Chest Wall Reconstruction Using Titanium Mesh in a Dog with Huge Thoracic Extraskeletal Osteosarcoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
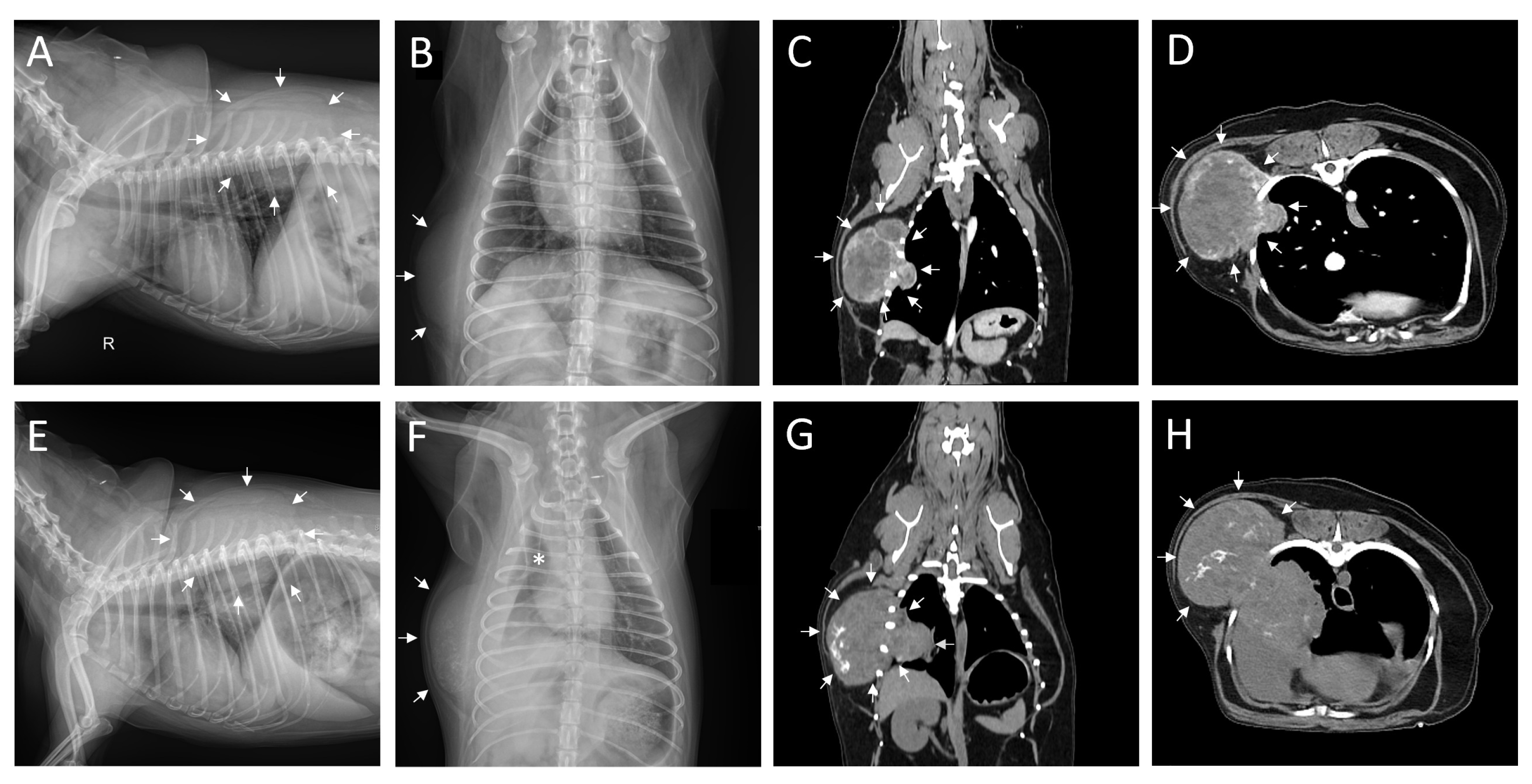
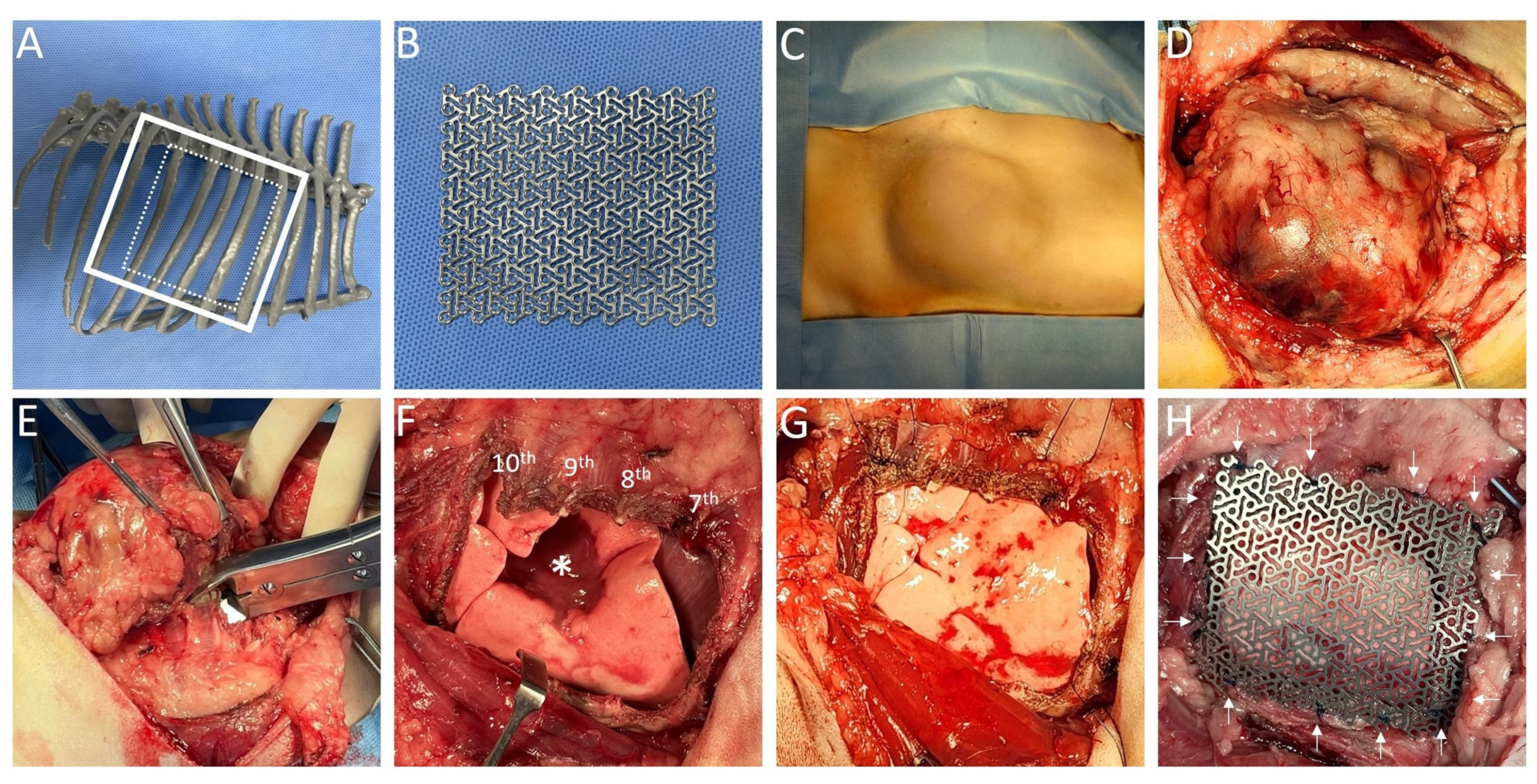
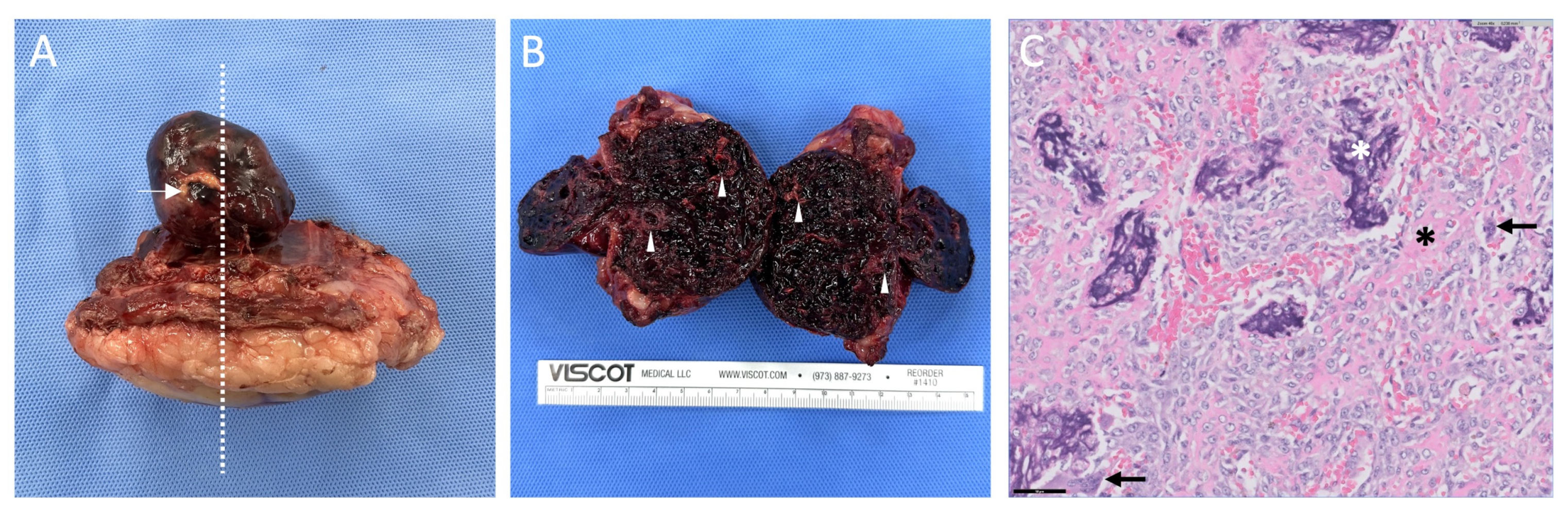
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feeney, D.A.; Johnston, G.R.; Grindem, C.B.; Toombs, J.P.; Caywood, D.D.; Hanlon, G.F. Malignant neoplasia of canine ribs: Clinical, radiographic, and pathologic findings. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1982, 180, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matthiesen, D.T.; Clark, G.N.; Orsher, R.J.; Pardo, A.O.; Glennon, J.; Patnaik, A.K. En bloc resection of primary rib tumors in 40 dogs. Vet. Surg. 1992, 21, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martano, M.; Boston, S.; Morello, E. Respiratory Tract and Thorax. In Veterinary Surgical Oncology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 393–468. [Google Scholar]
- Cordella, A.; Stock, E.; Bertolini, G.; Strohmayer, C.; Serra, G.D.; Saunders, J. CT features of primary bone neoplasia of the thoracic wall in dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2023, 64, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liptak, J.M.; Kamstock, D.A.; Dernell, W.S.; Monteith, G.J.; Rizzo, S.A.; Withrow, S.J. Oncologic outcome after curative-intent treatment in 39 dogs with primary chest wall tumors (1992–2005). Vet. Surg. 2008, 37, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Moya, M.; Nirula, R.; Biffl, W. Rib fixation: Who, What, When? Trauma Surg. Acute Care Open 2017, 2, e000059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Yukioka, T.; Yamaguti, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Goto, H.; Matsuda, H.; Shimazaki, S. Surgical stabilization of internal pneumatic stabilization? A prospective randomized study of management of severe flail chest patients. J. Trauma 2002, 52, 727–732, discussion 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liptak, J.M.; Dernell, W.S.; Rizzo, S.A.; Monteith, G.J.; Kamstock, D.A.; Withrow, S.J. Reconstruction of chest wall defects after rib tumor resection: A comparison of autogenous, prosthetic, and composite techniques in 44 dogs. Vet. Surg. 2008, 37, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Battisti, A.; Polton, G.; de Vries, M.; Friend, E. Chest wall reconstruction with latissimus dorsi and an autologous thoracolumbar fascia graft in a dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2015, 56, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfacree, Z.J.; Baines, S.J.; Lipscomb, V.J.; Grierson, J.; Summers, B.A.; Brockman, D.J. Use of a latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap for one-stage reconstruction of the thoracic wall after en bloc resection of primary rib chondrosarcoma in five dogs. Vet. Surg. 2007, 36, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, O.P.; Ogden, D.M. Lateralization of the diaphragm for thoracic wall reconstruction in a dog. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2021, 258, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, E.; Kudo, A.; Sato, A.; Yoshida, H.; Yamauchi, A.; Oshita, R.; Takagi, S. Thoracic Wall Reconstruction with Dorsal Diaphragmatic Traction and Preservation of Diaphragmatic Attachments in a Dog with Resection of the 11–13th Ribs. Animals 2022, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Song, Y.; Song, W.; Kim, M.-C.; Lee, J.-M.; Park, H.; Moon, J.; Cheong, J. Surgical Resection and Polypropylene Mesh Reconstruction for Canine Chest Wall Soft Tissue Sarcoma. J. Vet. Clin. 2024, 41, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Ishigaki, K.; Sakurai, N.; Heishima, T.; Yoshida, O.; Asano, K. Reconstruction surgery using polypropylene mesh after extensive resection of a costal osteosarcoma in a dog. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e31389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigeler, A.; Druecke, D.; Hakimi, M.; Duchna, H.-W.; Goertz, O.; Homann, H.-H.; Lehnhardt, M.; Steinau, H.-U. Reconstruction of the thoracic wall-long-term follow-up including pulmonary function tests. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2009, 394, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.A.; Brouchet, L. Prosthetic reconstruction of the chest wall. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2010, 20, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aprile, V.; Korasidis, S.; Crisci, R.; Ambrogi, M.C. Chest wall reconstruction with a novel titanium mesh after partial sternectomy for chondrosarcoma. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 30, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, I.; Evans, P.L.; Goodrum, H.; Warbrick-Smith, J.; Bragg, T. Chest wall reconstruction with an anatomically designed 3-D printed titanium ribs and hemi-sternum implant. 3D Print. Med. 2020, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joalsen, I.; Christian, D.; Rosalie, A.; Angga, M. Reconstruction with titanium mesh following wide excision in chest wall myxofibrosarcoma: A case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 77, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Guo, X.; Wang, L. Mastery of chest wall reconstruction with a titanium sternum-rib fixation system: A case series. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 5064–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, P.; Fabbri, N.; Quarantotto, F.; Tamburini, N.; Cavallesco, G. Titanium mesh in chest wall stabilization and reconstruction: A single center experience. Curr. Chall. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, G.; Hayes-Jordan, A. Chest wall reconstruction after tumor resection. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 27, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, S.; Brandolini, J.; Pardolesi, A.; Argnani, D.; Mengozzi, M.; Dell’amore, A.; Solli, P. Materials and techniques in chest wall reconstruction: A review. J. Vis. Surg. 2017, 3, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, J.T.; Song, K.; Avansino, J.R.; Mesher, A.; Waldhausen, J.H. Novel titanium constructs for chest wall reconstruction in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburini, N.; Grossi, W.; Sanna, S.; Campisi, A.; Londero, F.; Maniscalco, P.; Dolci, G.; Quarantotto, F.; Daddi, N.; Morelli, A.; et al. Chest wall reconstruction using a new titanium mesh: A multicenters experience. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 3459–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, C.J.; Caywood, D.D. Management of thoracic trauma and chest wall reconstruction. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1987, 17, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossum, T.W. Small Animal Surgery, 4th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brodey, R.S.; Riser, W.H. Canine osteosarcoma. A clinicopathologic study of 194 cases. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1969, 62, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Heyman, S.J.; Diefenderfer, D.L.; Goldschmidt, M.H.; Newton, C.D. Canine axial skeletal osteosarcoma. A retrospective study of 116 cases (1986 to 1989). Vet. Surg. 1992, 21, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenbach, A.; Anderson, M.; Dambach, D.; Sorenmo, K.; Shofer, F. Extraskeletal osteosarcomas in dogs: A retrospective study of 169 cases (1986–1996). J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1998, 34, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckett, M.E.; MacDonald-Dickinson, V.; Dickinson, R.M. Extraskeletal osteosarcoma associated with a benign hair follicle tumor in a dog. Can. Vet. J. 2020, 61, 525–529. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, M.; Owaki, K.; Hirata, A.; Murakami, M.; Sakai, H. Extraskeletal osteosarcoma associated with two different types of synthetic fibers derived from a surgical swab in a dog. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Aper, R.L.; Fauber, A.; Blevins, W.E.; Ramos-Vara, J.A. Extraskeletal osteosarcoma associated with retained surgical sponge in a dog. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2006, 18, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norrdin, R.W.; Lebel, J.L.; Chitwood, J.S. Extraskeletal osteosarcoma in a dog. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1971, 158, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, A.K.; Liu, S.; Johnson, G.F. Extraskeletal osteosarcoma of the liver in a dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1976, 17, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Koie, H.; Shibuya, H.; Suzuki, K. Extraskeletal osteosarcoma in the pericardium of a dog. Vet. Rec. 2004, 155, 780–781. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, C.T.E.; Medeiros, F.P.; Martins, R. Primary omentum extraskeletal osteosarcoma in a dog: Case report. Braz. J. Vet. Med. 2023, 45, e000423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, B.V.; Myers, R.K. Extraskeletal osteosarcoma of the mandibular salivary gland in a dog. Vet. Pathol. 1999, 36, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremolada, G.; Griffin, L.; Manchester, A.C.; Aboellail, T.; Lapsley, J.M.; Selmic, L.E. Primary extraskeletal osteosarcoma of the post-hepatic caudal vena cava in a dog-Case report. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1197236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, N.; Yamazoe, H.; Wada, A.; Nagata, K. A dog with extraskeletal osteosarcoma of the salivary glands survived long-term, following surgical resection and adjuvant therapy. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 85, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntz, C.A.; Dernell, W.; Powers, B.; Withrow, S. Extraskeletal osteosarcomas in dogs: 14 cases. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1998, 34, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guim, T.N.; de Cecco, B.S.; Laisse, C.J.M.; Schmitt, B.; Henker, L.C.; Vieira, C.d.R.; Driemeier, D.; Pavarini, S.P.; Sonne, L. Epidemiological and pathologic aspects of extra-skeletal osteosarcoma in dogs. Semin. Ciências Agrárias Londrina 2019, 40, 3089–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.G.; Dittmer, K.E. Tumors of Bone. In Tumors in Domestic Animals; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 356–424. [Google Scholar]
- Patnaik, A.K. Canine extraskeletal osteosarcoma and chondrosarcoma: A clinicopathologic study of 14 cases. Vet. Pathol. 1990, 27, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, L. Tumors of the Musculoskeletal System. In Bone Tumors in Domestic Animals: Comparative Clinical Pathology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 31–156. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Tang, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.; Gong, Z.; Duan, L. Chest wall reconstruction with two types of biodegradable polymer prostheses in dogs. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2008, 34, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tian, H.; Zhou, T.; Chen, H.; Li, C.; Jiang, Z.; Lao, L.; Kahn, S.A.; Duarte, M.E.L.; Zhao, J.; Daubs, M.D.; et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 promotes osteosarcoma growth by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 1638–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adli Azam, M.R.; Raja Amin, R.M. Huge Chest Wall Tumour Resection and Reconstruction using Titanium Mesh. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 22, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.-Y.; Sun, L.-L.; Li, H.-Y.; Ye, Z.-M. Prognostic Significance of Serum Alkaline Phosphatase Level in Osteosarcoma: A Meta-Analysis of Published Data. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 160835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doklestic, K.; Karamarkovic, A.; Bumbasirevic, V.; Stefanovic, B.; Gregoric, P.; Radenkovic, D.; Bajec, D. Spontaneous rupture of giant liver hemangioma: Case report. Srp. Arh. Celok. Lek. 2013, 141, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, D.; Selmic, L.E.; Kendall, A.R.; Powers, B.E. Outcome following treatment of soft tissue and visceral extraskeletal osteosarcoma in 33 dogs: 2008–2013. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moores, A.L.; Halfacree, Z.J.; Baines, S.J.; Lipscomb, V.J. Indications, outcomes and complications following lateral thoracotomy in dogs and cats. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2007, 48, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, W.-J.; Kwak, H.-H.; Kim, J.; Woo, H.-M. Chest Wall Reconstruction Using Titanium Mesh in a Dog with Huge Thoracic Extraskeletal Osteosarcoma. Animals 2024, 14, 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182635
Jung W-J, Kwak H-H, Kim J, Woo H-M. Chest Wall Reconstruction Using Titanium Mesh in a Dog with Huge Thoracic Extraskeletal Osteosarcoma. Animals. 2024; 14(18):2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182635
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Woo-June, Ho-Hyun Kwak, Junhyung Kim, and Heung-Myong Woo. 2024. "Chest Wall Reconstruction Using Titanium Mesh in a Dog with Huge Thoracic Extraskeletal Osteosarcoma" Animals 14, no. 18: 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182635
APA StyleJung, W.-J., Kwak, H.-H., Kim, J., & Woo, H.-M. (2024). Chest Wall Reconstruction Using Titanium Mesh in a Dog with Huge Thoracic Extraskeletal Osteosarcoma. Animals, 14(18), 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14182635





