Simple Summary
Freshwater ecosystems are important for global diversity and are subject to anthropogenic impacts. Knowing the biodiversity of these sites is important, and a revolutionary method to survey this is currently the use of environmental DNA (eDNA) released by organisms into the environment. In this study, eDNA evaluation was used to analyze water samples obtained from Lake Poma, Piana degli Albanesi Lake and Lake Scanzano. The results showed that by using eDNA, it was possible to provide the first snapshot of vertebrate biodiversity in these three lakes. Moreover, the results also showed that eDNA could be a useful tool to evaluate the ecology of the environment.
Abstract
Freshwater ecosystems play a key role in global diversity and are subject to a series of anthropic impacts, often leading to biodiversity loss. The organisms inhabiting these sites continuously release DNA into the environment through cells, excrement, gametes and/or decomposing matter; thus, evaluation of this eDNA could revolutionize the monitoring of biodiversity. In this study, environmental DNA metabarcoding was used for the first time in three Sicilian lakes: Lake Poma, Piana degli Albanesi Lake and Lake Scanzano. Results obtained provide the first snapshot of vertebrate biodiversity in these three lakes, where little is known, to provide valuable information useful for creating a baseline of knowledge regarding the biodiversity in these three lakes. Another important result was the detection of marine species, most likely due to some kind of anthropogenic contamination. Environmental DNA is a useful tool to evaluate both biodiversity and the ecological status of the environment; it has the potential to complement traditional methods, and the use of both approaches may offer a more comprehensive understanding of the ecosystem.
1. Introduction
Freshwater ecosystems are of fundamental importance as they play a key role in ensuring global diversity and provide invaluable goods and services for various forms of life on Earth [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. These environments are currently undergoing substantial change due to anthropic impact. Although little studied, they are most affected by the creation of cultivated land, which inevitably leads to the fragmentation and/or destruction of natural habitats and water pollution [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. In addition, rapid urbanization and industrialization processes (wastewater from agriculture or households) are dictating significant changes [15]. Lastly, it is important to note that changes in land use can alter the inputs of river systems and therefore affect aquatic communities by reducing the supply of terrestrial carbon and influencing the retention of organic matter, thereby leading to the decline of aquatic biodiversity [7,16,17,18,19]. For these reasons, it is extremely important to learn as much as possible about the species that live in freshwater environments, analyzing both single groups of organisms, such as fish, algae or invertebrates, and entire multitrophic communities [17,20,21]. In this context, biomonitoring is known to be fundamental for ecological assessment and is at the basis of environmental protection [22]. In recent years, the monitoring technique which uses environmental DNA has become increasingly widespread, revolutionizing traditional methods of biomonitoring, especially in freshwater ecosystems [7,23,24,25,26,27].
Some authors claim that traditional methods of identification based on morphology are often too costly in terms of time, work, disturbance of the habitat and even difficulty in finding the required taxonomic skills. For these authors, a metabarcoding technique applied to environmental samples, such as DNA released into the environment, would overcome these obstacles by providing large-scale spatial resolution and high-quality levels of biomonitoring [24,28].
This technique consists the extraction and analysis of genetic material released into the environment through feces, saliva, urine and skin cells, obtained directly from the environmental samples of water, soil, sediment or ice [29]. The method relies on the detection of a short fragment of DNA for the identification of the species and different taxa using the “DNA barcode”, a standardized DNA region [30,31]. It is a technique which has already been applied to the monitoring of aquatic communities (e.g., microbes, algae, macroinvertebrates, fish and mammals), demonstrating its ability to identify the presence of rare, invasive, extinct species or those difficult to detect using conventional methods [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. With specific reference to the Region of Sicily, knowledge of the species present in freshwater environments is currently highly fragmentary (e.g., based on information from the population) and no official scientific documents linked to the sites describe vertebrate biodiversity exhaustively. In the light of human impact and climate change today, this information is fundamental in the provision of a baseline to understand if change will occur at a biodiversity level. This study focused on three Sicilian Lakes: Lake Poma, Lake Scanzano and Lake Piana degli Albanesi, three important artificial basins which supply fresh water to the urban centers of the area [43]. Due to their naturalistic importance, in 1994, Lake Poma and, in 1999, Lake Piana degli Albanesi were recognized by the Sicilian Region as Protection Oasis and Wildlife Refuge. For the same reason, Lake Piana degli Albanesi is a protected area under the Habitats Directive (ITA020013 Lake of Piana degli Albanesi). In particular, we applied the environmental DNA technique to detect the taxa and characterize the vertebrate coenoses in these lakes, where knowledge of vertebrate biodiversity is currently scarce or largely undocumented. In particular, the aims of this research within these three wetlands were to use eDNA to have the first snapshot of vertebrate biodiversity in these three lakes, where little is known to provide valuable information useful for creating a baseline of knowledge regarding the biodiversity in these three lakes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Lakes Description
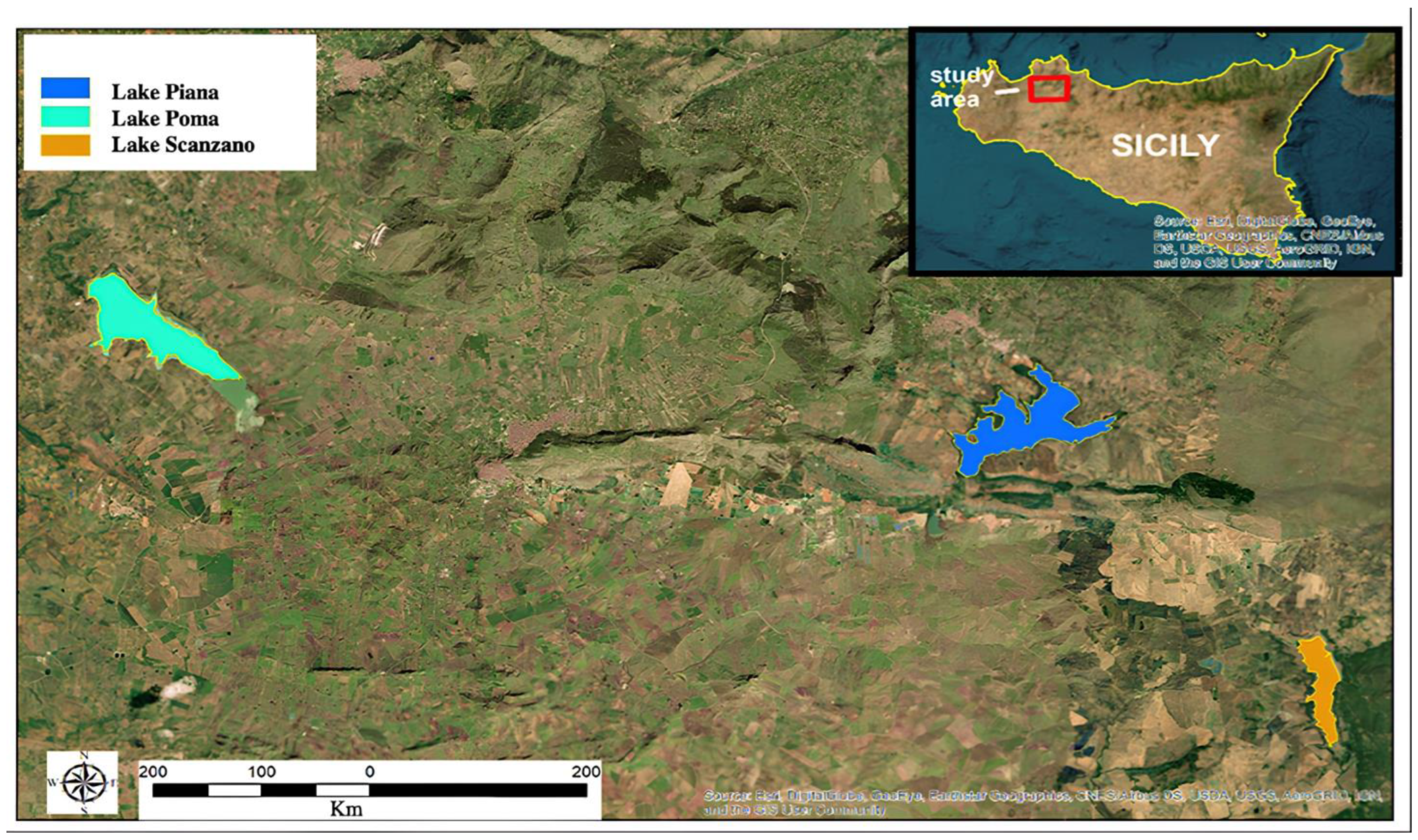
Three artificial basins located in the province of Palermo were selected for sampling: Lake Poma, Lake Scanzano and Piana degli Albanesi Lake (Figure 1). All the lakes analyzed have dams. The first is located in Partinico (37°59′17.45″ N–13°6′6.76″ E) at an altitude of 198 m above sea level (asl). It covers an area of approximately 268 hectares and has a perimeter of 11.1 km; the second is located in Piana degli Albanesi (hereinafter referred to as called Lake Piana, 37°58′20.54″ N–13°17′58.34″ E) at an altitude of 606 m asl, has an area of approximately of 289 hectares and a perimeter of 16.6 km; the third is located in Piana degli Albanesi (and only partially in the municipality of Monreale, 37°55′31.84″–13°22′7.55″ EN) at an altitude of 518 m asl, with an area of 101 hectares and a perimeter of 7.6 km. All three lakes are primarily situated in agricultural areas, with the water being used for both irrigation and to supply a number of urban centers with fresh water. The lakes are fed partly by rainwater and partly by influx from rivers [43].
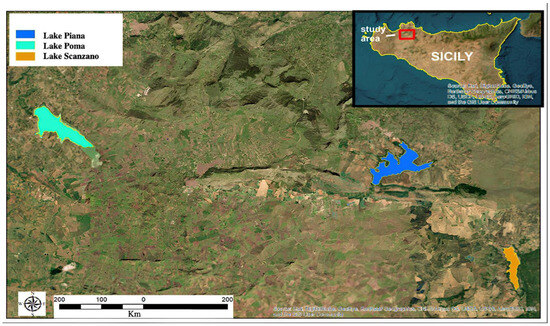
Figure 1.
Sicilian lakes in which eDNA was evaluated.
In Table 1, the different types of land use are listed (Corine Biotopes; carta HABITAT 1:10.000″ of the Regione Siciliana) together with their surface area in hectares by applying a buffer of 1 km with respect to the perimeter of each lake.

Table 1.
Different types of land use (Corine Biotopes; carta HABITAT 1:10.000″ of the Regione Siciliana) and their surface in hectares by applying a buffer of 1 km with respect to the perimeter in three Sicilian lakes.
2.2. Water Sampling and eDNA Extraction
The water samples were collected in the months of October and November 2022 from Lake Poma (UTMWGS84 333224,4206239), Lake Piana (UTMWGS84 350642,4204113) and Lake Scanzano (UTMWGS84 3566384198788). Each lake was sampled in three different points that being influx to the lake, confluence in the dam (there is a dam in all lakes) and halfway. For each point mentioned, the sampling was done in the middle of the water column and repeated three times, sampling 2 L for each replicate using sterile glass bottles (autoclaved and cleaned also using a 10% HCl acid-rinse). During transportation, the water samples were kept in a cool and dark place. After reaching the laboratory of the STEBICEF Department at the University of Palermo, the samples were vacuum-filtered in a sterile environment (vacuum filter systems HC Series, Cheimika-HC/SLGS/F05002, Pellezzano, Italy), using nitrocellulose membranes (MF-Millipore, 0.22 µm MCE Membrane, 47 mm, Merck, GSWP04700, Darmstadt, Germany). More specifically, one filter was used for each 2 L replicate. As a control sample, MilliQ water was filtered using other filters to monitor contamination during the filtration process. Several decontamination precautions were used, including UV light. Vacuum filtration funnels, tweezers, scissors and the filter processing environment were also cleaned using 10% bleach and 96% ethanol. In accordance with Thomsen et al. [42], each filter was cut into small 1 mm strips to facilitate the eDNA extraction process, which was performed using DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kits (Qiagen). Each eDNA sample was stored at −20 °C.
2.3. eDNA Library Preparation and Bioinformatics Analysis
Metabarcoding analysis of eDNA samples was performed by IGA Technology Services s.r.l. (Udine, Italy) The PCR amplification consisted of two steps; the first step was performed with primers that amplified 106 bp from the 12S rRNA region [44].
The PCR mix in the final volume of 25 µL contained 12.5 µL 2 × KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (Roche, Wilmington, MA, USA), 2.5 µL of the forward primer 12SV5-F 5′-ACTGGGGATTAGATACCC-3′ (with Illumina adaptor 2 µM) and 2.5 µL of the reverse primer 12SV5-R 5′-TAGAACAGGCTCCTCTAG-3′ (with Illumina adaptor 2 µM). After adding 50 ng of the DNA extract, this mix was incubated using the following PCR conditions: initial denaturation for 3 min at 95 °C, 30 cycles of denaturation for 30 s at 95 °C, annealing for 30 s at 55 °C and extension for 30 s at 72 °C and a final extension for 4 min at 72 °C.
PCR products were purified using 1.6X Ampure XP beads (Beckman Coulter Life Sciences, Indianapolis, IN, USA) and eluted in 35 µL Tris-HCl pH 8.0 buffer. For the second step (the index PCR), 7.5 µL of the purified PCR product was added to a PCR mix containing 12.5 µL 2 × KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (Roche, Wilmington, MA, USA) and 2.5 µL of each index primer Nextera XT (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). PCR conditions for the index PCR were: initial denaturation for 3 min at 95 °C, 9 cycles of denaturation for 30 s at 95 °C, annealing for 30 s at 55 °C and extension for 30 s at 72 °C and a final extension for 5 min at 72 °C. After measuring with the Qubit 1X dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), the indexed PCR products were equimolarly pooled and sent for sequencing using the Illumina MiSeq 2 × 300 bp platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Base calling, demultiplexing and adapter masking were performed on instruments with the MiSeq Reporter.
An internal pipeline was created to analyze the metabarcoding sequences. Where the amplicon length was permissive with respect to the read sequencing length, 3′-ends of pairs were overlapped with flash v. 1.2.11 [45] and parameters “--max-overlap 70 --min-overlap 8” (to generate consensus pseudo-reads), while non-overlapping reads were maintained as separated pairs. We retained both overlapping and non-overlapping reads. Primer sequences used to amplify the variable 12S region were removed, with cutadapt v. 2.7 [46] and parameters: “--discard-untrimmed --minimum-length 70 --overlap 10 --times 2 --error-rate 0.15”. Reads were retained if they maintained a minimum length of 70 bp. Low-quality bases at 3′ tails of reads were trimmed with the erne-filter v. 1.4.3 [47] and parameters: “--min-size 70”. The QIIME pipeline v. 1.9.1 [48] was then executed. The library was scanned for the presence of chimeras with the VSEARCH algorithm v. 2.14.1 [49]. The Operational Taxonomic Unit (OTU) picking process was performed in “open-reference” mode against the 12S Vertebrate Reference Set for the RDP Classifier release v2.0.0 database https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/391459819 [50,51,52]. Reference sequences were obtained from the NCBI nucleotide database (accessed on July 2021) and MitoFish (accessed on March 2020). This version contains 19,654 reference sequences and 15,007 taxa at all ranks, including 9564 species. Taxonomy is based on the NCBI taxonomy database. Taxonomy was assigned to OTUs using the pre-defined taxonomy mapping file of the reference sequences, with the RDP classifier v. 2.2 [51]. Only OTU matching with 97% minimum identity threshold and with minimum confidence threshold of 0.50 were retained and subjected to further classification.
2.4. Data Analysis
Using exclusively the qualitative–quantitative list of the wild species identified by the eDNA of this study, in the ecosystems of these three Sicilian lakes, the specific richness values (S) and the biodiversity indices (H′) calculated with the Shannon algorithm were determined. The coenoses found in the three lakes were then compared, by calculating the values of both qualitative similarities (with the Sorensen index) and qualitative–quantitative similarities (with the Bray–Curtis and Morisita index). To correct the significant asymmetry in the number of fragments found among different vertebrate taxa, we conducted a base-10 logarithmic transformation of the fragment counts for biodiversity and similarity calculations.
3. Results
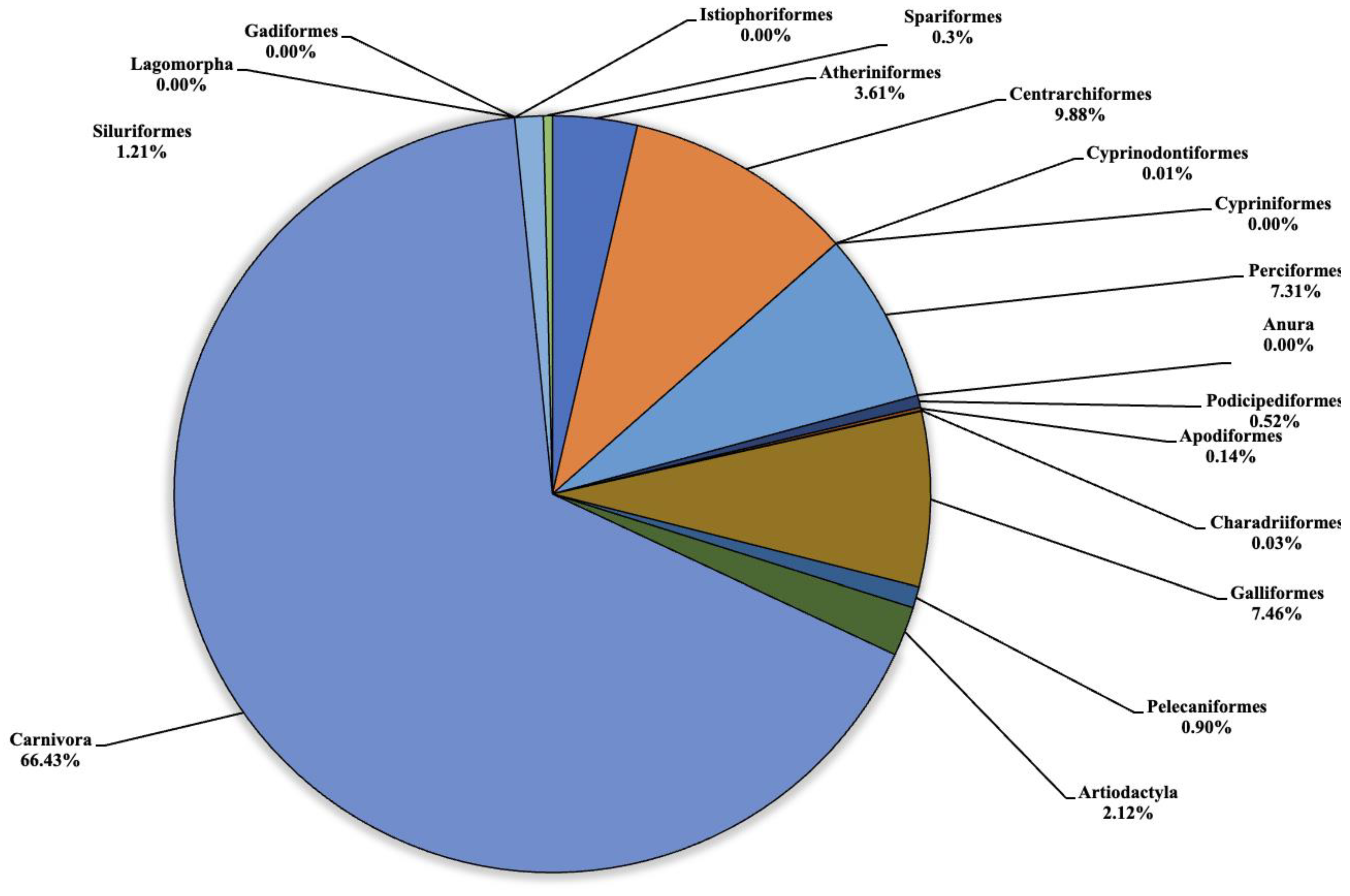
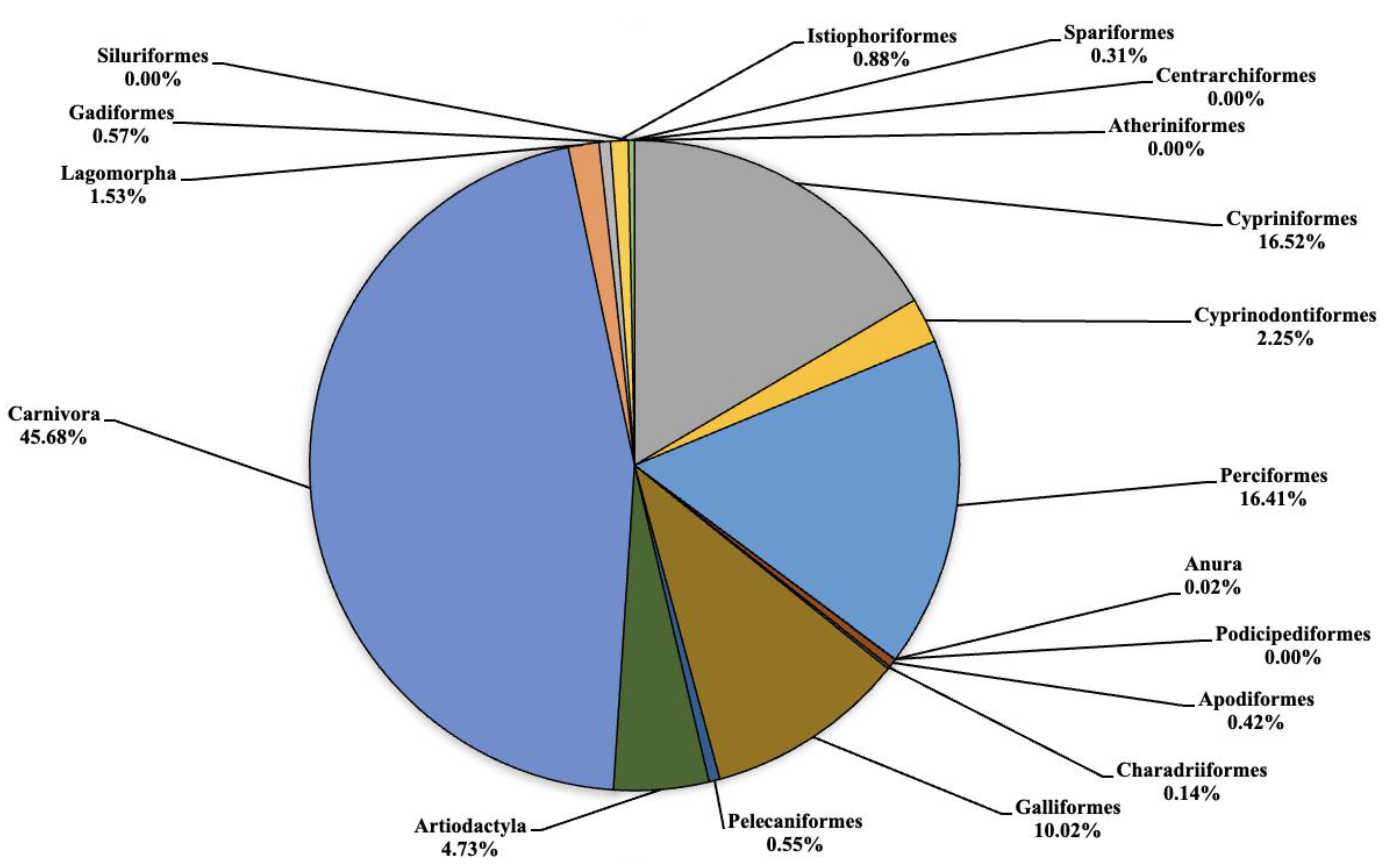
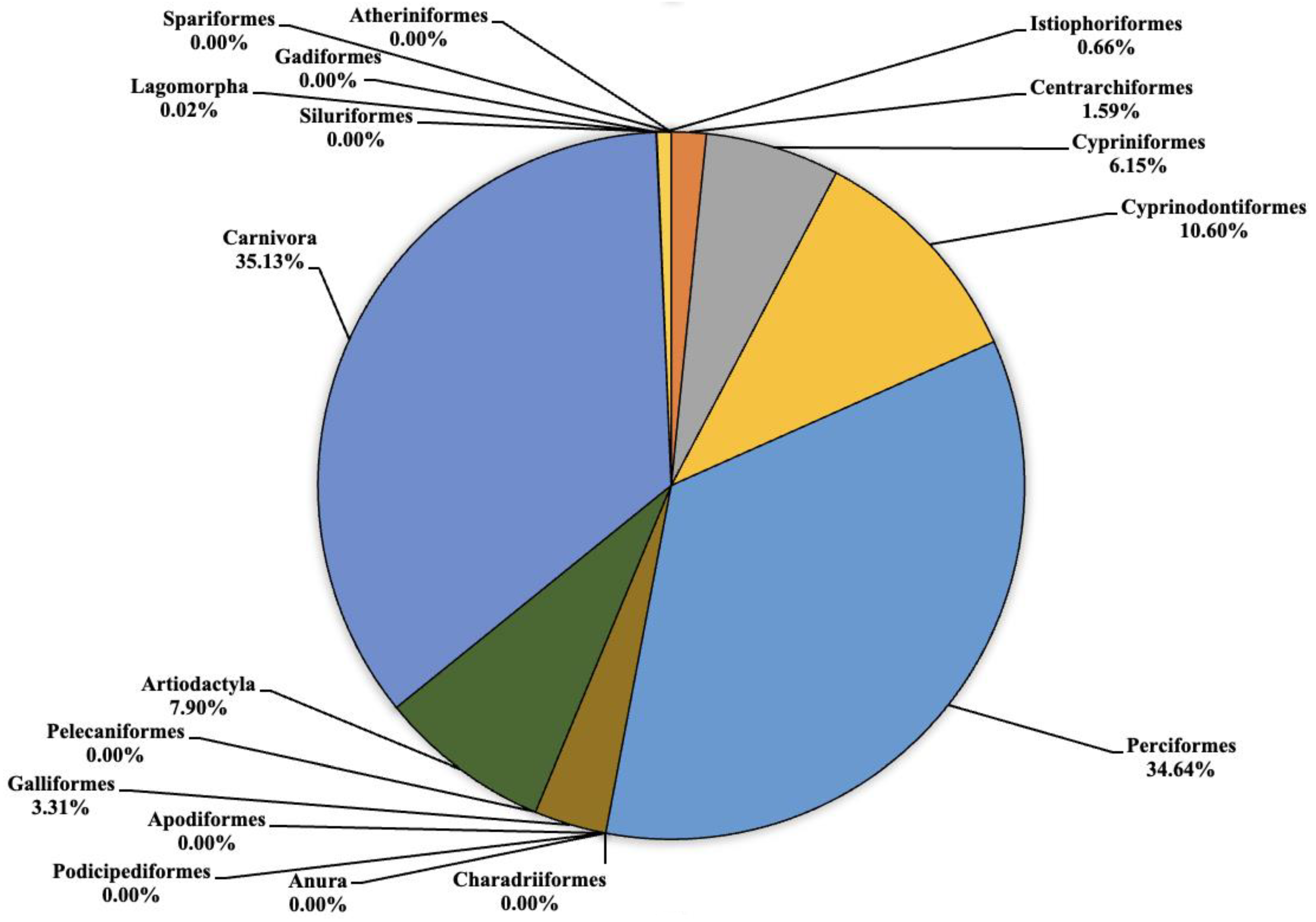
The analysis carried out on the eDNA samples obtained from the three Sicilian lakes showed an average number of fragment readings equal to: 124,781, 99,534 and 106,403 from Lake Poma, Lake Piana and Lake Scanzano, respectively. The data obtained were subsequently processed and cleaned to extrapolate only the fragments of interest to the study. Analysis allowed for taxonomic discrimination from the phylum to species level, with the most comprehensive results achieved at the order level. Table 2 shows the data relating to the number of fragments identified for each order in each lake analyzed. Total cleaned frequencies used to analyze the taxonomic order were 7247, 10,010.7 and 8052.5 for Lake Poma, Lake Piana and Lake Scanzano. These data are detailed and described as percentages for each site in the pie charts shown in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4, highlighting differences or similarities found between the sites.

Table 2.
Taxonomic order identified by analyzing eDNA. Average final-fragments read for each order were reported for each lake. The total number of cleaned frequencies per lake was also reported.
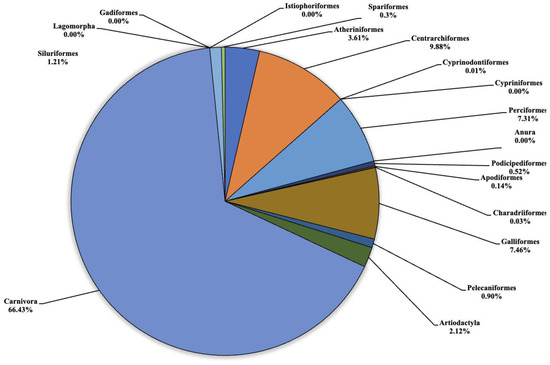
Figure 2.
Pie chart (expressed as a percentage) representing the taxonomic orders identified in Lake Poma.
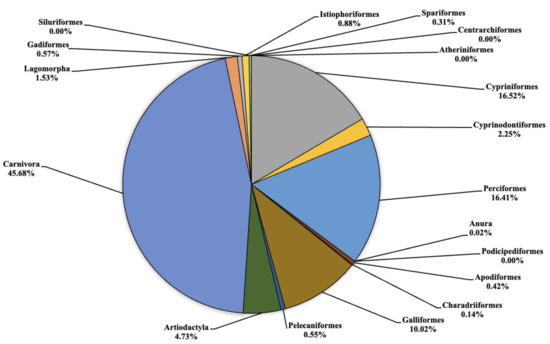
Figure 3.
Pie chart (expressed as a percentage) representing the taxonomic orders identified in Lake Piana.
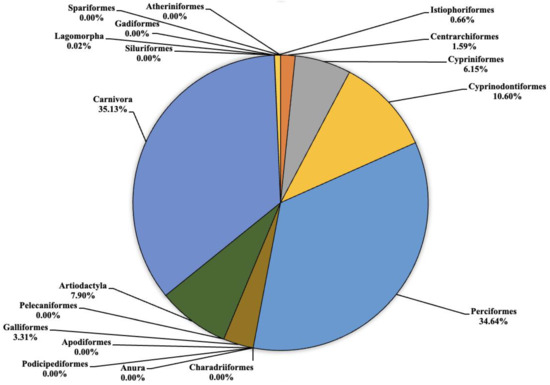
Figure 4.
Pie chart (expressed as a percentage) representing the taxonomic orders identified in Lake Scanzano.
Regarding Lake Poma (Figure 2), the highest number of fragments concerned the orders of Atheriniformes (3.61%), Centrarchiformes (9.88%), Perciformes (7.31%), Galliformes (7.46%), Artiodactyla (2.12%) and Carnivora (66.43%). For the orders of Cypriniformes, Anura, Lagomorpha, Gadiforme and Istiophoriformes, no eDNA fragments were identified. Very low quantities of fragments were detected for Cyprinodontiformes, Apodiformes, Charadriiformes and Spariformes, recorded as 0.5 (0.01%), 10.5 (0.03%), 2 and 28 (0.3%), respectively. Finally, for the orders of Podicipediformes, Pelecaniformes and Siluriformes, low but noteworthy levels were found in the number of fragments, which were 37.5 (0.52%), 65.5 (0.90%) and 88 (1.21%), respectively.
In Lake Piana (Figure 3) the highest number of fragments concerned the orders of Cypriniformes, Cyprinodontiformes, Perciformes, Galliformes, Artiodactyla and Carnivora that were equal to 1653.3 (16.52%), 225 (2.25%), 1642.3 (16.41%), 1003 (10.02%), 473.3 (4.73%) and 4572.7 (45.68%), respectively. No eDNA fragments were identified for the orders of Atheriniformes, Centrarchiformes, Podicipediformes and Siluriformes. Very low quantities of fragments were detected for Anura, Charadriiformes and Spariformes at 1.7 (0.02%), 14 (0.14%) and 30.7 (0.31%), respectively. Finally, for the orders of Apodiformes, Pelecaniformes, Gadiformes and Istiophoriformes, low but noteworthy levels were found regarding the number of fragments at 42.3 (0.42%), 54.7 (0.55%), 56.7 (0.57%) and 88.3 (0.88%), respectively. On the other hand, some orders detected in Lake Piana, such as Cyprinifromes, Anura, Lagomorpha, Gadiformes and Istiophoriformes, were not detected in Lake Poma.
As regards to Lake Scanzano (Figure 4), the highest number of fragments concerned the orders of Cypriniformes, Cyprinodontiformes, Perciformes, Galliformes, Artiodactyla and Carnivora, which were equal to 495 (6.15%), 853.5 (10.60%), 2789 (34.64%), 266.5 (3.31%), 636 5 (7.90%) and 2829 (35.13%), respectively. Furthermore, in most cases, the number of fragments obtained was even greater than those obtained in Lake Piana. No eDNA fragments were identified for the orders of Atheriniformes, Anura, Podicipediformes, Apodiformes, Charadriiformes, Pelecaniformes, Gadiformes, Siluriformes or Spariformes. Lower amounts of fragments were found for Centrarchiformes and Istiophoriformes at 128 (1.59%) and 53 (0.66%) respectively. In conclusion, for Lagomorpha, the lowest quantities of fragments were detected, which was equal to two (0.02%). Compared to the other two lakes, there were a greater number of orders for which no eDNA fragments were identified. Several absent orders were found to be present in the other two lakes, such as Pelecaniformes, Artiodactyla, Apodiformes and Charadriiformes. An absence of Atherinifromes, Podicipedifromes and Siluriformes orders was also found in Lake Piana. The same was observed for Anura and Gadiformes when compared to Lake Poma.
In various cases, environmental DNA analysis led to the identification of the species present within different orders. Our results highlighted the possibility to identify different types of species indicated in Table 3 and divided these into four categories: wild aquatic species (sensu strictu), other wild species, domestic terrestrial species and marine species. The latter has been included in a separate category as the lakes collect freshwater and are not in communication with any marine environment, thus the presence of marine species was an expected result. Each single category is described respectively (Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8).

Table 3.
Species identified by analyzing eDNA. Average final-fragments read for each species and for each lake were recorded. The per-lake and per-category total number of cleaned frequencies was also recorded.
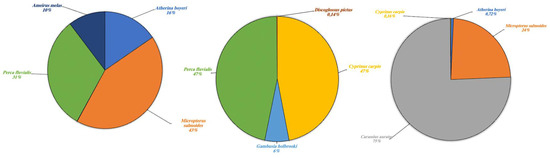
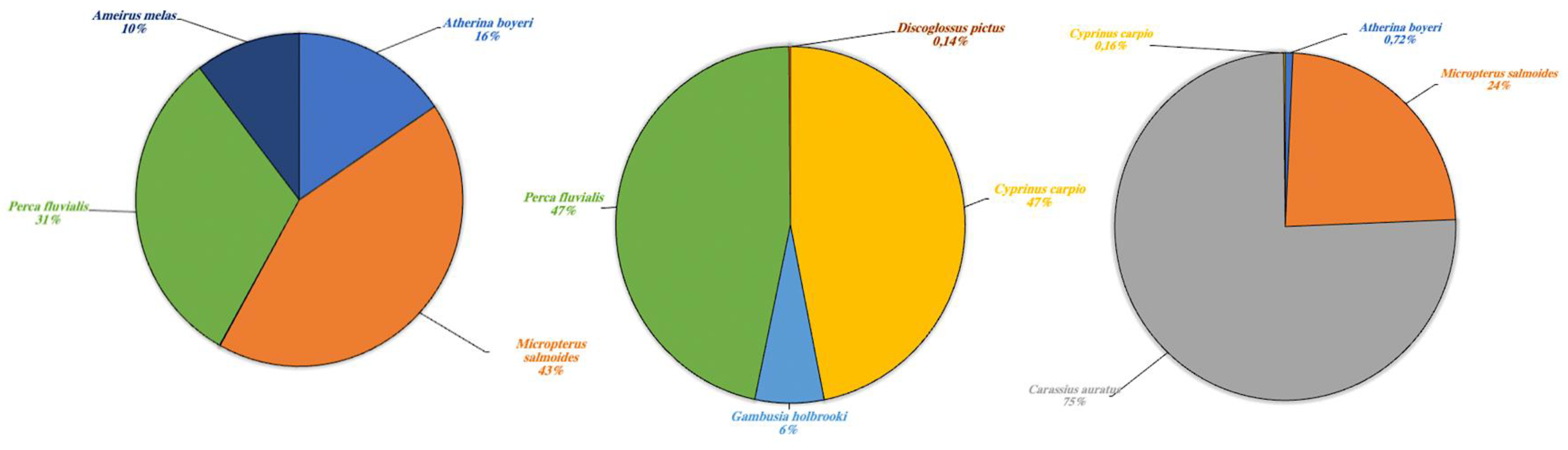
Figure 5.
Aquatic species detected in Lake Poma (left), Lake Piana (center) and Lake Scanzano (right) using eDNA analysis. The results are expressed in percentages of DNA fragments obtained.
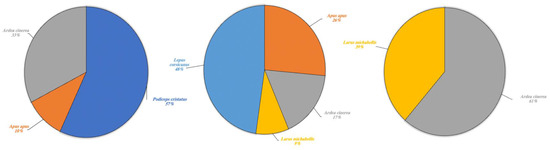
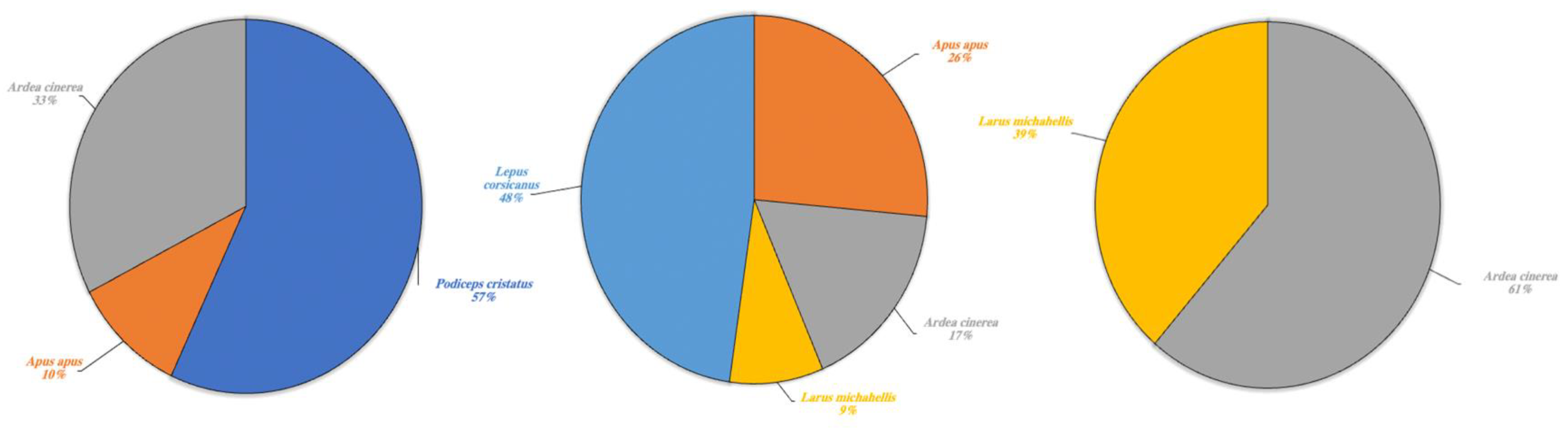
Figure 6.
Other wild species detected in Lake Poma (left), Lake Piana (center) and Lake Scanzano (right) using eDNA analysis. The results are expressed in percentages of DNA fragments obtained.
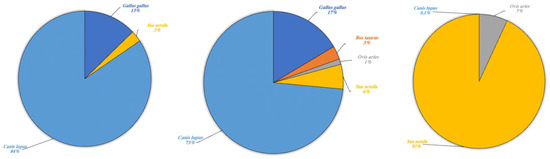
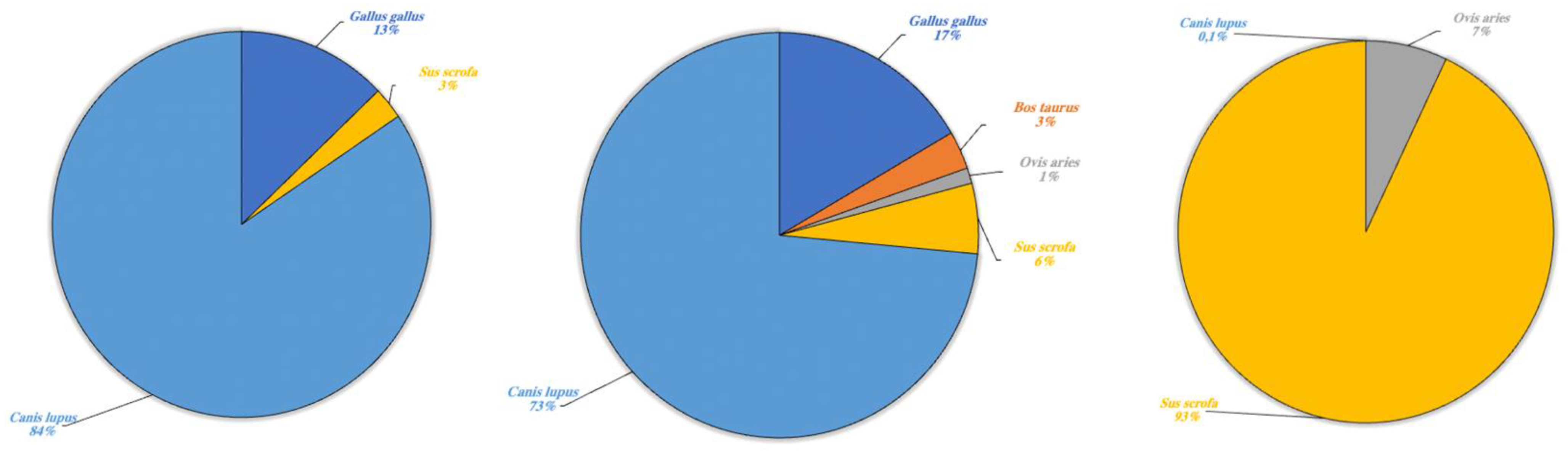
Figure 7.
Domestic terrestrial species detected in Lake Poma (left), Lake Piana (center) and Lake Scanzano (right) using eDNA analysis. The results are expressed in percentages of DNA fragments obtained.
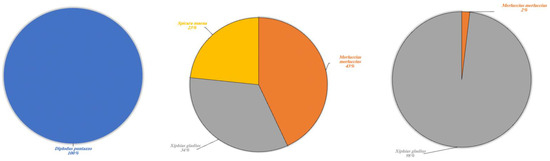
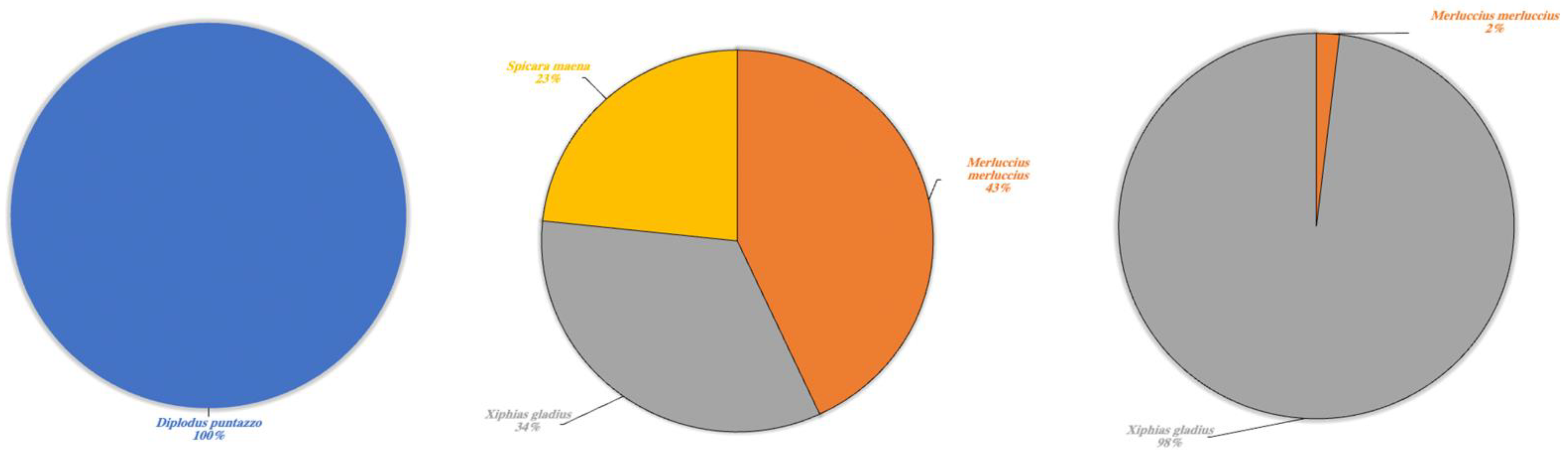
Figure 8.
Marine species detected in Lake Poma (left), Lake Piana (center) and Lake Scanzano (right) using eDNA analysis. The results are expressed in percentages of DNA fragments obtained.
Results for aquatic species are detailed in Figure 5 and expressed as a percentage of fragments obtained. The highest fragment percentages in Lake Poma were obtained for species Micropterus salmoides, Perca fluviatilis, Atherina boyeri and Ameirus melas (43%, 31%, 16% and 10%, respectively). High fragment percentages in Lake Piana were observed in P. fluviatilis (47%) only. Discoglossus pictus, Cyprinus carpio and Gambusia holbrooki, not found in Lake Poma, showed fragment percentages of 0.14%, 47% and 6%, respectively. Finally, regarding Lake Scanzano, the highest fragment percentage was identified for Carassius auratus (75%), a species seemingly not present in the other two lakes. However, similar to Lake Poma, fragments of M. salmoides and A. boyeri were identified, albeit at lower percentages (24% and 0.72%, respectively), and similar to Lake Piana, fragments of C. carpio were found, although, once again, at much a lower percentage (0.16%).
Other wildlife species for which eDNA fragments were detected in the three lakes are shown in percentages in Figure 6. A high fragment percentage were detected in Lake Poma for Podiceps cristatus (57%) and limited fragment percentages for Apus apus and Ardea cinerea at 10% and 33%, respectively. In Lake Piana, the highest fragment percentages concerned the species Lepus corsicanus (48%) and A. apus, although this last species was found at a higher rate (26%) than in Lake Poma. Similar to Lake Scanzano, fragments of A. cinerea and L. michahellis were also detected. In Lake Piana, however, detection rates were lower (17% and 9%, respectively), whilst in Lake Scanzano, these two species were the only fragments identified (61% and 39%, respectively).
Regarding domestic terrestrial species (Figure 7) in Lake Poma, Canis lupus (84%) was detected with the highest fragment percentage and G. gallus (13%) and S. scrofa (3%) with the two lower rates.
Likewise, in Lake Piana, the highest fragment percentage was recorded for C. lupus (73%) and lower percentages for G. gallus (17%) and S. scrofa (3%). However, fragments of B. taurus and O. aries were also detected in Lake Piana at 3% and 1%, respectively. Lastly, in Lake Scanzano, a high fragment percentage was detected only for S. scrofa (93%), with lower percentages recorded for O. aries and C. lupus at 7% and 0.1%, respectively.
To conclude, a fascinating result concerned the detection of eDNA fragments of typically marine species (Figure 8). In Lake Poma, Diplodus puntazzo was detected at a rate of 100%, whilst Merluccius merluccius and Xiphias gladius were detected in Lake Piana and Lake Scanzano at differing percentages. In more detail, rates were found to be 43% and 34%, respectively, in Lake Piana and 2% and 98% in Lake Scanzano. Moreover, fragments of Spicara maena (23%) were only detected in Lake Piana.
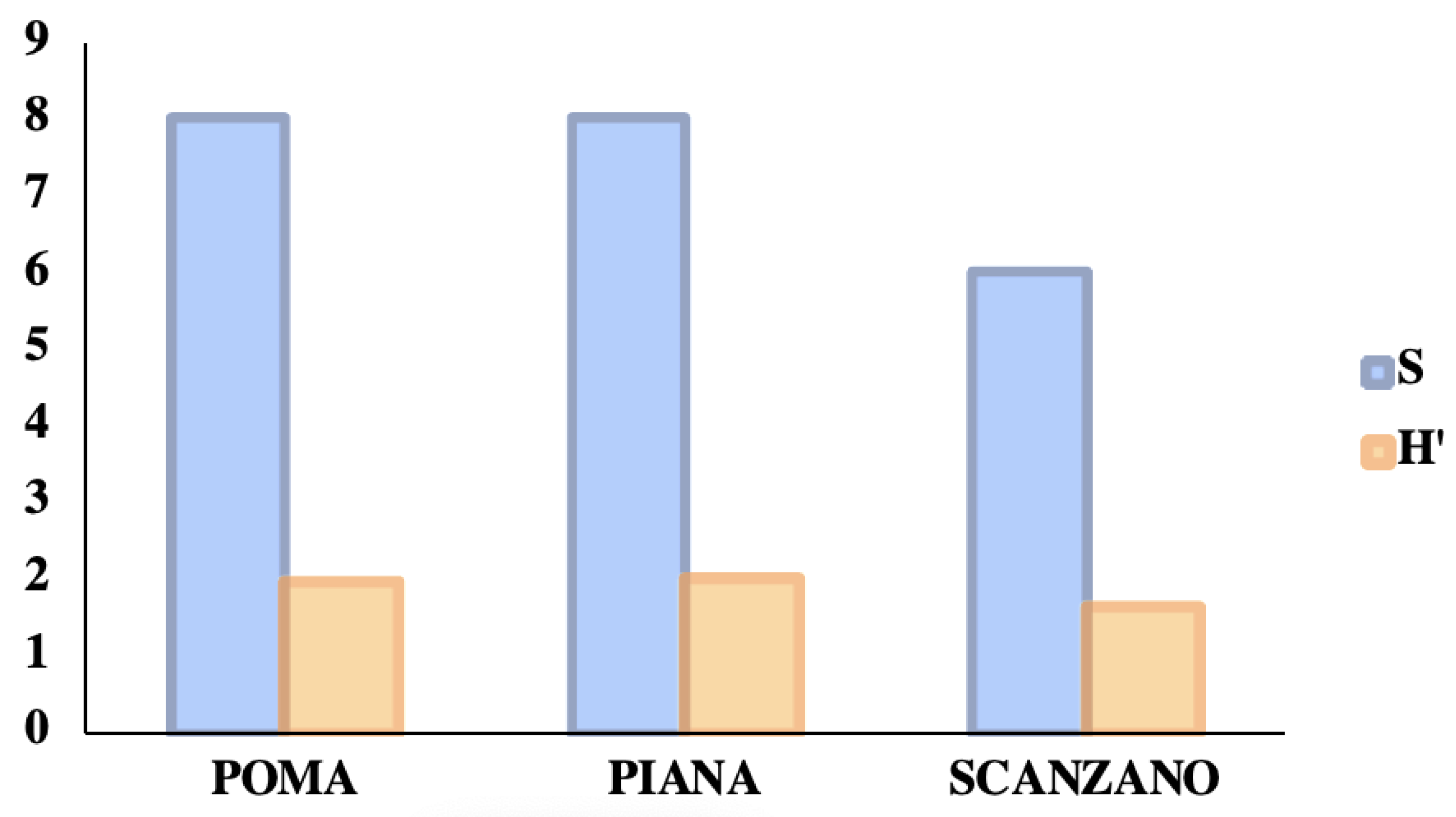
Figure 9 shows the number of taxa and the values of the biodiversity index (relative to wild vertebrates) found in the three lakes examined and compared. Lake Piana was the lake with the highest specific richness and biodiversity values, while Lake Scanzano was found to be the lowest.
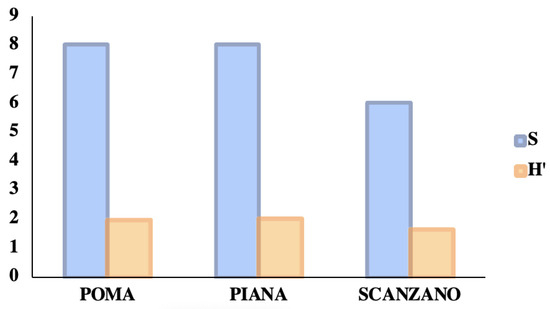
Figure 9.
A comparison between the number of taxa and the values of the biodiversity index (relative to wild vertebrates) in three lakes. In detail, the specific richness values (S) and the biodiversity indices (H′) calculated with the Shannon algorithm.
Despite the similarity of these values, the coenoses of the three lakes were found to be quite different from each other. In fact, by comparing the similarity values found, there are differences of at least 50% from a qualitative point of view and at least 60% from a qualitative–quantitative point of view (Table 4).

Table 4.
Matrix of qualitative and qualitative–quantitative similarity of the fauna from the three lakes (0 = no similarity; 1 = maximum similarity).
Regarding the environmental typologies around the three lakes, Table 5 shows the number of habitats found and the relative diversity values.

Table 5.
Number of habitats (S) and the diversity values (H’) in the three lakes.
Once again, the values were quite similar to each other. However, unlike the data observed regarding the fauna, habitat comparison yielded a value of less than 50% similarity only in the case of the Bray–Curtis index (Table 6).

Table 6.
Matrix of qualitative and qualitative–quantitative similarity of the habitat of the three lakes (0 = no similarity; 1 = maximum similarity).
4. Discussion
Biomonitoring is essential to analyze the biological diversity, contamination and ecological status of the ecosystems examined [53,54,55]. Among the different approaches, one of the most important in recent years is based on the detection and characterization of DNA released by organisms into the environment and that are classified into two types: organismic and extraorganismic [56,57].
In this study, the environmental DNA technique was applied to three Sicilian lakes in order to provide the first snapshot of vertebrate biodiversity in these three lakes that would be useful to create a baseline of knowledge regarding the biodiversity in these three lakes. Our preliminary eDNA results showed differences between the three lakes, in contrast with high similarity found in the composition of surrounding habitats, an issue that will need to be further investigated. Regarding aquatic orders, fragments of Cypriniformes, Cyprinodontiformes, Perciformes, Centrarchiformes and Atheriniformes were identified, although detected in differing abundances in the three sites. Similar results were observed by analyzing the number of fragments of other orders. In regards to the orders and wild aquatic species, we had sporadic information based on our knowledge, sightings or information collected from the local population and amateur fishermen, which reported both about the species that we identified with eDNA and also about the species that were not identified with eDNA in our study [58,59,60]. Regarding the last ones, the not revealing of their eDNA could be due to the lack of a DNA barcode in the reference libraries [61,62,63]. Despite this, these results constitute the first snapshot of the three lakes to be further explored and expanded in future sampling, also during other seasons. A particularly important result of the eDNA approach concerned the ability to verify the presence of species that were not strictly aquatic, however dependent on these ecosystems to some extent. Species such as Podiceps cristatus and Ardea cinerea, which nest in these environments, Apus apus, a species which uses the reservoirs for drinking, or Larus michahellis, which is present all year round, were identified. However, this is a relatively low number of species compared to those actually present. This fact depends partially on the sampling period but also on the phenology of the species. Bird species (both migratory and sedentary) in these areas are, in reality, much more numerous, not to mention the known presence of amphibians and reptiles not yet detected by eDNA. Indeed, during sampling, bird species such as Egretta garzetta, Bubulcus ibis, Anas plathyrhyncos, Gallinula chloropus, Actitis hypoleucos and Ardea alba were observed, and reptiles, such as Natrix helvetica [64], or amphibians, such as Xenopus laevis or Bufo bufo [65,66,67], as well as being known to the area, were also seen during sample collection.
The different biodiversity values could be due to a number of factors, such as water sampling (e.g., the need to increase sampling to cover a wider surface area) or the degradation processes of the DNA released into the environment. Indeed, it is important to consider that environmental DNA is a heterogeneous mixture of genetic materials, including chromosomes and plasmids protected inside cells, or other types of cellular debris and extracellular DNA fragments that are floating in the environment [68]. It has also been observed that the methods of preservation and extraction of the sample can also influence the final result [34,69,70,71,72]. Regardless of the nature of the DNA released into the environment, it is clear that its fate can differ as it encounters factors and/or conditions which either protect it and keep it intact or degrade it [73,74,75,76,77]. It is known rather that the resistance of environmental DNA in water samples depends on the characteristics of the molecule (length, conformation, sequence) and on environmental characteristics [78]. For example, environmental temperatures or salinity conditions, or the availability of oxygen, ultraviolet or solar radiation, can also influence the degradation of the molecule through denaturation processes [79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89]. Even microbial communities and extracellular enzymes can influence the degradation processes [90].
Abiotic and biotic conditions of the studied ecosystem could also have an influence on the performance of the primer, which can vary under differing conditions [91,92]. In addition, studies on target 16s sequencing of mock communities reported large deviations from expected values, dependent on sequencing primers, extraction methods and the sequencing platform applied [93]. The choice of primer pairs that allow DNA amplification of specific taxonomic groups and discriminate between species is crucial. A large variety of primer pairs have been developed, either universally or specifically, to amplify target clades [94,95,96,97]. Multiprimer comparison generally found considerable differences in the amplified taxonomic specificity and species discrimination power both in silico and in situ [98]. Thus, to increase the ability of species detection, it would be appropriate to use different primer pairs in combination [99].
To implement DNA metabarcoding for the identification of species and ecosystem biomonitoring, we need reliable sequence reference libraries of the known taxa [61]. Currently, the incompleteness of DNA barcode reference libraries represents a significant limit to unveiling total biodiversity, especially of an aquatic ecosystem and species from lakes. Among aquatic taxa, species-rich groups, such as arthropods and polychaetes, or economically important fish are better represented in libraries, while specific taxonomic groups, at the local/regional level in particular, are completely absent [61,62,63]. Results of metagenomic analyses highlighted the presence of different categories of species. Some of these concerned the category of wild aquatic species in the strict sense, typical of these sites. The ability to use eDNA to detect species of fish present in freshwater environments certainly offers new possibilities for less invasive censuses and for the creation and/or updating of regional fish maps. However, an extremely important result regarded the acquisition of information on other wild species or domestic terrestrial species. As far as the presence of domestic species is concerned, this could be due, in some cases, such as Bos taurus, Ovis aries and Canis lupus familiaris, to the shepherds’ habit of keeping these species near to reservoirs for water supply. In other cases, the presence of eDNA, such as that of Gallus gallus and Sus scrofa, linked to anthropic activities or farming in the surrounding area, could reach the water body by soil leaching or through discharges into small watercourses that flow into the reservoirs [100,101,102].
On the other hand, the presence of marine fish species, typically used for human nutrition, could only be explained by waste disposal in these waters. This could be due to anthropic impacts that influence freshwater environments today [103,104], although fisheries sector businesses would seem to be absent from the area. Thus, differences between the three lakes, to our knowledge, are not correlated to the presence of particular anthropic activities nearby. Taken together, our results highlighted the ability to use environmental DNA evaluation not only as a tool for biodiversity census but also as a tool to evaluate the ecological status of aquatic environments. Our results confirmed that this technique has the potential to complement traditional methods, although using both approaches may offer a more comprehensive understanding of the ecosystem [105].
5. Conclusions
The results of this study confirmed the considerable potential of environmental DNA analysis as a tool to evaluate not only the species in a given site but also its ecological status. Results presented in this study show that DNA release into the environment could be useful to identify both strictly aquatic species and terrestrial species that use these sites as a source of water supply. Moreover, our results showed that the use of eDNA can be inserted in a much broader context than a simple census, i.e., in the evaluation of the ecological status of the ecosystem in question. It seems, for example, that environmental DNA could allow us to identify the presence of anthropogenic impacts from the illegal dumping of fishing waste. In this regard, our results detected marine species which could not be in these lakes otherwise, as the water bodies are not in communication with the marine environment. Despite this, our results confirmed that the exclusive use of this technique to replace conventional techniques entirely is not yet possible. There are still too many variables that influence the persistence of environmental DNA, and the detection or otherwise of some species cannot necessarily be connected to their absence or presence. Another important issue concerns the standardization of protocols used due to considerable deviations from the expected values, which are largely dependent on extraction methods, specificity sequencing primers and the sequencing platform applied.
Moreover, it is worth noting that our results could depend on a series of factors, including the lack of DNA barcoding of different taxa in the reference libraries, on the selection of appropriate primer pairs or on the need to use more than one pair to detect a wide range of taxa.
Conventional taxonomic skills today cannot be replaced entirely if we are to ensure the correct characterization of the biodiversity of a given site. However, results obtained undoubtedly provide a satisfactory starting point for the creation of a fish map of these sites and for a census of the biodiversity present, that can be broadened by carrying out further samplings in different seasons.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M., M.V. and V.A.; methodology, M.M., M.L.V., A.V., R.B. and S.R.; software, M.M., M.L.V. and S.R.; validation, M.M., M.V., S.R. and M.L.V.; formal analysis, M.M., S.R., M.L.V. and M.V.; investigation, M.M., A.V., M.V., S.R. and M.L.V.; resources, M.M. and V.A.; data curation, M.M., M.V., S.R. and M.L.V.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M., M.V., S.R. and M.L.V.; writing—review and editing, M.M., M.V., S.R., M.L.V. and V.A.; visualization, M.M., M.V., S.R. and M.L.V.; supervision, V.A., M.L.V. and M.V.; project administration L.B.H. and V.A., funding acquisition, M.M., L.B.H. and V.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded thanks to co-financing by the European Union–FESR o FSE, PON Ricerca e Innovazione 2014-2020–DM 1062/202. Moreover, this research was funded also thanks to co-financing by the Interreg Italia-Malta, Bythos Extend Project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Non-public data for privacy, contact the authors.
Acknowledgments
To carry out these studies, authorizations were obtained from Regione Sicilia, Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale (ISPRA), Città Metropolitana di Palermo e Ministero della Transizione Ecologica-Direzione Generale per il Patrimonio Naturalistico e Mare, Div. III Strategie della Biodiversità.
Conflicts of Interest
Slobodanka Radovic was employed by the company IGA Technology Services Srl. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Cardinale, B.J.; Duffy, J.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Perrings, C.; Venail, P.; Narwani, A.; Mace, G.M.; Tilman, D.; Wardle, D.A.; et al. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature 2012, 486, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, C.J.; Altermatt, F. Landscape configuration alters spatial arrangement of terrestrial-aquatic subsidies in headwater streams. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin, J.D.; Altermatt, F.; Finn, D.S.; Heino, J.; Olden, J.D.; Pauls, S.U.; Lytle, D.A. The role of dispersal in river network metacommunities: Patterns, processes, and pathways. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 63, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Fang, Y.; Jawitz, J.W.; Yan, J.; Cui, B. River network connectivity and fish diversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, S.; Settele, J.; Brondízio, E.S.; Ngo, H.T.; Agard, J.; Arneth, A.; Balvanera, P.; Brauman, K.A.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Chan, K.M.A.; et al. Pervasive human-driven decline of life on Earth points to the need for transformative change. Science 2019, 366, eaax3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tickner, D.; Opperman, J.J.; Abell, R.; Acreman, M.; Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E.; Cooke, S.J.; Dalton, J.; Darwall, W.; Edwards, G.; et al. Bending the curve of global freshwater biodiversity loss: An emergency recovery plan. BioScience 2020, 70, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Altermatt, F.; Yang, J.; An, S.; Li, A.; Zhang, X. Human activities’ fingerprint on multitrophic biodiversity and ecosystem functions across a major river catchment in China. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 6867–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J. Anthropogenic stresses on the world’s big rivers. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Thieme, M.; Geenen, B.; Tickner, D.; Antonelli, F.; Babu, S.; Borrelli, P.; Cheng, L.; Crochetiere, H.; et al. Mapping the world’s free-flowing rivers. Nature 2019, 569, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belletti, B.; Garcia de Leaniz, C.; Jones, J.; Bizzi, S.; Börger, L.; Segura, G.; Castelletti, A.; van de Bund, W.; Aarestrup, K.; Barry, J.; et al. More than one million barriers fragment Europe’s rivers. Nature 2020, 588, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stets, E.G.; Sprague, L.A.; Oelsner, G.P.; Johnson, H.M.; Murphy, J.C.; Ryberg, K.; Vecchia, A.V.; Zuellig, R.E.; Falcone, J.A.; Riskin, M.L. Landscape drivers of dynamic change in water quality of US rivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4336–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, K.S.; Cazelles, K.; MacDougall, A.S.; Fussmann, G.F.; Bieg, C.; Cristescu, M.; Fryxell, J.M.; Gellner, G.; Lapointe, B.; Gonzalez, A. Landscape modification and nutrient-driven instability at a distance. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalipour, M.; Antczak, E.; Dostál, T.; Jabbarian Amiri, B. Influences of landscape configuration on river water quality. Forests 2022, 13, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; McIlroy, S.E.; Archana, A.; Baker, D.M.; Panagiotou, G. A pollution gradient contributes to the taxonomic, functional, and resistome diversity of microbial communities in marine sediments. Microbiome 2019, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finderup Nielsen, T.; Sand-Jensen, K.; Dornelas, M.; Bruun, H.H. More is less: Net gain in species richness, but biotic homogenization over 140 years. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.L.; Yeo, D.C.; Tan, H.H.; Fikri, A.H.; Ewers, R.M. Land-use change is associated with a significant loss of freshwater fish species and functional richness in Sabah, Malaysia. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 222, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounand, I.; Little, C.J.; Harvey, E.; Altermatt, F. Cross-ecosystem carbon flows connecting ecosystems worldwide. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, J.C. Revisiting the fates of dead leaves that fall into streams. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2019, 50, 547–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Geng, M.; Yu, J.; Du, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Su, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, F. Eutrophication decrease compositional dissimilarity in freshwater plankton communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.; Wang, P.; Xu, Q.; Zeng, T.; Ding, M.; Nie, M.; Zhang, H.; Huang, G. Coupled effects of landscape structures and water chemistry on bacterioplankton communities at multi-spatial scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karr, J.R. Biological monitoring and environmental assessment: A conceptual framework. Environ. Manag. 1987, 11, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altermatt, F.; Little, C.J.; Maechler, E.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Blackman, R.C. Uncovering the complete biodiversity structure in spatial networks: The example of riverine systems. Oikos 2020, 129, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Fronhofer, E.A.; Mächler, E.; Walser, J.C.; Altermatt, F. Environmental DNA reveals that rivers are conveyer belts of biodiversity information. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taberlet, P.; Bonin, A.; Zinger, L.; Coissac, E. Environmental DNA: For Biodiversity Research and Monitoring; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, K. Microplastics in inland freshwater environments with different regional functions: A case study on the Chengdu Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Burton, G.A. Zooplankton community profiling in a eutrophic freshwater ecosystem-lake tai basin by DNA metabarcoding. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Zhao, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. eDNA metabarcoding revealed differential structures of aquatic communities in a dynamic freshwater ecosystem shaped by habitat heterogeneity. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Hajibabaei, M.; Rieseberg, L.H. Environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Gregory, T.R. The promise of DNA barcoding for taxonomy. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Smith, M.A.; Janzen, D.H.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Whitfield, J.B.; Hebert, P.D. A minimalist barcode can identify a specimen whose DNA is degraded. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, J.; Froese, D.G.; MacPhee, R.D.E.; Roberts, R.G.; Arnold, L.J.; Reyes, A.V.; Rasmussen, M.; Nielsen, R.; Brook, B.W.; Robinson, S.; et al. Ancient DNA reveals late survival of mammoth and horse in interior Alaska. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22352–22357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson-Carpenter, L.L.; McLachlan, J.S.; Jackson, S.T.; Kuch, M.; Lumibao, C.Y.; Poinar, H.N. Ancient DNA from lake sediments: Bridging the gap between paleoecology and genetics. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerde, C.L.; Mahon, A.R.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. “Sight-unseen” detection of rare aquatic species using environmental DNA. Conserv. Lett. 2011, 4, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Pilliod, D.S.; Arkle, R.S.; Waits, L.P. Molecular detection of vertebrates in stream water: A demonstration using rocky mountain tailed frogs and IDAHO giant salamanders. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiiesalu, I.; Opik, M.; Metsis, M.; Lilje, L.; Davison, J.; Vasar, M.; Moora, M.; Zobel, M.; Wilson, S.D.; Partel, M. Plant species richness belowground: Higher richness and new patterns revealed by next-generation sequencing. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2004–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, A.N.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Jiang, X.; Dang, C.; Ma, T.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Xie, S.; et al. Integrated biogeography of planktonic and sedimentary bacterial communities in the Yangtze River. Microbiome 2018, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gweon, H.S.; Bowes, M.J.; Moorhouse, H.L.; Oliver, A.E.; Bailey, M.J.; Acreman, M.C.; Read, D.S. Contrasting community assembly processes structure lotic bacteria metacommunities along the river continuum. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Han, D.; Yan, L.; Yan, S.; Zha, J.; Shen, J. Assessment of benthic invertebrate diversity and river ecological status along an urbanized gradient using environmental DNA metabarcoding and a traditional survey method. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 806, 150587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yan, Z.; Hänfling, B.; Zheng, X.; Wang, P.; Fan, J.; Li, J. Methodology of fish eDNA and its applications in ecology and environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhan, A.; Dong, C.; Zhao, J.; Yao, M. Environmental DNA captures native and non-native fish community variations across the lentic and lotic systems of a megacity. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabk0097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Møller, P.R.; Rasmussen, M.; Willerslev, E. Detection of a diverse marine fish fauna using environmental DNA from seawater samples. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, S.; Barone, R.; Naselli Flores, L.; Fradà Orestano, C.; Dongarrà, G.; Lugaro, A.; Genchi, G. Limnological studies on lake and reservoires of Sicily. Nat. Sicil. 1993, 17 (Suppl. S2), 3–292. [Google Scholar]
- Riaz, T.; Shehzad, W.; Viari, A.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E. ecoPrimers: Inference of new DNA barcode markers from whole genome sequence analysis. Nucl. Acids Res. 2011, 39, e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, C.; Scalabrin, S.; Morgante, M.; Giorgi, F.M. An extensive evaluation of read trimming effects on Illumina NGS data analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. Peer J. 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Miya, M.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Iwasaki, W.; Kumar, S. MitoFish and MiFish Pipeline: A mitochondrial genome database of fish with an analysis pipeline for environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, T.M. terrimporter/12SvertebrateClassifier: 12S Vertebrate Classifier v2.0.0-ref (v2.0.0-ref) [Computer Software]. Zenodo. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/terrimporter/12SvertebrateClassifier (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Golden, N.H.; Rattner, B.A. Ranking terrestrial vertebrate species for utility in biomonitoring and vulnerability to environmental contaminants. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology: Continuation of Residue Reviews; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 67–136. [Google Scholar]
- Vivien, R.; Wyler, S.; Lafont, M.; Pawlowski, J. Molecular barcoding of aquatic oligochaetes: Implications for biomonitoring. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Der Heyde, M.; Bunce, M.; Wardell-Johnson, G.; Fernandes, K.; White, N.E.; Nevill, P. Testing multiple substrates for terrestrial biodiversity monitoring using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ezpeleta, N.; Morissette, O.; Bean, C.W.; Manu, S.; Banerjee, P.; Lacoursière-Roussel, A.; Beng, K.C.; Alter, S.E.; Roger, F.; Holman, L.E.; et al. Trade-offs between reducing complex terminology and producing accurate interpretations from environmental DNA: Comment on “Environmental DNA: What’s behind the term?” by Pawlowski et al., (2020). Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 4601–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, L.E. The emergence of eDNA: An interdisciplinary tool helps monitor biodiversity and health. BioScience 2022, 72, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vari, A. Atlante della Biodiversità della Sicilia: Vertebrati Terrestri; Arpa Sicilia: Palermo, Italy, 2008; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Valvo, M.; Massa, B.; Sarà, M. Uccelli e paesaggio in Sicilia alle soglie del terzo millennio. Nat. Sicil. 1993, 17, 1–376. [Google Scholar]
- Lo Valvo, M.; Faraone, F.P.; Giacalone, G.; Lillo, F. Fauna di Sicilia. Anfibi. In Monografie Naturalistiche; Edizioni Danaus: Palermo, Italy, 2017; Volume 5, 136p. [Google Scholar]
- Weigand, H.; Beermann, A.J.; Čiampor, F.; Costa, F.O.; Csabai, Z.; Duarte, S.; Geiger, M.F.; Grabowski, M.; Rimet, F.; Rulik, B.; et al. DNA barcode reference libraries for the monitoring of aquatic biota in Europe: Gap-analysis and recommendations for future work. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specchia, V.; Francesco, Z.; Tzafesta, E.; Pinna, M. Gap Analysis for DNA Barcodes of Aquatic Macroinvertebrate Species in the Southeast of Italy. In ARPHA Conference Abstracts. 2021. Available online: https://iris.unisalento.it/handle/11587/450780 (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Tzafesta, E.; Saccomanno, B.; Zangaro, F.; Vadrucci, M.R.; Specchia, V.; Pinna, M. DNA Barcode gap analysis for multiple marker genes for phytoplankton species biodiversity in mediterranean aquatic ecosystems. Biology 2022, 11, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraone, F.P.; Giacalone, G.; Lo Valvo, M. Dati preliminari sulla biometria, il cromatismo e la dieta di una popolazione di Natrix natrix della Sicilia occidentale. In Proceedings of the VIII Congresso Nazionale Societas Herpetologica Italica, Chieti, Italy, 22–26 September 2010; Di Tizio, L., Di Cerbo, A.R., Di Francesco, N., Cameli, A., Eds.; Ianieri Edizioni: Pescara, Italy, 2010; pp. 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Lillo, F.; Marrone, F.; Sicilia, A.; Castelli, G.; Zava, B. An invasive population of Xenopus laevis (Daudin, 1802) in Italy. Herpetozoa 2005, 18, 63–64. [Google Scholar]
- Faraone, F.P.; Lillo, F.; Giacalone, G.; Lo Valvo, M. The large invasive population of Xenopus laevis in Sicily, Italy. Amphib. Reptial. 2008, 29, 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Giacalone, G.; La Piana, F.; Lillo, F.; Lo Valvo, M. Analisi di contenuti stomacali di B. bufo: Considerazioni ecologiche e comportamentali. In Proceedings of the 6th Congresso Nazionale della Societas Herpetologica Italica, Roma, Italy, 27 September–1 October 2006; pp. 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Siuda, W.; Chrost, R. Concentration and susceptibility of dissolved DNA for enzyme degradation in lake water-some methodological remarks. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 21, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Miaud, C.; Pompanon, F.; Taberlet, P. Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples. Biol. Lett. 2008, 4, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foote, A.D.; Thomsen, P.F.; Sveegaard, S.; Wahlberg, M.; Kielgast, J.; Kyhn, L.A.; Salling, A.B.; Galatius, A.; Orlando, L.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Investigating the potential use of environmental DNA (eDNA) for genetic monitoring of marine mammals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, P.F.; Kielgast, J.; Iversen, L.L.; Wiuf, C.; Rasmussen, M.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Orlando, L.; Willerslev, E. Monitoring endangered freshwater biodiversity using environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2565–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilliod, D.S.; Goldberg, C.S.; Arkle, R.S.; Waits, L.P. Estimating occupancy and abundance of stream amphibians using environmental DNA from filtered water samples. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 70, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietramellara, G.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Ascher, J.; Nannipieri, P. Persistence of transgenic and not transgenic extracellular DNA in soil and bacterial transformation. Riv. Biol. Forum 2006, 99, 37–68. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Billingsley, K.; Ward, O. Composting: A potentially safe process for disposal of genetically modified organisms. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2006, 26, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy-Booth, D.J.; Campbell, R.G.; Gulden, R.H.; Hart, M.M.; Powell, J.R.; Klironomos, J.N.; Pauls, K.P.; Swanton, C.J.; Trevors, J.T.; Dunfield, K.E. Cycling of extracellular DNA in the soil environment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2977–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.M.; Johnsen, P.J.; Bensasson, D.; Daffonchio, D. Release and persistence of extracellular DNA in the environment. Environ. Biosaf. Res. 2007, 6, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietramellara, G.; Ascher, J.; Borgogni, F.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Guerri, G.; Nannipieri, P. Extracellular DNA in soil and sediment: Fate and ecological relevance. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2009, 45, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; Turner, C.R.; Jerde, C.L.; Renshaw, M.A.; Chadderton, W.L.; Lodge, D.M. Environmental conditions influence eDNA persistence in aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreader, C.A. Persistence of PCR-detectable Bacteroides distasonis from human feces in river water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 4103–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofreiter, M.; Serre, D.; Poinar, H.N.; Kuch, M.; Pääbo, S. Ancient DNA. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravanat, J.; Douki, T.; Cadet, J. Direct and indirect effects of UV radiation on DNA and its components. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2001, 63, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohland, N.; Hofreiter, M. Ancient DNA extraction from bones and teeth. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, S.; Shimazu, Y. Persistence of host-specific Bacteroides prevotella 16S rRNA genetic markers in environmental waters: Effects of temperature and salinity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, S.; Crotti, E.; Mapelli, F.; Tamagnini, I.; Corselli, C.; Daffonchio, D. DNA is preserved and maintains transforming potential after contact with brines of the deep anoxic hypersaline lakes of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Saline Syst. 2008, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, C.; Beolchini, F.; Dell’Anno, A. Damage and degradation rates of extracellular DNA in marine sedime implications for the preservation of gene sequences. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 3939–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potè, J.; Ackermann, R.; Wildi, W. Plant leaf mass loss and DNA release in freshwater sediments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, L.K.; Stelzer, E.A.; Bertke, E.E.; Fong, D.L.; Stoeckel, D.M. Relative decay of Bacteroidales microbial source tracking markers and cultivated Escherichia coli in freshwater microcosms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3255–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, H.C.; Shanks, O.C.; Sivaganesan, M.; Haugland, R.A.; Field, K.G. Differential decay of human faecal Bacteroides in marine and freshwater. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 3235–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.H.; Wang, L.; Le, Y.Q.; Hu, J.J. Persistence and renaturation efficiency of thermally treated waste recombinant DNA in defined aquatic microcosms. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic 2012, 47, 1975–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dove, N.C.; Barnes, M.E.; Moreland, K.; Graham, R.C.; Berhe, A.A.; Hart, S.C. Depth dependence of climatic controls on soil microbial community activity and composition. ISME Commun. 2021, 1, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, K.Y.K.; Fong, J.J.; Lam, I.P.Y.; Dudgeon, D. Pitfalls during in silico prediction of primer specificity for eDNA surveillance. Ecosphere 2020, 11, e03193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Yao, M. A comprehensive and comparative evaluation of primers for metabarcoding eDNA from fish. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 1609–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouhy, F.; Clooney, A.G.; Stanton, C.; Claesson, M.J.; Cotter, P.D. 16S rRNA gene sequencing of mock microbial populations-impact of DNA extraction method, primer choice and sequencing platform. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, M.; Pilgrim, E.; Knapp, M.; Yoder, C.; Santo Domingo, J.; Banerji, A. High-throughput environmental DNA analysis informs a biological assessment of an urban stream. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stat, M.; John, J.; Di Battista, J.D.; Newman, S.J.; Bunce, M.; Harvey, E.S. Combined use of eDNA metabarcoding and video surveillance for the assessment of fish biodiversity. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 33, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, W.J.; Garcia-Robledo, C.; Uriarte, M.; Erickson, D.L. DNA barcodes for ecology, evolution, and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Zhan, A.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Haffner, G.D.; MacIsaac, H.J. Early detection of a highly invasive bivalve based on environmental DNA (eDNA). Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylemans, J.; Furlan, E.M.; Gleeson, D.M.; Hardy, C.M.; Duncan, R.P. Does size matter? An experimental evaluation of the relative abundance and decay rates of aquatic environmental DNA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 6408–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco, F.A.; Richards, E.; Flück, B.; Valentini, A.; Altermatt, F.; Brosse, S.; Walser, J.C.; Eme, D.; Marques, V.; Manel, S.; et al. Comparing the performance of 12S mitochondrial primers for fish environmental DNA across ecosystems. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Schoups, G.; Van De Giesen, N. Organic pollution of rivers: Combined threats of urbanization, livestock farming and global climate change. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullo, E.; Finzi, A.; Guarino, M. Environmental impact of livestock farming and Precision Livestock Farming as a mitigation strategy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2751–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patarón, E.R.O.; Guambo, V.M.V.; Orozco, E.G.; Casco, E.R.G. Anthropic activities and risks of contamination due to the emission of liquid waste in agriculture. Ann. For. Res. 2023, 66, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar]
- Dodds, W.K.; Perkin, J.S.; Gerken, J.E. Human impact on freshwater ecosystem services: A global perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9061–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.P.; Banaszak, A.T.; Villafañe, V.E.; Narvarte, M.A.; González, R.A.; Helbling, E.W. Anthropogenic pollution of aquatic ecosystems: Emerging problems with global implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, C.S.; Turner, C.R.; Deiner, K.; Klymus, K.E.; Thomsen, P.F.; Murphy, M.A.; Spear, S.F.; McKee, A.; Oyler-McCance, S.J.; Cornman, R.S.; et al. Critical considerations for the application of environmental DNA methods to detect aquatic species. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).