Alterations in the Intestinal Microbiome and Metabolic Profile of British Shorthair Kittens Fed with Milk Replacer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Milk Replacers
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Fecal Microbiota Analysis
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Fecal Inflammatory Markers
2.5. Fecal Metabolomics Analysis
2.6. Fecal Supernatant Antioxidant Capacity Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
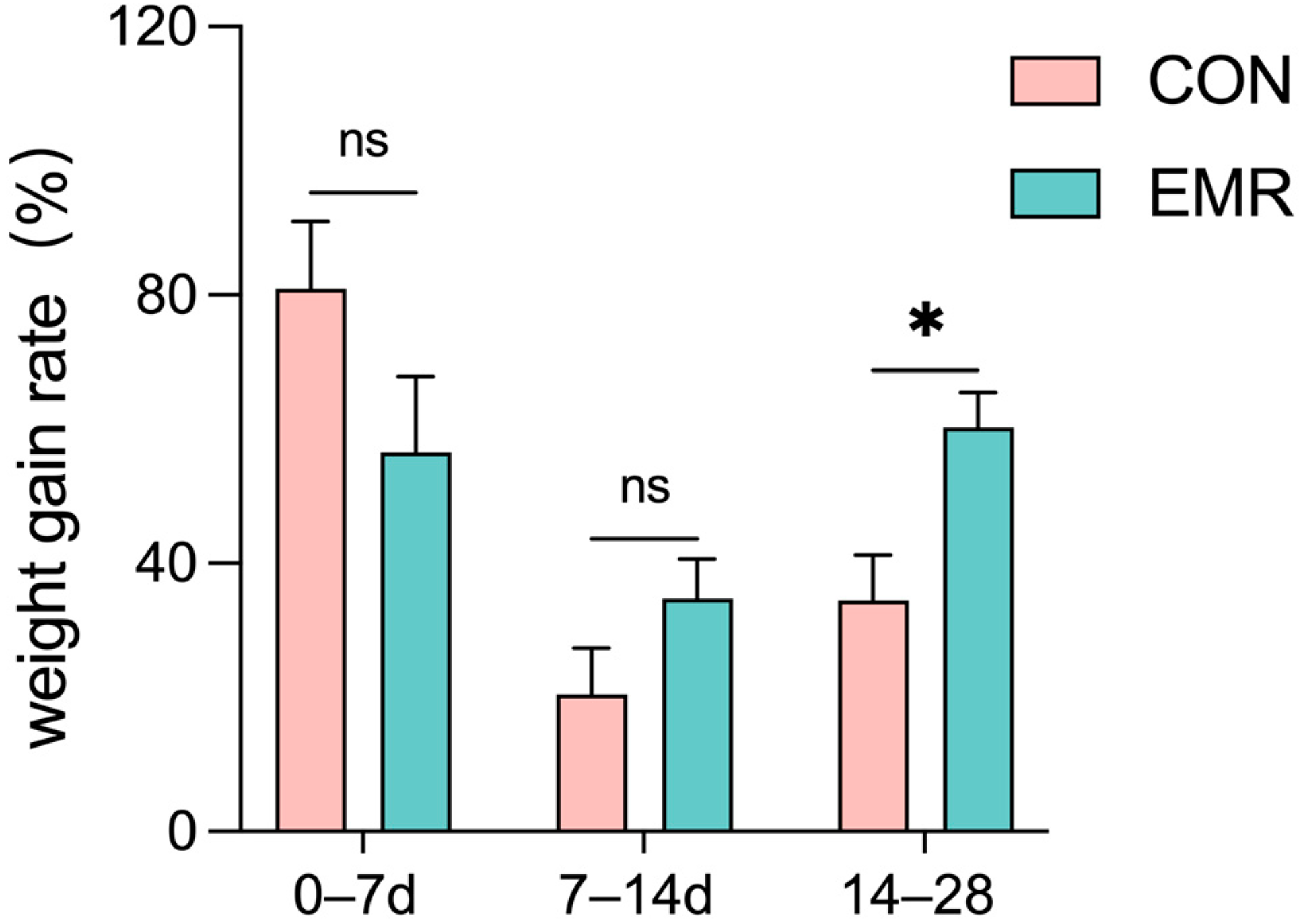
3.1. Growth Perfromence
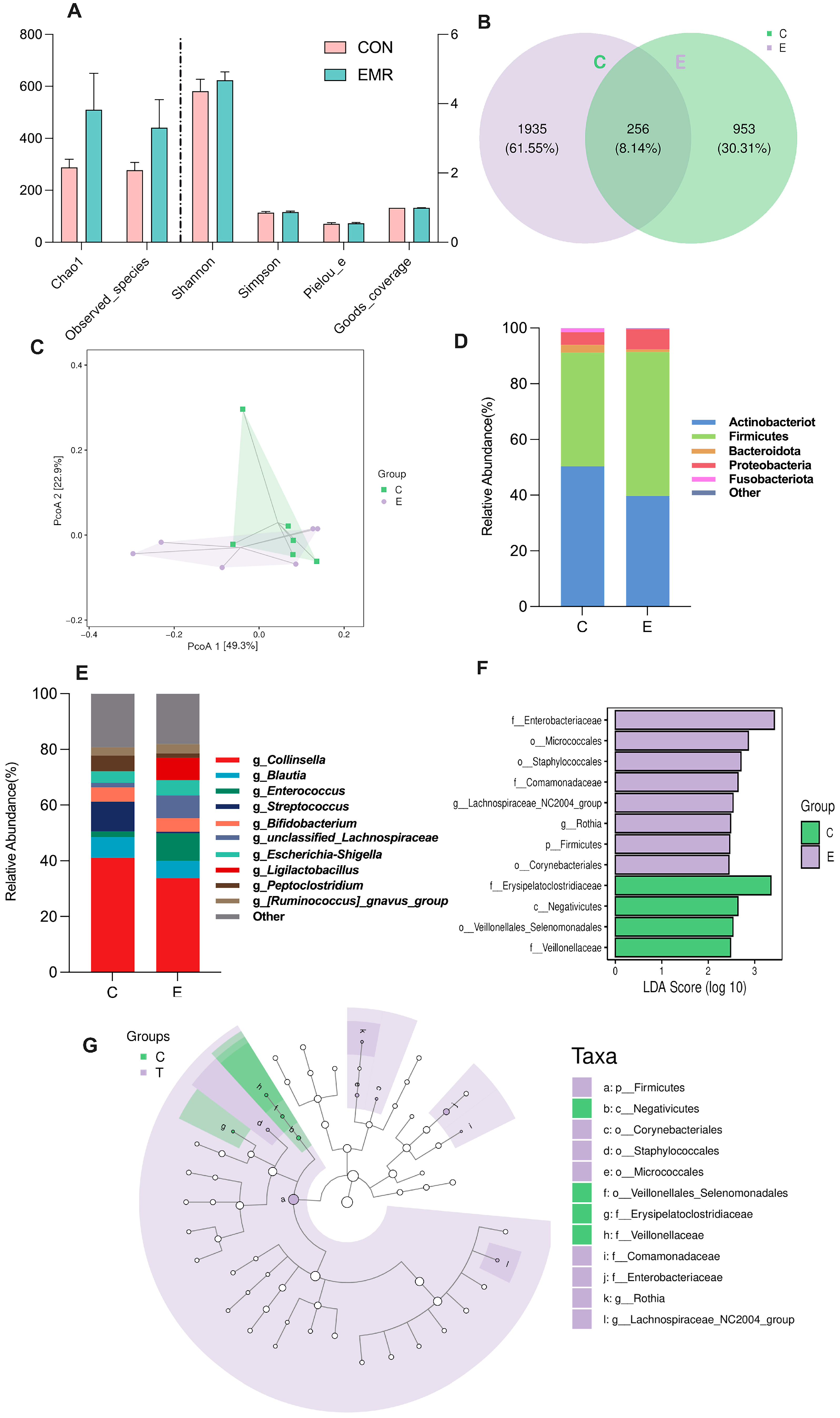
3.2. Analysis of Microbiota Composition
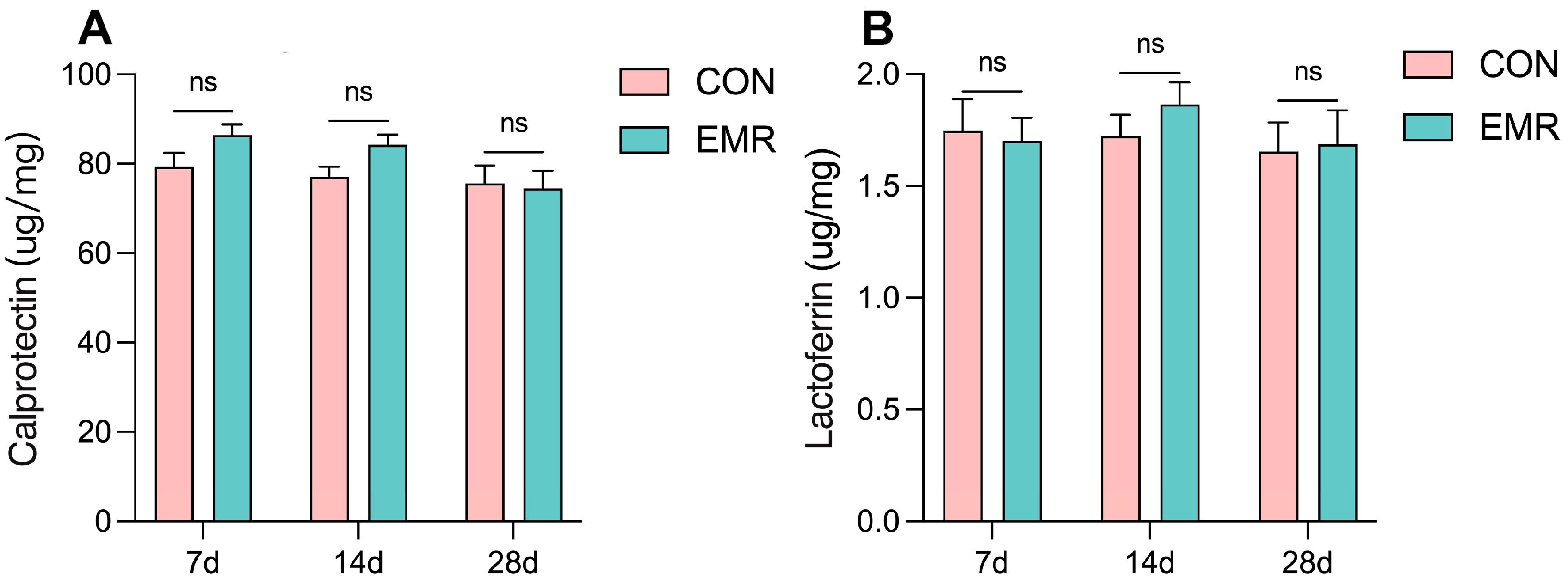
3.3. Fecal-Related Inflammatory Indicators
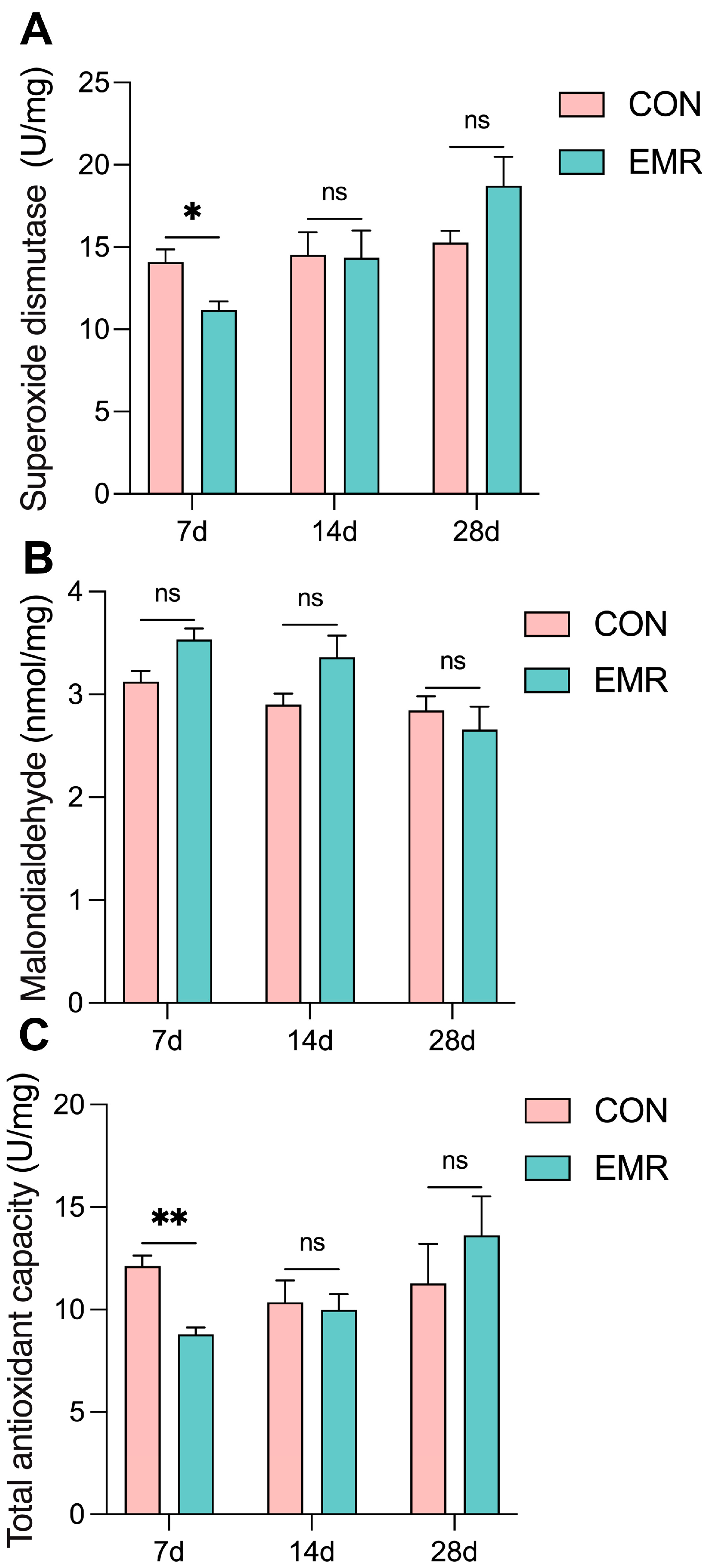
3.4. Fecal Antioxidant Capacity
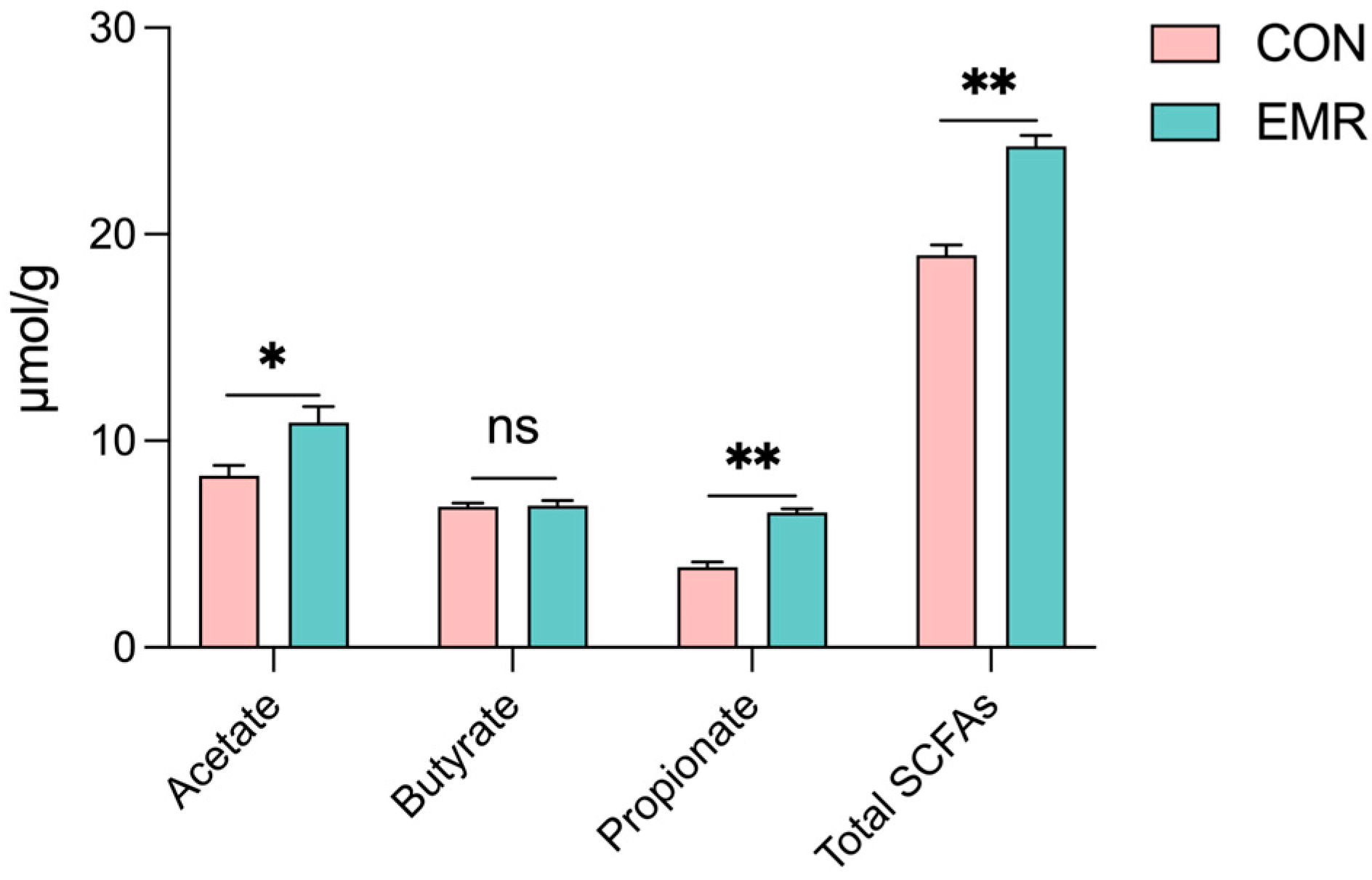
3.5. Microbiota-Derived SCFA Production
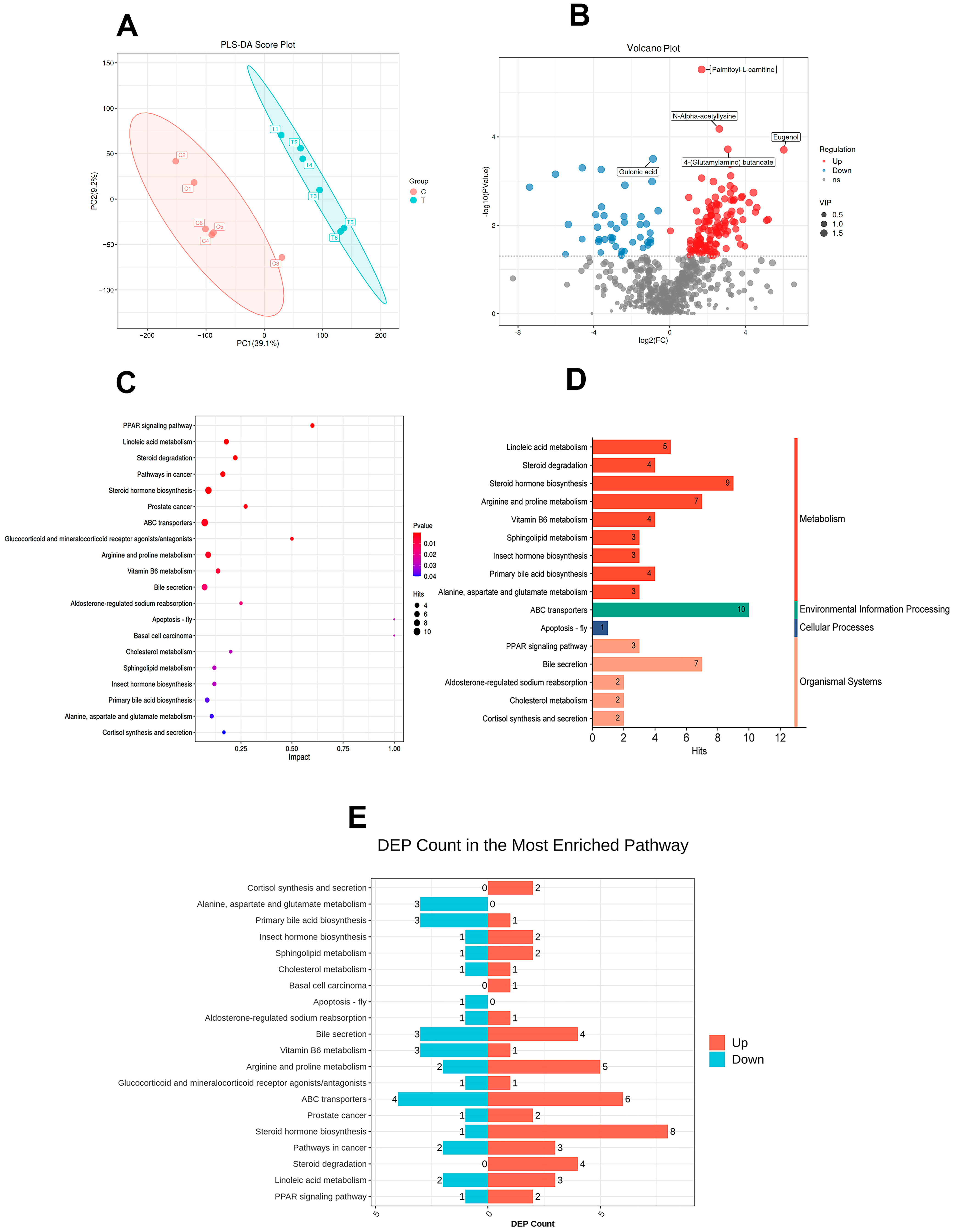
3.6. Analysis of Fecal Metabolites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mori, E.; Menchetti, M.; Camporesi, A.; Cavigioli, L.; Tabarelli De Fatis, K.; Girardello, M. License to Kill? Domestic Cats Affect a Wide Range of Native Fauna in a Highly Biodiverse Mediterranean Country. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, A.; Masson, M.; Corbière, F.; Mila, H.; Mariani, C.; Grellet, A.; Chastant-Maillard, S. Epidemiological Analysis of Reproductive Performances and Kitten Mortality Rates in 5303 Purebred Queens of 45 Different Breeds and 28,065 Kittens in France. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, K.H.N.P.; Fuchs, K.D.M.; Corrêa, J.V.; Chiacchio, S.B.; Lourenço, M.L.G. Neonatology: Topics on Puppies and Kittens Neonatal Management to Improve Neonatal Outcome. Animals 2022, 12, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, M.C.; Fusi, J. Feline Neonatology: From Birth to Commencement of Weaning—What to Know for Successful Management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münnich, A.; Küchenmeister, U. Causes, Diagnosis and Therapy of Common Diseases in Neonatal Puppies in the First Days of Life: Cornerstones of Practical Approach. Reprod. Domest. Anim. Zuchthyg. 2014, 49 (Suppl. S2), 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, A.; Truchet, L.; Langbein-Detsch, I.; Müller, E.; Giger, U. Neuigkeiten zur praktischen ABC-Blutgruppen-Bestimmung bei Katzen: Vermeidung akuter hämolytischer Transfusionsreaktionen und der neonatalen Isoerythrolyse. Tierärztl. Prax. Ausg. K Kleintiere Heimtiere 2019, 47, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Dingess, K.A. The Functional Power of the Human Milk Proteome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chastant-Maillard, S.; Aggouni, C.; Albaret, A.; Fournier, A.; Mila, H. Canine and Feline Colostrum. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2017, 52, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Lumbreras, A.E.V.; Vagni, S.; Dell’Anno, M.; Bontempo, V. Nutritional and Functional Properties of Colostrum in Puppies and Kittens. Animals 2021, 11, 3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, M.A.; Levy, J.K.; MacDonald, K.; Tucker, S.J.; Crawford, P.C. Immunoglobulin Concentrations in Feline Colostrum and Milk, and the Requirement of Colostrum for Passive Transfer of Immunity to Neonatal Kittens. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2006, 8, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, Y.; Zicker, S.C.; Lepine, A.; Lönnerdal, B. Changes in Nutrient and Protein Composition of Cat Milk during Lactation. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1997, 58, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinze, C.R.; Freeman, L.M.; Martin, C.R.; Power, M.L.; Fascetti, A.J. Comparison of the Nutrient Composition of Commercial Dog Milk Replacers with That of Dog Milk. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 244, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallès, J.-P.; Bosi, P.; Smidt, H.; Stokes, C.R. Nutritional Management of Gut Health in Pigs around Weaning. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007, 66, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, R.I.; Sghir, A.; Gaskins, H.R. Developmental Microbial Ecology of the Neonatal Gastrointestinal Tract. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 1035S–1045S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penders, J.; Thijs, C.; Vink, C.; Stelma, F.F.; Snijders, B.; Kummeling, I.; van den Brandt, P.A.; Stobberingh, E.E. Factors Influencing the Composition of the Intestinal Microbiota in Early Infancy. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Geng, H.; Du, C.; Chou, P.M.; Bu, H.-F.; Wang, X.; Swaminathan, S.; Tan, S.C.; Ridlon, J.M.; De Plaen, I.G.; et al. Feeding Mode Influences Dynamic Gut Microbiota Signatures and Affects Susceptibility to Anti-CD3 mAb-Induced Intestinal Injury in Neonatal Mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2022, 323, G205–G218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddington, R.K.; Sangild, P.T. COMPANION ANIMALS SYMPOSIUM: Development of the Mammalian Gastrointestinal Tract, the Resident Microbiota, and the Role of Diet in Early Life1. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 1506–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ali, I.; Lei, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Yang, C.; Li, L. Effect of a Multistrain Probiotic on Feline Gut Health through the Fecal Microbiota and Its Metabolite SCFAs. Metabolites 2023, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Mu, C.; Su, Y.; Yu, K.; Zhu, W. Long-Term Effects of Early Antibiotic Intervention on Blood Parameters, Apparent Nutrient Digestibility, and Fecal Microbial Fermentation Profile in Pigs with Different Dietary Protein Levels. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelena, E.; Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Carroll, K.M.; Begley, P.; O’Hagan, S.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Wilson, I.D.; et al. Development of a Robust and Repeatable UPLC−MS Method for the Long-Term Metabolomic Study of Human Serum. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; Masson, P.; Michopoulos, F.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Loftus, N.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global Metabolic Profiling of Animal and Human Tissues via UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cao, J.; Geng, A.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Chu, Q.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Integration of GC-MS and LC-MS for Metabolite Characteristics of Thigh Meat between Fast- and Slow-Growing Broilers at Marketable Age. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessen, R.; Kavanagh, K. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Promoting and Supporting Breastfeeding. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weary, D.M.; Jasper, J.; Hötzel, M.J. Understanding Weaning Distress. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 110, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravi, F.; Wiens, F.; Decarli, A.; Dal Pont, A.; Agostoni, C.; Ferraroni, M. Impact of Maternal Nutrition on Breast-Milk Composition: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 646–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, K.L.; DePeters, E.J.; Rogers, Q.R.; Taylor, S.J. Influences of Stage of Lactation, Teat Position and Sequential Milk Sampling on the Composition of Domestic Cat Milk (Felis catus). J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2004, 88, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remillard, R.L.; Pickett, J.P.; Thatcher, C.D.; Davenport, D.J. Comparison of Kittens Fed Queen’s Milk with Those Fed Milk Replacers. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1993, 54, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, J.E.; Spor, A.; Scalfone, N.; Fricker, A.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R.; Angenent, L.T.; Ley, R.E. Succession of Microbial Consortia in the Developing Infant Gut Microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4578–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buddington, R.K.; Weiher, E. The Application of Ecological Principles and Fermentable Fibers to Manage the Gastrointestinal Tract Ecosystem. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1446S–1450S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, L.E.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Assessment of Microbial Diversity along the Feline Intestinal Tract Using 16S rRNA Gene Analysis: Intestinal Microbial Communities in Healthy Cats. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 66, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, G.T.; Vasconcelos, Q.D.J.S.; Aragão, G.F. Fructooligosaccharides on Inflammation, Immunomodulation, Oxidative Stress, and Gut Immune Response: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Tan, D.; Yang, Z.; Tang, J.; Bai, W.; Tian, L. Fermentation Patterns of Prebiotics Fructooligosaccharides-SCFA Esters Inoculated with Fecal Microbiota from Ulcerative Colitis Patients. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 180, 114009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zhou, H.; Qian, J.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cong, J. Compound Prebiotics as Prophylactic and Adjunctive Treatments Ameliorate DSS-Induced Colitis through Gut Microbiota Modulation Effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.; Piceno, Y.M.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Pahl, M.; Andersen, G.L.; Vaziri, N.D. Expansion of Urease- and Uricase-Containing, Indole- and p-Cresol-Forming and Contraction of Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Producing Intestinal Microbiota in ESRD. Am. J. Nephrol. 2014, 39, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, A.; Stewart, L.; Blanchard, J.; Leschine, S. Untangling the Genetic Basis of Fibrolytic Specialization by Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcaceae in Diverse Gut Communities. Diversity 2013, 5, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, P.O.; Martin, J.C.; Lawley, T.D.; Browne, H.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Bernalier-Donadille, A.; Duncan, S.H.; O’Toole, P.W.; Scott, K.P.; Flint, H.J. Polysaccharide Utilization Loci and Nutritional Specialization in a Dominant Group of Butyrate-Producing Human Colonic Firmicutes. Microb. Genomics 2016, 2, e000043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckhed, F.; Roswall, J.; Peng, Y.; Feng, Q.; Jia, H.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhong, H.; et al. Dynamics and Stabilization of the Human Gut Microbiome during the First Year of Life. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesta, M.; Janssens, G.P.J.; Debraekeleer, J.; De Wilde, R. The Effect of Oligofructose and Inulin on Faecal Characteristics and Nutrient Digestibility in Healthy Cats. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2001, 85, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggers, D.S.; Xenoulis, P.G.; Karra, D.A.; Enderle, L.L.; Köller, G.; Böttcher, D.; Steiner, J.M.; Heilmann, R.M. Fecal Calprotectin Concentrations in Cats with Chronic Enteropathies. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, R.M.; Riggers, D.S.; Trewin, I.; Köller, G.; Kathrani, A. Treatment Success in Cats with Chronic Enteropathy Is Associated with a Decrease in Fecal Calprotectin Concentrations. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1390681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, Q.; Chang, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Ge, S.; Xiong, W. Effects of Lactoferrin and Lactobacillus Supplementation on Immune Function, Oxidative Stress, and Gut Microbiota in Kittens. Animals 2024, 14, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michałek, M.; Tabiś, A.; Pasławska, U.; Noszczyk-Nowak, A. Antioxidant Defence and Oxidative Stress Markers in Cats with Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A Pilot Study. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, E.R.; Lam, Y.K.; Uhlig, H.H. Short-Chain Fatty Acids: Linking Diet, the Microbiome and Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, X.; Fei, W.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, C. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Immunity, Inflammation and Metabolism. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-T.; Hsieh, Y.-T.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chen, M.-J. Improving Effect of a Probiotic Mixture on Memory and Learning Abilities in D-Galactose–Treated Aging Mice. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y. Chitosan Enhances Intestinal Health in Cats by Altering the Composition of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Metabolites 2023, 13, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, M. Noninvasive Metabolic Profiling for Painless Diagnosis of Human Diseases and Disorders. Future Sci. OA 2016, 2, FSO106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Locher, K.P. Structure and Mechanism of Human ABC Transporters. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2023, 52, 275–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.K.S.; Peixoto, C.A. Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Inflammation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, K.; Brasel, K. Bile Metabolism and Lithogenesis. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 94, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djuricic, I.; Calder, P.C. Beneficial Outcomes of Omega-6 and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Human Health: An Update for 2021. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensink, R.P.; Zock, P.L.; Kester, A.D.; Katan, M.B. Effects of Dietary Fatty Acids and Carbohydrates on the Ratio of Serum Total to HDL Cholesterol and on Serum Lipids and Apolipoproteins: A Meta-Analysis of 60 Controlled Trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froyen, E.; Burns-Whitmore, B. The Effects of Linoleic Acid Consumption on Lipid Risk Markers for Cardiovascular Disease in Healthy Individuals: A Review of Human Intervention Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, D.E.; Jackson, M.I. Dietary Fatty Acids Change Circulating Fatty Acids, Microbial Putrefactive Postbiotics and Betaine Status in the Cat. Animals 2020, 10, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Dietary Composition | % | Nutrient Content | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goat milk power | 36.00 | Moisture | 3.50 |
| Whey protein concentrate | 27.72 | Crude protein | 33.00 |
| Cream powder | 20.00 | Crude fat | 39.00 |
| Cheese powder | 4.00 | Ash | 4.00 |
| Sunflower seed oil powder | 6.00 | Calcium | 1.10 |
| Flaxseed oil powder | 1.00 | Phosphorus | 0.80 |
| Palmitic triglyceride | 1.00 | ||
| Calcium hydrogen phophate | 1.10 | ||
| Tricalcium phosphate | 0.60 | ||
| Fructooligosaccharide | 1.00 | ||
| L-arginine | 0.60 | ||
| Fish oil powder | 0.35 | ||
| Taurine | 0.25 | ||
| Colostrum Powder | 0.10 | ||
| Arachidonic acid | 0.10 | ||
| Salt | 0.10 | ||
| Lactoferrin | 0.03 | ||
| Mineral complexes and vitamins 2 | 0.05 |
| Kitten Age/Week | Number of Meals/Days | mL of Milk per Meal |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 | 2–4 |
| 2 | 6 | 5–10 |
| 3 | 5 | 10–15 |
| 4 | 5 | 10–15 |
| 5 | 4 | 10–15 |
| Litters | CON | EMR | Male:Female |
|---|---|---|---|
| Litter 1 | N = 2 | N = 2 | 3:1 |
| Litter 2 | N = 2 | N = 2 | 1:1 |
| Litter 3 | N = 2 | N = 2 | 1:3 |
| Total | N = 6 | N = 6 | 1:1 |
| Experimental Time (Day) | CON | EMR |
|---|---|---|
| BW (g) | BW (g) | |
| 0 | 138.33 ± 6.78 | 139.87 ± 10.92 |
| 7 | 249.50 ± 15.67 | 222.72 ± 24.26 |
| 14 | 297.00 ± 14.76 | 298.38 ± 30.99 |
| 28 | 396.83 ± 20.78 | 470.72 ± 40.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, L. Alterations in the Intestinal Microbiome and Metabolic Profile of British Shorthair Kittens Fed with Milk Replacer. Animals 2024, 14, 2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162346
Wang C, Zhu Q, Li Y, Guo J, Li L. Alterations in the Intestinal Microbiome and Metabolic Profile of British Shorthair Kittens Fed with Milk Replacer. Animals. 2024; 14(16):2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162346
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cheng, Qi Zhu, Yinan Li, Jiaxing Guo, and Lian Li. 2024. "Alterations in the Intestinal Microbiome and Metabolic Profile of British Shorthair Kittens Fed with Milk Replacer" Animals 14, no. 16: 2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162346
APA StyleWang, C., Zhu, Q., Li, Y., Guo, J., & Li, L. (2024). Alterations in the Intestinal Microbiome and Metabolic Profile of British Shorthair Kittens Fed with Milk Replacer. Animals, 14(16), 2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14162346







