Effects of Maternal Supplementation with Organic Trace Minerals including Zinc, Manganese, Copper, and Cobalt during the Late and Post-Partum Periods on the Health and Immune Status of Japanese Black Calves
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cow Management and Dietary Treatments
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Flowcytometry
2.3.1. Cell Preparation
2.3.2. Cell Sorting
2.4. Total RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR Analysis of Cytokines
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
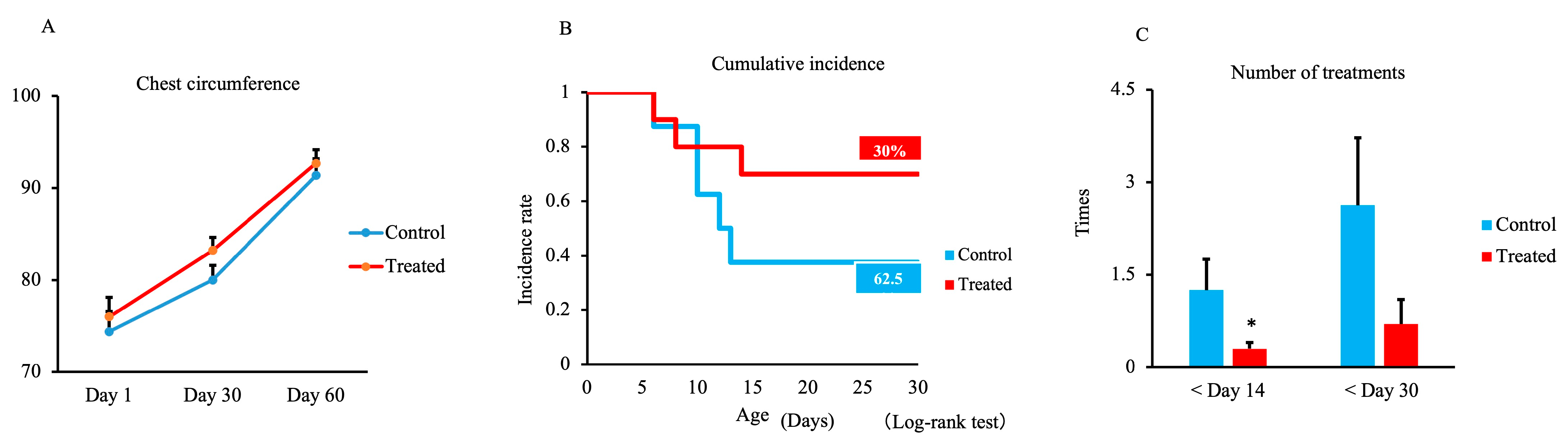
3.1. Chest Circumference, Respiratory and Digestive Disease Incidence, and Treatment
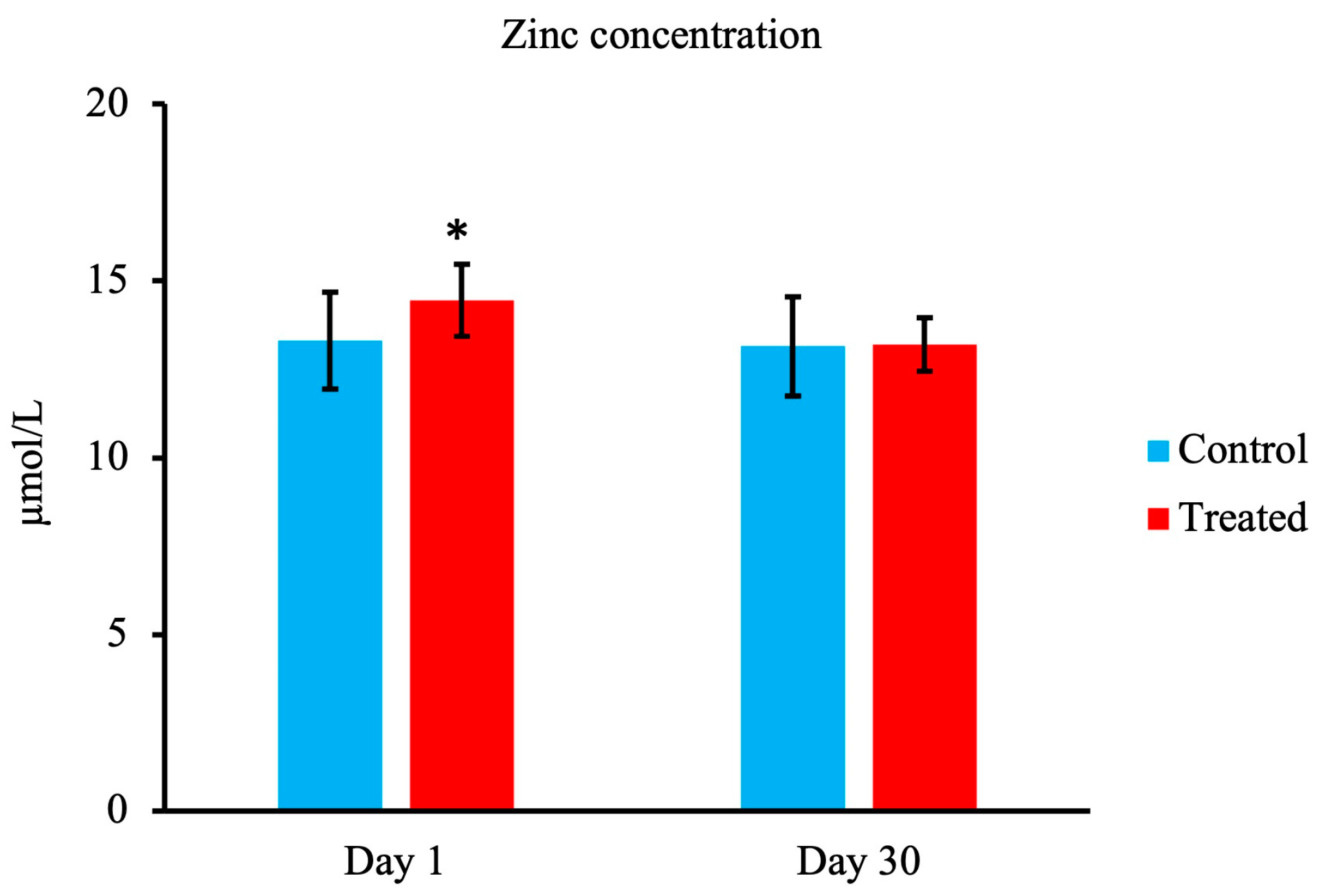
3.2. Zn Concentration
3.3. Lymphocyte Count and Percentages of Lymphocytes and Monocytes
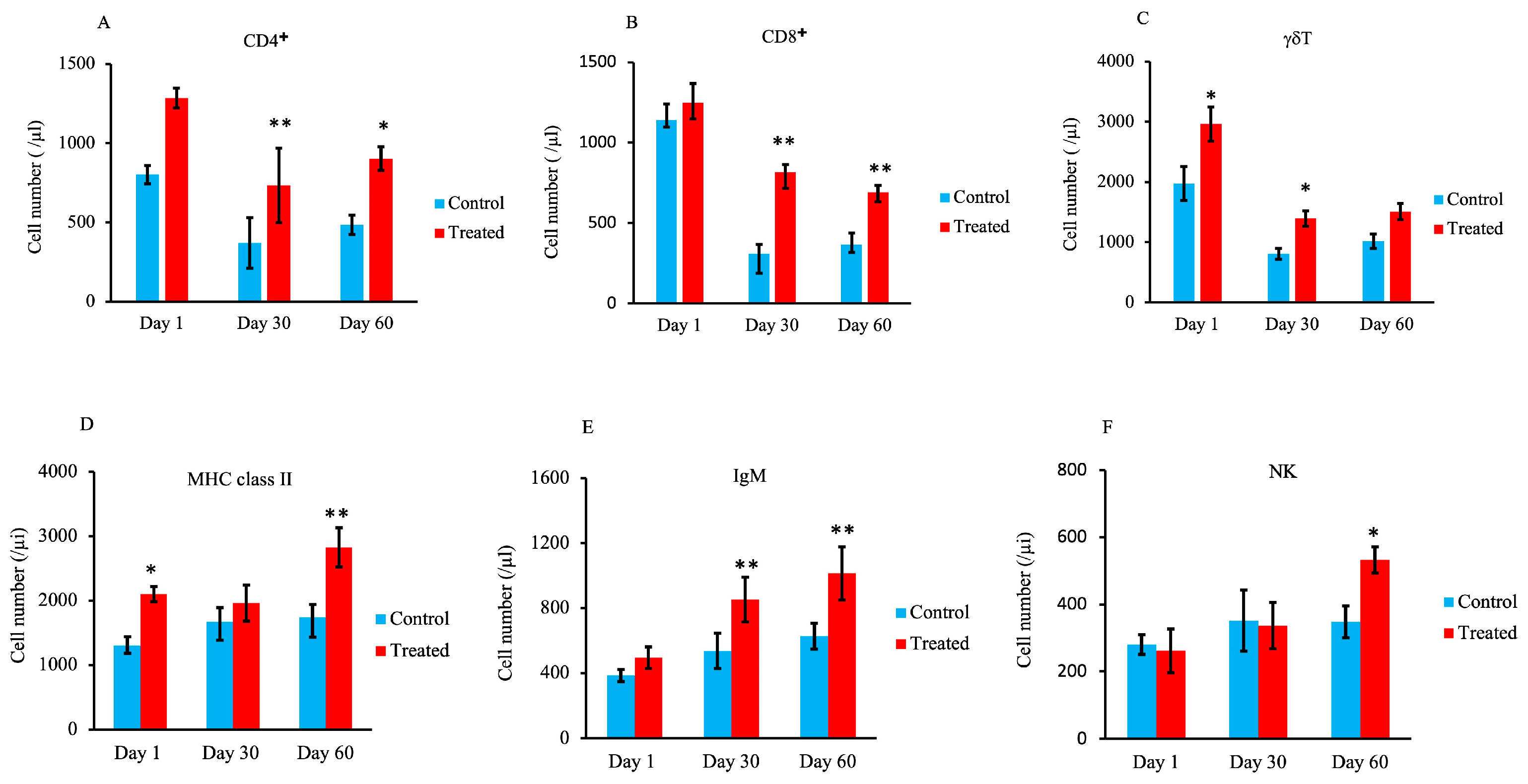
3.4. Lymphocyte Subset Analysis
3.5. Cytokine-Encoding mRNA Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, G.; Bazer, F.W.; Wallace, J.M.; Spencer, T.E. Board-invited review: Intrauterine growth retardation: Implications for the animal sciences. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 2316–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavatte-Palmer, P.; Velazquez, M.A.; Jammes, H.; Duranthon, V. Review: Epigenetics, developmental programming and nutrition in herbivores. Animal 2018, 12, S363–S371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidiroglou, M.; Knipfel, J.E. Maternal-fetal relationships of copper, manganese, and sulfur in ruminants. A review. J. Dairy. Sci. 1981, 64, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranade, R.; Talukder, S.; Muscatello, G.; Celi, P. Assessment of oxidative stress biomarkers in exhaled breath condensate and blood of dairy heifer calves from birth to weaning. Vet. J. 2014, 202, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuelo, A. Symposium review: Late-gestation maternal factors affecting the health and development of dairy calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3882–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacometo, C.B.; Alharthi, A.S.; Zhou, Z.; Luchini, D.; Loor, J.J. Maternal supply of methionine during late pregnancy is associated with changes in immune function and abundance of microRNA and mRNA in Holstein calf polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J. Dairy. Sci. 2018, 101, 8146–8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, T.L.; Whittier, J.C.; Geary, T.W.; Kimberling, C.V.; Johnson, A.B. Effects of trace mineral supplementation on cow-calf performance, reproduction, and immune function. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2000, 16, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquess, R.S.; Cooke, R.F.; Rodrigues, M.C.; Cappellozza, B.I.; Mills, R.R.; Larson, C.K.; Moriel, P.; Bohnert, D.W. Effects of organic or inorganic cobalt, copper, manganese, and zinc supplementation to late-gestating beef cows on productive and physiological responses of the offspring. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Emon, M.; Sanford, C.; McCoski, S. Impacts of bovine trace mineral supplementation on maternal and offspring production and health. Animals 2020, 10, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, K.M.; Cooke, R.F.; Colombo, E.A.; Rett, B.; de Sousa, O.A.; Harvey, L.M.; Russell, J.R.; Pohler, K.G.; Brandao, A.P. Supplementing organic-complexed or inorganic Co, Cu, Mn, and Zn to beef cows during gestation: Physiological and productive response of cows and their offspring until weaning. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 99, skab095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostetler, C.E.; Kincaid, R.L.; Mirando, M.A. The role of essential trace elements in embryonic and fetal development in livestock. Vet. J. 2003, 166, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepper, M.R.; Black, M.M. B12 in fetal development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spears, J.W. Organic trace minerals in ruminant nutrition. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996, 58, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swecker, W.S. Trace mineral feeding and assessment. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2014, 30, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, A.K.; Pfaender, S.; Hagmeyer, S.; Tarana, L.; Mattes, A.K.; Briel, F.; Küry, S.; Boeckers, T.M.; Grabrucker, A.M. Characterization of zinc amino acid complexes for zinc delivery in vitro using Caco-2 cells and enterocytes from hiPSC. BioMetals 2017, 3, 643–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, R.S.; Cooke, R.F.; Rodrigues, M.C.; Moriel, P.; Bohnert, D.W. Impact of cow body condition score during gestation on the weaning performance of the offspring. Livest. Sci. 2016, 191, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funston, R.N.; Larson, D.M.; Vonnahme, K.A. Effects of maternal nutrition on conceptus growth and offspring performance: Implications for beef cattle production. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, E205–E215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirement of Beef Cattle, 8th ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; 242p. [Google Scholar]
- Baakhtari, M.; Imaizumi, N.; Kida, T.; Yanagita, T.; Ramah, A.; Ahmadi, P.; Takebe, N.; Iwamoto, Y.; Korosue, K.; Tsuzuki, N.; et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids on immune status of young racing horses. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isashiki, Y.; Ohashi, Y.; Imatake, S.; Baakhtari, M.; Ramah, A.; Kida, T.; Yanagita, T.; Yasuda, M. Studies on the immune status of calves with chronic inflammation and thymus atrophy. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, H. The mammary gland and neonate mucosal immunity. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1999, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, I.; Mee, J.F.; Earley, B.; More, S.J. Calf health from birth to weaning. I. General aspects of disease prevention. Ir. Vet. J. 2011, 64, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, G.A.; Rosa, D.E.; Turic, E.; Relling, A.E.; Galarza, E.; Fazzio, L.E. Effects of copper and zinc supplementation on weight gain and hematological parameters in pre-weaning calves. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2018, 185, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godden, S.M.; Lombard, J.E.; Woolums, A.R. Colostrum management for dairy calves. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2019, 35, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, A.J.; Heinrichs, A.J. Invited review: The importance of colostrum in the newborn dairy calf. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 2733–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enjalbert, F.; Lebreton, P.; Salat, O. Effects of copper, zinc and selenium status on performance and health in commercial dairy and beef herds: Retrospective study. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2006, 90, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, Y.; Dufrasne, I. Selenium in cattle: A review. Molecules 2016, 21, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springman, S.A.; Maddux, J.; Drewnoski, M.E.; Funston, R.N. Effect of injectable trace on reproductive performance in beef heifers. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2018, 34, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, R.S.; Ireland, F.A.; Shike, D.W. Influence of repeated trace mineral injections during gestation on beef heifer and subsequent calf performance. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2019, 3, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Brattain, R.S.; Shike, D.W. Effects of maternal supplementation with an injectable trace mineral containing copper, manganese, zinc, and selenium on subsequent steer finishing phase performance and carcass characteristics. Animals 2020, 10, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidiroglou, M. Trace elements in the fetal and neonate ruminant: A review. Can. Vet. J. 1980, 21, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Underwood, E.J.; Suttle, N.F. The Mineral Nutrition of Livestock, 3rd ed.; CAB International: Oxon, UK, 1999; pp. 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Sprinkle, J.E.; Cuneo, S.P.; Frederick, H.M.; Enns, R.M.; Schafer, D.W.; Carstens, G.E.; Daugherty, S.B.; Noon, T.H.; Rickert, B.M.; Reggiardo, C. Effects of a long-acting, trace mineral, reticulorumen bolus on range cow productivity and trace mineral profiles. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 1439–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacometo, C.B.; Osorio, J.S.; Socha, M.; Correa, M.N.; Piccioli-Cappelli, F.; Trevisi, E.; Loor, J.J. Maternal consumption of organic trace minerals alters calf systemic and neutrophil mRNA and microRNA indicators of inflammation and oxidative stress. J. Dairy. Sci. 2015, 98, 7717–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, A.G.V.; Lima, F.S.; Bicalho, M.L.S.; Kussler, A.; Lima, S.F.; Felippe, M.J.; Bicalho, R.C. Effect of an injectable trace mineral supplement containing selenium, copper, zinc, and manganese on immunity, health, and growth of dairy calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 4216–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, P.; Benedetti, G.; Albarede, F.; Miossec, P. Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, R.S.; Volk, M.J.; Ireland, F.; Shike, D.W. Effects of maternal supplementation with an injectable trace mineral on subsequent calf performance and inflammatory response. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 4475–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafer-Weaver, K.A.; Corl, C.M.; Sordillo, L.M. Shifts in bovine CD4+ subpopulations increase T-helper-2 compared with T-helper-1 effector cells during the postpartum period. J. Dairy. Sci. 1999, 82, 1696–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervevan, J.; Chakrabarti, L.A. Role of CD4+ T cells in the control of viral infections: Recent advances and open questions. Int. J Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidlaw, B.J.; Craft, J.E.; Kaech, S.M. The multifaceted role of CD4+ T cells in CD8+ T cell memory. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, H.J.; Biffar, L.; Steinbach, S.; Guzman, E.; Connelley, T.; Morrison, I.; Vordermeier, H.M.; Villarreal-Ramos, B. Ag85A-specific CD4+ T cell lines derived after boosting BCG-vaccinated cattle with Ad5-85A possess both mycobacterial growth inhibition and anti-inflammatory properties. Vaccine 2018, 36, 2850–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ten Bruggencate, S.J.M.; Hillyer, L.M.; Woodward, B.D. The proportion of CD45RA CD62L (Quiescent-Phenotype) T cells within the CD8 subset increases in advanced weight loss in the protein- or energy-deficient weanling mouse. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 3266–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harp, J.A.; Waters, T.E.; Goff, J.P. Lymphocyte subsets and adhesion molecule expression in milk and blood of periparturient dairy cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 102, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrzad, J.; Janssen, D.; Duchateau, L.; Burvenich, C. Increase of Escherichia coli inoculum doses accelerates CD8+ T-cell trafficking in primiparous bovine mammary gland. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Goff, J.P.; Kehrli, M.E.; Harp, J.A. Phenotype analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in periparturient dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germain, R.N. T-cell development and the CD4-CD8 lineage decision. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, K.M.; McGuire, T.C.; Fraser, D.G.; Hines, S.A. Rhodococcus equi-infected macrophages are recognized and killed by CD8+ T lymphocytes in a major histocompatibility complex class I-unrestricted fashion. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 7073–7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnecke, B.J.; Foote, M.R.; Smith, J.M.; Pesch, B.A.; van Amburgh, M.E. Composition and functional capacity of blood mononuclear leukocyte populations from neonatal calves on standard and intensified milk replacer diets. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3592–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopp, P.; Howard, C.J.; Hope, J.C. Flow cytometric detection of gamma interferon can effectively discriminate mycobacterium bovis BCG-vaccinated cattle from M. bovis- infected cattle. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2006, 13, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, S.J.; Hope, J.C. Enhanced secretion of interferon-γ by bovine γδ T cells induced by coculture with mycobacterium bovis-infected dendritic cells: Evidence for reciprocal activating signals. J. Immunol. 2009, 126, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, E.; Hope, J.; Taylor, G.; Smith, A.L.; Cubillos-Zapata, C.; Charleston, B. Bovine γδ T cells are a major regulatory T cell subset. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, J.L.; Sacco, R.E.; Baldwin, C.L.; Telfer, J.C.; Palmer, M.V.; Ray Waters, W. The role of gamma delta T cells in immunity to Mycobacterium bovis infection in cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 159, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Sentsui, H.; Inoshima, Y.; Inumaru, S. Increase in γδ T cells in the blood of cattle persistently infected with bovine leukemia virus following administration of recombinant bovine IFN-γ. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2004, 10, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambayashi, T.; Laufer, T.M. Atypical MHC class II-expressing antigen-presenting cells: Can anything replace a dendritic cell? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, J.Y.; Chai, J.G.; Lechler, R. Antigen presentation by mouse CD4+ T cells involving acquired MHC class II: Peptide complexes: Another mechanism to limit clonal expansion? Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2003, 101, 2704–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Glovert, D.M.; Brownstein, D.; Burchett, S.; Larsen, A.; Wilson, C.B. Expression of HLA class II antigens and secretion of interleukin-1 by monocytes and macrophages from adults and neonates. Immunology 1987, 61, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Menge, C.; Neufeld, B.; Hirt, W.; Bauerfeind, R.; Baljer, G.; Wieler, L.H. Phenotypical characterization of peripheral blood leucocytes in the newborn calf. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 1999, 46, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonnecke, B.J.; Waters, W.R.; Foote, M.R.; Horst, R.L.; Fowler, M.A.; Miller, B.L. In vitro effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α secretion by blood leukocytes from young and adult cattle vaccinated with mycobacterium bovis BCG. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2003, 73, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaraman, V.; Nonnecke, B.J.; Horst, R.L. Effects of replacement of native Fat in colostrum and milk with coconut oil on fat-soluble vitamins in serum and immune function in calves. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 2380–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boes, M. Mice deficient in secreted IgM impaired IgG antibody responses in enhanced B1 cell development. J. Immunol. 1998, 166, 4476–4787. [Google Scholar]
- Heyman, B.; Pilstrom, L.; Shulman, M.J. Complement activation is required for IgM-mediated enhancement of the antibody response. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 167, 1999–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, C.A.; Mahan, S.; Entrican, G.; Hope, J.C. Interactions between natural killer cells and dendritic cells favour T helper1-type responses to BCG in calves. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelemy, A.; Sencio, V.; Soulard, D.; Deruyter, L.; Faveeuw, C.; le Goffic, R.; Trottein, F. Interleukin-22 immunotherapy during severe influenza enhances lung tissue integrity and reduces secondary bacterial systemic invasion. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86, e00706–e00717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menge, C.; Blessenohl, M.; Eisenberg, T.; Stamm, I.; Baljer, G. Bovine ileal intraepithelial lymphocytes represent target cells for Shiga toxin 1 from Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, K.; Kataoka, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Kirisawa, R.; Iwai, H. Detection of cytokines in bovine colostrum. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2000, 76, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gengelbach, G.P.; Spears, J.W. Effects of dietary copper and molybdenum on copper status, cytokine production, and humoral immune response of calves. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 3286–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaleco, S.; Swainson, L.; Dardalhon, V.; Burjanadze, M.; Kinet, S.; Taylor, N. Homeostasis of naive and memory CD4 + T cells: IL-2 and IL-7 differentially regulate the balance between proliferation and fas-mediated apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Yu, A.; Dee, M.J.; Malek, T.R. IL-2R signaling is essential for functional maturation of regulatory T cells during thymic development. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyman, O.; Sprent, J. The role of interleukin-2 during homeostasis and activation of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendickova, K.; Fric, J. Roles of IL-2 in bridging adaptive and innate immunity, and as a tool for cellular immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liblau, R.S.; Singer, S.M.; McDevitt, H.O. Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cells in the pathogenesis of organ-specific autoimmune diseases. Immunol. Today 1995, 16, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Else, K.J.; Finkelman, F.D.; Maliszewski, C.R.; Grencis, R.K. Cytokine-mediated regulation of chronic intestinal helminth infection. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.E.; Maizels, R.M. Diversity and dialogue in immunity to helminths. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, C.M.; Snelgrove, R.J. Type 2 immunity: Expanding our view. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaat1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, P. IL-1 2: Initiation cytokine for cell-mediated immunity. Science 1993, 260, 496–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, P.; Reiser, H. IL-4: Role in disease and regulation of production. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 113, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinchieri, G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | Primer | Sequences | Product Size | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Base Pairs) | ||||
| GAPDH | F | GTTCAACGGCACAGTCAAGGCAGAG | 123 | NM_001034034 |
| R | ACCACATACTCAGCACCAGCATCAC | |||
| IL-1β | F | GCCTACGCACATGTCTTCCA | 111 | NM_174093 |
| R | TGCGTCACACAGAAACTCGTC | |||
| IL-2 | F | TGCTGGATTTACAGTTGCTT | 111 | XM_024976996 |
| R | TCAATTCTGTAGCGTTAACCT | |||
| IL-4 | F | ATCAAAACGCTGAACATCCTC | 142 | NM_173921 |
| R | TCCTGTAGATACGCCTAAGCTC | |||
| IL-6 | F | AGCTCTCATTAAGCGCATGG | 168 | NM_173923 |
| R | ATCGCCTGATTGAACCCAG | |||
| IL-10 | F | GGCCTGACATCAAGGAGCAC | 103 | NM_174088 |
| R | CTCTTGTTTTCGCAGGGCAGA | |||
| IL-12 | F | CCGCATTCCTACTTCTCCCT | 178 | XM_027545793 |
| R | ACACAGATGCCCATTCACT | |||
| IFN-γ | F | TGATTCAAATTCCGGTGGAT | 108 | NM_174086 |
| R | TCTTCCGCTTTCTGAGGTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramah, A.; Kato, T.; Shinya, U.; Baakhtari, M.; Imatake, S.; Jadi, A.R.; Yasuda, M. Effects of Maternal Supplementation with Organic Trace Minerals including Zinc, Manganese, Copper, and Cobalt during the Late and Post-Partum Periods on the Health and Immune Status of Japanese Black Calves. Animals 2023, 13, 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233679
Ramah A, Kato T, Shinya U, Baakhtari M, Imatake S, Jadi AR, Yasuda M. Effects of Maternal Supplementation with Organic Trace Minerals including Zinc, Manganese, Copper, and Cobalt during the Late and Post-Partum Periods on the Health and Immune Status of Japanese Black Calves. Animals. 2023; 13(23):3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233679
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamah, Amany, Tomohiro Kato, Urara Shinya, Mahmoud Baakhtari, Shoichiro Imatake, Arvendi Rachma Jadi, and Masahiro Yasuda. 2023. "Effects of Maternal Supplementation with Organic Trace Minerals including Zinc, Manganese, Copper, and Cobalt during the Late and Post-Partum Periods on the Health and Immune Status of Japanese Black Calves" Animals 13, no. 23: 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233679
APA StyleRamah, A., Kato, T., Shinya, U., Baakhtari, M., Imatake, S., Jadi, A. R., & Yasuda, M. (2023). Effects of Maternal Supplementation with Organic Trace Minerals including Zinc, Manganese, Copper, and Cobalt during the Late and Post-Partum Periods on the Health and Immune Status of Japanese Black Calves. Animals, 13(23), 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233679








