conditions (e.g., when employing different anesthetic agents, using different times of exposure, multiple and/or consecutive exposures, life stages, and fish species). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study reporting the effect of an anesthetic bath on the skin microbiome of farmed Atlantic salmon, paving the way for a new research line on fish health and welfare.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ani15111566/s1, Figure S1: RAS unit description. (a) stocking tank; (b) recirculation water-pumps; (c) protein skimmer; (d) fluidized biofilter; (e) one out of two UV sterilization filter tank; Figure S2: Ordination diagram showing the first two axes of PCO analysis of the bacterial community present in the salmon skin mucus samples (ANE—skin mucus with anesthesia, CTR—skin mucus without anesthesia); Figure S3: Bacterial species α-diversity measures (Observed OTUs, Chao1 index and Pielou’s evenness index) in the salmon skin samples (Skin) and in the water samples (water); Figure S4: Relative abundance of dominant OTUs (≥20,000 sequence reads) in the salmon skin microbiome (Skin); Figure S5: Relative abundance of the four most dominant orders and genera detected in water samples. Skin—salmon skin microbiome; Water—water samples; Table S1: OTU table with taxonomic classification (AN—salmon skin samples with anesthesia; NO—salmon skin samples without) anesthesia); Table S2: PERMANOVA main test (F value and P value) between salmon skin samples with and without anesthesia, for each OTU; Table S3: Taxonomic affiliation of the most abundant OTUs in salmon skin mucus and water samples (≥20,000 sequences) including OTU-numbers (OTU); number of sequence reads; taxonomic assignment; their closest relatives (using Blast); with respective accession number (Acession); sequence identity (Sq ident); and their source; Table S4: Values of temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), salinity, oxi-redution potential, ammonia, nitrites, nitrates and phosphates in the aquaculture compartments. Sup—Supply water samples; Bio—Biofilter water sample; Table S5: OTU table with taxonomic classification (Skin—salmon skin mucus; Water—water samples); Table S6: OTUs forming the skin core microbiome of Atlantic salmon.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.M., T.P. and R.C.; methodology, P.M, T.P. and N.R.; formal analysis, P.M.; writing—original draft preparation, P.M. and R.C.; writing—review and editing, T.P. and N.R.; funding acquisition, R.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by project CITAQUA, “Desenvolvimento do Projeto de Reforço do Polo de Aveiro (H4)”, framed within Measure 10 of Investment TC-C10-i01—Hub Azul—Rede de Infraestruturas para a Economia Azul, financed by the Recovery and Resilience Plan (RRP) and supported by Fundo Azul of the Portuguese Government. It was also partially supported by “Projecto Salmão”, a research project promoted by Seaculture—Aquicultura, S.A., a company from the Jerónimo Martins Agro-Alimentar Group, under the coordination of Pedro Encarnação. We acknowledge the financial support to UID Centro de Estudos do Ambiente e Mar (CESAM) + LA/P/0094/2020 by FCT/MEC through national funds.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Raw sequence files supporting the results of this article are available in NCBI SRA: Accession number PRJNA1102691.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Nuno Dolgner and Eduardo Freitas for their technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Esteban, M.Á. An Overview of the Immunological Defenses in Fish Skin. ISRN Immunol. 2012, 2012, 853470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamed, S.; Guardiola, F.A.; Mars, M.; Esteban, M.Á. Pathogen Bacteria Adhesion to Skin Mucus of Fishes. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiralongo, F.; Messina, G.; Lombardo, B.M.; Longhitano, L.; Volti, G.L.; Tibullo, D. Skin Mucus of Marine Fish as a Source for the Development of Antimicrobial Agents. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 541853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Das, S.K.; Samal, J.; Thatoi, H.N. Epidermal Mucus, a Major Determinant in Fish Health: A Review. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 19, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.-C.; Chen, L.-H.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Liou, C.-Y.; Chen, H.-C.; Lu, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-L. Teleost Skin Microbiome: An Intimate Interplay between the Environment and the Host Immunity. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 139, 108869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruijn, I.; Liu, Y.; Wiegertjes, G.F.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Exploring Fish Microbial Communities to Mitigate Emerging Diseases in Aquaculture. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fix161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, R.; Severino, R.; Silva, S.M. Signatures of Dysbiosis in Fish Microbiomes in the Context of Aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 16, 706–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Boutin, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Derome, N. Teleost Microbiomes: The State of the Art in Their Characterization, Manipulation and Importance in Aquaculture and Fisheries. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorgen-Ritchie, M.; Clarkson, M.; Chalmers, L.; Taylor, J.F.; Migaud, H.; Martin, S.A.M. Temporal Changes in Skin and Gill Microbiomes of Atlantic Salmon in a Recirculating Aquaculture System—Why Do They Matter? Aquaculture 2022, 558, 738352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, M.; Soares, F.; Aragão, C.; Almeida, A.C.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Ribeiro, L. Efficiency of 2-Phenoxyethanol and Clove Oil for Reducing Handling Stress in Reared Meagre, Argyrosomus regius (Pisces: Sciaenidae). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2016, 47, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowker, J.D.; Trushenski, J.T.; Bowman, M. Efficacy of Eugenol to Lightly Sedate Freshwater Salmonids for an Extended Time Period. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2019, 81, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.-W.; Ding, H.-T.; Dong, X.-J.; Zhang, J.-J.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Chen, X.-N.; Cheng, H.-L.; Ding, Z.-J.; Xu, J.-H. Effects of Tricaine Methanesulfonate (MS-222) on Sedation and Responses of Yellow Catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) Subjected to Simulated Transportation Stress. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadoul, B.; Geffroy, B. Measuring Cortisol, the Major Stress Hormone in Fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, N.; Le, Q.; Hu, J.; Yang, Y.; Kuang, S.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Y.; Gu, W.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Influence of Anaesthetic Stress on the Immune System of Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus) under the Process of Treatment and Low Concentration Transport by MS-222 and Eugenol. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 3138–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, G.K.; Heath, D.D. Comparison of Tricaine Methanesulphonate (MS222) and Clove Oil Anaesthesia Effects on the Physiology of Juvenile Chinook Salmon Oncorhynchus tshawytscha (Walbaum). Aquac. Res. 2000, 31, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahl, I.H.; Samuelsen, O.; Kiessling, A. Anaesthesia of Farmed Fish: Implications for Welfare. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 38, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022: Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- Føre, H.M.; Thorvaldsen, T.; Osmundsen, T.C.; Asche, F.; Tveterås, R.; Fagertun, J.T.; Bjelland, H. V Technological Innovations Promoting Sustainable Salmon (Salmo salar) Aquaculture in Norway. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Pires, A.C.C.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Quintino, V.; Calado, R.; Gomes, N.C.M. Molecular Analysis of Bacterial Communities and Detection of Potential Pathogens in a Recirculating Aquaculture System for Scophthalmus maximus and Solea senegalensis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, D.; Canada, P.; Marques Silva, S.; Ribeiro, N.; Diniz, P.; Xavier, R. Disruption of the Skin, Gill, and Gut Mucosae Microbiome of Gilthead Seabream Fingerlings after Bacterial Infection and Antibiotic Treatment. FEMS Microbes 2023, 4, xtad011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.H.; Wang, L. Current Status of Genome Sequencing and Its Applications in Aquaculture. Aquaculture 2017, 468, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, T.; Marcelino, J.; Ricardo, F.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Calado, R. Bacterial Communities 16S rDNA Fingerprinting as a Potential Tracing Tool for Cultured Seabass Dicentrarchus labrax. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global Patterns of 16S RRNA Diversity at a Depth of Millions of Sequences per Sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. S1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakakhel, M.A.; Bibi, N.; Mahboub, H.H.; Wu, F.; Sajjad, W.; Din, S.Z.U.; Hefny, A.A.; Wang, W. Influence of Biosynthesized Nanoparticles Exposure on Mortality, Residual Deposition, and Intestinal Bacterial Dysbiosis in Cyprinus carpio. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 263, 109473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cole, J.R. Updated RDP Taxonomy and RDP Classifier for More Accurate Taxonomic Classification. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2024, 13, e0106323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, C.; Gismervik, S.; Iversen, M.; Kolarevic, J.; Nilsson, J.; Stien, L.; Turnbull, J. Welfare Indicators for Farmed Atlantic Salmon: Tools for Assessing Fish Welfare; Nofima: Tromsø, Norway, 2018; ISBN 978-82-8296-556-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lokesh, J.; Kiron, V. Transition from Freshwater to Seawater Reshapes the Skin-Associated Microbiota of Atlantic Salmon. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Hagen, L.H.; Porcellato, D.; Jørgensen, S.M.; Pope, P.B.; Vaaje-Kolstad, G. The Skin-Mucus Microbial Community of Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rud, I.; Kolarevic, J.; Holan, A.B.; Berget, I.; Calabrese, S.; Terjesen, B.F. Deep-Sequencing of the Bacterial Microbiota in Commercial-Scale Recirculating and Semi-Closed Aquaculture Systems for Atlantic Salmon Post-Smolt Production. Aquac. Eng. 2017, 78, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, P.J.; Bowen, J.L.; Tlusty, M.F. The Skin Microbiome of Cow-Nose Rays (Rhinoptera bonasus) in an Aquarium Touch-Tank Exhibit. Zoo Biol. 2017, 36, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowrey, L.; Woodhams, D.C.; Tacchi, L.; Salinas, I. Topographical Mapping of the Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Microbiome Reveals a Diverse Bacterial Community with Antifungal Properties in the Skin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6915–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemer, B.; Gulati, S.; Bergna, A.; Rändler, M.; Cernava, T.; Witzel, K.; Berg, G.; Grosch, R. Biotic and Abiotic Stress Factors Induce Microbiome Shifts and Enrichment of Distinct Beneficial Bacteria in Tomato Roots. Phytobiomes J. 2022, 6, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M.A.; Leff, L.G. Nutrients and Other Abiotic Factors Affecting Bacterial Communities in an Ohio River (USA). Microb. Ecol. 2007, 54, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, C.; Vanberg, C.; Mikkelsen, H.; Sørum, H. Co-Infection of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar), by Moritella viscosa and Aliivibrio wodanis, Development of Disease and Host Colonization. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunder, T.; Sørum, H.; Holstad, G.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Mowinckel, P.; Brenner, D.J. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Vibrio viscosus Sp. Nov. and Vibrio wodanis sp. Nov. Isolated from Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) with “Winter Ulcer”. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 427–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klakegg, Ø.; Myhren, S.; Juell, R.A.; Aase, M.; Salonius, K.; Sørum, H. Improved Health and Better Survival of Farmed Lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus) after a Probiotic Bath with Two Probiotic Strains of Aliivibrio. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, M.; Coca, Y.; Suárez, R.; de Oca, M.M.; Bledsoe, J.W.; Burbulis, I.; Caro, D.; Pontigo, J.P.; Maracaja-Coutinho, V.; Arias-Carrasco, R.; et al. Salmo Salar Skin and Gill Microbiome during Piscirickettsia salmonis Infection. Animals 2023, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viver, T.; Ruiz, A.; Bertomeu, E.; Martorell-Barceló, M.; Urdiain, M.; Grau, A.; Signaroli, M.; Barcelo-Serra, M.; Aspillaga, E.; Pons, A.; et al. Food Determines Ephemerous and Non-Stable Gut Microbiome Communities in Juvenile Wild and Farmed Mediterranean Fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 889, 164080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerezo-Ortega, I.M.; Di Zeo-Sánchez, D.E.; García-Márquez, J.; Ruiz-Jarabo, I.; Sáez-Casado, M.I.; Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Tapia-Paniagua, S.T. Microbiota Composition and Intestinal Integrity Remain Unaltered after the Inclusion of Hydrolysed Nannochloropsis gaditana in Sparus aurata Diet. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, C.; Bolton-Warberg, M.; Hinchcliffe, J.; Davies, R.; Whelan, S.; Wan, A.H.L.; Fitzgerald, R.D.; Davies, S.J.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Smith, C.J. Temporal Changes in the Gut Microbiota in Farmed Atlantic Cod (Gadus Morhua) Outweigh the Response to Diet Supplementation with Macroalgae. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrihan, S.; Itay, P.; Kroin, Y.; Davidovich, N.; Wosnick, N.; Tchernov, D.; Koh, X.P.; Lau, S.C.K.; Morick, D. Monitoring Fish Bacterial Pathogens of Wild Fish Species From the South China Sea by Applying Next-Generation Sequencing on Gill Tissue. J. Fish. Dis. 2025, 48, e14050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B.M.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S. A Review and New Insights to Antimicrobial Action of Local Anesthetics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect Dis. 2019, 38, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, M.E.; Berry, C.W. Antimicrobial Properties of Topical Anesthetic Liquids Containing Lidocaine or Benzocaine. Anesth. Prog. 1988, 35, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shephard, K.L. Functions for Fish Mucus. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1994, 4, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.; Sunyer, J.O.; Salinas, I. The Mucosal Immune System of Fish: The Evolution of Tolerating Commensals While Fighting Pathogens. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehler, C.E.; Secombes, C.J.; Martin, S.A.M. Environmental and Physiological Factors Shape the Gut Microbiota of Atlantic Salmon Parr (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2017, 467, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Gooneratne, R.; Lai, R.; Zeng, C.; Zhan, F.; Wang, W. The Gut Microbiome and Degradation Enzyme Activity of Wild Freshwater Fishes Influenced by Their Trophic Levels. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; McGinnity, P.; Dionne, M.; Letourneau, J.; Thonier, F.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Derome, N. The Biogeography of the Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Gut Microbiome. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, T.M.U.; Consuegra, S.; Hitchings, M.; de Leaniz, C.G. Interpopulation Variation in the Atlantic Salmon Microbiome Reflects Environmental and Genetic Diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00691-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malick, R.C.; Bera, A.K.; Chowdhury, H.; Bhattacharya, M.; Abdulla, T.; Swain, H.S.; Baitha, R.; Kumar, V.; Das, B.K. Identification and Pathogenicity Study of Emerging Fish Pathogens Acinetobacter junii and Acinetobacter pittii Recovered from a Disease Outbreak in Labeo catla (Hamilton, 1822) and Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (Valenciennes, 1844) of Freshwater Wetland in West Bengal, India. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Sandve, S.R.; Padra, J.T.; Hagen, L.H.; Lindén, S.; Pope, P.B.; Arntzen, M.Ø.; Vaaje-Kolstad, G. The Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Skin–Mucus Proteome and Its Nutrient Potential for the Resident Bacterial Community. Genes 2019, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benediktsdo, E.; Verdonck, L.; Spro, C.; Helgason, S.; Swings, J. Characterization of Vibrio viscosus and Vibrio wodanis Isolated at Different Geographical Locations: A Proposal for Reclassification of Vibrio viscosus as Moritella viscosa comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, C.; Valenzuela, C.; Barrientos, J.; Paredes, J.; Leal, P.; Maldonado, M.; Godoy, F.; Osorio, C. Bacteriostatic Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus Activity of Pseudoalteromonas sp. Strains DIT09, DIT44 and DIT46 Isolated from Southern Chilean Intertidal Perumytilus purpuratus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Gupta, P.; Dhawan, A. Paenibacillus Polymyxa as a Water Additive Improved Immune Response of Cyprinus carpio and Disease Resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquac. Rep. 2016, 4, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnecki, A.M.; Brennan, N.P.; Schloesser, R.W.; Rhody, N.R. Shifts in the Skin-Associated Microbiota of Hatchery-Reared Common Snook Centropomus undecimalis During Acclimation to the Wild. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanczyk, H.; Ast, J.C.; Higgins, M.J.; Carson, J.; Dunlap, P.V. Reclassification of Vibrio fischeri, Vibrio logei, Vibrio salmonicida and Vibrio wodanis as Aliivibrio fischeri gen. nov., comb. nov., Aliivibrio logei comb. nov., Aliivibrio salmonicida comb. nov. and Aliivibrio wodanis comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2823–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauger, E.; Smolowitz, R.; Uhlinger, K.; Casey, J.; Gómez-Chiarri, M. Vibrio harveyi and Other Bacterial Pathogens in Cultured Summer Flounder, Paralichthys dentatus. Aquaculture 2006, 260, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Austin, B. Pathogenicity of Vibrio harveyi to Salmonids. J. Fish. Dis. 2000, 23, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla, I.; Arijo, S.; Chabrillon, M.; Diaz, P.; Martinez-Manzanares, E.; Balebona, M.; Morinigo, M. Vibrio Species Isolated from Diseased Farmed Sole, Solea senegalensis (Kaup), and Evaluation of the Potential Virulence Role of Their Extracellular Products. J. Fish Dis. 2003, 26, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balebona, M.C.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Faris, A.; Krovacek, K.; Månsson, I.; Bordas, M.A.; Borrego, J.J. Influence of Salinity and pH on the Adhesion of Pathogenic Vibrio Strains to Sparus aurata Skin Mucus. Aquaculture 1995, 132, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordas, M.A.; Balebona, M.C.; Zorrilla, I.; Borrego, J.J.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Moriñigo, M. Kinetics of Adhesion of Selected Fish-Pathogenic Vibrio Strains to Skin Mucus of Gilt-Head Sea Bream (Sparus aurata L.). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3650–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly-Guillou, M. Clinical Impact and Pathogenicity of Acinetobacter. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, A.; González, J.M.; Moran, M.A. Overview of the Marine Roseobacter Lineage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5665–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alvise, P.; Melchiorsen, J.; Porsby, C.; Nielsen, K.; Gram, L. Inactivation of Vibrio anguillarum by Attached and Planktonic Roseobacter Cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2366–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelm, M.; Bergh, Ø.; Riaza, A.; Nielsen, J.; Melchiorsen, J.; Jensen, S.; Duncan, H.; Ahrens, P.; Birkbeck, H.; Gram, L. Selection and Identification of Autochthonous Potential Probiotic Bacteria from Turbot Larvae (Scophthalmus maximus) Rearing Units. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 27, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, P.; Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Pires, A.C.C.; Marques, B.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Quintino, V.; Gomes, N.C.M. Seasonal Patterns of Bacterioplankton Composition in a Semi-Intensive European Seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) Aquaculture System. Aquaculture 2018, 490, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, F. Fish Diseases and Disorders. In Viral, Bacterial and Fungal Infections; Woo, P.T.K., Bruno, D.W., Eds.; CABI: Oxfordshire, UK, 2011; Volume 3, ISBN 978-1-84593-554-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyat, M.S.; Labib, H.M.; Mahmoud, H.K. A Probiotic Cocktail as a Growth Promoter in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Appl. Aquac. 2014, 26, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenen, O. Major Bacterial Diseases Affecting Aquaculture. In Proceedings of the Aquatic AMR Workshop 1, Mangalore, India, 10–11 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, D.; Mooney, J.; Ryan, D.; Powell, E.; Hiney, M.; Smith, P.R.; Powell, R. Detection of Aeromonas salmonicida, Causal Agent of Furunculosis in Salmonid Fish, from the Tank Effluent of Hatchery-Reared Atlantic Salmon Smolts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3874–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D.W.; Hastings, T.S.; Wootten, R. Outbreak of a Cold Water Vibriosis in Atlantic Salmon in Scotland. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1985, 5, 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kashulin, A.; Seredkina, N.; Sørum, H. Cold-Water Vibriosis. The Current Status of Knowledge. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).