Zoonotic Parasites in Artiodactyls with Emphasis on the Feral Boar in the Atlantic Forest, State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
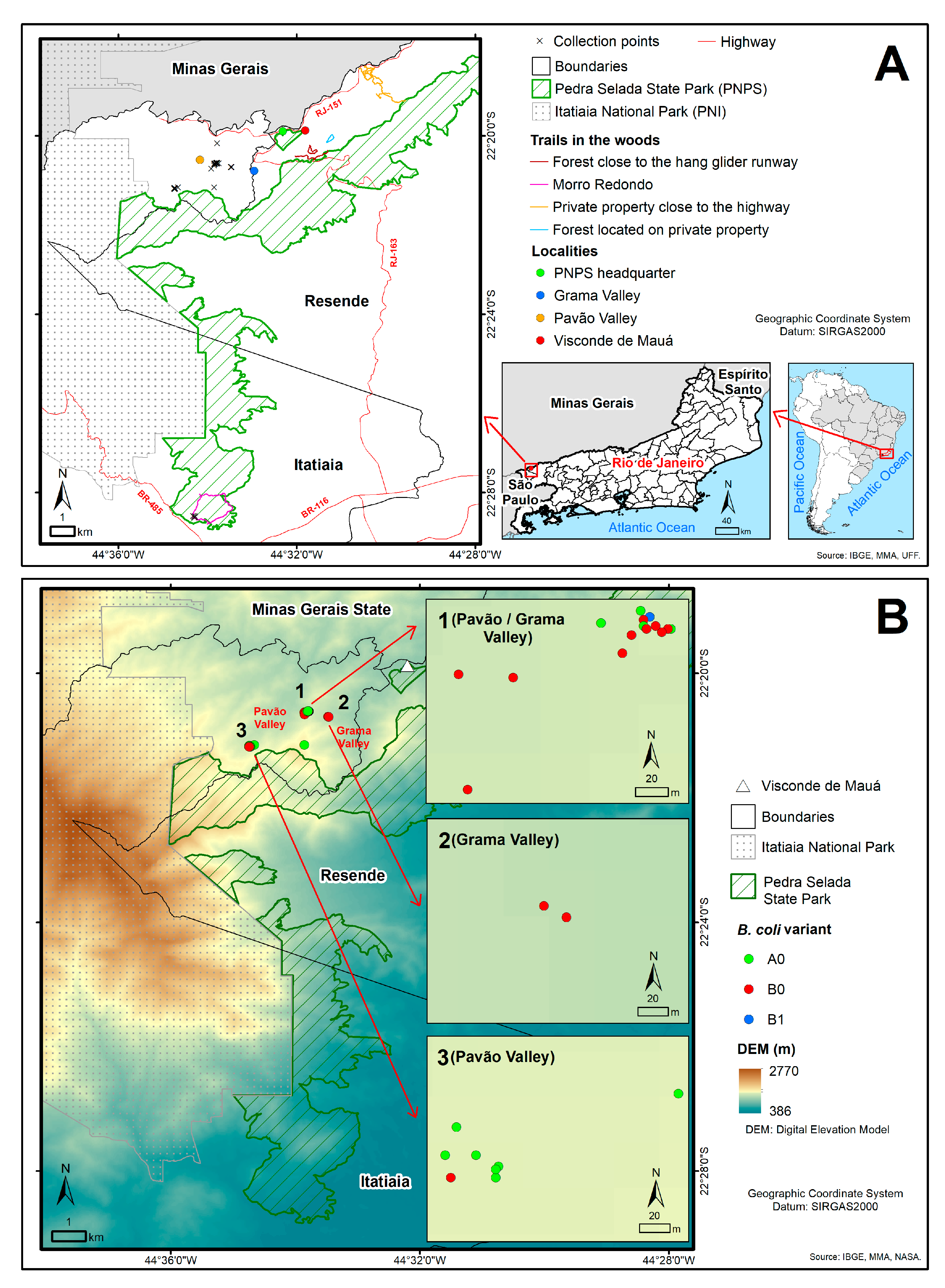
2.1. Fecal Sample Collection Site
2.2. Collection of Fecal Samples
2.3. Host Identification—Macroscopic Morphological Analysis
2.4. Host Identification—Molecular Analysis
2.5. Microscopic Parasitological Diagnosis
2.6. Molecular Analysis of Ciliated Protozoa
2.7. Analysis of the Results
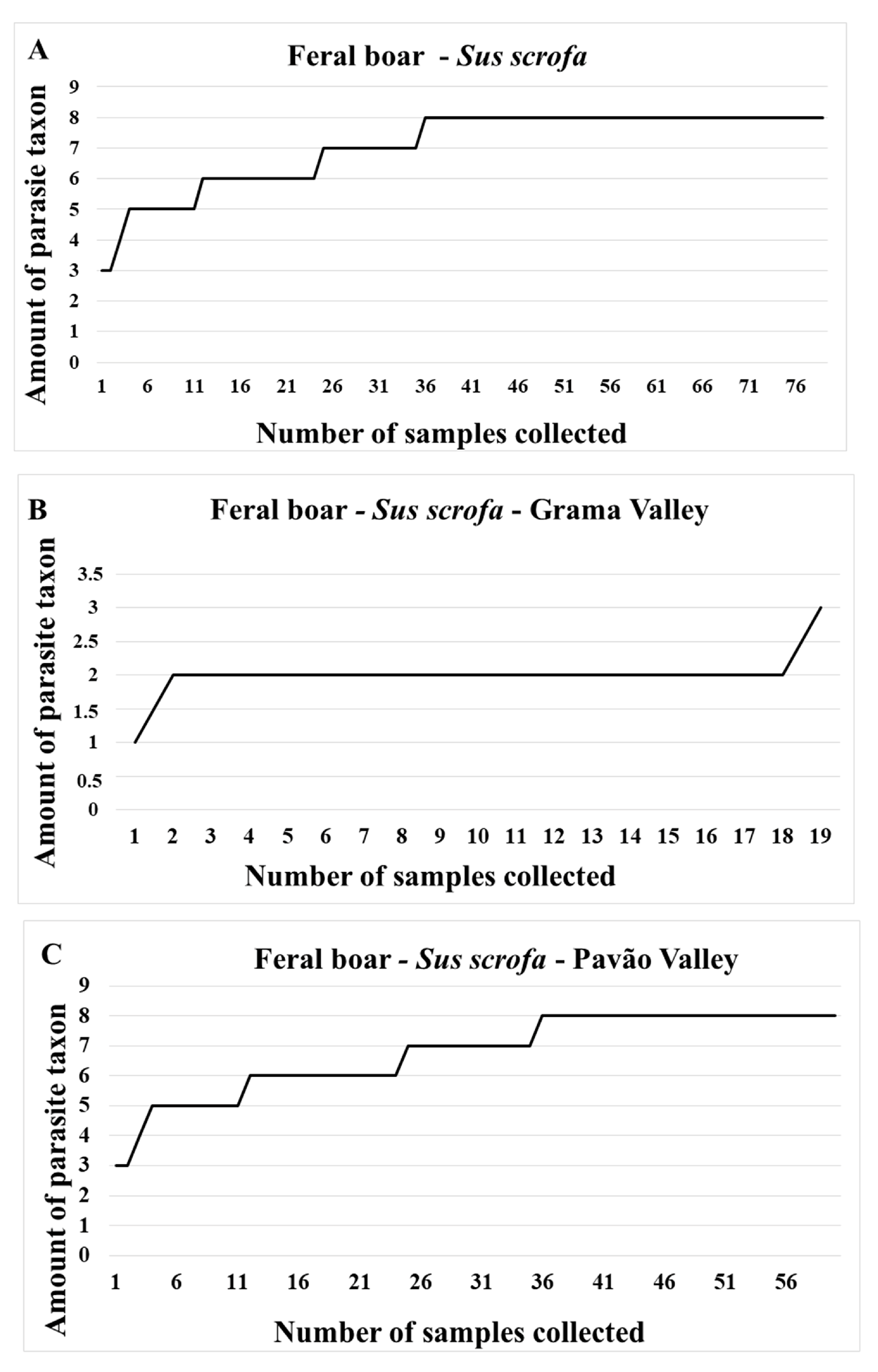
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiepolo, L.M.; Tomas, W.M. Ordem Artiodactyla. In Mamíferos do Brasil; Reis, N.R., Peracchi, A.L., Pedro, A.W., Lima, I.P., Eds.; Zoologia e Ecologia de Mamíferos: Londrina, Brazil, 2006; pp. 283–304. [Google Scholar]
- Lui, J.F. Estudo citogenético de javalis puros (Sus scrofa scrofa) e híbridos nas regiões sudeste e sul do Brasil. Rev. Educ. Contin. CRMV-SP 2000, 3, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, C.A. Porcos Selvagens no Parque Nacional do Itatiaia: Distribuição e Impactos. 2015; pp. 1–25. Available online: https://www.icmbio.gov.br/parnaitatiaia/images/stories/boletins_de_pesquisa/bpni_v21_2.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Crema, T.D.; Henkes, J.A. Uma análise sobre os impactos ambientais de espécies exóticas no Bioma Pampa: Da proliferação ao controle necessário das populações de Sus scrofa. Rev. Elet. Cien. UERGS 2021, 7, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, T.A. Uso de Habitat e Padrão de Atividade do Javali em Áreas do Domínio Atlântico. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de São João Del-Rei, São João del Rei, Minas Gerais, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aranda, C.; Serrano-Martínez, E.; Tantaleán, M.; Quispe, M.; Casas, G. Identificación y frecuencia de parásitos gastrointestinales en félidos silvestres en cautiverio en el Perú. Rev. Investig. Vet. Perú 2013, 24, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangini, P.R.; Vidolin, G.P.; Velastin, G.O. Pesquisa de macroparasitos em carnívoros selvagens: Uma ferramenta para a conservação. In Manejo e Conservação de Carnívoros Neotropicais; Morato, R.G., Rodrigues, F.H.G., Eizirik, E., Mangini, P.R., Azevedo, F.C.C., Marinho-Filho, J.J., Eds.; IBAMA: São Paulo, Brazil, 2006; pp. 307–323. [Google Scholar]
- Barutzki, D.; Schaper, R. Endoparasites in dogs and cats in Germany 1999–2002. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 90, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulin, R. The functional importance of parasites in animal communities: Many roles at many levels? Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvopina, M.; Caballero, H.; Morita, T.; Korenaga, M. Case Report: Human Pulmonary Infection by the Zoonotic Metastrongylus salmi Nematode. The First Reported Case in the Americas. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 871–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, K.J.L.; Calegar, D.A.; Santos, J.P.; Bacelar, P.A.A.; Coronato-Nunes, B.; Reis, E.R.C.; Bóia, M.N.; Carvalho-Costa, F.A.; Jaeger, L.H. Genetic diversity of Ascaris spp. infecting humans and pigs in distinct Brazilian regions, as revealed by mitochondrial DNA. PloS ONE 2019, 14, e0218867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.K.M.; Dib, L.V.; Amendoeira, M.R.; Class, C.C.; Pinheiro, J.L.; Fonseca, A.B.M.; Barbosa, A.D.S. Balantidiasis in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop. 2021, 223, 106069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, H.H.; Takeuchi-Storm, N.; Enemark, H.L.; Nielsen, S.T.; Larsen, G.; Chriél, M. Surveillance of important bacterial and parasitic infections in Danish wild boars (Sus scrofa). Acta Vet. Scand. 2020, 62, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaymani-Mohammadi, S.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Zoonotic implications of the swine-transmitted protozoal infections. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 10, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, S.A.; Dib, L.V.; Bastos, O.M.; Amendoeira, M.R.R. Balantidiasis. In Textbook of Parasitic Zoonoses, Microbial Zoonoses; Parija, S.C., Chaudhury, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapure, 2022; pp. 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, F.L.; Ramirez-Avila, L. Current world status of Balantidium coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, V. Balantidium coli. In Parasitic Protozoa; Kreier, J.P., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Horefti, E. The Importance of the One Health Concept in Combating Zoonoses. Pathogens 2023, 12, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parques Estaduais Rio de Janeiro. 2017. Available online: http://parquesestaduais.inea.rj.gov.br/peps.php (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Dib, L.V.; Palmer, J.P.S.; Class, C.S.C.; Pinheiro, J.L.; Ramos, R.C.F.; Dos Santos, C.R.; Fonseca, A.B.M.; Rodríguez-Castro, K.G.; Gonçalves, C.F.; Galetti, P.M., Jr.; et al. Non-invasive sampling in Itatiaia National Park, Brazil: Wild mammal parasite detection. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chame, M. Terrestrial Mammal Feces: A Morphometric Summary and Description. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2003, 98, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, P.L.; Tomás, W.M. Guia de Rastros e Outros Vestígios de Mamíferos do Pantanal, 2nd ed.; Embrapa Pantanal: Corumbá, Brasil, 2008; 139p. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves, P.B.; Graeff, V.G.; Lion, M.B.; Oliveira, L.R.; Eizirik, E. DNA barcoding meets molecular scatology: Short mtDNA sequences for standardized species assignment of carnivore noninvasive samples. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2012, 12, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caparroz, R.; Mantellatto, A.M.; Bertioli, D.J.; Figueiredo, M.G.; Duarte, J.M. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome and a set of polymorphic microsatellite markers through next-generation sequencing for the brown brocket deer Mazama gouazoubira. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2015, 38, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasue, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Honma, D.; Nishibori, N.; Nishibori, M.; Wada, Y. Genbank AP003427. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/AP003427 (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Ritchie, L.S. An ether sedimentation technique for routine stool examinations. Bull. U S Army Med. Dep. 1948, 8, 326. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.H.; Bullock, S.L.; Melvin, D.M.; Spruill, C.L. Ethyl Acetate as a substitute for diethyl ether in the formalin-ether sedimentation technique. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1979, 10, 852–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheather, A.L. The detection of intestinal protozoa and mange parasites by a flotation technique. J. Comp. Pathol. Ther. 1923, 36, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Bonfim, T.C.; Gomes, R.S. Comparação da eficiência da técnica de sedimentação pelo formaldeído-éter e da técnica de centrífugo-flutuação modificada na detecção de cistos de Giardia sp. e oocistos de Cryptosporidium sp. em amostras fecais de bezerros. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2003, 12, 135–137. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, A. O Schistosomum mansoni e a schistosomatose segundo observações feitas no Brasil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1919, 11, 121–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.S.; Ponce-Gordo, F.; Dib, L.V.; Uchôa, C.M.A.; Bastos, O.M.P.; Pissinatti, A.; Amendoeira, M.R.R. First molecular characterization of Balantioides coli (Malmsten, 1857) isolates maintained in vitro culture and from feces of captive animals, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2017, 10, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Gordo, F.; Jiménez-Ruiz, E.; Martínez-Díaz, R.A. Tentative identification of Balantidium from ostriches (Struthio camelus) as Balantidium coli-like by analysis of polymorphic DNA. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 157, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomajbiková, K.; Oboromik, M.; Horák, A.; Petrzelkova, K.J.; Grim, J.N.; Levecke, B.; Todd, A.; Mulama, M.; Kiyang, J.; Modrý, D. Novel Insights into the genetic diversity of Balantidium and Balantidium-like cyst—forming ciliates. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, J.N.; Buonanno, F. A re-description of the ciliate genus and type species Balantidium entozoon. Eur. J. Protistol. 2009, 45, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.-D.G. Analysis of intraspecific sequence variation among eight isolates of the rumen symbiont, Isotricha prostoma (Ciliophora), from two continents. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 445–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modrý, D.; Petrzelková, K.J.; Pomajbíková, K.; Tokiwa, T.; Krizek, J.; Imai, S.; Vallo, P.; Profousová, I.; Slapeta, J. The occurrence and ape-to-ape transmission of the entodiniomorphid ciliate Troglodytella abrassarti in captive gorillas. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2009, 56, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. Past: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. Available online: https://palaeo-electronica.org/2001_1/past/past.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Colwell, R.K.; Coddington, J.A. Estimating terrestrial biodiversity through extrapolation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1994, 345, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, C.J. Ecological Methodology, 2nd ed.; Longman: Harlow, UK; Addison Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 1–624. [Google Scholar]
- Dib, L.V. Helmintos e Protozoários Gastrintestinais em Material Fecal de Mamíferos Carnívoros e Artiodáctilos do Parque Nacional de Itatiaia, Brasil. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal Fluminense, Niterói, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Castro, K.G.; Saranholi, B.H.; Bataglia, L.; Blanck, D.V.; Galetti, P.M., Jr. Molecular species identification of scat samples of South American felids and canids. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2018, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-la-Muela, N.; Hernández-de-Luján, S.; Ferre, I. Helminths of wild boar in Spain. J. Wildl. Dis. 2001, 37, 840–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, C.B.; Madeira de Carvalho, L.; Fazendeiro, I.; Castro Rego, F.; Afonso-Roque, M. Contribution for the knowledge of wild boar (Sus scrofa L.) helmintic fauna in Tapada Nacional de Mafra, an enclosured hunting area. Rev. Iber. Parasitol. 2004, 64, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Brandão, M.L.; Chame, M.; Cordeiro, J.L.P.; Chaves, S.A.M. Diversidade de helmintos intestinais em mamíferos silvestres e domésticos na Caatinga do Parque Nacional Serra da Capivara, Sudeste do Piauí, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2009, 18, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, H.C.D. Helmintos Intestinais de Tayassuidae e Suidae (Mammalia: Artiodactyla) no Pantanal: Um Estudo Sobre a Circulação de Espécies na Reserva Particular do Patrimônio Nacional SESC Pantanal e Seu Entorno Barão de Melgaço, Mato Grosso, Brasil. Master’s Thesis, Escola Nacional de Saúde Pública, Fundação Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, M.; Sarkari, B.; Mowlavi, G.R. Helminth parasites of wild boars, Sus scrofa, in Bushehr Province, Southwestern Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2016, 11, 377–382. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5256055/pdf/IJPA-11-377.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2022). [PubMed]
- De-la-Rosa-Arana, J.L.; Ponce-Noguez, J.B.; Reyes-Rodríguez, N.E.; Veja-Sánchez, V.; Zepeda-Velázquez, A.P.; Martínez-Juárez, V.M.; Gómez-De-Anda, F.R. Helminths of the wild boar (Sus scrofa) from units of conservation management and sustainable use of wildlife installed in the eastern economic region of Mexico. Animals 2021, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, C.H. Ecologia e Manejo de Javali (Sus scrofa L.) na América do Sul. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- González, S.; Aristimuño, M.P.; Elizondo, C.; Bidegaray-Batista, L.; de Faria Peres, P.H.; Duarte, J.M.B. Molecular Ecology of the Southern Gray Brocket Deer (Mazama gouazoubira Fischer, 1814). In Conservation Genetics in Mammals; Ortega, J., Maldonado, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Saavedra, L.F.; Ângulo, S.; Gonzales, J.L. Uso de metodologías de censos muestrales indirectos de fecas para evaluar endoparásitos en mamíferos silvestres: Un ensayo en la Reserva Privada de San Miguelito, Santa Cruz, Bolivia. Ecol. Boliv. 2009, 44, 56–61. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.bo/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1605-25282009000100006 (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- Holsback, L.; Cardoso, M.J.; Fagnani, R.; Patelli, T.H. Natural infection by endoparasites among free-living wild animals. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2013, 22, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dantas, C.S.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Vilela, V.L.R. Endoparasitos em veados-catingueiros (Mazama gouazoubira) mantidos em cativeiro no Semiárido Paraibano. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Vet. 2019, 26, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaymani-Mohammadi, S.; Rezaian, M.; Hooshyar, H.; Mowlavi, G.R.; Babaei, Z.; Anwar, M.A. Intestinal Protozoa in Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) in Western Iran. J. Wildl. Dis. 2004, 40, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodangeh, S.; Azami, D.; Daryani, A.; Gholami, S.; Sharif, M.; Mobedi, I.; Sarvi, S.; Soleymani, E.; Rahimi, M.T.; Pirestani, M.; et al. Parasitic helminths in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Mazandaran Province, Northern Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2018, 13, 416–422. [Google Scholar]
- De-laán-Gómez, C.; Serna-Lagunes, R.; Collado, N.M.; Romero-Salas, D.; Ávila-Nájera, D.M.; Zetina-Córdobra, P. Endoparasites in captive Odocoilleus virginianus and Mazama temama in Veracruz, México. Rev. Mex. Ciênc. Pecu. 2019, 10, 986–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plano de Manejo, P. ICMBiO. 2012. Available online: https://www.icmbio.gov.br/parnaitatiaia (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Ponce Gordo, F.; Salamaca, F.F.; Martínez, D.R. Genetic heterogeneity in Internal transcribed spacer genes of Balantidium coli (Litostomatea, Ciliophora). Protist 2011, 162, 774–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadimi, S.N.; Abedini, M.R.; Sarkari, B.; Savardashtaki, A.; Mikaeili, F. Neobalantidium coli: First molecular identification from the Eurasian wild boar, Sus scrofa in Bushehr Province, Southwestern Iran. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 6, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Yao, Q.; Dong, H.P.; Wang, S.S.; Chen, R.R.; Song, J.K.; Yan, W.C.; Zhao, G.H. Molecular characterization of Balantioides coli in pigs from Shaanxi province, northwestern China. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3075–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.-W.; Park, J.-H.; Moon, B.-Y.; Lee, K.; Lee, W.-K.; Kwak, D.; Lee, S.H. Identification of Zoonotic Balantioides coli in Pigs by Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) and Its Distribution in Korea. Anim. 2021, 11, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério do Meio Ambiente. Plano nacional de prevenção, controle e monitoramento do javali (Sus scrofa) no Brasil. 2017; pp. 1–119. Available online: https://www.gov.br/ibama/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/arquivos/arquivos-pdf/2017-planojavali-2017-2022-pdf (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Barriga, O.O. Veterinary Parasitology; Greyden Press: Dayton, OH, USA, 1995; pp. 1–293. [Google Scholar]
- IBAMA, Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis. Manual de boas práticas para o controle de javali: IBAMA. 2020; pp. 1–42. Available online: https://www.gov.br/ibama/pt-br/assuntos/notas/2020/manejo-e-controle-de-javalis/20201217Manual_do_Javali_Digital.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2021).


| Parasites | Pavão Valley (n = 72) | Grama Valley (n = 24) | Morro Redondo (n = 5) | Total of Samples (n = 101) | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sus scrofa (n = 60) | UIS artiodactyl (n = 12) | Sus scrofa (n = 19) | UIS Artiodactyl (n = 5) | Mazama gouazoubira (n = 1) | UIS Artiodactyl (n = 4) | |||
| Protozoa | 29 (48.3%) | 2 (16.6%) | 9 (47.3%) | 1 (20%) | - | 41 (40.5%) | ||
| Phylum Ciliophora cyst | 27 (45%) | 2 (16.6%) | 10 (52.6%) | 1 (20%) | - | - | 40 (39.6%) | 0.00 * |
| Unsporulated coccidian oocysts | 3 (5%) | - | - | - | - | - | 3 (2.9%) | 0.243 |
| Helmints | 22 (36.6%) | 2 (16.6%) | 3 (15.7%) | - | 1 (100%) | - | 28 (27.7%) | |
| Ascaris sp. | 9 (15%) | - | 2 (10.5%) | - | 1 (100%) | - | 12 (11.8%) | 0.004 * |
| Metastrongylus sp. | 5 (8.3%) | 1 (8.3%) | - | - | - | 6 (5.9%) | 0.027 * | |
| Strongyle | 4 (6.6%) | - | - | - | - | 4 (3.9%) | 0.118 | |
| Trichuris sp. | 4 (6.6%) | - | - | - | - | 4 (3.9%) | 0.118 | |
| Nematode larva | 6 (10%) | 1 (8.3%) | 1 (5.2%) | - | - | 8 (7.9%) | 0.005 * | |
| Unidentified nematode egg | 1 (1.6%) | - | - | - | - | 1 (1%) | 1 | |
| Total parasite positivity | 54 (53.4%) | |||||||
| Sus scrofa | Richness | Dominance | Diversity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon (H’) | p Value | Simpson (D) | p Value | |||
| Pavão Valley | 8 | 2.623 | 1.672 | 0.001 * | 7.377 | 0.041 * |
| Grama Valley | 3 | 6.213 | 6.871 | 3.787 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinheiro, J.L.; Bruno, S.F.; Dib, L.V.; Dos Santos, C.R.; Class, C.S.C.; Corrêa, L.L.; Studart Lima, M.; Motoyama, P.R.A.; Guimarães, R.J.P.S.; Amendoeira, M.R.R.; et al. Zoonotic Parasites in Artiodactyls with Emphasis on the Feral Boar in the Atlantic Forest, State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Animals 2023, 13, 3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233611
Pinheiro JL, Bruno SF, Dib LV, Dos Santos CR, Class CSC, Corrêa LL, Studart Lima M, Motoyama PRA, Guimarães RJPS, Amendoeira MRR, et al. Zoonotic Parasites in Artiodactyls with Emphasis on the Feral Boar in the Atlantic Forest, State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Animals. 2023; 13(23):3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233611
Chicago/Turabian StylePinheiro, Jessica L., Sávio F. Bruno, Laís V. Dib, Claudijane R. Dos Santos, Camila S. C. Class, Laís L. Corrêa, Marcelo Studart Lima, Paulo Rogério A. Motoyama, Ricardo J. P. S. Guimarães, Maria Regina R. Amendoeira, and et al. 2023. "Zoonotic Parasites in Artiodactyls with Emphasis on the Feral Boar in the Atlantic Forest, State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil" Animals 13, no. 23: 3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233611
APA StylePinheiro, J. L., Bruno, S. F., Dib, L. V., Dos Santos, C. R., Class, C. S. C., Corrêa, L. L., Studart Lima, M., Motoyama, P. R. A., Guimarães, R. J. P. S., Amendoeira, M. R. R., & Barbosa, A. S. (2023). Zoonotic Parasites in Artiodactyls with Emphasis on the Feral Boar in the Atlantic Forest, State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Animals, 13(23), 3611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233611






