Effects of Diets Based on Hydrolyzed Chicken Liver and Different Protein Concentrations on the Formation and Deamination of Biogenic Amines and Total Antioxidant Capacity of Dogs
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Housing
2.2. Diets
2.3. Biogenic Amine Analysis
2.4. Plasma Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) and Diamine Oxidase (DAO) Activities and Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC)
2.5. Calculations and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biogenic Amines in Protein Sources and Diets
3.2. Biogenic Amines Intake and Fecal Excretion
3.3. Balance of Biogenic Amines
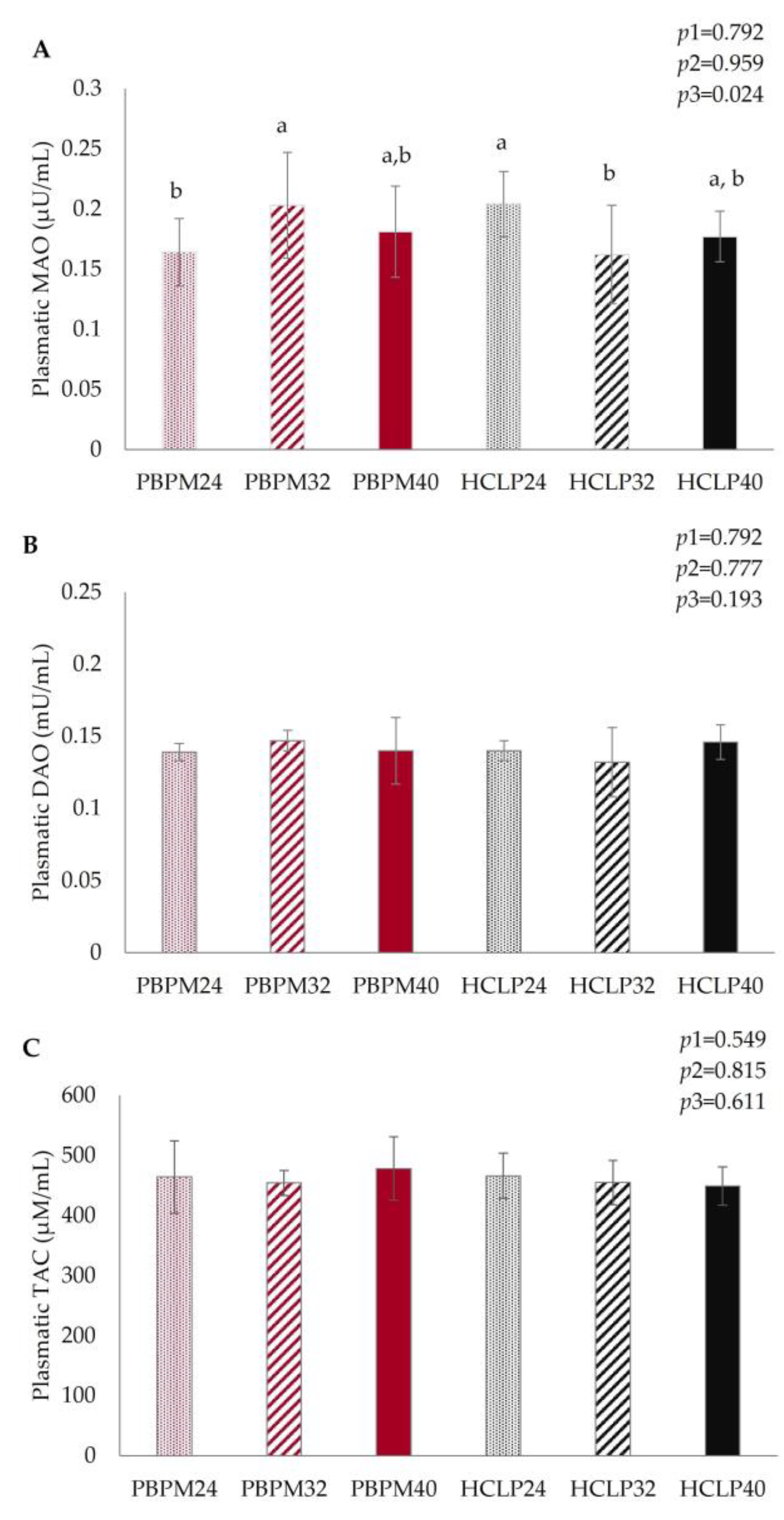
3.4. Plasmatic Activities of MAO, DAO, and TAC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ten Brink, B.; Damink, C.; Joosten, H.M.L.J.; Huis in’t Veld, J.H.J. Occurrence and formation of biologically active amines in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1990, 11, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddern, V.; Mazzuco, H.; Fonseca, F.N.; De Lima, G.J.M.M. A review on biogenic amines in food and feed: Toxicological aspects, impact on health and control measures. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2019, 59, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Impact of Biogenic Amines on Food Quality and Safety. Foods 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cave, N.J. Hydrolyzed protein diets for dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2006, 36, 1251–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Alvarez, O.; Chamorro, S.; Brenes, A. Protein hydrolysates from animal processing by-products as a source of bioactive molecules with interest in animal feeding: A review. Food Res. Int. 2015, 73, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.; Wu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Wang, G.; Wu, G. Protein hydrolysates in animal nutrition: Industrial production, bioactive peptides, and functional significance. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laflamme, D. Development and validation of a body condition score system for dogs: A clinical tool. Canine Pract. 1997, 22, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, M.; Li, K.; Liu, S.; Lin, D.K.J. Balanced incomplete Latin square designs. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2013, 143, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEDIAF—The European Pet Food Industry Federation. Nutritional Guidelines for Complete and Complementary Foods for Dogs and Cats; FEDIAF Press: Bruxeles, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- NRC. National Research Council. Nutrient Requirements of Dogs and Cats; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; 419p. [Google Scholar]
- Vale, S.R.; Gloria, M.B.A. Determination of biogenic amines in cheese. J. AOAC Int. 1997, 80, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójcik, W.; Łukasiewicz-Mierzejewska, M.; Damaziak, K.; Bień, D. Biogenic Amines in Poultry Meat and Poultry Products: Formation, Appearance, and Methods of Reduction. Animals 2022, 12, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, D.E.; Giombelli, A.; Botelho, B.G.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Gloria, M.B.A. Feasibility of using free bioactive amines and amino acids for quality assessment and discrimination of animal meals. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2023, 302, 115676. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, A.K.; Mohammed, R.R.; Ameen, P.S.M.; Abas, Z.A.; Ekici, K. Presence of biogenic amines in food and their public health implications: A review. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamim, N.M.; Doerr, J.A. Effect of putrefaction of poultry carcasses prior to rendering on biogenic amine production. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2003, 12, 456–460. [Google Scholar]
- Blachier, F.; Mariotti, F.; Huneau, J.F.; Tomé, D. Effects of amino acid-derived luminal metabolites on the colonic epithelium and physiopathological consequences. Amino Acids 2007, 33, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalač, P.; Krausová, P. A review of dietary polyamines: Formation, implications for growth and health and occurrence in foods. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Kalač, P. Health effects and occurrence of dietary polyamines: A review for the period 2005–mid 2013. Food Chem. 2014, 161, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Chmiel, M.; Roszko, M.; Hać-Szymańczuk, E.; Cegiełka, A.; Adamczak, L.; Florowski, T.; Pietrzak, D.; Bryła, M.; Świder, O. Changes in the microbiological quality and content of biogenic amines in chicken fillets packed using various techniques and stored under different conditions. Food Microbiol. 2022, 102, 103920. [Google Scholar]
- Löser, C.; Eisel, A.; Harms, D.; Fölsch, U.R. Dietary polyamines are essential luminal growth factors for small intestine and colonic mucosal growth and development. Gut 1999, 44, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, C.F.D.; Bortolo, M.; Marx, F.R.; Trevizan, L. Characterisation of spray dried hydrolysed chicken liver powder: Effects on palatability and digestibility when included as single source of animal protein in dog diets. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 2086–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, W.; Zadeh, K.; Vekariya, R.; Ge, Y.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Tryptophan Metabolism and Gut-Brain Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2973. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Sun, S.; Wang, P.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wang, X. The Mechanism of Secretion and Metabolism of Gut-Derived 5-Hydroxytryptamine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7931. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roager, H.M.; Licht, T.R. Microbial tryptophan catabolites in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, L.; Xiao, H.; Lin, C.; Lam, Y.Y.; Wong, H.L.X.; Gong, M.; Wu, G.; Deng, Y.; Ning, Z.; Huang, C.; et al. Gut microbiota-derived tryptamine impairs insulin sensitivity. bioRxiv, 2022; preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.S.; Backus, B.; Harris, M.; Rourke, P. Distribution of diamine oxidase and imidazole-N-methyltransferase along the gastrointestinal tract. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1969, 31, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Soh, P.X.Y.; Cely, J.M.M.; Mortlock, S.A.; Jara, C.J.; Booth, R.; Natera, S.; Roessner, U.; Crossett, B.; Cordwell, S.; Khatkar, M.S.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of 74 plasma metabolites of German shepherd dogs reveal two metabolites associated with genes encoding their enzymes. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berlowitz, I.; Egger, K.; Cumming, P. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition by Plant-Derived β-Carbolines; Implications for the Psychopharmacology of Tobacco and Ayahuasca. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 886408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elias, R.J.; Kellerby, S.S.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant activity of proteins and peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarmadi, B.H.; Ismail, A. Antioxidative peptides from food proteins: A review. Peptides 2010, 31, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Lao, F.; Pan, X.; Wu, J. Food Protein-Derived Antioxidant Peptides: Molecular Mechanism, Stability and Bioavailability. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1622. [Google Scholar]
- Miltenburg, T.Z.; da Silva, M.U.; Bosch, G.; Vasconcellos, R.S. Effects of enzymatically hydrolysed poultry byproduct meal in extruded diets on serum angiotensin-converting enzyme activity and aldosterone in cats. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 75, 64–77. [Google Scholar]
| Ingredients, g/kg as Is | Diet 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBPM24 | PBPM32 | PBPM40 | HCLP24 | HCLP32 | HCLP40 | |
| Brewers rice | 54.9 | 44.9 | 34.6 | 52.5 | 42.2 | 30.5 |
| Hydrolyzed chicken liver powder | - | - | - | 14.4 | 21.9 | 31.0 |
| Poultry by-product meal | 12.5 | 20.3 | 28.7 | - | - | - |
| Maize gluten meal | 11.6 | 15.9 | 20.0 | 11.6 | 15.9 | 20.0 |
| Swine blood plasma | 1.95 | 2.66 | 3.38 | 1.95 | 2.66 | 3.38 |
| Sugarcane fiber | 3.2 | 3.11 | 3.00 | 3.65 | 3.80 | 4.00 |
| Salt | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Premix mineral/vitamin 2 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| Limestone | 0.08 | - | - | 1.53 | 2.11 | 2.41 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 2.05 | 1.14 | 0.08 | 1.56 | 0.65 | 0.16 |
| Choline chloride | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.5 |
| Potassium chloride | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.46 | 0.55 | 0.42 | 0.27 |
| Phosphoric acid | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Added by coating after extrusion, g/kg | ||||||
| Poultry fat | 9.87 | 8.33 | 6.69 | 8.85 | 7.02 | 4.98 |
| Palatant enhancer 3 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| Analyzed chemical composition, % dry matter basis | ||||||
| Dry matter | 93.6 | 92.6 | 93.6 | 92.5 | 93.3 | 93.5 |
| Crude protein | 24.2 | 32.6 | 41.1 | 25.2 | 31.5 | 39.3 |
| Acid-hydrolyzed fat | 13.4 | 13.8 | 12.3 | 13.0 | 11.9 | 13.2 |
| Ash | 6.50 | 5.91 | 6.85 | 6.45 | 6.05 | 6.79 |
| Crude fiber | 10.2 | 7.83 | 9.04 | 5.80 | 9.88 | 6.15 |
| Starch | 47.7 | 37.9 | 31.0 | 44.5 | 39.2 | 30.4 |
| Gelatinization index of starch | 92.7 | 99.0 | 90.7 | 97.6 | 93.3 | 91.7 |
| Gross energy, kcal/kg | 4921 | 5164 | 5246 | 5023 | 4961 | 5166 |
| Metabolizable energy, kcal/kg | 3842 | 3464 | 3338 | 3537 | 3256 | 3586 |
| Biogenic Amines 1 | Total Amines 2 | BAI 3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | CAD | TYR | HIS | AGM | SPD | PHE | SPM | |||
| Ingredient 4, mg/kg as is | ||||||||||
| PBPM | 648 | 784 | 556 | 39.3 | 33.7 | 34.3 | ND | ND | 2095 | 2027 |
| HCLP | 15.2 | 42.4 | 105 | 12.6 | 3.82 | 243 | 3.63 | 489 | 915 | 175 |
| Diet 5, mg/kg as is | ||||||||||
| PBPM24 | 69.8 (81.0) | 87.3 (98.0) | 68.2 (69.5) | 9.73 (4.91) | ND (4.21) | 5.78 (4.29) | 5.87 (ND) | ND (ND) | 247 (262) | 235 (253) |
| PBPM32 | 132 (132) | 152 (159) | 119 (113) | 9.70 (7.98) | 7.09 (6.84) | 13.6 (6.96) | 3.46 (ND) | ND (ND) | 437 (425) | 413 (412) |
| PBPM40 | 174 (186) | 218 (225) | 161 (160) | 18.4 (11.3) | 9.80 (9.67) | 13.5 (9.84) | ND (ND) | ND (ND) | 595 (601) | 572 (582) |
| HCLP24 | ND (2.19) | 0.40 (6.11) | 0.43 (15.1) | ND (1.81) | ND (0.55) | ND (35.0) | ND (0.52) | 0.67 (70.4) | 1.50 (132) | 1 (25) |
| HCLP32 | 12.5 (3.33) | 18.5 (9.29) | 36.5 (23.0) | 5.97 (2.76) | 1.39 (0.84) | 48.2 (53.2) | 5.99 (0.79) | 53.4 (107) | 183 (200) | 73 (38) |
| HCLP40 | 15.0 (4.71) | 17.4 (13.1) | 39.1 (32.6) | 6.14 (3.91) | 1.71 (1.18) | 53.0 (75.3) | 6.82 (1.13) | 75.2 (152) | 214 (284) | 78 (54) |
| Biogenic Amines 2 | Total Amines 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | CAD | TYR | HIS | AGM | SPD | PHE | SPM | |||
| PS 4 | PBPM | 153 ± 52.9 a | 186 ± 65.6 a | 142 ± 46.6 a | 15.4 ± 5.08 a | 6.82 ± 5.17 a | 13.4 ± 4.54 b | 3.88 ± 3.17 b | ND b | 521 ± 175 a |
| HCLP | 10.8 ± 8.06 b | 14.3 ± 10.2 b | 30.0 ± 21.7 b | 4.78 ± 3.51 b | 1.22 ± 0.91 b | 39.9 ± 29.4 a | 5.05 ± 3.74 a | 51.0 ± 38.4 a | 157 ± 115 b | |
| CPC 5 | 24% | 44.1 ± 46.6 c | 55.4 ± 58.0 c | 43.3 ± 45.3 c | 6.14 ± 6.50 c | ND c | 3.65 ± 3.86 b | 3.71 ± 3.92 b | 0.42 ± 0.45 c | 157 ± 164 c |
| 32% | 88.4 ± 77.0 b | 104 ± 86.0 b | 94.7 ± 53.9 b | 9.50 ± 2.58 b | 5.18 ± 3.69 b | 37.0 ± 21.6 a | 5.68 ± 1.59 a | 31.8 ± 33.4 b | 376 ± 168 b | |
| 40% | 114 ± 101 a | 141 ± 127 a | 120 ± 77.8 a | 14.7 ± 7.92 a | 6.89 ± 5.15 a | 39.3 ± 24.5 a | 4.02 ± 4.22 b | 44.3 ± 46.6 a | 483 ± 246 a | |
| PBPM | 24% | 88.2 ± 10.7 c | 110 ± 13.4 c | 86.2 ± 10.5 c | 12.3 ± 1.50 b | ND d | 7.30 ± 0.89 c | 7.41 ± 0.90 a | ND c | 312 ± 38.0 c |
| 32% | 162 ± 7.48 b | 186 ± 8.61 b | 146 ± 6.75 b | 11.9 ± 0.55 b | 8.70 ± 0.40 b | 16.7 ± 0.77 b | 4.24 ± 0.20 b | ND c | 536 ± 24.8 b | |
| 40% | 209 ± 19.8 a | 262 ± 24.7 a | 193 ± 18.3 a | 22.1 ± 2.09 a | 11.8 ± 1.11 a | 16.1 ± 1.53 b | ND c | ND c | 714 ± 67.5 a | |
| HCLP | 24% | ND e | 0.50 ± 0.06 d | 0.54 ± 0.07 e | ND d | ND d | ND d | ND c | 0.84 ± 0.10 c | 1.89 ± 0.23 e |
| 32% | 14.8 ± 1.49 de | 22.0 ± 2.21 d | 43.4 ± 4.35 d | 7.10 ± 0.71 c | 1.65 ± 0.17 c | 57.3 ± 5.75 a | 7.12 ± 0.71 a | 63.5 ± 6.37 b | 217 ± 21.8 d | |
| 40% | 17.7 ± 1.53 d | 20.5 ± 1.78 d | 46.1 ± 3.99 d | 7.23 ± 0.63 c | 2.01 ± 0.17 c | 62.5 ± 5.41 a | 8.03 ± 0.70 a | 88.6 ± 7.68 a | 253 ± 21.9 cd | |
| p | PS | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| CPC | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| PS × CPC | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| Biogenic Amines 2 | Total Amines 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | CAD | TYR 4 | HIS | SPD | PHE | SPM 4 | TRY | |||
| PS 5 | PBPM | 19.7 ± 17.5 | 3.92 ± 6.62 | 2.60 ± 4.08 | 0.40 ± 0.45 | 6.17 ± 4.43 | 0.36 ± 0.52 | 2.86 ± 6.12 | 0.59 ± 0.78 | 36.6 ± 28.0 |
| HCLP | 21.7 ± 19.8 | 1.99 ± 4.03 | 1.68 ± 1.30 | 0.27 ± 0.34 | 10.7 ± 8.46 | 0.62 ± 0.46 | 2.70 ± 4.07 | 1.32 ± 1.26 | 41.0 ± 21.8 | |
| CPC 6 | 24% | 16.3 ± 15.5 | 1.65 ± 2.42 | 1.65 ± 1.32 | 0.26 ± 0.31 | 10.9 ± 9.16 | 0.47 ± 0.49 | 0.97 ± 1.14 | 0.97 ± 1.14 | 34.4 ± 21.2 |
| 32% | 17.2 ± 17.5 | 2.00 ± 3.42 | 1.54 ± 1.83 | 0.33 ± 0.49 | 9.03 ± 6.71 | 0.53 ± 0.60 | 0.64 ± 0.98 | 0.64 ± 0.98 | 36.1 ± 22.3 | |
| 40% | 28.7 ± 20.9 | 5.22 ± 8.35 | 3.24 ± 4.69 | 0.41 ± 0.41 | 5.45 ± 3.50 | 0.48 ± 0.44 | 1.25 ± 1.17 | 1.25 ± 1.17 | 46.1 ± 30.4 | |
| PBPM | 24% | 19.7 ± 14.1 | 1.90 ± 2.91 | 1.35 ± 0.63 | 0.24 ± 0.28 | 7.15 ± 4.85 | 0.63 ± 0.64 | 1.57 ± 3.85 | 0.25 ± 0.41 | 32.8 ± 19.7 |
| 32% | 16.1 ± 16.9 | 3.52 ± 4.41 | 2.17 ± 2.39 | 0.53 ± 0.62 | 6.95 ± 5.14 | 0.28 ± 0.50 | 6.02 ± 9.41 | 0.57 ± 0.89 | 36.1 ± 28.2 | |
| 40% | 23.4 ± 23.1 | 6.33 ± 10.4 | 4.28 ± 6.71 | 0.45 ± 0.42 | 4.40 ± 3.33 | 0.18 ± 0.32 | 0.98 ± 2.41 | 0.96 ± 0.90 | 41.0 ± 38.0 | |
| HCLP | 24% | 12.8 ± 17.3 | 1.40 ± 2.07 | 1.94 ± 1.79 | 0.28 ± 0.36 | 14.6 ± 11.3 | 0.31 ± 0.21 | 2.85 ± 5.04 | 1.69 ± 1.21 | 35.9 ± 24.4 |
| 32% | 18.2 ± 19.6 | 0.48 ± 0.85 | 0.91 ± 0.81 | 0.14 ± 0.21 | 11.1 ± 7.89 | 0.78 ± 0.63 | 3.60 ± 4.4.60 | 0.72 ± 1.14 | 36.0 ± 17.4 | |
| 40% | 34.1 ± 19.0 | 4.10 ± 6.46 | 2.19 ± 0.88 | 0.38 ± 0.43 | 6.49 ± 3.65 | 0.77 ± 0.32 | 1.64 ± 2.71 | 1.54 ± 1.41 | 51.2 ± 23.0 | |
| p | PS | 0.719 | 0.719 | 0.639 | 0.308 | 0.052 | 0.113 | 0.377 | 0.050 | 0.583 |
| CPC | 0.130 | 0.080 | 0.144 | 0.651 | 0.155 | 0.941 | 0.491 | 0.388 | 0.435 | |
| PS × CPC | 0.430 | 0.225 | 0.605 | 0.405 | 0.623 | 0.045 | 0.786 | 0.332 | 0.862 | |
| Biogenic Amines 2 | Total Amines 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUT | CAD | TYR | HIS | AGM | SPD | PHE | SPM | TRY | |||
| PS 4 | PBPM | 133 ± 53.9 a | 182 ± 63.7 a | 139 ± 45.2 a | 15.0 ± 5.04 a | 6.82 ± 5.17 a | 7.20 ± 6.70 b | 3.52 ± 3.01 b | −2.86 ± 6.12 b | −0.59 ± 0.78 | 484 ± 172 a |
| HCLP | −10.9 ± 18.5 b | 13.4 ± 10.3 b | 30.3 ± 20.9 b | 4.51 ± 3.55 b | 1.22 ± 0.91 b | 29.2 ± 33.0 a | 4.43 ± 3.53 a | 48.3 ± 38.9 a | −1.32 ± 1.26 | 116 ± 113 b | |
| CPC 5 | 24% | 27.8 ± 44.6 b | 59.1 ± 57.4 c | 46.0 ± 45.2 c | 5.88 ± 6.51 c | 0 c | −7.24 ± 11.3 b | 3.24 ± 3.77 b | −1.79 ± 4.27 c | −0.97 ± 1.14 | 122 ± 165 c |
| 32% | 71.2 ± 80.1 a | 102 ± 84.6 b | 93.2 ± 53.3 b | 9.17 ± 2.44 b | 5.18 ± 3.69 b | 28.0 ± 19.5 a | 5.15 ± 1.43 a | 26.9 ± 35.3 b | −0.64 ± 0.98 | 340 ± 169 b | |
| 40% | 84.8 ± 108 a | 136 ± 126 a | 116 ± 76.5 a | 14.3 ± 7.88 a | 6.89 ± 5.15 a | 33.9 ± 23.7 a | 3.54 ± 3.92 b | 43.0 ± 46.4 a | −1.25 ± 1.17 | 437 ± 252 a | |
| PBPM | 24% | 68.5 ± 10.3 c | 108 ± 13.5 c | 84.8 ± 10.2 c | 12.1 ± 1.37 b | 0 d | 0.15 ± 4.64 c | 6.78 ± 1.04 a | −1.57 ± 3.85 c | −0.25 ± 0.41 | 279 ± 28.8 c |
| 32% | 146 ± 18.5 b | 183 ± 12.1 b | 144 ± 7.88 b | 11.4 ± 0.92 b | 8.70 ± 0.40 b | 9.72 ± 4.89 bc | 3.96 ± 0.41 b | −6.02 ± 9.41 c | −0.57 ± 0.89 | 400 ± 33.9 b | |
| 40% | 186 ± 29.8 a | 255 ± 22.1 a | 189 ± 15.8 a | 21.7 ± 1.91 a | 11.8 ± 1.11 a | 11.8 ± 3.87 b | −0.18 ± 0.32 c | −0.98 ± 2.41 c | −0.96 ± 0.90 | 673 ± 68.8 a | |
| HCLP | 24% | −12.8 ± 17.3 d | −0.07 ± 0.53 d | −0.67 ± 0.30 e | −0.28 ± 0.36 d | 0 d | −14.6 ± 11.3 d | −0.31 ± 0.21 c | −2.01 ± 5.02 c | −1.69 ± 1.21 | 34.0 ± 24.3 e |
| 32% | −3.42 ± 20.4 d | 21.5 ± 2.43 d | 42.5 ± 4.77 d | 6.96 ± 0.74 c | 1.65 ± 0.17 c | 46.2 ± 3.56 a | 6.34 ± 0.96 a | 59.9 ± 6.51 b | −0.72 ± 1.14 | 181 ± 29.0 d | |
| 40% | −16.4 ± 18.6 d | 16.4 ± 7.66 d | 43.9 ± 4.63 d | 6.86 ± 0.86 c | 2.01 ± 0.17 c | 56.0 ± 7.13 a | 7.26 ± 0.68 a | 87.0 ± 8.89 a | −1.54 ± 1.41 | 201 ± 32.4 d | |
| p | PS | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.050 | <0.0001 |
| CPC | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.388 | <0.0001 | |
| PS × CPC | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.332 | <0.0001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinto, C.F.D.; Monteiro, C.F.C.; Bortolo, M.; Marx, F.R.; Model, J.F.A.; Vinagre, A.S.; Trevizan, L. Effects of Diets Based on Hydrolyzed Chicken Liver and Different Protein Concentrations on the Formation and Deamination of Biogenic Amines and Total Antioxidant Capacity of Dogs. Animals 2023, 13, 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162578
Pinto CFD, Monteiro CFC, Bortolo M, Marx FR, Model JFA, Vinagre AS, Trevizan L. Effects of Diets Based on Hydrolyzed Chicken Liver and Different Protein Concentrations on the Formation and Deamination of Biogenic Amines and Total Antioxidant Capacity of Dogs. Animals. 2023; 13(16):2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162578
Chicago/Turabian StylePinto, Caroline Fredrich Dourado, Camila Figueiredo Carneiro Monteiro, Marcelino Bortolo, Fábio Ritter Marx, Jorge Felipe Argenta Model, Anapaula Sommer Vinagre, and Luciano Trevizan. 2023. "Effects of Diets Based on Hydrolyzed Chicken Liver and Different Protein Concentrations on the Formation and Deamination of Biogenic Amines and Total Antioxidant Capacity of Dogs" Animals 13, no. 16: 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162578
APA StylePinto, C. F. D., Monteiro, C. F. C., Bortolo, M., Marx, F. R., Model, J. F. A., Vinagre, A. S., & Trevizan, L. (2023). Effects of Diets Based on Hydrolyzed Chicken Liver and Different Protein Concentrations on the Formation and Deamination of Biogenic Amines and Total Antioxidant Capacity of Dogs. Animals, 13(16), 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162578







