Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sex Determination in the Great Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo) Based on External Measurements
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ageing and Morphometric Measurements
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castro, M.; Masero, J.A.; Pérez-Hurtado, A.; Amat, J.A.; Megina, C. Sex-related seasonal differences in the foraging strategy of the Kentish Plover. Condor 2009, 111, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camphuysen, K.C.J.; Shamoun-Baranes, J.; van Loon, E.E.; Bouten, W. Sexually distinct foraging strategies in an omnivorous seabird. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, W. Immature dunlins Calidris alpina migrate towards wintering grounds later than adults in years of low breeding success. J. Ornithol. 2015, 156, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meissner, W.; Krupa, R. Sex-related differences in autumn migration timing of adult common sandpipers Actitis hypoleucos (Linnaeus, 1758) (Charadriiformes: Scolopacidae). Eur. Zool. J. 2017, 84, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, I. Population Limitation in Birds; Academic Press: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eerden, M.R.; Munsterman, M.J. Sex and age dependent distribution in wintering cormorants Phalacrocorax carbo sinensis in western Europe. Ardea 1995, 83, 285–297. [Google Scholar]
- Snell, K.R.S.; Frederiksen, M.; Bregnballe, T. Differential spatial migration programmes are both sex and age specific for migratory great cormorants. J. Ornithol. 2021, 162, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, F.; Wilson, R.; Dell’Arciprete, P.; Shepard, E.; Laich, A.G. Women from Venus, men from Mars: Inter-sex foraging differences in the imperial cormorant Phalacrocorax atriceps a colonial seabird. Oikos 2011, 120, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laich, A.G.; Quintana, F.; Shepard, E.L.C.; Wilson, R.P. Intersexual differences in the diving behaviour of Imperial Cormorants. J. Ornithol. 2012, 153, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Watanuki, Y. Sex and individual differences in foraging behavior of Japanese cormorants in years of different prey availability. J. Ethol. 2002, 20, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalinger, B.; Oehm, J.; Zeisler, C.; Vorhauser, J.; Traugott, M. Sex-specific prey partitioning in breeding piscivorous birds examined via a novel, noninvasive approach. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 8985–8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, C.; Marinao, C.; Suárez, N.; Kasinsky, T.; Yorio, P. Patterns of sexual segregation in the use of trophic resources in breeding Imperial Cormorants. Mar. Biol. 2022, 169, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schjørring, S.; Gregersen, J.; Bregnballe, T. Sex difference in criteria determining fidelity towards breeding sites in the great cormorant. J. Anim. Ecol. 2000, 69, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Hoyo, J.; Elliott, A.; Sargatal, J. Handbook of the Birds of the World. Volume 1. Ostrich to Ducks; Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, Spain, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, J.J.; Tatner, P. Sexing Wrens Troglodytes troglodytes indigenus using morphological measurements and discriminant analysis. Bird Study 1996, 43, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.; Hernández, M.; Arizaga, J.; Miranda, R.; Amezcua, A. Sex differentiation of Corn Buntings Miliaria calandra wintering in northern Spain. Ring. Migr. 2005, 2, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, W. Sex determination of juvenile Dunlins migrating through the Polish Baltic region. J. Field Ornithol. 2005, 76, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, W.; Pilacka, L. Sex identification of adult Dunlins Calidris alpina alpina migrating in autumn through Baltic region. Ornis Fenn. 2008, 85, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Poisbleau, M.; Demongin, L.; van Noordwijk, H.J.; Strange, I.J.; Quillfeldt, P. Sexual dimorphism and use of morphological measurements to sex adults, immatures and chicks of rockhopper penguins. Ardea 2010, 98, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.; Double, M.C.; Orr, K.; Dawson, R.J.G. A DNA test to sex most birds. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridolfsson, A.-K.; Ellegren, H. A simple and universal method for molecular sexing of non-ratite birds. J. Avian Biol. 1999, 20, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacalaza, V.E.; Hall, M.A. Sexing adult King Cormorants (Phalacrocorax albiventer) by discriminant analysis. Col. Waterbirds 1988, 11, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, B.; Bolton, M. Sexing shags Phalacrocorax aristotelis from external measurements using discriminant analysis. Ring. Migr. 1997, 18, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaux, R.; Baroni, A. Sexual size dimorphism in the Antarctic Shag. Waterbirds 2000, 23, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, F.; Somoza, G.; Uhart, M.; Cassará, C.; Gandini, P.; Frere, E. Sex determination of adult Rock Shags by molecular sexing and morphometric parameters. J. Field Ornithol. 2003, 74, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, J.; Johnston, G. Morphological sex determination in Black-Faced Cormorants (Phalacrocorax fuscescens). Waterbirds 2013, 36, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koffijberg, K.; van Eerden, M.R. Sexual dimorphism in the Cormorant Phalacrocorax carbo sinensis: Possible implications for differences in structural size. Ardea 1995, 83, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Liordos, V.; Goutner, V. Sex determination of Great Cormorants (Phalacrocorax carbo sinensis) using morphometric measurements. Waterbirds 2008, 31, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, W.; Fischer, I. Sexing of common gull, Larus canus, using linear measurements. Folia Zool. 2017, 66, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Abreu, F.H.T.; Schietti, J.; Anciães, M. Spatial and environmental correlates of intraspecific morphological variation in three species of passerine birds from the Purus-Madeira interfluvium, Central Amazonia. Evol. Ecol. 2018, 32, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghiu, A.R.; Valkenburg, T.; Cotão, A.; Casero, M.; Azevedo, F. Sexual dimorphism and determination of sex of Yellow-legged gulls (Larus michahellis lusitanius) in southern Portugal. Airo 2020, 27, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, W.; Kośmicki, A.; Niemczyk, A.; Fischer, I. Development of sexual dimorphism and sexing of Baltic herring gull Larus argentatus argentatus in successive age classes. Waterbirds 2017, 40, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorofeev, D.; Ivanov, A.; Khudyakova, E.; Verkuil, Y.; Piersma, T.; Meissner, W. Biometric variability and sexual size dimorphism in the Great Knot Calidris tenuirostris. Eur. Zool. J. 2024, 91, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J. Identification of European Non-Passerines; British Trust for Ornithology: Thetford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ovegård, M.K.; Jepsen, N.; Bergenius Nord, M.; Petersson, E. Cormorant predation effects on fish populations: A global meta-analysis. Fish Fish. 2021, 22, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Källo, K.; Birnie-Gauvin, K.; Jepsen, N.; Aarestrup, K. Great cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo sinensis) predation on adult anadromous brown trout (Salmo trutta). Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2023, 32, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruge, K.S.; Tanabe, S.; Fukuda, M.; Yamagishi, S.; Tatsukawa, R. Accumulation pattern of persistent organochlorine residues in common cormorants (Phalacrocorax carbo) from Japan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1997, 34, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, R.; Barrett, R.T.; Pedersen, T. Foraging strategies of Great Cormorants Phalacrocorax carbo carbo wintering north of the Arctic Circle. Bird Study 2001, 48, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čech, M.; Čech, P.; Kubečka, J.; Prchalová, M.; Draštík, V. Size selectivity in summer and winter diets of Great Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo): Does it reflect season-dependent difference in foraging efficiency? Waterbirds 2008, 31, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonteneau, F.; Paillisson, J.-M.; Marion, L. Relationships between bird morphology and prey selection in two sympatric Great Cormorant Phalacrocorax carbo subspecies during winter. Ibis 2009, 151, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, P.; Meissner, W. Bird Ringing Station Manual; De Gruyter Open Ltd.: Warsaw, Poland, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lovich, J.E.; Gibbons, J.W. A review of techniques for quantifying sexual size dimorphism. Growth Dev. Aging 1992, 56, 269–281. [Google Scholar]
- Shealer, D.A.; Cleary, C.M. Sex determination of adult Black Terns by DNA and morphometrics: Tests of sample size, temporal stability and geographic specificity in the classification accuracy of discriminant function models. Waterbirds 2007, 30, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, J.T.; Takekawa, J.Y.; Bluso, J.D.; Yee, J.L.; Eagles-Smith, C.A. Gender identification of Caspian Terns using external morphology and discriminant function analysis. Wilson J. Ornithol. 2008, 120, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza, A.; Hidalgo, J.; Ocio, G.; Rodríguez, P. Sexual size dimorphism and determination of sex in Atlantic Yellow-legged Gulls Larus michahellis lusitanius from northern Spain. Ardeola 2008, 55, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, J.K. Prediction intervals—A review. Commun. Stat.–Theor. M. 1989, 18, 2393–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using Multivariate Statistics; Harper Collins College Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Svensson, L. Identification Guide to European Passerines; British Trust for Ornithology: Thetford, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Svagelj, W.S.; Quintana, F. Sexual size dimorphism and sex determination by morphometric measurements in breeding Imperial Shags (Phalacrocorax atriceps). Waterbirds 2007, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glahn, J.F.; McCoy, R.B. Measurements of wintering Double-crested Cormorants and discriminant models of sex. J. Field Ornithol. 1995, 66, 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Sikora, A.; Dubiec, A. Sex identification of Jack Snipe Lymnocryptes minimus by discriminant analysis of morphometric measurements. Ardea 2007, 95, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, K.; Foster, R. Use of external biometrics to sex Carrion Crow Corvus corone, Rook C. frugilegus and Western Jackdaw C. monedula in Northern England. Ring. Migr. 2010, 25, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meissner, W.; Krupa, R. Identifying the sex of the common sandpiper (Actitis hypoleucos) by linear measurements. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 2016, 53, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.R.; Cherel, Y.; Bost, C.A.; Tremblay, Y. Chick-rearing Crozet Shags (Phalacrocorax melanogenis) display sex-specific foraging behaviour. Antarct. Sci. 2007, 19, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nishiumi, I.; Naito, Y. Sexual differences in the diet of king cormorants at Macquarie Island. Polar. Biol. 1996, 16, 75636377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liordos, V.; Goutner, V. Sexual differences in the diet of great cormorants Phalacrocorax carbo sinensis wintering in Greece. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2009, 55, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, L. Where two subspecies meet: Origin, habitat choice and niche segregation of Cormorants Phalacrocorax c. carbo and P. c. sinensis in the common wintering area (France), in relation to breeding isolation in Europe. Ardea 1995, 83, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Newson, S.E.; Hughes, B.; Russell, I.C.; Ekins, G.R.; Sellers, R.M. Subspecific differentiation and distribution of Great Cormorants Phalacrocorax carbo in Europe. Ardea 2004, 92, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Marion, L.; Le Gentil, J. Ecological segregation and population structuring of the Cormorant Phalacrocorax carbo in Europe, in relation to the recent introgression of continental and marine subspecies. Evol. Ecol. 2006, 20, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, L.; Le Gentil, J. Habitat specialisation affects fitness of the marine and continental Cormorant subspecies in a recently evolved sympatric area. Ardea 2021, 109, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransson, T.; Petterson, J. Svensk Ringmӓrkningsatlas; Naturhistoriska Riksmuseet: Stockholm, Sweden, 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bakken, V.; Runde, O.; Tjørve, E. Norsk Ringmerkingsatlas; Stavanger Museum: Stavanger, Norway, 2003; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bairlein, F.; Dierschke, J.; Dierschke, V.; Salewski, V.; Geiter, O.; Hüppop, K.; Kӧppen, U.; Fiedler, W. Atlas des Vogelzugs; AULA: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chaika, C. Analysis of the recovery data of the Great Cormorant Phalacrocorax carbo ringed in the Russian Federation and on the territory of former Soviet states in 1939–2014. Ardea 2021, 109, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
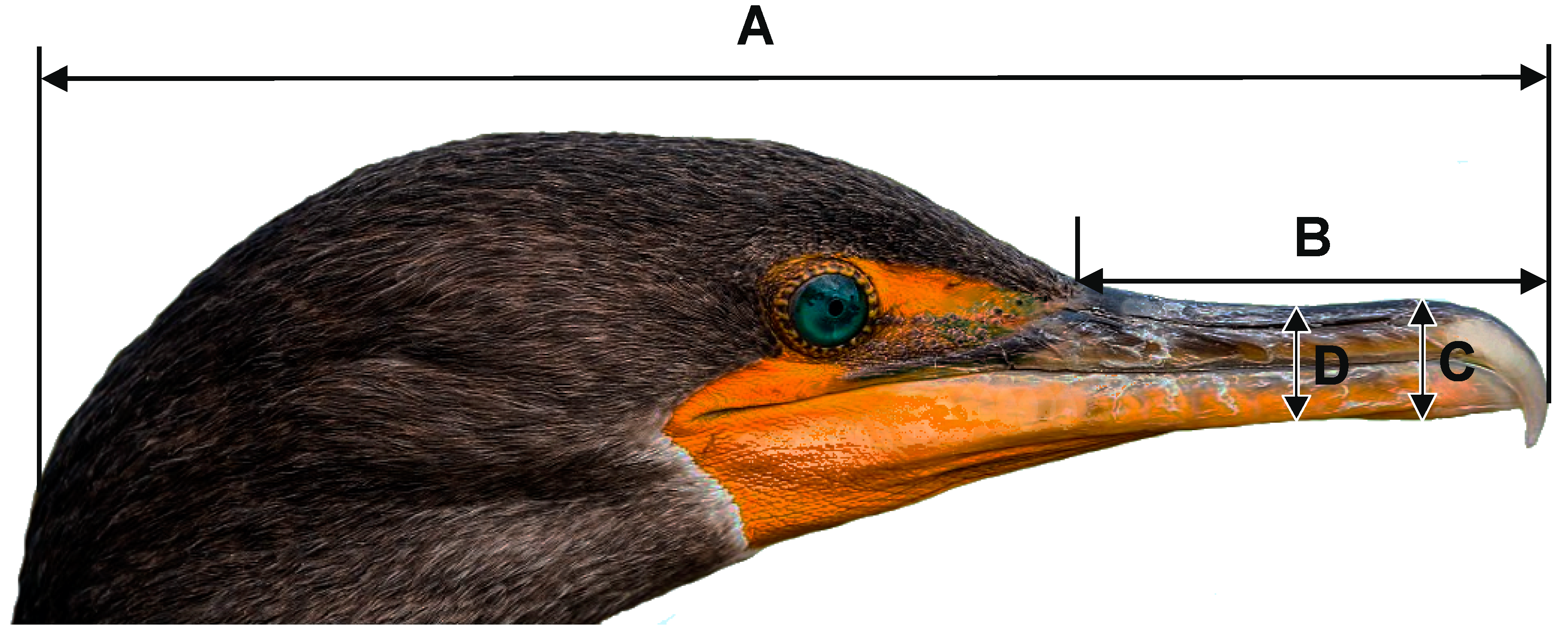


| Measurement [mm] | Males | Females | t-Test | SDI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | V | N | Mean | V | N | t | p | ||
| Wing length | 352.8 | 2.1% | 218 | 332.2 | 2.7% | 139 | 24.24 | p < 0.001 | 6.2% |
| Bill length | 70.60 | 4.4% | 188 | 63.53 | 5.2% | 109 | 18.97 | p < 0.001 | 11.1% |
| Maximum bill depth | 14.51 | 5.5% | 188 | 12.91 | 6.9% | 111 | 15.78 | p < 0.001 | 12.4% |
| Minimum bill depth | 13.26 | 4.9% | 147 | 11.70 | 5.2% | 89 | 18.16 | p < 0.001 | 13.3% |
| Tarsus length | 69.19 | 3.8% | 109 | 64.73 | 3.8% | 72 | 11.51 | p < 0.001 | 6.9% |
| Equation | Correctly Sexed | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | All | |
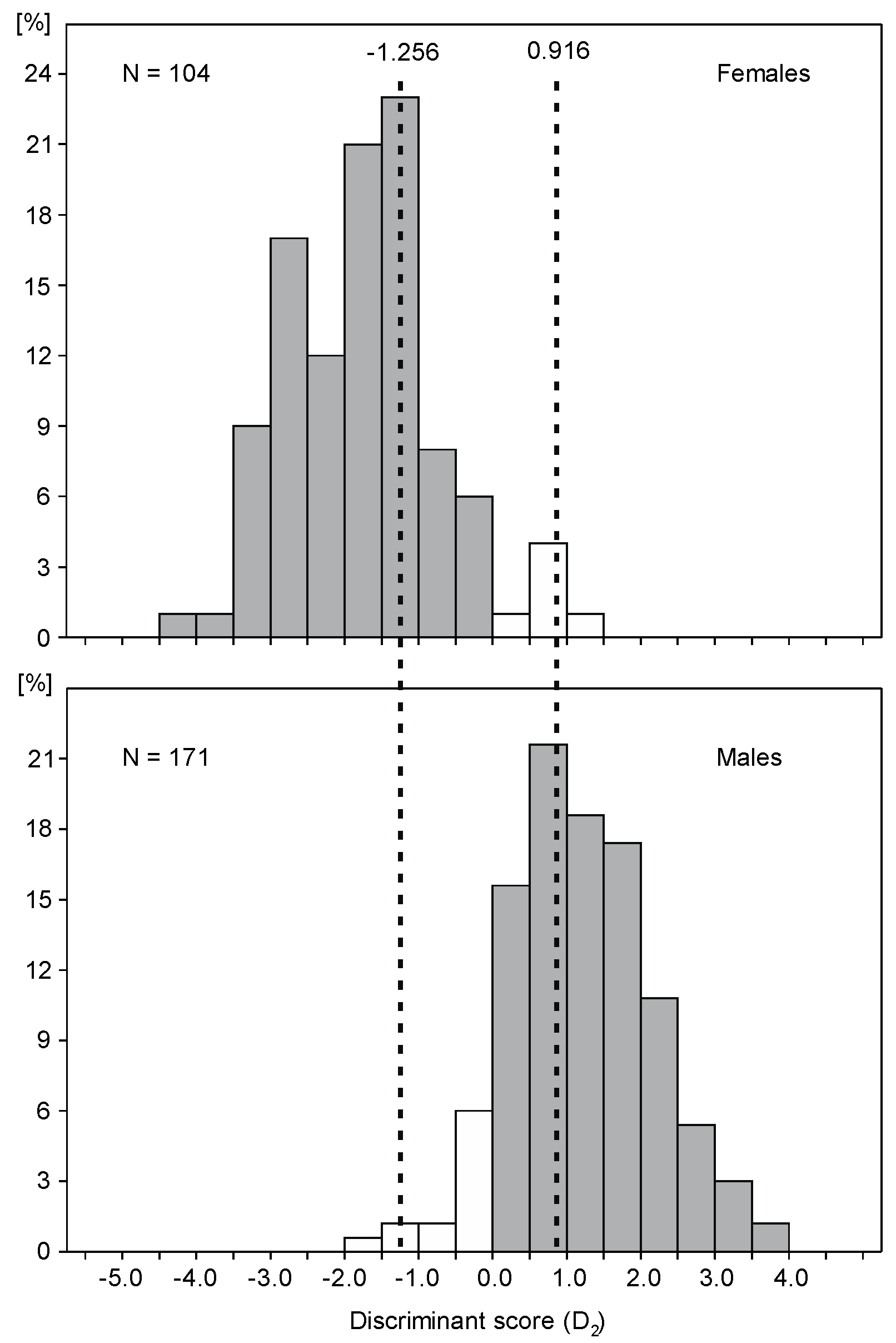
| D1 = 0.073·WL + 0.082·BL + 0.785·MBD − 40.623 | 95.4% | 91.5% | 93.9% |
| D2 = 0.087·WL + 0.161·BL − 40.843 | 96.3% | 91.3% | 93.8% |
| Population | Equation | Correctly Sexed | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | All | ||
| Greece | D = 0.073·WL + 0.123·BL + 0.310·TL − 53.693 | 94.2% | 95.1% | 94.6% |
| The Netherlands | D = 0.086·WL + 0.148·BL − 39.869 | 89.6% | 96.6% | 92.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meissner, W.; Goc, M.; Zaniewicz, G. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sex Determination in the Great Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo) Based on External Measurements. Animals 2024, 14, 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162389
Meissner W, Goc M, Zaniewicz G. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sex Determination in the Great Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo) Based on External Measurements. Animals. 2024; 14(16):2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162389
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeissner, Włodzimierz, Michał Goc, and Grzegorz Zaniewicz. 2024. "Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sex Determination in the Great Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo) Based on External Measurements" Animals 14, no. 16: 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162389
APA StyleMeissner, W., Goc, M., & Zaniewicz, G. (2024). Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Sex Determination in the Great Cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo) Based on External Measurements. Animals, 14(16), 2389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162389






