Important Role of the Ihh Signaling Pathway in Initiating Early Cranial Remodeling and Morphological Specialization in Cromileptes altivelis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Comparison of Bone Morphology
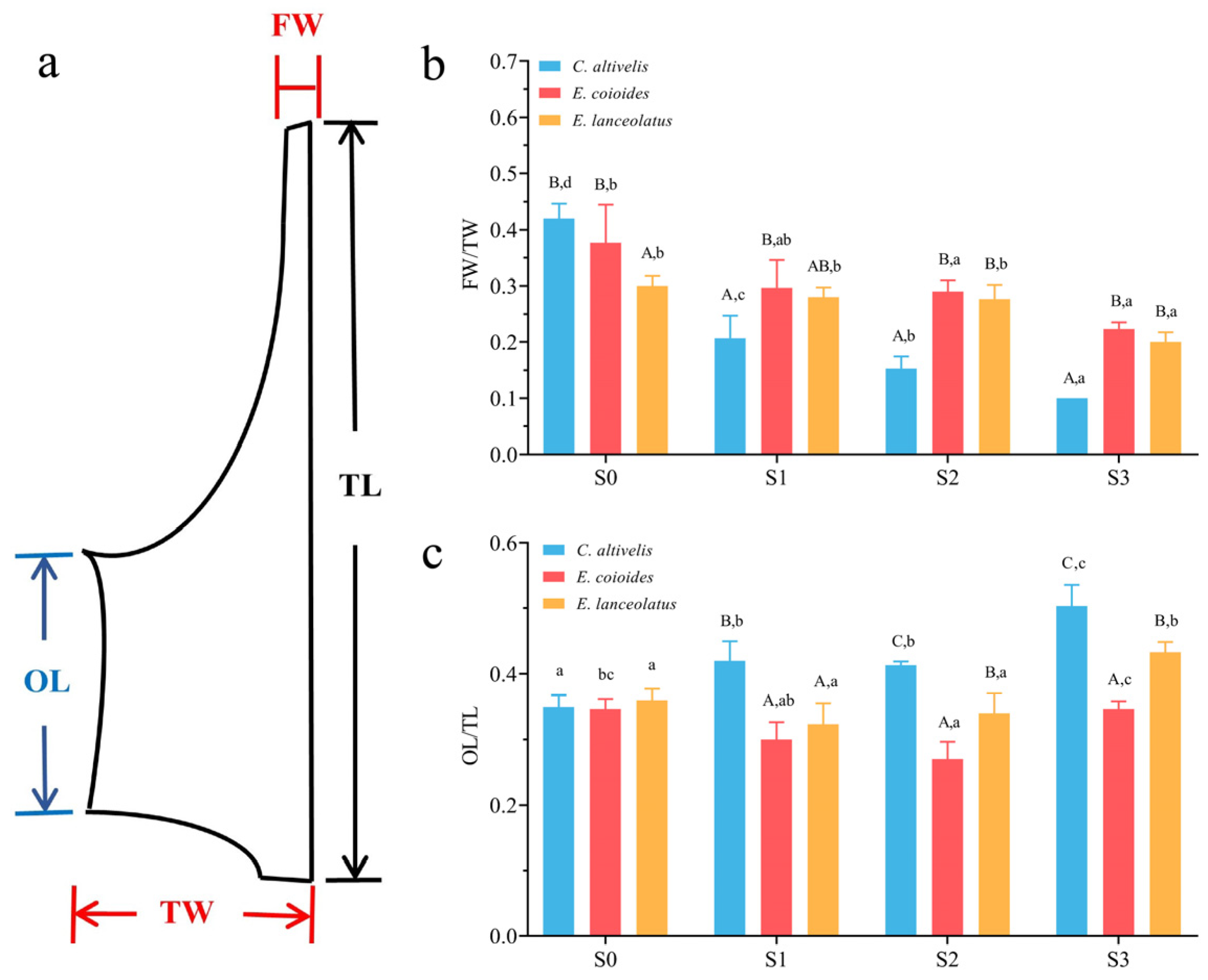
2.3. Quantification of Bone Sections
2.4. Sequence Analysis and qPCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
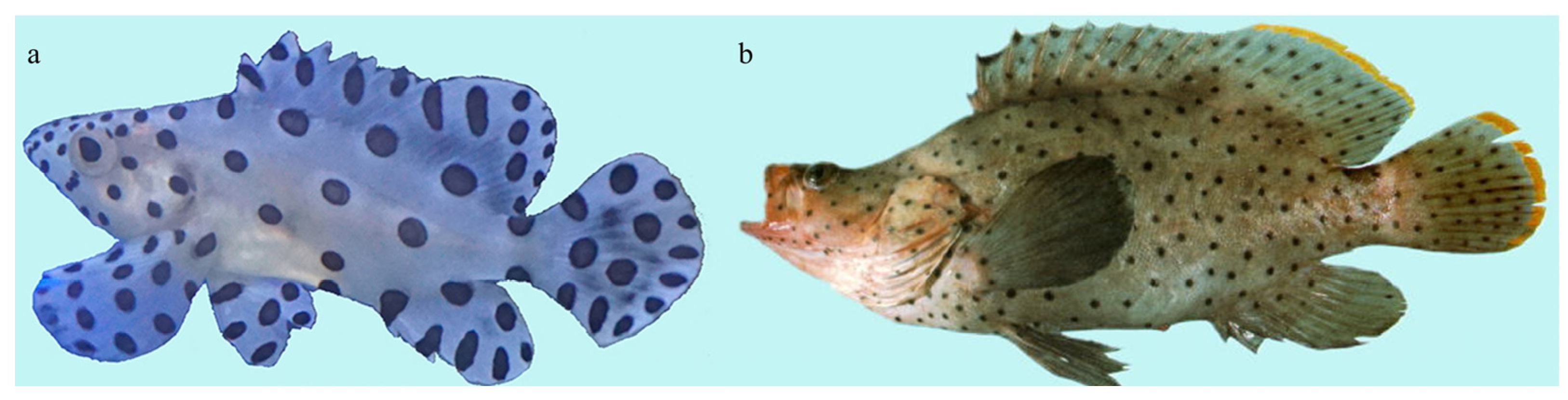
3.1. Identification of Skeletal Elements and Developmental Node in Morphological Specialization of C. altivelis
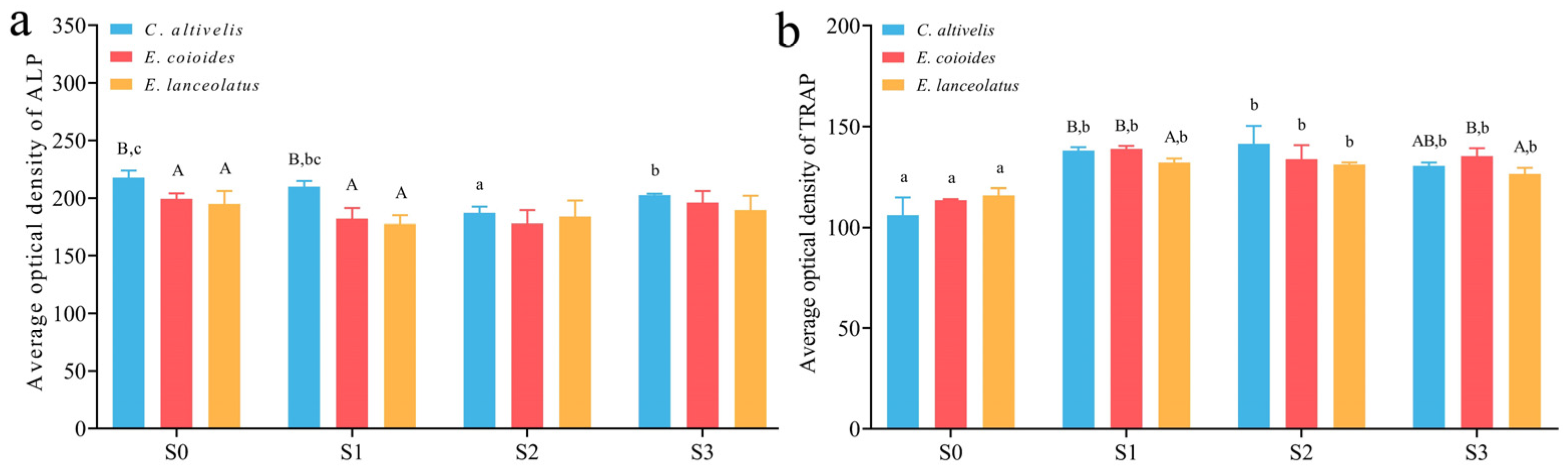
3.2. Frozen Sections and Staining of Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts
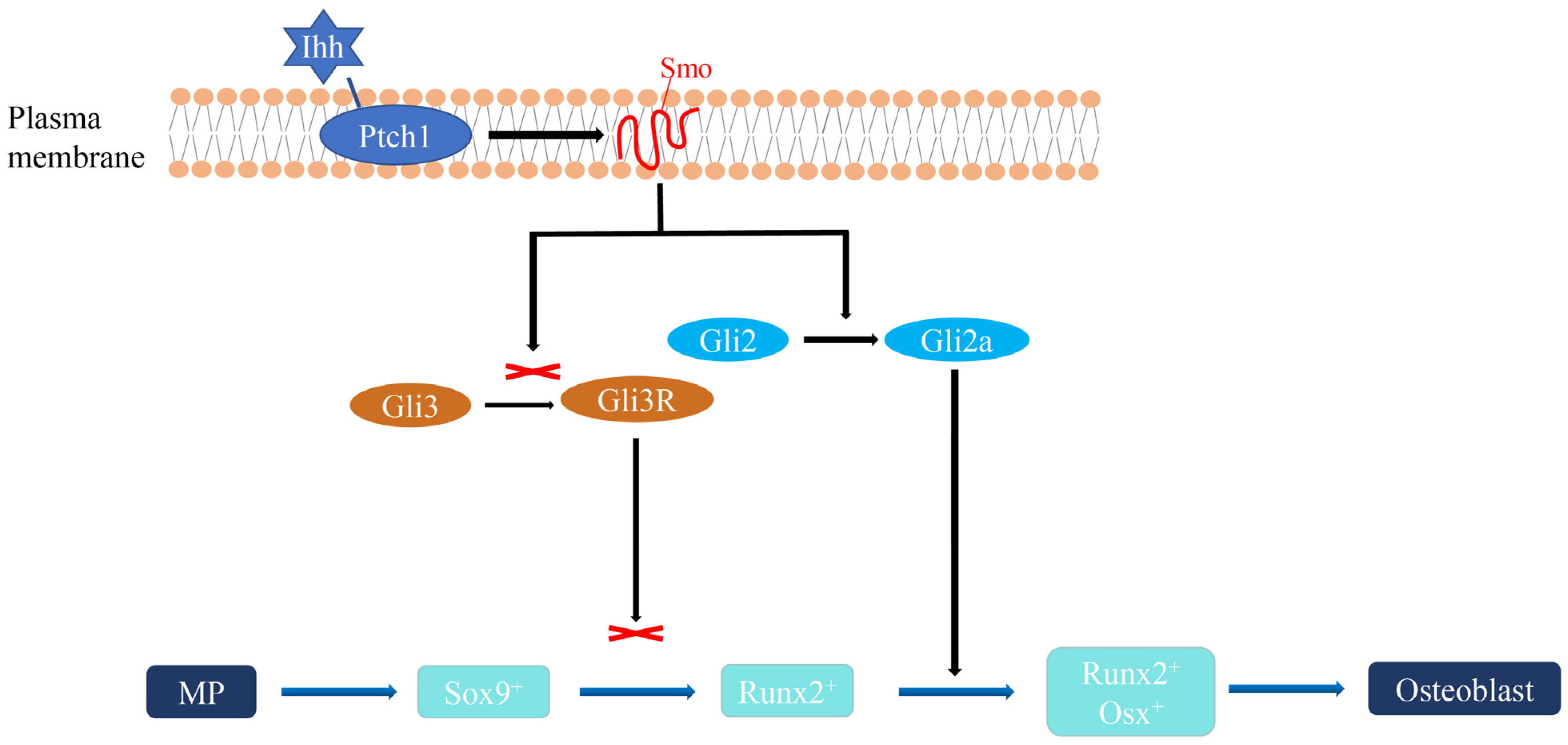
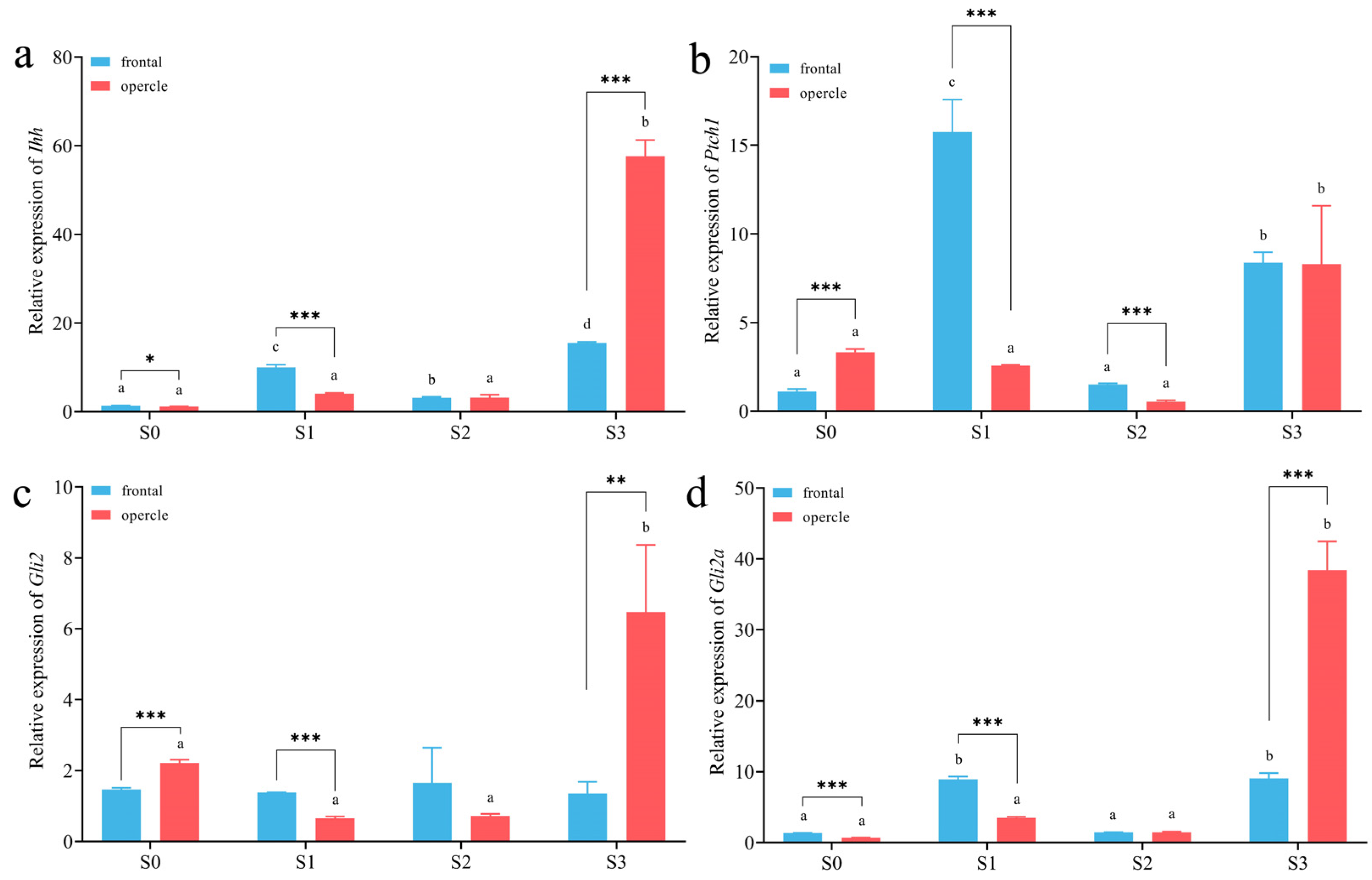
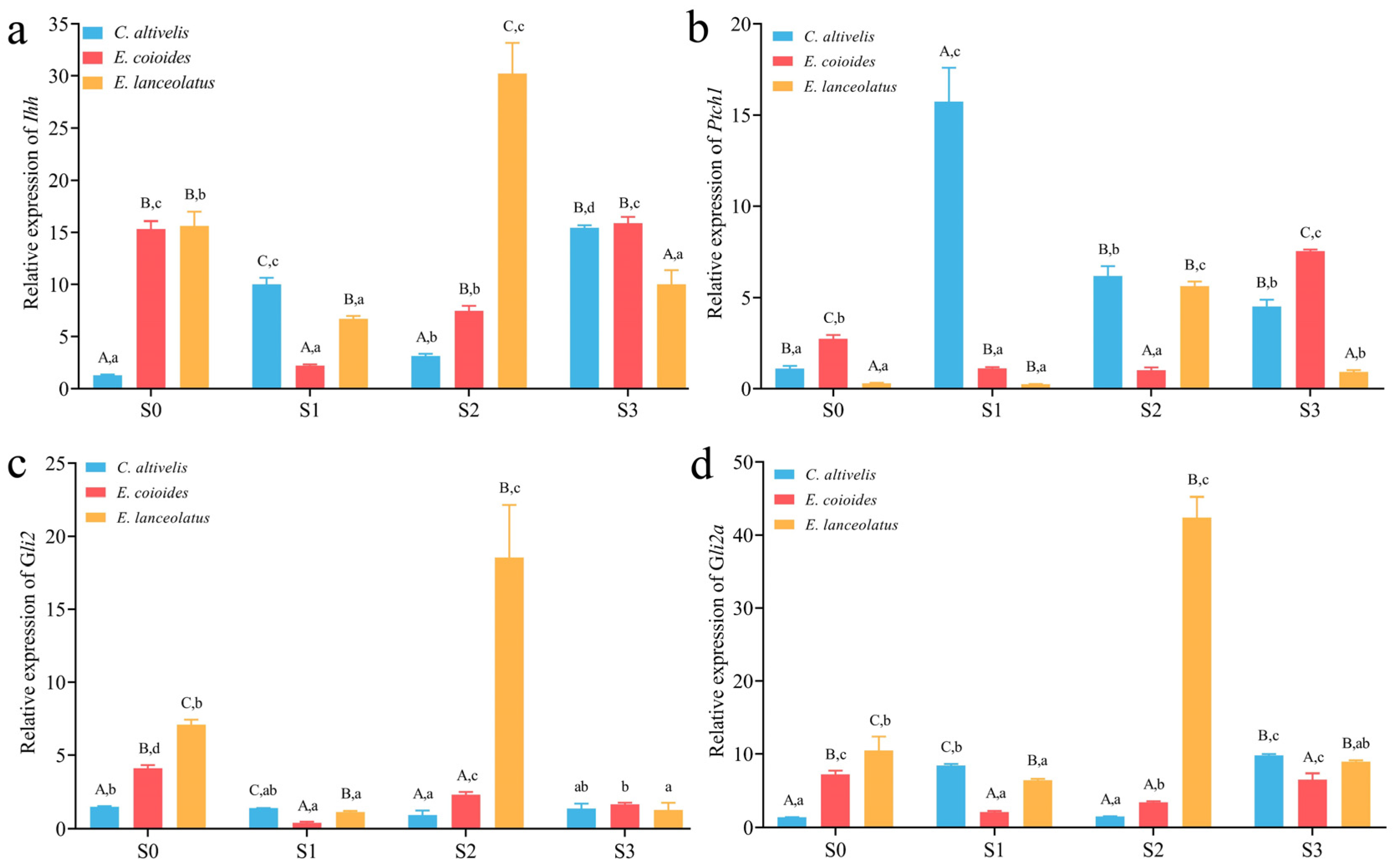
3.3. Expression Level of Ihh Pathway Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farias, I.P.; Ortí, G.; Meyer, A. Total evidence: Molecules, morphology, and the phylogenetics of cichlid fishes. J. Exp. Zool. 2000, 288, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschick, M.; Indermaur, A.; Salzburger, W. Convergent Evolution within an Adaptive Radiation of Cichlid Fishes. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2362–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rintelen, T.V.; Wilson, A.B.; Meyer, A.; Glaubrecht, M. Escalation and trophic specialization drive adaptive radiation of freshwater gastropods in ancient lakes on Sulawesi, Indonesia. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, M.T.; de Mitcheson, Y.S.; Heemstra, P.C. Groupers of the World: A Field and Market Guide; NISC (Pty) Ltd.: Grahamstown, South Africa, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Zhuang, X.; Guo, F.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q. Molecular phylogenetic relationships of China Seas groupers based on cytochrome b gene fragment sequences. Sci. China C Life Sci. 2006, 49, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, L.; Weng, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Meng, Z.; Liu, X. Chromosome Genome Assembly of Cromileptes altivelis Reveals Loss of Genome Fragment in Cromileptes Compared with Epinephelus Species. Genes 2021, 12, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heemstra, P.C.; Randall, J.E. FAO Species Catalogue. v16: Groupers of the World (Family Serranidae, Subfamily Epinephelinae); FAO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Navon, D.; Male, I.; Tetrault, E.R.; Aaronson, B.; Karlstrom, R.O.; Albertson, R.C. Hedgehog signaling is necessary and sufficient to mediate craniofacial plasticity in teleosts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 19321–19327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijlsma, M.F.; Spek, C.A.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Hedgehog: An unusual signal transducer. Bioessays 2004, 26, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartz, M.E.; Nguyen, V.; McCarthy, N.Q.; Eberhart, J.K. Hh signaling regulates patterning and morphogenesis of the pharyngeal arch-derived skeleton. Dev. Biol. 2012, 369, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, K.; Hata, A. Indian hedgehog gene is a target of the bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 18544–18549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Chung, U.I.; Ohba, S.; McMahon, J.; Kronenberg, H.M.; McMahon, A.P. Ihh signaling is directly required for the osteoblast lineage in the endochondral skeleton. Development 2004, 131, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, R.; Milenkovic, L.; Scott, M.P. Patched1 regulates hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium. Science 2007, 317, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbit, K.C.; Aanstad, P.; Singla, V.; Norman, A.R.; Stainier, D.Y.; Reiter, J.F. Vertebrate Smoothened functions at the primary cilium. Nature 2005, 437, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Jacques, B.; Hammerschmidt, M.; McMahon, A.P. Indian hedgehog signaling regulates proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes and is essential for bone formation. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.; Chang, L.; Nguyen, A.; James, A.W. A review of hedgehog signaling in cranial bone development. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhotra, A.; Shah, H.N.; Levi, B.; Longaker, M.T. Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingerkus, G.; Uhler, L.D. Enzyme clearing of alcian blue stained whole small vertebrates for demonstration of cartilage. Stain. Technol. 1977, 52, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Wei, C.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, Y. Screening of stable internal reference genes by quantitative real-time PCR in humpback grouper Cromileptes altivelis. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 1985–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seehausen, O. African cichlid fish: A model system in adaptive radiation research. Proc. R. Soc. B 2006, 273, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.G.; Ruber, L.; Newton, J.; Dasmahapatra, K.K.; Balarin, J.D.; Bruun, K.; Day, J.J. Niche divergence facilitated by fine-scale ecological partitioning in a recent cichlid fish adaptive radiation. Evolution 2016, 70, 2718–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.Y.; Craig, M.T.; Choat, J.H.; van Herwerden, L. The historical biogeography of groupers: Clade diversification patterns and processes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 100, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Ding, S. Epinephelus rankini Whitley, 1945, a valid species of grouper (Teleostei, Perciformes, Epinephelidae) from Western Australia and southeast Indonesia. Biodivers. Data J. 2022, 10, e90472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frable, B.W.; Tucker, S.J.; Walker, H. A new species of grouper, Epinephelus craigi (Perciformes: Epinephelidae), from the South China Sea. J. Ichthyol. Res. 2019, 66, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase, version (07/2023). Available online: https://www.fishbase.org (accessed on 7 July 2023).
- Pierce, S.E.; Angielczyk, K.D.; Rayfield, E.J. Morphospace occupation in thalattosuchian crocodylomorphs: Skull shape variation, species delineation and temporal patterns. Palaeontology 2009, 52, 1057–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, M.; Yamamura, K.-I. Cranial bone morphometric study among mouse strains. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjidakis, D.J.; Androulakis, I.I. Bone remodeling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1092, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano-Lopes, J.; Canhao, H.; Fonseca, J.E.J.A.R.P. Osteoblasts and bone formation. Acta Reum. Port. 2007, 32, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.H.; Chen, F.M.; Li, A. Research progress on the hedgehog signalling pathway in regulating bone formation and homeostasis. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- True, J.R.; Carroll, S.B. Gene co-option in physiological and morphological evolution. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002, 18, 53–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenebeck, J.J.; Hutchinson, S.A.; Byers, A.; Beale, H.C.; Carrington, B.; Faden, D.L.; Rimbault, M.; Decker, B.; Kidd, J.M.; Sood, R.; et al. Variation of BMP3 contributes to dog breed skull diversity. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencer, E.S.; Warren, W.C.; Harrison, R.; McCune, A.R. The Cyprinodon variegatus genome reveals gene expression changes underlying differences in skull morphology among closely related species. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, H.; Sabrautzki, S.; Przemeck, G.K.; Leuchtenberger, S.; Lorenz-Depiereux, B.; Becker, L.; Rathkolb, B.; Horsch, M.; Garrett, L.; Ostereicher, M.A.; et al. The First Scube3 Mutant Mouse Line with Pleiotropic Phenotypic Alterations. G3 2016, 6, 4035–4046. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, R.B.; Hu, Y.; Albertson, R.C.; Kocher, T.D. Craniofacial divergence and ongoing adaptation via the hedgehog pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13194–13199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.P.; Conlon, R.A.; Rossant, J. Expression of the fibroblast growth factor receptor FGFR-1/flg during gastrulation and segmentation in the mouse embryo. Dev. Biol. 1992, 152, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, T.F.; Yang, Y. Wnt and hedgehog signaling pathways in bone development. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2008, 90, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Andre, P.; Ye, L.; Yang, Y.Z. The Hedgehog signalling pathway in bone formation. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2015, 7, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abzhanov, A.; Rodda, S.J.; McMahon, A.P.; Tabin, C.J. Regulation of skeletogenic differentiation in cranial dermal bone. Development 2007, 134, 3133–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Borger, C.; More, H.; Sturmbauer, C. The Role of Alternative Splicing and Differential Gene Expression in Cichlid Adaptive Radiation. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 2764–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, K.J.; Concannon, M.; Navon, D.; Wang, J.; Ea, I.; Groveas, K.; Campbell, C.; Albertson, R.C. Foraging environment determines the genetic architecture and evolutionary potential of trophic morphology in cichlid fishes. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 6012–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Rabie, A.; Hägg, U. Indian hedgehog: A mechanotransduction mediator in condylar cartilage. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, S.W. Formation of the Vertebrate Face: Epigenetic and Functional Influences. Am. Zool. 1993, 33, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowlan, N.C.; Prendergast, P.J.; Murphy, P. Identification of Mechanosensitive Genes during Embryonic Bone Formation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q. Indian hedgehog is an essential component of mechanotransduction complex to stimulate chondrocyte proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35290–35296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Jia, R.; Yu, H.; Liang, Y.; Chen, C.; Pang, Z. Developmental and Morphological Characteristics of Embryo, Larval, Juvenile, and Young Fish, Cromileptes altivelis. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2014, 35, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, D.J.; Fei, D.L.; Riobo, N.A. The Hedgehog signal transduction network. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, re6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q. The Role and Mechanism of Hedgehog Pathway in Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Bone Development and Bone Tumor Formation. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
| Developmental Stage | Total Length |
|---|---|
| S0 | 3.0–4.0 cm |
| S1 | 5.0–6.0 cm |
| S2 | 7.0–8.0 cm |
| S3 | 9.0–10 cm |
| Primers | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon Seizes (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| Ihhb-F | GGGTAGAGGCTATGGCAAGAG | 183 |
| Ihhb-R | TTGAAGATGATGTCGGGGTTGTAG | |
| Ptch1-F | CGCTCCACCTACAACATCTCAC | 118 |
| Ptch1-R | TTCTATCTTTCCACCGCCACT | |
| Gli2-F | AGAACGGTAACTCCACTTATCCAC | 198 |
| Gli2-R | TGTGCTGCTCTGAAATCATCACC | |
| Gli2a-F | CGAAGCGACGCACCTCCTA | 94 |
| Gli2a-R | CCTCAATCTTGCCATCCACA | |
| EF-1α-F EF-1α-R | CAACTTCAACGCCCAGGTCA CTCATGTCACGCACAGCAAAA | 276 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, X.; Deng, S.; Liu, Q.; Wu, L.; Zhuang, X.; Ding, S. Important Role of the Ihh Signaling Pathway in Initiating Early Cranial Remodeling and Morphological Specialization in Cromileptes altivelis. Animals 2023, 13, 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243840
Cao X, Deng S, Liu Q, Wu L, Zhuang X, Ding S. Important Role of the Ihh Signaling Pathway in Initiating Early Cranial Remodeling and Morphological Specialization in Cromileptes altivelis. Animals. 2023; 13(24):3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243840
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Xiaoying, Shunyun Deng, Quanyin Liu, Lisheng Wu, Xuan Zhuang, and Shaoxiong Ding. 2023. "Important Role of the Ihh Signaling Pathway in Initiating Early Cranial Remodeling and Morphological Specialization in Cromileptes altivelis" Animals 13, no. 24: 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243840
APA StyleCao, X., Deng, S., Liu, Q., Wu, L., Zhuang, X., & Ding, S. (2023). Important Role of the Ihh Signaling Pathway in Initiating Early Cranial Remodeling and Morphological Specialization in Cromileptes altivelis. Animals, 13(24), 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243840





