C1 Facetectomy and Ventral Fixation of Occipitoatlantoaxial Complex for Concurrent Congenital Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation and Atlantoaxial Instability in a Toy Poodle
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
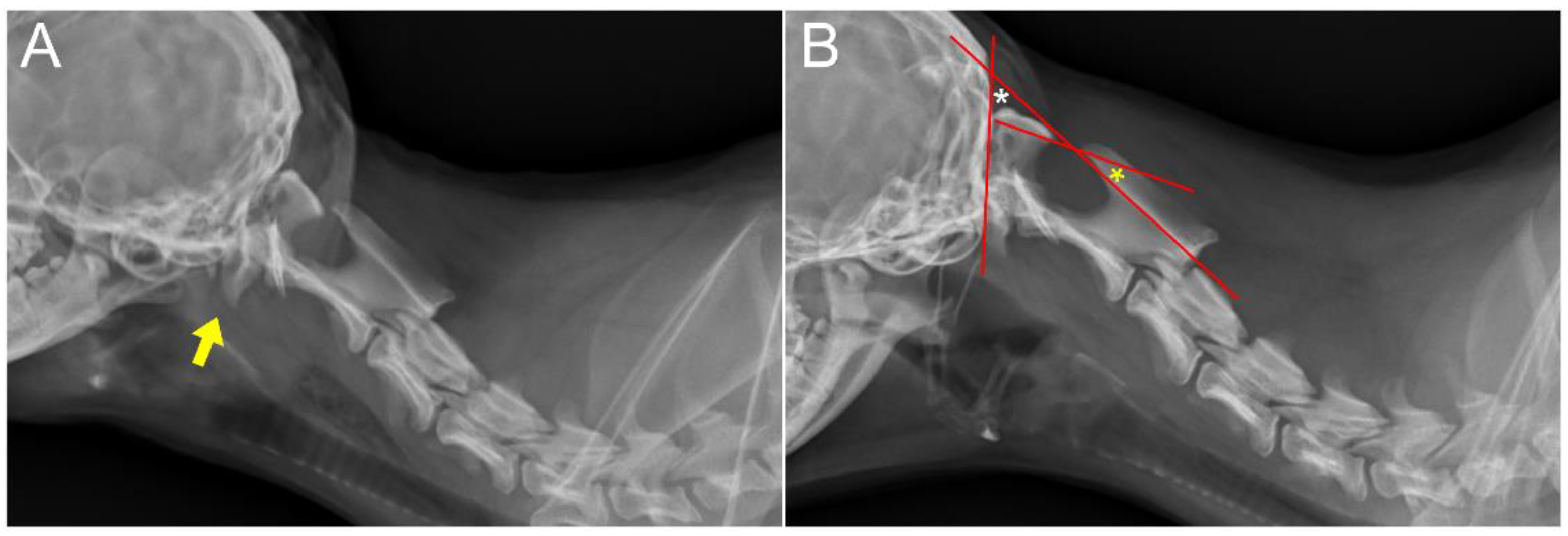
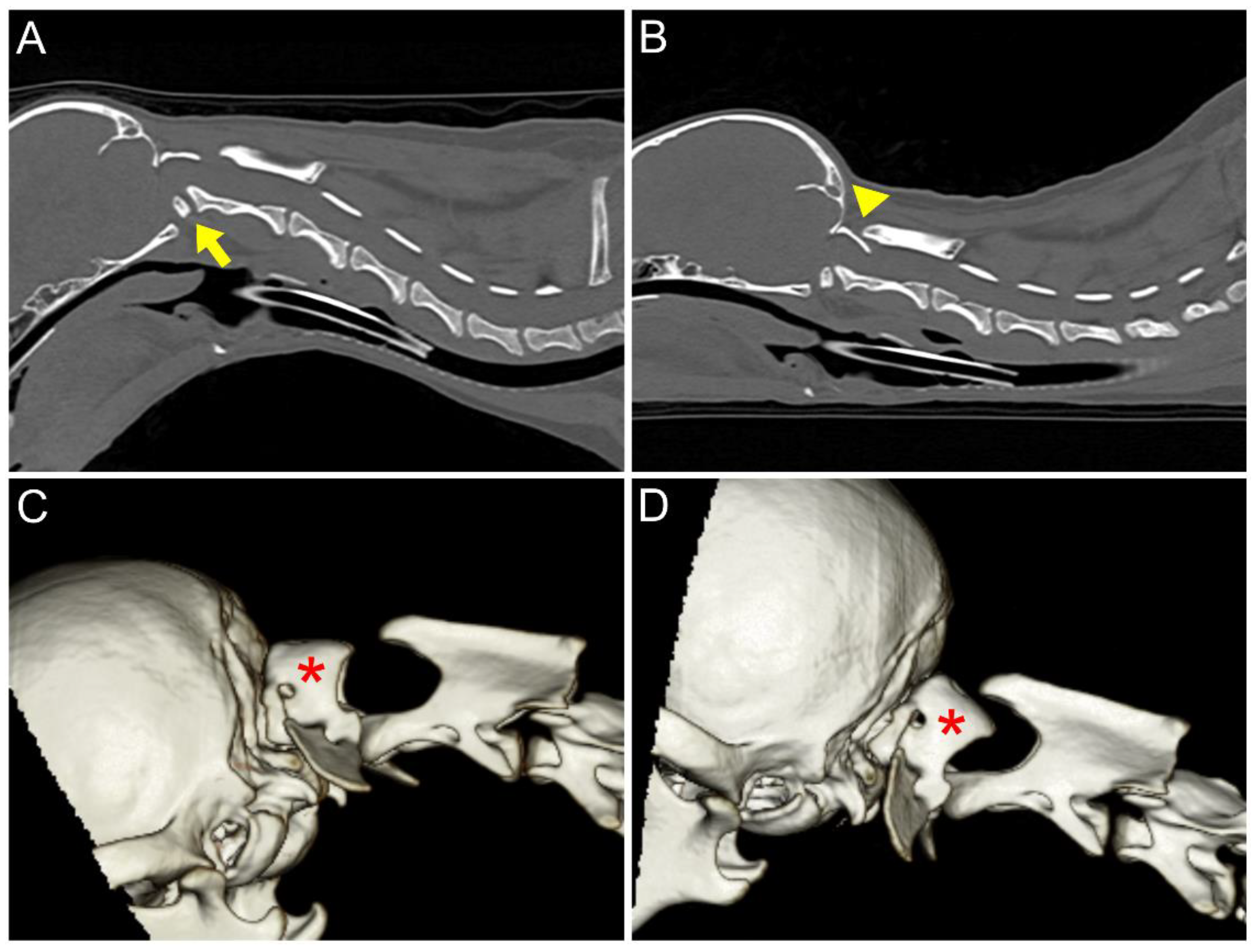
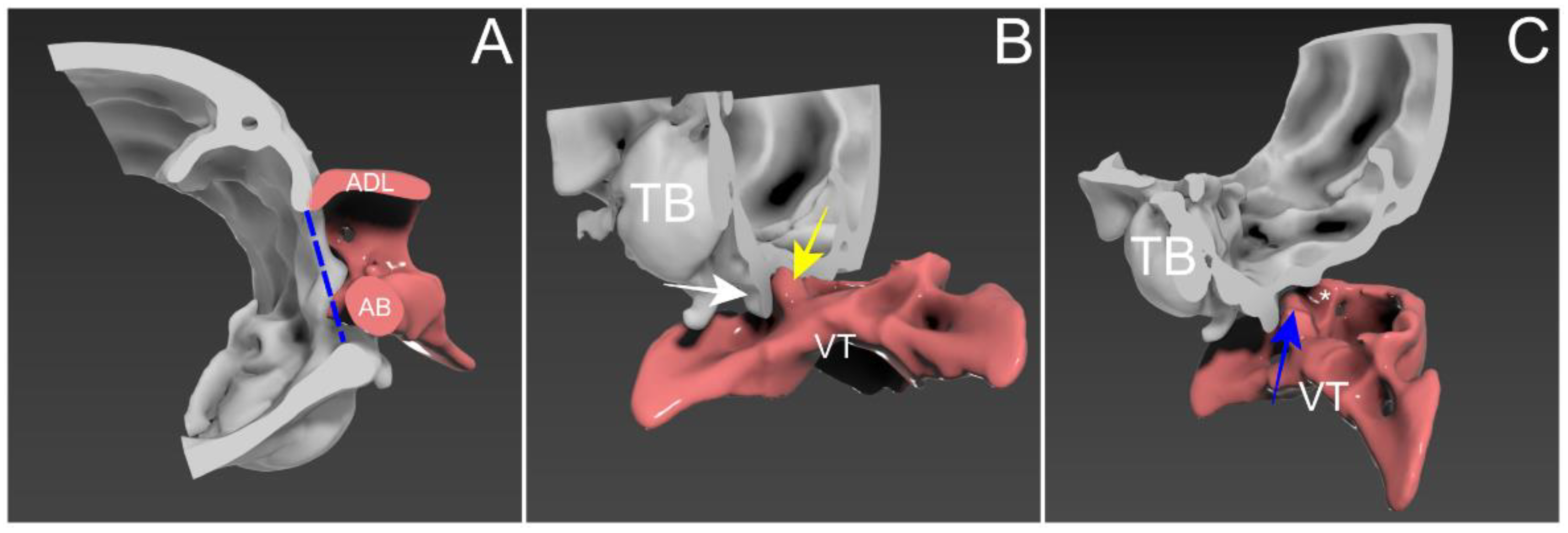
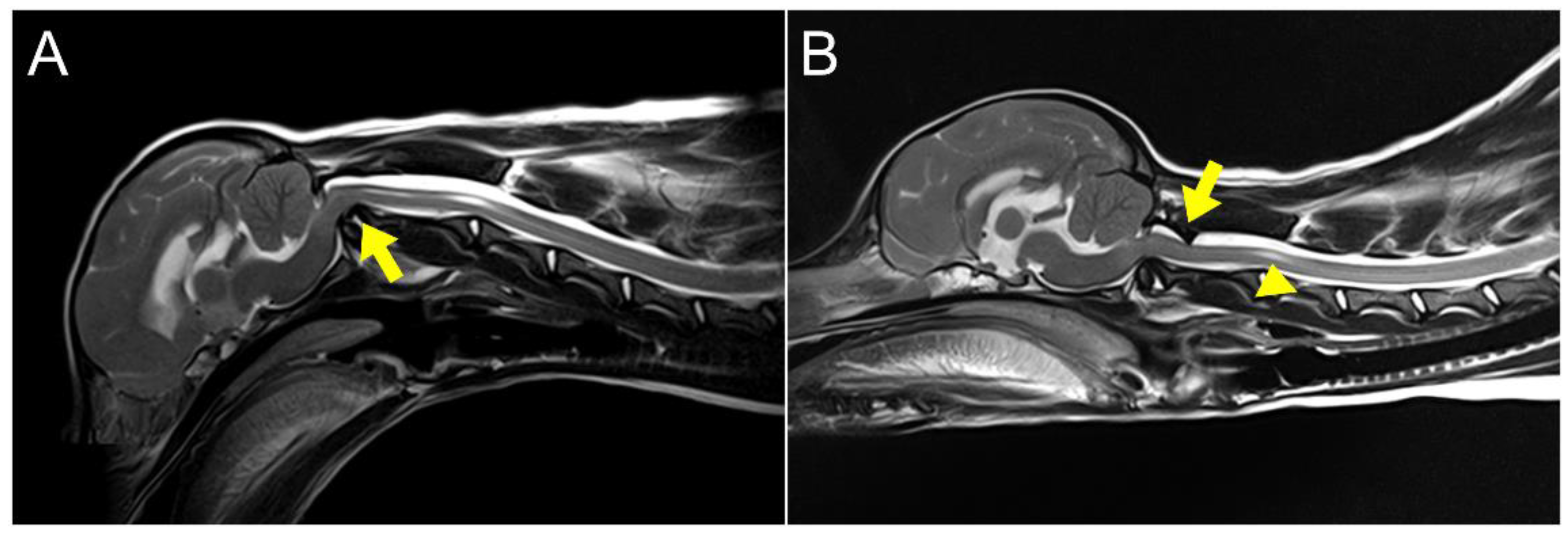
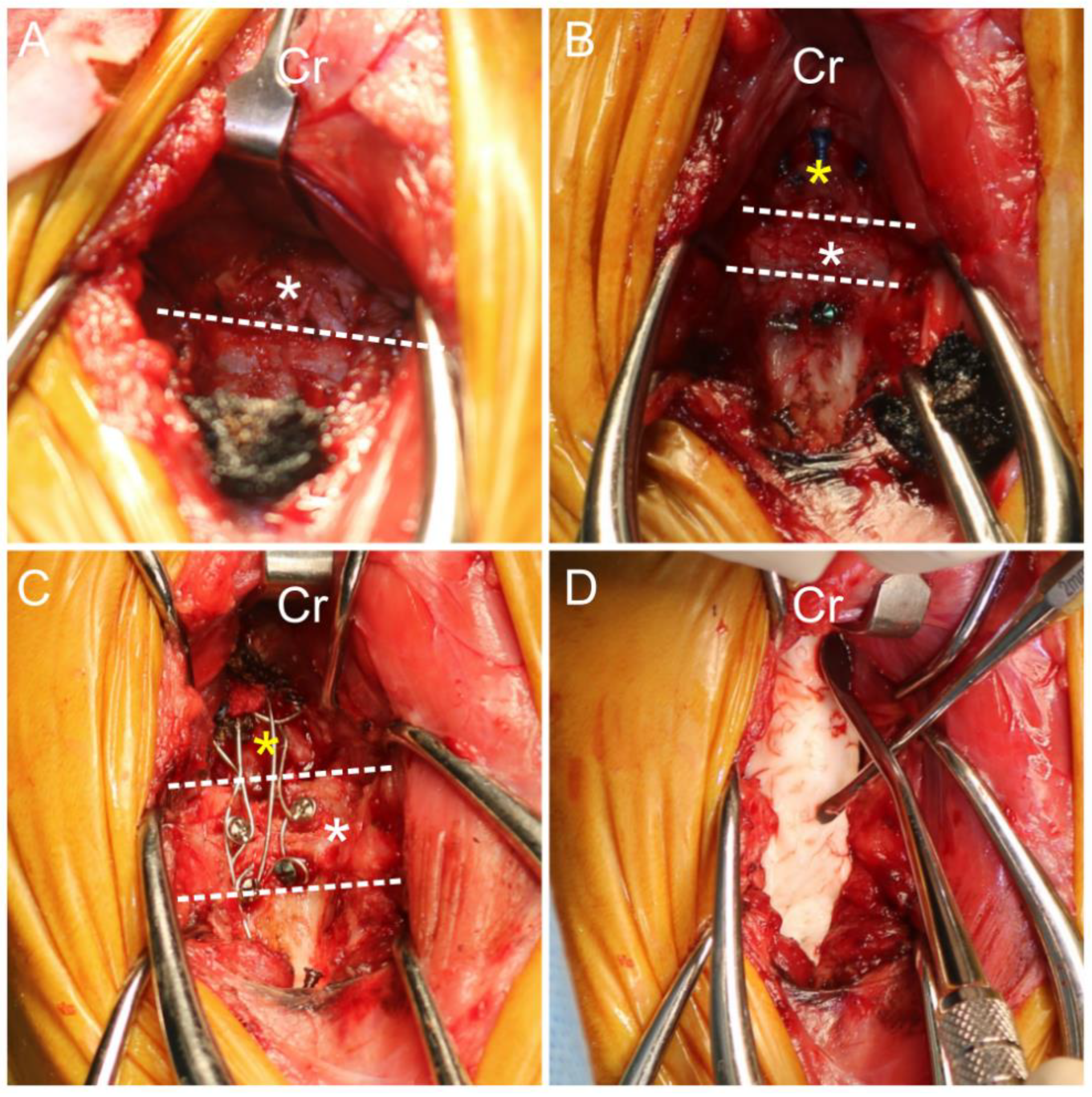
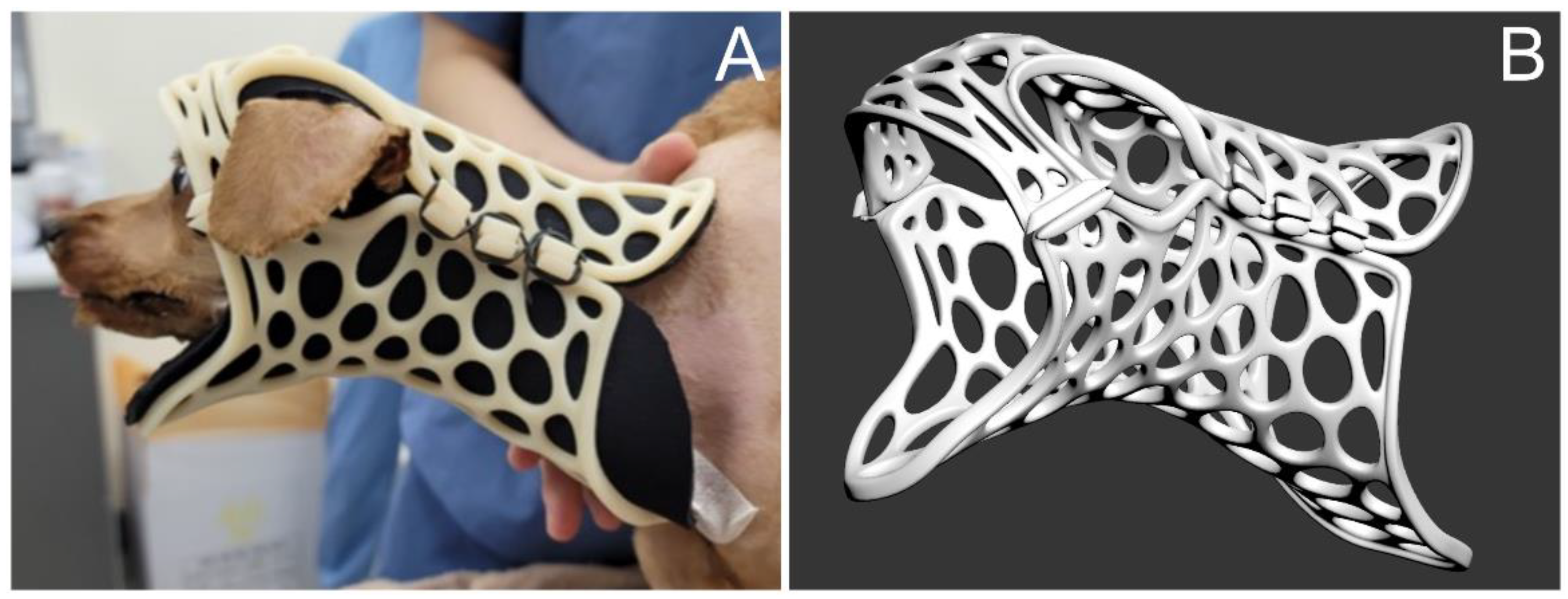
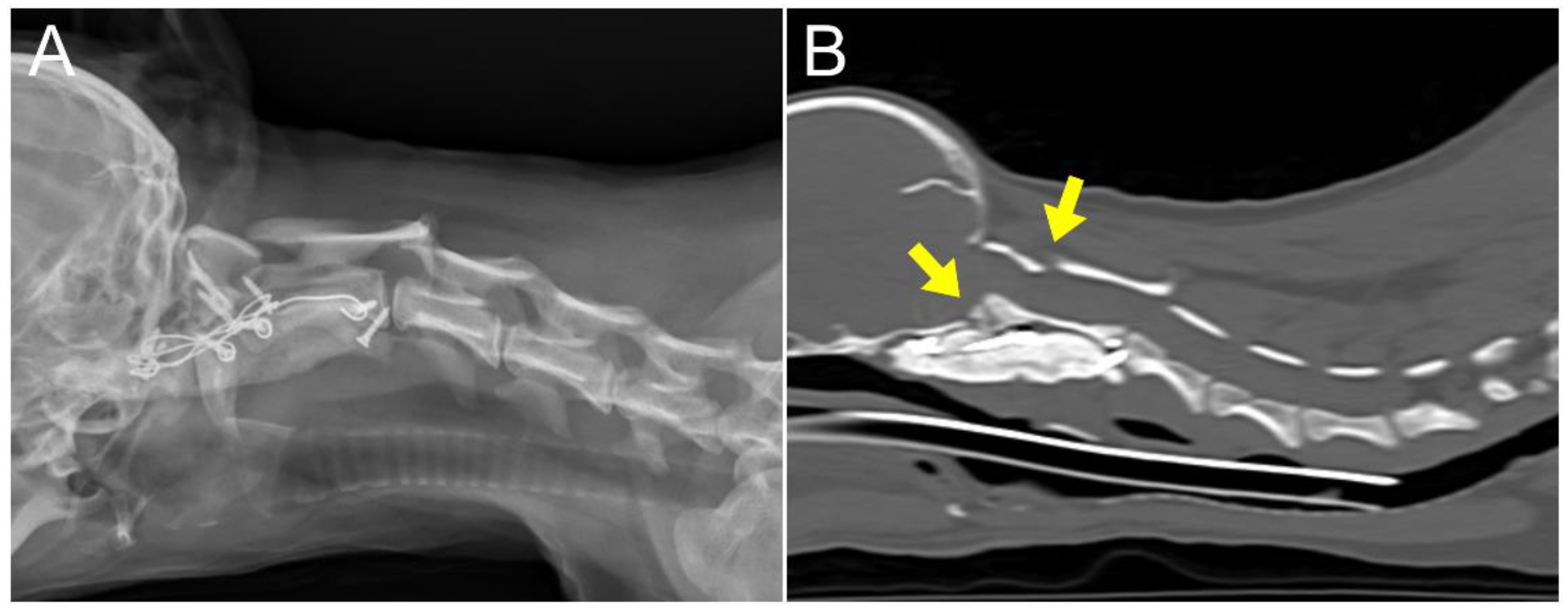
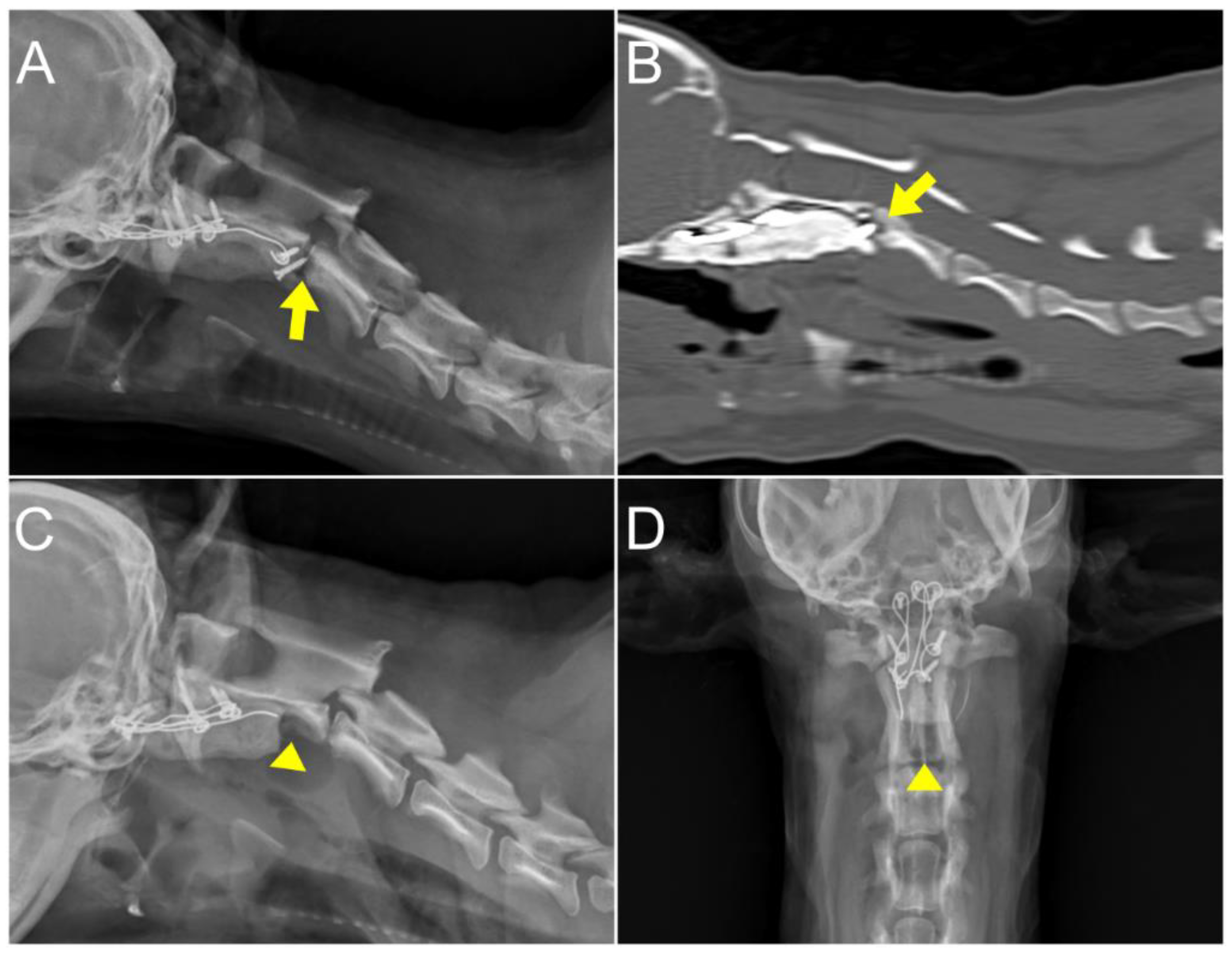
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joaquim, A.F.; Schroeder, G.D.; Vaccaro, A.R. Traumatic atlanto-occipital dislocation—A comprehensive analysis of all case series found in the spinal trauma literature. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2021, 15, 724–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlinger, M.; Charles, Y.P.; Adam, P.; Bierry, G.; Dosch, J.C.; Steib, J.P.; Bonnomet, F. Survivor of a traumatic atlanto-occipital dislocation. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2011, 97, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dolera, M.; Malfassi, L.; Bianchi, C.; Carrara, N.; Corbetta, L.; Finesso, S.; Marcarini, S.; Mazza, G.; Pavesi, S.; Sala, M. Zygomatic arch-atlas wing stabilization in 5 dogs with atlanto-occipital dislocation. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, D.J.; Loughin, C.A.; Dewey, C.W.; Marino, L.J.; Sackman, J.J.; Lesser, M.L.; Akerman, M.B. Morphometric features of the craniocervical junction region in dogs with suspected Chiari-like malformation determined by combined use of magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, C.W.; Da Costa, R.C. Practical Guide to Canine and Feline Neurology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Rotter, C.; Rusbridge, C.; Fitzpatrick, N. Occipitoatlantoaxial malformation in a dog treated with a custom-made implant. VCOT Open 2020, 3, e170–e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowler, S.P.; Galea, G.L.; Rusbridge, C. Morphogenesis of canine Chiari malformation and secondary syringomyelia: Disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Itamoto, K.; Eto, S.; Haraguchi, T.; Nishikawa, S.; Tani, K.; Itoh, Y.; Hiyama, M.; Iseri, T.; Nakaichi, M.; et al. Craniocervical junction abnormalities with atlantoaxial subluxation caused by ventral subluxation of C2 in a dog. Open Vet. J. 2017, 7, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Onodera, R.; Sakamoto, R.; Taniguchi, Y.; Hirai, S.; Matsubayashi, Y.; Kato, S.; Oshima, Y.; Tanaka, S. Congenital atlanto-occipital dislocation in a patient with Down syndrome: A case report. Skeletal Radiol. 2023, 52, 1785–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, G.C.; Kinsman, M.J.; Nazar, R.G.; Hruska, R.T.; Mansfield, K.J.; Boakye, M.; Rahme, R. Atlanto-occipital dislocation. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traynelis, V.C.; Marano, G.D.; Dunker, R.O.; Kaufman, H.H. Traumatic atlanto-occipital dislocation: Case report. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 65, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lye, G.; Mathis, K.; Hill, S.; Cattin, R.; Hartman, A. Computed Tomographic Diagnosis of Traumatic Atlanto-occipital Rotatory Luxation and Successful Closed Reduction in a Dog. VCOT Open 2020, 3, e164–e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, F.; Flueckiger, M.; Montavon, P.M. Traumatic atlanto-occipital luxation in a dog: Associated hypoglossal nerve deficits and use of 3-dimensional computed tomography. Vet. Surg. 2003, 32, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamoun, J.M.; Riddick, L.; Powell, R.W. Atlanto-occipital subluxation/dislocation: A “survivable” injury in children. Am. Surg. 1999, 65, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, D.; Nemzek, W.R.; Zovickian, J. Atlanto-occipital dislocation: Part 1 normal occipital condyle C: 1: Interval in 89 children. Neurosurgery 2007, 61, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, S.W. Surgical management of traumatic atlanto-occipital instability in a dog. Vet. Surg. 1978, 7, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, K.; Oliver, J., Jr. Traumatic atlanto-occipital dislocation in two dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1978, 173, 1324–1327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buks, Y.; Snelling, S.; Yates, G. Ventral fixation of chronic atlanto-occipital luxation in a dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 52, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, R.C.; Moon, C.; Zeiler, G.E.; Lobetti, R.G. Short-term clinical outcomes of 220 dogs with thoraco-lumbar disc disease treated by mini-hemilaminectomy. JSAVA 2020, 91, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.A.; Renberg, W.C.; Roush, J.K.; Hallman, M.R.; Mauler, D.A.; Milliken, G.A. Flexed radiographic angles for determination of atlantoaxial instability in dogs. Vet. Surg. 2019, 48, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Khandelwal, N.; Mathuria, S.N.; Singh, P.; Pathak, A.; Suri, S. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of craniovertebral junction abnormalities. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2007, 31, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolcun, J.P.; Chieng, L.O.; Madhavan, K.; Wang, M.Y. The role of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Asian Spine J. 2017, 11, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.; Hughes, E.; Gurney, M. Co-induction of anaesthesia with alfaxalone and midazolam in dogs: A randomized, blinded clinical trial. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2019, 46, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wininger, F. Atlantoaxial subluxation. In Current Techniques in Canine and Feline Neurosurgery; Brisson, B., Andy, A.S., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, S.G.; Bagley, R.S.; Silver, G.M.; Moore, M.; Tucker, R.L. Outcomes and complications associated with ventral screws, pins, and polymethyl methacrylate for atlantoaxial instability in 12 dogs. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2004, 40, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shores, A.; Tepper, L.C. A modified ventral approach to the atlantoaxial junction in the dog. Vet. Surg. 2007, 36, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblond, G.; Gaitero, L.; Moens, N.M.; Zur Linden, A.; James, F.M.; Monteith, G.; Runciman, J. Canine atlantoaxial optimal safe implantation corridors–description and validation of a novel 3D presurgical planning method using OsiriX™. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.L. Recognition and assessment of acute pain in the dog. In Pain Management in Veterinary Practice; Egger, C.M., Love, L., Doherty, T., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Hwang, T.S.; Jung, D.I.; Jeong, H.J.; Huh, C. Successful management of and recovery from multiple cranial nerve palsies following surgical ventral stabilization in a dog with atlantoaxial subluxation. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappin, M.R.; Dow, S. Traumatic atlanto-occipital luxation in a cat. Vet. Surg. 1983, 12, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, H.; Robles, J.C. Diagnosis and treatment of a chronic atlanto-occipital subluxation in a dog. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2007, 43, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorjonen, D.C.; Powe, T.A.; West, M.; Edmonds, S. Ventral Surgical Fixation and Fusion for Atlanto-occipital Subluxation in a Goat. Vet. Surg. 1983, 12, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, A.; Nishimura, R. Surgical stabilization of the atlanto-occipital overlap with atlanto-axial instability in a dog. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 64, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, F.; Hakozaki, T.; Kouno, S.; Suzuki, S.; Sato, A.; Kanno, N.; Harada, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Hara, Y. Atlantooccipital overlapping and its effect on outcomes after ventral fixation in dogs with atlantoaxial instability. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerda-Gonzalez, S.; Dewey, C.W.; Scrivani, P.V.; Kline, K.L. Imaging features of atlanto-occipital overlapping in dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2009, 50, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetti, N.; Kråkenes, J.; Eide, G.E.; Rørvik, J.; Gilhus, N.E.; Espeland, A. Are MRI high-signal changes of alar and transverse ligaments in acute whiplash injury related to outcome? BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2010, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, D.A.; Smith, M.M.; Grant, J.W.; Rockhill, A.D. Evaluation of bending strength of five interdental fixation apparatuses applied to canine mandibles. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1993, 54, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanz, O.I.; Lewis, D.D.; Madison, J.B.; Miller, G.J.; Martin, D.E. A biomechanical comparison of screw and wire fixation with and without polymethylmethacrylate re-enforcement for acetabular osteotomy stabilization in dogs. Vet. Surg. 1999, 28, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forterre, F.; Zorgevica-Pockevica, L.; Precht, C.; Haenssgen, K.; Stein, V.; Düver, P. Clinical Evaluation of a New Surgical Augmentation Technique for Transarticular Atlantoaxial Fixation for Treatment of Atlantoaxial Instability. Animals 2023, 13, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, C.D.; Stoessel, K. Surgical site infections: Epidemiology, microbiology and prevention. J. Hosp. Infect. 2008, 70, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanotti, B.; Nicola, Z.; Angela, V.; Massimo, R.; Alex, A.; Camillo, P. Cranioplasty: Review of materials. J. Craniofac Surg. 2016, 27, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, S.M.; Bedigrew, K.M.; Wenke, J.C. Development of a hematogenous implant-related infection in a rat model. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.-B.; Jeong, J.-M.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Jeong, S.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, H.-B. C1 Facetectomy and Ventral Fixation of Occipitoatlantoaxial Complex for Concurrent Congenital Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation and Atlantoaxial Instability in a Toy Poodle. Animals 2024, 14, 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131886
Kim K-B, Jeong J-M, Jeon Y-J, Jeong S-M, Kim D-H, Lee H-B. C1 Facetectomy and Ventral Fixation of Occipitoatlantoaxial Complex for Concurrent Congenital Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation and Atlantoaxial Instability in a Toy Poodle. Animals. 2024; 14(13):1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131886
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyung-Bin, Jae-Min Jeong, Young-Jin Jeon, Seong-Mok Jeong, Dae-Hyun Kim, and Hae-Beom Lee. 2024. "C1 Facetectomy and Ventral Fixation of Occipitoatlantoaxial Complex for Concurrent Congenital Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation and Atlantoaxial Instability in a Toy Poodle" Animals 14, no. 13: 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131886
APA StyleKim, K.-B., Jeong, J.-M., Jeon, Y.-J., Jeong, S.-M., Kim, D.-H., & Lee, H.-B. (2024). C1 Facetectomy and Ventral Fixation of Occipitoatlantoaxial Complex for Concurrent Congenital Atlanto-Occipital Dislocation and Atlantoaxial Instability in a Toy Poodle. Animals, 14(13), 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131886





