Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Dogs: Evaluating Imaging Parameters and Methodological Variability in Global Longitudinal Strain Assessment
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Evaluate how key imaging parameters (frame rate, heart rate, transducer frequency, and foreshortening) affect GLS measurements in clinically healthy dogs.
- Compare the performance of GE Healthcare’s 2D strain and AFI in speckle-tracking echocardiography.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
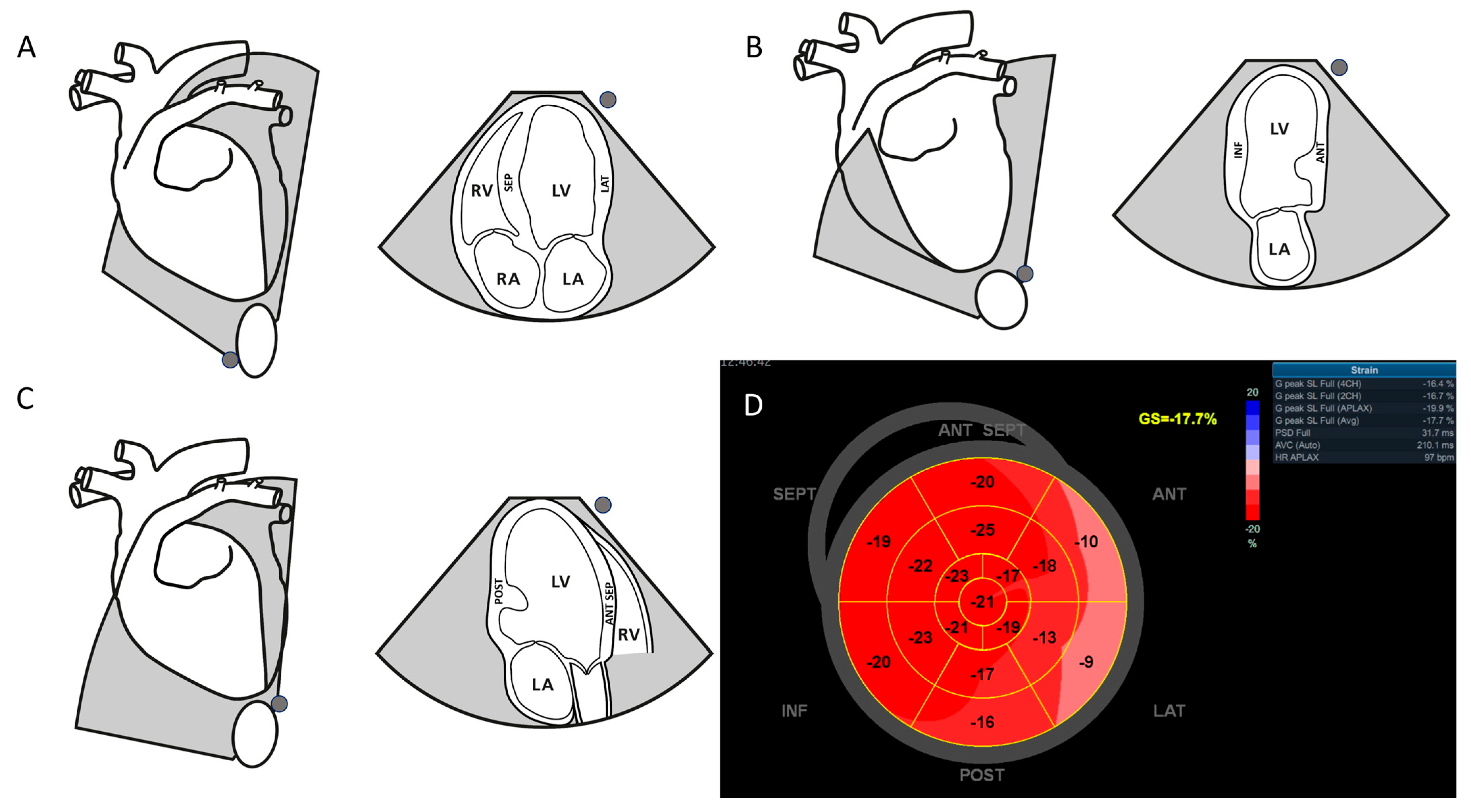
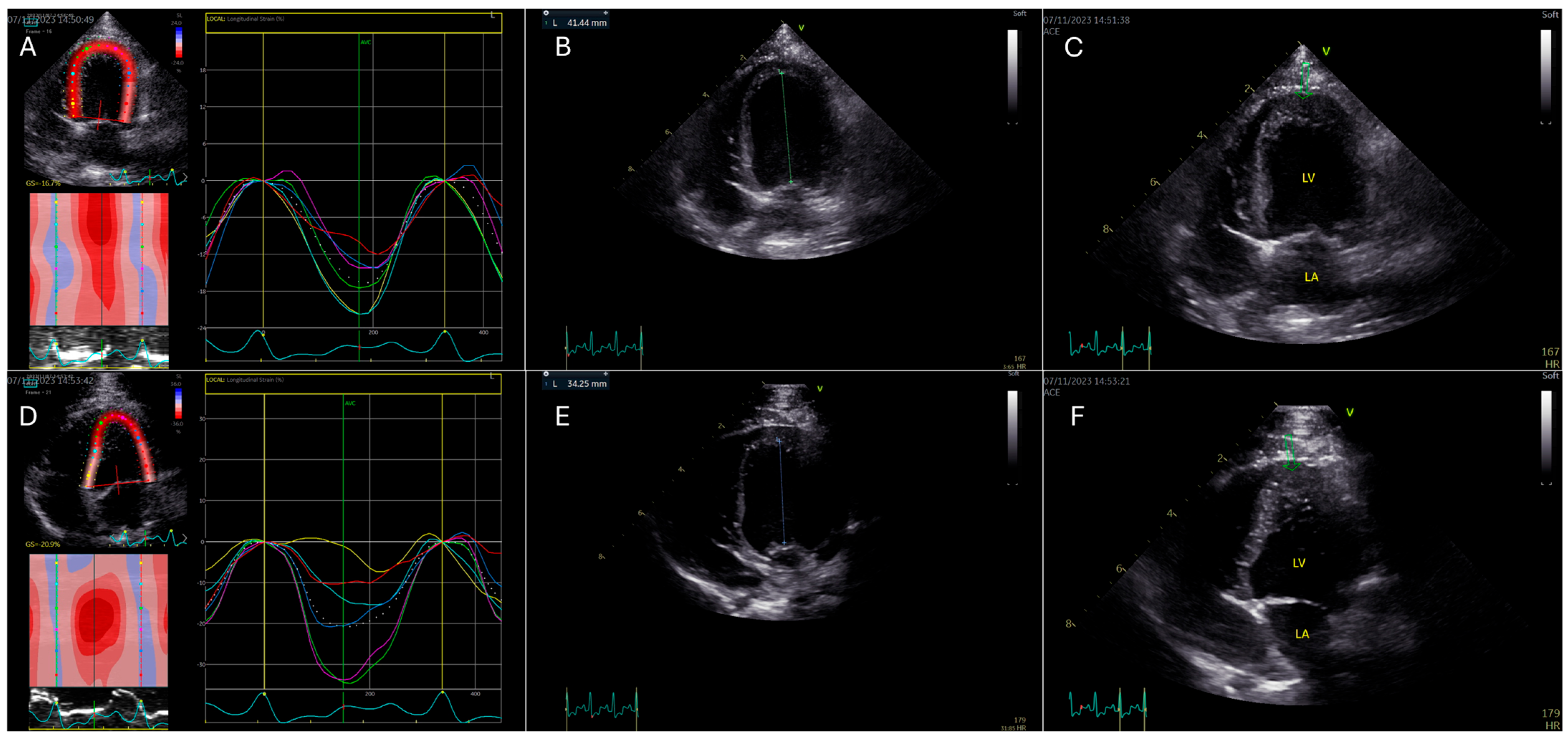
2.2. Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography
2.3. Offline Analysis, Brondby, Denmark
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2D-STE | Two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography |
| 2D Strain | Quantitative analysis for 2D strain |
| A2C | Automated function imaging |
| A4C | Apical two-chamber |
| AFI | Apical four-chamber |
| APLAX | Apical long axis |
| CV | Coefficient of variance |
| ECG | Electrocardiography |
| FR | Frame rate |
| FPS | Frames per second |
| GLS | Global longitudinal strain |
| HR | Heart rate |
| MHz | Megahertz |
| ROI | Region of interest |
References
- Blessberger, H.; Binder, T. Two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: Basic principles. Heart BCS 2010, 96, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, M.; Kasliwal, R.R. How do I do it? Speckle-tracking echocardiography. Indian Heart J. 2013, 65, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, J.U.; Pedrizzette, G.; Lysyansky, P.; Marwick, T.; Houle, J.M.; Baumann, R.; Pedri, S.; Ito, Y.; Abe, Y.; Metz, S.; et al. Definitions for a common standard for 2D speckle tracking echocardiography: Consensus document of the EACVI/ASE/Industry task force to standardize deformation imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, I.; Pugliese, N.R.; Santini, V.; Conte, L.; Bello, V.D. Speckle-tracking imaging, principles and clinical applications: A review for clinical cardiologists. In Echocardiography in Heart Failure and Cardiac Electrophysiology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandel, M.; Lehmkuhl, H.; Knosalla, C.; Suramelashvili, N.; Hetzer, R. Strain and strain rate imaging by echocardiography—Basic concepts and clinical applicability. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2009, 5, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westrup, U.; McEvoy, F.J. Speckle tracking echocardiography in mature Irish Wolfhound dogs: Technical feasibility, measurement error and reference intervals. Acta Vet. Scand. 2013, 55, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamabe, L.; Mandour, A.S.; Shimada, K.; Uemura, A.; Yilmaz, Z.; Nagaoka, K.; Tanaka, R. Role of two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography in early detection of left ventricular dysfunction in dogs. Animals 2021, 11, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzsch, S.; Wess, G. Two-dimensional speckle tracking-derived global longitudinal strain in healthy Doberman Pinschers: Method evaluation, variability, and reference values. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2023, 45, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamabe, L.; Shimada, K.; Mandour, A.S.; Yoshida, T.; Hirose, M.; Hendawy, H.; El-Husseiny, H.M.; Tanaka, R. Evaluation of left ventricular function in healthy retrievers using standard and 2D speckle-tracking echocardiography. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunose, K.; Zhang, Y.; Mazgalev, T.N.; Thomas, J.D.; Popovic, Z.V. Left ventricular strain distribution in healthy dogs and in dogs with tachycardia-induced dilated cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2013, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Matsumoto, H.; Teshima, T.; Koyama, H. Influence of heart rate on myocardial function using two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography in healthy dogs. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2013, 15, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Matsumoto, H.; Teshima, T.; Koyama, H. Effect of age on myocardial function assessed by two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography in healthy beagle dogs. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2015, 15, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondillo, S.; Galderisi, M.; Mele, D.; Cameli, M.; Lomoriello, V.S.; Zaca, V.; Ballo, P.; D’Andrea, A.; Muaru, D.; Lose, M.; et al. Speckle-tracking echocardiography: A new technique for assessing myocardial function. J. Ultrasound Med. 2011, 30, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, P.; Phelan, D.; Klein, A. Myocardial strain measured by speckle-tracking echocardiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, S.; Duchenne, J.; Mirea, O.; Pagourelias, E.D.; Bézy, S.; Cvijic, M.; Beela, A.D.; Thomas, J.D.; Badano, L.P.; Voigt, J.U. Impact of apical foreshortening on deformation measurements: A report from the EACVI-ASE strain standardization task force. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 21, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’hooge, J.; Barbosa, D.; Gao, H.; Claus, P.; Prater, D.; Hamilton, J.; Lysyansky, P.; Abe, Y.; Ito, Y.; Houle, H.; et al. Two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography: Standardization efforts based on synthetic ultrasound data. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonagura, J.D.; Fuentes, V.L. Echocardiography in Small Animal Diagnostic Ultrasound, 3rd ed.; Mattoon, J.S., Nyland, T.G., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Loius, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 217–331. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.E.; Barac, A.; Thavendiranathan, P.; Scherrer-Crosbie, M. Strain imaging in cardio-oncology. JACC CardioOncology 2020, 2, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-J.C.; Beqiri, A.; Lewandowski, A.J.; Puyol-Antón, E.; Markham, D.C.; King, A.P.; Leeson, P.; Lamata, P. Beyond Simpson’s Rule: Accounting for Orientation and Ellipticity Assumptions. Ultrasound Med. 2022, 48, 2476–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarelli, G.; Toaldo, M.B.; Bouvard, J.; Claus, T.M.; Del Palacio, J.F. Variability among strain variables derived from two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography in dogs by use of various software. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 80, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth. Anal. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wess, G.; Keller, L.J.M.; Klausnitzer, M.; Killich, M.; Hartmann, K. Comparison of longitudinal myocardial tissue velocity, strain, and strain rate measured by two-dimensional speckle tracking and by color tissue Doppler imaging in healthy dogs. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2011, 13, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, E.; Camacho, B.; Mrevlje, B.; Brandenburg, H.; Ren, C.B. Echocardiography core laboratory validation of a novel vendor-independent web-based software for the assessment of left ventricular global longitudinal strain. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 31, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.; Kuyt, K.; Oxborough, D.; Stout, M. Practical tips and tricks in measuring strain, strain rate and twist for the left and right ventricles. Echo Res. Pract. 2019, 6, R87–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.A.; Levy, P.T.; Sekarski, T.J.; Hamvas, A.; Holland, M.R.; Singh, G.K. Effects of frame rate on two-dimensional speckle tracking-derived measurements of myocardial deformation in premature infants. Echocardiography 2015, 32, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, F.J.; Svendsen, J.H.; Køber, L.; Højberg, S.; Haugan, K.; Jensen, J.S.; Biering-Sørensen, T. Impact of transducer frequency setting on speckle tracking measures. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 34, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blessberger, H.; Bergler-Klein, J.; Graf, D.; Syeda, B.; Wagner, H.; Kammler, J.; Steinwender, C.; Binder, R. Speckle tracking-derived longitudinal strain: Validation and influence of scanner settings. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Matsumoto, H.; Teshima, T.; Koyama, H. Clinical assessment of systolic myocardial deformations in dogs with chronic mitral valve insufficiency using two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography. J. Vet. Cardiol. 2013, 15, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbowska-Drabik, K.; Hamala, P.; Roszczyk, N.; Lipiec, P.; Plewka, M.; Krecki, R.; Kasprzak, J.D. Feasibility and correlation of standard 2D speckle tracking echocardiography and automated function imaging derived parameters of left ventricular function during dobutamine stress test. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 30, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cohort 1 | Cohort 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Patients included | 16 | 10 |
| Age (years) | 2.9 (1.3–4.8) | 2.0 (1–4) |
| Breed | ||
| CKCS | 11 (68.75%) | 5 (50%) |
| Miniature bull terrier | 1 (6.25%) | 0 (0%) |
| Broholmer | 1 (6.25%) | 0 (0%) |
| Bull terrier | 1 (6.25%) | 0 (0%) |
| Shih Tzu | 0 (0%) | 1 (10%) |
| Chihuahua | 0 (0%) | 1 (10%) |
| Danish–Swedish farm dog | 0 (0%) | 1 (10%) |
| Jack Russell | 0 (0%) | 1 (10%) |
| Small mix | 2 (12.5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Medium mix | 0 (0%) | 1 (10%) |
| Heart rate (bmp) | 128 (85–159) | 112 (91–146) |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 12 (75%) | 7 (70%) |
| Male | 4 (25%) | 3 (30%) |
| Weight (kg) | 11.7 (4.6–45.0) | 8.6 (3.7–21.9) |
| Body Condition Score (Grade 1-9) | 4.8 (4–7) | 4.6 (4–5) |
| Parameter | n | Mean ± SD | Min. | Max. | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLSA4C | 16 | −19.19% ± 4.11% | −12.90% | −25.70% | - |
| GLSA4C-Zoom | 16 | −19.67% ± 4.35% | −12.90% | −30.30% | 0.57 |
| GLSA4C↑Frame rate | 16 | −18.07% ± 2.61% | −14.10% | −22.30% | 0.15 |
| GLSA4C-Foreshortening | 13 | −21.32% ± 3.51% | −16.50% | −30.20% | <0.01 |
| GLSA4C↑HR | 11 | −22.15% ± 4.08% | −17.80% | −30.30% | 0.02 |
| GLSA4C-Frequency | 15 | −19.35% ± 3.46% | −12.80% | −26.70% | 0.47 |
| 2D Strain | AFI | p-Value | r-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLS | −20.04% ± 2.88% | −17.67% ± 1.61% | <0.01 | 0.87 |
| GLSAPLEX | −20.17% ± 4.40% | −17.49% ± 2.72% | 0.03 | 0.61 |
| GLSA4C | −20.27% ± 3.08% | −18.26% ± 1.66% | <0.01 | 0.83 |
| GLSA2C | −19.70% ± 3.18% | −17.24% ± 2.38% | <0.01 | 0.87 |
| 2D Strain | AFI | |
|---|---|---|
| Intra-observer repeatability CV | ||
| GLS | 3.86% | 2.61% |
| GLSAPLAX | 7.37% | 3.91% |
| GLSA4C | 8.17% | 4.06% |
| GLSA2C | 7.33% | 3.46% |
| Inter-observer repeatability CV | ||
| GLS | 4.24% | 5.66% |
| GLSAPLAX | 8.71% | 8.29% |
| GLSA4C | 8.08% | 5.26% |
| GLSA2C | 6.45% | 6.77% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mogensen, J.E.; Bach, M.B.T.; Bay, P.G.; Varlik, T.; Willesen, J.L.; Gleerup, C.H.; Koch, J. Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Dogs: Evaluating Imaging Parameters and Methodological Variability in Global Longitudinal Strain Assessment. Animals 2025, 15, 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111523
Mogensen JE, Bach MBT, Bay PG, Varlik T, Willesen JL, Gleerup CH, Koch J. Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Dogs: Evaluating Imaging Parameters and Methodological Variability in Global Longitudinal Strain Assessment. Animals. 2025; 15(11):1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111523
Chicago/Turabian StyleMogensen, Jonas E., Maiken B. T. Bach, Pernille G. Bay, Tuğba Varlik, Jakob L. Willesen, Caroline H. Gleerup, and Jørgen Koch. 2025. "Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Dogs: Evaluating Imaging Parameters and Methodological Variability in Global Longitudinal Strain Assessment" Animals 15, no. 11: 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111523
APA StyleMogensen, J. E., Bach, M. B. T., Bay, P. G., Varlik, T., Willesen, J. L., Gleerup, C. H., & Koch, J. (2025). Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Dogs: Evaluating Imaging Parameters and Methodological Variability in Global Longitudinal Strain Assessment. Animals, 15(11), 1523. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15111523







