Bisphenol A Interferes with Redox Balance and the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Xenopus tropicalis during Embryonic Development
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Exposure and Sampling
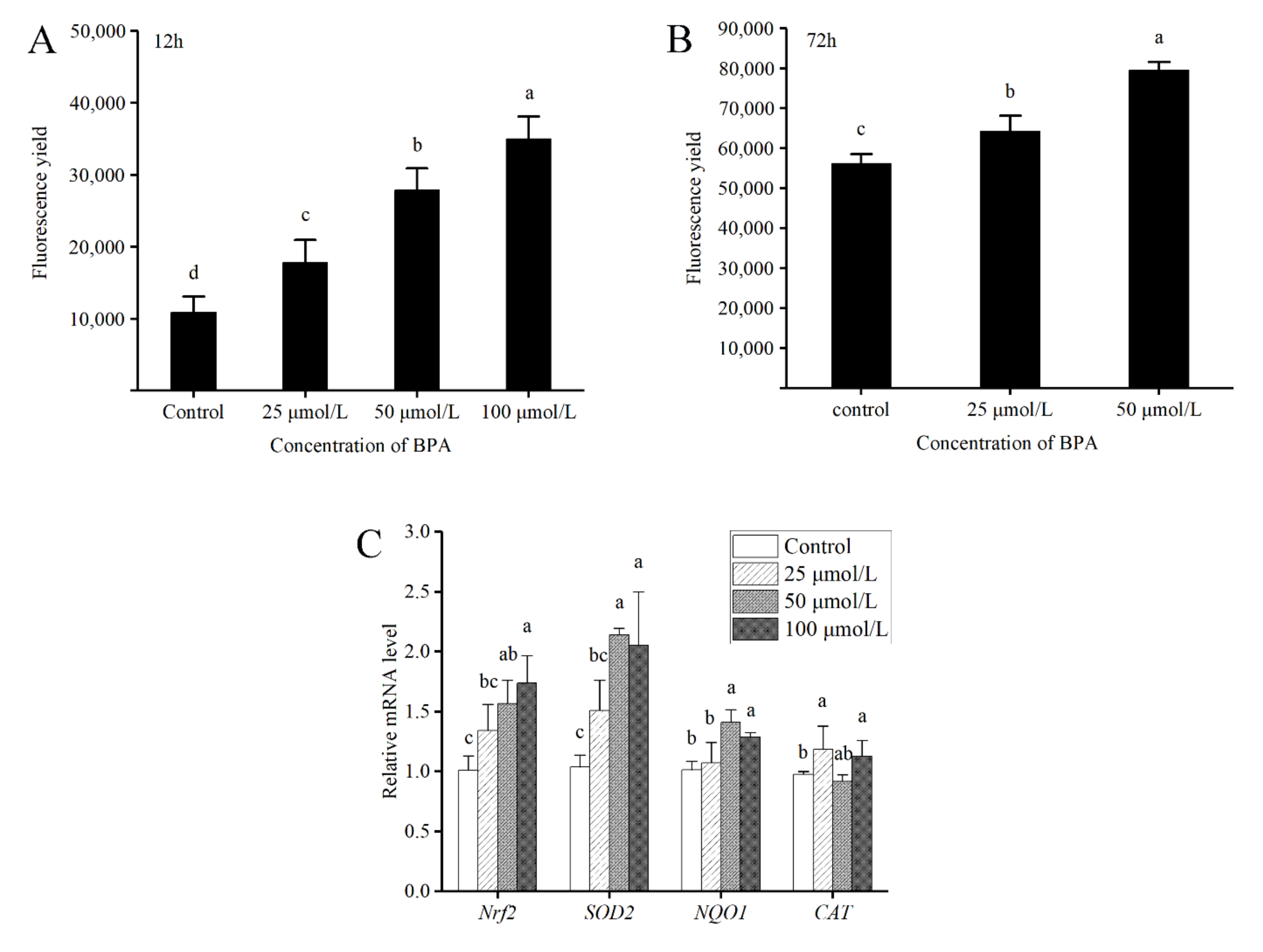
2.2. Detection of Levels of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.3. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-qPCR)
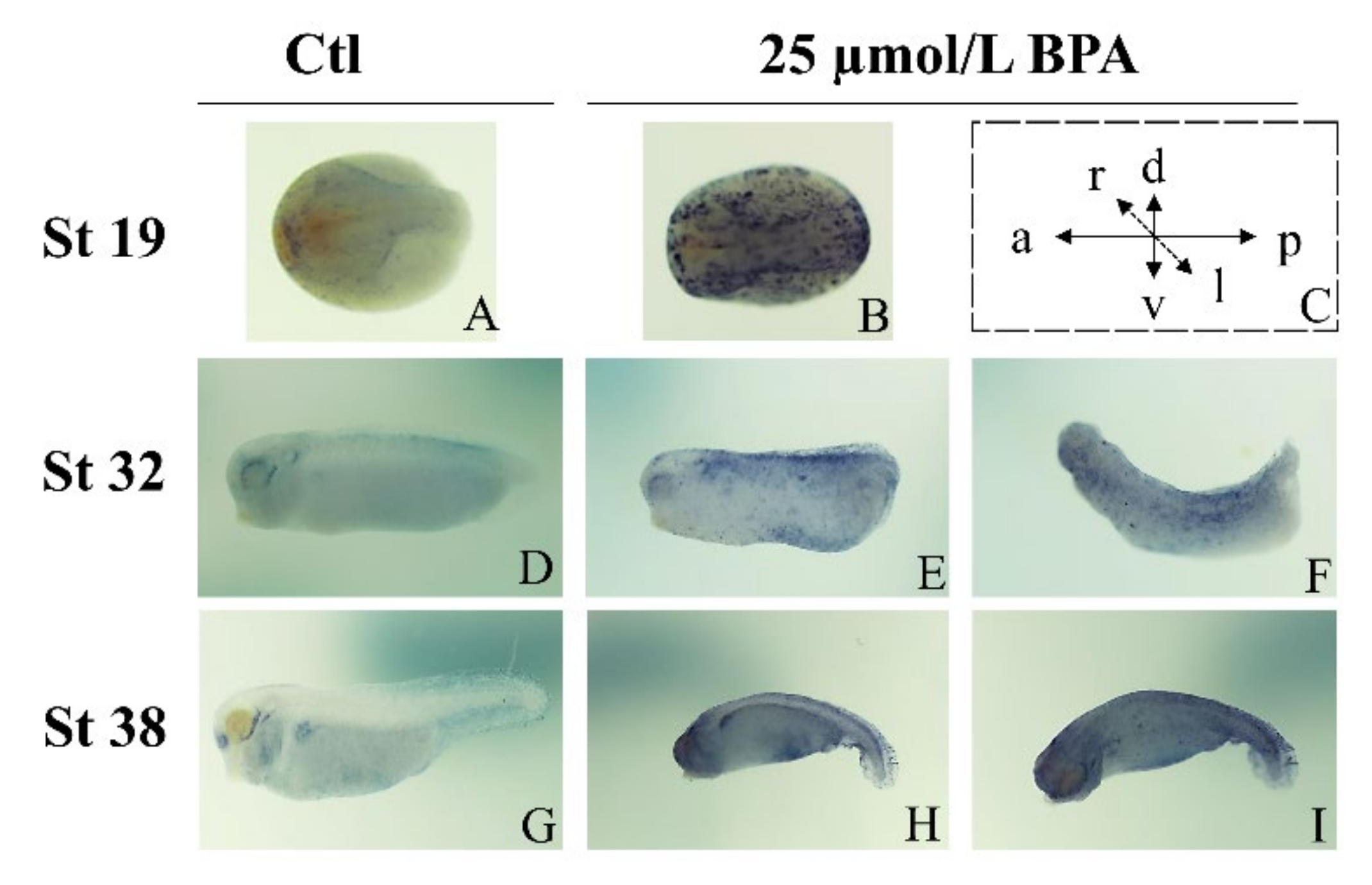
2.4. Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization (WISH)
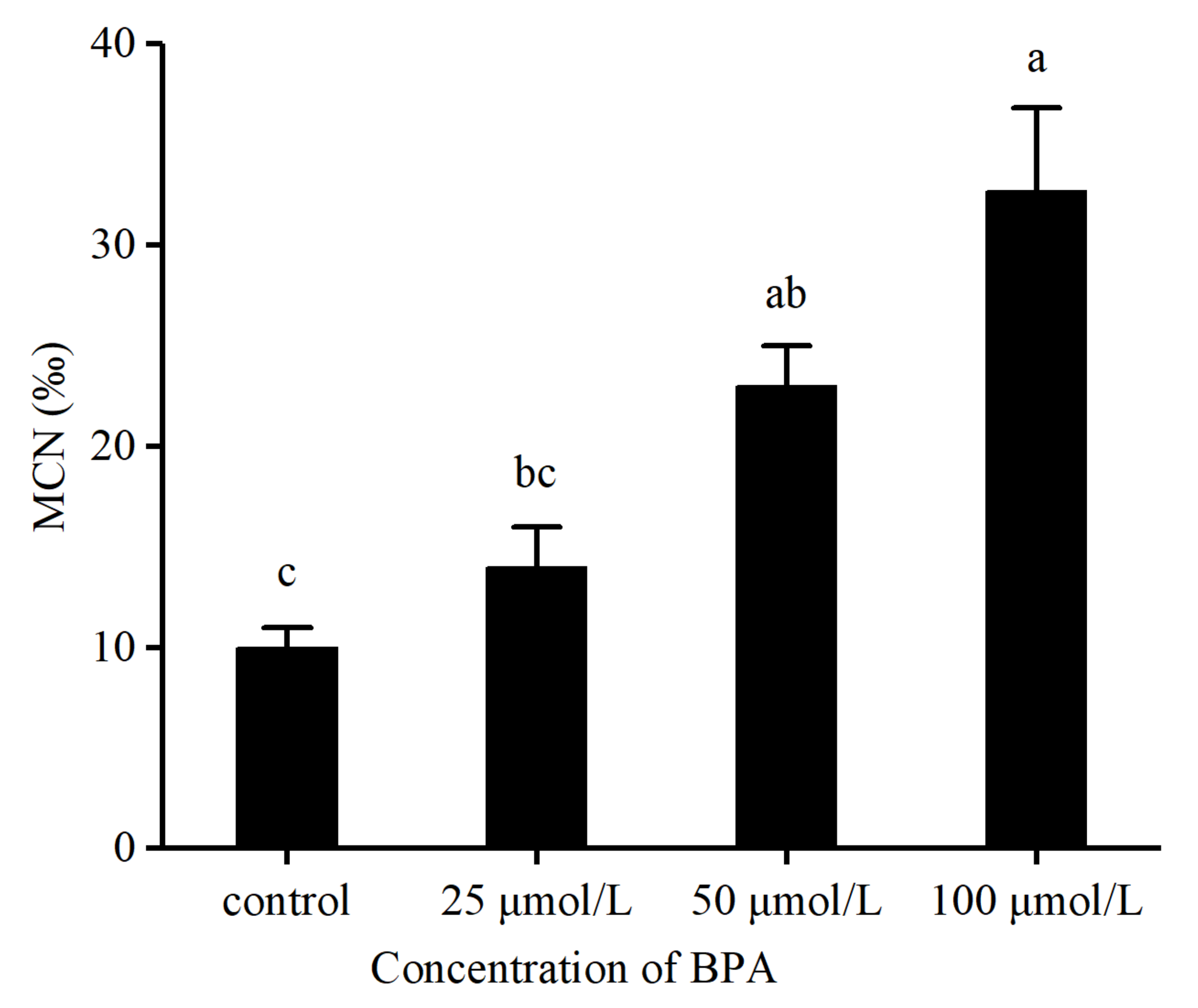
2.5. Micronucleus Test
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. BPA Causes DNA Damage in the Tadpole
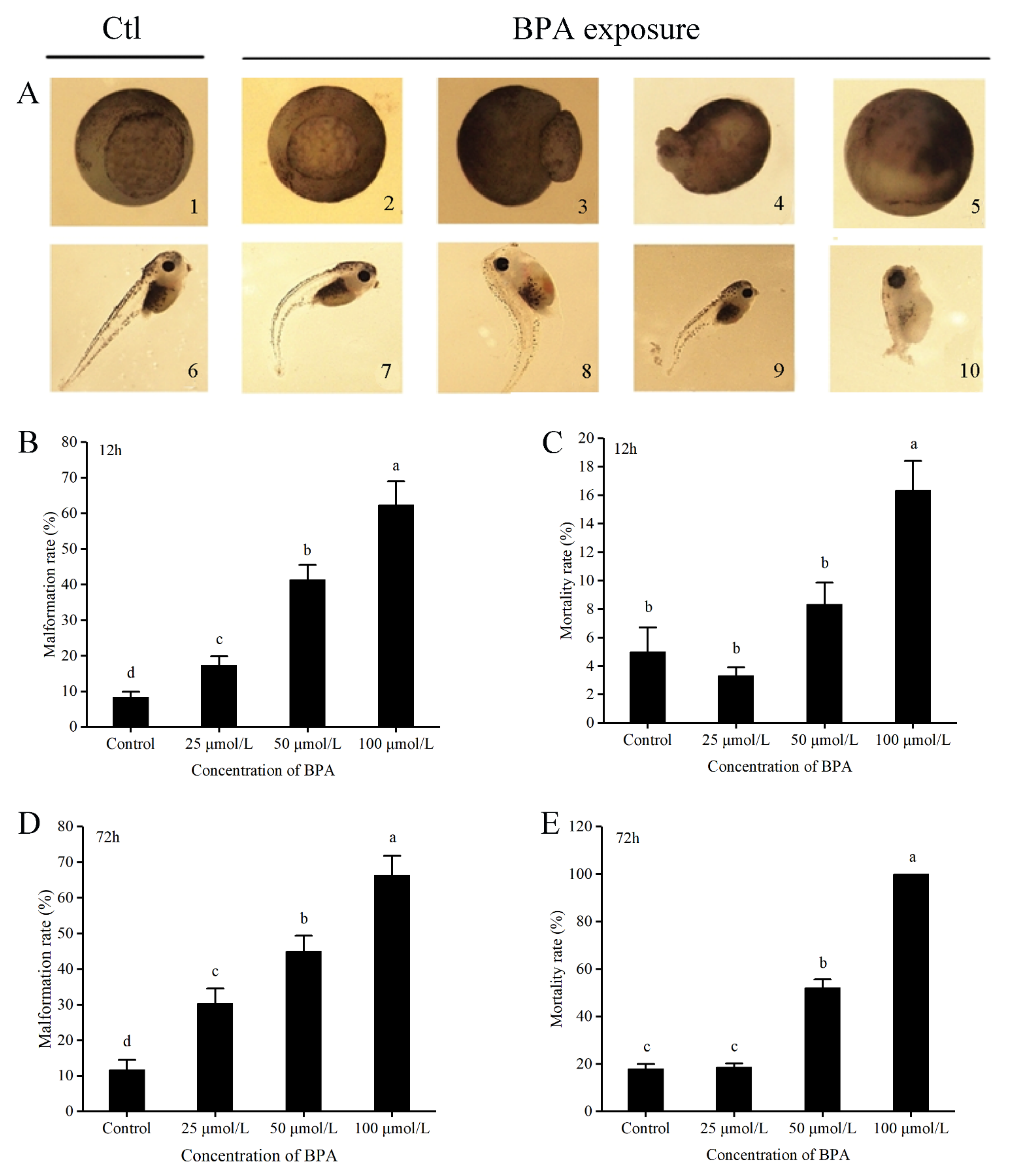
3.2. BPA Is Teratogenic to X. tropicalis Embryos
3.3. BPA Enhances Antioxidant Signaling during Embryonic Development
3.4. BPA Interferes with the Spatiotemporal Expression Patterns of Nrf2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.Q.; Wong, C.K.C.; Zheng, J.S.; Bouwman, H.; Barra, R.; Wahlström, B.; Neretin, L.; Wong, M.H. Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: A review of sources, environmental levels, and potential human health impacts. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olea, N.; Pulgar, R.; Perez, P.; Olea-Serrano, F.; Sonnenschein, C. Estrogenicity of resin-based composites and sealants used in dentistry. Environ. Health Perspect. 1996, 104, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotons, J.A.; Olea-Serrano, M.F.; Villalobos, M.; Pedraza, V.; Olea, N. Xenoestrogens released from lacquer coatings in food cans. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, E.; Bono-Blay, F.; Cirillo, T.; Montuori, P.; Lacorte, S. Migration of phthalates, alkylphenols, bisphenol A and di (2-ethylhexyl) adipate from food packaging. Food Control 2012, 27, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.R.; Wang, K.; Yu, J.; Yu, Z.X.; Yu, X.B.; Zhang, Z.Z. Distribution and fate modeling of 4-nonylphenol, 4-t-octylphenol, and bisphenol A in the Yong River of China. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Hua, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, R.; Dong, L.; Hu, B.X.; Zhang, J. Environmental behavior and potential driving force of bisphenol A in the Elbe River: A long-term trend study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.; Sankar, M.S.; Vattikuti, S.; Dash, P.; Arslan, Z. Pollution assessment and land use land cover influence on trace metal distribution in sediments from five aquatic systems in southern USA. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Whitfield, M.; Biggs, J.; Bray, S.; Fox, G.; Nicolet, P.; Sear, D. Comparative biodiversity of rivers, streams, ditches and ponds in an agricultural landscape in Southern England. Biol. Conserv. 2004, 115, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.; von Fumetti, S.; Kelly-Quinn, M. The importance of small waterbodies for biodiversity and ecosystem services: Implications for policy makers. Hydrobiologia 2017, 793, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Magdalena, P.; Ropero, A.B.; Soriano, S.; García-Arévalo, M.; Ripoll, C.; Fuentes, E.; Quesada, I.; Nadal, Á. Bisphenol-A acts as a potent estrogen via non-classical estrogen triggered pathways. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 355, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, H.; Abizaid, A. A plurality of molecular targets: The receptor ecosystem for bisphenol-A (BPA). Horm. Behav. 2018, 101, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monneret, C. What is an endocrine disruptor? Comptes Rendus Biol. 2017, 340, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imaoka, S.; Mori, T.; Kinoshita, T. Bisphenol A causes malformation of the head region in embryos of Xenopus laevis and decreases the expression of the ESR-1 gene mediated by Notch signaling. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwamuro, S.; Sakakibara, M.; Terao, M.; Ozawa, A.; Kurobe, C.; Shigeura, T.; Kato, M.; Kikuyama, S. Teratogenic and anti-metamorphic effects of bisphenol A on embryonic and larval Xenopus laevis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2003, 133, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimeier, R.A.; Shi, Y.-B. Amphibian metamorphosis as a model for studying endocrine disruption on vertebrate development: Effect of bisphenol A on thyroid hormone action. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 168, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, N.R. Induction of oxidative stress by bisphenol A and its pleiotropic effects. Environ. Mol. Mutagenesis 2017, 58, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, E.; Cheng, C.Y. Impacts of environmental toxicants on male reproductive dysfunction. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 32, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonelli, C.; Chio, I.I.C.; Tuveson, D.A. Transcriptional regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murakami, S.; Motohashi, H. Roles of Nrf2 in cell proliferation and differentiation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xenbase. X. tropicalis RNA-Seq Data. Available online: https://www.xenbase.org/gene/expression.do?method=displayGenePageExpression&geneId=943925&tabId=1 (accessed on 29 March 2022).
- Faber, J.; Nieuwkoop, P.D. Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin): A systematical & chronological survey of the development from the fertilized egg till the end of metamorphosis. Q. Rev. Biol. 1994, 33, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kais, B.; Schneider, K.; Keiter, S.; Henn, K.; Ackermann, C.; Braunbeck, T. DMSO modifies the permeability of the zebrafish (Danio rerio) chorion-implications for the fish embryo test (FET). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 140–144, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantle, J.A.; Dumont, J.N.; Finch, R.A.; Linder, G. Atlas of Abnormalities: A Guide for the Performance of FETAX, 2nd ed.; Oklahoma State University Press: Stillwater, OK, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, G.K.; Singh, V.; Mandal, P.; Singh, P.; Golla, U.; Baranwal, S.; Chauhan, S.; Tomar, R.S. Ebselen induces reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated cytotoxicity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with inhibition of glutamate dehydrogenase being a target. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.W.; Hwang, K.J.; Kwon, H.C.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, K.W.; Oh, K.S. Detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptosis in human fragmented embryos. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 13, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughal, B.B.; Leemans, M.; Spirhanzlova, P.; Demeneix, B.; Fini, J.-B. Reference gene identification and validation for quantitative real-time PCR studies in developing Xenopus laevis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, P. Hes5.9 coordinate FGF and notch signaling to modulate gastrulation via regulating cell fate specification and cell migration in Xenopus tropicalis. Genes 2020, 11, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzbacherová, V.; Šiviková, K.; Holečková, B.; Dianovský, J. Micronucleus assay in genotoxicity assessment. Acta Fytotech. Zootech. 2016, 19, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solnica-Krezel, L.; Sepich, D.S. Gastrulation: Making and shaping germ layers. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 687–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oka, T.; Adati, N.; Shinkai, T.; Sakuma, K.; Nishimura, T.; Kurose, K. Bisphenol A induces apoptosis in central neural cells during early development of Xenopus laevis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 312, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopel, C.F.V.; Sousa, C.; Machado, M.R.F.; Santos, W.G.D. BPA toxicity during development of zebrafish embryo. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 81, 437447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castritsi-Catharios, J.; Syriou, V.; Miliou, H.; Zouganelis, G.D. Toxicity effects of bisphenol A to the nauplii of the brine shrimp Artemia franciscana. Biol. Res. 2013, 19, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Janzen, F.J.; Tucker, J.K.; Paukstis, G.L. Experimental analysis of an early life-history stage: Avian predation selects for larger body size of hatchling turtles. J. Evol. Biol. 2000, 13, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancio, A.L.; Cole, K.D.; Dominguez, A.R.; Cohenour, E.R.; Kadie, J.; Maloney, W.C.; Cilliers, C.; Schuh, S.M. Bisphenol A, bisphenol AF, di-n-butyl phthalate, and 17β−estradiol have shared and unique dose-dependent effects on early embryo cleavage divisions and development in Xenopus laevis. Reprod. Toxicol. 2019, 84, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, K.; Okada, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Imaoka, S. Bisphenol A disrupts Notch signaling by inhibiting gamma-secretase activity and causes eye dysplasia of Xenopus laevis. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sommer, S.; Buraczewska, I.; Kruszewski, M. Micronucleus Assay: The state of art, and future directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Ji, W. Assessment of the genotoxicity in toad Bufo raddei exposed to petrochemical contaminants in Lanzhou Region, China. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 2007, 629, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, N.R.; Erdem, C.; Stefanick, D.F.; Horton, J.K.; Pawel, J.; Miral, D.; Wilson, S.H. Bisphenol A promotes cell survival following oxidative DNA damage in mouse fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huc, L.; Lemarié, A.; Guéraud, F.; Héliès-Toussaint, C. Low concentrations of bisphenol A induce lipid accumulation mediated by the production of reactive oxygen species in the mitochondria of HepG2 cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laforgia, N.; Mauro, D.A.; Guarnieri, F.G.; Varvara, D.; Cosmo, L.D.; Panza, R.; Capozza, M.; Baldassarre, M.E.; Resta, N. The role of oxidative stress in the pathomechanism of congenital malformations. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 7404082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, J.; Rozman, R. Oxidative stress, tissue remodeling and regression during amphibian metamorphosis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 145, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, T.; Ushio-Fukai, M. Superoxide dismutases: Role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1583–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhao, J.; Huang, X.; Song, L.; Luo, J.; Ma, L.; Li, S.; Qin, X. Association between catalase gene polymorphisms and risk of chronic hepatitis B, hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in Guangxi population: A case-control study. Medicine 2015, 94, e702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, T.; Mahadevan, J.; Bogachus, L.; Hahn, S.; Robertson, R.P. Nrf2/antioxidant pathway mediates β cell self-repair after damage by high-fat diet–induced oxidative stress. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e92854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karve, T.M.; Rosen, E.M. B-cell translocation gene 2 (BTG2) stimulates cellular antioxidant defenses through the antioxidant transcription factor NFE2L2 in human mammary epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 31503–31514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouvier, E.; Brouillard, F.; Molet, J.; Claverie, D.; Cabungcal, J.-H.; Cresto, N.; Doligez, N.; Rivat, C.; Do, K.Q.; Bernard, C.; et al. Nrf2-dependent persistent oxidative stress results in stress-induced vulnerability to depression. Mol. Psychiatr. 2017, 22, 1701–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chepelev, N.L.; Enikanolaiye, M.I.; Chepelev, L.L.; Almohaisen, A.; Chen, Q.X.; Scoggan, K.A.; Coughlan, M.C.; Cao, X.L.; Jin, X.; Willmore, W.G. Bisphenol A activates the Nrf1/2-antioxidant response element pathway in HEK 293 cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.J.; Dudakov, J.A.; Takahashi, K.; Shieh, J.H.; Velardi, E.; Holland, A.M.; Singer, N.V.; West, M.L.; Smith, O.M.; Young, L.F.; et al. Nrf2 regulates haematopoietic stem cell function. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, N.; Shin, S.; Slocum, S.L.; Agoston, E.S.; Wakabayashi, J.; Kwak, M.K.; Misra, V.; Biswal, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. Regulation of notch1 signaling by Nrf2: Implications for tissue regeneration. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, S.; Shimizu, R.; Romeo, P.-H.; Yamamoto, H.; Motohashi, H. Keap1-Nrf2 system regulates cell fate determination of hematopoietic stem cells. Genes Cells 2014, 19, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genes | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| NQO1 | TTTTGTCCTTTACTACGGGG | CACTCTTCTGCTATCTCTGT |
| Nrf2 | CACCAGAGACGAGCAAAGAG | CTTTGTCTGCTGGAGGGAGT |
| SOD2 | GCCAATCAAGACCCTCTACAA | TTTCGGCTACATTCTCCCAGT |
| CAT | ACTGCAGAGCCAAGGTGTTT | TATCGGGGTCCTTCAGGTGT |
| β-actin | GCTGCTTCTTCTTCATCAT | TTGGCATAGAGGTCCTTAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Zhong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, L.; Chen, P. Bisphenol A Interferes with Redox Balance and the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Xenopus tropicalis during Embryonic Development. Animals 2022, 12, 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12070937
Chen H, Zhong K, Zhang Y, Xie L, Chen P. Bisphenol A Interferes with Redox Balance and the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Xenopus tropicalis during Embryonic Development. Animals. 2022; 12(7):937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12070937
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hongjun, Keke Zhong, Yongpu Zhang, Lei Xie, and Peichao Chen. 2022. "Bisphenol A Interferes with Redox Balance and the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Xenopus tropicalis during Embryonic Development" Animals 12, no. 7: 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12070937
APA StyleChen, H., Zhong, K., Zhang, Y., Xie, L., & Chen, P. (2022). Bisphenol A Interferes with Redox Balance and the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Xenopus tropicalis during Embryonic Development. Animals, 12(7), 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12070937






