Phylomitogenomic Analyses Provided Further Evidence for the Resurrection of the Family Pseudoacanthocephalidae (Acanthocephala: Echinorhynchida)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasite Collection and Species Identification
2.2. Molecular Procedures
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
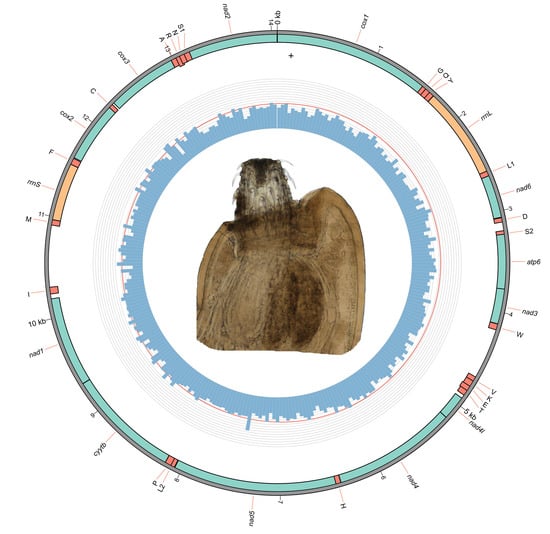
3.1. Morphology of Pseudoacanthocephalus bufonis (Figure 1, Table 3)
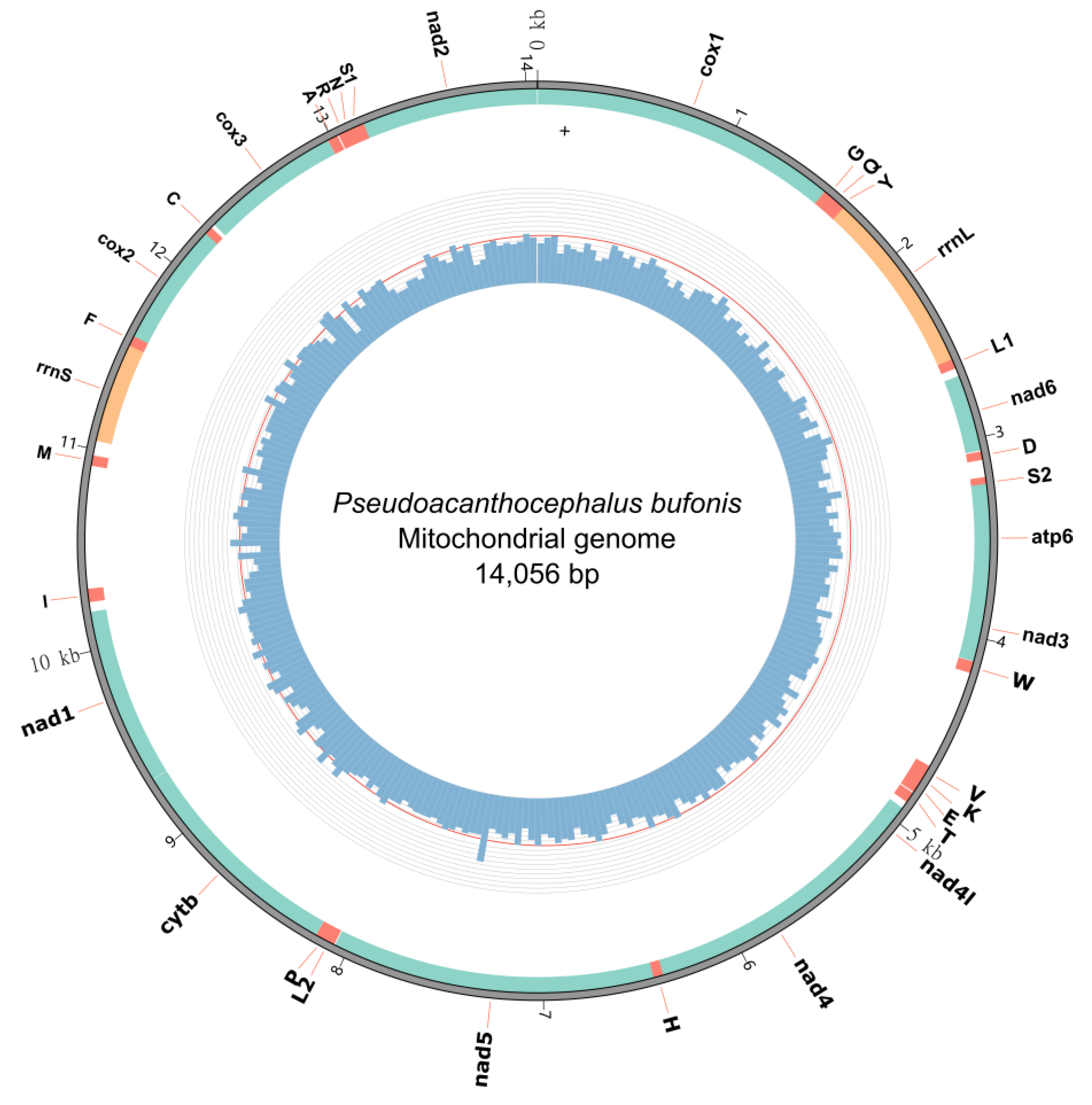
3.2. Gene Content and Organization of the Mitogenome
3.3. Protein-Coding Genes and Codon Usage
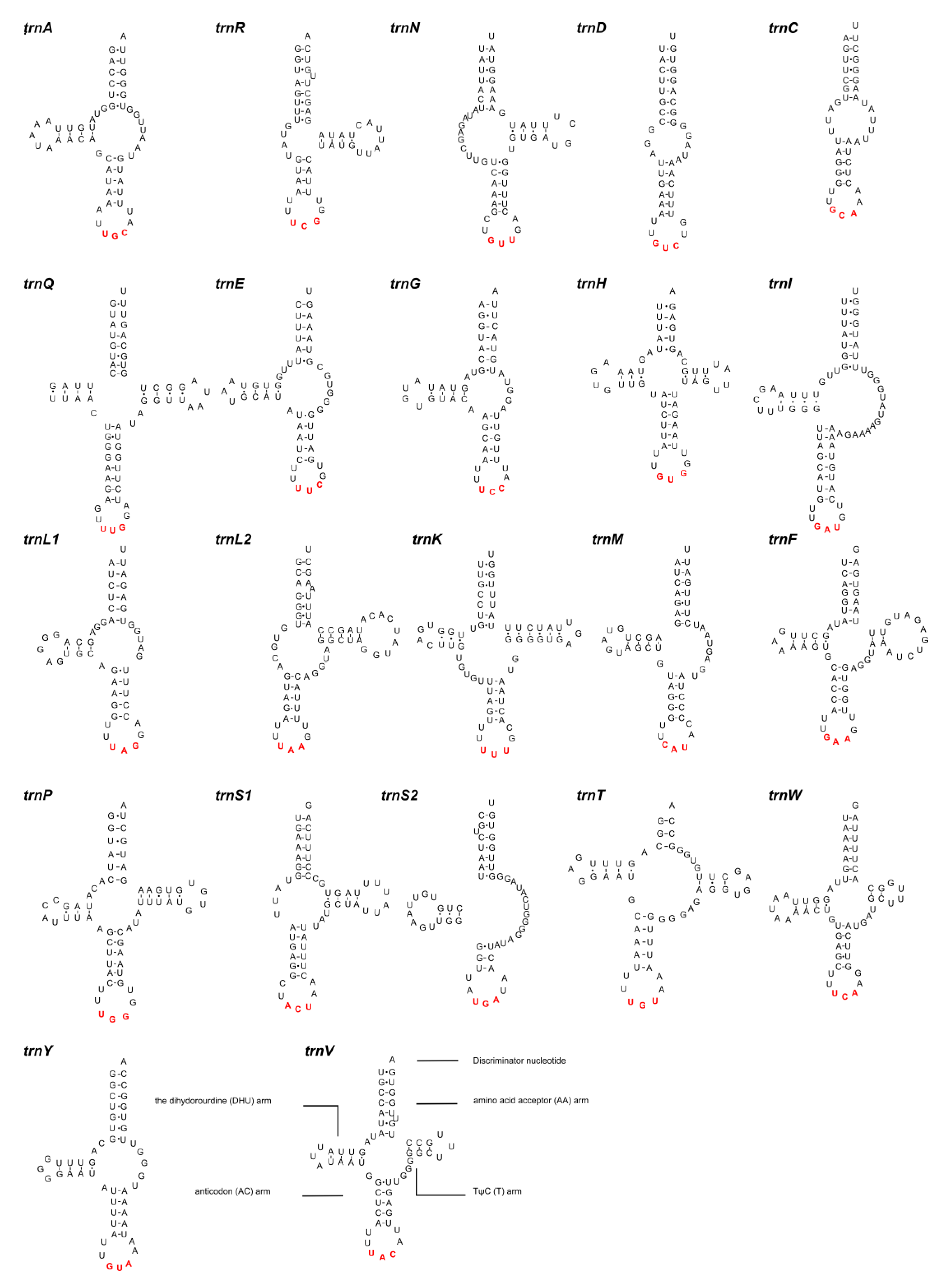
3.4. Ribosomal and Transfer RNAs
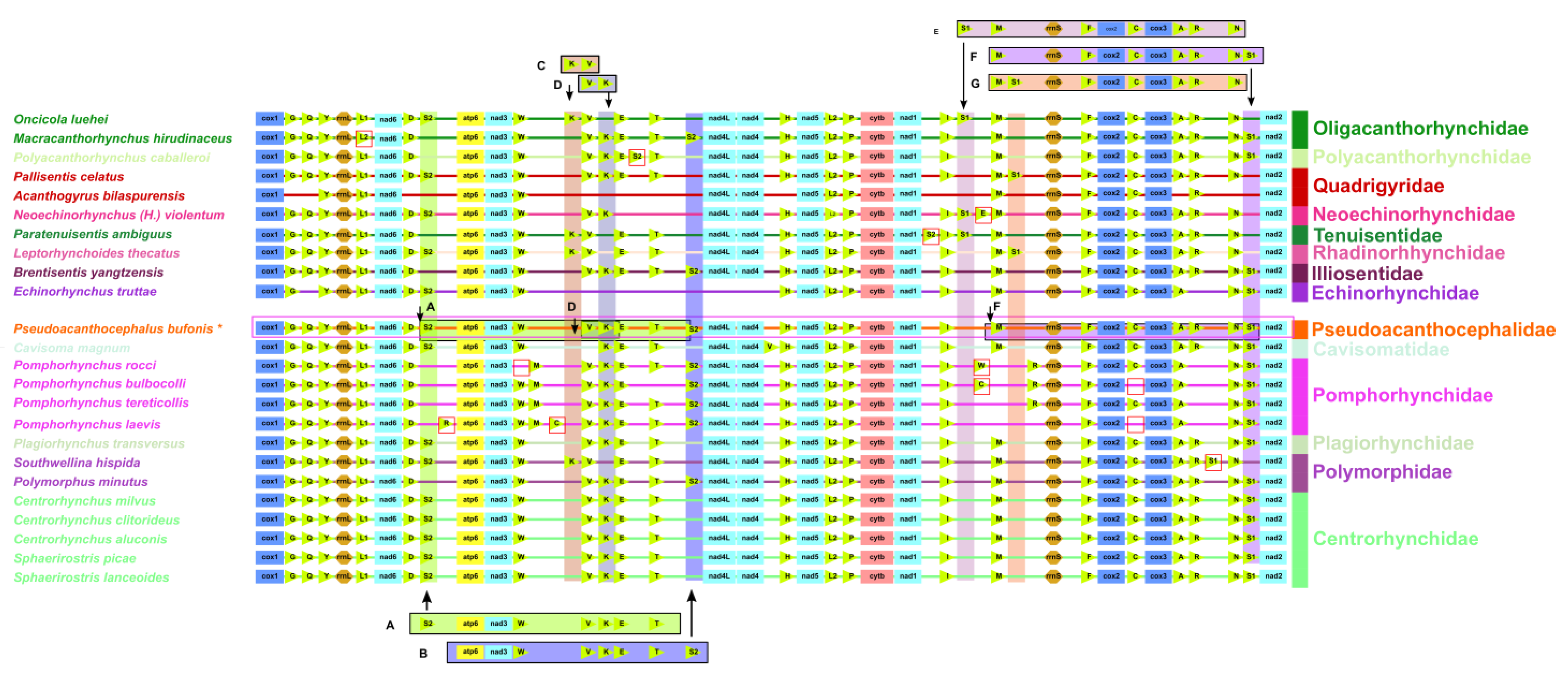
3.5. Gene Order
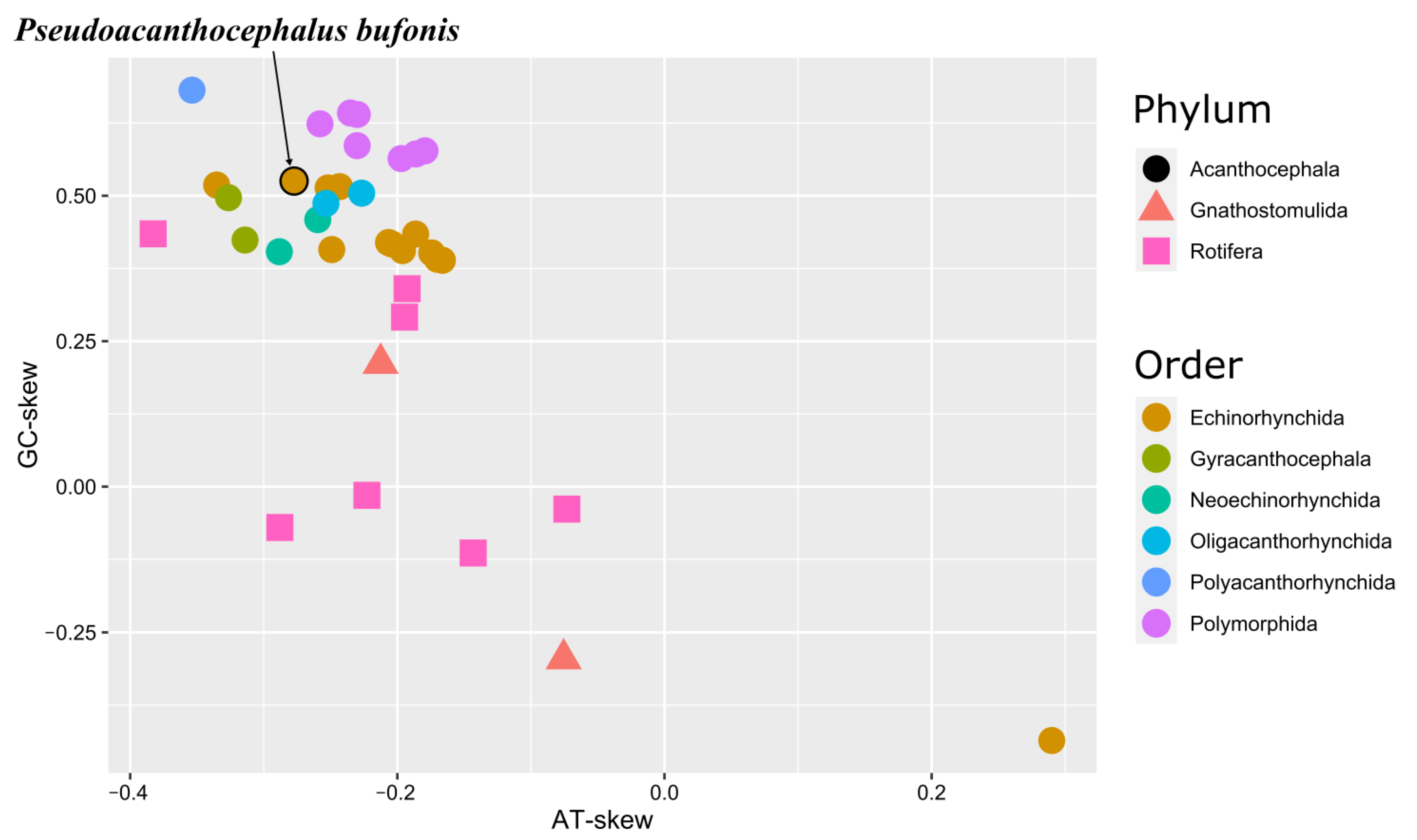
3.6. Non-Coding Regions
3.7. Molecular Phylogeny
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amin, O.M. Classification of the Acanthocephala. Folia. Parasitol. 2013, 60, 273–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguti, S. Acanthocephala. In Systema Helminthum; Interscience Publishers John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1963; Volume V, pp. 1–423. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, C.R. Ecology of the Acanthocephala; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-521-85008-7. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, G.D. Development and life cycles. In Biology of Acanthocephala; Crompton, D.W.T., Nickol, B.B., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985; pp. 273–286. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, O.M. Key to the families and subfamilies of acanthocephala, with the Erection of a new class (Polyacanthocephala) and a new order (Polyacanthorhynchida). J. Parasitol. 1987, 73, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huston, D.C.; Smales, L.R. Proposal of Spinulacorpus biforme (Smales, 2014) n. g., n. comb. and the Spinulacorpidae n. fam. to resolve paraphyly of the acanthocephalan family Rhadinorhynchidae Lühe, 1912. Syst. Parasitol. 2020, 97, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-Q. Animal biodiversity: An outline of higher-level classification and survey of taxonomic richness. Zootaxa 2011, 3148, 63–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Near, T.J.; Garey, J.R.; Nadler, S.A. Phylogenetic relationships of the Acanthocephala inferred from 18S ribosomal DNA Sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1998, 10, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Varela, M.; Pérez-Ponce de León, G.; de la Torre, P.; Cummings, M.P.; Sarma, S.S.S.; Laclette, J.P. Phylogenetic relationships of Acanthocephala based on analysis of 18S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 2000, 50, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Varela, M.; Cummings, M.P.; Pérez-Ponce de León, G.; Gardner, S.L.; Laclette, J.P. Phylogenetic analysis based on 18S ribosomal RNA gene sequences supports the existence of class Polyacanthocephala (Acanthocephala). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2002, 23, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Near, T.J. Acanthocephalan phylogeny and the evolution of parasitism1. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweyen, L.; Klimpel, S.; Palm, H.W. Molecular phylogeny of the Acanthocephala (class Palaeacanthocephala) with a paraphyletic assemblage of the orders Polymorphida and Echinorhynchida. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Varela, M.; Nadler, S.A. Phylogenetic relationships of Palaeacanthocephala (Acanthocephala) inferred from SSU and LSU rDNA gene sequences. J. Parasitol. 2005, 91, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Varela, M.; Nadler, S.A. Phylogenetic relationships among Syndermata inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial gene sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 40, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, M.; Sultana, T.; Min, G.-S.; Park, Y.C.; García-Varela, M.; Nadler, S.A.; Park, J.-K. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Oncicola luehei (Acanthocephala: Archiacanthocephala) and its phylogenetic position within Syndermata. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Varela, M.; Andrade-Gómez, L. First steps to understand the systematics of Echinorhynchidae Cobbold, 1876 (Acanthocephala), inferred through nuclear gene sequences. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 81, 102264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Varela, M.; Park, J.-K.; Hernández-Orts, J.S.; Pinacho-Pinacho, C.D. Morphological and molecular data on a new species of Plagiorhynchus Lühe, 1911 (Acanthocephala: Plagiorhynchidae) from the long-billed curlew (Numenius americanus) from northern Mexico. J. Helminthol. 2019, 94, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, M.; Kim, J.; Park, J.-K. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Southwellina hispida supports monophyly of Palaeacanthocephala (Acanthocephala: Polymorphida). Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazi, M.; Kim, J.; García-Varela, M.; Park, C.; Littlewood, D.T.J.; Park, J.-K. Mitogenomic phylogeny of Acanthocephala reveals novel class relationships. Zool. Scr. 2016, 45, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Wey-Fabrizius, A.R.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Witek, A.; Schill, R.O.; Sugár, L.; Herlyn, H.; Hankeln, T. Phylogenetic analyses of endoparasitic Acanthocephala based on mitochondrial genomes suggest secondary loss of sensory organs. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 66, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Li, H.; Liu, G.-H.; Wang, W.; James, P.; Colwell, D.D.; Tran, A.; Gong, S.; Cai, W.; Shao, R. Mitochondrial genome fragmentation unites the parasitic lice of eutherian mammals. Syst. Biol. 2019, 68, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Suleman; Ma, J.; Khan, M.S.; Wu, S.-S.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Li, L. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Centrorhynchus milvus (Acanthocephala: Polymorphida) and its phylogenetic implications. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Suleman; Ma, J.; Khan, M.S.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ahmad, M.S.; Zhu, X.-Q. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Sphaerirostris picae (Rudolphi, 1819) (Acanthocephala: Centrorhynchidae), representative of the genus Sphaerirostris. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2213–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Li, L.; Suleman; Zhao, Q.; Bannai, M.A.; Mohammad, E.T.; Khan, M.S.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Ma, J. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Cavisoma magnum (Acanthocephala: Palaeacanthocephala), first representative of the family Cavisomidae, and its phylogenetic implications. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 80, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, N.; Suleman; Ahmad, M.S.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ullah, H.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Ma, J. Mitochondrial DNA dataset suggest that the genus Sphaerirostris Golvan, 1956 is a synonym of the genus Centrorhynchus Lühe, 1911. Parasitology 2020, 147, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smales, L.R.; Allain, S.J.R.; Wilkinson, J.W.; Harris, E. A new species of Pseudoacanthocephalus (Acanthocephala: Echinorhynchidae) from the guttural toad, Sclerophrys gutturalis (Bufonidae), introduced into Mauritius, with comments on the implications of the introductions of toads and their parasites into the UK. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichelin, S.; Cribb, T.H. The status of the Diplosentidae (Acanthocephala: Palaeacanthocephala) and a new family of acanthocephalans from Australian wrasses (Pisces: Labridae). Folia Parasitol. Praha 2001, 48, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicovich, P.E.; Lanfranchi, A.L.; Farber, M.D.; Marvaldi, A.E.; Luque, J.L.; Timi, J.T. Genetic and morphological evidence reveals the existence of a new family, genus and species of Echinorhynchida (Acanthocephala). Folia Parasitol. Praha 2014, 61, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, S. Phylogeny of the Acanthocephala based on morphological characters. Syst. Parasitol. 2001, 48, 81–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Varela, M.; Pérez-Ponce de León, G. Validating the systematic position of Profilicollis Meyer, 1931 and Hexaglandula Petrochenko, 1950 (Acanthocephala: Polymorphidae) using cytochrome c oxidase (Cox 1). J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrochenko, V.I. Thorny-headed worms (Acanthocephala) of U. S. S. R. amphibians. In Contributions on Helminthology in Commemoration of the Birthday of K. I. Skrjabin; Petrov, A.M., Ed.; Izdatel’stvo Akademii Nauk SSSR: Moscow, Russia, 1953; pp. 507–517. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, C.R.; Murray, J. A redescription of Acanthocephalus bufonis (Shipley, 1903) Southwell and Macfie, 1925 (Acanthocephala: Echinorhynchidae) from the black-spotted toad, Bufo melanostictus, from Bogor, Indonesia. Can. J. Zool. 1982, 60, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y. Studies on the life history of Pseudoacanthpcephalus bufonis (Shipley, 1903) Petrotschenko, 1958. J. Fujian Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 1989, 5, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, S.E.; Duszynski, D.W.; Nickol, B.B. Acanthocephala from Amphibians in China with the description of a new species of Pseudoacanthocephalus (Echinorhynchida). J. Parasitol. 2009, 95, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, A.E. On the ento-parasites collected by the “Skeat-Expedition” to Lower Siam and the Malay Peninsula in the years 1899–1900. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1903, 2, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, P.H.; Fernando, C.H. On Acanthocephalus bufonis (Shipley) a Common Parasite of Malayan amphibians. Bull. natn. Mus. Singap. 1967, 33, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn, H.; Röhrig, H. Ultrastructure and overall organization of ligament sac, uterine bell, uterus and vagina in Paratenuisentis ambiguus (Acanthocephala, Eoacanthocephala)—The character evolution within the Acanthocephala. Acta Zool. Stockholm 2003, 84, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.-Y.; Zhang, C.-J.; Lv, L. Comparative description of the mitochondrial genome of Scaphidium formosanum Pic, 1915 (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae: Scaphidiinae). Zootaxa 2021, 4941, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, S. MitoZ: A toolkit for animal mitochondrial genome assembly, annotation and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Lorenz, R. The ViennaRNA Web Services. In RNA Bioinformatics; Picardi, E., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1269, pp. 307–326. ISBN 978-1-4939-2291-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bernt, M.; Merkle, D.; Ramsch, K.; Fritzsch, G.; Perseke, M.; Bernhard, D.; Schlegel, M.; Stadler, P.F.; Middendorf, M. CREx: Inferring genomic rearrangements based on common intervals. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2957–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, J.S.; Mathews, D.H. RNAstructure: Software for RNA secondary structure prediction and analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.D. Python implementation of codon adaptation index. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscuolo, A.; Gribaldo, S. BMGE (Block Mapping and Gathering with Entropy): A new software for selection of phylogenetic informative regions from multiple sequence alignments. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lartillot, N.; Rodrigue, N.; Stubbs, D.; Richer, J. PhyloBayes MPI: Phylogenetic reconstruction with infinite mixtures of profiles in a parallel environment. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lartillot, N.; Philippe, H. A bayesian mixture model for across-site heterogeneities in the amino-acid replacement process. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartillot, N.; Philippe, H. Computing bayes factors using thermodynamic integration. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartillot, N.; Brinkmann, H.; Philippe, H. Suppression of long-branch attraction artefacts in the animal phylogeny using a site-heterogeneous model. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.-Q.; Gascuel, O.; Lartillot, N. Empirical profile mixture models for phylogenetic reconstruction. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golombek, A.; Tobergte, S.; Struck, T.H. Elucidating the phylogenetic position of Gnathostomulida and first mitochondrial genomes of Gnathostomulida, Gastrotricha and Polycladida (Platyhelminthes). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 86, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. Terrace aware data structure for phylogenomic inference from supermatrices. Syst. Biol. 2016, 65, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinauer, M.L.; Nickol, B.B.; Broughton, R.; Ortí, G. First sequenced mitochondrial genome from the phylum Acanthocephala (Leptorhynchoides thecatus) and its phylogenetic position within Metazoa. J. Mol. Evol. 2005, 60, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.S.; Nie, P. The complete mitochondrial genome of Pallisentis celatus (Acanthocephala) with phylogenetic analysis of Acanthocephalans and Rotifers. Folia Parasitol. 2013, 60, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Zhang, D.; Deng, S.; Ding, D.; Liao, F.; Liu, L. The complete mitochondrial genome of Acanthosentis cheni (Acanthocephala: Quadrigyridae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2016, 1, 797–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Jiang, H. The complete mitochondrial genome of Hebesoma Violentum (Acanthocephala). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2018, 3, 582–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.-T.; Cai, J.-Z.; Li, C.-H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J.; Ma, D.-D.; Li, Y.-P.; Zhang, Y.-M. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Echinorhynchus gymnocyprii (Acanthocephala: Echinorhynchidae) in schizothoracine fishes (Cyprinidae: Schizothoracinae) in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Parasite. Vector 2020, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauer, K.; Hellmann, S.L.; Groth, M.; Fröbius, A.C.; Zischler, H.; Hankeln, T.; Herlyn, H. The genome, transcriptome, and proteome of the fish parasite Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Suleman; Khan, M.S.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ullah, H.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Ma, J. Characterization of the complete mitogenome of Centrorhynchus clitorideus (Meyer, 1931) (Palaeacanthocephala: Centrorhynchidae), the largest mitochondrial genome in Acanthocephala, and its phylogenetic implications. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2020, 237, 111274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpert, F.; Podsiadlowski, L. The complete mitochondrial genome of the common sea slater, Ligia oceanica (Crustacea, Isopoda) bears a novel gene order and unusual control region features. BMC Genomics 2006, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Zhang, D.; Gao, J.-W.; Cheng, X.-F.; Xie, M.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.-A. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Brentisentisyangtzensis Yu & Wu, 1989 (Acanthocephala, Illiosentidae). ZooKeys 2019, 861, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, H.; Zhao, W.-T.; Kibet, C.J.; Sitko, J.; Nie, P. Morphological and complete mitogenomic characterisation of the Acanthocephalan Polymorphus minutus infecting the duck anas platyrhynchos. Folia Parasitol. 2021, 68, e015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Varela, M.; González-Oliver, A. The systematic position of Leptorhynchoides (Kostylew, 1924) and Pseudoleptorhynchoides (SalgadoMaldonado, 1976), inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA gene sequences. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Varela, M.; Pérez-Ponce de León, G.; Aznar, F.J.; Nadler, S.A. Phylogenetic relationship among genera of Polymorphidae (Acanthocephala), inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial gene sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 68, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkach, V.V.; Lisitsyna, O.I.; Crossley, J.L.; Binh, T.T.; Bush, S.E. Morphological and molecular differentiation of two new species of Pseudoacanthocephalus Petrochenko, 1958 (Acanthocephala: Echinorhynchidae) from amphibians and reptiles in the Philippines, with identification key for the genus. Syst. Parasitol. 2013, 85, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlyn, H.; Piskurek, O.; Schmitz, J.; Ehlers, U.; Zischler, H. The syndermatan phylogeny and the evolution of acanthocephalan endoparasitism as inferred from 18S rDNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, A.; Herlyn, H.; Meyer, A.; Boell, L.; Bucher, G.; Hankeln, T. EST based phylogenomics of Syndermata questions monophyly of Eurotatoria. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wey-Fabrizius, A.R.; Herlyn, H.; Rieger, B.; Rosenkranz, D.; Witek, A.; Welch, D.B.M.; Ebersberger, I.; Hankeln, T. Transcriptome data reveal syndermatan relationships and suggest the evolution of endoparasitism in Acanthocephala via an epizoic stage. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Ghaffar, F.; Morsy, K.; Abdel-Gaber, R.; Mehlhorn, H.; Al Quraishy, S.; Mohammed, S. Prevalence, morphology, and molecular analysis of Serrasentis sagittifer (Acanthocephala: Palaeacanthocephala: Rhadinorhynchidae), a parasite of the gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata (Sparidae). Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Fernandes, V.S.; Amin, O.; Borges, J.N.; Santos, C.P. A new species of the Acanthocephalan genus Filisoma (Cavisomidae) from perciform fishes in Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Acta Parasit. 2019, 64, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Phylum/Class | Order | Family | Species | Accession | Length | AT% | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outgroup | |||||||
| Gnathostomulida | Bursovaginoidea | Gnathostomulidae | Gnathostomula armata | NC_026983 | 14,030 | 80.2 | [55] |
| Gnathostomula paradoxa | NC_026984 | 14,197 | 71.8 | [55] | |||
| Ingroup | |||||||
| Rotifera | Bdelloidea | Philodinidae | Rotaria rotatoria | NC_013568 | 15,319 | 73.2 | [58] |
| Philodina citrina | FR856884 | 14,003 | 77.7 | [20] | |||
| Monogononta | Brachionidae | Brachionus calyciflorus | KX822781 | 27,683 | 68.7 | [59] | |
| Brachionus plicatilis | NC_010484 | 12,672 | 62.9 | [60] | |||
| Brachionus rubens | MN256532 | 13,795 | 67.2 | [61] | |||
| Proalidae | Proales similis | MN970216 | 16,819 | 67.2 | [62] | ||
| Seisonidea | Seisonidae | Seison sp. | KP742964 | 15,120 | 70.0 | [63] | |
| Acanthocephala | |||||||
| Archiacanthocephala | Oligacanthorhynchida | Oligacanthorhynchidae | Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus | NC_019808 | 14,282 | 65.2 | [20] |
| Oncicola luehei | NC_016754 | 14,281 | 60.2 | [15] | |||
| Eoacanthocephala | Gyracanthocephala | Quadrigyridae | Pallisentis celatus | NC_022921 | 13,855 | 61.5 | [64] |
| Acanthogyrus bilaspurensis | MT476589 | 13,360 | 59.3 | unpublished | |||
| Neoechinorhynchida | Neoechinorhynchidae | Neoechinorhynchus violentum | KC415004 | 13,393 | 59.4 | [65] | |
| Tenuisentidae | Paratenuisentis ambiguus | NC_019807 | 13,574 | 66.9 | [20] | ||
| Palaeacanthocephala | Echinorhynchida | Cavisomidae | Cavisoma magnum | MN562586 | 13,594 | 63.0 | [24] |
| Echinorhynchidae | Echinorhynchus truttae | NC_019805 | 13,659 | 63.1 | [20] | ||
| Pseudoacanthocephalidae | Pseudoacanthocephalus bufonis | MZ958236 | 14,056 | 58.4 | present study | ||
| Illiosentidae | Brentisentis yangtzensis | MK651258 | 13,864 | 68.3 | [66] | ||
| Pomphorhynchidae | Pomphorhynchus bulbocolli | JQ824371 | 13,915 | 59.9 | unpublished | ||
| Pomphorhynchus laevis | JQ809446 | 13,889 | 57.1 | unpublished | |||
| Pomphorhynchus rocci | JQ824373 | 13,845 | 60.7 | unpublished | |||
| Pomphorhynchus tereticollis | JQ809451 | 13,965 | 56.9 | unpublished | |||
| Rhadinorhynchidae | Leptorhynchoides thecatus | NC_006892 | 13,888 | 71.4 | [67] | ||
| Polymorphida | Centrorhynchidae | Centrorhynchus clitorideus | MT113355 | 15,884 | 55.5 | [68] | |
| Centrorhynchus milvus | MK922344 | 14,314 | 54.5 | [22] | |||
| Centrorhynchus aluconis | KT592357 | 15144 | 54.5 | [19] | |||
| Sphaerirostris lanceoides | MT476588 | 13,478 | 58.0 | [25] | |||
| Sphaerirostris picae | MK471355 | 15,170 | 58.1 | [23] | |||
| Polymorphidae | Polymorphus minutus | MN646175 | 14,149 | 64.4 | [69] | ||
| Southwellina hispida | NC_026516 | 14,742 | 63.9 | [18] | |||
| Plagiorhynchidae | Plagiorhynchus transversus | NC_029767 | 15,477 | 61.1 | [19] | ||
| Polyacanthocephala | Polyacanthorhynchida | Polyacanthorhynchidae | Polyacanthorhynchus caballeroi | NC_029766 | 13,956 | 56.3 | [19] |
| Partition Scheme (t) | Model | Parameters (k) | ln (Lik) | AIC | ΔAIC | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NP (1) | mtZOA + F + R5 + C60 | 150 | −64,770.62 | 129,841.23 | 130,683.08 | |
| MP (2) | - | 112 | −64,937.53 | 130,099.06 | 257.83 | 130,727.65 |
| NP (1) | mtZOA + F + R5 | 90 | −65,020.09 | 130,220.18 | 378.94 | 130,725.29 |
| FP (12) | - | 287 | −64,983.58 | 130,541.16 | 699.92 | 132,151.90 |
| Host | Polypedates megacephalus | Bufo melanostictus, Rana cancrivora, Takydromus sexlineatus | Bufo melanostictus | Polypedates megacephalus, P. mutus, Fejervarya limnocharis, Limnonectes kuhlii, Philautus odontotarsus, Odorrana versabilis, Rana livida, Amolops sp. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locality | China | Indonesia | China | China | ||||
| Source | Present study | Kennedy (1982) [32] | Wang (1989) [33] | Bush (2009) [34] | ||||
| Characteristics | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female |
| Trunk length | 5.43–8.98 | 10.0–18.0 | 5.29–9.38 | 11.2–16.1 | 6.80–8.00 | 15.0–20.0 | 5.70–11.8 | 15.3–28.0 |
| Trunk width | 1.00–1.50 | 0.98–1.45 | 0.98–1.51 | 1.13–2.10 | 0.88–1.52 | 1.40–1.60 | 1.00–2.20 | 1.10–2.30 |
| Proboscis length | 0.31–0.50 | 0.38–0.53 | 0.31–0.44 | 0.33–0.54 | 0.48–0.52 | 0.56–0.64 | 0.41–0.54 | 0.41–0.54 |
| Proboscis width | 0.28–0.31 | 0.30–0.41 | 0.17–0.31 | 0.22–0.33 | 0.32–0.45 | 0.32–0.46 | 0.28–0.36 | 0.28–0.36 |
| Lemnisci length | 0.48–0.95 | 0.59–1.23 | 0.74–1.32 | 1.16–1.70 | 0.96–1.44 | 0.72–1.44 | 0.80–1.42 | 0.80–1.42 |
| Proboscis receptacle length | 0.41–0.71 | 0.58–0.91 | 0.65–0.90 | 0.88–1.10 | 0.96–1.12 | 0.88–1.12 | 0.69–0.95 | 0.69–0.95 |
| Proboscis receptacle width | 0.25–0.30 | 0.25–0.45 | 0.19–0.35 | 0.31–0.53 | 0.21–0.32 | 0.24–0.32 | 0.27–0.35 | 0.27–0.35 |
| Size of the anterior testis | 0.45–0.80 | N/A | 0.47–0.79 | N/A | 0.56–0.68 | N/A | 0.51–0.95 | N/A |
| × 0.40–0.62 | × 0.31–0.53 | × 0.40–0.48 | × 0.29–0.58 | |||||
| Size of the posterior testis | 0.45–0.74 | N/A | 0.54–0.72 | N/A | 0.52–0.72 | N/A | 0.51–0.95 | N/A |
| × 0.37–0.65 | × 0.28–0.50 | × 0.48–0.51 | × 0.29–0.58 | |||||
| Cement-gland length | 0.76–1.46 | N/A | – | N/A | – | N/A | 0.77–1.51 | N/A |
| Size of the copulatory bursa | 0.40–0.46 | N/A | – | N/A | – | N/A | – | N/A |
| × 0.46–0.84 | ||||||||
| Uterine bell length | N/A | 0.34–0.62 | N/A | – | N/A | 0.80–0.85 | N/A | 0.45–0.68 |
| Uterus length | N/A | 0.26–0.47 | N/A | – | N/A | – | N/A | 0.29–0.38 |
| Size of the egg | N/A | 0.06–0.09 | N/A | 0.08–0.09 | N/A | 0.06–0.09 | N/A | 0.06–0.07 |
| × 0.02–0.03 | × 0.02–0.03 | × 0.02–0.03 | × 0.02 | |||||
| Gene | Type | Start | End | Length | Start Codon | Stop Codon | Anticodon | Gap or Overlap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cox1 | CDS | 1 | 1539 | 1539 | GTG | TAG | −2 | |
| trnG | tRNA | 1538 | 1589 | 52 | UCC | −11 | ||
| trnQ | tRNA | 1579 | 1641 | 63 | UUG | −13 | ||
| trnY | tRNA | 1629 | 1679 | 51 | GUA | 1 | ||
| rrnL | rRNA | 1681 | 2588 | 908 | 0 | |||
| trnL1 | tRNA | 2589 | 2638 | 50 | UAG | 0 | ||
| nad6 | CDS | 2639 | 3063 | 425 | GTG | TA | 4 | |
| trnD | tRNA | 3068 | 3111 | 44 | GUC | 85 | ||
| trnS2 | tRNA | 3197 | 3253 | 57 | UGA | −22 | ||
| atp3 | CDS | 3232 | 3771 | 540 | ATA | TAA | −1 | |
| nad3 | CDS | 3771 | 4118 | 348 | ATG | TAA | 1 | |
| trnW | tRNA | 4120 | 4179 | 60 | UCA | 0 | ||
| NCR2 | Non-coding region | 4180 | 4682 | 503 | 0 | |||
| trnV | tRNA | 4683 | 4742 | 60 | UAC | −14 | ||
| trnK | tRNA | 4729 | 4793 | 65 | UUU | −11 | ||
| trnE | tRNA | 4783 | 4833 | 51 | UUC | 5 | ||
| trnT | tRNA | 4839 | 4894 | 56 | UGU | 35 | ||
| nad4l | CDS | 4930 | 5172 | 243 | GTG | TAA | 0 | |
| nad4 | CDS | 5173 | 6397 | 1225 | ATG | T | 1 | |
| trnH | tRNA | 6399 | 6453 | 55 | GUG | −6 | ||
| nad5 | CDS | 6448 | 8067 | 1620 | GTG | TAG | 4 | |
| trnL2 | tRNA | 8072 | 8133 | 62 | UAA | −23 | ||
| trnP | tRNA | 8111 | 8173 | 63 | UGG | 0 | ||
| cytb | CDS | 8174 | 9298 | 1125 | TTG | TAA | 1 | |
| nad1 | CDS | 9300 | 10,190 | 891 | ATT | TAA | 47 | |
| trnI | tRNA | 10,238 | 10,305 | 68 | GAU | 0 | ||
| NCR1 | Non-coding region | 10,306 | 10,915 | 610 | 0 | |||
| trnM | tRNA | 10,916 | 10,969 | 54 | CAU | 0 | ||
| rrnS | rRNA | 10,970 | 11,541 | 572 | 0 | |||
| trnF | tRNA | 11,542 | 11,605 | 64 | GAA | 8 | ||
| cox2 | CDS | 11,614 | 12,216 | 603 | TTG | TAG | −2 | |
| trnC | tRNA | 12,215 | 12,256 | 42 | GCA | 19 | ||
| cox3 | CDS | 12,276 | 12,978 | 703 | GTG | T | 0 | |
| trnA | tRNA | 12,979 | 13,032 | 54 | UGC | 5 | ||
| trnR | tRNA | 13,038 | 13,089 | 52 | UCG | −20 | ||
| trnN | tRNA | 13,070 | 13,127 | 58 | GUU | −10 | ||
| trnS1 | tRNA | 13,118 | 13,174 | 57 | ACU | −1 | ||
| nad2 | CDS | 13,175 | 14,055 | 882 | GTG | TAA | 1 |
| Location | A% | T% | C% | G% | AT% | AT-Skew | GC-Skew | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole mitochondrial genome | 34.35 | 37.31 | 9.87 | 31.71 | 58.42 | −0.28 | 0.53 | 14,056 |
| Protein coding genes (PCGs) | 18.88 | 38.07 | 9.27 | 33.78 | 56.95 | −0.45 | 2.65 | 10,144 |
| 1st codon | 21.58 | 30.12 | 9.58 | 38.72 | 51.70 | −0.18 | 3.04 | 3383 |
| 2nd codon | 13.07 | 47.97 | 10.68 | 28.28 | 61.05 | −0.90 | 1.65 | 3381 |
| 3rd codon | 21.98 | 36.12 | 7.54 | 34.35 | 58.11 | −0.34 | 3.56 | 3380 |
| tRNAs | 25.20 | 37.48 | 10.50 | 26.82 | 62.68 | −0.20 | 0.44 | 1238 |
| rRNAs | 28.18 | 35.54 | 10.61 | 25.68 | 63.72 | −0.12 | 0.42 | 63.72 |
| rrnS | 27.97 | 37.06 | 8.74 | 26.22 | 65.03 | −0.14 | 0.50 | 65.03 |
| rrnL | 28.30 | 34.58 | 11.78 | 25.33 | 62.89 | −0.10 | 0.37 | 62.89 |
| Non-coding region 1 | 28.36 | 33.61 | 19.34 | 18.69 | 61.97 | −0.08 | −0.02 | 610 |
| Non-coding region 2 | 26.64 | 30.22 | 5.57 | 37.57 | 56.86 | −0.06 | 0.74 | 503 |
| Codon | aa | No. | % | Codon | aa | No. | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAA | * | 6 | 0.18 | TTA | Leu | 183 | 5.44 |
| TAG | * | 3 | 0.09 | TTG | Leu | 188 | 5.58 |
| GCA | Ala | 48 | 1.43 | AAA | Lys | 34 | 1.01 |
| GCC | Ala | 16 | 0.48 | AAG | Lys | 12 | 0.36 |
| GCG | Ala | 20 | 0.59 | ATA | Met | 86 | 2.55 |
| GCT | Ala | 50 | 1.49 | ATG | Met | 90 | 2.67 |
| CGA | Arg | 10 | 0.30 | TTC | Phe | 28 | 0.83 |
| CGC | Arg | 3 | 0.09 | TTT | Phe | 186 | 5.52 |
| CGG | Arg | 9 | 0.27 | CCA | Pro | 27 | 0.80 |
| CGT | Arg | 18 | 0.53 | CCC | Pro | 14 | 0.42 |
| AAC | Asn | 9 | 0.27 | CCG | Pro | 8 | 0.24 |
| AAT | Asn | 49 | 1.46 | CCT | Pro | 23 | 0.68 |
| GAC | Asp | 10 | 0.30 | AGA | Ser | 36 | 1.07 |
| GAT | Asp | 43 | 1.28 | AGC | Ser | 20 | 0.59 |
| TGC | Cys | 16 | 0.48 | AGG | Ser | 108 | 3.21 |
| TGT | Cys | 60 | 1.78 | AGT | Ser | 55 | 1.63 |
| CAA | Gln | 9 | 0.27 | TCA | Ser | 20 | 0.59 |
| CAG | Gln | 11 | 0.33 | TCC | Ser | 4 | 0.12 |
| GAA | Glu | 23 | 0.68 | TCG | Ser | 5 | 0.15 |
| GAG | Glu | 53 | 1.57 | TCT | Ser | 45 | 1.34 |
| GGA | Gly | 36 | 1.07 | ACA | Thr | 18 | 0.53 |
| GGC | Gly | 28 | 0.83 | ACC | Thr | 12 | 0.36 |
| GGG | Gly | 304 | 9.03 | ACG | Thr | 12 | 0.36 |
| GGT | Gly | 114 | 3.39 | ACT | Thr | 39 | 1.16 |
| CAC | His | 10 | 0.30 | TGA | Trp | 29 | 0.86 |
| CAT | His | 38 | 1.13 | TGG | Trp | 106 | 3.15 |
| ATC | Ile | 19 | 0.56 | TAC | Tyr | 23 | 0.68 |
| ATT | Ile | 129 | 3.83 | TAT | Tyr | 108 | 3.21 |
| CTA | Leu | 35 | 1.04 | GTA | Val | 139 | 4.13 |
| CTC | Leu | 2 | 0.06 | GTC | Val | 41 | 1.22 |
| CTG | Leu | 51 | 1.51 | GTG | Val | 176 | 5.23 |
| CTT | Leu | 55 | 1.63 | GTT | Val | 205 | 6.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, T.-Y.; Yang, R.-J.; Lü, L.; Ru, S.-S.; Wayland, M.T.; Chen, H.-X.; Li, Y.-H.; Li, L. Phylomitogenomic Analyses Provided Further Evidence for the Resurrection of the Family Pseudoacanthocephalidae (Acanthocephala: Echinorhynchida). Animals 2023, 13, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13071256
Zhao T-Y, Yang R-J, Lü L, Ru S-S, Wayland MT, Chen H-X, Li Y-H, Li L. Phylomitogenomic Analyses Provided Further Evidence for the Resurrection of the Family Pseudoacanthocephalidae (Acanthocephala: Echinorhynchida). Animals. 2023; 13(7):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13071256
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Tian-You, Rui-Jia Yang, Liang Lü, Si-Si Ru, Matthew Thomas Wayland, Hui-Xia Chen, Yuan-Hao Li, and Liang Li. 2023. "Phylomitogenomic Analyses Provided Further Evidence for the Resurrection of the Family Pseudoacanthocephalidae (Acanthocephala: Echinorhynchida)" Animals 13, no. 7: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13071256
APA StyleZhao, T.-Y., Yang, R.-J., Lü, L., Ru, S.-S., Wayland, M. T., Chen, H.-X., Li, Y.-H., & Li, L. (2023). Phylomitogenomic Analyses Provided Further Evidence for the Resurrection of the Family Pseudoacanthocephalidae (Acanthocephala: Echinorhynchida). Animals, 13(7), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13071256