Morphology of Larger Salivary Glands in Peccaries (Pecari tajacu Linnaeus, 1758)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Location and Collection of Material
2.2. Euthanasia Protocol
2.3. Macroscopic Analysis
2.4. Microscopic Analysis
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Macroscopic Studies
3.1.1. Parotid Gland
3.1.2. Mandibular Gland
3.1.3. Sublingual Gland
3.2. Microscopic Studies
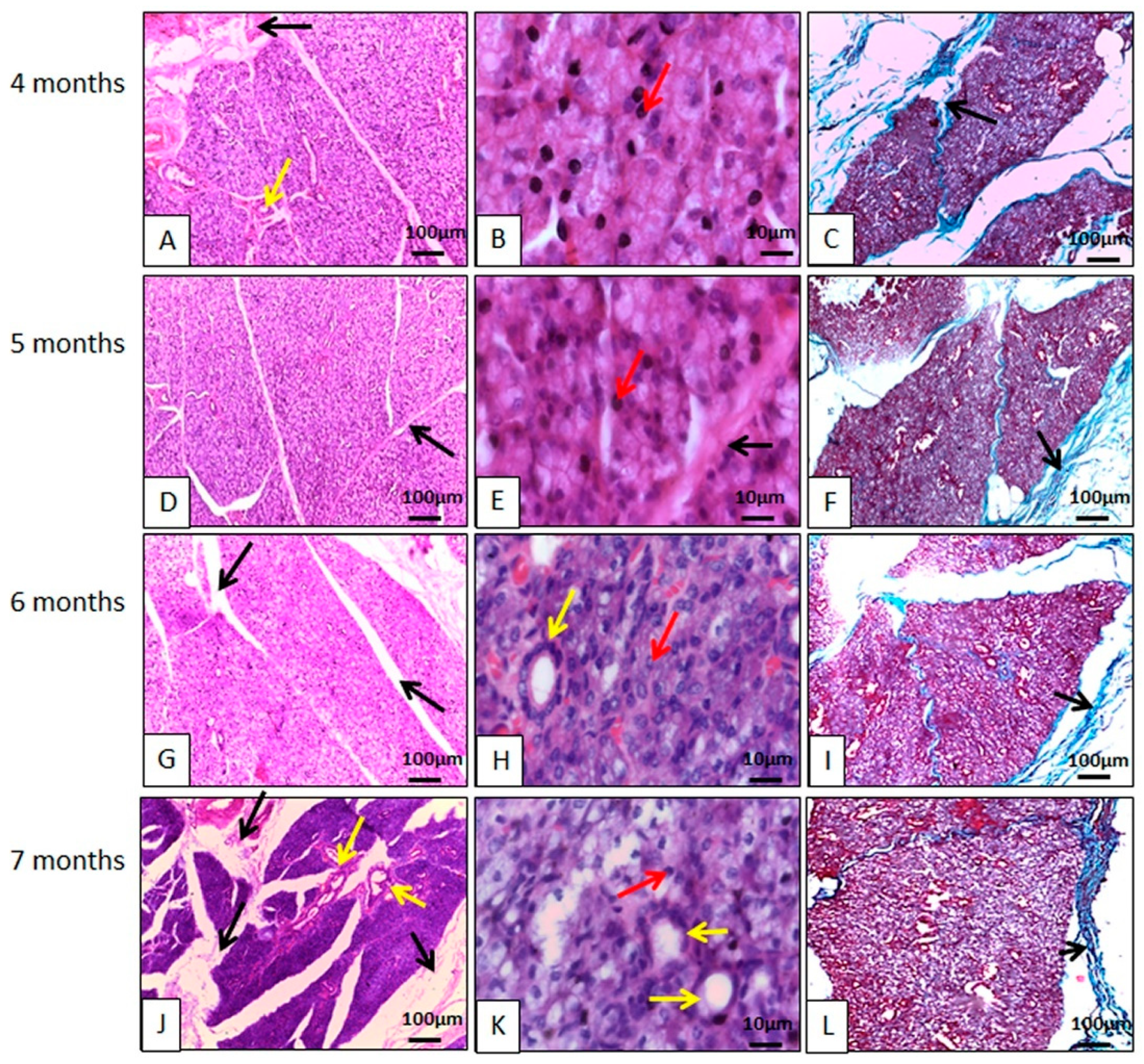
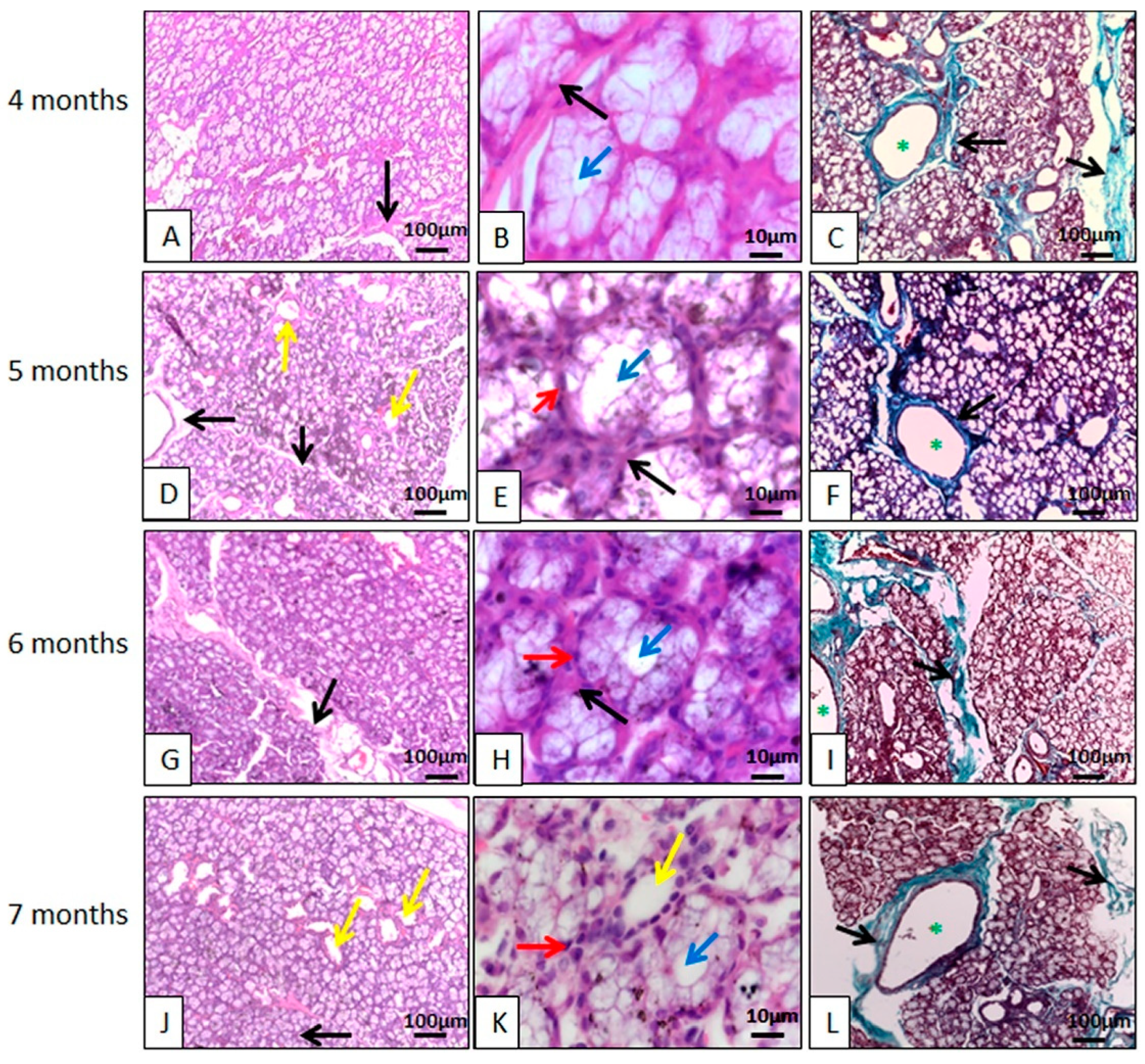
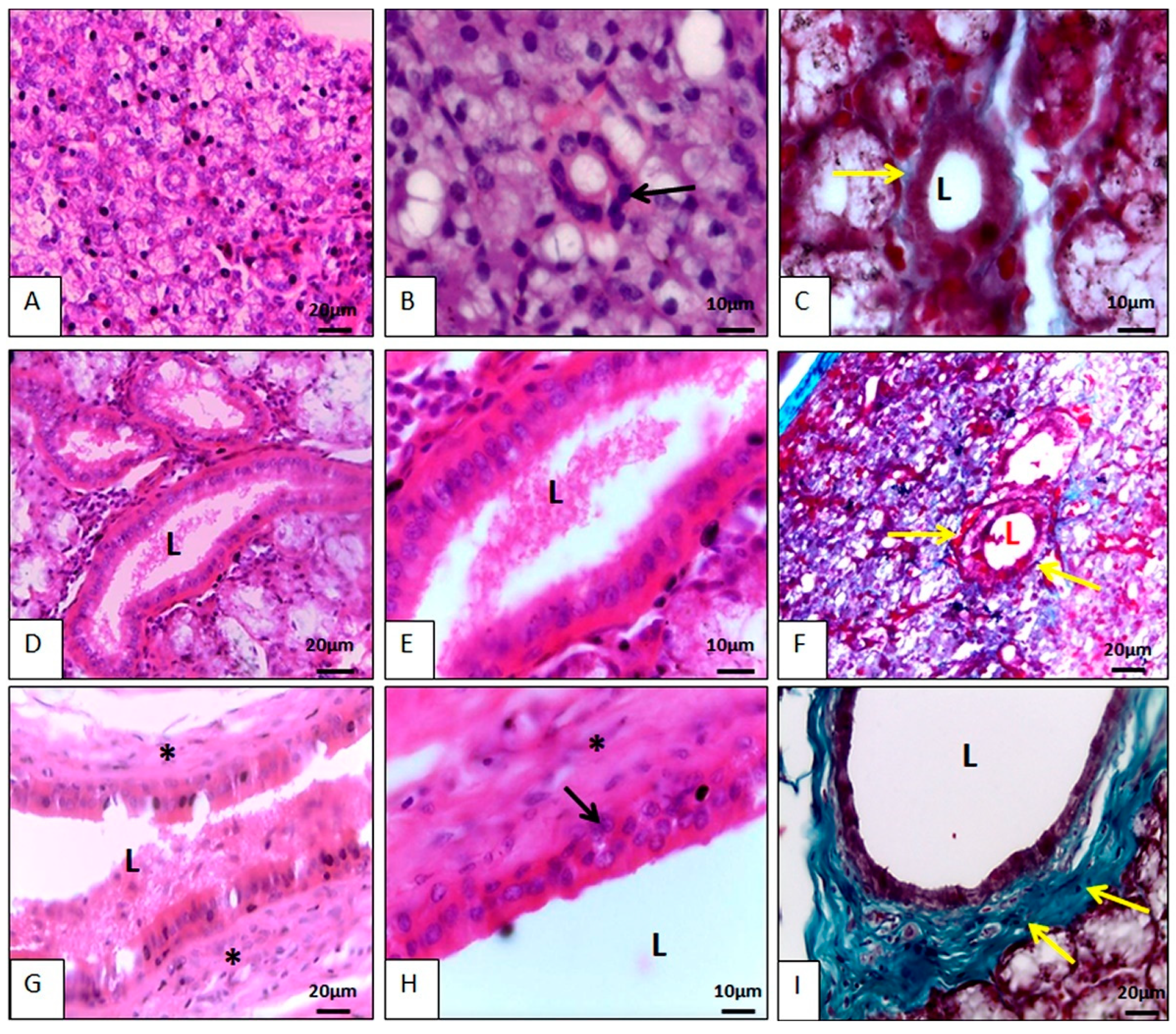
3.2.1. Histology
Parotid Gland Microscopy
Mandibular Gland Microscopy
Sublingual Gland Microscopy
Salivary Gland Duct Microscopy
3.3. Histochemistry
3.3.1. Parotid Gland Histochemistry
3.3.2. Mandibular Gland Histochemistry
3.3.3. Sublingual Histochemistry
3.4. Immunohistochemistry
3.4.1. Parotid Gland Immunohistochemistry
3.4.2. Mandibular Gland Immunohistochemistry
3.4.3. Sublingual Glands Immunohistochemistry
3.5. Electron Microscopy
3.5.1. Parotid Gland Electron Microscopy
3.5.2. Mandibular Gland Electron Microscopy
3.5.3. Sublingual Glands Electron Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pedersen, A.M.; Bardow, A.; Jensen, S.B.; Nauntofte, B. Saliva and Gastrointestinal Functions of Taste, Mastication, Swallowing, and Digestion. Oral Dis. 2002, 8, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavri, G.; Škrlep, M.; Rutland, C.S.; Potočnik, B.; Batorek-Lukač, N.; Kubale, V. Salivary Gland Adaptation to Dietary Inclusion of Hydrolysable Tannins in Boars. Animals 2022, 12, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, P.; Hagen, F.K.; Hardt, M.; Liao, L.; Yan, W.; Arellanno, M.; Bassilian, S.; Bedi, G.S.; Boontheung, P.; Cociorva, D.; et al. The proteomes of human parotid and submandibular/sublingual gland salivas collected as the ductal secretions. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 1994–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira Júnior, C.M.; Bezerra, F.V.F.; Câmara, F.V.; Vale, A.M.; Oliveira, G.B.; Silva, A.R.; Ambrosio, C.E.; Oliveira, M.F. Morfologia das glândulas salivares maiores em cutias (Dasyprocta leporina Linnaeus, 1766). Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2016, 36, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poddar, S.; Jacob, S. Gross and Microscopic Anatomy of the Major Salivary Glands of the Ferret. Acta Anat. 1977, 98, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Song, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S. Histological and ultrastructural characterization of developing miniature pig salivary glands. Anat. Rec. 2010, 293, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.J.; Tandler, B. Mammalian evolution at the cellular level. In Current Mammalogy; Genoways, H.H., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 38–53. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, C.J.; Tandler, B.; Nagato, T. Evolutionary divergence of salivary gland acinar cells: A format for understanding molecular evolution. In Biology of the Salivary Glands; Dobrosielski-Vergona, K., Ed.; CRS Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 39–80. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.J.; Bae, C.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Choi, B.D.; Yoon, M.H.; Jeong, M.J. Comparative ultrastructure of secretory granules of the submandibular gland in the Korean Spider Shrew, Sorex caecutiens, the Lesser White-toothed Shrew, Crocidura suaveolens and the Big White-toothed Shrew, Crocidura lasiura. Appl. Microsc. 2012, 42, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maša, M.; Čandek-Potokar, M.; Fazarinc Jeong, S.J.; Jeong, M.J. Ultrastructure of acinar secretory granules of submandibular and parotid salivary gland in the Korean striped field mouse, Apodemus agrarius (Rodentia, Murinae). Appl. Microsc. 2017, 47, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sowls, L.K. Javelinas and Other Peccaries: Their Biology, Management and Use, 2nd ed.; University of Texas Press: Austin, TX, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, L.E.; Garbino, G.S.T.; Gasparini, G.M.; Dutra, R.P. Unraveling the Nomenclatural Puzzle of the Collared and White-Lipped Peccaries (Mammalia, Cetartiodactyla, Tayassuidae). Zootaxa 2020, 4851, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deustch, L.A.; Puglia, L.R.P. Os Animais Silvestres: Proteção, Doenças e Manejo; Globo: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Scherle, W. A simple method for volumetry of organs in quantitative stereology. Mikroskopie 1970, 26, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Tolosa, E.M.C.; Rodrigues, C.J.; Behemer, O.A.; Freitas-Neto, A.G. Manual de Técnicas para Histologia Normal e Patológica, 2nd ed.; Manole: São Paulo, Brazil, 2003; p. 241. [Google Scholar]
- Çınar, K.; Öztop, M.; Özkarasu, B. Glycoconjugate composition of ovine parotid glands elucidated by lectins. J. Morphol. Sci. 2016, 33, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikpegbu, E.; Nlebedum, U.; Nnadozie, O.; Agbakwuru, I. Histology of the Parotid Salivary Gland of the African Squirrel Palm (Epixerus ebii). Rev. Fac. Cienc. Vet. Univ. Cent. Venez. 2013, 54, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, K.F.; Souza, D.R.; Ferreira, L.S.; Chela, P.R.; Helrigle, C.; Araújo, E.G. Morphological aspects of the salivary glands of Crab-eating racoon (Procyon cancrivorus). Acta Scientiarum. Biol. Sci. 2013, 35, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S. Morphological characteristics of submandibular glands of miniature pig. Chin. Med. J. 2005, 118, 1368–1373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, T.S.B.; Faria Júnior, W.H.D.; Ferreira, J.S.; Carvalho, C.C.D.; Marques, V.B. Macroscopic and microscopic characterization of the parotid gland in capybara (Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris, Linnaeus, 1766). Rev. Bras. Hig. Sanidade Anim. 2019, 13, 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarm, A.; Ortmann, S.; Wolf, C.; Streich, W.J.; Clauss, M. Passage marker excretion in red kangaroo (Macropus rufus), collared peccary (Pecari tajacu) and colobine monkeys (Colobus angolensis, C. polykomos, Trachypithecus johnii). J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2009, 311, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshell, J.L.; Wilborn, W.H. Histology and ultrastructure of the pig parotid gland. Am. J. Anat. 1978, 152, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, P.K.; Parkash, T.; Singh, A. Morphological analysis of parotid salivary gland of pig (Sus scrofa). Haryana Vet. J. 2021, 60, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Štembírek, J.; Kyllar, M.; Putnová, I.; Stehlík, L.; Buchtová, M. The pig as an experimental model for clinical craniofacial research. Lab. Anim. 2012, 46, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.S.B.; Silva, A.L.D.A.; Cruvinel, T.M.D.A.; Passarelli, P.M.; Loureiro, M.E.R.; Marques, V.B. Anatomical characteristics of the major salivary glands of puma (Puma concolor Linnaeus, 1771). Cienc. Anim. Bras. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, W.J. Microscopy of the koala mandibular (Submandibular) glands. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2010, 39, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.C.; Oliveira, V.C.; Viana, D.C.; Lobo, L.M.; Ambrósio, C.E.; Assis-Neto, A.C.; Carvalho, A.F.; Mançanares, C.A.F. Análise microscópica e ultraestrutural das glândulas salivares mandibulares de Procyon cancrivorus. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2013, 33, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.J.; Ferris, R.L. Surgery for Malignant Sublingual and Minor Salivary Gland Neoplasms. Adv. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2016, 78, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Dellmann, H.D.; Eurell, J.A. Digestive System. In Text Book of Veterinary Histology, 5th ed.; William and Wilkins: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan, S.; Basha, S.H.; Ramesh, G.; Ushakumary; Rajathi, S.; Kumaravel, A. Histomorphology of parotid salivary gland in sheep (Ovis aries). Indian J. Vet. Anat. 2013, 25, 92–93. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.D.; Sasan, J.S.; John, M.A.; Choudhury, A.R. Gross and microscopic characterization of the parotid salivary gland of sheep. Indian Vet. J. 2015, 92, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.D.; Singh, O. Prenatal and neonatal development of mandibular salivary gland of Indian buffalo. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2017, 45, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.H.; Atri, A. Ultrastructure of parotid and mandibular glands of camel (Camelus dromedarius). J. Appl. Anim. Res. 1994, 6, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, V.V.; Nogueira, J.C. Histology and mucosubstance histochemistry of the parotid gland in suckling, prepuberal and puberal zebus (Bos indicus). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2007, 10, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentle, R.G.; Hume, I.D.; Kennedy, M.S.; Stafford, K.J.; Potter, M.A.; Springett, B.P.; Haslett, S. The histology and morphometrics of the major salivary glands of four species of wallabies (Marsupialia: Macropodiae) from Kawau Island, New Zealand. J. Zool. Lond. 2002, 257, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.J. Applied Veterinary Histology, 3rd ed.; Mosby Year Book: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, H.; Kanno, T.; Tamamura, R.; Nakada, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Kaneda, T.; Endoh, M.; Wakamatsu, Y.; Suzuki, K. Histological features of the submandibular glands in the gray short-tailed opossum (Monodelphis domestica). J. Hard Tissue Biol. 2014, 23, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.A.; Van Lennep, E.W. The Morphology of Salivary Glands; Academic Press: London, UK, 1978; pp. 129–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K.; Nasjleti, C.E.; Han, S.S. The secretion processes in mucous and serous secretory cells of the rat sublingual gland. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1972, 38, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashina, S.; Tamaki, H.; Katsumata, O. The serous demilune of rat sublingual gland is an artificial structure produced by conventional fixation. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 1999, 62, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shackleford, J.M.; Klapper, C.E. Structure and carbohydrate histochemistry of mammalian salivary glands. Am. J. Anat. 1962, 11, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, J. Lectins for Histochemical Demonstration of Glycans. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 136, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munyala, R.; Liumsiricharoen, M.; Pongket, P.; Prapong, T.; Suprasert, A. Glycoconjugates in the Secretory Epithelium of the Mandibular Salivary Gland of Malayan Pangolin (Manis javanica). J. Vet. Med. 2009, 19, 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- Sobral, A.P.V.; Rego, M.J.B.M.; Cavalacanti, C.L.B.; Carvalho Junior, L.B.; Beltrão, E.I. ConA and UEA-I Lectin Histochemistry of Parotid Gland Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma. J. Oral Sci. 2010, 52, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ikeda, R.; Aiyama, S. Developmental Changes in Sugar Residues and Secretory Protein in Mucous Cell of the Early Postnatal Rat Parotid Gland. Anat. Rec. 1999, 255, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, R.F.T.; Benbow, E.W.; Lofthouse, A.K.; Stoddart, R.W. Human Salivary Gland Glycoconjugates: A Lectin Histochemical Study. Histochem. J. 1989, 21, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnyane, I.K.M.; Wresdiyati, T.; Wibawan, I.W.T.; Winarto, A.; Agungpriyono, S. The Morphological Study of Salivary Gland of the Lesser Mouse Deer (Tragulus javanicus) with Special Reference to the Distribution of Glycoconjugates and Lysozyme. In Proceedings of the AZWMP, Bangkok, Thailand, 26–29 October 2006; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Gargiulo, A.M.; Pedini, V.; Ceccarelli, P. Lectin Histochemistry of Glycoconjugates in Horse Salivary Glands. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 1993, 22, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pícoli, L.C.; Dias, F.J.; Issa, J.P.M.; Ogawa, K.; Ciena, A.; Iyomasa, M.M.; Lopes, R.A.; Watanabe, I. Ultrastructure of submandibular salivary glands of mouse: TEM and HRSEM observations. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2011, 74, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Lecithins | Abbreviation |
Carbohydrate Binding Specificity | Concentration (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canavalia ensiformis | Con-A | αMan > αGlc > αGlcNAc | 0.29 mg/mL |
| Bandeiraea simplicifolia | BSA-I-B4 | αGal > αGalNAc | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Triticum vulgaris | WGA | GlcNAc(β1,4GlcNAc)1–2 > βGlcNAc > Neu5Ac | 0.1 mg/mL |
| Arachis hypogaea | PNA | Galß1,3GalNAc > α and βGal | 0.1 mg/mL |
| Months | Parotid | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Antimere | Left Antimere | |||||||
| L | W | T | WE | L | W | T | WE | |
| 4M | 45.95 | 9.70 | 2.84 | 3.2396 | 45.01 | 10.30 | 2.77 | 2.8311 |
| 4F | 46.11 | 16.37 | 2.19 | 3.6318 | 45.16 | 16.54 | 2.67 | 3.6437 |
| 5F | 41.43 | 18.67 | 3.08 | 5.7121 | 42.97 | 13.70 | 3.48 | 5.0375 |
| 5M | 43.03 | 16.97 | 5.75 | 5.7953 | 43.65 | 15.86 | 3.85 | 5.1178 |
| 6F | 46.24 | 18.95 | 7.80 | 5.6066 | 47.93 | 16.70 | 6.24 | 5.4242 |
| 6M | 53.22 | 14.79 | 6.32 | 5.1561 | 48.70 | 21.07 | 6.53 | 5.2172 |
| 7F | 55.82 | 15.76 | 6.47 | 6.1577 | 48.70 | 21.07 | 6.53 | 5.8981 |
| 7M | 56.95 | 12.52 | 9.53 | 6.1032 | 58.01 | 10.30 | 9.77 | 6.2119 |
| Months | Mandibular | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Antimere | Left Antimere | |||||||
| L | W | T | WE | L | W | T | WE | |
| 4F | 16.85 | 23.60 | 7.12 | 3.6871 | 17.22 | 20.13 | 6.77 | 3.2964 |
| 4M | 14.24 | 25.72 | 8.38 | 3.8879 | 17.90 | 23.70 | 6.02 | 3.9315 |
| 5F | 15.10 | 24.25 | 7.01 | 2.7472 | 15.47 | 26.46 | 7.21 | 2.8340 |
| 5M | 14.76 | 21.29 | 6.74 | 3.0371 | 17.12 | 22.99 | 7.60 | 3.1759 |
| 6F | 25.46 | 17.22 | 6.67 | 2.4162 | 24.90 | 16.44 | 8.48 | 2.3522 |
| 6M | 20.34 | 27.02 | 8.85 | 2.8896 | 18.09 | 23.38 | 8.11 | 3.3432 |
| 7F | 22.53 | 29.21 | 9.85 | 2.5533 | 20.28 | 27.27 | 9.30 | 2.0701 |
| 7M | 20.17 | 27.02 | 8.85 | 2.7839 | 18.09 | 23.38 | 8.46 | 2.9218 |
| Months | Polystomatic Sublingual | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Antimere | Left Antimere | |||||||
| L | W | T | WE | L | W | T | WE | |
| 4F | 35.08 | 5.19 | 2.80 | 0.8186 | 32.33 | 6.44 | 2.55 | 0.6738 |
| 4M | 34.78 | 7.67 | 3.26 | 0.8671 | 26.82 | 6.37 | 2.83 | 0.9401 |
| 5F | 34.62 | 6.33 | 2.29 | 0.8056 | 33.13 | 6.62 | 2.48 | 0.6538 |
| 5M | 23.90 | 7.84 | 2.58 | 0.8396 | 22.01 | 8.52 | 2.64 | 0.9265 |
| 6F | 33.30 | 7.43 | 3.74 | 1.1818 | 32.88 | 7.15 | 3.83 | 1.0788 |
| 6M | 28.52 | 9.04 | 4.23 | 0.8511 | 29.58 | 10.05 | 3.65 | 0.7884 |
| 7F | 31.52 | 8.54 | 4.19 | 1.5468 | 32.55 | 10.11 | 3.44 | 1.7033 |
| 7M | 32.27 | 9.34 | 3.97 | 1.2518 | 31.44 | 9.75 | 3.88 | 1.3398 |
| Months | Monostomatic Sublingual | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Antimere | Left Antimere | |||||||
| L | W | T | WE | L | W | T | WE | |
| 4M | 12.30 | 8.84 | 2.13 | 0.4833 | 12.01 | 7.47 | 2.20 | 0.2764 |
| 4F | 12.25 | 4.91 | 1.27 | 0.3826 | 12.40 | 5.17 | 1.68 | 0.2774 |
| 5F | 16.98 | 7.60 | 3.74 | 0.2685 | 15.64 | 8.78 | 3.54 | 0.4397 |
| 5M | 10.62 | 7.18 | 3.61 | 0.4676 | 11.96 | 6.45 | 4.16 | 0.3986 |
| 6F | 14.14 | 7.61 | 3.06 | 0.3211 | 13.40 | 9.88 | 3.52 | 0.5843 |
| 6M | 17.78 | 8.45 | 3.47 | 0.4725 | 16.34 | 8.76 | 3.11 | 0.5663 |
| 7F | 17.96 | 9.37 | 3.69 | 0.9533 | 17.70 | 9.78 | 3.11 | 0.7434 |
| 7M | 17.38 | 9.48 | 3.47 | 0.7206 | 18.36 | 9.45 | 3.66 | 0.6892 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Júnior, C.M.O.; Júnior, H.N.d.A.; Tertulino, M.D.; Guerra, R.R.; Rola, L.D.; Silva, A.R.d.; Moura, C.E.B.d.; Oliveira, M.F.d. Morphology of Larger Salivary Glands in Peccaries (Pecari tajacu Linnaeus, 1758). Animals 2024, 14, 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14192891
Júnior CMO, Júnior HNdA, Tertulino MD, Guerra RR, Rola LD, Silva ARd, Moura CEBd, Oliveira MFd. Morphology of Larger Salivary Glands in Peccaries (Pecari tajacu Linnaeus, 1758). Animals. 2024; 14(19):2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14192891
Chicago/Turabian StyleJúnior, Carlos Magno Oliveira, Hélio Noberto de Araújo Júnior, Moisés Dantas Tertulino, Ricardo Romão Guerra, Luciana Diniz Rola, Alexandre Rodrigues da Silva, Carlos Eduardo Bezerra de Moura, and Moacir Franco de Oliveira. 2024. "Morphology of Larger Salivary Glands in Peccaries (Pecari tajacu Linnaeus, 1758)" Animals 14, no. 19: 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14192891
APA StyleJúnior, C. M. O., Júnior, H. N. d. A., Tertulino, M. D., Guerra, R. R., Rola, L. D., Silva, A. R. d., Moura, C. E. B. d., & Oliveira, M. F. d. (2024). Morphology of Larger Salivary Glands in Peccaries (Pecari tajacu Linnaeus, 1758). Animals, 14(19), 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14192891






