Identification and Functional Analysis of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase g2e3 in Chinese Tongue Sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Euthanasia and Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals and Samples
2.3. Cloning and Phylogenetic Analysis of Cs-g2e3
2.4. Expression Pattern of Cs-g2e3 in Different Tissues and Stages of C. semilaevis
2.5. In Situ RNA Hybridization
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. The Knockdown Effect of Cs-g2e3 siRNA in C. semilaevis Gonad Cells
2.8. In Vivo RNAi-Mediated Cs-g2e3 Knockdown in the Gonads of C. semilaevis
2.9. Construction of Promoter Plasmids, the Interaction between Cs-g2e3 and Transcription Factors, and Co-Transfection and Dual Luciferase Assay in C. semilaevis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
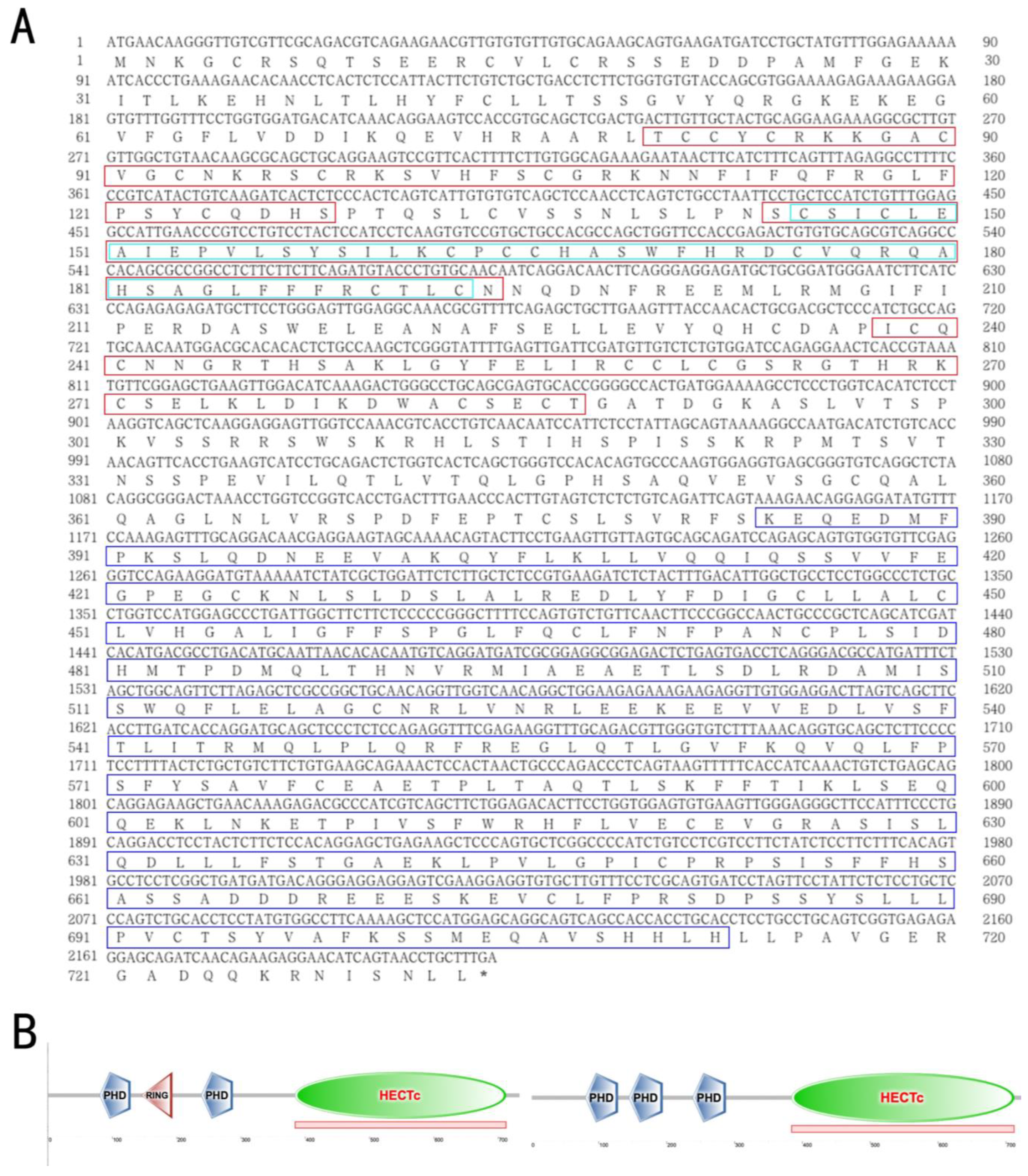
3.1. The Structural and Phylogenetic Analyses of g2e3 in C. semilaevis
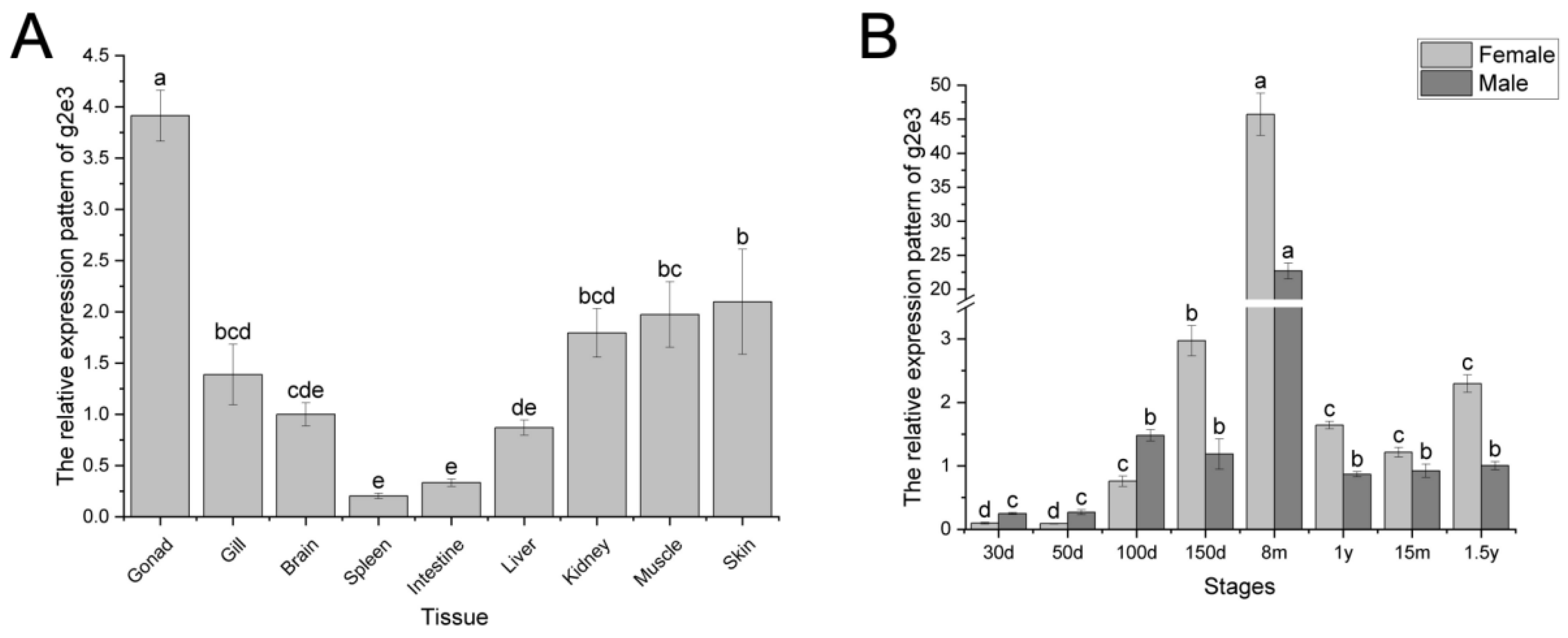
3.2. Expression Pattern of Cs-g2e3 in C. semilaevis
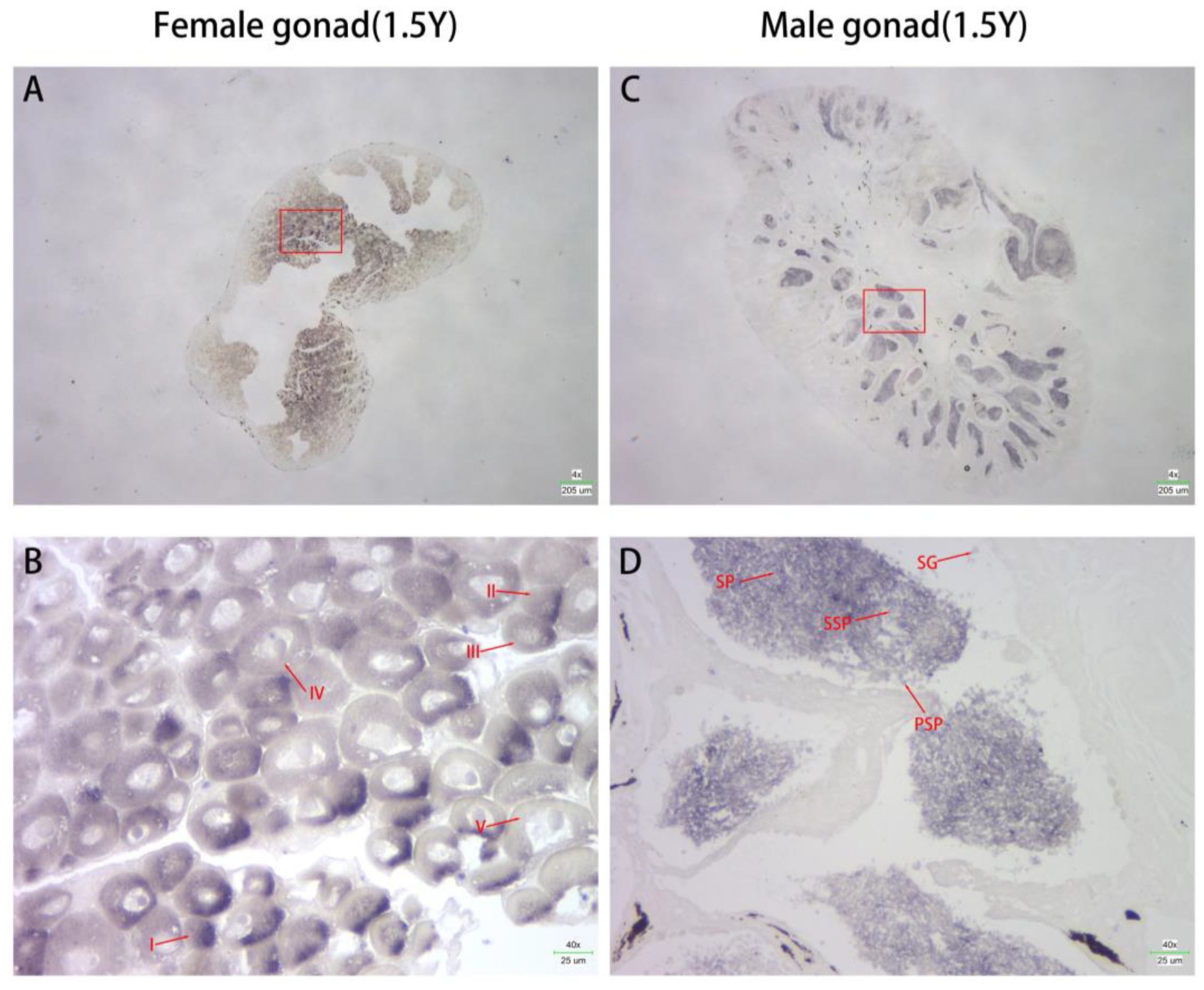
3.3. Localization of Cs-g2e3 mRNA in the Gonads of C. semilaevis
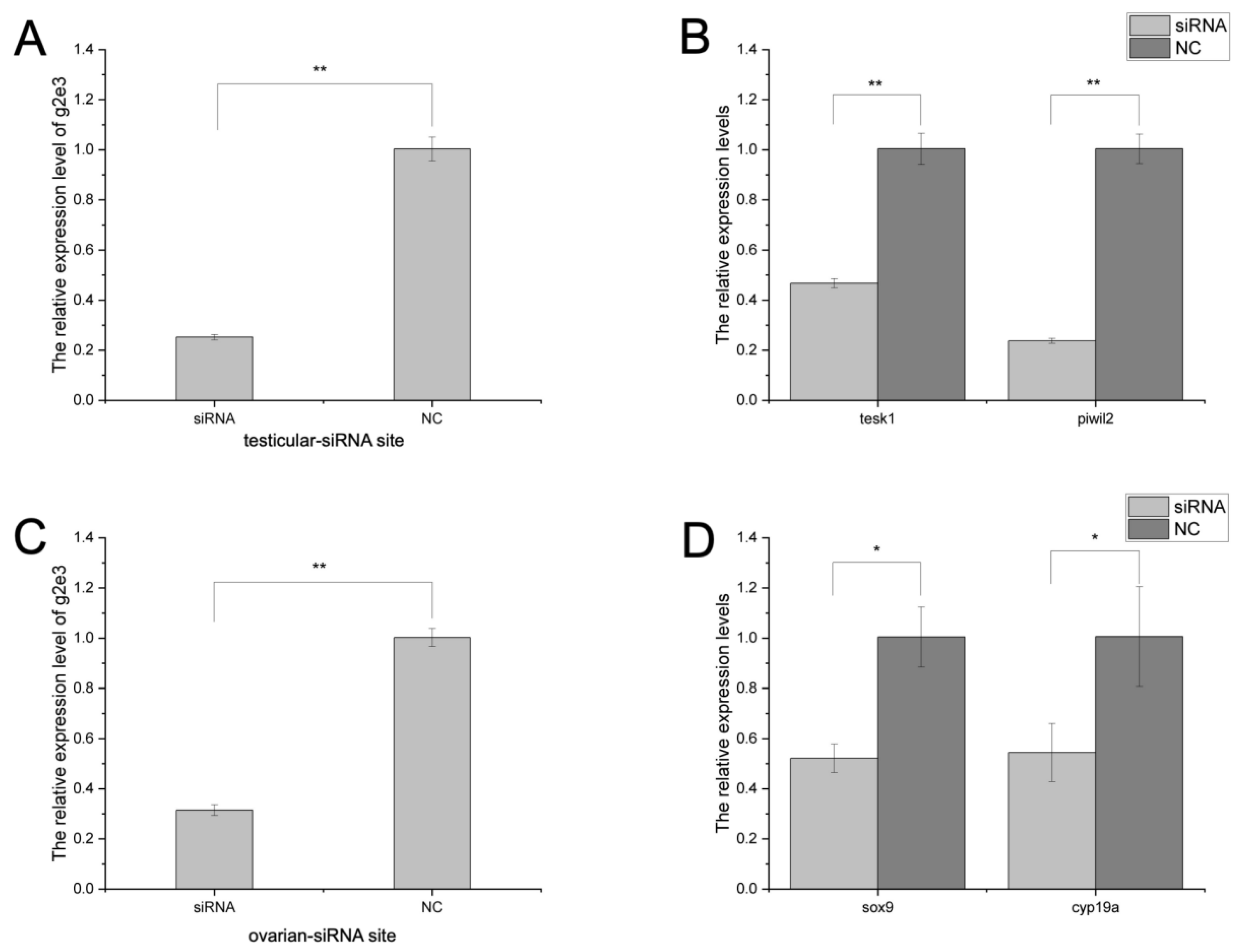
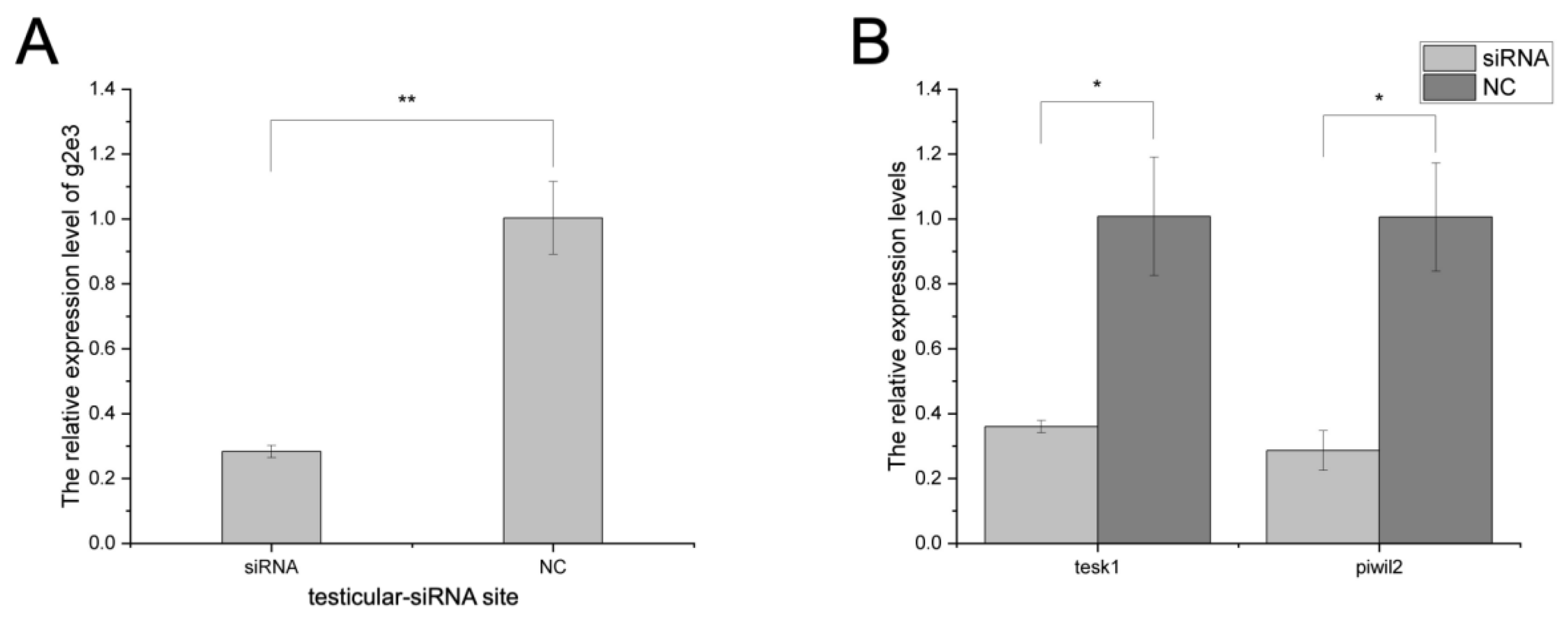
3.4. The Knockdown Effects on Cs-g2e3 and Other Related Genes by siRNA Transfection in Gonadal Germ Cell Lines
3.5. In Vivo RNA Interference in C. semilaevis
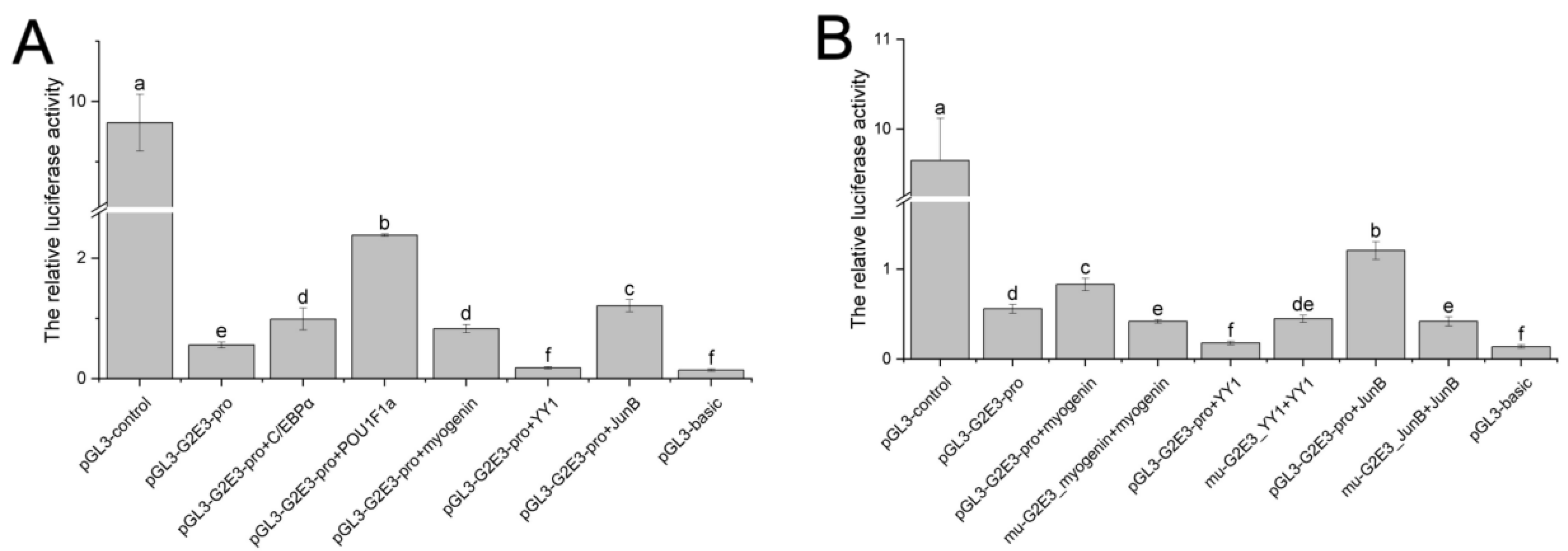
3.6. Detection and Analysis of the Activity of the Cs-g2e3 Promoter and the Regulation of Transcription Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.L.; Tian, Y.S.; Yang, J.F.; Shao, C.W.; Ji, X.S.; Zhai, J.M.; Liao, X.L.; Zhuang, Z.M.; Su, P.Z.; Xu, J.Y.; et al. Artificial gynogenesis and sex determination in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Jiang, J.; Liu, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Chromosome mapping of 18S rDNA and 5S rDNA by dual-color fluorescence in situ hybridization in the half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 10761–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, G.; Shao, C.; Huang, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, P.; Song, W.; An, N.; Chalopin, D.; Volff, J.N.; et al. Whole-genome sequence of a flatfish provides insights into ZW sex chromosome evolution and adaptation to a benthic lifestyle. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Jin, C.; Du, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, Q. Transcriptome profiling insights the feature of sex reversal induced by high temperature in Tongue Sole Cynoglossus semilaevis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, K.; Feng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Tang, L.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Piferrer, F.; Shao, C. Transcriptome of gonads from high temperature induced sex reversal during sex determination and differentiation in Chinese Tongue Sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Ni, Y.; Min, S.; Ming, L.; Qian, Y.; Cen, X.; Wang, J.; Tong, X. The ontogenesis of catabolic abilities and energy metabolism during endogenous nutritional periods of tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. J. Fish Biol. 2021, 99, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Shao, C. The role of Z chromosome localization gene psmd9 in spermatogenesis of Cynoglossus semilaevis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.Y.; Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Tan, F.; Liu, Q.; Yang, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. Single-cell-resolution transcriptome map revealed novel genes involved in testicular germ cell progression and somatic cells specification in Chinese tongue sole with sex reversal. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 1151–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanover, A.; Heller, H.; Elias, S.; Haas, A.L.; Hershko, A. ATP-dependent conjugation of reticulocyte proteins with the polypeptide required for protein degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, F.; Bahrami-Amiri, A.; Babahajian, A.; Shahsavari Nia, K.; Yousefifard, M. Ubiquitin C-Terminal Hydrolase-L1 (UCH-L1) in prediction of computed tomography findings in traumatic brain injury; a meta-analysis. Emergency 2018, 6, e62. [Google Scholar]
- Dikic, I.; Robertson, M. Ubiquitin ligases and beyond. BMC Biol. 2012, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Toma-Fukai, S.; Shimizu, T. Structural diversity of ubiquitin E3 ligase. Molecules 2021, 26, 6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Luo, Z.Q. Post-translational regulation of ubiquitin signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickart, C.M. Back to the future with ubiquitin. Cell 2004, 116, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudenon, S.; Huibregtse, J.M. High-level expression and purification of recombinant E1 enzyme. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 398, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Valimberti, I.; Tiberti, M.; Lambrughi, M.; Sarcevic, B.; Papaleo, E. E2 superfamily of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes: Constitutively active or activated through phosphorylation in the catalytic cleft. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndsen, C.E.; Wolberger, C. New insights into ubiquitin E3 ligase mechanism. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, A.; Stengel, F.; Zhang, Z.; Enchev, R.I.; Kong, E.H.; Morris, E.P.; Robinson, C.V.; da Fonseca, P.C.; Barford, D. Structural basis for the subunit assembly of the anaphase-promoting complex. Nature 2011, 470, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.S. Transcript profile analyses of maize silks reveal effective activation of genes involved in microtubule-based movement, ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation, and transport in the pollination process. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtake, F.; Baba, A.; Takada, I.; Okada, M.; Iwasaki, K.; Miki, H.; Takahashi, S.; Kouzmenko, A.; Nohara, K.; Chiba, T.; et al. Dioxin receptor is a ligand-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nature 2007, 446, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotin, D.; Kumar, S. Physiological functions of the HECT family of ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, D.M.; Lissounov, A.; Brzovic, P.S.; Klevit, R.E. UBCH7 reactivity profile reveals parkin and HHARI to be RING/HECT hybrids. Nature 2011, 474, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.S.; Pandolfi, P.P. The HECT family of E3 ubiquitin ligases and PTEN. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Argiles-Castillo, D.; Kane, E.I.; Zhou, A.; Spratt, D.E. HECT E3 ubiquitin ligases—Emerging insights into their biological roles and disease relevance. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs228072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, W.S.; Helton, E.S.; Banerjee, S.; Venable, M.; Johnson, L.; Schoeb, T.R.; Kesterson, R.A.; Crawford, D.F. G2e3 is a dual function ubiquitin ligase required for early embryonic development. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 22304–22315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.R.; Ling, L.B.; Huang, H.H.; Lin, J.J.; Fugmann, S.D.; Yang, S.Y. Evidence for parallel evolution of a gene involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20170324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Baxter, E.M.; Van Doren, M. Phf7 controls male sex determination in the Drosophila germline. Dev. Cell. 2012, 22, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.M.; Oleński, K.; Ruść, A.; Kaminski, S. Genome-wide association study for semen volume and total number of sperm in Holstein-Friesian bulls. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 151, 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Paradowska, A.S.; Miller, D.; Spiess, A.N.; Vieweg, M.; Cerna, M.; Dvorakova-Hortova, K.; Bartkuhn, M.; Schuppe, H.C.; Weidner, W.; Steger, K. Genome wide identification of promoter binding sites for H4K12ac in human sperm and its relevance for early embryonic development. Epigenetics 2012, 7, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Kang, J.Y.; Wei, L.; Yang, X.; Sun, H.; Yang, S.; Lu, L.; Yan, M.; Bai, M.; Chen, Y.; et al. PHF7 is a novel histone H2A E3 ligase prior to histone-to-protamine exchange during spermiogenesis. Development 2019, 146, dev175547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoheir, K.M.; Darwish, A.M.; Liguo, Y.; Ashour, A.E. Transcriptome comparisons detect new genes associated with apoptosis of cattle and buffaloes preantral follicles. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, W.S.; Banerjee, S.; Crawford, D.F. RNF138/NARF is a cell cycle regulated E3 ligase that poly-ubiquitinates g2e3. JSM Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 2, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, L.S.; Al Smadi, M.A.; Koch, H.; Abdul-Khaliq, H.; Meese, E.; Abu-Halima, M. Towards a more comprehensive picture of the microRNA-23a/b-3p impact on impaired male fertility. Biology 2023, 12, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Songlin, C.; Fengtao, G.; Liang, M.; Qiaomu, H.; Wentao, S.; Weiqun, L. SCAR-transformation of sex-specific SSR marker and its application in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semiliaevis). J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2014, 22, 787–792. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, C.; Choudhury, D.R.; Ranjan, A.; Raipuria, R.K.; Dubey, K.K.D.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, C.; Manzoor, M.M.; Kumar, A.; et al. Isolation, characterization, and expression analysis of NAC transcription factor from andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) nees and their role in andrographolide production. Genes 2024, 15, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Shi, W.; Pawar, R.A.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Cong, W.; Hu, Q.; Lu, T.; et al. beta-Actin is a useful internal control for tissue-specific gene expression studies using quantitative real-time PCR in the half-smooth tongue sole Cynoglossus semilaevis challenged with LPS or Vibrio anguillarum. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Lyu, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Wen, H.; Shi, B. Integrated lncRNA and mRNA transcriptome analyses in the ovary of Cynoglossus semilaevis reveal genes and pathways potentially involved in reproduction. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 671729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Lu, D.; Lin, H. Gonadotropin-Inhibitory hormone, the piscine ortholog of LPXRFa, participates in 17β-Estradiol feedback in female goldfish reproduction. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, A.; Wang, T.Z.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.F.; Sha, Z.X.; Chen, S.L. Establishment and characterization of an ovarian cell line from half-smooth tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 86, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Sha, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, N.; Chen, S.L. Establishment and characterization of a testicular cell line from the half-smooth tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Gao, D.; Lu, J.; Sun, X. Transcriptome profiling reveals the sexual dimorphism of gene expression patterns during gonad differentiation in the half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Liu, G.; Liu, S.; Chen, S. Characterization of the cyp19a1a gene from a BAC sequence in half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis) and analysis of its conservation among teleosts. Acta Oceanol. 2013, 32, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshima, J.; Ohashi, K.; Okano, I.; Nunoue, K.; Kishioka, M.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T.; Hirai, M.; Baba, T.; Mizuno, K. Identification and characterization of a novel protein kinase, TESK1, specifically expressed in testicular germ cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 31331–31337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, W.; Li, W.; Wang, F.; Cheng, J. DNA methylation mediates sperm quality via piwil1 and piwil2 regulation in Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ruan, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Xiao, M.; Xu, H. Tissue expression and promoter activity analysis of the porcine TNFSF11 gene. Theriogenology 2024, 226, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Q. Ubiquitin-Proteasome system-regulated protein degradation in spermatogenesis. Cells 2022, 11, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shang, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, W.; He, Y.; Chen, K.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, R. Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-L1 (Uch-L1) correlates with gonadal transformation in the rice field eel. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman-Trufero, M.; Dillon, N. The UBE2D ubiquitin conjugating enzymes: Potential regulatory hubs in development, disease and evolution. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1058751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, E.I.; Beasley, S.A.; Schafer, J.M.; Bohl, J.E.; Lee, Y.S.; Rich, K.J.; Bosia, E.F.; Spratt, D.E. Redefining the catalytic HECT domain boundaries for the HECT E3 ubiquitin ligase family. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20221036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.J.; Liang, C.G.; Guo, M.S.; Ge, S.Q.; Mu, S.M.; Su, W.Q.; Liu, X.H. Ultrastructure of spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis in the half-smooth tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. Acta Zool. Sin. 2008, 54, 356–365. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.K.; Liu, X.Z.; Wen, H.S.; Xu, Y.J.; Zhang, L.J. Histological observation on gonadal sex differentiation in Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther. Mar. Fish. Res. 2006, 27, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Qiao, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Luo, W.; Feng, Y. Localization and regulatory function of Yin Yang 1 (YY1) in chicken testis. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2022, 297, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, Y.P.; Choi, D.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, C.G. YY1 and CP2c in unidirectional spermatogenesis and stemness. Dev. Reprod. 2020, 24, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.D.; Kang, K.; Kim, J. YY1’s role in DNA methylation of peg3 and xist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 5656–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Chae, J.H.; Cheon, Y.P.; Kim, C.G. Reciprocal localization of transcription factors YY1 and CP2c in spermatogonial stem cells and their putative roles during spermatogenesis. Acta Histochem. 2016, 118, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayyar, B.; Kataruka, S.; Suresh Akhade, V.; Rao, M.R.S. Molecular functions of Mrhl lncRNA in mouse spermatogenesis. Reproduction 2023, 166, R39–R50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Hu, Y.C.; Liu, H.; Shi, Y. Loss of YY1 impacts the heterochromatic state and meiotic double-strand breaks during mouse spermatogenesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 6245–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Zhou, Q.; Meng, Y.; Guo, W.; Tang, Q.; Mei, J. RNA binding proteins are potential novel biomarkers of egg quality in yellow catfish. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Reyero, N.; Villeneuve, D.L.; Kroll, K.J.; Liu, L.; Orlando, E.F.; Watanabe, K.H.; Sepúlveda, M.S.; Ankley, G.T.; Denslow, N.D. Expression signatures for a model androgen and antiandrogen in the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) ovary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2614–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, N. Genome-wide analysis of BMP/GDF family and DAP-seq of YY1 suggest their roles in Cynoglossus semilaevis sexual size dimorphism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Product Length (bp) | Tm Values (°C) | Purposes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| g2e3-F | GCCACGTAACCCCATAT | 2869 | 52 | sequence validation |
| g2e3-R | AACGCAAGCAGTAGAACAG | |||
| β-actin-RT-F | TTCCAGCCTTCCTTCCTT | 124 | 53 | qRT-PCR |
| β-actin-RT-R | TACCTCCAGACAGCACAG | |||
| g2e3-RT-F | GTGTTCGAGGGTCCAGAAGG | 126 | 58 | qRT-PCR |
| g2e3-RT-R | GAAGCCAATCAGGGCTCCAT | |||
| Y-g2e3-F | ATTTAGGTGACACTATAGAA CTGCAGGAAGTCCGTTCACT | 556 | 65 | ISH |
| Y-g2e3-R | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG GGCCCAGTCTTTGATGTCCA | |||
| sox9-RT-F | AAGAACCACACAGATCAAGACAGA | 150 | 57 | qRT-PCR |
| sox9-RT-R | TAGTCATACTGTGCTCTGGTGATG | |||
| cyp19a-RT-F | GGTGAGGATGTGACCCAGTGT | 230 | 56 | qRT-PCR |
| cyp19a-RT-R | ACGGGCTGAAATCGCAAG | |||
| tesk1-RT-F | GCAGAAACTCTCTCACCCCAACA | 290 | 59 | qRT-PCR |
| tesk1-RT-R | CCAGACCAAAGTCCGTCACCA | |||
| piwil2-RT-F | CGTCACCTTCGCTCCAAAT | 171 | 56 | qRT-PCR |
| piwil2-RT-R | TCTTCGTCGTCCGTTCGC | |||
| g2e3-P-F | AGATCTGCGATCTAAGTAAGCT GCGTCCTCCAGTTTGGCTA | 1540 | 68 | Promoter cloning |
| g2e3-P-R | CAACAGTACCGGAATGCCAAGCT CGCTTTTCTTCCGTTCCG | |||
| Cs-sex-F | CCTAAATGATGGATGTAGATTCTGTC | 169/134 | 56 | sex determination |
| Cs-sex-R | GATCCAGAGAAAATAAACCCAGG | |||
| g2e3-835-F | GCAACAAUCAGGACAACUUTT | siRNA | ||
| g2e3-835-R | AAGUUGUCCUGAUUGUUGCTT | |||
| g2e3-1562-F | CCGUGAAGAUCUCUACUUUTT | siRNA | ||
| g2e3-1562-R | AAAGUAGAGAUCUUCACGGTT | |||
| g2e3-1928-F | GCAGACGUUGGGUGUCUUUTT | siRNA | ||
| g2e3-1928-R | AAAGACACCCAACGUCUGCTT |
| Groups | Firefly Luciferase | Renilla Luciferase | The Relative Luciferase Value (±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pGL3-g2e3-pro | 640,038 | 1,102,383 | 0.56 ± 0.05 |
| 571,785 | 954,903 | ||
| 511,223 | 1,016,504 | ||
| pGL3-g2e3-p + C/EBPα | 640,123 | 586,912 | 0.99 ± 0.18 |
| 706,702 | 644,511 | ||
| 391,717 | 499,763 | ||
| pGL3-g2e3-p + POU1F1a | 941,729 | 395,459 | 2.38 ± 0.02 |
| 786,581 | 327,948 | ||
| 984,677 | 417,072 | ||
| pGL3-g2e3-p + myogenin | 812,538 | 1,023,484 | 0.83 ± 0.07 |
| 868,884 | 950,887 | ||
| 883,088 | 1,132,129 | ||
| pGL3-g2e3-p + YY1 | 365,876 | 1,897,689 | 0.18 ± 0.02 |
| 305,774 | 1,580,501 | ||
| 321,856 | 1,940,210 | ||
| pGL3-g2e3-p + JunB | 143,5884 | 1,269,235 | 1.21 ± 0.10 |
| 134,7471 | 1,020,311 | ||
| 1,462,650 | 1,236,206 | ||
| mu-g2e3_myogenin + myogenin | 841,408 | 1,980,682 | 0.42 ± 0.02 |
| 851,162 | 1,927,374 | ||
| 742,405 | 1,831,696 | ||
| mu-g2e3_YY1 + YY1 | 1,565,732 | 3,620,141 | 0.45 ± 0.04 |
| 1,682,182 | 3,401,520 | ||
| 1,014,972 | 2,447,655 | ||
| mu-g2e3_JunB + JunB | 339,348 | 854,085 | 0.42 ± 0.05 |
| 293,453 | 623,706 | ||
| 356,566 | 937,653 | ||
| pGL3-control | 7,175,562 | 766,433 | 9.65 ± 0.47 |
| 9,262,670 | 909,082 | ||
| 12,162,782 | 1,294,003 | ||
| pGL3-Basic | 105,484 | 765,987 | 0.14 ± 0.02 |
| 107,500 | 648,147 | ||
| 139,058 | 1,061,613 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Z.; Luo, J.; Cheng, F.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Lin, M.; Sun, Y.; Chen, S. Identification and Functional Analysis of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase g2e3 in Chinese Tongue Sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. Animals 2024, 14, 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14172579
Cui Z, Luo J, Cheng F, Xu W, Wang J, Lin M, Sun Y, Chen S. Identification and Functional Analysis of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase g2e3 in Chinese Tongue Sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. Animals. 2024; 14(17):2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14172579
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Zhongkai, Jun Luo, Fangzhou Cheng, Wenteng Xu, Jialin Wang, Mengjiao Lin, Yuqi Sun, and Songlin Chen. 2024. "Identification and Functional Analysis of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase g2e3 in Chinese Tongue Sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis" Animals 14, no. 17: 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14172579
APA StyleCui, Z., Luo, J., Cheng, F., Xu, W., Wang, J., Lin, M., Sun, Y., & Chen, S. (2024). Identification and Functional Analysis of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase g2e3 in Chinese Tongue Sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis. Animals, 14(17), 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14172579






