Effect of Warming on Personality of Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) and Medaka Fish (Oryzias latipes)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Animals and Rearing Conditions
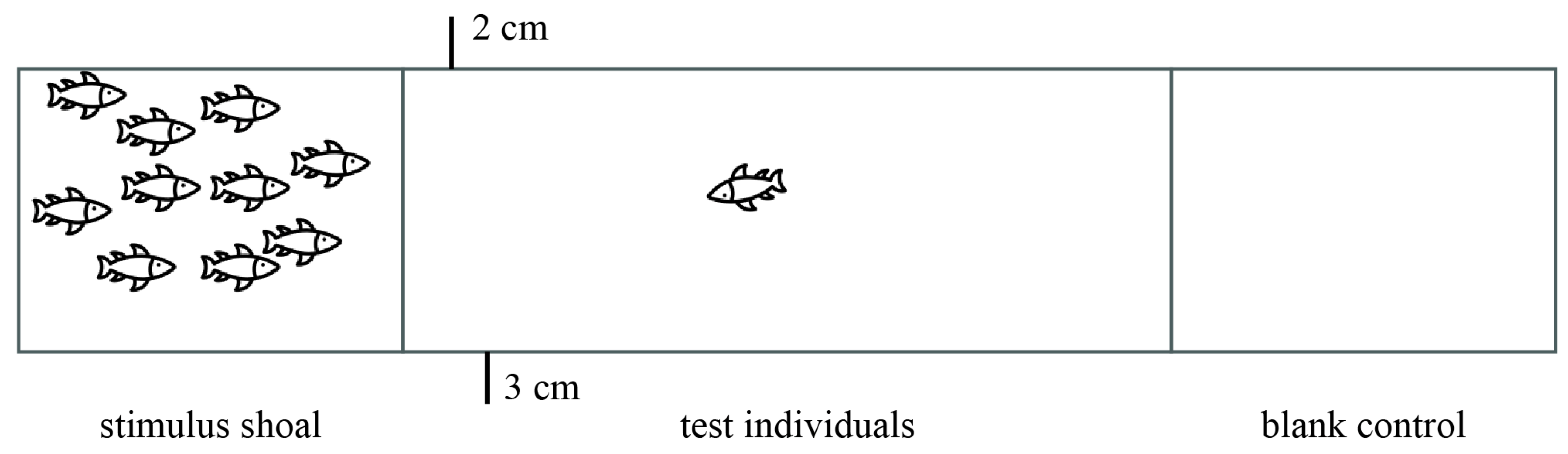
2.2. Sociability Assay
2.3. Boldness Assay
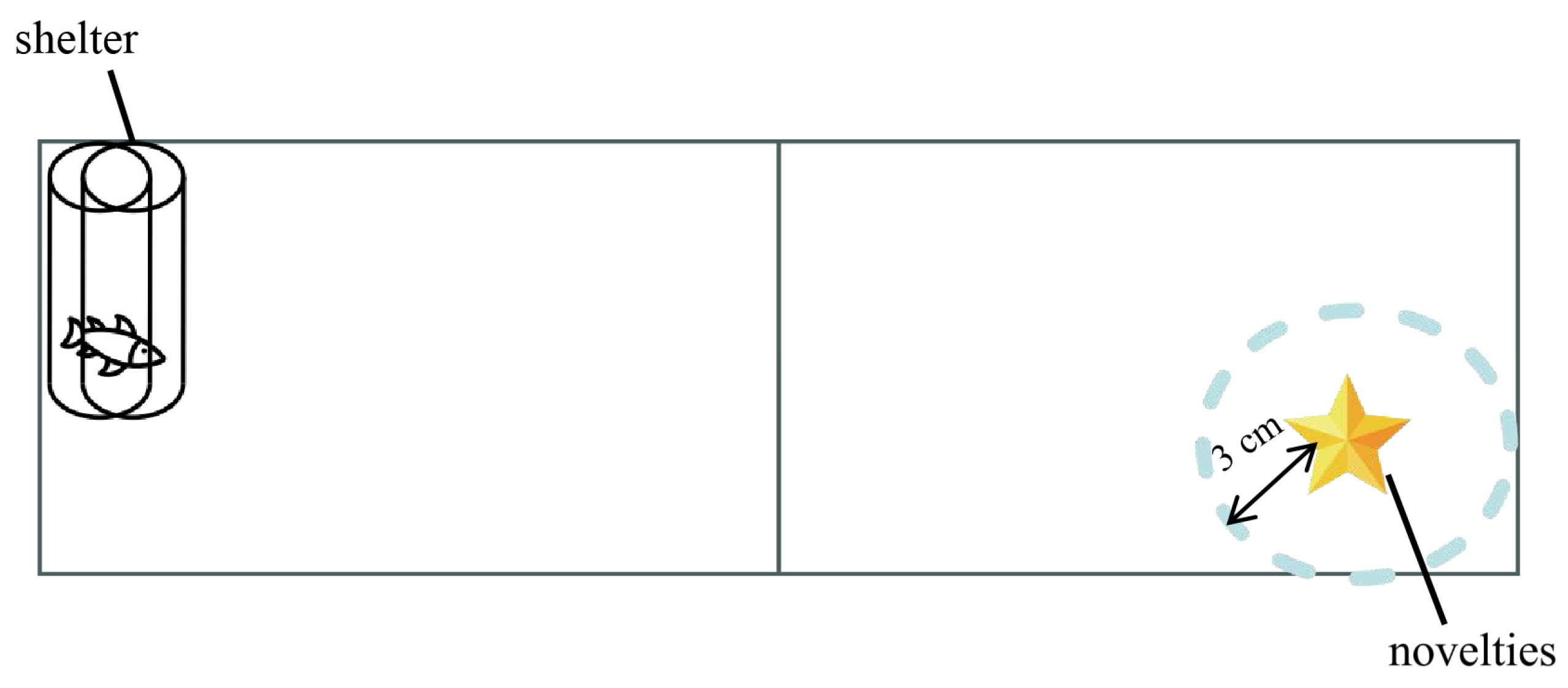
2.4. Exploration Assay
2.5. Novelty Assay
2.6. Ethical Statement
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Repeatability Estimates
3.2. Behavioral Syndromes
3.3. Effects of Factors on Behavioral Traits
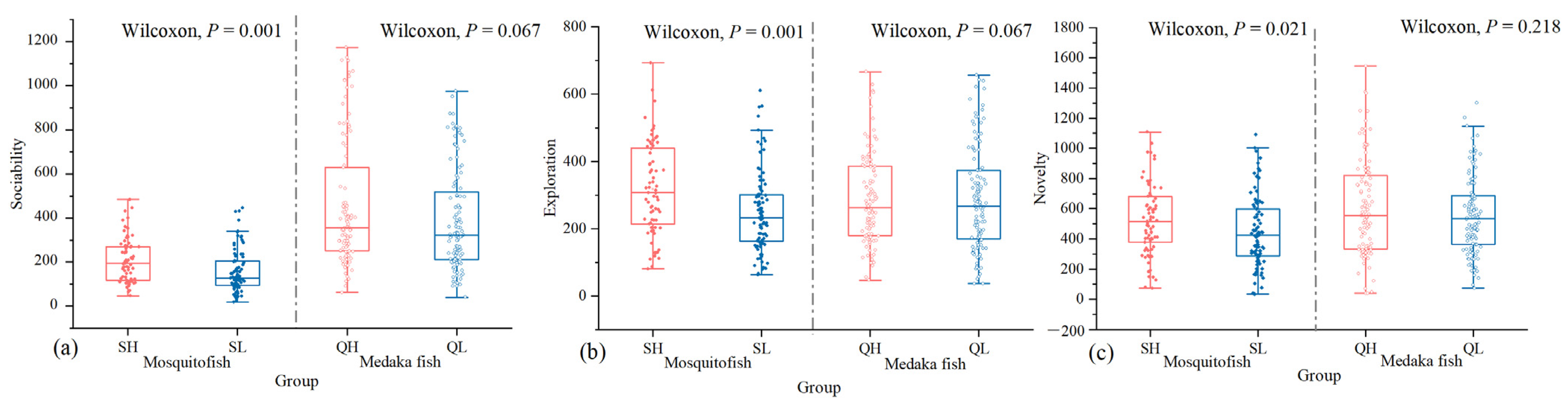
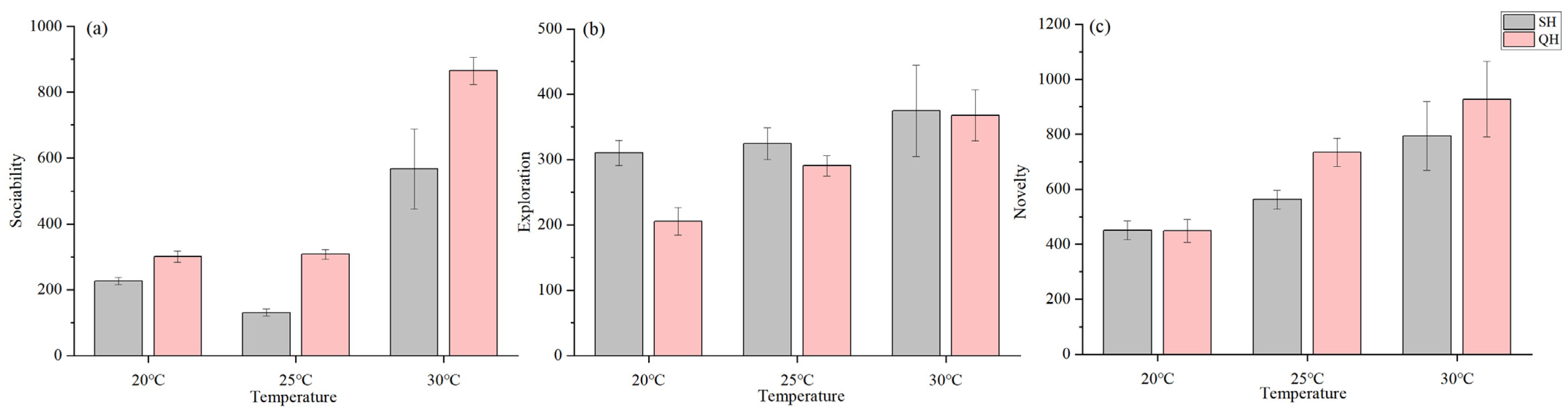
3.3.1. Sociability
3.3.2. Exploration
3.3.3. Novelty
3.3.4. Boldness
4. Discussion
4.1. Behavioral Repeatability and Behavioral Syndromes
4.2. Effects of Temperature on Personality
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lipczynska-Kochany, E. Effect of climate change on humic substances and associated impacts on the quality of surface water and groundwater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 1548–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, J.; Sharma, A.K. A comprehensive review of climate change’s imprint on ecosystems. J. Water Clim. Change 2023, 14, 4273–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Jiang, X.; Hu, C.; Chen, D. More frequent summer heat waves in southwestern China linked to the recent declining of Arctic sea ice. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, G.; Alfieri, L.; Wyser, K.; Mentaschi, L.; Betts, R.A.; Carrao, H.; Spinoni, J.; Vogt, J.; Feyen, L. Global changes in drought conditions under different levels of warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Yao, F.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H. Drivers to dust emissions over dust belt from 1980 to 2018 and their variation in two global warming phases. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, M.B.; Rahbek, C. How does climate change affect biodiversity? Science 2006, 313, 1396–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez, S.; Arets, E.; Alkemade, R.; Verwer, C.; Leemans, R. Assessing the impacts of climate change on biodiversity: Is below 2 °C enough? Clim. Change 2019, 154, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz, J.J.; Terwin, J.R.; Whitlatch, R.B.; Osman, R.W. Linking climate change and biological invasions: Ocean warming facilitates nonindigenous species invasions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15497–15500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, K.J.; Bhagwat, S.A. Biodiversity and climate change. Science 2009, 326, 806–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, N.A.; Ainsworth, E.A.; Bahuguna, R.N.; Broadley, M.R.; Busch, W.; Carpita, N.C.; Castrillo, G.; Chory, J.; DeHaan, L.R.; Duarte, C.M.; et al. Climate change challenges, plant science solutions. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 24–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandalinas, S.I.; Balfagón, D.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Mittler, R. Plant responses to climate change: Metabolic changes under combined abiotic stresses. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 3339–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.K.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Egidi, E.; Guirado, E.; Leach, J.E.; Liu, H.; Trivedi, P. Climate change impacts on plant pathogens, food security and paths forward. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, S.; Sidhu, G.P.S. Climate change regulated abiotic stress mechanisms in plants: A comprehensive review. Plant Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, S.; Lane, J.E. Climate change and mammals: Evolutionary versus plastic responses. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, J.; Kamilar, J.M.; Beaudrot, L.; Reed, K.E. Strong influence of palaeoclimate on the structure of modern African mammal communities. Proc. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20161207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, A.J.; Thomson, J.S.; Smith, C.; Burton, H.C.; Davis, B.; Watts, P.C.; Sneddon, L.U. Environmental change alters personality in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Anim. Behav. 2013, 85, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Niella, Y.; Butcher, P.; Holmes, B.; Barnett, A.; Harcourt, R.J. Forecasting intraspecific changes in distribution of a wide-ranging marine predator under climate change. Oecologia 2022, 198, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellard, C.; Thuiller, W.; Leroy, B.; Genovesi, P.; Bakkenes, M.; Courchamp, F. Will climate change promote future invasions? Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 3740–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, B.; Aldridge, D.C. Evaluating the combined threat of climate change and biological invasions on endangered species. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 160, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juette, T.; Cucherousset, J.; Cote, J. Animal personality and the ecological impacts of freshwater non-native species. Curr. Zool. 2014, 60, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilizzi, L.; Copp, G.H.; Hill, J.E.; Adamovich, B.; Aislabie, L.; Akin, D.; Al-Faisal, A.J.; Almeida, D.; Azmai, M.A.; Bakiu, R.J. A global-scale screening of non-native aquatic organisms to identify potentially invasive species under current and future climate conditions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 788, 147868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez, J.M.; D’Antonio, C.M.; Dukes, J.S.; Grosholz, E.D.; Olden, J.D.; Sorte, C.J.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Bradley, B.A.; Early, R.; Ibáñez, I.; et al. Will extreme climatic events facilitate biological invasions? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahel, F.J.; Olden, J.D. Assessing the effects of climate change on aquatic invasive species. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorte, C.J.; Ibáñez, I.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Molinari, N.A.; Miller, L.P.; Grosholz, E.D.; Diez, J.M.; D’Antonio, C.M.; Olden, J.D.; Jones, S.J.; et al. Poised to prosper? A cross-system comparison of climate change effects on native and non-native species performance. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, G.; Perkins, D.M.; Brown, L.E. Climate change and freshwater ecosystems: Impacts across multiple levels of organization. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. B 2010, 365, 2093–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Maldonado, S.; Camacho-Cervantes, M. Effect of a temperature gradient on the behaviour of an endangered Mexi-can topminnow and an invasive freshwater fish. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facon, B.; Genton, B.J.; Shykoff, J.; Jarne, P.; Estoup, A.; David, P. A general eco-evolutionary framework for understanding bioinvasions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, T.; Sih, A.; Cote, J.; Fogarty, S.; Weinersmith, K. Personality traits and dispersal tendency in the invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Proc. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, R.A.; Badyaev, A.V. Coupling of dispersal and aggression facilitates the rapid range expansion of a passerine bird. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15017–15022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, S.; Cote, J.; Sih, A. Social personality polymorphism and the spread of invasive species: A model. Am. Nat. 2011, 177, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudio, C.; Gherardi, F. Animal personalities matter for biological invasions. Behavioral syndromes: An ecological and evolutionary overview. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 281, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapple, D.G.; Simmond, S.M.; Wong, B.B. Can behavioral and personality traits influence the success of unintentional species introductions? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 271, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehage, J.S.; Sih, A. Dispersal Behavior, Boldness, and the Link to Invasiveness: A Comparison of Four Gambusia Species. Biol. Invasions 2004, 221, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J. The role of behavior in the success of invasive crustaceans. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Phy. 2010, 811, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sih, A.; Bell, A.; Johnson, J.C. Behavioral syndromes: An ecological and evolutionary overview. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 197, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, I.F.A.; Paranhos, C.O.; Bonifácio, C.T.; Favero, G.C.; Luz, R.K. Influence of personality traits on reproduction and sperm quality of Oreochromis Niloticus. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Phy. 2023, 991, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.; Weissing, F.J. An explanatory framework for adaptive personality differences. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. B 2010, 365, 3959–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santicchia, F.; Gagnaison, C.; Bisi, F.; Martinoli, A.; Matthysen, E.; Bertolino, S.; Wauters, L.A. Habitat-dependent effects of personality on survival and reproduction in red squirrels. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2018, 72, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, J.; Fogarty, S.; Brodin, T.; Weinersmith, K.; Sih, A. Personality-dependent dispersal in the invasive mosquitofish: Group composition matters. Proc. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, D.M. Biological invasions: Lessons for ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1993, 84, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, P.B.; Marchetti, M.P. Predicting invasion success: Freshwater fishes in California as a model. BioScience 2006, 56, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, J.; Clobert, J. Social personalities influence natal dispersal in a lizard. Proc. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Catot, G.; Magellan, K.; García-Berthou, E. Temperature-specific competition between invasive mosquitofish and an endangered cyprinodontid fish. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudina, S.; Hock, K.; Žganec, K. The role of aggression in range expansion and biological invasions. Curr. Zool. 2014, 60, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.A.; Sgrò, C.M. Climate change and evolutionary adaptation. Nature 2011, 470, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.P.; Pilastro, A.; Schlupp, I. Ecology and Evolution of Poeciliid Fishes. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 166, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, F.; Zhan, F.; Li, C. Environmental temperature during early life affects the personality of mosquitofish in adulthood. Curr. Zool. 2021, 67, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, G.H. Plague Minnow or Mosquito Fish? A Review of the Biology and Impacts of Introduced Gambusia Species. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. S 2008, 39, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Berthou, E.; Alcaraz, C.; Pou-Rovira, Q.; Zamora, L.; Coenders, G.; Feo, C. Introduction pathways and establishment rates of invasive aquatic species in Europe. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgers, L.; Schwarzer, J. The untapped potential of medaka and its wild relatives. Elife 2019, 8, 46994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogowski, D.L.; Stockwell, C.A. Assessment of Potential Impacts of Exotic Species on Populations of a Threatened Species, White Sands Pupfish, Cyprinodon tularosa. Biol. Invasions 2005, 8, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferderer, A.; Davis, A.R.; Wong, M.Y. Temperature and body size influence personality and behavioural syndromes in an invasive crayfish. Anim. Behav. Anim. Behav. 2022, 190, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollan, K.R.; Trumble, I.M.; Reifeis, S.A.; Ferrer, O.; Bay, C.P.; Baldoni, P.L.; Hudgens, M.G. Precise and accurate power of the rank-sum test for a continuous outcome. J. Biopharm. Stat. 2020, 30, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.; Morrissey, M.B. The distinction between repeatability and correlation in studies of animal behaviour. Anim. Behav. 2021, 175, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffel, M.A.; Nakagawa, S.; Schielzeth, H.; Goslee, S. rptR: Repeatability estimation and variance decomposition by generalized linear mixed-effects models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polverino, G.; Buchholz, K.M.; Goulet, C.T.; Michelangeli, M.; Chapple, D.G. Temporal repeatability of behaviour in a lizard: Implications for behavioural syndrome studies. Evol. Ecol. 2023, 37, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruelheide, H.; Tichý, L.; Chytrý, M.; Jansen, F. Implementing the formal language of the vegetation classification expert systems (ESy) in the statistical computing environment R. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2021, 24, 12562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Mao, L. glmm. hp: An R package for computing individual effect of predictors in generalized linear mixed models. Plant Ecol. 2022, 15, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peignier, M.; Araya-Ajoy, Y.G.; Ringler, M.; Ringler, E. Personality traits differentially affect components of reproductive success in a Neotropical poison frog. Proc. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2023, 290, 20231551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Su, L.; Zhang, X.J.A. Risk Predictability in Early Life Shapes Personality of Mosquitofish in Adulthood. Animals 2023, 13, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamin, T.; Morinay, J.; Germain, M.; Récapet, C.; Doligez, B. Behavioural syndrome between boldness and aggressiveness and link with reproductive success in a wild bird population. Anim. Behav. 2023, 197, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R.; Fernandes, Y.; Pereira, T. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) responds to the animated image of a predator: Towards the development of an automated aversive task. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 201, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.M.; Hankison, S.J.; Laskowski, K.L. The repeatability of behaviour: A meta-analysis. Anim. Behav. 2009, 77, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.E. Primates in Communities: The Ecology of Competitive, Predatory, Parasitic and Mutualistic Interactions between Primates and Other species. Biol. Anthropol. 2012, 3, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Dosmann, A.J.; Brooks, K.C.; Mateo, J.M. Within-Individual Correlations Reveal Link Between a Behavioral Syndrome, Condition, and Cortisol in Free-Ranging Belding’s Ground Squirrels. Ethology 2014, 121, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, A.C.; Carl, T.; Foerster, K. Repeatability and consistency of individual behaviour in juvenile and adult Eurasian harvest mice. Sci. Nat. 2017, 104, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhill, V.; Pandelis, G.G.; Papuga, J.; Sabol, A.C.; Rife, A.; Rubi, T.; Hoffman, S.M.G.; Dantzer, B. Personality and behavioral syndromes in two Peromyscus species: Presence, lack of state dependence, and lack of association with home range size. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2021, 75, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réale, D.; Reader, S.M.; Sol, D.; McDougall, P.T.; Dingemanse, N.J. Integrating animal temperament within ecology and evolution. Biol. Rev. 2007, 82, 291–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilakouta, N.; O’Donnell, P.J.; Crespel, A.; Levet, M.; Claireaux, M.; Humble, J.L.; Kristjánsson, B.K.; Skúlason, S.; Lindström, J.; Metcalfe, N.B.; et al. A warmer environment can reduce sociability in an ectotherm. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 29, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cote, J.; Fogarty, S.; Sih, A. Individual sociability and choosiness between shoal types. Anim. Behav. 2012, 83, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliason, E.J.; Clark, T.D.; Hague, M.J.; Hanson, L.M.; Gallagher, Z.S.; Jeffries, K.M.; Gale, M.K.; Patterson, D.A.; Hinch, S.G.; Farrell, A.P. Differences in Thermal Tolerance Among Sockeye Salmon Populations. Science 2011, 332, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, M.; Bridger, D.; Biro, P.A. How does temperature affect behaviour? Multilevel analysis of plasticity, personality and predictability in hermit crabs. Anim. Behav. 2013, 86, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couchoux, C.; Garant, D.; Aubert, M.; Clermont, J.; Réale, D. Behavioral variation in natural contests: Inte-grating plasticity and personality. Behav. Ecoloy 2021, 32, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, A.L.; Wright, P.C.; Louis, E.E.; Bradley, B.J. Communal nesting, kinship, and maternal success in a social primate. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2013, 67, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altizer, S.; Nunn, C.L.; Thrall, P.H.; Gittleman, J.L.; Antonovics, J.; Cunningham, A.A.; Dobson, A.P.; Ezenwa, V.; Jones, K.E.; Pedersen, A.B.; et al. Social organization and parasite risk in mammals: Integrating theory and empirical studies. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. S. 2003, 34, 517–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnally, E.L.; Capitanio, J.P.; Leibel, R.; Deng, L.; LeDuc, C.; Haghighi, F.; Mann, J.J. Epigenetic regulation of serotonin transporter expression and behavior in infant rhesus macaques. Genes Brain Behav. 2010, 9, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, A.I. Evolutionary models of metabolism, behaviour and personality. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. B 2010, 365, 3969–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A.; Johnston, N.M. Scaling of metabolic rate with body mass and temperature in teleost fish. J. Anim. Ecol. 1999, 68, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biro, P.A.; Beckmann, C.; Stamps, J.A. Small within-day increases in temperature affects boldness and alters personality in coral reef fish. Proc. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Guerrero, J.A.; Lerma, M.; Mellink, E.; Suazo-Guillén, E.; Peñaloza-Padilla, E.A. Environmentally-mediated flexible foraging strategies in brown boobies in the Gulf of California. Ardea 2016, 104, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Blackburn, T.M.; Dyer, E.E.; Genovesi, P.; Hulme, P.E.; Jeschke, J.M.; Essl, F. No saturation in the accumulation of alien species worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.S.; Jablonski, P.G. Alternative reproductive tactics shape within-species variation in behavioral syndromes. Behav. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelangeli, M.; Chapple, D.G.; Goulet, C.T.; Bertram, M.G.; Wong, B.B. Behavioral syndromes vary among geographically distinct populations in a reptile. Behav. Ecol. 2018, 30, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réale, D.; Garant, D.; Humphries, M.M.; Bergeron, P.; Careau, V.; Montiglio, P.O. Personality and the emergence of the pace-of-life syndrome concept at the population level. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. B 2010, 365, 4051–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.J.; Zhang, N.; Fan, J. Personality and cognition: Shoal size discrimination performance is related to boldness and sociability among ten freshwater fish species. Anim. Cogn. 2024, 27, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Behavior | Response Variable | Group | R ± SE | CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociability | distance travelled near stimulus shoal (cm) | warming group | 0.333 ± 0.174 | 0.002, 0.591 |
| control group | 0.333 ± 0.118 | 0.152, 0.597 | ||
| percentage of time spent near stimulus shoal (%) | warming group | 0.332 ± 0.138 | 0.111, 0.630 | |
| control group | 0.332 ± 0.167 | 0.010, 0.578 | ||
| Exploration | distance travelled (cm) | warming group | 0.333 ± 0.136 | 0.134, 0.644 |
| control group | 0.333 ± 0.126 | 0.139, 0.623 | ||
| percentage of time spent moving (%) | warming group | 0.327 ± 0.145 | 0.107, 0.649 | |
| control group | 0.324 ± 0.128 | 0.139, 0.611 | ||
| Novelty | distance travelled (cm) | warming group | 0.333 ± 0.134 | 0.120, 0.643 |
| control group | 0.333 ± 0.120 | 0.149, 0.607 | ||
| percentage of time spent moving (%) | warming group | 0.292 ± 0.193 | 0.004, 0.686 | |
| control group | 0.299 ± 0.174 | 0.001, 0.633 | ||
| Boldness | time spent continuously outside the shelter (s) | warming group | 0.287 ± 0.146 | 0.001, 0.576 |
| control group | 0.291 ± 0.172 | 0.060, 0.621 |
| Behavior | Response Variable | Group | R ± SE | CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociability | distance travelled near stimulus shoal (cm) | warming group | 0.333 ± 0.112 | 0.173, 0.612 |
| control group | 0.333 ± 0.108 | 0.178, 0.595 | ||
| percentage of time spent near stimulus shoal (%) | warming group | 0.331 ± 0.115 | 0.161, 0.601 | |
| control group | 0.331 ± 0.158 | 0.176, 0.606 | ||
| Exploration | distance travelled (cm) | warming group | 0.333 ± 0.114 | 0.167, 0.595 |
| control group | 0.333 ± 0.110 | 0.171, 0.593 | ||
| percentage of time spent moving (%) | warming group | 0.325 ± 0.125 | 0.136, 0.617 | |
| control group | 0.324 ± 0.154 | 0.149, 0.581 | ||
| Novelty | distance travelled (cm) | warming group | 0.333 ± 0.110 | 0.177, 0.591 |
| control group | 0.333 ± 0.109 | 0.179, 0.591 | ||
| percentage of time spent moving (%) | warming group | 0.297 ± 0.139 | 0.045, 0.605 | |
| control group | 0.297 ± 0.152 | 0.039, 0.601 | ||
| Boldness | time spent continuously outside the shelter (s) | warming group | 0.291 ± 0.134 | 0.100, 0.620 |
| control group | 0.291 ± 0.157 | 0.129, 0.588 |
| Sociability | Exploration | Novelty | Boldness | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociability | Among-individual | - | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| Within-individual | - | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.20 | |
| Phenotypic | - | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.19 | |
| Exploration | Among-individual | −0.51, 0.56 | - | 0.36 | 0.08 |
| Within-individual | 0.08, 0.40 | - | 0.43 | 0.25 | |
| Phenotypic | 0.06, 0.33 | - | 0.42 | 0.21 | |
| Novelty | Among-individual | −0.63, 0.68 | −0.32, 0.80 | - | 0.21 |
| Within-individual | 0.08, 0.39 | 0.23, 0.59 | - | 0.14 | |
| Phenotypic | 0.07, 0.34 | 0.29, 0.55 | - | 0.14 | |
| Boldness | Among-individual | −0.83, 0.87 | −0.48, 0.62 | −0.79, 0.89 | - |
| Within-individual | 0.05, 0.35 | 0.07, 0.42 | −0.05, 0.31 | - | |
| Phenotypic | 0.05, 0.34 | 0.08, 0.36 | −0.02, 0.28 | - |
| Sociability | Exploration | Novelty | Boldness | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociability | Among-individual | - | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
| Within-individual | - | 0.47 | 0.27 | 0.15 | |
| Phenotypic | - | 0.43 | 0.24 | 0.14 | |
| Exploration | Among-individual | −0.46, 0.50 | - | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Within-individual | 0.37, 0.57 | - | 0.45 | 0.20 | |
| Phenotypic | 0.33, 0.53 | - | 0.41 | 0.19 | |
| Novelty | Among-individual | −0.48, 0.51 | −0.48, 0.50 | - | −0.02 |
| Within-individual | 0.14, 0.39 | 0.34, 0.56 | - | 0.06 | |
| Phenotypic | 0.13, 0.36 | 0.30, 0.51 | - | 0.05 | |
| Boldness | Among-individual | −0.48, 0.47 | −0.76, 0.79 | −0.45, 0.44 | - |
| Within-individual | 0.02, 0.28 | 0.07, 0.32 | −0.08, 0.20 | - | |
| Phenotypic | 0.02, 0.27 | 0.07, 0.31 | −0.07, 0.19 | - |
| Variables | Fixed Effects | Sum Sq | DenDF | F Value | p Value | Deviation Explained (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociability a | species | 13.8733 | 13.8733 | 167.6957 | ˂0.001 | 18.60 |
| group | 1.5948 | 1.5948 | 19.2778 | ˂0.001 | 6.880 | |
| acclimated temperature | 7.0356 | 7.0356 | 85.0438 | ˂0.001 | 17.34 | |
| species × group | 0.7601 | 0.7601 | 9.1877 | 0.003 | 22.10 | |
| Species × acclimated temperature | 1.051 | 1.051 | 12.7043 | ˂0.001 | 35.08 | |
| Exploration b | species | 0.0096 | 157.33 | 0.1757 | 0.676 | 5.160 |
| group | 0.19341 | 150.97 | 3.5389 | 0.062 | 10.49 | |
| acclimated temperature | 1.92932 | 281.49 | 35.3014 | ˂0.001 | 32.89 | |
| species × group | 0.24494 | 160.88 | 4.4817 | 0.036 | 10.74 | |
| Species × acclimated temperature | 0.63009 | 295.84 | 11.5289 | ˂0.001 | 40.72 | |
| Novelty c | species | 0.92054 | 147.64 | 11.2268 | 0.001 | 10.86 |
| group | 0.48735 | 141.58 | 5.9437 | 0.016 | 15.53 | |
| acclimated temperature | 1.52759 | 272.37 | 18.6303 | ˂0.001 | 27.80 | |
| species × group | 0.14318 | 151.12 | 1.7462 | 0.188 | 19.33 | |
| Species × acclimated temperature | 0.0828 | 287.2 | 1.0098 | 0.316 | 26.49 | |
| Boldness d | species | 1.45385 | 386 | 1.3447 | 0.247 | 14.85 |
| group | 0.67566 | 386 | 0.6249 | 0.430 | 25.74 | |
| acclimated temperature | 0.40093 | 386 | 0.3708 | 0.543 | 16.83 | |
| species × group | 1.18148 | 386 | 1.0928 | 0.297 | 29.70 | |
| Species × acclimated temperature | 0.56241 | 386 | 0.5202 | 0.471 | 12.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Yao, B.; Tan, Z.; Mao, C.; Ma, Y.; Qu, J. Effect of Warming on Personality of Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) and Medaka Fish (Oryzias latipes). Animals 2024, 14, 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142101
Wang R, Yao B, Tan Z, Mao C, Ma Y, Qu J. Effect of Warming on Personality of Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) and Medaka Fish (Oryzias latipes). Animals. 2024; 14(14):2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142101
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rong, Baohui Yao, Zhaoxian Tan, Chengjie Mao, Yonggui Ma, and Jiapeng Qu. 2024. "Effect of Warming on Personality of Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) and Medaka Fish (Oryzias latipes)" Animals 14, no. 14: 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142101
APA StyleWang, R., Yao, B., Tan, Z., Mao, C., Ma, Y., & Qu, J. (2024). Effect of Warming on Personality of Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) and Medaka Fish (Oryzias latipes). Animals, 14(14), 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14142101






