Comparative Histology and Histochemistry of the Parotid Gland and Mandibular Gland in the Lowland Tapir (Tapirus terrestris Perissodactyla) and Aardvark (Orycteropus afer Tubulidentata)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Tissue Samples
2.3. Ethical Statement
3. Results
3.1. Parotid Gland Histology and Histochemistry
3.2. Mandibular Gland Histology and Histochemistry
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dyce, K.M.; Sack, W.O.; Wensing, C.J.G. Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy, 2nd ed.; W.B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria. In International Committee on Veterinary Gross Anatomical Nomenclature, 6th ed.; Editorial Committee: Hannover, Germany; Ghent, Belgium; Columbia, MO, USA; Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2017.
- Nickel, R.; Schummer, A.; Seiferle, E. Lehrbuch der Anatomie der Haustiere; Verlag Paul Parey: Berlin/Hamburg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski, K. Histologia; Państwowy Zakład Wydawnict Lekarskich (PZWL): Warsaw, Poland, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Amano, O.; Mizobe, K.; Bando, Y.; Sakiyama, K. Anatomy and Histology of Rodent and Human Major Salivary Glands. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2012, 45, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawes, C.; Pedersen, A.M.; Villa, A.; Ekström, J.; Proctor, G.B.; Vissink, A.; Aframian, D.; McGowan, R.; Aliko, A.; Narayana, N.; et al. The functions of human saliva: A review sponsored by the World Workshop on Oral Medicine VI. Arch. Oral Biol. 2015, 60, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaholt, P.K.; Parkash, T.; Singh, A. Morphological analysis of parotid gland of pig (Sus scrofa). Haryana Vet. 2021, 60, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Genkins, G.N. Saliva. In The Physiology and Biochemistry of the Mouth, 4th ed.; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1978; pp. 284–359. [Google Scholar]
- Khojasteh, S.M.B.; Delashoub, M. Microscopic anatomy of the parotid and submandibular salivary glands in European hamster (Cricetus cricetus L.). Int. Res. J. Appl. Basic Sci. 2012, 3, 1544–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Mese, H.; Matsuo, R. Salivary secretion taste and hyposalivation. J. Oral Rehabil. 2007, 34, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, F.Y.; Darvish, N.; Shahri, M. Comparative histological and histochemical inter-species investigation of mammalian sub mandibular salivary glands. Res. J. App. Sci. 2009, 4, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Roa, I.; del Sol, M. Parotid Gland Comparative Microscopic Anatomy. Int. J. Morphol. 2019, 37, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, M.E.; Arriaga, A.; Busso, C.; Caranza, M. Histological study of parotid, submaxillary and von Ebner salivary glands in chronic alcoholics. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 1999, 12, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Igbokwe, C.O. Ultrastructure of the parotid salivary gland in the greater cane rats (Thryonomys swinderianus). J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2018, 6, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikpegbu, E.; Nlebedum, U.; Nnadozie, O.; Agbakwuru, I. Histology of the parotid salivary gland of the African palm squirrel (Epixerus ebii). Rev. Fac. Cienc. Vet. 2013, 54, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ikpegbu, E.; Nlebedum, U.; Nnadozie, O.; Agbakwuru, I. Microscopic study of the submandibular salivary gland of adult African giant pouched rat (Cricetomys gambianus, Waterhouse 1840). Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 27, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijpe, J.; Meijer, J.M.; Bootsma, H.; van der Wal, J.E.; Spijkervet, F.K.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Vissink, A.; Ihrler, S. Clinical and histologic evidence of salivary gland restoration supports the efficacy of rituximab treatment in Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, S.P.; Williamson, R.T. A review of saliva: Normal composition, flow, and function. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2001, 85, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, A.A. Anatomical and histological study of molar salivary gland in domestic cat. Iran. J. Vet. Res. Shiraz Univ. 2010, 11, 164–167. [Google Scholar]
- Ruxanda, F.; Raţiu, C.; Matosz, B.; Constantinescu, R.; Miclăuş, V. First evidence of histological and histochemical intraspecific differences in salivary glands in Brown Norway and albino Wistar rats. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2018, 42, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandler, B.; Gresik, E.W.; Nagato, T.; Phillips, C.J. Secretion by striated ducts of mammalian major salivary glands: Review from an ultrastructural, functional, and evolutionary perspective. Anat. Rec. 2001, 264, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalukian, S.C.; de Bustos, M.S.; Lizárraga, R.L. Diet of lowland tapir (Tapirus terrestris) in El Rey National Park, Salta, Argentina. Integr. Zool. 2013, 8, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.J.; Medici, E.P.; Naranjo, E.J.; Novarino, W.; Leonardo, R.S. Distribution, habitat and adaptability of the genus Tapirus. Integr. Zool. 2012, 7, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.A.; Silva, A.; Campos-Arceiz, A.; Zavada, M.S. On tapir ecology, evolution and conservation: What we know and future perspectives-part II. Integr. Zool. 2013, 8, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goździewska-Harłajczuk, K.; Hamouzová, P.; Kleckowska-Nawrot, J.; Barszcz, K.; Cížek, P. Microstructure of the Surface of the Tongue and Histochemical Study of the Lingual Glands of the Lowland Tapir (Tapirus terrestris Linnaeus, 1758) (Perissodactyla: Tapiridae). Animals 2020, 10, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibert, F.; Sabatier, D.; Andrivot, J.; Scotti-Saintagne, C.; Gonzalez, S.; Prévost, M.-F.; Grenand, P.; Chave, J.; Caron, H.; Richard-Hansen, C. Botany, genetics and ethnobotany: A crossed investigation on the elusive tapir’s diet in French Guiana. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, M.W.; Janovec, J.P.; Cornejo, F. Frugivory and seed dispersal by the lowland tapir Tapirus terrestris in the Peruvian Amazon. Biotropica 2010, 42, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, P.D.; Lokvam, J.; Rudolph, K.; Bromberg, K.; Sackett, T.E.; Wright, L.; Brenes-Arguedas, T.; Dvorett, D.; Ring, S.; Clark, A.; et al. Divergent defensive strategies of young leaves in two species of Inga. Ecology 2005, 86, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeland, W.J.; Janzen, D.H. Strategies in herbivory by mammals: The role of plant secondary compounds. Am. Nat. 1974, 108, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, H.N. Contributions to the anatomy of the tapir. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1850, 1850, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, M.; Dowler, R.C. Tapirus terrestris . Mamm. Spec. 1994, 481, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quittarelli, G.; Dellovo, M.C. Studies on exocrine secretions. Histochemie 1969, 19, 199–223. [Google Scholar]
- Goździewska-Harłajczuk, K.; Klećkowska-Nawrot, J.; Barszcz, K. Macroscopic and microscopic study of the tongue of the aardvark (Orycteropus afer, Orycteropodidae). Tissue Cell 2018, 54, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knöthig, J. Biology of the aardvark (Orycteropus afer). Master’s Thesis, Ruprecht-Karls-Universität, Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Melton, D.A. The biology of aardvark (Tubulidentata—Orycteropodidae). Mammal Rev. 1976, 6, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.A.; Lindsey, P.A.; Skinner, J.D. The feeding ecology of the aardvark Orycteropus afer. J. Arid Environ. 2002, 50, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, J.D.; Chimimba, C.T. The Mammals of the Southern African Sub-Region; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rahm, U. Tubulidentates: Aardvark. In Grzimek’s Encyclopedia of Mammals; Parker, S.P., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 4, pp. 450–458. [Google Scholar]
- Crompton, J. Ways of the Ant; Collins: New York, NY, USA, 1954; ISBN 9780941130844. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.D.; Richardson, P.R.K.; Woodall, P.F. Functional analysis of the feeding apparatus and digestive tract anatomy of the arrdwolf Proteles cristatus. J. Zool. 1992, 228, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.D. The Influence of Seasonality and Quality of Diet on the Metabolism of the Aardwolf, Proteles cristatus (Sparrman 1783). Master’s Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.D. Aardwolf adaptations: A review: Animals. Trans. R. Soc. South Afr. 2004, 59, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codón, S.M.; Estecondo, S.; Casanave, E.B. Histological study of the salivary glands in Dasypus hybridus (mammalia, dasypodidae). Int. J. Morphol. 2003, 21, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalquest, W.W.; Werner, H.J. The parotid gland of an Anteater Tamadua tetradactyla. Am. Maidland Nat. 1952, 48, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estecondo, S.; Codon, S.M.; Casanave, E.B. Histologia del tracto digestive de Chaetophractus villosus (Desmarest, 1804) y Chaetophractus vellerosus (Gray, 1865). Mammaila, Dasypodidae. Iheringia 1995, 78, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, W.J. Microscopy of the Echidna sublingual glands. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2011, 40, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lennep, E.W.; Kennesson, A.R.; Young, J.A.; Hales, J.R.S. Morphology, histochemistry and physiology of the major salivary glands in the echidna Tachyglossus aculeatus (Monotremata). J. Morphol. 1979, 159, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.F.; Chang, C.-Y.; Yang, C.W.; Dierefeld, E.S. Aspects of Digestive Anatomy, Feed Intake and Digestion in the Chinese Pangolin (Manis pentadactyla) at Taipei Zoo. Zoo Biol. 2015, 34, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, W.; Beyer, C.; Wissdorf, H. Lectin histochemistry of salivary glands in the giant ant-eater (Myrmecopahaga tridactyla). Histol. Histopathol. 1993, 8, 305–316. [Google Scholar]
- Munyala, R.; Liumsiricharoen, M.; Pongket, P. Glycoconjugates in the secretory epithelium of the mandibular salivary gland of Malayan pangolin (Manis javanica). KKU Vet. J. 2009, 19, 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- Munyala, R.; Liumsiricharoen, M.; Pongket, P. Histochemical detection of glycoconjugates in the parotid salivary gland of Malayan pangolin (Manis javanica). KKU Vet. J. 2009, 8, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira Firmino, M.; da Silva Pereira, H.C.; Carvalho, L.R.R.A.; Guerra, R.R. External and digestive system morphology of the Tamandua tetradactyla. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2020, 49, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackleford, J.M. The salivary glands and salivary bladder of nine-banded armadillo. Anat. Rec. 1963, 145, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.M.; Pigman, W. Preparation and characterization of armadillo submandibular glycoproteins. Biochem. J. 1977, 161, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.M.; Malinowski, C.E.; Herp, A. Isolation of an acidic protein from the armadillo submandibular gland. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1979, 581, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.M.; Slomiany, A.; Herp, A.; Slomiany, B.L. Structural studies on the carbohydrate units of armadillo submandibular glycoprotein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1979, 578, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.M.; Shen, F.-S.; Herp, A.; Song, S.-C.; Wu, J.H. Fraction A of armadillo submandibular glycoprotein and its desialylated product as sialyl-Tn and Tn receptors for lectin. FEBS Lett. 1995, 360, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aureli, G.; Ferri, G.; Castellani, A.A. Content of sialic acid in serous glands of eguines. Nature 1961, 190, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, A.J.E. Note on rhinoceros salivary glands. J. Zool. Lond. 1982, 196, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Aglio, C.; Maranesi, M.; Pascucci, L.; Mercati, F.; Ceccarelli, P. Immunohistochemical distribution of lectin receptor in the major salivary glands of horses. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 1116–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, K.; Jogahara, T.; Oda, S.; Honda, M. Scanning transmission electron microscopic analysis of nitrogen generated by 3, 3′-diaminobenzidine-besed peroxidase reaction with resin ultrathin sections of rhinoceros parotid gland acinar cells. Microscopy 2019, 68, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, A.O.; Abdel-Rahman, Y.A.; Abou-Elmagd, A. The fine structure of parotid salivary gland in donkey. Assiut. Vet. Med. J. 1995, 32, 18–38. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, J.; Schumacher, J. Diseases of salivary glands and ducts of the horse. Equine. Vet. Edu. 1995, 7, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Otsuka, J. On the fine structure of salivary glands horse. I. parotid gland. Bull. Fag. Agric. Kagoshima Univ. 1977, 27, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, R.A.; Abood, D.A. Morphological Features of Parotid and Mandibular Salivary Glands in Local Breed Donkey (Equus asinus). Teikyo Med. J. 2022, 45, 4935–4945. [Google Scholar]
- Burck, N.C. Technika histologiczna. PZWL Warszawa 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Gamble, M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 6th ed.; Churchill Livingstone Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, F. Histotechnology a Self-Instructional Text, 1st ed.; ASCP: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Munakata, H.; Isemura, M.; Yosizawa, Z. An application of the high-iron diamine staining for detection of sulfated glycoproteins (glycopeptides) in electrophoresis on cellulose acetate membrane. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1985, 145, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, D.C.; Hrapchak, B.B. Theory and Practice Histotechnology, 2nd ed.; CV Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Spicer, S.C.; Henson, J.G. Methods for localizing mucosubstances in epithelial and connective tissue. In Series on Methods and Achievements in Experimental Pathology; Bajusz, E., Jamin, F., Eds.; S Karger Press: Basel, Switzerland, 1967; Volume 2, pp. 78–112. [Google Scholar]
- International Committee on Veterinary Histological Nomenclature (ICVHN). Nomina Histologica Veterinaria; International Committee on Veterinary Histological Nomenclature (ICVHN): New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Estecondo, S.; Codon, S.M.; Casanave, E.B. Histological study of the salivary glands in Zaedyus pichiy (Mammalia, Xenarthra, Dasypodidae). Int. J. Morph. 2005, 23, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, D.; Bin-Meferij, M.M.; El-Kott, A.F.; Abd El-Maksud, M.M.; Negm, S. Histology and histochemistry of the major salivary glands in the southern white-breasted hedgehog (Erinaceus concolor). Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2022, 52, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, H.F. On the fine structure of the parotid gland of mouse and rat. Am. J. Anat. 1961, 108, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, R.S. Myoepithelium of salivary glands. Micro Res. Tech. 1994, 27, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.D.; Singh, O. Morphological and histochemical characteristics of parotid salivary glands in neonates of Indian buffalo. J. Anim. Res. 2017, 7, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandler, B.; Erlandson, R.A. Ultrastructure of baboon parotid gland. Anat. Rec. 1976, 184, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, M.; Ichikawa, A. The fine structure of the parotid gland of the Mongolian gerbil, Meriones meridianus. Arch. Histol. Jpn. 1975, 38, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, W.; Shalaan, S.A.; Misk, N.A.; Ibrahim, A. Surgical Anatomy, Morphometry, and Histochemistry of Major Salivary Glands in Dogs: Updates and Recommendations. Int. J. Vet. Health Sci. Res. 2020, 8, 252–259. [Google Scholar]
- Poddar, S.; Jacob, S. Gross and microscopic anatomy of the major salivary glands of the ferret. Cells Tissues Organs 1977, 98, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, L.H.; Shackleford, J.M. Electron microscopy of squirrel monkey parotid glands. Ala. J. Med. Sci. 1970, 7, 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Cowley, L.H.; Shackleford, J.M. An ultrastructural study of the submandibular glands of the squirrel monkey, Sairniri sciureus. J. Morphol. 1970, 132, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnyane, I.K.M.; Zuki, A.B.; Noordin, M.M.; Agungpriyono, S. Histological study of the parotid and mandibular glands of barking deer (Muntiacus muntjak) with special references to the distribution of carbohydrate content. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2010, 39, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgin, C.J.; Wilson, D.E.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Rylands, A.B.; Lacher, T.E.; Sechrest, W. Illustrated Checklist of the Mammals of the World; Part 2; Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Genus Ceratotherium. In Mammals Species of World. A Taxonomic and Geographic References, 3rd ed.; John Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Delsuc, F.; Metcalf, J.L.; Wegener Parfrey, L.; Song, S.J.; González, A.; Knight, R. Convergence of gut microbiomes in myrmecophagous mammals. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1301–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava de Moraes, F. Alguns dados morfológicos associados ao estudo histoquímico dos polissacarídeos em glândulas salivares de animais pertencentes às seguintes ordens: Marsupialia, Chiroptera, Primates, Edentata, Lagomorpha, Rodentia, Carnivora e Artiodactyla (Mammalia). Revta. Fac. Odont. Univ. Sâo Paulo 1965, 3, 233–290. [Google Scholar]
- Allio, R.; Teullet, S.; Lutgen, D.; Magdeleine, A.; Koual, R.; Tilak, M.-K.; de Thoisy, B.; Emerling, C.A.; Lefébure, T.; Delsuc, F. Comparative transcriptomics reveals divergent paths of chitinase evolution 2 underlying dietary convergence in ant-eating mammals. Biorxiv 2022, 11, 518312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Neto, E.M. As interações homem/Xenarthra: Tamanduás, Preguiças e Tatus no folclore ameríndio. Actual. Biol. 2000, 22, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.A.; Skinner Frssaf, J.D. Adaptations of the aardvark for survival in the Karoo: A review. Trans. R. Soc. South Afr. 2004, 59, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertassoni, A. Family Myrmecophagidae (Anteaters). In Handbook of the Mammals of the World. Part 8: Insectivores, Sloths and Colugos; Mittermeier, R.A., Wilson, D.E., Eds.; Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, Spain, 2018; pp. 89–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, K.D.; Gaudin, T.J. Xenarthra and Pholidota (Armadillos, Anteaters, Sloths and Pangolins); John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Amerongen, A.V.; Bolscher, J.G.; Veerman, E.C. Salivary mucins diversity. J. Glycobiol. 1995, 5, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabak, L.A. In defense of the oral cavity structure, biosynthesis and function of salivary mucins. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1995, 57, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano, J.; Dinis, M.T.; Sarasquete, C. Histomorphological characteristics of the intestine of the Senegal Sole, Solea senegalensis. Eur. J. Histochem. 1999, 43, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Nakhoul, S.A.; Nakhoul, N.L.; Wheeler, S.A.; Haque, S.; Wang, P.; Brown, K.; Orlando, G.; Orlando, R.C. Characterization of esophageal submucosal glands in pig tissue and cultures. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2007, 52, 3054–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzing, J.E.; Woodall, P.F. The rostral nasal anatomy of the two elephant shrews. J. Anat. 1988, 157, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, P.J.; Suchar, L.A.; Robbins, C.T.; Hagerman, A.E. Tannin-binding proteins in saliva of deer and their absence in saliva of sheep and cattle. J. Chem. Ecol. 1989, 15, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooday, G.W. The ecology of chitin degradation. Adv. Microbiol. Ecol. 1990, 11, 387–430. [Google Scholar]
- Simunek, J.; Hodrova, B.; Bartonova, H.; Kopecny, J. Chitinolytic bacteria of the mammal digestive tract. Folia Microbiol. 2001, 46, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
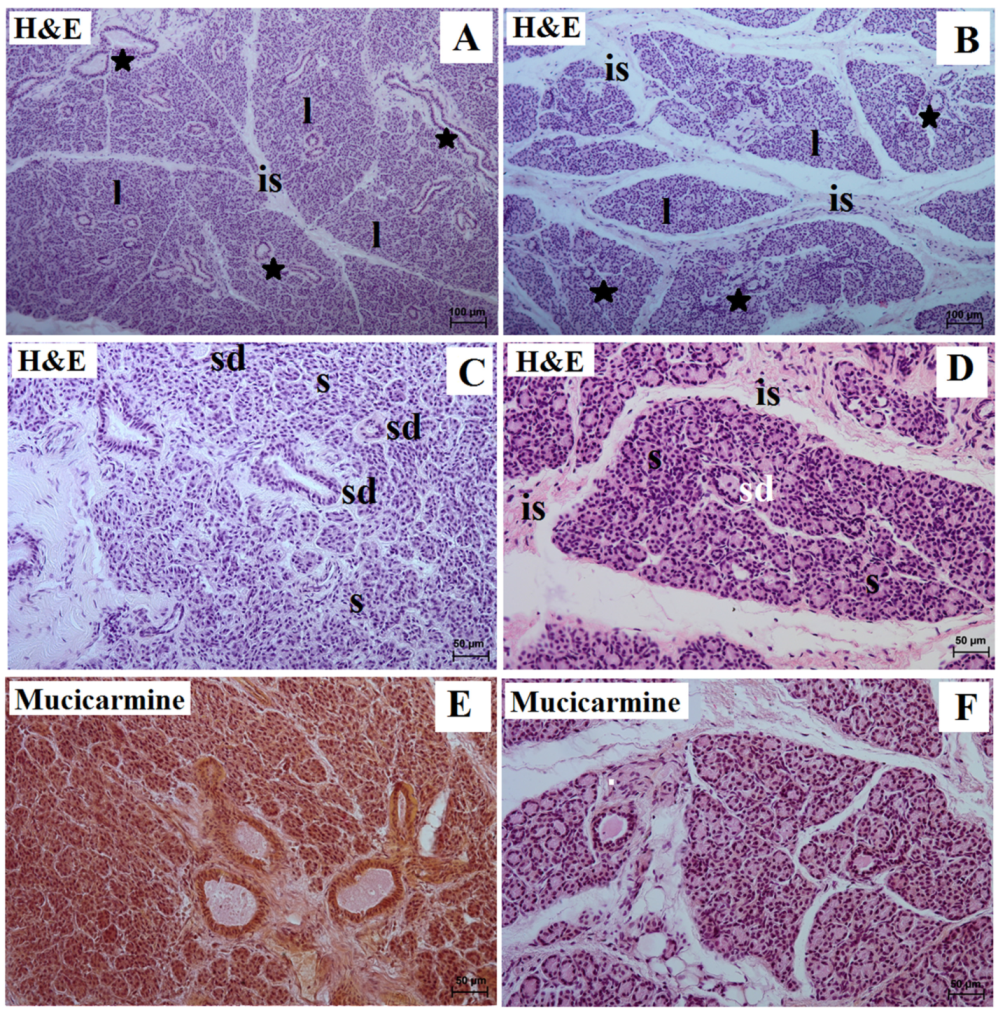
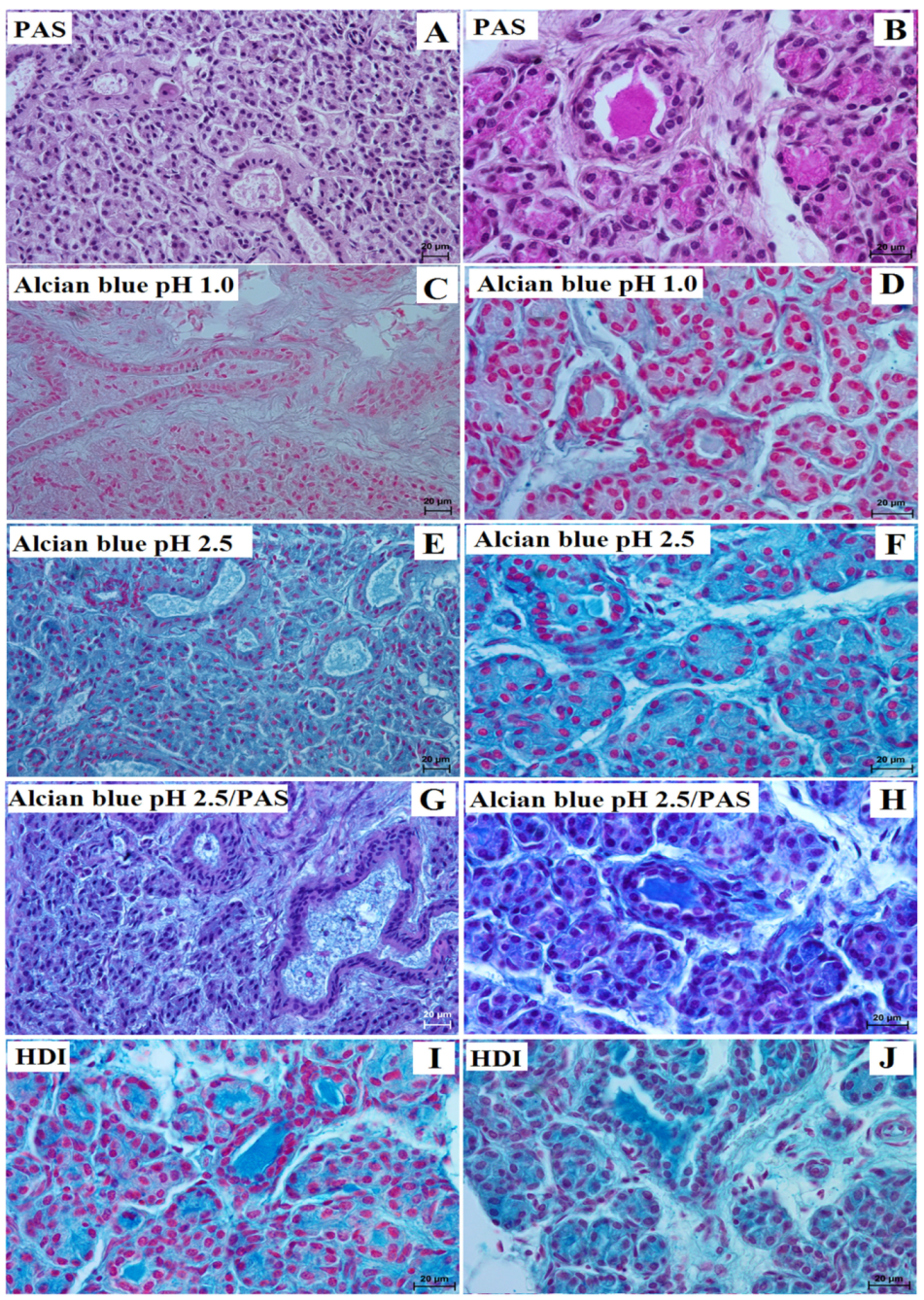
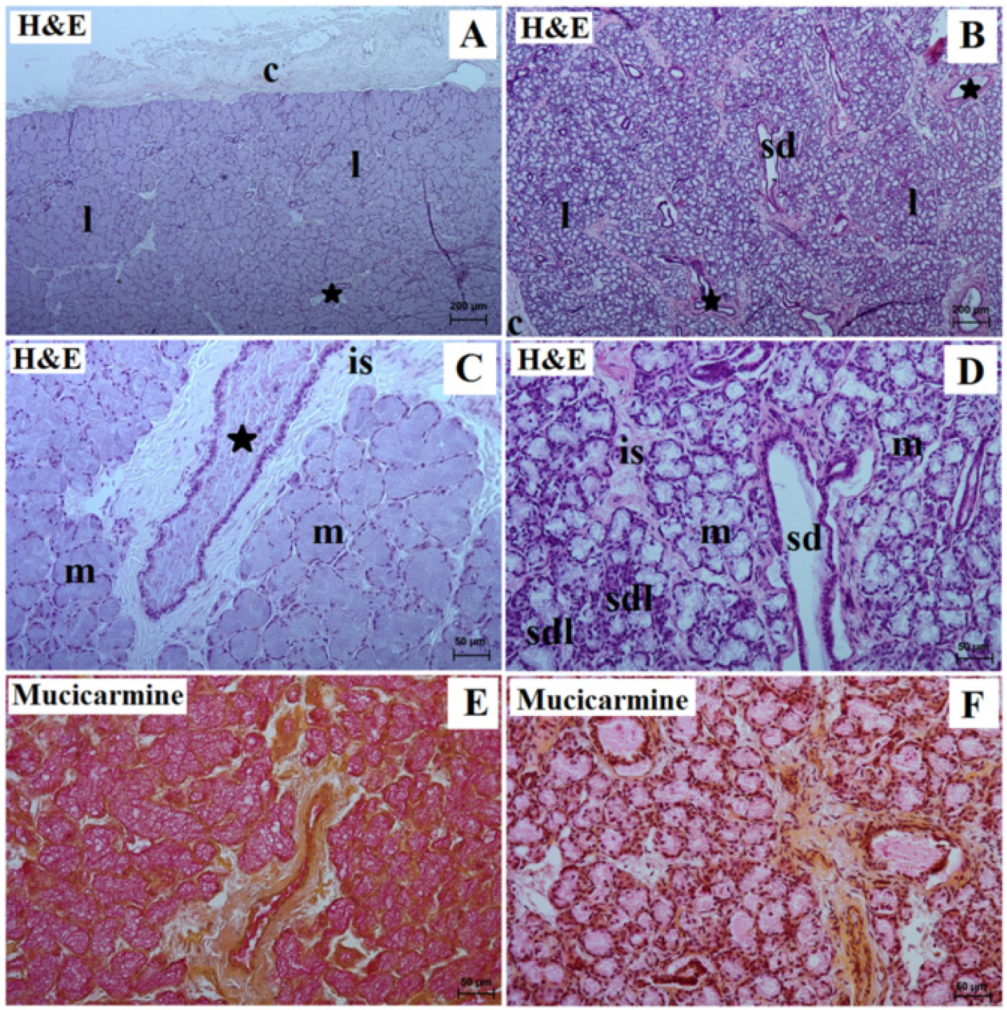
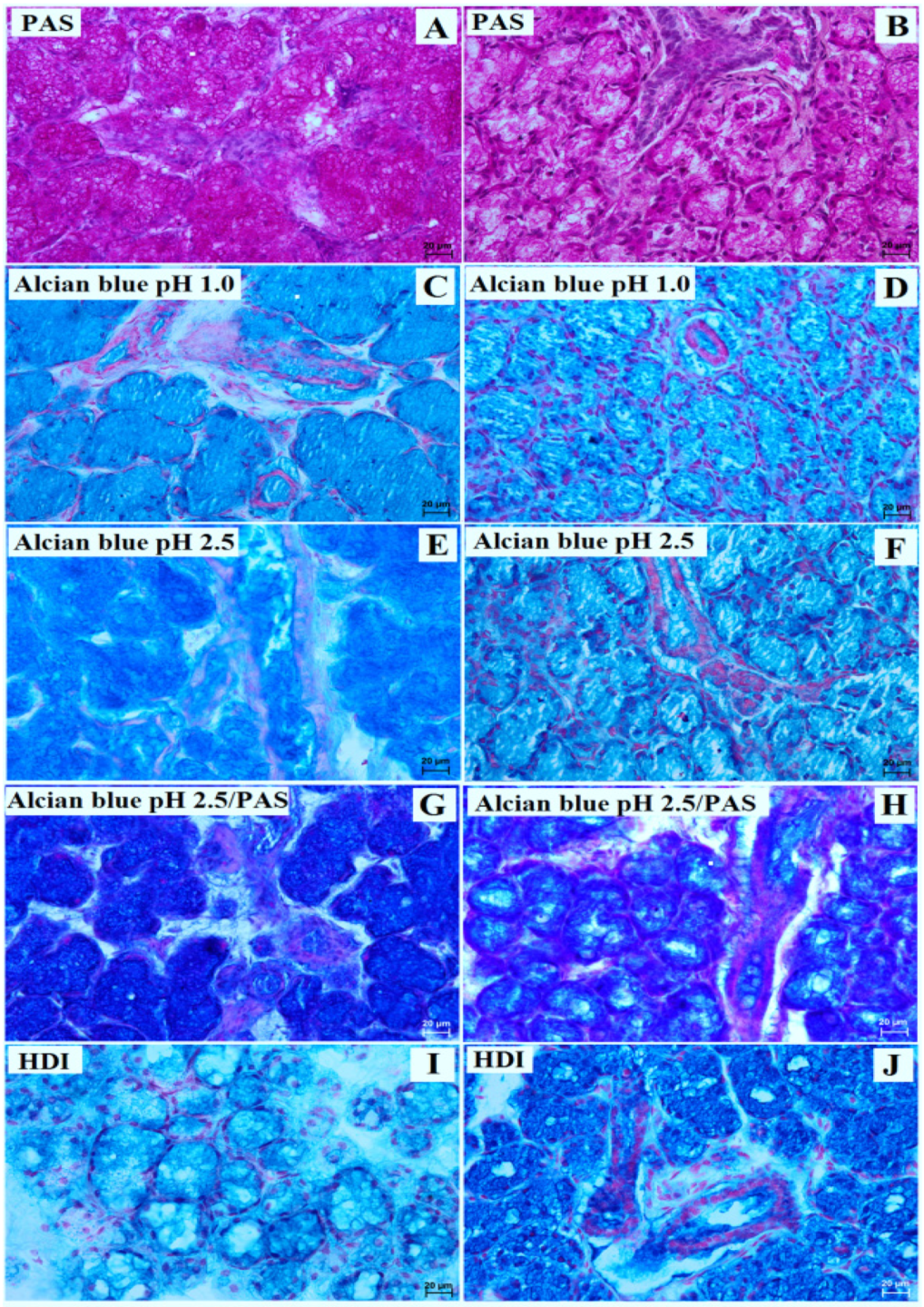
| Lowland Tapir | Aardvark | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items of Evaluation | Parotid Gland | Mandibular Gland | Parotid Gland | Mandibular Gland |
| Gland capsule | thin | thick | thin | thick |
| Interlobar septa | thin | thin | thick | thin |
| Lobes | different size (small, medium, large); various shapes (oval, elongated, triangular, quadrangular) | Very large | small and very numerous, ovoid-like shape | Very large |
| Type of gland | multilobed branched alveolar complex | multilobed branched tubular complex | multilobed branched alveolar complex | multilobed branched tubuloalveolar complex |
| Type of secretion | serous | mucous | serous | mucoserous |
| Secretory units | acini—single conical cells; average outer diameter—36.0 µm | tubules—tall conical cells with very small lumen, basophilic cytoplasm; average outer diameter—85.0 µm | acini—single conical cells; average outer diameter—25.0 µm | tubules—low pyramidal cells with a wide base and outer diameter average of 42.0 µm; acini (serous demilunes)—outer diameter average of 18.0 µm |
| Interlobar ducts | taller columnar cells with central or basally located oval or round nuclei; broad with wide lumina; very numerous | single columnar epithelium with centrally located nuclei; few | taller columnar cells with central or basally located oval or round nuclei; small with narrow lumina; few | single columnar epithelium with centrally located nuclei, well developed |
| Striated ducts | cuboidal or columnar cells with basal striations; many | simple cuboidal epithelium with basal striations; few | cuboidal or columnar cells with basal striations; rare | simple cuboidal epithelium with basal striations; very numerous |
| Mucicarmine stain | negative (−) reaction in the secretory units and ducts system | strong (+++) reaction in the mucous cells and ducts system | negative (−) reaction in the acini, striated ducts, and interlobar ducts | negative reaction (−) in the mucous units and ducts system, negative (−) reaction in the serous demilunes |
| PAS stain | negative (−) reaction in the acini; interlobar ducts with strong (+++) reaction; striated ducts with strong (+++) reaction | strong (+++) reaction in the tubules and all ducts system | strong (+++) reaction in the acini; interlobar ducts with strong (+++) reaction; striated ducts with slight (−/+) reaction | strong (+++) reaction in the tubules and all ducts system |
| Alcian blue pH 1.0 stain | acini, interlobar ducts, and striated ducts with negative (−) reaction | strong (+++) reaction in the tubules and all ducts system | acini, interlobar ducts, and striated ducts with negative (−) reaction | strong (+++) reaction in the tubules and all ducts system |
| Alcian blue pH 2.5 stain | acini, interlobar and striated ducts with strong (+++) reaction | strong (+++) reaction in the tubules and all ducts system | acini, interlobar and striated ducts with strong (+++) reaction | strong (+++) reaction in the tubules and all ducts system |
| Alcian blue pH 2.5/PAS stain | acini, interlobar and striated ducts with strong (+++) reaction—blue color | strong (+++) reaction in the tubules and all ducts system (blue color) | acini, interlobar and striated ducts with strong (+++) reaction—magenta color | strong (+++) reaction in the tubules and all ducts system (blue color) |
| HDI stain | middle (++) reaction in the acini and system ducts | strong (+++) reaction in the tubules and all ducts system | strong (+++) reaction in the acini and the system ducts | strong (+++) reaction in the tubules and all ducts system |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klećkowska-Nawrot, J.; Barszcz, K.; Miniajluk, J.P.; Melnyk, O.; Goździewska-Harłajczuk, K. Comparative Histology and Histochemistry of the Parotid Gland and Mandibular Gland in the Lowland Tapir (Tapirus terrestris Perissodactyla) and Aardvark (Orycteropus afer Tubulidentata). Animals 2023, 13, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101684
Klećkowska-Nawrot J, Barszcz K, Miniajluk JP, Melnyk O, Goździewska-Harłajczuk K. Comparative Histology and Histochemistry of the Parotid Gland and Mandibular Gland in the Lowland Tapir (Tapirus terrestris Perissodactyla) and Aardvark (Orycteropus afer Tubulidentata). Animals. 2023; 13(10):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101684
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlećkowska-Nawrot, Joanna, Karolina Barszcz, Jan Paweł Miniajluk, Oleksii Melnyk, and Karolina Goździewska-Harłajczuk. 2023. "Comparative Histology and Histochemistry of the Parotid Gland and Mandibular Gland in the Lowland Tapir (Tapirus terrestris Perissodactyla) and Aardvark (Orycteropus afer Tubulidentata)" Animals 13, no. 10: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101684
APA StyleKlećkowska-Nawrot, J., Barszcz, K., Miniajluk, J. P., Melnyk, O., & Goździewska-Harłajczuk, K. (2023). Comparative Histology and Histochemistry of the Parotid Gland and Mandibular Gland in the Lowland Tapir (Tapirus terrestris Perissodactyla) and Aardvark (Orycteropus afer Tubulidentata). Animals, 13(10), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101684








