Porcine β-Defensin 2 Expressed in Pichia pastoris Alleviates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Intestinal Injury and Inflammatory Response in Mice
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Plasmids
2.2. Enzymes and Chemicals
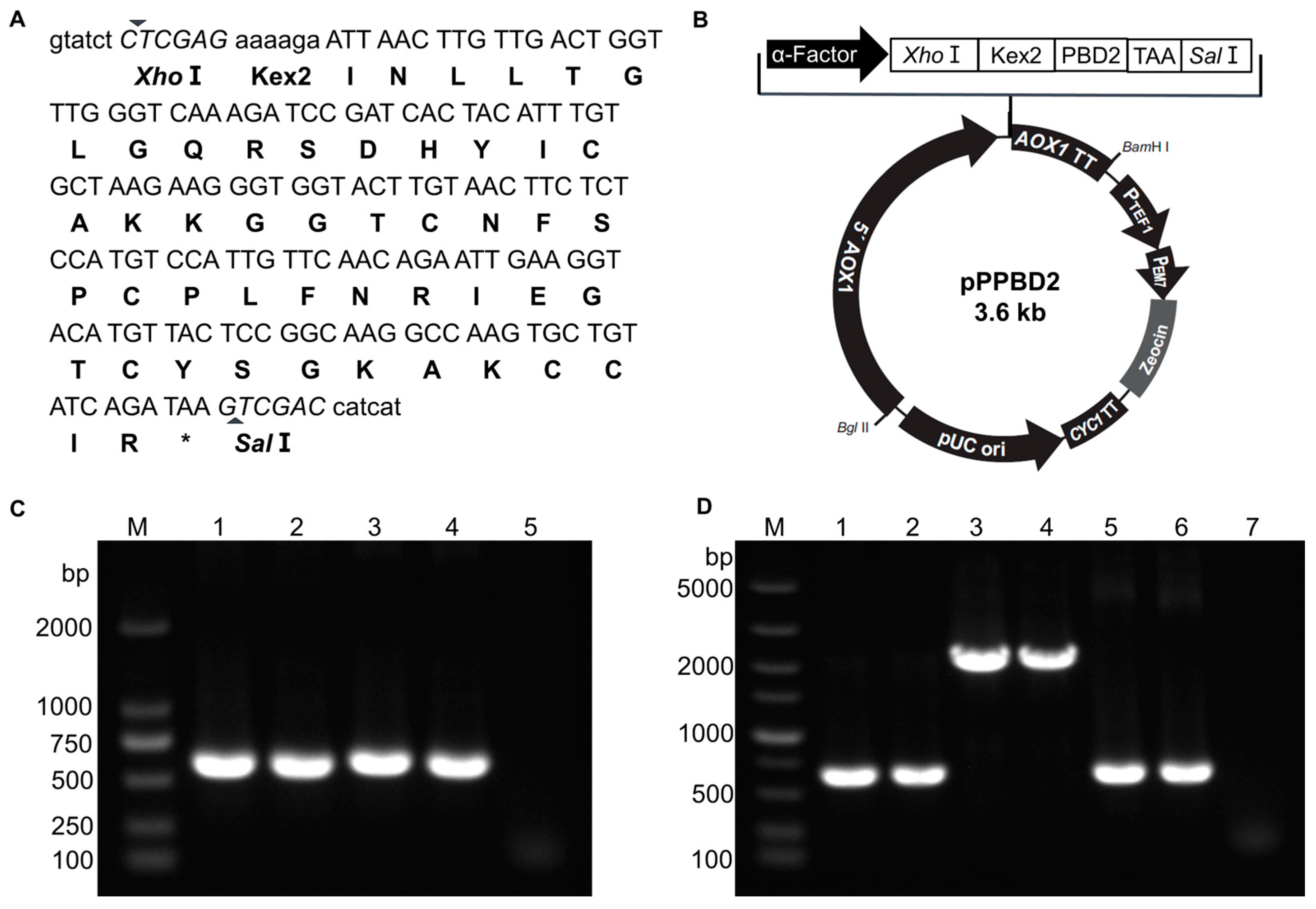
2.3. Construction of PBD2 Expression Plasmid pPPBD2
2.4. Transformation and Expression of rPBD2 in P. pastoris
2.5. Antimicrobial Titer Assay
2.6. Antibacterial Spectrum Assay
2.7. Stability Assay of Crude rPBD2
2.8. Animal Experiment Design
2.9. Clinical Symptoms and Sample Collection
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Construction of rPBD2 Expression Plasmid and Screening of Positive P. pastoris Transformants
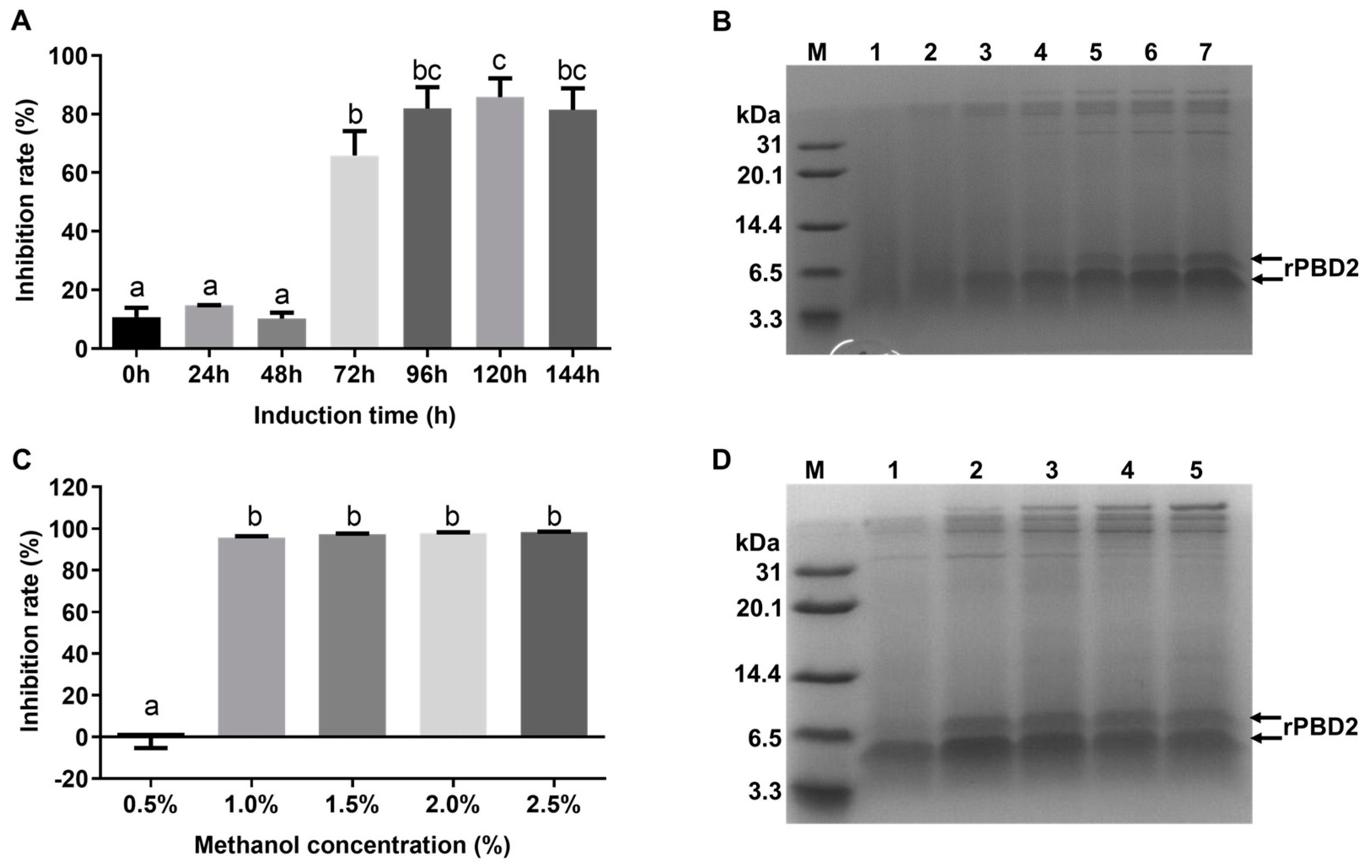
3.2. Screening of High-Expression Strain for rPBD2
3.3. Optimization of Induction Conditions
3.4. Antimicrobial Spectrum of Crude rPBD2
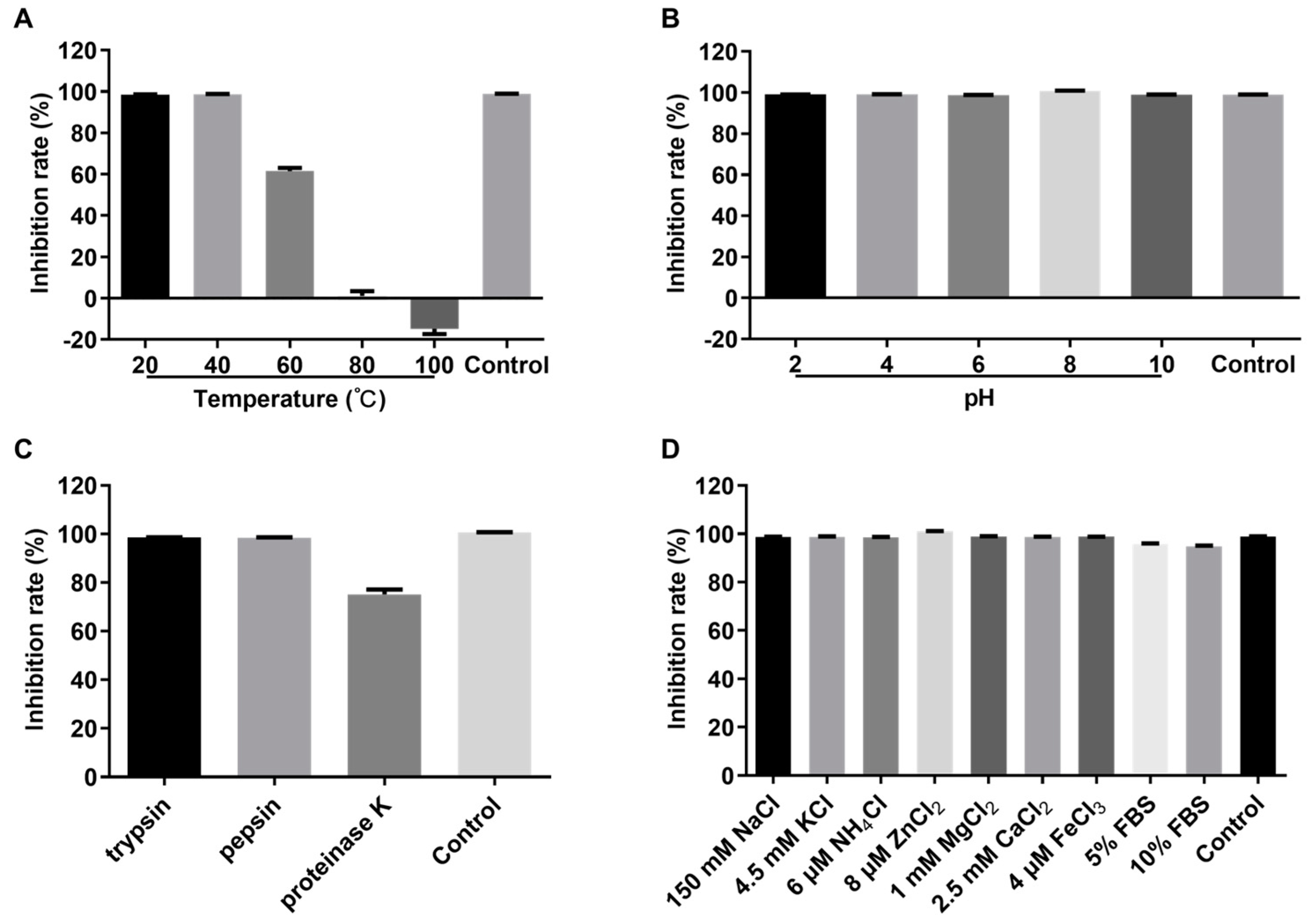
3.5. Stability of Crude rPBD2
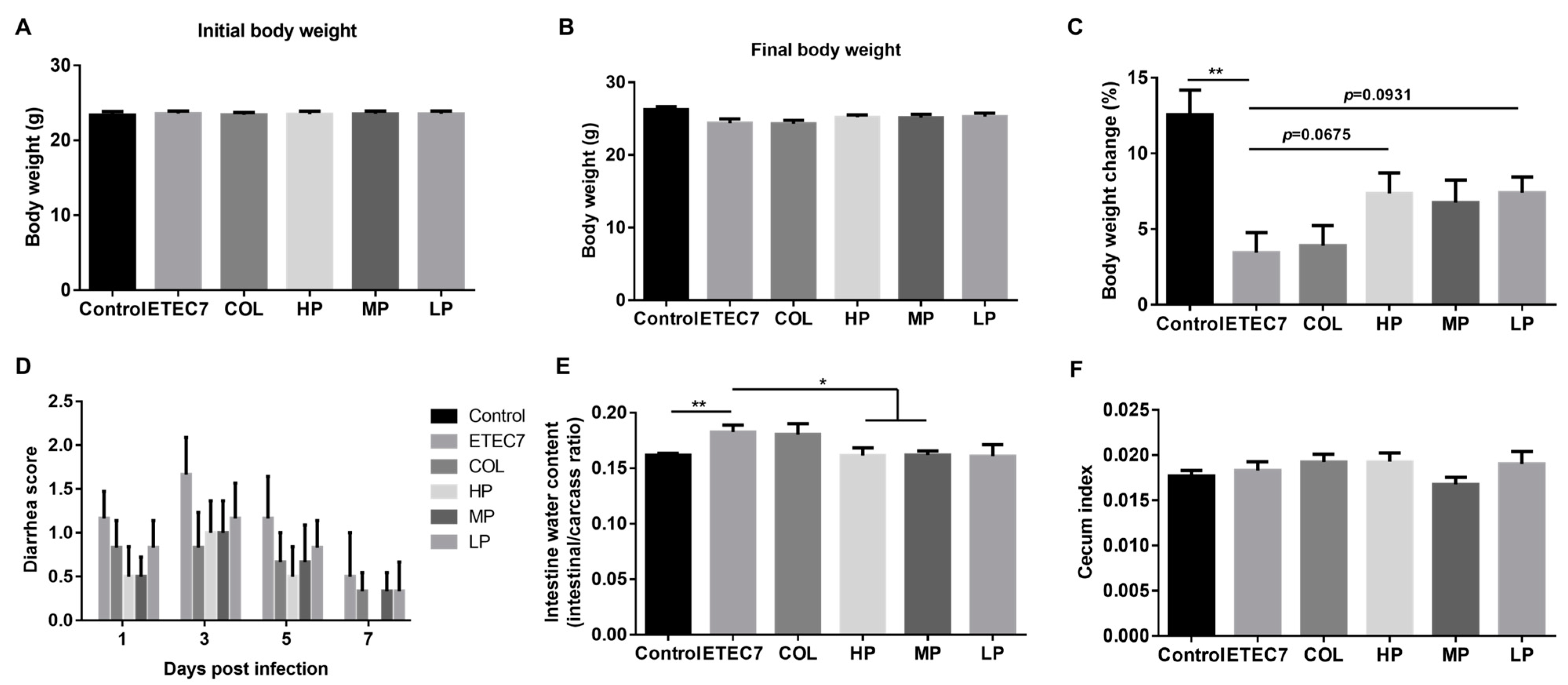
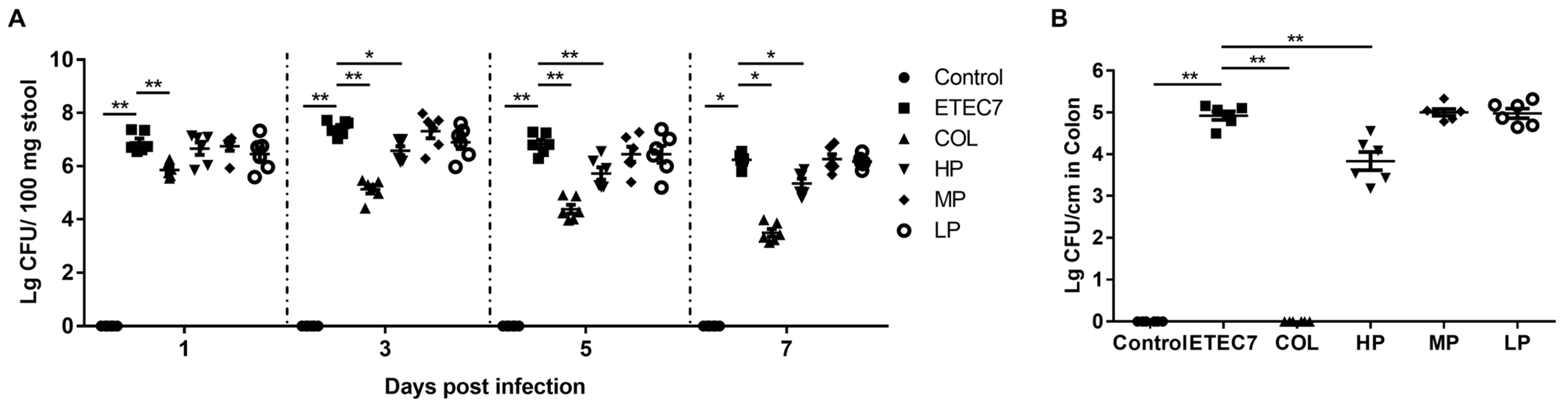
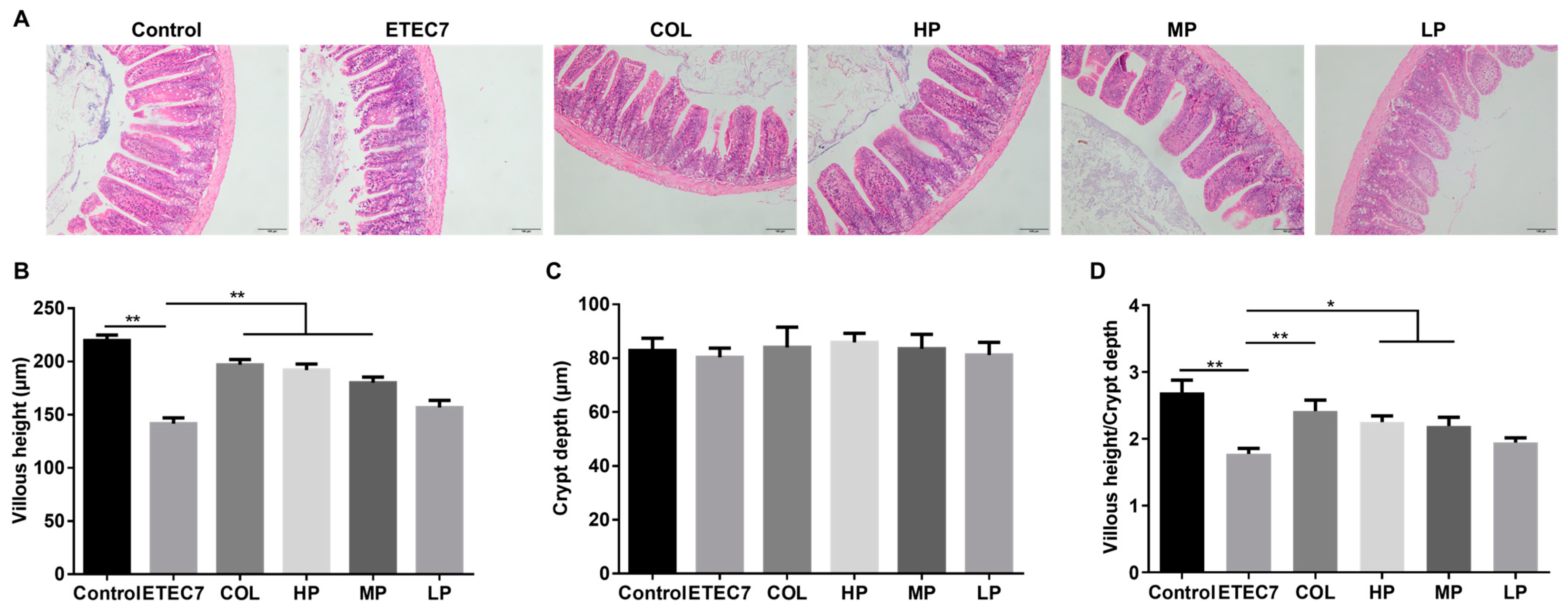
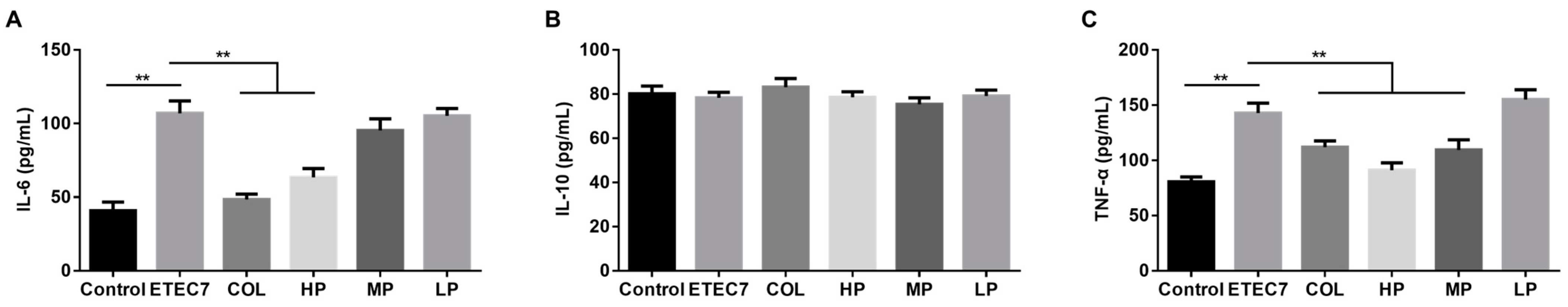
3.6. Efficacy of Crude rPBD2 on ETEC K88-Infected Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jesser, K.J.; Levy, K. Updates on defining and detecting diarrheagenic Escherichia coli pathotypes. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 33, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, F.; Svennerholm, A.M.; Faruque, A.S.; Sack, R.B. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in developing countries: Epidemiology, microbiology, clinical features, treatment, and prevention. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Keck, J.; Ram, P.K.; Crump, J.A.; Miller, M.A.; Mintz, E.D. Part III. Analysis of data gaps pertaining to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infections in low and medium human development index countries, 1984–2005. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Kim, S.W. Intestinal challenge with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in pigs, and nutritional intervention to prevent postweaning diarrhea. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 3, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, J.D.; Isaacson, R.E.; Schifferli, D.M. Animal Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7, 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0006-2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierick, M.; Van der Weken, H.; Rybarczyk, J.; Vanrompay, D.; Devriendt, B.; Cox, E. Porcine and Bovine Forms of Lactoferrin Inhibit Growth of Porcine Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Degrade Its Virulence Factors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00524-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratto, A.; Torricelli, M.; Sebastiani, C.; Ciullo, M.; Felici, A.; Biagetti, M. Survey on resistance occurrence for F4(+) and F18(+) enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) among pigs reared in Central Italy regions. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.L.; Li, Q.; Burrough, E.R.; Kenne, D.; Sahin, O.; Gould, S.A.; Patience, J.F. Effects of an F18 enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli challenge on growth performance, immunological status, and gastrointestinal structure of weaned pigs and the potential protective effect of direct-fed microbial blends. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Ji, P. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection of weaned pigs: Intestinal challenges and nutritional intervention to enhance disease resistance. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 885253–885267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Cai, S.; Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Huang, S.; Li, N.; Liu, H.; Ding, X.; et al. Therapeutic administration of the recombinant antimicrobial peptide microcin J25 effectively enhances host defenses against gut inflammation and epithelial barrier injury induced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1018–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Yin, J.; Xiao, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, G.; Tan, B.; Li, N.; Peng, Y.; Li, T.; Zeng, B.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota-Derived GABA Mediates Interleukin-17 Expression during Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infection. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresse, R.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Fleury, M.A.; Van de Wiele, T.; Forano, E.; Blanquet-Diot, S. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in Postweaning Piglets: Understanding the Keys to Health. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 851–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekagul, A.; Tangcharoensathien, V.; Yeung, S. Patterns of antibiotic use in global pig production: A systematic review. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2019, 7, 100058–100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekhlas, D.; Sanjuán, J.M.O.; Manzanilla, E.G.; Leonard, F.C.; Argüello, H.; Burgess, C.M. Comparison of antimicrobial resistant Escherichia coli isolated from Irish commercial pig farms with and without zinc oxide and antimicrobial usage. Gut Pathog. 2023, 15, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimpețeanu, O.M.; Pogurschi, E.N.; Popa, D.C.; Dragomir, N.; Drăgotoiu, T.; Mihai, O.D.; Petcu, C.D. Antibiotic Use in Livestock and Residues in Food-A Public Health Threat: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun-Mei, E.; Zeng, J.M.; Yuan, H.; Lu, Y.; Cai, R.X.; Chen, C. Sub-inhibitory concentrations of fluoroquinolones increase conjugation frequency. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.R.; D’Argenio, D.A.; MacCoss, M.J.; Zhang, Z.; Jones, R.A.; Miller, S.I. Aminoglycoside antibiotics induce bacterial biofilm formation. Nature 2005, 436, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Microbiological effects of sublethal levels of antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; An, F.; Zhang, T.; Lou, M.; Guo, J.; Liu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, R. Antimicrobial peptides: An alternative to traditional antibiotics. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 265, 116072–116089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque-Borda, C.A.; Primo, L.; Medina-Alarcón, K.P.; Campos, I.C.; Nascimento, C.F.; Saraiva, M.M.S.; Berchieri Junior, A.; Fusco-Almeida, A.M.; Mendes-Giannini, M.J.S.; Perdigão, J.; et al. Antimicrobial Peptides: A Promising Alternative to Conventional Antimicrobials for Combating Polymicrobial Biofilms. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2410893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, Z.; Kumar, A.; Raje, M.; Raje, C.I. Antimicrobial peptides: An alternative strategy to combat antimicrobial resistance. Drug Discov. Today 2025, 30, 104305–104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Li, J.; Yao, Z.; Li, M. A review on the alternatives to antibiotics and the treatment of antibiotic pollution: Current development and future prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171757–171774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hao, W.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, J.; Deng, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Antimicrobial peptides, conventional antibiotics, and their synergistic utility for the treatment of drug-resistant infections. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1377–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; He, Y.; Ye, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, H.; Xu, N.; Liang, S. Little Antimicrobial Peptides with Big Therapeutic Roles. Protein Pept. Lett. 2019, 26, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, F.; Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Xie, C.; Zhang, J.; Thacker, P.A.; Qiao, S. Effects of the antimicrobial peptide cecropin AD on performance and intestinal health in weaned piglets challenged with Escherichia coli. Peptides 2012, 35, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cao, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Antimicrobial peptide KR-32 alleviates Escherichia coli K88-induced fatty acid malabsorption by improving expression of fatty acid transporter protein 4 (FATP4)1. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 2342–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Huang, S.; Jiang, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G.; Huang, J. Porcine β-Defensin 114: Creating a Dichotomous Response to Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Luo, Y.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; He, J. NF-κB-dependent induction of porcine β-defensin 114 regulates intestinal epithelium homeostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Timonet, A.; Castillo-Martín, M.; Pereira, B.A.; Pinart, E.; Bonet, S.; Yeste, M. Evaluation of porcine beta defensins-1 and -2 as antimicrobial peptides for liquid-stored boar semen: Effects on bacterial growth and sperm quality. Theriogenology 2018, 111, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, A.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Zhou, R. Porcine β-defensin 2 confers enhanced resistance to swine flu infection in transgenic pigs and alleviates swine influenza virus-induced apoptosis possibly through interacting with host SLC25A4. Antivir. Res. 2022, 201, 105292–105302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Gao, C.Y.; Xiao, C.B.; Li, C.L. Preparation of polyclonal antibody against porcine beta defensin 2 and identification of its distribution in tissues of pig. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 18863–18871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldhuizen, E.J.; Rijnders, M.; Claassen, E.A.; van Dijk, A.; Haagsman, H.P. Porcine beta-defensin 2 displays broad antimicrobial activity against pathogenic intestinal bacteria. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, A.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ivanova, I.V.; He, X.; Zhang, B.; Song, W. High-level expression, purification and characterisation of porcine β-defensin 2 in Pichia pastoris and its potential as a cost-efficient growth promoter in porcine feed. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5487–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Qi, Y.; Wang, A.; Huang, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, R. Porcine β-defensin 2 inhibits proliferation of pseudorabies virus in vitro and in transgenic mice. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Xu, L.; Shi, B.; Deng, H.; Lai, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z. Oral administration of synthetic porcine beta-defensin-2 improves growth performance and cecal microbial flora and down-regulates the expression of intestinal toll-like receptor-4 and inflammatory cytokines in weaned piglets challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, H.; Xia, X.; Xiong, H.; Song, D.; Zong, X.; Wang, Y. Porcine β-defensin 2 attenuates inflammation and mucosal lesions in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1882–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, A.; Xie, L.; Song, W.; Wang, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, D.; Li, F. Use of recombinant porcine β-defensin 2 as a medicated feed additive for weaned piglets. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26790–26797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Gu, M.; Zhan, F.; Cai, H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, K.; Li, C. Porcine beta defensin 2 attenuates inflammatory responses in IPEC-J2 cells against Escherichia coli via TLRs-NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lian, S.; Shen, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, C. Recombinant porcine beta defensin 2 alleviates inflammatory responses induced by Escherichia coli in IPEC-J2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Jin, H.; Huang, Q.; Li, L.; Zhou, R. Porcine Beta-Defensin 2 Provides Protection Against Bacterial Infection by a Direct Bactericidal Activity and Alleviates Inflammation via Interference With the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, A.; Huang, C.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q.; et al. Pigs Overexpressing Porcine β-Defensin 2 Display Increased Resilience to Glaesserella parasuis Infection. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, Y.T.; Tan, M.F.; Zhang, H.W.; Liu, W.Q.; Zou, G.; Zhang, L.S.; Zhang, C.Y.; Deng, S.M.; Yu, L.; et al. Overexpression of Porcine Beta-Defensin 2 Enhances Resistance to Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae Infection in Pigs. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 2836–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, A.; Huang, C.; Sun, Y.; Song, B.; Zhou, R.; Li, L. Generation of Marker-Free pbd-2 Knock-in Pigs Using the CRISPR/Cas9 and Cre/loxP Systems. Genes 2020, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Jiang, C. Antimicrobial peptides: Structure, mechanism, and modification. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 255, 115377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, S.; Turton, K.L.; Kainth, T.; Kumar, A.; Wieden, H.J. Strategies for improving antimicrobial peptide production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 59, 107968–107984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Qian, P.; Gao, D.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Ji, H.; Wang, S.; Li, X. Characterization and genomics analysis of phage PGX1 against multidrug-resistant enterotoxigenic E. coli with in vivo and in vitro efficacy assessment. Anim. Dis. 2024, 4, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schägger, H. Tricine-SDS-PAGE. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senbagam, D.; Gurusamy, R.; Senthilkumar, B. Physical chemical and biological characterization of a new bacteriocin produced by Bacillus cereus NS02. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 6, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yao, Z.; Qiu, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, T.; et al. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is a predominant pathotype in healthy pigs in Hubei Province of China. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxad260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledwaba, S.E.; Costa, D.V.S.; Bolick, D.T.; Giallourou, N.; Medeiros, P.; Swann, J.R.; Traore, A.N.; Potgieter, N.; Nataro, J.P.; Guerrant, R.L. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli Infection Induces Diarrhea, Intestinal Damage, Metabolic Alterations, and Increased Intestinal Permeability in a Murine Model. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 595266–595283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Yan, Y.; Huang, J.; Yin, B.; Pan, Y.; Ma, L. Cortex Phellodendri extract’s anti-diarrhea effect in mice related to its modification of gut microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109720–109731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.W.; Tian, S.X.; Gao, W.; Yang, N.; Qu, P.; Liu, D.; Jiao, J.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.J. Recombinant expression and biological characterization of the antimicrobial peptide fowlicidin-2 in Pichia pastoris. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Song, X.Y.; Huang, X.X.; Zhao, W.D. Molecular cloning, expression and characterization of the porcine β defensin 2 in E. coli. Protein Pept. Lett. 2013, 20, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Cui, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Liu, L. Expression and antimicrobial activity of the recombinant bovine lactoferricin in Pichia pastoris. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2024, 9, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Jiang, H.; Si, X.; Xin, Q.; Meng, D.; Chen, P.; Mao, X. Boosting expression level of plectasin in recombinant Pichia pastoris via 2A self-processing peptide assembly. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 3669–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Shan, H.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Qin, Z. High expression of antimicrobial peptides cathelicidin-BF in Pichia pastoris and verification of its activity. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1153365–1153374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, N.; Teng, D.; Mao, R.; Hao, Y.; Wang, J. Expression and characterization of the new antimicrobial peptide AP138L-arg26 anti Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Gong, G.; Pan, J.; Han, S.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Xie, L. High level expression and purification of recombinant human serum albumin in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2018, 147, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.X.; Gao, C.Y.; Zhao, Q.J.; Li, C.L. Antimicrobial characterization of site-directed mutagenesis of porcine beta defensin 2. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeck, V.; Cox, E.; Verdonck, F.; Joensuu, J.J.; Goddeeris, B.M. Influence of porcine intestinal pH and gastric digestion on antigenicity of F4 fimbriae for oral immunisation. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 98, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisetta, G.; Di Luca, M.; Esin, S.; Florio, W.; Brancatisano, F.L.; Bottai, D.; Campa, M.; Batoni, G. Evaluation of the inhibitory effects of human serum components on bactericidal activity of human beta defensin 3. Peptides 2008, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, T.; Zhan, N.; Sun, T.; Shan, A. Effects of the antimicrobial peptide WK3 on diarrhea, growth performance and intestinal health of weaned piglets challenged with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88. Food Nutr. Res. 2021, 65, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yu, H.; Qiao, S. Lasso Peptide Microcin J25 Effectively Enhances Gut Barrier Function and Modulates Inflammatory Response in an Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Challenged Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Zong, X.; Jin, M.; Min, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. Mechanisms and regulation of defensins in host defense. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 300–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y. Recombinant expression of porcine lactoferrin peptide LF-6 with intein technology and its immunomodulatory function in ETEC K88-infected mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 39, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Zeng, H.; Hou, M.; Li, Z.; Mu, C.; Zhu, W.; Hang, S. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum L47 and inulin alleviate enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli induced ileal inflammation in piglets by upregulating the levels of α-linolenic acid and 12,13-epoxyoctadecenoic acid. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 14, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, X.; You, J.; Zou, T. A blend of formic acid, benzoic acid, and tributyrin alleviates ETEC K88-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction by regulating intestinal inflammation and gut microbiota in a murine model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 114, 109538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Su, G.; Wu, A.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Mao, X.; Zheng, P.; Yu, J.; et al. Bombyx mori gloverin A2 alleviates enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced inflammation and intestinal mucosa disruption. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Koci, M.; Si, D.; Ahmad, B.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J.; Aihemaiti, M.; Zhang, M. A Novel Cecropin-LL37 Hybrid Peptide Protects Mice Against EHEC Infection-Mediated Changes in Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Inflammation, and Impairment of Mucosal Barrier Functions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Fu, Q.; Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, D.; Mao, X.; Yu, B.; Zheng, P.; Huang, Z.; et al. Human β-Defensin 118 Attenuates Escherichia coli K88-Induced Inflammation and Intestinal Injury in Mice. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| PBD2F | GCTAAAGAAGAAGGGGTATCTCTCGAGAAAAGAATTAACTTGTTGACTGGTTTG |
| PBD2R | TCAATGATGATGATGATGATGGTCGACTTATCTGATACAGCACTTGGCCTT |
| 5′AOX1 | GACTGGTTCCAATTGACAAGC |
| 3′AOX1 | GCAAATGGCATTCTGACATCC |
| Categories | Genus | Strains | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-negative bacteria | Escherichia | E. coli ETEC7 | 88.71 ± 0.45 |
| E. coli ETEC17 | 90.15 ± 0.45 | ||
| E. coli ETEC20 | 89.83 ± 0.60 | ||
| E. coli EPEC28 | 92.16 ± 0.38 | ||
| E. coli EPEC48 | 91.95 ± 0.30 | ||
| E. coli EPEC66 | 91.57 ± 0.26 | ||
| E. coli EPEC133 | 89.52 ± 0.56 | ||
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 83.03 ± 0.94 | ||
| E. coli 72 | 91.15 ± 0.46 | ||
| E. coli PCN033 | 90.26 ± 0.64 | ||
| Salmonella | S. typhimurium ATCC 14028 | 88.46 ± 0.31 | |
| S. typhimurium CVCC 542 | 89.07 ± 0.72 | ||
| S. typhimurium CVCC 212197 | 89.10 ± 0.94 | ||
| S. pullorum C79-13 | 77.44 ± 0.52 | ||
| Pasteurella | P. multocida 9261 | 78.48 ± 2.57 | |
| P. multocida HB03 | 75.44 ± 0.30 | ||
| Actinobacillus | A. pleuropneumoniae 4074 | 82.84 ± 0.84 | |
| Gram-positive bacteria | Staphylococcus | S. aureus ATCC 29213 | 88.56 ± 0.54 |
| S. aureus 1213M4A | 82.51 ± 1.43 | ||
| Streptococcus | S. suis SC19 | 77.47 ± 0.72 | |
| S. suis 0810 | 66.31 ± 1.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhuo, W.; Li, T.; Jiang, T.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, R. Porcine β-Defensin 2 Expressed in Pichia pastoris Alleviates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Intestinal Injury and Inflammatory Response in Mice. Animals 2025, 15, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101389
Wang S, Li H, Huang Y, Zhuo W, Li T, Jiang T, Huang Q, Zhou R. Porcine β-Defensin 2 Expressed in Pichia pastoris Alleviates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Intestinal Injury and Inflammatory Response in Mice. Animals. 2025; 15(10):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101389
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuaiyang, Huaixia Li, Yaxue Huang, Wenxiao Zhuo, Tingting Li, Tingting Jiang, Qi Huang, and Rui Zhou. 2025. "Porcine β-Defensin 2 Expressed in Pichia pastoris Alleviates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Intestinal Injury and Inflammatory Response in Mice" Animals 15, no. 10: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101389
APA StyleWang, S., Li, H., Huang, Y., Zhuo, W., Li, T., Jiang, T., Huang, Q., & Zhou, R. (2025). Porcine β-Defensin 2 Expressed in Pichia pastoris Alleviates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Intestinal Injury and Inflammatory Response in Mice. Animals, 15(10), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15101389





