Identification and Functional Assignment of Genes Implicated in Sperm Maturation of Tibetan Sheep
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. RNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and Sequencing
2.4. Differential Expression Analysis and Data Processing
2.5. Evaluation of Functional Enrichment
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR as an RNA-Seq Validation Tool
3. Results
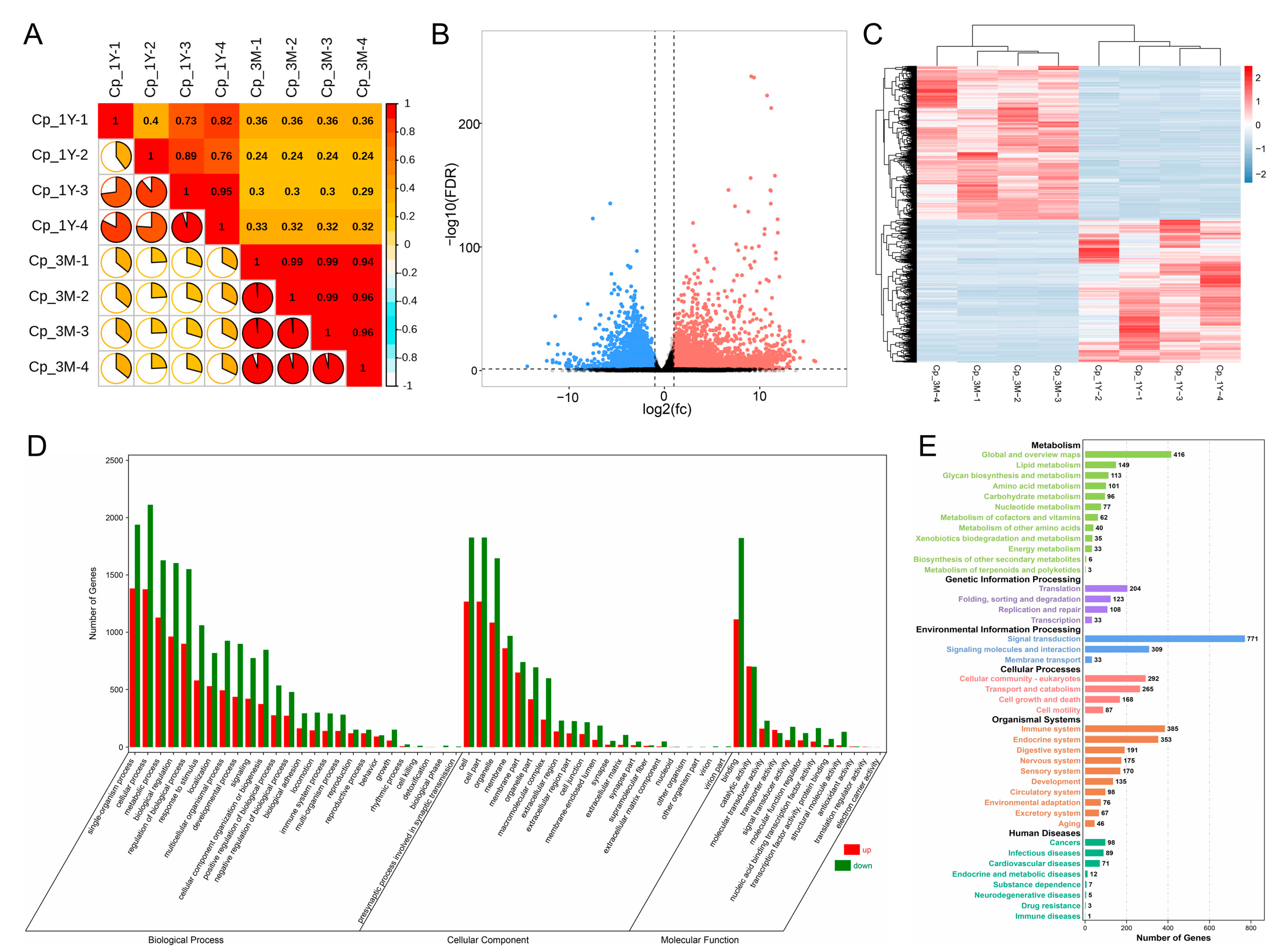
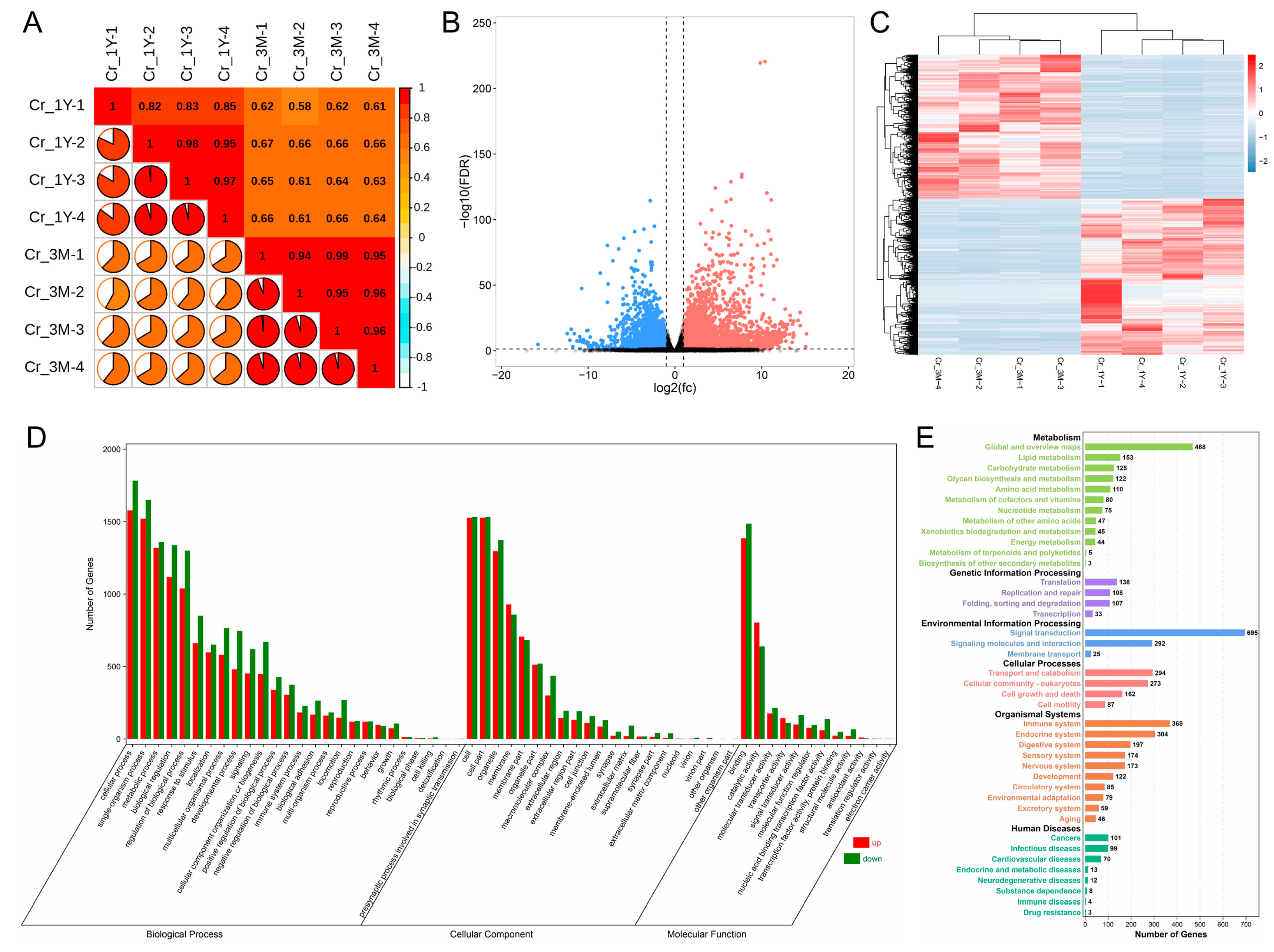
3.1. Overview of Transcriptome Data
3.2. Differentially Expressed Gene Analysis and Functional Analysis
3.2.1. Identification and Functional Analysis of Differential Expression Genes in Caput Epididymis before and after Puberty
3.2.2. Identification and Functional Analysis of Differential Expression Genes in Corpus Epididymis before and after Puberty
3.2.3. Analysis of Pre- and Post-Pubertal Cauda Epididymal Gene Expression Differences and Their Functional Significance
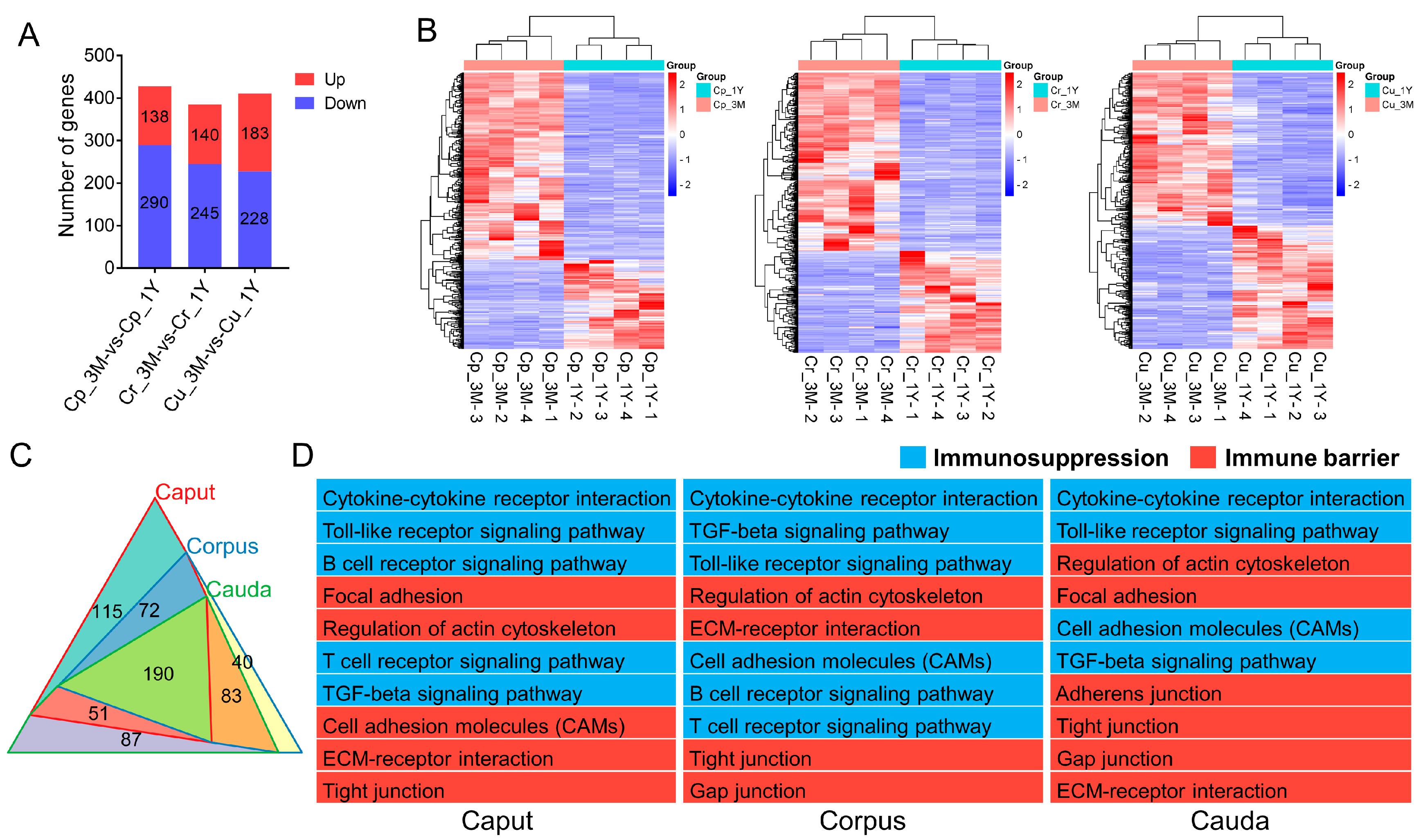
3.2.4. Region-Specific Gene Expression and Functional Analysis
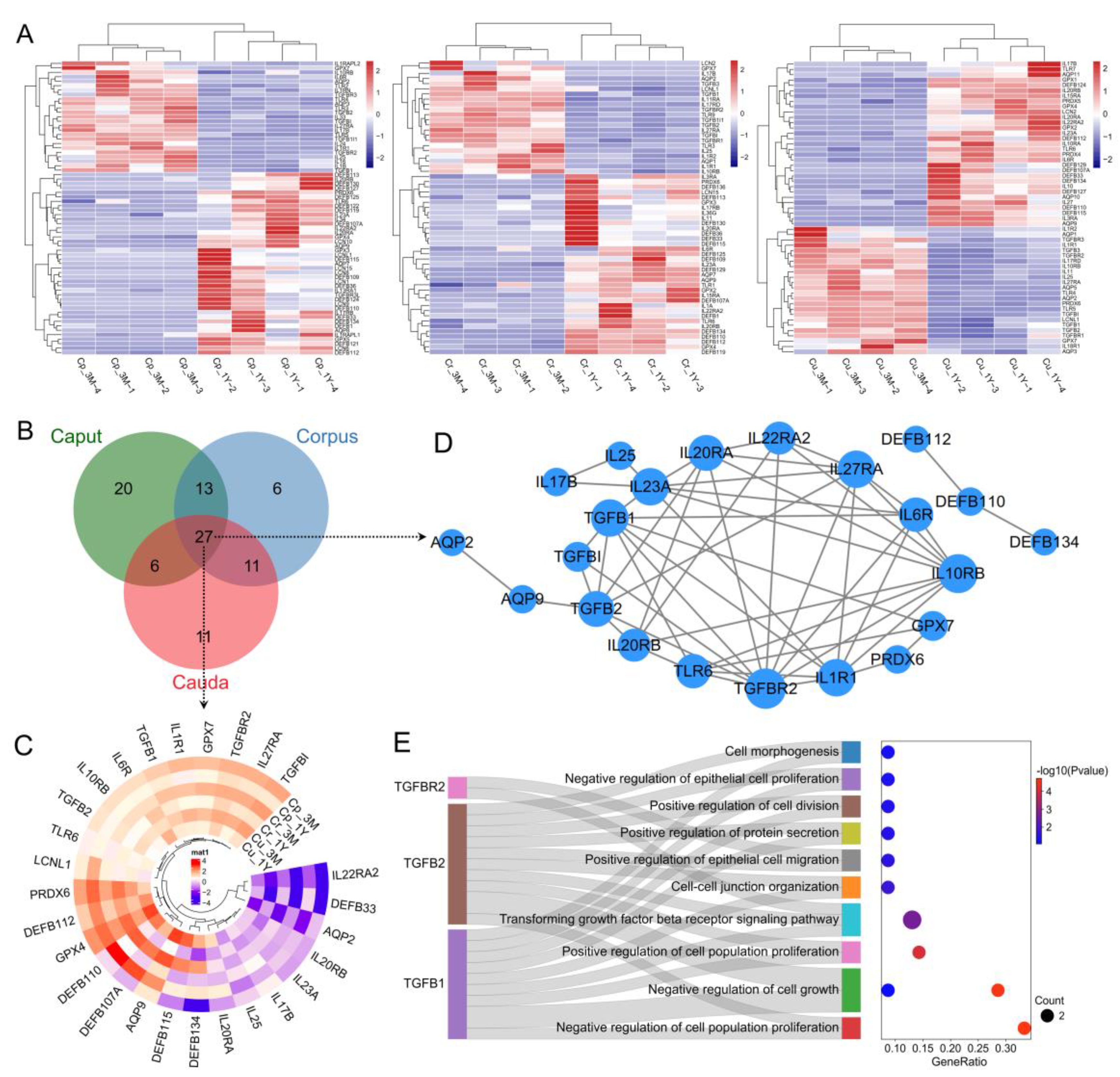
3.2.5. Screening and Functional Analysis of Epididymal Immunoprotection-Related Genes
3.2.6. Analysis of DEGs Associated with Sperm Maturation
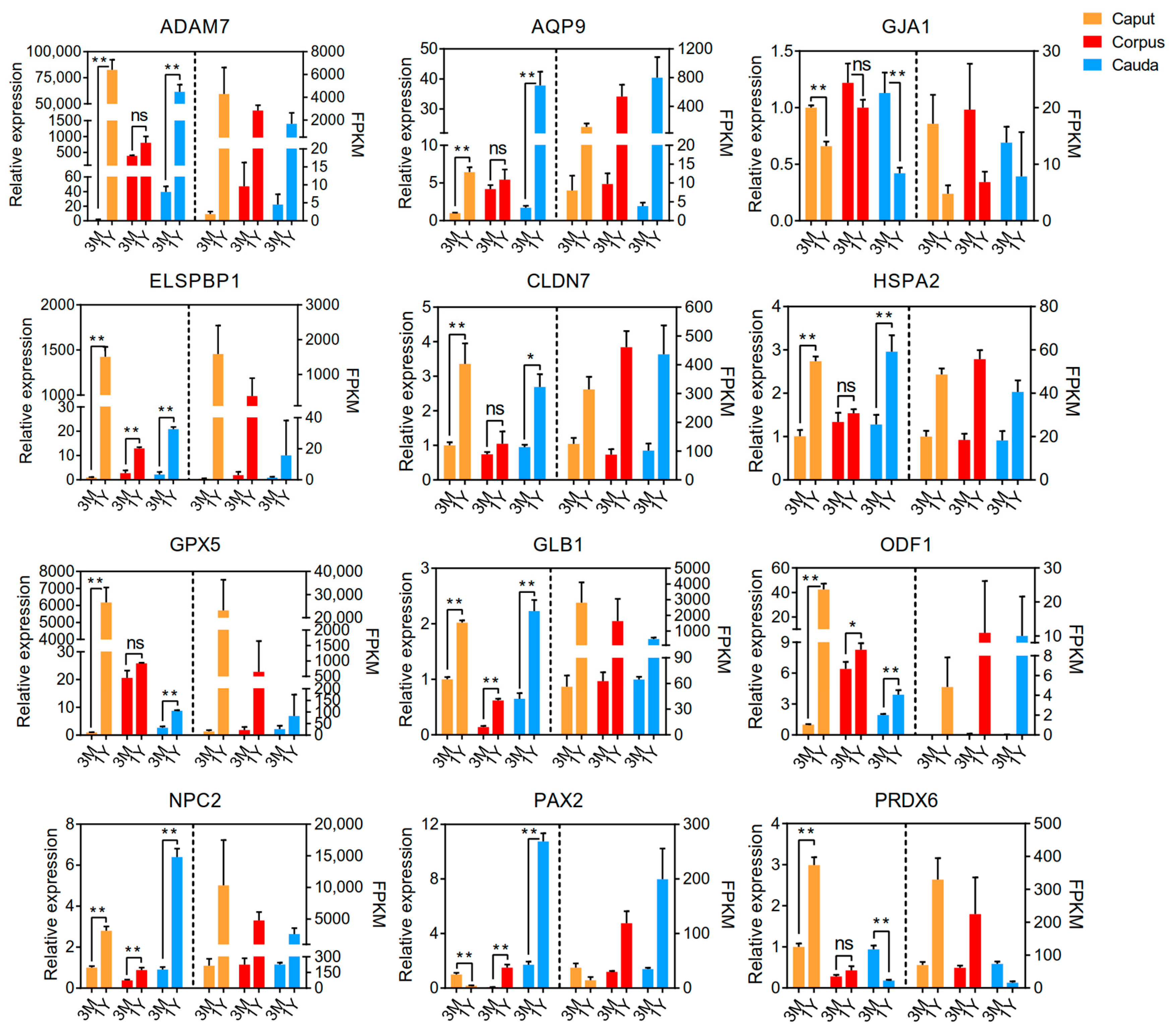
3.3. qPCR Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornwall, G.A. New insights into epididymal biology and function. Hum. Reprod. Update 2009, 15, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Alves, M.; Belleannée, C. Contribution of epididymal epithelial cell functions to sperm epigenetic changes and the health of progeny. Hum. Reprod. Update 2021, 28, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Fan, X.; Zhang, T.; Song, H.; Bian, X.; Nai, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Expression of selenium-independent glutathione peroxidase 5 (GPx5) in the epididymis of Small Tail Han sheep. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, J.A.; Leir, S.H.; Eggener, S.E.; Harris, A. Region-specific innate antiviral responses of the human epididymis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 473, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrachina, F.; Battistone, M.; Castillo, J.; Mallofré, C.; Jodar, M.; Breton, S.; Oliva, R. Sperm acquire epididymis-derived proteins through epididymosomes. Hum. Reprod. 2022, 37, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, E.; Carrell, D.; Aston, K.; Jenkins, T.; Yeste, M.; Salas-Huetos, A. The role of the epididymis and the contribution of epididymosomes to mammalian reproduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipilä, P.; Björkgren, I. Segment-specific regulation of epididymal gene expression. Reproduction 2016, 152, R91–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervasi, M.; Visconti, P. Molecular changes and signaling events occurring in spermatozoa during epididymal maturation. Andrology 2017, 5, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; De Iuliis, G.N.; Dun, M.D.; Nixon, B. Characteristics of the epididymal luminal environment responsible for sperm maturation and storage. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.; Johnston, D.; Finger, J.; Jelinsky, S. Differential gene expression among the proximal segments of the rat epididymis is lost after efferent duct ligation. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimon, V.; Koukoui, O.; Calvo, E.; Sullivan, R. Region-specific gene expression profiling along the human epididymis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 13, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Zhai, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Fu, X.; Zhang, M. Study on the region-specific expression of epididymis mRNA in the rams. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, C.; Scarlata, E. The protection of mammalian spermatozoa against oxidative stress. Reproduction 2022, 164, F67–F78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; O’Flaherty, C. In vivo oxidative stress alters thiol redox status of peroxiredoxin 1 and 6 and impairs rat sperm quality. Asian J. Androl. 2017, 19, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistone, M.; Mendelsohn, A.; Spallanzani, R.; Brown, D.; Nair, A.; Breton, S. Region-specific transcriptomic and functional signatures of mononuclear phagocytes in the epididymis. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2020, 26, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Liang, G.; Hawken, P.A.; Malecki, I.A.; Cozens, G.; Vercoe, P.E.; Martin, G.B.; Guan, L.L. Roles of small RNAs in the effects of nutrition on apoptosis and spermatogenesis in the adult testis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Liang, G.; Martin, G.B.; Guan, L.L. Functional changes in mRNA expression and alternative pre-mRNA splicing associated with the effects of nutrition on apoptosis and spermatogenesis in the adult testis. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Liang, G.; Hawken, P.A.; Meachem, S.J.; Malecki, I.A.; Ham, S.; Stewart, T.; Guan, L.L.; Martin, G.B. Nutrition affects Sertoli cell function but not Sertoli cell numbers in sexually mature male sheep. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2014, 28, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, T.; Liu, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y. Characterization of GLOD4 in Leydig cells of Tibetan sheep during different stages of maturity. Genes 2019, 10, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.; Antonescu, C.; Chang, T.; Mendell, J.; Salzberg, S. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Washington, A.; Hinton, B. Initial segment differentiation begins during a critical window and is dependent upon lumicrine factors and SRC proto-oncogene (SRC) in the mouse. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 95, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, J.; Yang, R.; Leir, S.; Eggener, S.; Harris, A. Expression profiles of human epididymis epithelial cells reveal the functional diversity of caput, corpus and cauda regions. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 22, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.; Mieusset, R. The human epididymis: Its function in sperm maturation. Hum. Reprod. Update 2016, 22, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, I.; Angel, C.; Yang, H.; Zoidis, E.; Pan, B.; Wu, Z.; Ming, Z.; Zeng, C.; Meng, Q.; Han, H.; et al. Role of selenium and selenoproteins in male reproductive function: A review of past and present evidences. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.; Huang, S.; Tsai, H.; Wu, C.; Hsieh, T. HDAC6 is a prognostic biomarker that mediates IL-13 expression to regulate macrophage polarization through AP-1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zeng, R.; Kou, J.; Xiong, X.; Yao, Y.; Fu, W.; Yin, S.; Lan, D. GPR50 participates in and promotes yak oocyte maturation: A new potential oocyte regulatory molecule. Theriogenology 2022, 181, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, B.; De Boer, I.; Tang, C.; Mayer, P.; Zelnick, L.; Afkarian, M.; Heinecke, J.; Himmelfarb, J. A cluster of proteins implicated in kidney disease is increased in high-density lipoprotein isolated from hemodialysis subjects. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2792–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Quansah, E.; Yuan, M.; Gou, Q.; Mengal, K.; Li, P.; Wu, S.; Xu, C.; Yi, C.; Cai, X. Region-specific gene expression in the epididymis of yak. Theriogenology 2019, 139, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Yu, X.; Chaurand, P.; Araki, Y.; Lareyre, J.; Caprioli, R.; Orgebin-Crist, M.; Matusik, R. Epididymis-specific lipocalin promoters. Asian J. Androl. 2007, 9, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.; Blake, J.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.; Davis, A.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.; Eppig, J.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; San Gabriel, M.; Zini, A.; Chan, P.; O’flaherty, C. Low amounts and high thiol oxidation of peroxiredoxins in spermatozoa from infertile men. J. Androl. 2012, 33, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Gao, N.; Fan, D.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, W.; Wang, P.; An, J. Zika virus disrupts the barrier structure and Absorption/Secretion functions of the epididymis in mice. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijak, M.; Meinhardt, A. The testis in immune privilege. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 213, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, X.; Luo, R.; An, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y. Integrating miRNA and mRNA profiling to assess the potential miRNA-mRNA modules linked with testicular immune homeostasis in sheep. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 647153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mital, P.; Hinton, B.; Dufour, J. The blood-testis and blood-epididymis barriers are more than just their tight junctions. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 84, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedger, M. Immunophysiology and pathology of inflammation in the testis and epididymis. J Androl. 2011, 32, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, M.; Cyr, D. The blood-epididymis barrier and inflammation. Spermatogenesis 2014, 4, e979619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, S.; Nair, A.; Battistone, M. Epithelial dynamics in the epididymis: Role in the maturation, protection, and storage of spermatozoa. Andrology 2019, 7, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, C.; Cyr, D.G. Role of specificity protein-1 and activating protein-2 transcription factors in the regulation of the gap junction protein beta-2 gene in the epididymis of the rat. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 94, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, C.; He, C.; Mei, C.; Liao, A.; Huang, D. The immune characteristics of the epididymis and the immune pathway of the epididymitis caused by different pathogens. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabory, E.; Damon, C.; Lenoir, A.; Henry-Berger, J.; Vernet, P.; Cadet, R.; Saez, F.; Drevet, J. Mammalian glutathione peroxidases control acquisition and maintenance of spermatozoa integrity. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, V.; Donnard, E.; Gellatly, K.; Rasmussen, M.; Kucukural, A.; Yukselen, O.; Garber, M.; Sharma, U.; Rando, O. An atlas of cell types in the mouse epididymis and vas deferens. eLife 2020, 9, e55474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; Förster, H.; Boersma, A.; Seiler, A.; Wehnes, H.; Sinowatz, F.; Neumüller, C.; Deutsch, M.; Walch, A.; Hrabé De Angelis, M.; et al. Mitochondrial glutathione peroxidase 4 disruption causes male infertility. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.; Yenugu, S.; Radhakrishnan, Y.; Avellar, M.; Petrusz, P.; French, F. Characterization and functions of beta defensins in the epididymis. Asian J. Androl. 2007, 9, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkgren, I.; Alvarez, L.; Blank, N.; Balbach, M.; Turunen, H.; Laajala, T.; Toivanen, J.; Krutskikh, A.; Wahlberg, N.; Huhtaniemi, I.; et al. Targeted inactivation of the mouse epididymal beta-defensin 41 alters sperm flagellar beat pattern and zona pellucida binding. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 427, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Cai, Y.; Sang, Y.; Blecha, F.; Zhang, G. Cross-species analysis of the mammalian beta-defensin gene family: Presence of syntenic gene clusters and preferential expression in the male reproductive tract. Physiol. Genom. 2005, 23, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, S.; Yin, Q.; Tang, C.; Ni, Z.; Fei, J.; Zhang, Y. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing reveals the synergistic effects of β-defensin family members on sperm maturation in rat epididymis. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyonnet, B.; Marot, G.; Dacheux, J.; Mercat, M.; Schwob, S.; Jaffrézic, F.; Gatti, J.J.B.G. The adult boar testicular and epididymal transcriptomes. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Wang, H.; Luo, R.; Shi, H.; Su, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y. Identification and Functional Assignment of Genes Implicated in Sperm Maturation of Tibetan Sheep. Animals 2023, 13, 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091553
Li T, Wang H, Luo R, Shi H, Su M, Wu Y, Li Q, Ma K, Zhang Y, Ma Y. Identification and Functional Assignment of Genes Implicated in Sperm Maturation of Tibetan Sheep. Animals. 2023; 13(9):1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091553
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Taotao, Huihui Wang, Ruirui Luo, Huibin Shi, Manchun Su, Yi Wu, Qiao Li, Keyan Ma, Yong Zhang, and Youji Ma. 2023. "Identification and Functional Assignment of Genes Implicated in Sperm Maturation of Tibetan Sheep" Animals 13, no. 9: 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091553
APA StyleLi, T., Wang, H., Luo, R., Shi, H., Su, M., Wu, Y., Li, Q., Ma, K., Zhang, Y., & Ma, Y. (2023). Identification and Functional Assignment of Genes Implicated in Sperm Maturation of Tibetan Sheep. Animals, 13(9), 1553. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091553





