Population Genetic Divergence among Worldwide Gene Pools of the Mediterranean Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Molecular Analyses
2.3. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity
3.2. Genetic Differentiation
4. Discussion
4.1. Genetic Diversity of M. galloprovincialis
4.2. Genetic Differentiation between Species
4.3. Genetic Differentiation within M. galloprovincialis
4.4. Patterns of Divergence in Parapatry
4.5. The Pacific Northeast
4.6. The Pacific Southeast
4.7. Australia and Japan
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hilbish, T.J.; Mullinax, A.; Dolven, S.I.; Meyer, A.; Koehn, R.K.; Rawson, P.D. Origin of the antitropical distribution pattern in marine mussels (Mytilus spp.): Routes and timing of transequatorial migration. Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehn, R.K. The genetics and taxonomy of species in the genus Mytilus. Aquaculture 1991, 94, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.H.; Seed, R.; Koehn, R.K. Allozymes and morphometric characters of three species of Mytilus in the northern and southern hemispheres. Mar. Biol. 1991, 111, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, E.M.; Doherty, S.; Howley, N. Genetic characterization of hybrid mussel (Mytilus) populations on Irish coasts. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. 2008, 88, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, E.M. Systematic and geographic distribution of Mytilus. In The mussel Mytilus: Ecology, Physiology, Genetics and Culture; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 25, pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ab Rahim, E.S.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Ingram, B.; Riginos, C.; Weston, K.J.; Sherman, C.D.H. Species composition and hybridization of mussel species (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) in Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 67, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbawicka, M.; Trucco, M.I.; Wenne, R. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in native South American Atlantic coast populations of smooth shelled mussels: Hybridization with invasive European Mytilus galloprovincialis. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belz, C.E.; Simone, L.; Silveira Júnior, N.; Baggio, R.; Gernet, M.; Birckolz, C. First record of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia, Mytilidae) in Brazil. Pap. Zool. 2020, 60, e20206007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.H.; Koehn, R.K. The mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis and M. trossulus on the Pacific coast of North America. Mar. Biol. 1988, 99, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarifeño, E.; Galleguillos, R.; Llanos-Rivera, A.; Arriagada, D.; Ferrada, S.; Canales-Aguirre, C.B.; Seguel, M. Erroneous identification of the mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck 1819) as the specie, Mytilus chilensis (Hupe 1854) in the Bay of Concepcion, Chile. Gayana Concepc. 2012, 76, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Morton, B.S. The introduction of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis into Hong Kong. Malacol. Rev. 1985, 18, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Hockey, P.A.R.; Van Erkom Schurink, C. The invasive biology of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis on the Southern African coast. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 1992, 48, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, R. Factors influencing shell shape in the mussel Mytilus edulis. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK 1968, 48, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.P.A. Hybridization in the sea. Adv. Mar. Biol. 1997, 31, 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Popovic, I.; Riginos, C. Comparative genomics reveals divergent thermal selection in warm- and cold-tolerant marine mussels. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larraín, M.A.; Díaz, N.F.; Lamas, C.; Uribe, C.; Araneda, C. Traceability of mussel (Mytilus chilensis) in southern Chile using microsatellite molecular markers and assignment algorithms, Exploratory survey. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Puente, B.; Guiñez, R.; Pita, A.; Miñambres, M.; Presa, P. Genotype by environment interaction for shell length in Mytilus galloprovincialis. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2020, 522, 151252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Río-Lavín, A.; Díaz-Arce, N.; Larraín, M.A.; Araneda, C.; Rodríguez-Ezpeleta, N.; Jiménez, E.; Pardo, M.A. Population structure and geographic origin assignment of Mytilus galloprovincialis mussels using SNPs. Aquaculture 2022, 55, 737836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.P.A.; Zbawicka, M.; Westfall, K.M.; Wenne, R. Invasive blue mussels threaten regional scale genetic diversity in mainland and remote offshore locations: The need for baseline data and enhanced protection in the Southern Ocean. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3182–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, I.; Bierne, N.; Gaiti, F.; Tanurdžić, M.; Riginos, C. Pre-introduction introgression contributes to parallel differentiation and contrasting hybridization outcomes between invasive and native marine mussels. J. Evol. Biol. 2021, 34, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.H.; Yoon, M.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, I.H.; Cho, I.Y.; An, H.S. Genetic analysis and population genetic structure of hard-shelled mussel, Mytilus coruscus Gould 1861 (Mytiloida: Mytilidae) from the coasts of South Korea based on mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase (COI) gene sequences. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouagajjou, Y.; Presa, P. The connectivity of Mytilus galloprovincialis in northern Morocco: A gene flow crossroads between continents. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 152, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbawicka, M.; Gardner, J.P.A.; Wenne, R. Cryptic diversity in smooth-shelled mussels on Southern Ocean islands: Connectivity, hybridisation and a marine invasion. Front. Zool. 2019, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalek, K.; Ventura, A.; Sanders, T. Mytilus hybridization and impact on aquaculture: A minireview. Mar. Genom. 2016, 27, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pita, A.; Casey, J.; Hawkins, S.J.; Villarreal, M.R.; Gutiérrez, M.; Cabral, H.N.; Carocci, F.; Abaunza, P.; Pascual, S.; Presa, P. Conceptual and practical advances in fish stock delineation. Fish. Res. 2016, 173, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz, A.P.; Presa, P. Regional patterns of microsatellite variation in Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Iberian Peninsula. Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouagajjou, Y.; Aghzar, A.; Miñambres, M.; Presa, P.; Perez, M. Differential gene flow between populations of M. galloprovincialis distributed along Iberian and North African coasts. Thalassas 2010, 25, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Lourenço, C.R.; Nicastro, K.R.; Serraao, E.A.; Castilho, R.; Zardi, G.I. Behind the mask: Cryptic genetic diversity of Mytilus galloprovincialis along southern European and northern African shores. J. Molluscan Stud. 2015, 81, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abada-Boudjema, Y.; Dauvin, J. Recruitment and life span of two natural mussel populations Perna perna (Linnaeus) and Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck) from the Algerian coast. J. Molluscan Stud. 1995, 61, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterno, M.; Bat, L.; Souissi, J.B.; Boscari, E.; Chassanite, A.; Congiu, L.; Guarnieri, G.; Kruschel, C.; Mačić, V.; Marino, I.A.M.; et al. A genome-wide approach to the phylogeography of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in the Adriatic and the Black Seas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz, A.P.; Presa, P. The genetic diversity pattern of Mytilus galloprovincialis in Galician Rias (NW Iberian estuaries). Aquaculture 2009, 287, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeb, C.A.; Avise, J.C. A genetic discontinuity in a continuously distributed species: Mitochondrial DNA in the American oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Genetics 1990, 124, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedgecock, D. Is gene flow from pelagic larval dispersal important in the adaptation and evolution of marine invertebrates? Bull. Mar. Sci. 1986, 39, 432–443. [Google Scholar]
- Bownes, S.J.; McQuaid, C.D. Will the invasive mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck replace the indigenous Perna perna L. on the south coast of South Africa? J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 338, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braby, C.E.; Somero, G.N. Ecological gradients and relative abundance of native (Mytilus trossulus) and invasive (Mytilus galloprovincialis) blue mussels in the California hybrid zone. Mar. Biol. 2006, 148, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, D.M.; Zbawicka, M.; Wenne, R.; Pocwierz-Kotus, A.; Molina, J.R.A.; Alves, L.P.; Rocha, R.M. Ecology and genetics of Mytilus galloprovincialis: A threat to bivalve aquaculture in southern Brazil. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, J.C.; Neill, P.E. Marine bioinvasions in the Southeastern Pacific: Status, ecology, economic impacts, conservation and management. In Biological Invasions of Marine Ecosystems: Patterns, Effects, and Management; Ecological Studies, 204, Rilov, G., Crooks, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species a Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database; The Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG): Auckland, New Zealand, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Saarman, N.P.; Kober, K.M.; Simison, W.B.; Pogson, G.H. Sequence-based analysis of thermal adaptation and protein energy landscapes in an invasive blue mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 2739–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, T.; David, A.A. Global connectivity patterns of the notoriously invasive mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. using archived CO1 sequence data. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Han, G.D.; Dong, Y.W. Rapid climate-driven evolution of the invasive species Mytilus galloprovincialis over the past century. Anthr. Coasts 2020, 3, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presa, P.; Guyomard, R. Conservation of microsatellites in three species of salmonids. J. Fish Biol. 1996, 49, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presa, P.; Pérez, M.; Diz, A.P. Polymorphic microsatellite markers for blue mussels (Mytilus spp.). Conserv. Genet. 2002, 3, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouagajjou, Y.; Presa, P.; Astorga, M.; Perez, M. Microsatellites of M. chilensis: A genomic print of its taxonomic status within Mytilus sp. J. Shellfish Res. 2011, 30, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; Presa, P. FENOSALT: Un método sintético para la extracción de ADN de peces y moluscos. In Métodos y Técnicas en Investigación Marina; García, J.M., Olabarría, C., Pérez, S., Rolán-Álvarez, E., Rosón, G., Eds.; TECNOS: Madrid, Spain, 2011; pp. 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, S. The Interpretation of population structure by F-statistics with special regard to systems of mating. Evolution 1965, 19, 395–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudet, J. Fstat (vers. 2.9.3): A computer program to calculate F-statistics. J. Hered. 1995, 86, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, F. genepop’007: A complete re-implementation of the genepop software for Windows and Linux. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete date via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1977, 39, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chapuis, M.P.; Estoup, A. Microsatellite null alleles and estimation of population differentiation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryman, N.; Palms, S. POWSIM: A computer program for assessing statistical power when testing for genetic differentiation. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 6, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L. Gst and its relatives do not measure differentiation. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 4015–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, G.; Jueterbock, A.; Kraemer, P.; Deppermann, J.; Harmand, P. Calculations of population differentiation based on Gst and D: Forget Gst but not all of statistics! Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 3845–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite v. 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corander, J.; Marttinen, P.; Sirén, J.; Tang, J. Enhanced Bayesian modelling in BAPS software for learning genetic structures of populations. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corander, J.; Sirén, J.; Arjas, E. Bayesian spatial modelling of genetic population structure. Comput. Stat. 2008, 23, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcamo, C.; Comesaña, A.S.; Winkler, F.M.; Sanjuan, A. Allozyme identification of mussels (Bivalvia: Mytilus) on the Pacific coast of South America. J. Shellfish Res. 2005, 24, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, E.M.; Wilkins, N.P. Ecological genetics of the mussels Mytilus edulis and M. galloprovincialis on the Irish coasts. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1981, 4, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, M.; Vaanto, R.L.; Thomas, F.; Rousset, F.; de Meeus, T.; Renaud, F. Heterozygote deficiency in the mussel Mytilus edulis species complex revisited. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 156, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ríos, C.; Sanz, S.; Saavedra, C.; Peña, J.B. Allozyme variation in populations of scallops, Pecten jacobaeus (L.) and P. maximus (L.) (Bivalvia: Pectinidae), across the Almería-Oran front. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 267, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouros, E.; Foltz, D.W. Possible explanations of heterozygote deficiency in bivalve molluscs. Malacologia 1984, 25, 583–591. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, G. Interpopulation variation in blue mussels, Mytilus edulis L., over short distances. Sarsia 2001, 86, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P. Modeling the genetic basis of heterosis: Tests of alternative hypotheses. Evolution 1997, 51, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos, C.; Canales, J.; Peña, J.B. Genotype dependent spawning: Evidence from a wild population of Pecten jacobaeus (L.) (Bivalvia: Pectinidae). J. Shellfish Res. 1996, 15, 645–651. [Google Scholar]
- Pompanon, F.; Bonin, A.; Bellemain, E.; Taberlet, P. Genotyping errors: Causes, consequences and solutions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.C.D.; Haydon, D.T. Maximum likelihood estimation of allelic dropout and false allele error rates from microsatellite genotypes in the absence of reference data. Genetics 2007, 175, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedgecock, D.; Li, G.; Hubert, S.; Bucklin, K.; Ribes, V. Widespread null alleles and poor cross-species amplification of microsatellite DNA loci cloned from the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, J. Effects of microsatellite null alleles on assignment testing. J. Hered. 2008, 99, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väinölä, R.; Hvilsom, M.M. Genetic divergence and a hybrid zone between Baltic and North Sea Mytilus populations. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1991, 43, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeij, G.J. Anatomy of an invasion: The trans-Arctic interchange. Paleobiology 1991, 17, 281–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, P.D.; Hilbish, T.J. Distribution of male and female mtDNA lineages in populations of blue mussels, Mytilus trossulus and M. galloprovincialis, along the Pacific coast of North America. Mar. Biol. 1995, 124, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguel, M. Evaluation of the taxonomic status of Mytilus chilensis using the mitochondrial gene citochrome C oxidase subunit I (COI). In Proceedings of the XXXI Congreso de Ciencias del Mar, Viña del Mar, Chile, 16–20 August 2011; p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- Śmietanka, B.; Burzyński, A. Disruption of doubly uniparental inheritance of mitochondrial DNA associated with hybridization area of European Mytilus edulis and Mytilus trossulus in Norway. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krapivka, S.; Toro, J.E.; Alcapan, A.C.; Astorga, M.; Presa, P.; Pérez, M.; Guin, R. Shell-shape variation along the latitudinal range of the Chilean blue mussel Mytilus chilensis (Hupe, 1854). Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Puente, B.; Pita, A.; Uribe, J.; Cuéllar Pinzón, J.; Guiñez, R.; Presa, P. A biogeography-based management for Mytilus chilensis: The genetic hodgepodge of Los Lagos versus the pristine hybrid zone of the Magellanic ecotone. Aquat. Conserv. 2020, 30, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daguin, C.; Borsa, P. Genetic Relationships of Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck Populations Xorldwide: Evidence from Nuclear-DNA Markers; Crame, A., Harper, E., Taylor, J., Eds.; Geological Society of London Special Publications: London, UK, 2000; Volume 177, pp. 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarifeño, E.; Galleguillos, R.; Gardner, J.; Lépez, I.; Arriagada, D.; Llanos, A.; Astete, S.; Ferrada, S.; Rodríguez, S.; Gacitúa, S. Presencia del mejillón, Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lmk) (Bivalvia, Mollusca) en las costas de la región del Biobío, Chile. In Proceedings of the XXV Congreso de Ciencias del Mar-XI Congreso Latino Americano de Ciencias del Mar, Viña del Mar, Chile, 16–20 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Galleguillos, R.; Tarifeno, E.; Ferrada, S. Las especies de mitílidos en las costas de Chile: Un análisis con marcadores moleculares. Proc. Foro Acuic. Rec. Mar. Rías Gal. 2009, 11, 505–506. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjuan, A.; Zapata, C.; Alvarez, G. Genetic differentiation in Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. Throughout the world. Ophelia 1997, 47, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintoré, J.; La Violette, P.E.; Blade, I.; Cruzado, A. A study of an intense density front in the Eastern Alboran Sea: The Almeria-Oran front. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1988, 18, 1384–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuan, A.; Zapata, C.; Alvarez, G. Mytilus galloprovincialis and M. edulis on the coasts of the Iberian Peninsula. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 113, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuan, A.; Comesaña, S.; de Carlos, A. Macrogeographic differentiation by mtDNA restriction site analysis in the SW European Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 198, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaziri, H.; Benazzou, T. Différenciation allozymique multilocus des populations de moule Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. Des côtes marocaines. C R Biol. 2002, 325, 1175–1183. (In French) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, R. Systematics, evolution and distribution of mussels belonging to the genus Mytilus: An overview. Am. Malacol. Bull. 1992, 9, 123–137. [Google Scholar]
- Geller, J.B.; Carlton, J.T.; Powers, D.A. PCR-based detection of mtDNA haplotypes of invading and native mussels on the northeastern Pacific coast: Latitudinal pattern of invasion. Mar. Biol. 1994, 119, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.T. The scale and ecological consequences of biological invasions in the world’s oceans. In Invasive Species and Biodiversity Management; Sandlund, O.T., Schei, P.J., Viken, A., Eds.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonham, M. Mini-review: Distribution of the Mediterranean mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia: Mytilidae), and hybrids in the northeast Pacific. J. Shellfish Res. 2004, 23, 535–543. [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood, B.L.; Sanders, J.G.; Somero, G.N. Transcriptomic responses to heat stress in invasive and native blue mussels (genus Mytilus): Molecular correlates of invasive success. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 213, 3548–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomanek, L.; Zuzow, M.J. The proteomic response of the mussel congeners Mytilus galloprovincialis and M. trossulus to acute heat stress: Implications for thermal tolerance and metabolic costs of thermal stress. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3559–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, B.L.; Somero, G.N. Invasive and native blue mussels (genus Mytilus) on the California coast: The role of physiology in a biological invasion. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 400, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraín, M.A.; Zbawicka, M.; Araneda, C.; Gardner, J.P.A.; Wenne, R. Native and invasive taxa on the Pacific coast of South America: Impacts on aquaculture, traceability and biodiversity of blue mussels (Mytilus spp.). Evol. Appl. 2018, 11, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.S.; Bilodeau, A.L.; Gilg, M.R.; Hilbish, T.J. Routes of introduction of the Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) to Puget Sound and Hood Canal. J. Shellfish Res. 2002, 21, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Rawson, P.D.; Agrawal, V.; Hilbish, T.J. Hybridization between the blue mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis and M. trossulus along the Pacific coast of North America: Evidence for limited introgression. Mar. Biol. 1999, 134, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawson, P.D.; Hilbish, T.J. Evolutionary relationships among the male and female mtDNA lineages in the Mytilus edulis species complex. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1995, 12, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gay, C. Historia Fisica y Politica de Chile Segun Documentos Adquiridos en Esta Republica Durante doce Anos de Residencia en Ella y Publicada Bajo los Auspicios del Supremo Gobierno; Gay, C., Johnston, I.M., Eds.; Museo de Historia Natural de Santiago de Chile: Santiago, Chile, 1854; Volume 8, 499p, Missouri Botanical Garden, Peter H. Raven Library; Available online: https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/16153144#page/4/mode/1up (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Astorga, M.P.; Cardenas, L.; Vargas, J. Phylogenetic approaches to delimit genetic lineages of the Mytilus complex of South America: How many species are there? J. Shellfish Res. 2015, 34, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L. Informe sobre una prospección arqueológica en Magallanes. An. Inst. De La Patagon. 1976, 7, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sarver, S.K.; Foltz, D.W. Genetic population structure of a species’ complex of blue mussels (Mytilus spp.). Mar. Biol. 1993, 117, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbi, S.R.; Kessing, B.D. Population biology of the Trans-Arctic exchange: mtDNA sequence similarity between Pacific and Atlantic Sea urchins. Evolution 1991, 45, 1790–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, T.A. Description of new marine shells, from Upper California. Collected by Thomas Nuttall, Esquire. J. Acad. Nat. Sci. 1837, 7, 227–268. [Google Scholar]
- Branch, G.M.; Steffani, C.N. Can we predict the effects of alien species? A case-history of the invasion of South Africa by Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 300, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrison, A.R.; Binns, M.A. Amidden excavation—Royal Tamanian Botanical Gardens, Hobart. Royal Society of Tasmania. Pap. Proc. 1984, 118, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.-S. Origin and dispersal of Mytilus edulis in Japan deduced from its present status of copepod parasitism. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1980, 25, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilkins, N.P.; Fujino, K.; Gosling, E.M. The Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. in Japan. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1983, 20, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, K.; Bierne, N.; Borsa, P.; Chenuil, A.; Féral, J. Pleistocene separation of mitochondrial lineages of Mytilus spp. mussels from Northern and Southern Hemispheres and strong genetic differentiation among southern populations. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 49, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, K.M.; Gardner, J.P.A. Genetic diversity of Southern hemisphere blue mussels (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) and the identification of non-indigenous taxa. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2010, 101, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, K.M.; Gardner, J.P.A. Interlineage Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. 1819 hybridization yields inconsistent genetic outcomes in the Southern hemisphere. Biol. Invasions 2013, 15, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, K.M.; Wimberger, P.H.; Gardner, J.P.A. An RFLP assay to determine if Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. (Mytilidae; Bivalvia) is of Northern or Southern Hemisphere origin. Mol. Ecol. Res. 2010, 10, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, I.; Matias, A.M.A.; Bierne, N.; Riginos, C. Twin introductions by independent invader mussel lineages are both associated with recent admixture with a native congener in Australia. Evol. Appl. 2019, 13, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbawicka, M.; Wenne, R.; Dias, J.; Gardner, J. Combined threats to native smooth-shelled mussels (genus Mytilus) in Australia: Bioinvasions and hybridization. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2021, 4, 1194–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
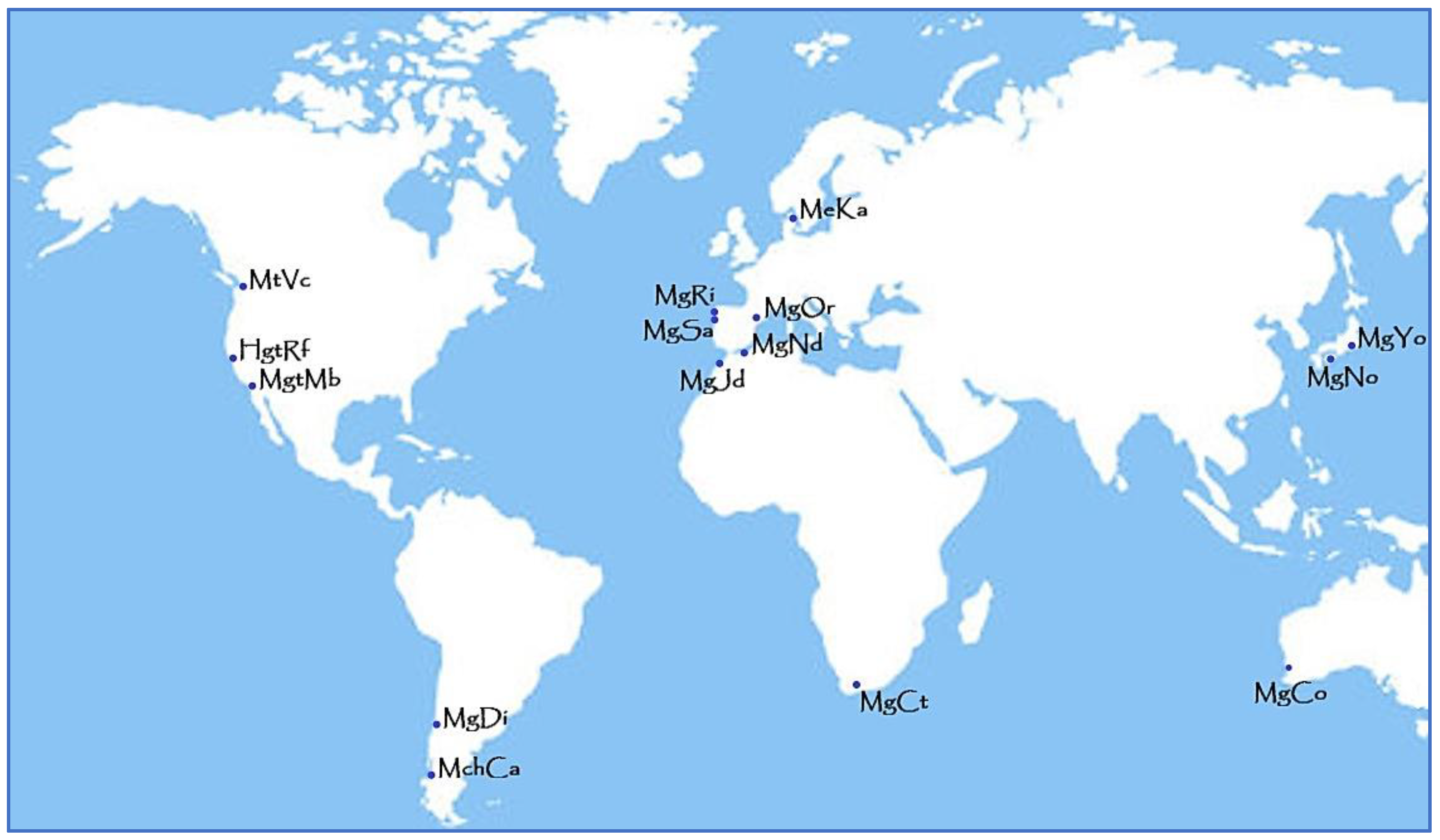
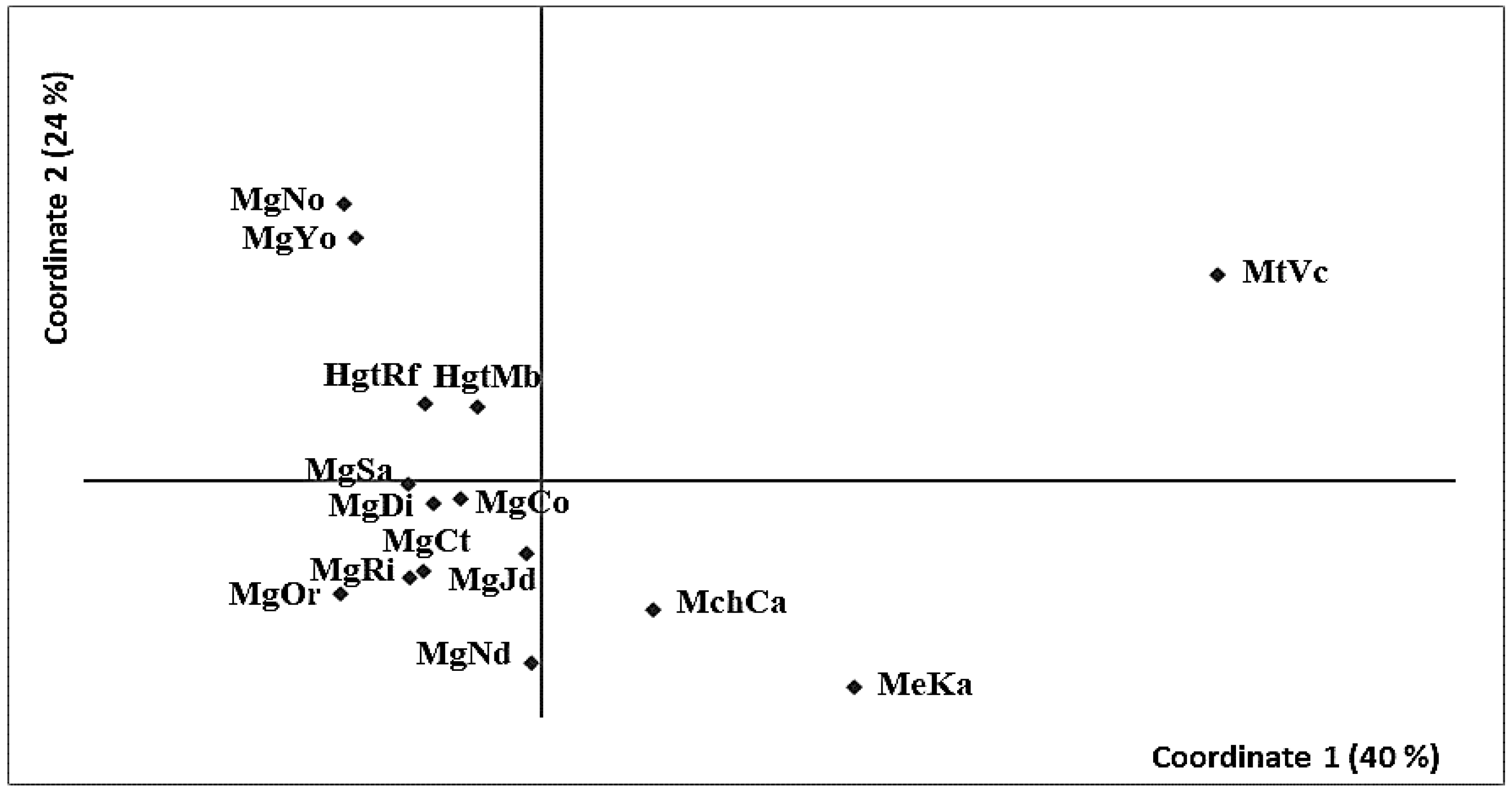
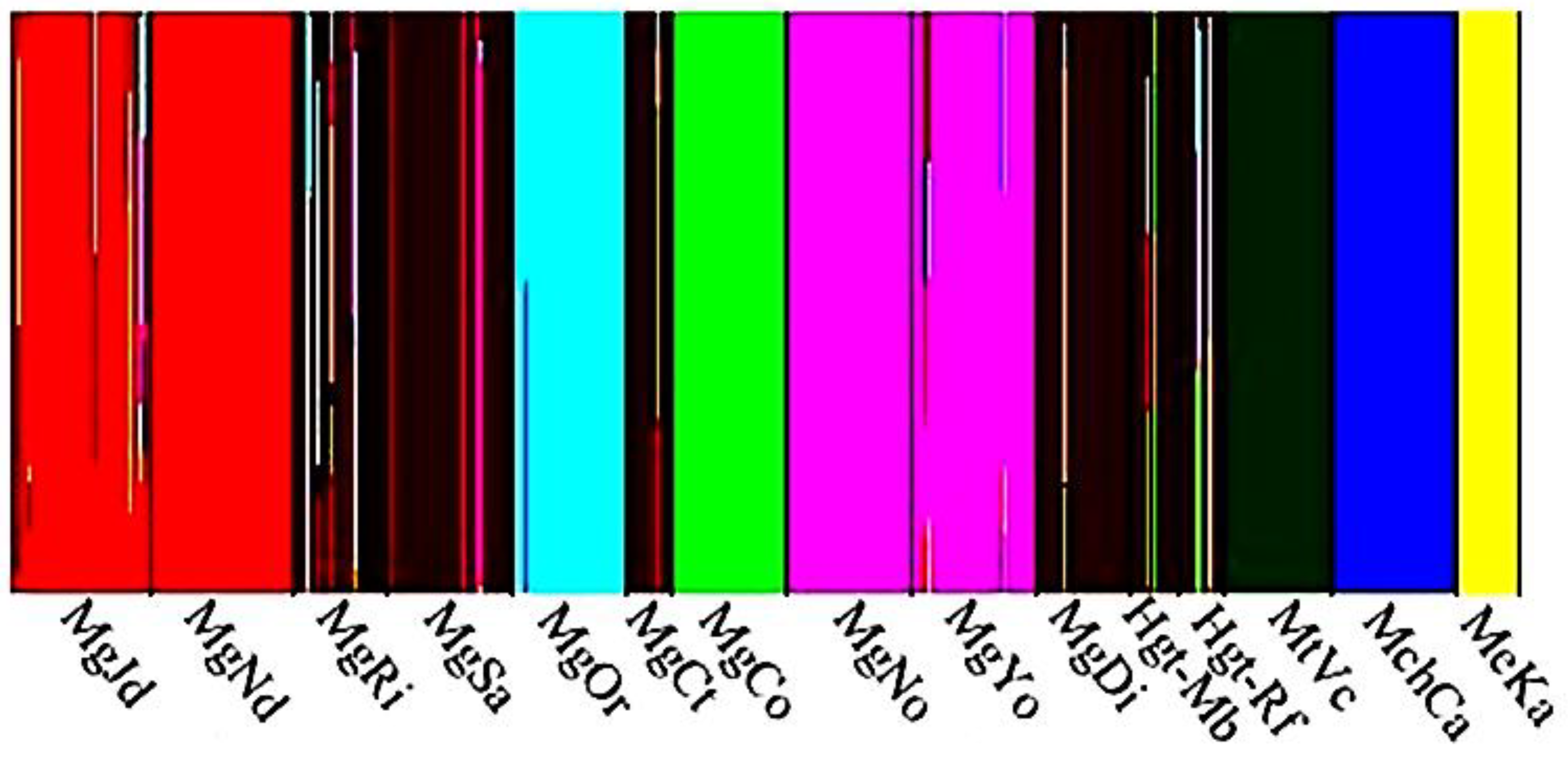
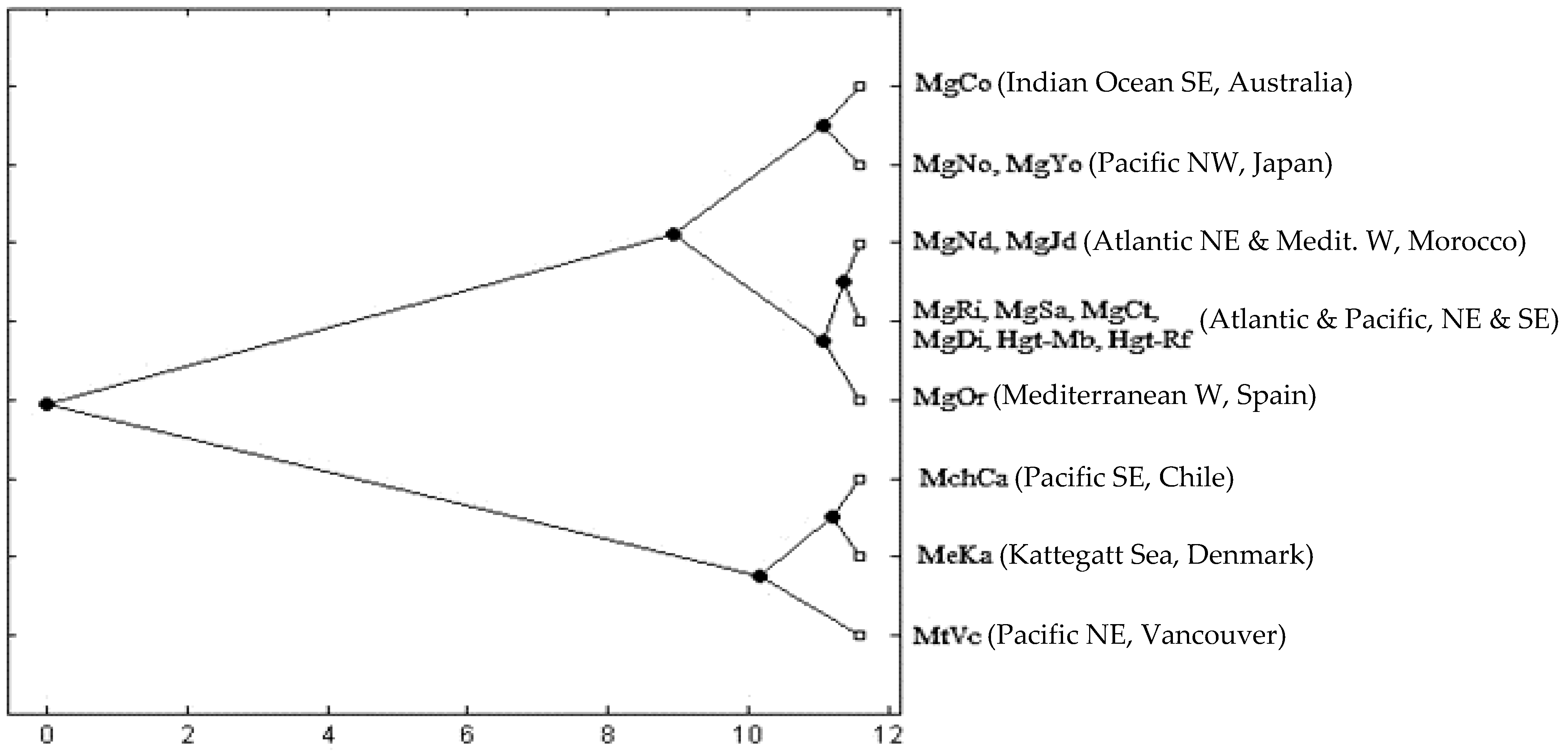
| Species | Ocean | Location | Code | Size | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. galloprovincialis | Atlantic Northeast (Spain) | Ribeira | MgRi | 40 | 42°32′ N/08°59′ W |
| Sanxenxo | MgSa | 40 | 42°23′ N/08°48′ W | ||
| Mediterranean West (Spain) | Oropesa | MgOr | 37 | 40°08′ N/00°15′ E | |
| Alboran Sea (Morocco) Atlantic Northeast (Morocco) | Nador | MgNd | 45 | 35°39’ N/03°03’ W | |
| El Jadida | MgJd | 45 | 32°39′ N/08°51′ W | ||
| Atlantic Southeast (South Africa) | Cape Town | MgCt | 14 | 33°54′ S/18°27′ E | |
| Pacific Southeast (Chile) | Dichato | MgDi | 30 | 36°32′ S/72°47′ W | |
| Pacific Northwest (Japan) | Nojima | MgNo | 40 | 32°59′ N/135°21′ E | |
| Yokohama | MgYo | 40 | 35°25′ N/139°39′ E | ||
| Indian Southeast (Australia) | Cockburn Sound | MgCo | 37 | 32°10′ S/115°43′ E | |
| M. galloprovincialis–M. trossulus | Pacific Northeast (USA) | California | HgtMb | 15 | 35°21′ N/120°51′ W |
| HgtRf | 15 | 37°57′ N/122°29′ W | |||
| M. chilensis | Pacific Southeast (Chile) | Caicaen | MchCa | 40 | 41°47′ S/73°10′ W |
| M. edulis | Atlantic Northeast (Denmark) | Kattegat | MeKa | 20 | 56°08′ N/10°14′ E |
| M. trossulus | Pacific Northeast (Canada) | Vancouver | MtVc | 34 | 49°16′ N/123°10′ W |
| Source of Variation | d.f. | Sum of Squares | Variance Components | Percentage of Variation | Fixation Indexes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. galloprovincialis | |||||
| Among samples | 11 | 216.636 | 0.259 | 9.64 | FST = 0.096 * |
| Among individuals within samples | 376 | 1153.357 | 0.630 | 23.37 | FIS = 0.258 * |
| Within individuals | 388 | 701.000 | 0.630 | 66.99 | FIT = 0.330 * |
| Total | 775 | 2070.994 | 2.696 | ||
| M. galloprovincialis (regional differentiation) | |||||
| Among groups | 5 | 141.122 | 0.125 | 4.61 | FCT = 0.046 * |
| Among samples within groups | 6 | 75.514 | 0.151 | 5.57 | FSC = 0.058 * |
| Among individuals within samples | 376 | 1153.357 | 0.630 | 23.23 | FIS = 0.258 * |
| Within individuals | 388 | 701.000 | 1.806 | 66.59 | FIT = 0.334 * |
| M. galloprovincialis (North vs. South Hemispheres) | |||||
| Among groups | 1 | 24.11 | 0.019 | 0.70 | FCT = 0.007 ns |
| Among samples within groups | 10 | 192.526 | 0.252 | 9.34 | FSC = 0.094 * |
| Among individuals within samples | 376 | 1153.357 | 0.630 | 23.27 | FIS = 0.258 * |
| Within individuals | 388 | 701.000 | 1.806 | 66.69 | FIT = 0.333 * |
| M. galloprovincialis vs. (M. chilensis, M. edulis and M. trossulus) | |||||
| Among groups | 1 | 83.690 | 0.197 | 6.82 | FCT = 0.068 * |
| Among samples within groups | 13 | 293.075 | 0.307 | 10.64 | FSC = 0.114 * |
| Among individuals within samples | 467 | 1414.498 | 0.642 | 22.22 | FIS = 0.269 * |
| Within individuals | 482 | 840.500 | 1.743 | 60.32 | FIT = 0.396 * |
| M. galloprovincialis vs. M. chilensis | |||||
| Among groups | 1 | 60.988 | 0.150 | 5.25 | FCT = 0.052 * |
| Among samples within groups | 12 | 216.636 | 0.228 | 7.98 | FSC = 0.084 * |
| Among individuals within samples | 454 | 1426.857 | 0.659 | 23.02 | FIS = 0.265 * |
| Within individuals | 468 | 854.000 | 1.824 | 63.75 | FIT = 0.362 * |
| M. galloprovincialis vs. M. edulis | |||||
| Among groups | 1 | 52.292 | 0.267 | 9.19 | FCT = 0.091 * |
| Among samples within groups | 12 | 216.636 | 0.242 | 8.33 | FSC = 0.091 * |
| Among individuals within samples | 414 | 1250.757 | 0.618 | 21.21 | FIS = 0.257 * |
| Within individuals | 428 | 764.000 | 1.785 | 61.27 | FIT = 0.387 * |
| M. galloprovincialis vs. M. trossulus | |||||
| Among groups | 1 | 195.329 | 0.761 | 23.01 | FCT = 0.230 * |
| Among samples within groups | 12 | 216.636 | 0.234 | 7.09 | FSC = 0.092 * |
| Among individuals within samples | 442 | 1304.740 | 0.638 | 19.28 | FIS = 0.275 * |
| Within individuals | 456 | 764.000 | 1.675 | 50.62 | FIT = 0.493 * |
| Total variance | |||||
| Among samples | 14 | 376.765 | 0.374 | 13.57 | FST = 0.135 * |
| Within samples | 467 | 1414.498 | 0.642 | 23.27 | FIS = 0.269 * |
| Within individuals | 482 | 840.500 | 1.743 | 63.16 | FIT = 0.368 * |
| Total | 963 | 2631.763 | 2.761 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouagajjou, Y.; Aghzar, A.; Presa, P. Population Genetic Divergence among Worldwide Gene Pools of the Mediterranean Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Animals 2023, 13, 3754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243754
Ouagajjou Y, Aghzar A, Presa P. Population Genetic Divergence among Worldwide Gene Pools of the Mediterranean Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Animals. 2023; 13(24):3754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243754
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuagajjou, Yassine, Adil Aghzar, and Pablo Presa. 2023. "Population Genetic Divergence among Worldwide Gene Pools of the Mediterranean Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis" Animals 13, no. 24: 3754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243754
APA StyleOuagajjou, Y., Aghzar, A., & Presa, P. (2023). Population Genetic Divergence among Worldwide Gene Pools of the Mediterranean Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Animals, 13(24), 3754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13243754






