Metagenomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Role of Gut Microbiome-Associated Metabolites in the Muscle Elasticity of the Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
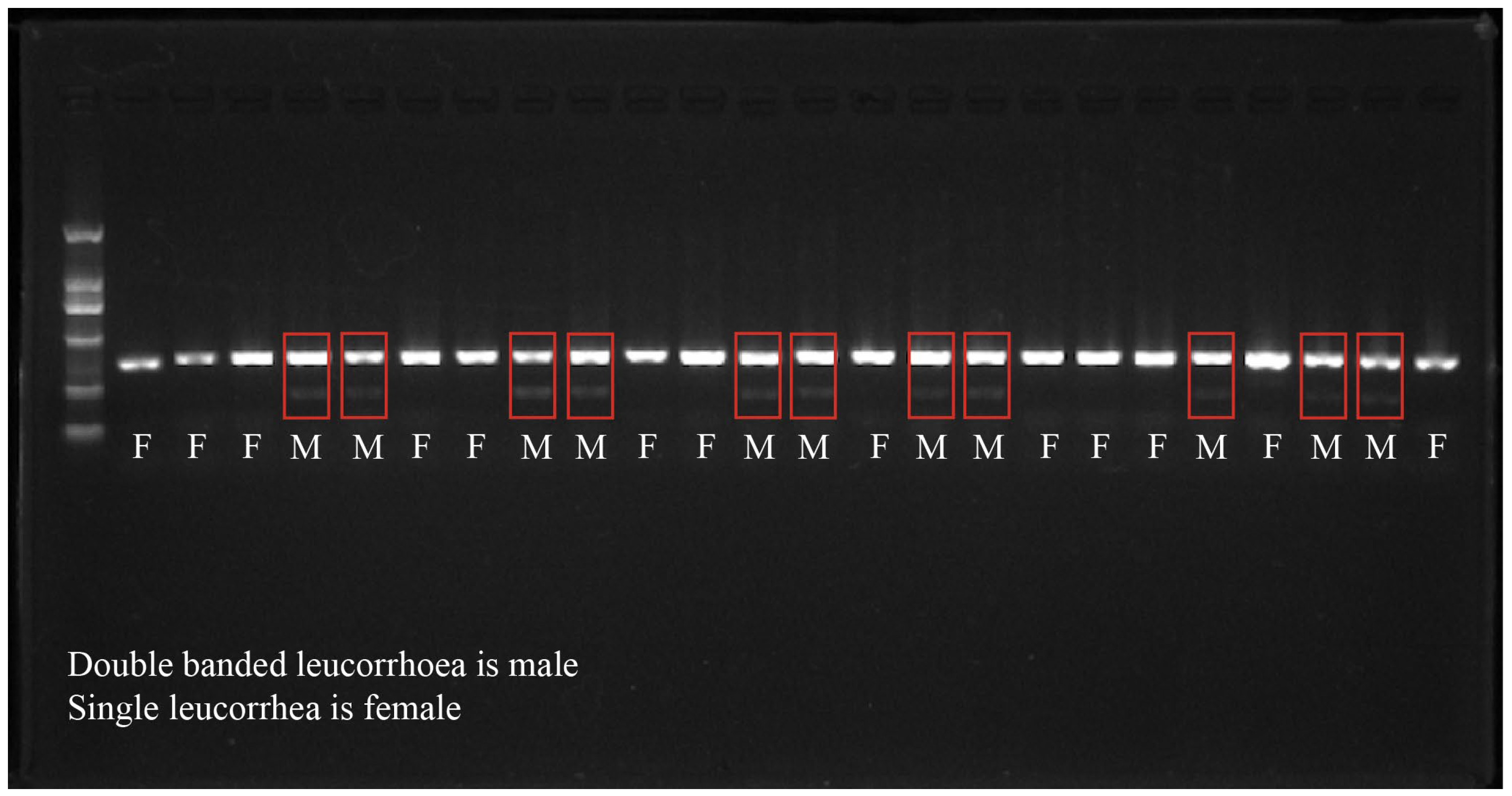
2.2. Sex Identification Method
2.3. Metagenomic Analysis
2.4. Metabolome Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
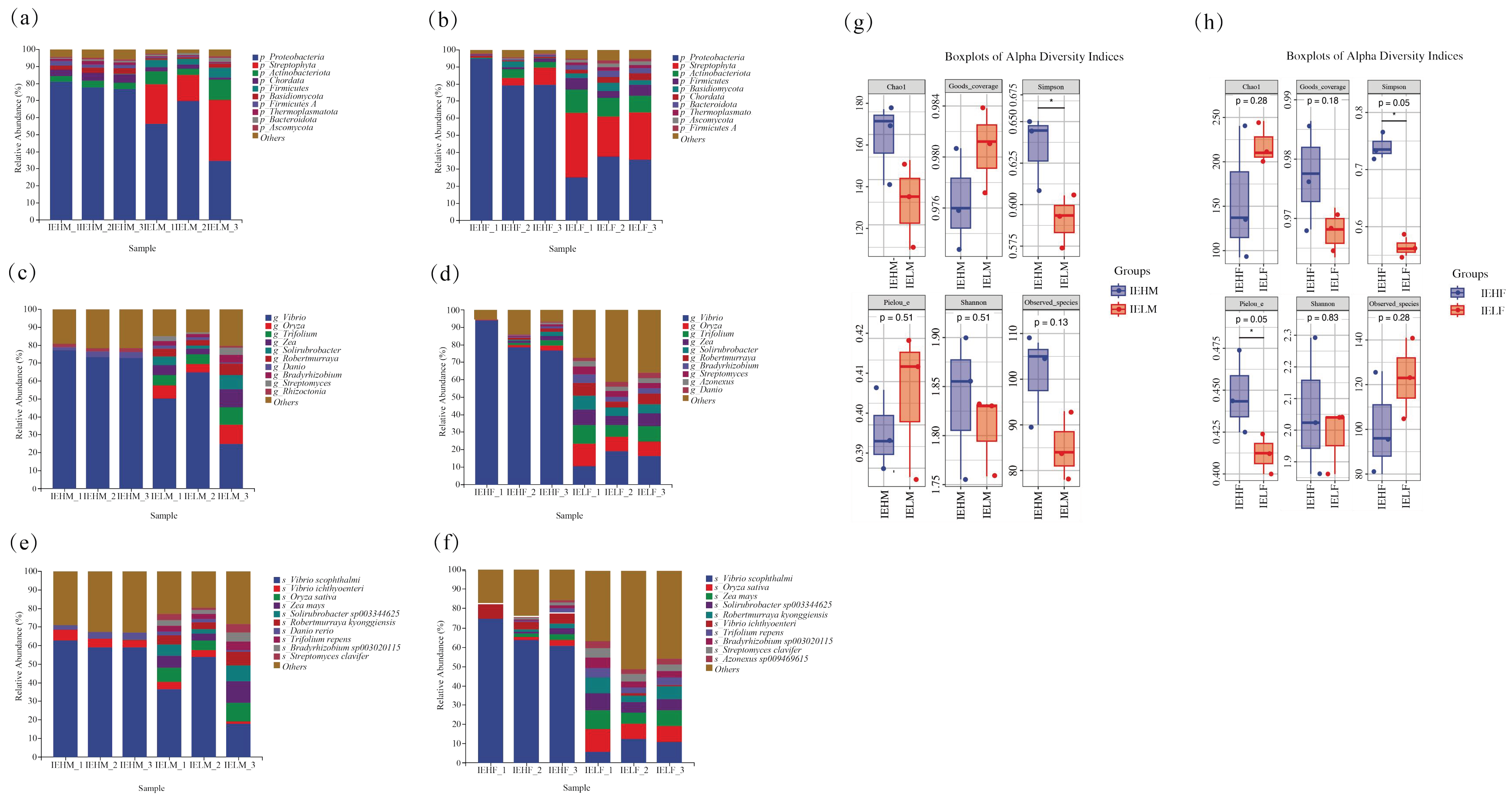
3.1. Composition and Structure of the Intestinal Flora of LYCs
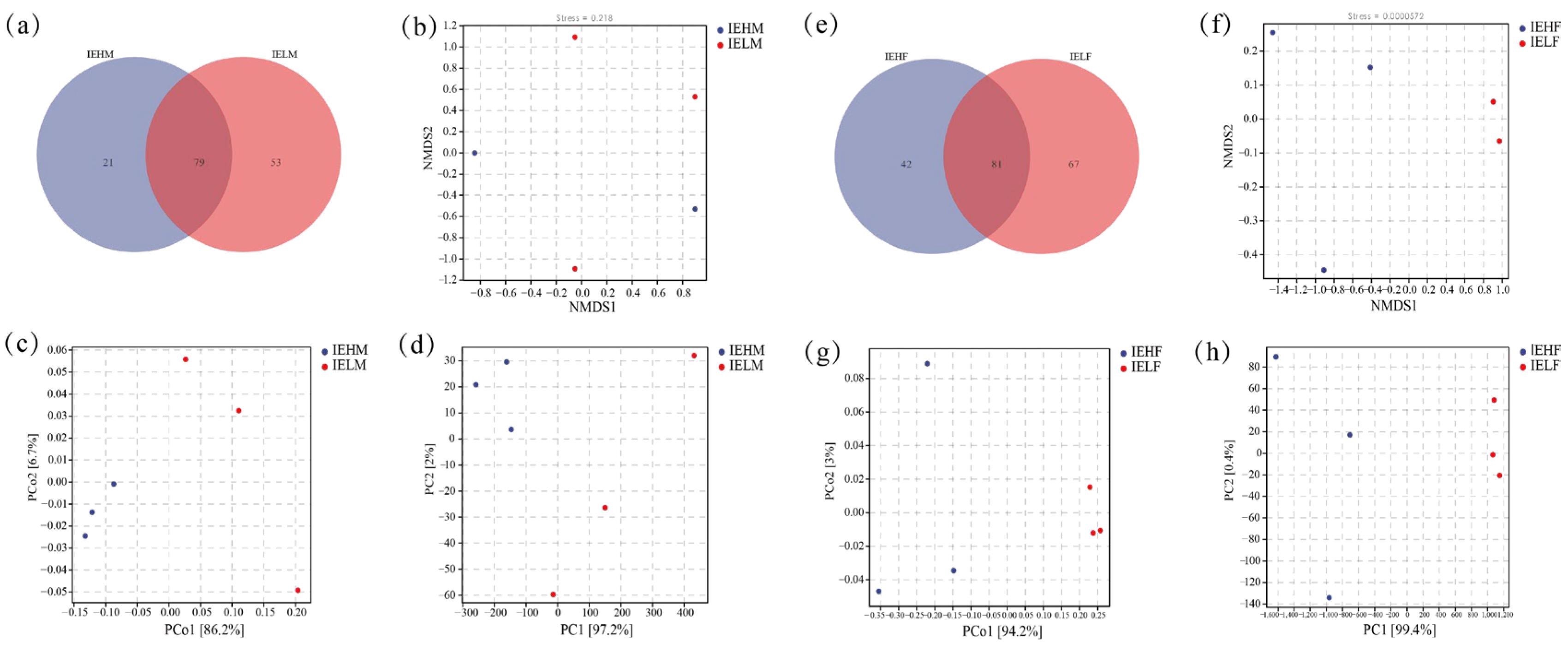
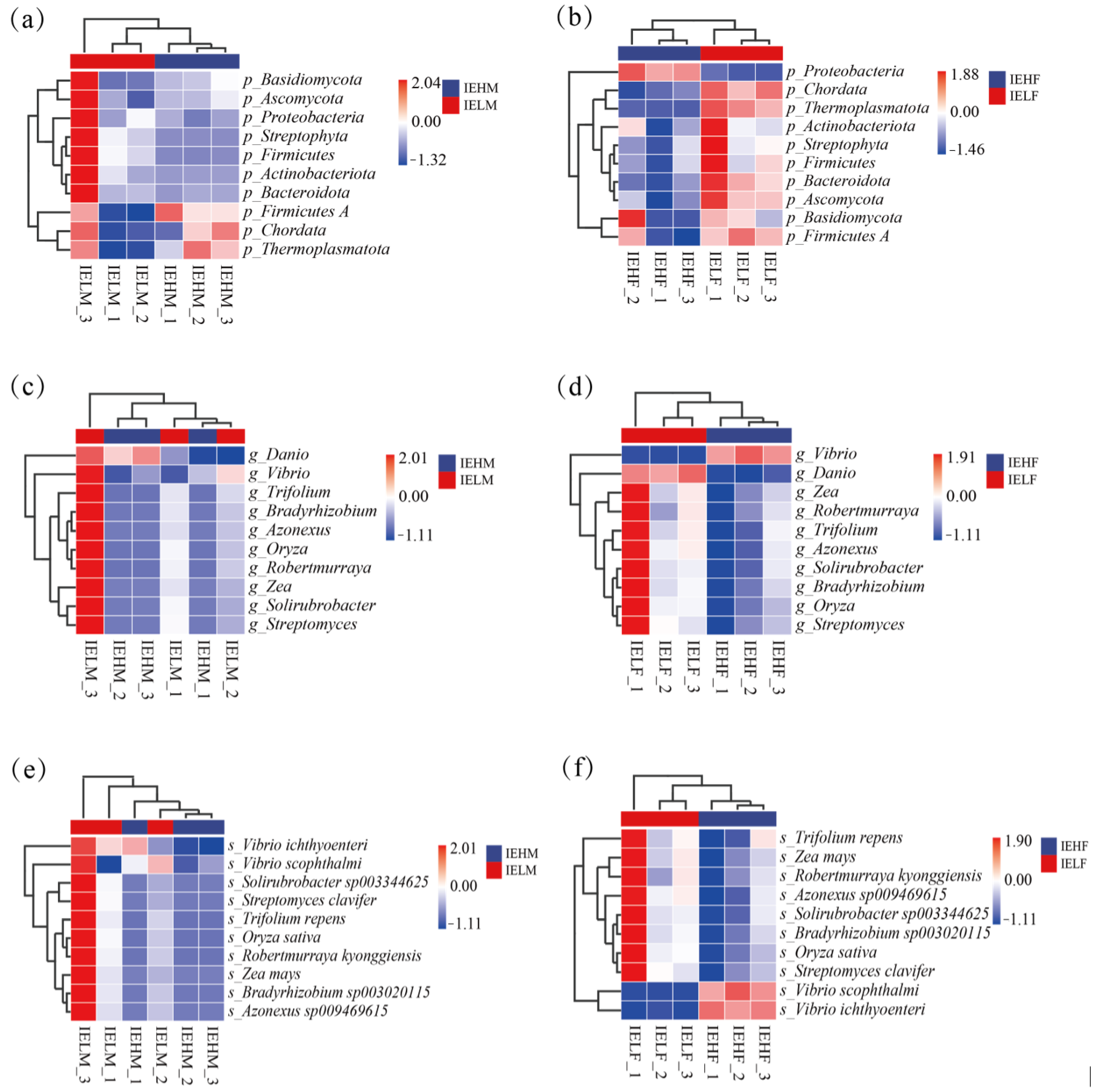
3.2. Analysis of Differences in the Compositional Structure of Intestinal Flora in LYCs with Different Muscle Elasticities
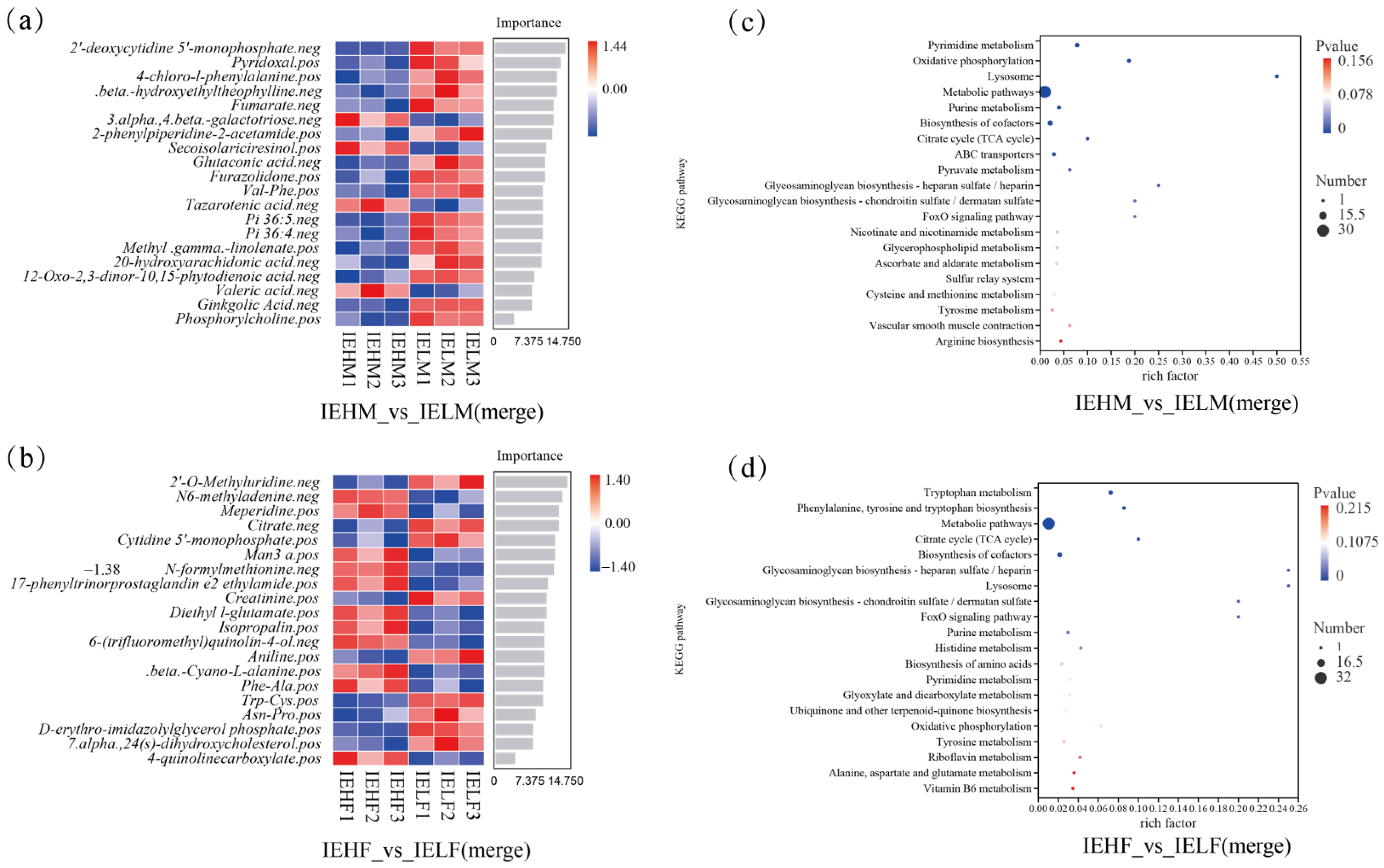
3.3. Metabolite Identification of LYC Intestinal Contents
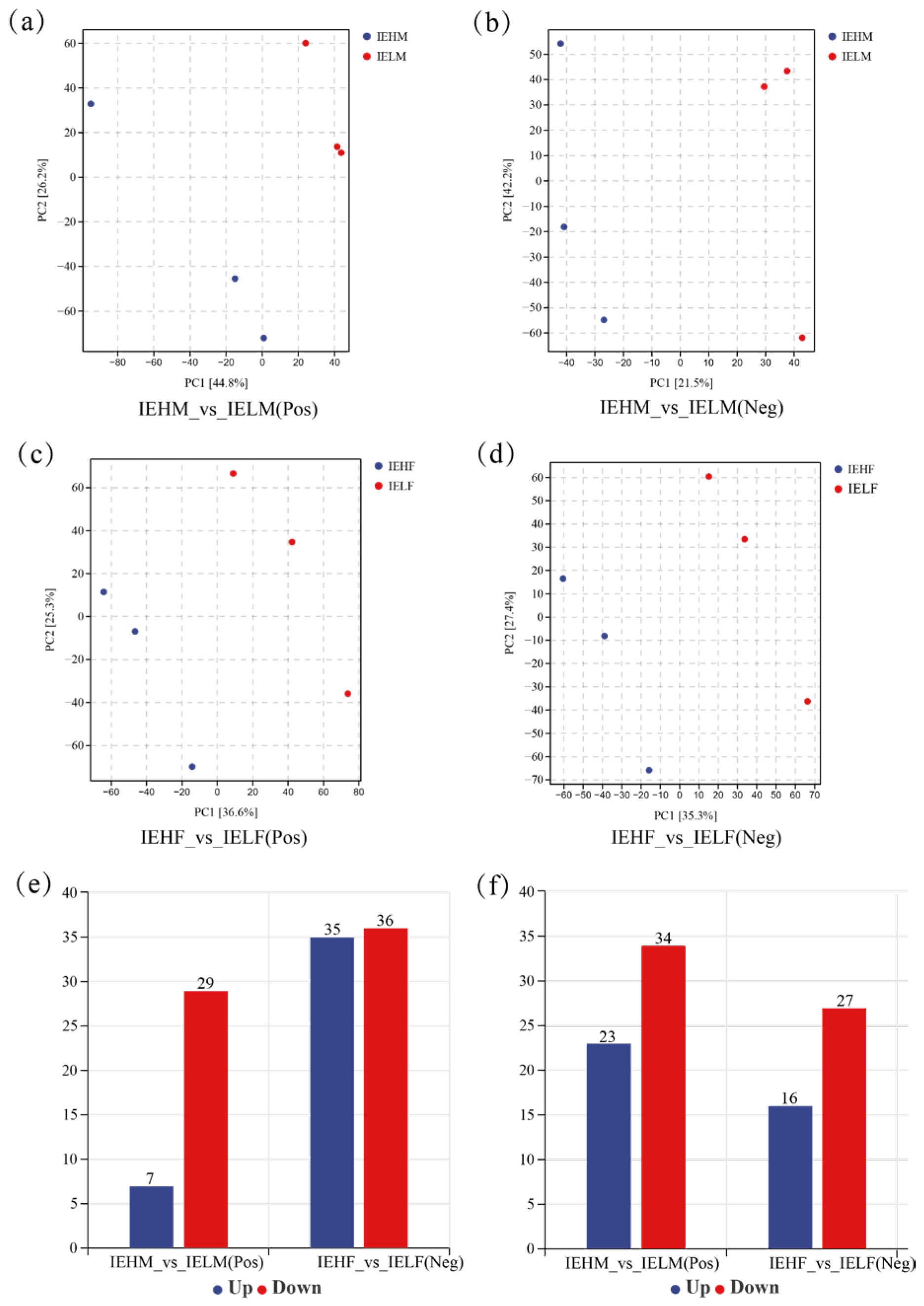
3.4. Analysis of Differential Metabolites of LYC Intestinal Contents
3.5. Metabolite Enrichment Analysis of the Intestinal Contents
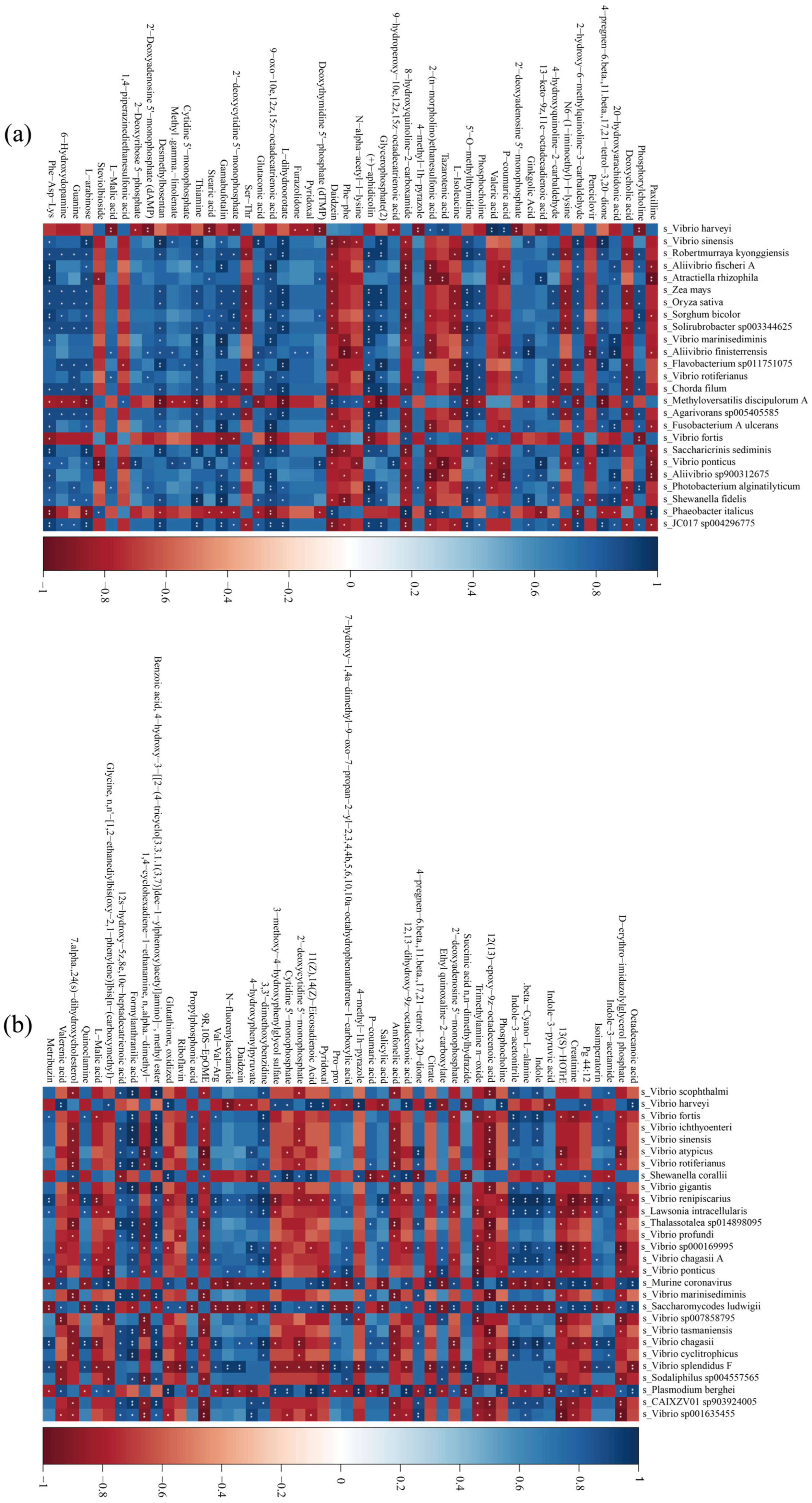
3.6. Gut Flora and Metabolite Association Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, Q.; Xie, Z.; Li, L.; Han, X.; Song, W. A Characterization of the RNA Modification Response to Starvation under Low Temperatures in Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Fishes 2024, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, C.; Cui, K.; Hao, T.; Yin, Z.; Xu, W.; Huang, W.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q. Nutritional programming of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae by dietary vegetable oil: Effects on growth performance, lipid metabolism and antioxidant capacity. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 129, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Xiang, Q.; Gao, Z.; Lan, T.; Jia, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Genomic selection for hypoxia tolerance in large yellow croaker. Aquaculture 2024, 579, 740212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Shan, X.; Chen, J.; Weng, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, H. Growth characteristics of cage-cultured large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Aquac. Rep. 2019, 16, 100242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Dong, L.; Xiao, S.; Han, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Genomewide association study for economic traits in the large yellow croaker with different numbers of extreme phenotypes. J. Genet. 2018, 97, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhong, Z.; Zhuang, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zou, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Evidence of virus-responsive pathways in response to poly I: C challenge in a muscle cell line derived from large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 100, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, J.; Lü, Z.; Deng, S. Identification of a large SNP dataset in Larimichthys crocea using specific-locus amplified fragment sequencing. Anim. Genet. 2018, 49, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Wang, Q.; Gu, S.; Jin, J.; Yang, N. Emerging perspectives in the gut–muscle axis: The gut microbiota and its metabolites as important modulators of meat quality. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lu, X.; Liang, H.; Ai, Q.; Mai, K. Effects of dietary levels of protein on growth, feed utilization and physiological parameters for juvenile Dabry’s sturgeon, Acipenser dabryanus. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Ma, J.; Pan, X.; Mu, H.; Li, J.; Shentu, J.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K. Dietary hydroxyproline improves the growth and muscle quality of large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, H.; Montero, M.; Gómez-Guillén, M.; Fernández-Martín, F.; Mørkøre, T.; Borderías, J. Collagen characteristics of farmed Atlantic salmon with firm and soft fillet texture. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginés, R.; Valdimarsdottir, T.; Sveinsdottir, K.; Thorarensen, H. Effects of rearing temperature and strain on sensory characteristics, texture, colour and fat of Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus). Food Qual. Prefer. 2003, 15, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, A.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zou, M.; Cao, S.; Qu, F.; Tang, J.; et al. Molecular Characterization of LKB1 of Triploid Crucian Carp and Its Regulation on Muscle Growth and Quality. Animals 2022, 12, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Johnston, I.; Alderson, R.; Sandham, C.; Mitchell, D.; Selkirk, C.; Dingwall, A.; Nickell, D.; Baker, R.; Robertson, B.; Whyte, D.; et al. Patterns of muscle growth in early and late maturing populations of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2000, 189, 307–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xia, J.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Li, L.; Tang, R.; Chi, W.; Li, D. Diet Affects Muscle Quality and Growth Traits of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus): A Comparison Between Grass and Artificial Feed. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesařová, E.; Ševčík, J.; Gaš, B.; Armstrong, D.W. Effects of partial/asymmetrical filling of micelles and chiral selectors on capillary electrophoresis enantiomeric separation: Generation of a gradient. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, N.; Kunisawa, J.; Kiyono, H. Dietary and Microbial Metabolites in the Regulation of Host Immunity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppé, E.; Burdet, C.; Grall, N.; de Lastours, V.; Lescure, F.-X.; Andremont, A.; Armand-Lefèvre, L. Impact of antibiotics on the intestinal microbiota needs to be re-defined to optimize antibiotic usage. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 24, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, F.; Jing, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Metabolites, gene expression, and gut microbiota profiles suggest the putative mechanisms via which dietary creatine increases the serum taurine and g-ABA contents in Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 49, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.R.; Ran, C.; Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z.G. Progress in fish gastrointestinal microbiota research. Rev. Aquac. 2017, 10, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, D.; Rao, C.; Li, L.; Guo, S.; Yang, S.; Cao, X. Improvement of intestinal barrier, immunity, and meat quality in common carp infected by Aeromonas hydrophila using probiotics. Aquac. Int. 2021, 30, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Ji, D.; Yao, J.; Zou, Y.; Yan, M. Comparative Analysis of Intestinal Characteristics of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) and Intestinal Flora with Different Growth Rates. Fishes 2022, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Gong, S.; Wu, X.; Zeng, L.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, C.; Song, L.; Liu, X. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Differences in Gene Expression in the Muscle of the Brown-Marbled Grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus) with Different Growth Rates. Fishes 2023, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.; Can, L.; Warner, R. The effect of exercise stress, adrenaline injection and electrical stimulation on changes in quality attributes and proteins in Semimembranosus muscle of lamb. Meat Sci. 2004, 68, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L. New insights into the interplay between intestinal flora and bile acids in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 10823–10839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüner, N.; Mattner, J. Bile Acids and Microbiota: Multifaceted and Versatile Regulators of the Liver–Gut Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Xia, B.; Tang, S.; Cao, A.; Liu, L.; Zhong, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. The Effect of Exogenous Bile Acids on Antioxidant Status and Gut Microbiota in Heat-Stressed Broiler Chickens. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 747136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Lyu, W.; Hong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Y. Gut Microbiota Influence Lipid Metabolism of Skeletal Muscle in Pigs. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 675445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganthi, M.; Abirami, G.; Jayanthi, M.; Kumar, K.A.; Karuppanan, K.; Palanisamy, S. A method for DNA extraction and molecular identification of Aphids. MethodsX 2023, 10, 102100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoyu, L.; Shijun, X.; Wanbo, L.; Zhiyong, W. Development and validation of sex-specific SNP markers in Larimichthys crocea. JFC 2018, 42, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.-Y.; Zhang, B.-Y.; Cai, G.-H.; Cai, G.-H.; Yang, H.-L.; Yang, H.-L.; Nie, Q.-J.; Nie, Q.-J.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Y.; et al. New insights on intestinal microorganisms and carbohydrate metabolism in fish. Aquac. Int. 2023, 32, 2151–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Yi, S.; Li, B.; Guo, F.; Peng, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Alvarez-Cohen, L.; Zhang, T. An integrated meta-omics approach reveals substrates involved in synergistic interactions in a bisphenol A (BPA)-degrading microbial community. Microbiome 2019, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Li, Y.; Song, H.; Bai, J.; Peng, N.; Ge, X.; Zhao, S. Quality improvement of soybean meal by simultaneous microbial fermentation and enzymolysis and untargeted metabolomic analysis of its metabolites. Food Biosci. 2024, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, D.L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Ning, Z.; Mayne, J.; Figeys, D. Metaproteomic and Metabolomic Approaches for Characterizing the Gut Microbiome. Proteomics 2019, 19, e1800363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, H.; Gangakhedkar, S.; Shah, R.P. Bioanalysis of Stress Biomarkers through Sensitive HILIC-MS/MS Method: A Stride toward Accurate Quantification of MDA, ACR, and CTA. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2024, 35, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Lu, M.; Wang, R.; An, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Xie, C.; Yu, C. How Much Storage Precision Can Be Lost: Guidance for Near-Lossless Compression of Untargeted Metabolomics Mass Spectrometry Data. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.S. Beware the IBM SPSS statistics® in multiple ROC curves analysis. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2023, 18, 1239–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Peng, S. Whole-Genome Methylation Sequencing of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Liver under Hypoxia and Acidification Stress. Mar. Biotechnol. 2023, 25, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, W.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ringø, E.; Olsen, R.E.; Clarke, J.L.; Xie, S.; et al. The Fish Microbiota: Research Progress and Potential Applications. Engineering 2023, 29, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Ou, W.; Chen, Q.; Ai, Q.; Zhang, W.; Mai, K.; Zhang, Y. Daidzein improved glucose homeostasis via PI3K/AKT and modulated the communities of gut microbiota in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquaculture 2023, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nay, K.; Jollet, M.; Goustard, B.; Baati, N.; Vernus, B.; Pontones, M.; Lefeuvre-Orfila, L.; Bendavid, C.; Rué, O.; Mariadassou, M.; et al. Gut bacteria are critical for optimal muscle function: A potential link with glucose homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2019, 317, E158–E171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M. Muscle wasting: The gut microbiota as a new therapeutic target? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2186–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parshukov, A.N.; Fokina, N.N.; Sukhovskaya, I.V.; Kantserova, N.P.; Lysenko, L.A. Infection and antibiotic treatment have prolonged effects on gut microbiota, muscle and hepatic fatty acids in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1709–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giron, M.; Thomas, M.; Dardavet, D.; Chassard, C.; Savary-Auzeloux, I. Gut microbes and muscle function: Can probiotics make our muscles stronger? J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 1460–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Xu, Y.; Qin, W.; Ren, J.; Jiang, Q.; Yan, X. Lactobacillus- derived protoporphyrin IX and SCFAs regulate the fiber size via glucose metabolism in the skeletal muscle of chickens. mSystems 2024, 9, e0021424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, F.; Li, D.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Y. Host-genotype-dependent cecal microbes are linked to breast muscle metabolites in Chinese chickens. iScience 2022, 25, 104469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Zhang, Y.W.; Yi, L.; Shi, M.Y.; Deng, D. Effects of different diets on growth performance, digestive enzyme activities and intestinal bacterial community of juvenile Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). Aquac. Rep. 2023, 30, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Shang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y. Comparison of gut microbial communities, free amino acids or fatty acids contents in the muscle of wild Aristichthys nobilis from Xinlicheng reservoir and Chagan lake. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Kuan, K.C.S.; Cao, X.; Wang, B.; Ren, Y. Effects of dietary oregano essential oil-mediated intestinal microbiota and transcription on amino acid metabolism and Aeromonas salmonicida resistance in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac. Int. 2023, 32, 1835–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, R.; Sun, J.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Ge, L.; Liu, Z. The intestinal microbiota contributes to the growth and physiological state of muscle tissue in piglets. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mente, E.; Deguara, S.; Santos, M.B.; Houlihan, D. White muscle free amino acid concentrations following feeding a maize gluten dietary protein in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2003, 225, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ling, F.; Xue, X.; He, X.; Zhai, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, G.; et al. Rice flowering improves the muscle nutrient, intestinal microbiota diversity, and liver metabolism profiles of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in rice-fish symbiosis. Microbiome 2022, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, C.; Mai, K.; He, G. Methionine deficiency affects myogenesis and muscle macronutrient metabolism in juvenile turbot Scophthalmus maximus. Aquaculture 2024, 578, 740013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.-Q.; Jiang, W.-D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Ren, H.-M.; Tang, L.; Li, S.-W.; Zhong, C.-B.; Zhang, R.-N.; Feng, L.; et al. Improvement of flesh quality, muscle growth and protein deposition in adult grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): The role of tryptophan. Aquaculture 2023, 577, 740005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah, K.; Huang, Q.-C.; Dong, X.-H.; Tan, B.-P.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S.-Y.; Yang, Q.-H.; Liu, H.-Y.; Yang, Y.-Z. Paenibacillus polymyxa improves the growth, immune and antioxidant activity, intestinal health, and disease resistance in Litopenaeus vannamei challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquaculture 2019, 518, 734563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ge, M.; Zheng, X.; Tao, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wang, G. Investigation of Vibrio alginolyticus, V. harveyi, and V. parahaemolyticus in large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea (Richardson) reared in Xiangshan Bay, China. Aquac. Rep. 2016, 3, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwankijudomkul, A.; Dong, H.T.; Longyant, S.; Sithigorngul, P.; Khunrae, P.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Senapin, S. Antigenicity of hypothetical protein HP33 of Vibrio harveyi Y6 causing scale drop and muscle necrosis disease in Asian sea bass. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 108, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Q.; Du, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qin, Y. Amino Acid-Induced Chemotaxis Plays a Key Role in the Adaptation of Vibrio harveyi from Seawater to the Muscle of the Host Fish. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Z.; Huang, H.; Qiao, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yue, Y.; Gao, Q.; Peng, S. Metagenomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Role of Gut Microbiome-Associated Metabolites in the Muscle Elasticity of the Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Animals 2024, 14, 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182690
Cheng Z, Huang H, Qiao G, Wang Y, Wang X, Yue Y, Gao Q, Peng S. Metagenomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Role of Gut Microbiome-Associated Metabolites in the Muscle Elasticity of the Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Animals. 2024; 14(18):2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182690
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Zhenheng, Hao Huang, Guangde Qiao, Yabing Wang, Xiaoshan Wang, Yanfeng Yue, Quanxin Gao, and Shiming Peng. 2024. "Metagenomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Role of Gut Microbiome-Associated Metabolites in the Muscle Elasticity of the Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea)" Animals 14, no. 18: 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182690
APA StyleCheng, Z., Huang, H., Qiao, G., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Yue, Y., Gao, Q., & Peng, S. (2024). Metagenomic and Metabolomic Analyses Reveal the Role of Gut Microbiome-Associated Metabolites in the Muscle Elasticity of the Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Animals, 14(18), 2690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182690




