Exploring ‘Wether’ Grazing Patterns Differed in Native or Introduced Pastures in the Monaro Region of Australia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
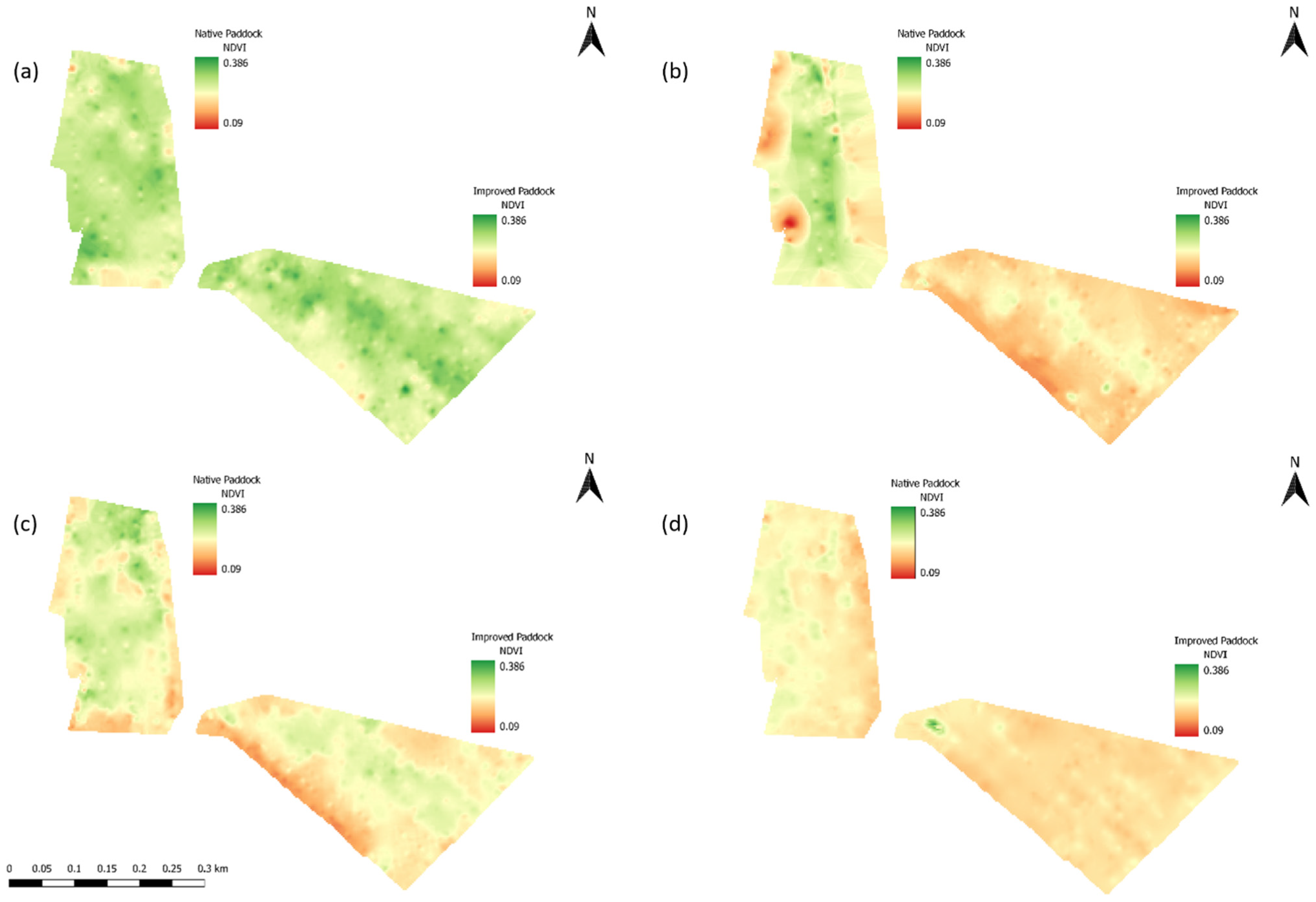
3. Results
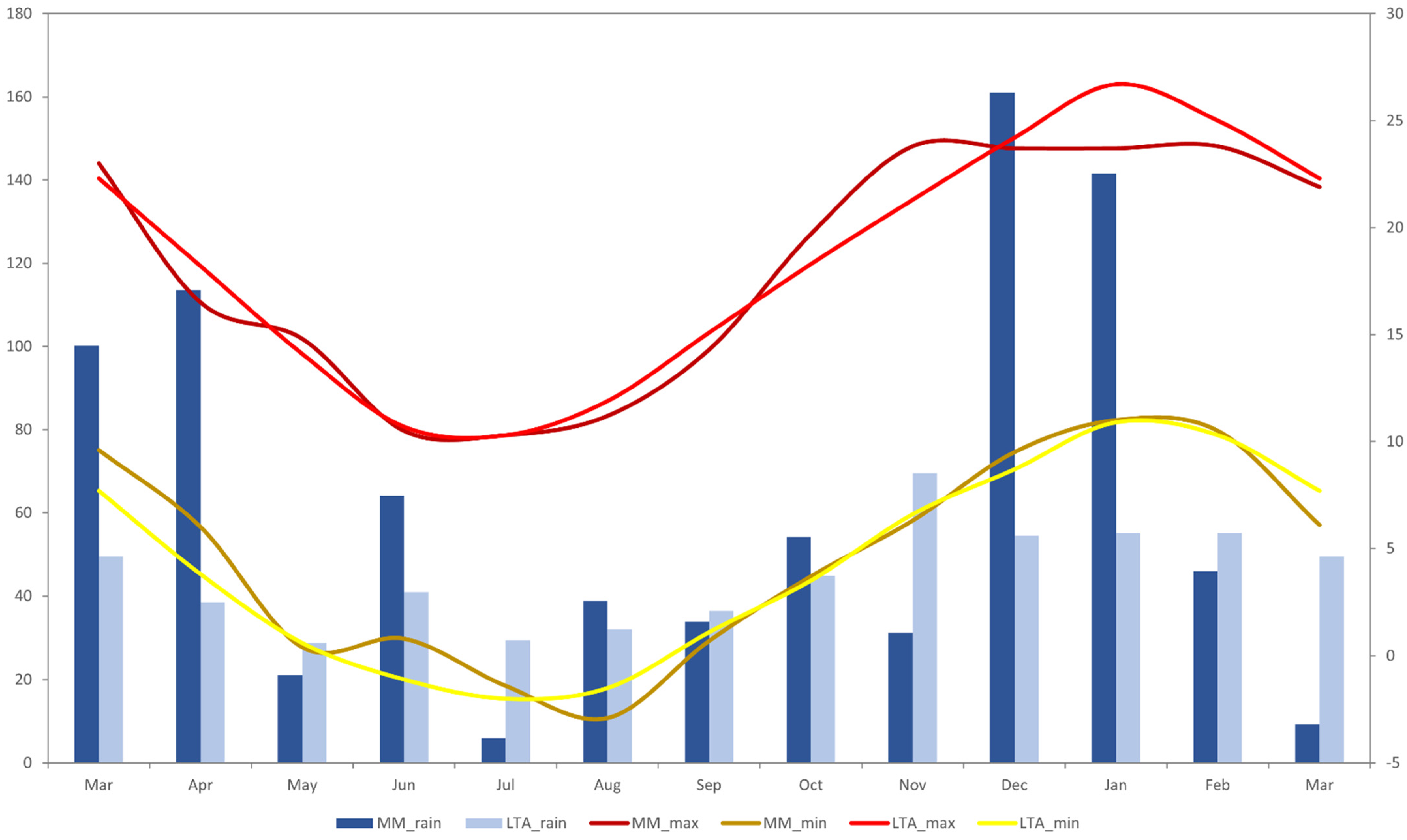
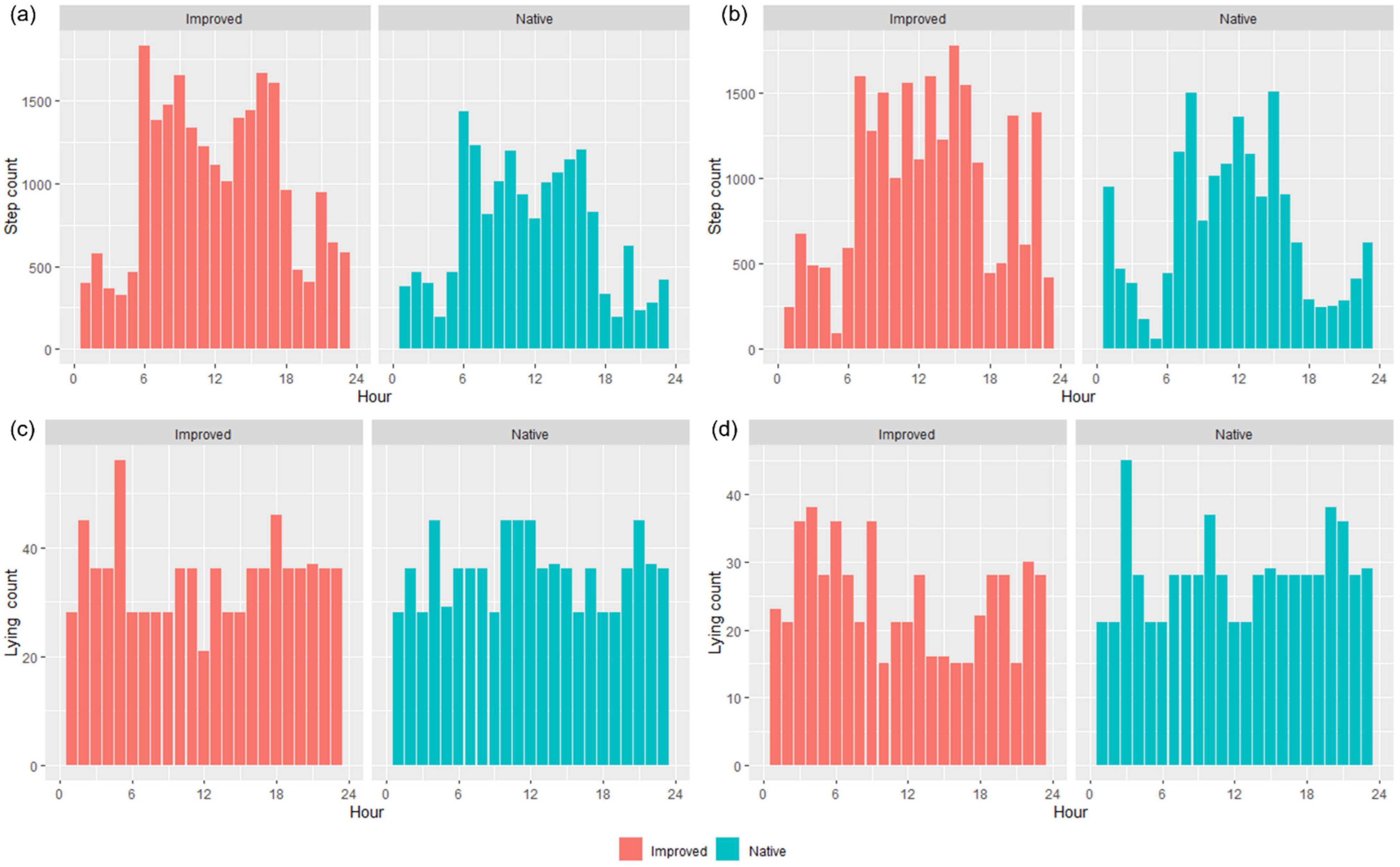
3.1. Movement Data
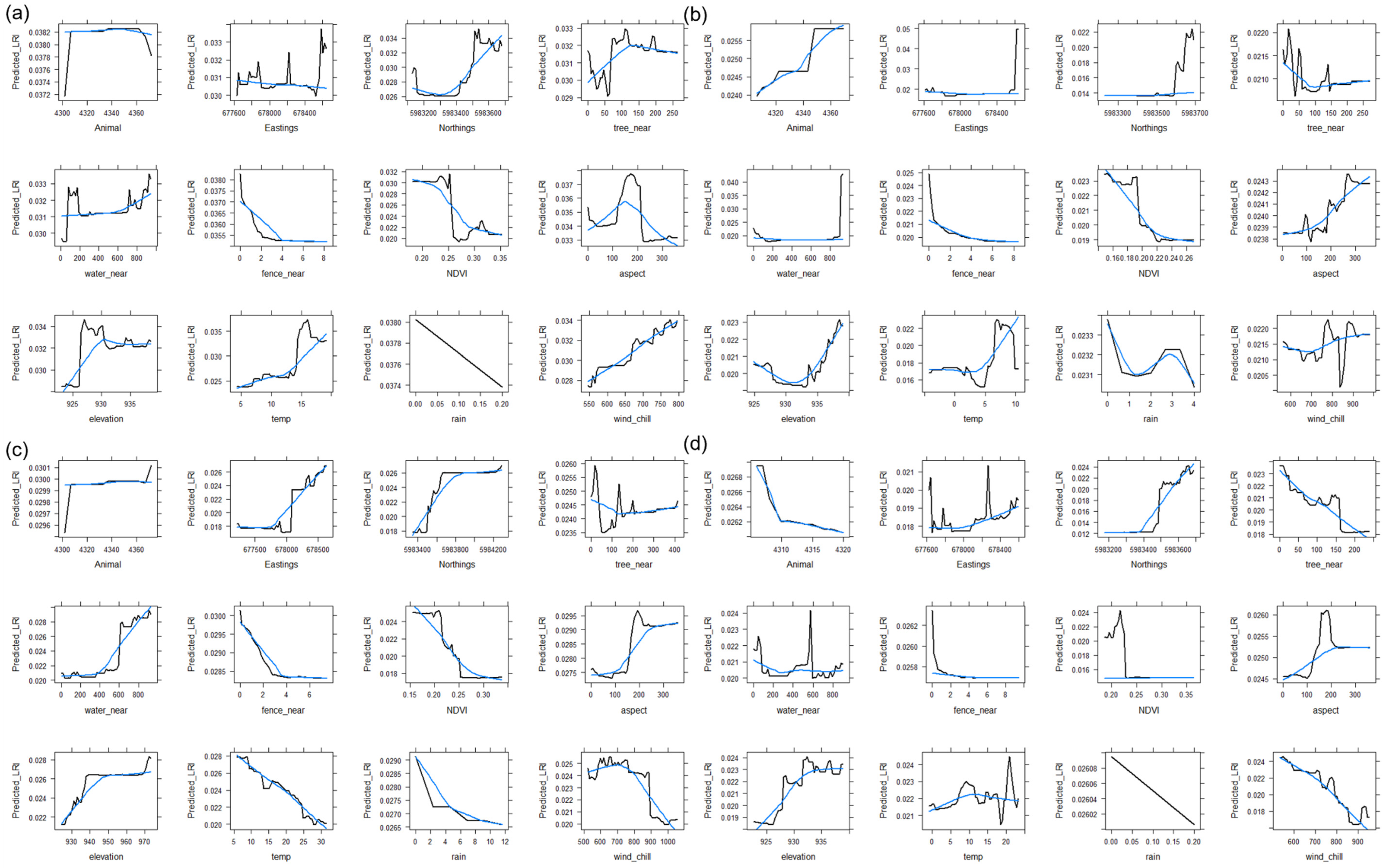
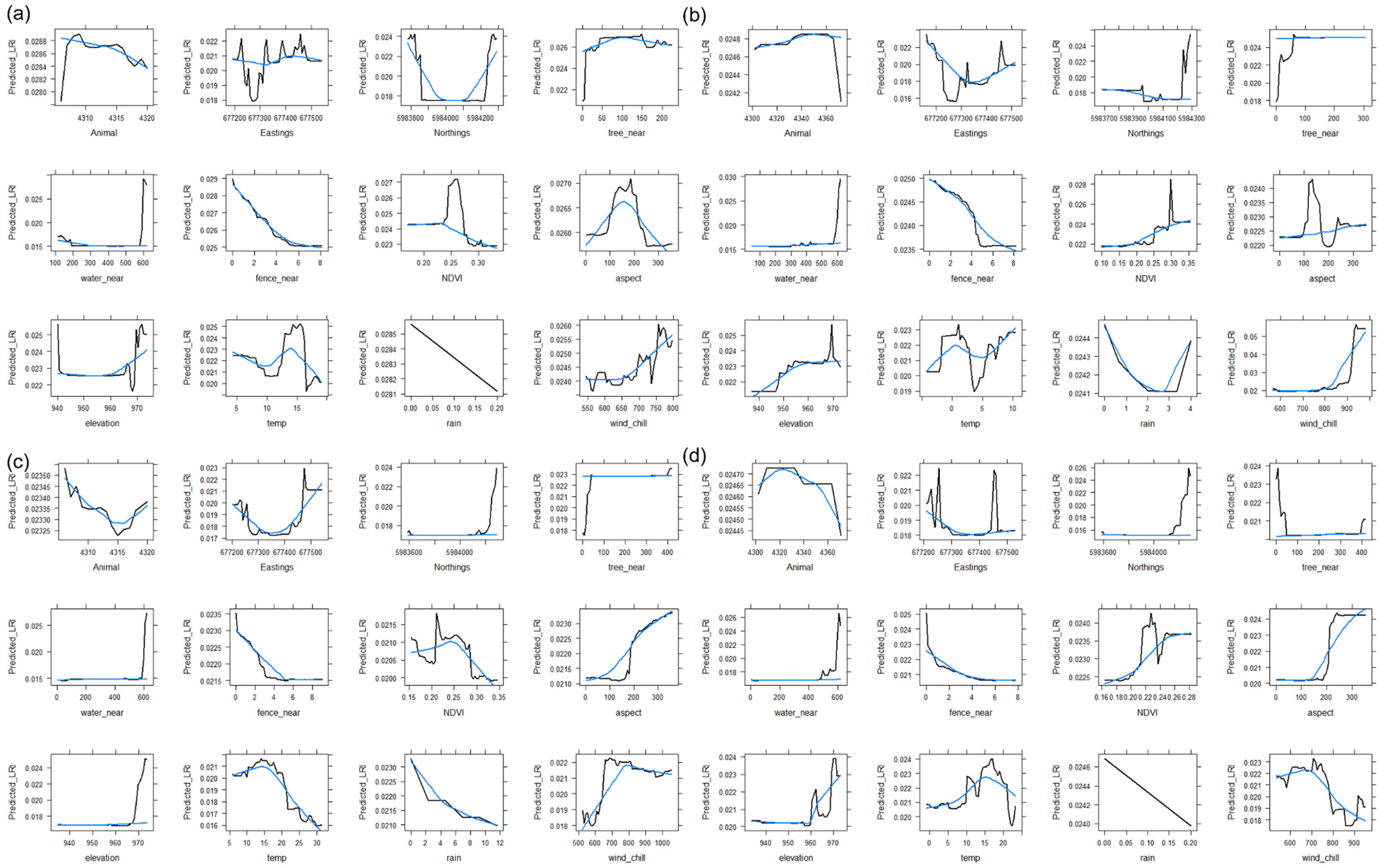
3.2. Random Forest Models
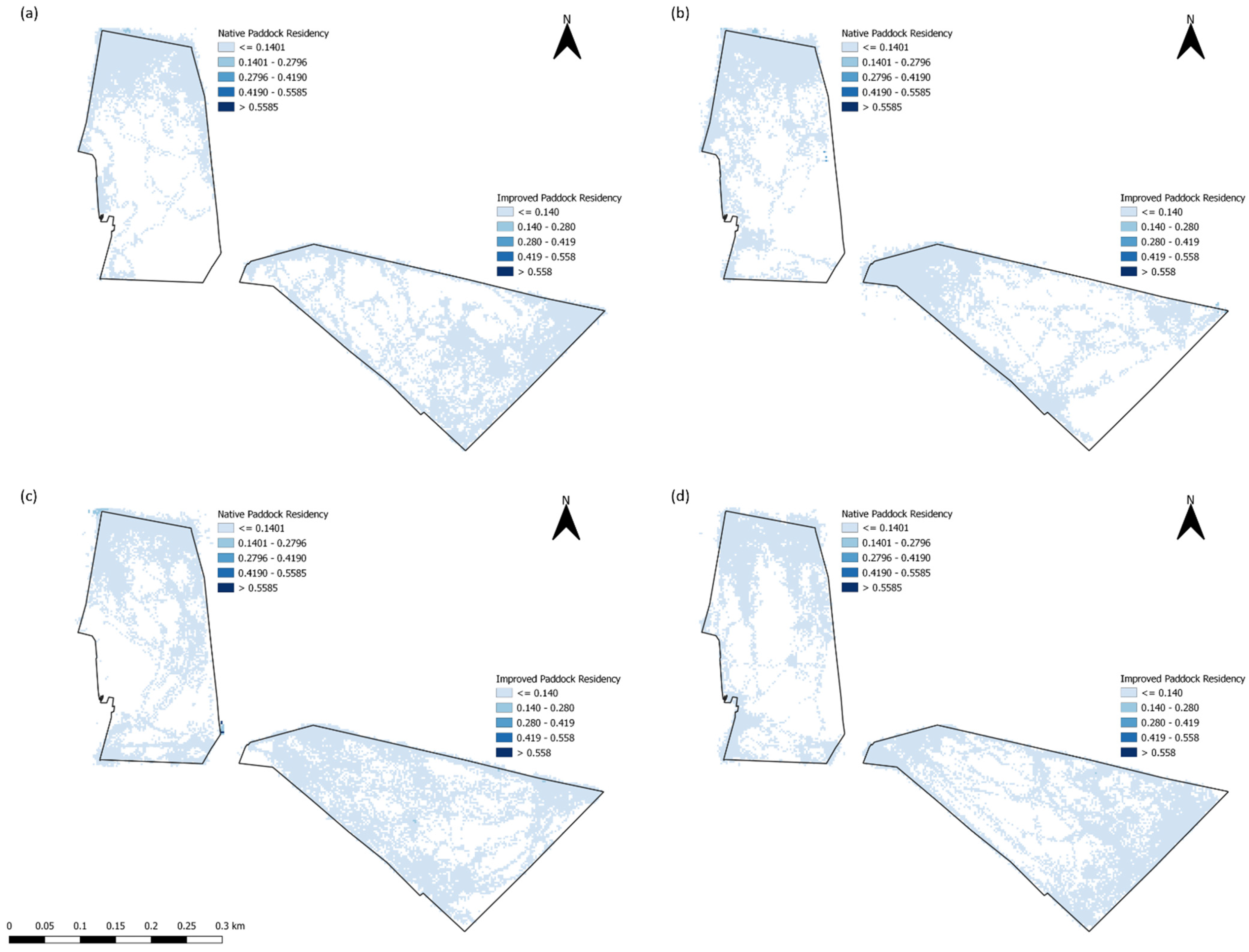
3.2.1. Improved Paddocks
3.2.2. Native Paddocks
3.3. Weight Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Movement Behavior Data
4.2. Random Forest Models
4.3. Implications of Research and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Bowman, J.L.; Kochanny, C.O.; Demarais, S.; Leopold, B.D. Evaluation of a GPS collar for white-tailed deer. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2000, 28, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, D.M.; Winters, C.; Estell, R.E.; Fredrickson, E.L.; Doniec, M.; Detweiler, C.; Rus, D.; James, D.; Nolen, B. Characterising the spatial and temporal activities of free ranging cows from GPS data. Rangel. J. 2012, 34, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putfarken, D.; Dengler, J.; Lehmann, S.; Hardtle, W. Site use of grazing cattle and sheep in a large-scale pasture landscape: A GPS/GIS assessment. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 111, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotter, M.; Lamb, D.; Hinch, G.N. GPS livestock tracking: A pasture utilisation monitor for the grazing industry. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference of the Grassland Society of NSW, Taree, Australia, 5–6 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Barwick, J.; Lamb, D.W.; Dobos, R.; Welch, M.; Trotter, M. Categorising sheep activity using a tri-axial accelerometer. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 145, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwick, J.; Lamb, D.; Dobos, R.; Schneider, D.; Welch, M.; Trotter, M. Predicting Lameness in Sheep Activity Using Tri-Axial Acceleration Signals. Animals 2018, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trénel, P.; Jensen, M.B.; Decker, E.L.; Skjøth, F. Technical note: Quantifying and characterizing behavior in dairy calves using the IceTag automatic recording device. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3397–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Schrader, L. A new method to measure behavioural activity levels in dairy cows. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2003, 83, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, D.; Kardailsky, I.; Parnell, J.; Badgery, W.B.; Ingram, L. Understanding sheep baa-haviour: Investigating the relationship between pasture and animal grazing patterns. Grassl. Res. 2022, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, B.; Boissy, A. Grazing behaviour of sheep in a situation of conflict between feeding and social motivations. Behav. Process. 2000, 49, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbald, A.M.; Hooper, R.J. Sociability and the willingness of individual sheep to move away from their companions in order to graze. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2004, 86, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, V. Walking, watering and grazing behaviour of merino sheep on two semi-arid rangelands in South-West New South Wales. Rangel. J. 1976, 1, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelena, P.; Sibbald, A.M.; Erhard, H.W.; McLeod, J.E. Effects of group size and personality on social foraging: The distribution of sheep across patches. Behav. Ecol. 2009, 20, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.M.M.; Celaya, R.; Benavides, R.; Jauregui, B.M.; Garcia, U.; Santos, A.S.; Garcia, R.R.; Rodrigues, M.A.M.; Osoro, K. Foraging behaviour of domestic herbivore species grazing on heathlands associated with improved pasture areas. Livest. Sci. 2013, 155, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.J. Behaviour of sheep and cattle in the more arid areas of Australia. In Proceedings of the Symposium held by the Rangelands Research Unit, Deniliquin, NSW, Australia, 26–27 October 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Burritt, E.A.; Mayland, H.F.; Provenza, F.D.; Miller, R.L.; Burns, J.C. Effect of added sugar on preference and intake by sheep of hay cut in the morning versus the afternoon. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2005, 94, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorini, P. Diurnal grazing pattern: It’s physiological basis and strategic management. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2012, 52, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, S.M. Diet preference for grass and legumes in free-ranging domestic sheep and cattle: Current theory and future application. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2006, 97, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.K.K.; Reddy, T.Y.; Umamaheswari, P. Influence of weather parameters on growth of sheep in sheep-based farming systems. J. Agrometeorol. 2005, 7, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land Management and Farming in Australia. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/industry/agriculture/land-management-and-farming-australia/2016-17 (accessed on 3 January 2023).
- Clements, B.W. The Grazier’s Guide to Pastures: Sowing and Managing Profitable Pastures in the Central and Southern Tablelands, Monaro and Upper South West Slopes of New South Wales; NSW Agriculture: Orange, NSW, Australia, 2003.
- Garden, D.L.; Dowling, P.M.; Eddy, D.A.; Nicol, H.I. The influence of climate, soil and management on the composition of native grass pastures on the central, southern and Monaro tablelands of New South Wales. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2001, 52, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate Statistics for Australian Locations-Cooma Airport, Site NUMBER 70217. 2023. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/data (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Zengeya, F.M.; Mutanga, O.; Murwira, A. Linking remotely sensed forage quality estimates from WorldView-2 multispectral data with cattle distribution in a savanna landscape. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, B.M.; McBratney, A.B.; Minasny, B. Vesper-spatial prediction software for precision agriculture. In Proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on Precision Agriculture, Montpellier, France, 18–20 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, J.K.; Cronin, G.M.; Gonzalez, L.A.; Hall, E.J.S.; Merchant, A.; Ingram, L. The effects of global navigation satellite system (GNSS) collars on cattle (Bos taurus) behaviour. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2017, 187, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, P.N. Handbook of Ethological Methods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Trotter, M.G.; Lamb, D.W.; Hinch, G.N.; Guppy, C.N. Global navigation system livestock tracking: System development and data interpretation. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2010, 50, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.E.; Pringle, M.J.; Bray, S.; Hall, T.J.; O’Reagain, P.O.; Phelps, D.; Cobon, D.H.; Bloesch, P.M.; Dalal, R.C. What determines soil organic carbon stocks in the grazing lands of north-eastern Australia? Soil Res. 2013, 51, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebel, F.; Dussault, C.; Masse, A.; Cote, S.D. Influence of habitat features and hunter behaviour on white-tailed deer harvest. J. Wildl. Manag. 2012, 76, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, L.M.; Garber, P.A. Foraging and spatial memory in wild Weddell’s Saddleback tamarins (Saguinus fuscicollis weddelli) when moving between distant and out-of-sight goals. Int. J. Primatol. 2013, 34, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Barthold, F.; Blank, B.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Digital mapping of soil organic matter stocks using random forest modelling in a semi-arid steppe ecosystem. Plant Soil 2011, 340, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, F.; Bishop, T.F.A.; Vervoot, R.W. Space-time modelling of groundwater level and salinity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, S.; Pourghasemi, H. A comparative assessment between three machine learning models and their performance comparison by bivariate and multivariate statistical methods in groundwater potential mapping. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 5217–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.J.; Cross, P.C.; Winnie, J.; Hay, C.; Bowers, J.; Getz, W.M. The utility of normalised difference vegetation index for predicting African buffalo forage quality. J. Wildl. Manag. 2012, 76, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, A.; McCaskill, M.; Cox, M.; Sharma, S. An SMS and Email Weather Warning System for Sheep Producers. In Environmental Software Systems. Infrastructures, Services and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, M.N.; Wager, S.; Probst, P. Ranger: A Fast Implementation of Random Forests, Version 0.12.1. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ranger (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- Greenwell, B. pdp: Partial Dependence Plots, Version 0.70. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pdp (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- Fox, J.; Wiesberg, S.; Price, B.; Adler, D.; Bates, D.; Baud-Bovy, G.; Bolker, B.; Ellison, S.; Firth, D.; Friendly, M.; et al. Car: Companion to Applied Regression, Version 3.0-12. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=car (accessed on 7 April 2022).
- R-Core-Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Ren, K.; Karlsson, J.; Liuska, M.; Hartikainen, M.; Hansen, I.; Jørgensen, G.H. A sensor-fusion-system for tracking sheep location and behaviour. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2020, 16, 1550147720921776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, F.A.P.; Borges, I.; Palkovič, L.; Rodina, J.; Oddy, V.H.; Dobos, R.C. Using a three-axis accelerometer to identify and classify sheep behaviour at pasture. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 181, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanetti, V.; Decandia, M.; Molle, G.; Acciaro, M.; Mameli, M.; Cabiddu, A.; Cossu, R.; Serra, M.G.; Manca, C.; Rassu, S.P.G.; et al. Automatic classification system for grazing, ruminating and resting behaviour of dairy sheep using a tri-axial accelerometer. Livest. Sci. 2017, 196, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallentine, J.F. Grazing Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Demment, M.W.; Soest, P.J.V. A Nutritional Explanation for Body-Size Patterns of Ruminant and Nonruminant Herbivores. Am. Nat. 1985, 125, 641–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, R.J.; Penning, P.D.; Harvey, A.; Champion, R.A. Diurnal patterns of intake rate by sheep grazing monocultures of ryegrass or white clover. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1997, 52, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illius, A.W.; Clark, D.A.; Hodgson, J. Discrimination and Patch Choice by Sheep Grazing Grass-Clover Swards. J. Anim. Ecol. 1992, 61, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curll, M.L.; Wilkins, R.J. Frequency and severity of defoliation of grass and clover by sheep at different stocking rates. Grass Forage Sci. 1982, 37, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, R.A.; Lagstrom, N.A.; Rook, A.J. Motivation of sheep to eat clover offered in a short-term closed economy test. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 108, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, R.; Southcott, W.; Turner, H. Grazing management of native pastures in the New England region of New South Wales. I. Pasture and sheep production with special reference to systems of grazing and internal parasites. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1959, 10, 530–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlands, J.; Bowles, J. Herbage intake and production of Merino sheep grazing native and improved pastures at different stocking rates. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1974, 14, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, A.; McIvor, J. Forage quality and feed intake responses of cattle to improved pastures, tree killing and stocking rate in open eucalypt woodlands of north-eastern Australia. J. Agric. Sci. 1998, 131, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perotto-Baldivieso, H.L.; Cooper, S.M.; Cibils, A.F.; Figueroa-Pagán, M.; Udaeta, K.; Black-Rubio, C.M. Detecting autocorrelation problems from GPS collar data in livestock studies. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 136, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, R.H.; Bissio, J.; Samuel, M.J.; Waggoner, J.R. Grazing systems, pasture size, and cattle grazing behaviour, distribution and gains. J. Rangel. Manag. 1993, 46, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, D.B.; Nolan, J.V.; Godwin, I.R.; Mayer, D.G.; Aoetpah, A.; Nguyen, T.; Baillie, N.D.; Rheinberger, T.E.; Lawlor, C. Water and feed intake responses of sheep to drinking water temperature in hot conditions. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2008, 48, 1044–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.R.; Moore, A.D.; Freer, M. GRAZPLAN: Decision support systems for Australian grazing enterprises—I. Overview of the GRAZPLAN project, and a description of the MetAccess and LambAlive DSS. Agric. Syst. 1997, 54, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kie, J.G.; Ager, A.A.; Bowyer, R.T. Landscape-level movements of North American elk (Cervus elaphus): Effects of habitat patch structure and topography. Landsc. Ecol. 2005, 20, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, B.G.; Beier, P. Quantifying the influence of topographic position on cougar movement in southern California, USA. J. Zool. 2007, 271, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.A.; Basson, M.; Bravington, M.V.; Gunn, J.S. Classifying movement behaviour in relation to environmental conditions using hidden Markov models. J. Anim. Ecol. 2009, 78, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.; Wilson, B.; Reid, N.; Bayerlein, L.; Koen, T.; Olupot, G. Examining the impact of shade on above-ground biomass and normalized difference vegetation index of C 3 and C 4 grass species in North-Western, NSW, Australia. Grass Forage Sci. 2015, 70, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.; Wilson, B.R.; Trotter, M.G.; Lamb, D.W.; Reid, N.; Koen, T.; Bayerlein, L. The patterns of grazed pasture associated with scattered trees across an Australian temperate landscape: An investigation of pasture quantity and quality. Rangel. J. 2011, 33, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.; Ash, A.J. The role of trees in enhancing soil nutrient availability for native perennial grasses in open eucalypt woodlands of north-east Queensland. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2001, 52, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.; Ash, A. Tree-grass relationships in open eucalypt woodlands of northeastern Australia: Influence of trees on pasture productivity, forage quality and species distribution. Agrofor. Syst. 1998, 40, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celaya, R.; Oliván, M.; Ferreira, L.; Martínez, A.; García, U.; Osoro, K. Comparison of grazing behaviour, dietary overlap and performance in non-lactating domestic ruminants grazing on marginal heathland areas. Livest. Sci. 2007, 106, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osoro, K.; García, U.; Jáuregui, B.; Ferreira, L.; Rook, A.; Celaya, R. Diet selection and live-weight changes of two breeds of goats grazing on heathlands. Animal 2007, 1, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celaya, R.; Benavides, R.; García, U.; Ferreira, L.; Ferre, I.; Martínez, A.; Ortega-Mora, L.; Osoro, K. Grazing behaviour and performance of lactating suckler cows, ewes and goats on partially improved heathlands. Animal 2008, 2, 1818–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osoro, K.; Ferreira, L.M.M.; García, U.; Celaya, R. Performance of domestic herbivores in marginal heathlands. In New Trends for Innovation in the Mediterranean Animal Production; Bouche, R., Derkimba, A., Casabianca, F., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.M.M.; Celaya, R.; Benavides, R.; García, U.; Osoro, K. Comparison of animal performance of domestic herbivores grazing on partially improved heath lands. In New Trends for Innovation in the Mediterranean Animal Production; Bouche, R., Derkimba, A., Casabianca, F., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, C.; Filippi, P.; González, L.A. The Relationship between Satellite-Derived Vegetation Indices and Live Weight Changes of Beef Cattle in Extensive Grazing Conditions. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homburger, H.; Schneider, M.K.; Hilfiker, S.; Lüscher, A. Inferring Behavioral States of Grazing Livestock from High-Frequency Position Data Alone. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, X.; Tsunekawa, A.; Peng, F.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Lian, J. Method for Classifying Behavior of Livestock on Fenced Temperate Rangeland in Northern China. Sensors 2019, 19, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, J.; Johnson, P.; Olson, K. Classifying season long livestock grazing behavior with the use of a low-cost GPS and accelerometer. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 181, 105957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | |||||||
| Improved | Native | Improved | Native | |||||
| AH | GH | AH | GH | AH | GH | SH | GH | |
| OOB R2 | 0.978 | 0.982 | 0.949 | 0.957 | 0.958 | 0.952 | 0.944 | 0.956 |
| MSE | 2.0 × 10−6 | 2.0 × 10−6 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 4.0 × 10−6 |
| Trial 3 | Trial 4 | |||||||
| Improved | Native | Improved | Native | |||||
| AH | GH | AH | GH | AH | GH | Ah | GH | |
| OOB R2 | 0.981 | 0.977 | 0.941 | 0.943 | 0.976 | 0.975 | 0.949 | 0.950 |
| MSE | 2.0 × 10−6 | 2.0 × 10−6 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 2.0 × 10−6 | 2.0 × 10−6 | 3.0 × 10−6 | 3.0 × 10−6 |
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | Trial 3 | Trial 4 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improved | Native | Improved | Native | Improved | Native | Improved | Native | |||||||||
| Variable | AH | GH | AH | GH | AH | GH | AH | GH | AH | GH | AH | GH | AH | GH | AH | GH |
| Animal (A) | 11th | 10th | 12th | 11th | 10th * | 10th * | 12th | 12th | 11th | 12th | 12th * | 12th | 10th * | 10th * | 11th | 12th |
| Eastings (EA) | 4th | 4th | 1st * | 1st * | 3rd | 1st | 1st | 2nd | 1st * | 1st * | 2nd * | 2nd * | 2nd * | 2nd * | 2nd * | 1st * |
| Northings (NO) | 1st | 1st * | 3rd | 2nd * | 1st | 4th | 3rd | 5th | 2nd * | 4th | 3rd | 3rd * | 1st * | 1st * | 1st * | 3rd * |
| Near distance to trees (NT) | 8th | 6th * | 7th | 6th * | 7th | 7th | 7th | 7th | 5th * | 8th * | 6th * | 5th * | 3rd * | 8th | 7th | 5th * |
| Near distance to water (NW) | 6th | 7th | 2nd | 3rd * | 4th | 3rd | 2nd | 4th | 3rd | 2nd * | 1st * | 1st * | 4th | 3rd | 3rd | 2nd * |
| Near distance to fences (NF) | 12th | 11th | 10th | 10th | 12th | 12th | 11th | 11th | 12th | 11th | 11th | 11th | 12th | 12th | 10th | 11th |
| NDVI | 2nd * | 2nd * | 8th * | 7th * | 8th | 8th | 8th | 8th | 4th * | 3rd * | 8th | 8th * | 6th * | 4th * | 8th | 8th * |
| Aspect (AS) | 9th | 9th | 9th | 8th * | 11th | 11th | 9th | 9th | 9th | 9th | 9th | 9th * | 9th | 9th | 9th * | 9th * |
| Elevation (EL) | 5th | 5th | 5th | 4th * | 6th | 6th | 5th | 3rd | 6th | 7th | 4th | 4th * | 7th | 5th | 5th | 4th * |
| Temperature (T) | 3rd * | 3rd * | 4th * | 5th * | 2nd * | 2nd * | 6th * | 6th * | 7th * | 6th * | 5th * | 6th * | 5th * | 6th * | 4th * | 6th * |
| Rainfall (R) | 10th * | 12th | 11th * | 12th * | 9th * | 9th * | 10th * | 10th * | 10th * | 10th * | 10th * | 10th * | 11th | 11th * | 12th | 10th * |
| Wind Chill (WC) | 7th * | 8th | 6th * | 9th * | 5th * | 5th * | 4th * | 1st * | 8th * | 5th * | 7th * | 7th | 8th * | 7th * | 6th * | 7th |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parnell, D.; Edwards, J.; Ingram, L. Exploring ‘Wether’ Grazing Patterns Differed in Native or Introduced Pastures in the Monaro Region of Australia. Animals 2023, 13, 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091500
Parnell D, Edwards J, Ingram L. Exploring ‘Wether’ Grazing Patterns Differed in Native or Introduced Pastures in the Monaro Region of Australia. Animals. 2023; 13(9):1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091500
Chicago/Turabian StyleParnell, Danica, Jack Edwards, and Lachlan Ingram. 2023. "Exploring ‘Wether’ Grazing Patterns Differed in Native or Introduced Pastures in the Monaro Region of Australia" Animals 13, no. 9: 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091500
APA StyleParnell, D., Edwards, J., & Ingram, L. (2023). Exploring ‘Wether’ Grazing Patterns Differed in Native or Introduced Pastures in the Monaro Region of Australia. Animals, 13(9), 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091500








