The Role of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea During Cycling and Animal Introduction in a Newly Commissioned Saltwater Aquarium
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Aquarium System and Water Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR, and Illumina Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics
2.4. Visualization and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Data Availability
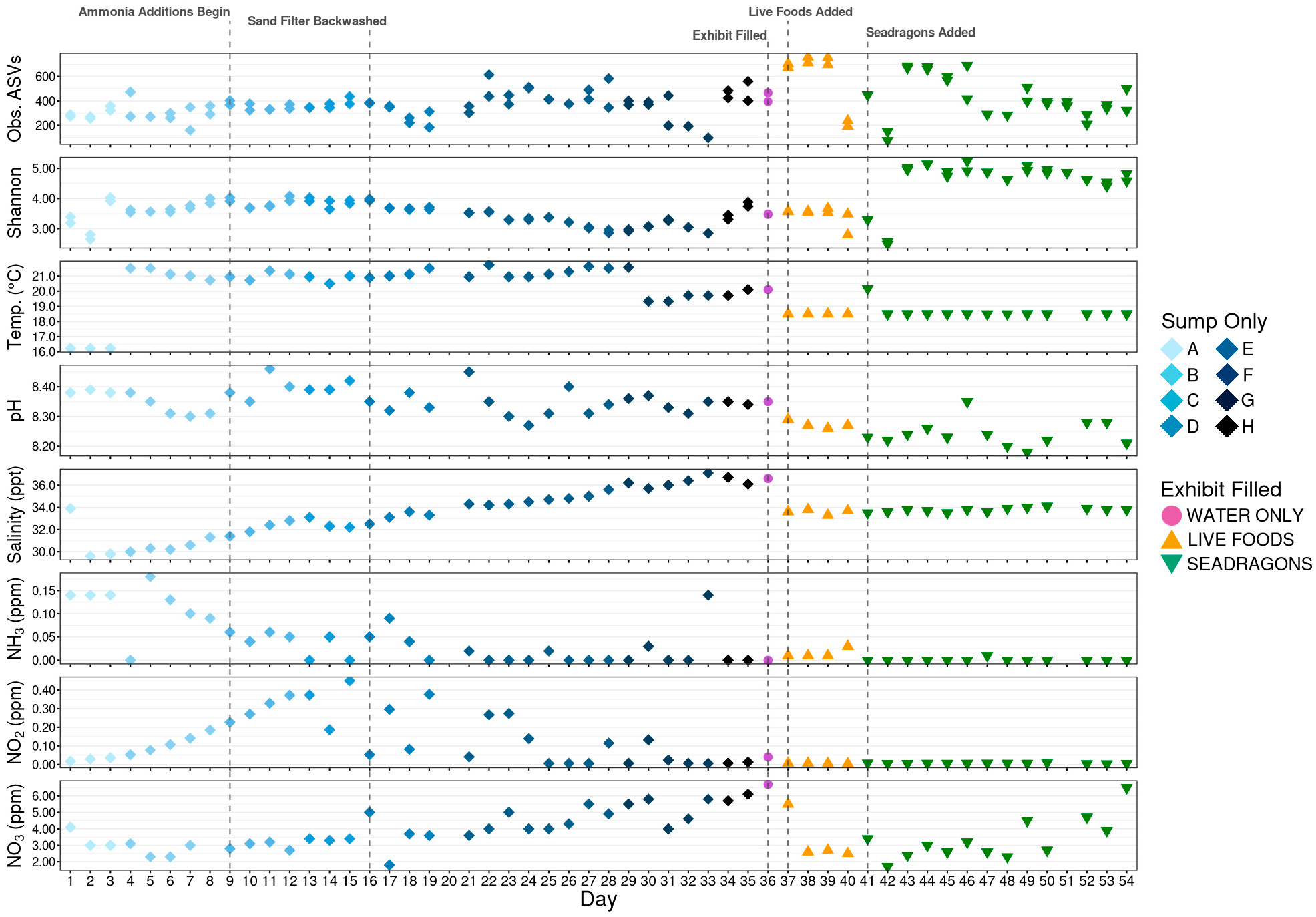
3. Results
3.1. Initial Sequencing Metrics
3.2. Alpha Diversity
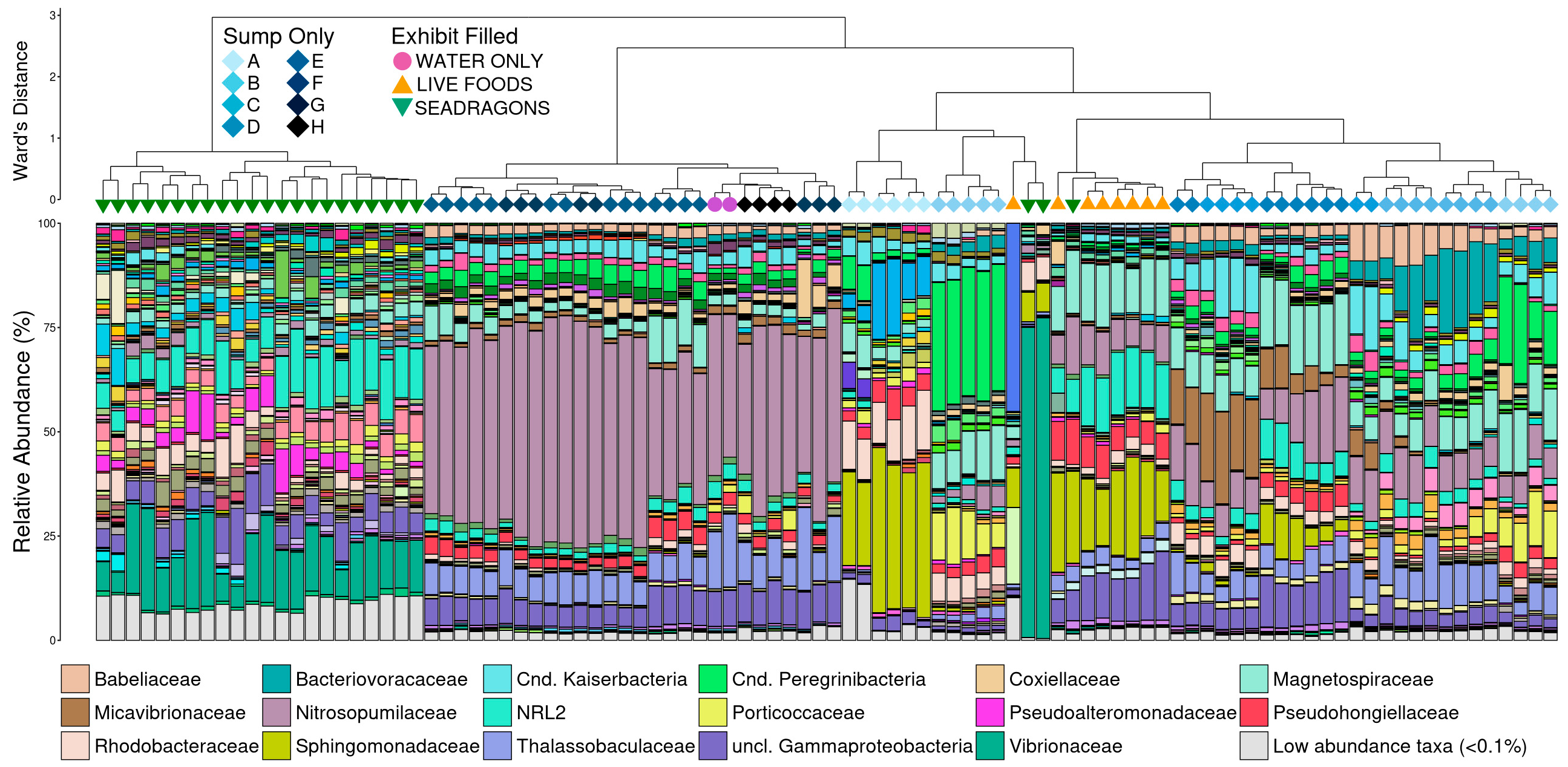
3.3. Microbial Community Structure
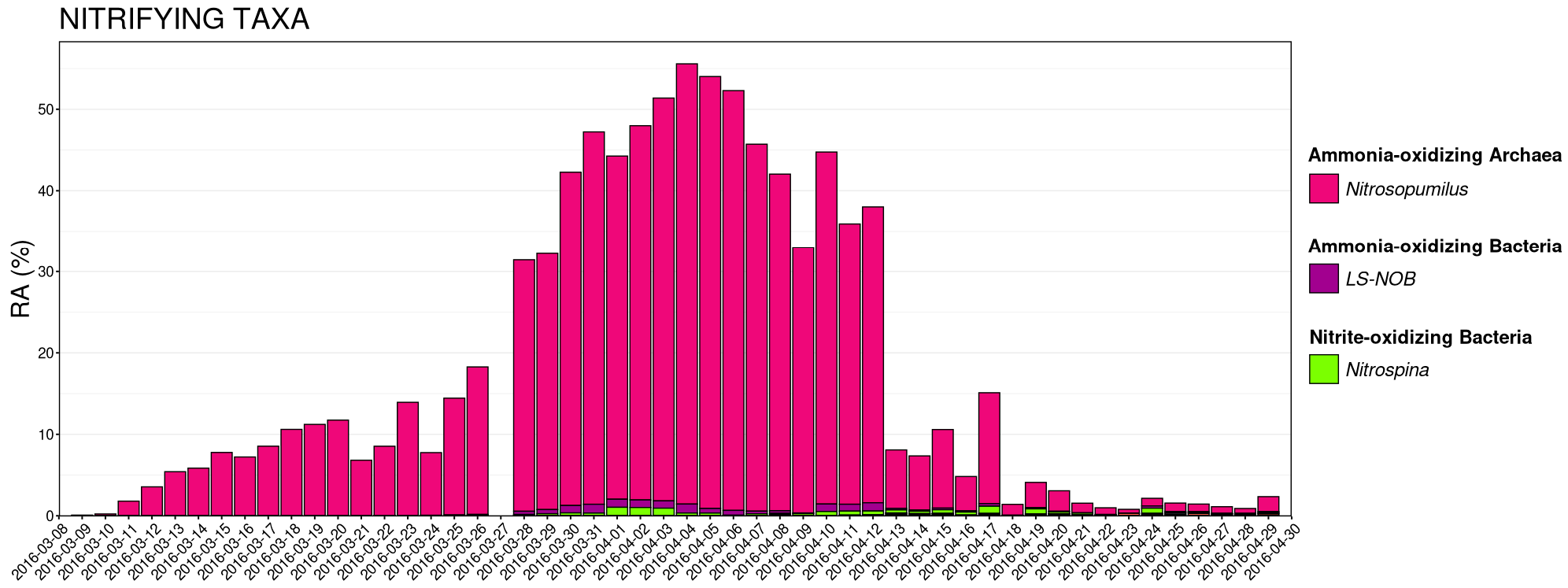
3.4. Nitrifying Microbial Taxa
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miranda, R.; Escribano, N.; Casas, M.; Pino-del-Carpio, A.; Villarroya, A. The Role of Zoos and Aquariums in a Changing World. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2023, 11, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Aber, J.D.; Erisman, J.W.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Howarth, R.W.; Cowling, E.B.; Cosby, B.J. The Nitrogen Cascade. BioScience 2003, 53, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading Dead Zones and Consequences for Marine Ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamper, M.A.; Semmen, K.J. The Mechanics of Aquarium Water Conditioning. In Fowler’s Zoo and Wild Animal Medicine Current Therapy; Rudolph, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi, S.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Sauder, L.A.; Mosquera, M.; Neufeld, J.D.; Boon, N. Temporal and Spatial Stability of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in Aquarium Biofilters. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e113515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, C.A.; Whitaker, B.R.; Clayton, L.A. Emergency and Critical Care of Fish. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2007, 10, 647–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, D.J.; Tsui, T.K.N. Ammonia toxicity in fish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 45, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathy, A.J.; Das, B.C.; Jifiriya, M.J.; Varghese, T.; Pillai, D.; Rejish Kumar, V.J. Ammonia induced toxico-physiological responses in fish and management interventions. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 452–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi-Tehrani, J.; Peyghan, R.; Shahriari, A.; Razijalali, M.; Ebrahimi, E. The influence of ammonia-N and salinity levels on oxidative stress markers, hepatic enzymes, and acid phosphatase activity in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiao, H.; Peng, L.; Meng, Y.; Song, G.; Luo, C.; Long, Y. Influence of High Temperature and Ammonia and Nitrite Accumulation on the Physiological, Structural, and Genetic Aspects of the Biology of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides). Antioxidants 2025, 14, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.M.; Puglis, H.J.; Kent, D.B.; Durán, J.L.; Bradshaw, L.M.; Farag, A.M. Ammonia and aquatic ecosystems—A review of global sources, biogeochemical cycling, and effects on fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklosz, J.C. Biological filtration. Mar. Aquar. 1970, 1, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Oshiki, M.; Satoh, H.; Okabe, S. Ecology and physiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 2784–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzenpichler, R. Diversity, Physiology, and Niche Differentiation of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7501–7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, H.; Lücker, S.; Albertsen, M.; Kitzinger, K.; Herbold, C.; Spieck, E.; Nielsen, P.H.; Wagner, M.; Daims, H. Expanded metabolic versatility of ubiquitous nitrite-oxidizing bacteria from the genus Nitrospira. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11371–11376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, M.M.; Neufeld, J.D. Comammox Nitrospira among dominant ammonia oxidizers within aquarium biofilter microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e00104-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suantika, G.; Pratiwi, M.; Situmorang, M.; Djohan, Y.; Muhammad, H.; Astuti, D. Ammonium removal by nitrifying bacteria biofilm on limestone and bioball substrate established in freshwater trickling biofilter. Poult. Fish. Wildl. Sci. 2016, 4, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yang, X.; Ou, D.; Lin, R.; Liu, X. Effects of live rock on removal of dissolved inorganic nitrogen in coral aquaria. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, D.D.; Drahos, D.D.; Marsh, L.; Flick, G.J., Jr. Evaluation of nitrifying bacteria product to improve nitrification efficacy in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 43, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bonn, W.; LaPointe, A.; Gibbons, S.M.; Frazier, A.; Hampton-Marcell, J.; Gilbert, J. Aquarium microbiome response to ninety-percent system water change: Clues to microbiome management. Zoo Biol. 2015, 34, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bonn, W.; Oliaro, F.; Pinnell, L. Whale-Associated Microbial Communities Remain Remarkably Stable despite Massive Water Community Disruption in a Managed Artificial Marine Environment. Oceans 2022, 3, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik, H.M.; Alexiev, A.; Aulakh, S.K.; Bharadwaj, L.; Flanagan, J.; Haggerty, J.M.; Hird, S.M.; Jospin, G.; Lang, J.M.; Sauder, L.A.; et al. Microbial community succession and nutrient cycling responses following perturbations of experimental saltwater aquaria. mSphere 2019, 4, e00043-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patin, N.V.; Pratte, Z.A.; Regensburger, M.; Hall, E.; Gilde, K.; Dove, A.D.M.; Stewart, F.J. Microbiome dynamics in a large artificial seawater aquarium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00179-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W.; Hyde, E.R.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Ackermann, G.; Humphrey, G.; Parada, A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Jansson, J.K.; Caporaso, J.G.; Fuhrman, J.A.; et al. Improved Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene (V4 and V4-5) and Fungal Internal Transcribed Spacer Marker Gene Primers for Microbial Community Surveys. mSystems 2016, 1, e00009-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, J.N.; Stine, O.C.; Bravo, H.C.; Pop, M. Differential abundance analysis for microbial marker-gene surveys. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Bittinger, K.; Charlson, E.S.; Hoffmann, C.; Lewis, J.; Wu, G.D.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Li, H. Associating microbiome composition with environmental covariates using generalized UniFrac distances. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, F.; Legendre, P. Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering method: Which algorithms implement Ward’s criterion? J. Classif. 2014, 31, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, R Package Version 2.5-5. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Arbizu, P.M. pairwiseAdonis: Pairwise Multilevel Comparison Using Adonis, R Package Version 0.0.1. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/pmartinezarbizu/pairwiseAdonis (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Hovanec, T.A.; DeLong, E.F. Comparative analysis of nitrifying bacteria associated with freshwater and marine aquaria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 2888–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovanec, T.A.; Taylor, L.T.; Blakis, A.; Delong, E.F. Nitrospira-Like Bacteria Associated with Nitrite Oxidation in Freshwater Aquaria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könneke, M.; Bernhard, A.E.; de la Torre, J.R.; Walker, C.B.; Waterbury, J.B.; Stahl, D.A. Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 2005, 437, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, D.A.; de la Torre, J.R. Physiology and Diversity of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauder, L.A.; Engel, K.; Stearns, J.C.; Masella, A.P.; Pawliszyn, R.; Neufeld, J.D. Aquarium Nitrification Revisited: Thaumarchaeota Are the Dominant Ammonia Oxidizers in Freshwater Aquarium Biofilters. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens-Habbena, W.; Berube, P.M.; Urakawa, H.; de la Torre, J.R.; Stahl, D.A. Ammonia oxidation kinetics determine niche separation of nitrifying Archaea and Bacteria. Nature 2009, 461, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens-Habbena, W.; Stahl, D.A. Chapter Nineteen—Nitrogen Metabolism and Kinetics of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea. In Methods in Enzymology; Klotz, M.G., Stein, L.Y., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 496, pp. 465–487. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, C.; Lax, S.; Larsen, P.; Stephens, B.; Hampton-Marcell, J.; Edwardson, C.F.; Henry, C.; Van Bonn, B.; Gilbert, J.A. Environmental sources of bacteria differentially influence host-associated microbial dynamics. mSystems 2018, 3, e00052-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribes, M.; Calvo, E.; Movilla, J.; Logares, R.; Coma, R.; Pelejero, C. Restructuring of the sponge microbiome favors tolerance to ocean acidification. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 8, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, L.G.E.; Leray, M.; O’Dea, A.; Yuen, B.; Peixoto, R.S.; Pereira, T.J.; Bik, H.M.; Coil, D.A.; Duffy, J.E.; Herre, E.A.; et al. Host-associated microbiomes drive structure and function of marine ecosystems. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Corte, D.; Srivastava, A.; Koski, M.; Garcia, J.A.L.; Takaki, Y.; Yokokawa, T.; Nunoura, T.; Elisabeth, N.H.; Sintes, E.; Herndl, G.J. Metagenomic insights into zooplankton-associated bacterial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanger, I.S.; Stefanschitz, J.; Schwert, Y.; Roth, O. The source of microbial transmission influences niche colonization and microbiome development. Proc. R. Soc. B 2024, 291, 20232036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
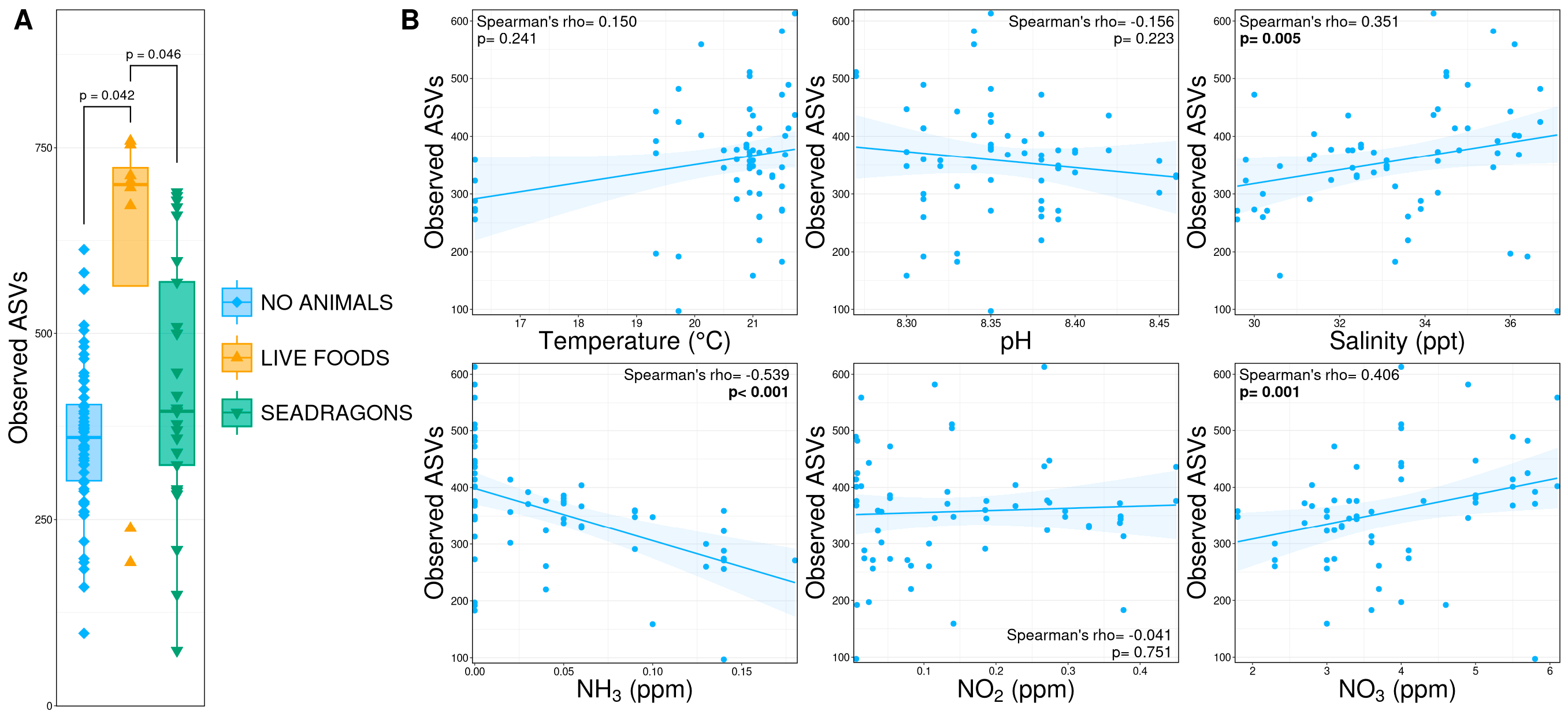
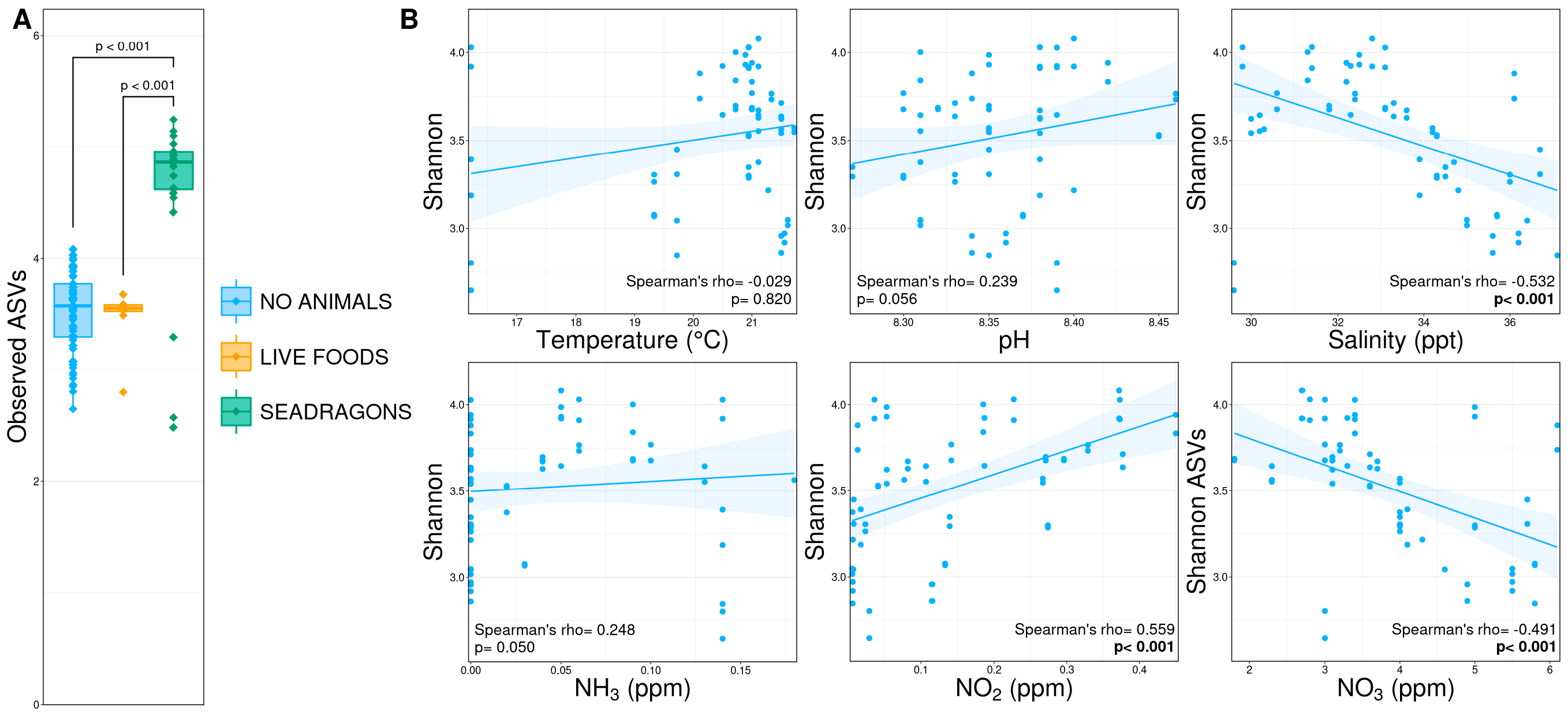

| Environmental Variable | Df | SS | Pseudo-F | R2 | p-adj. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 1 | 0.552 | 10.678 | 0.077 | 0.0001 |
| pH | 1 | 0.119 | 2.307 | 0.016 | 0.0567 |
| Salinity | 1 | 0.530 | 10.255 | 0.073 | 0.0001 |
| NH3 | 1 | 0.164 | 3.161 | 0.022 | 0.0156 |
| NO2 | 1 | 0.289 | 5.580 | 0.040 | 0.0009 |
| NO3 | 1 | 0.049 | 0.941 | 0.007 | 0.4127 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliaro, F.J.; Ajileye, O.; George, I.; Lamsal, S.; Mosley, I.A.; Ramirez, B.; Sanders, T.L.; Vanitshavit, V.; Van Bonn, W.; Pinnell, L.J. The Role of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea During Cycling and Animal Introduction in a Newly Commissioned Saltwater Aquarium. Animals 2025, 15, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101446
Oliaro FJ, Ajileye O, George I, Lamsal S, Mosley IA, Ramirez B, Sanders TL, Vanitshavit V, Van Bonn W, Pinnell LJ. The Role of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea During Cycling and Animal Introduction in a Newly Commissioned Saltwater Aquarium. Animals. 2025; 15(10):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101446
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliaro, Francis J., Oluwaseun Ajileye, Iris George, Sal Lamsal, Ilana A. Mosley, Bradly Ramirez, Tiana L. Sanders, Veerakit Vanitshavit, William Van Bonn, and Lee J. Pinnell. 2025. "The Role of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea During Cycling and Animal Introduction in a Newly Commissioned Saltwater Aquarium" Animals 15, no. 10: 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101446
APA StyleOliaro, F. J., Ajileye, O., George, I., Lamsal, S., Mosley, I. A., Ramirez, B., Sanders, T. L., Vanitshavit, V., Van Bonn, W., & Pinnell, L. J. (2025). The Role of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea During Cycling and Animal Introduction in a Newly Commissioned Saltwater Aquarium. Animals, 15(10), 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101446





