A Correlational Analysis of Phthalate Exposure and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Sarasota Bay, Florida (2010–2019)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dolphin Community and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Processing and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Methods
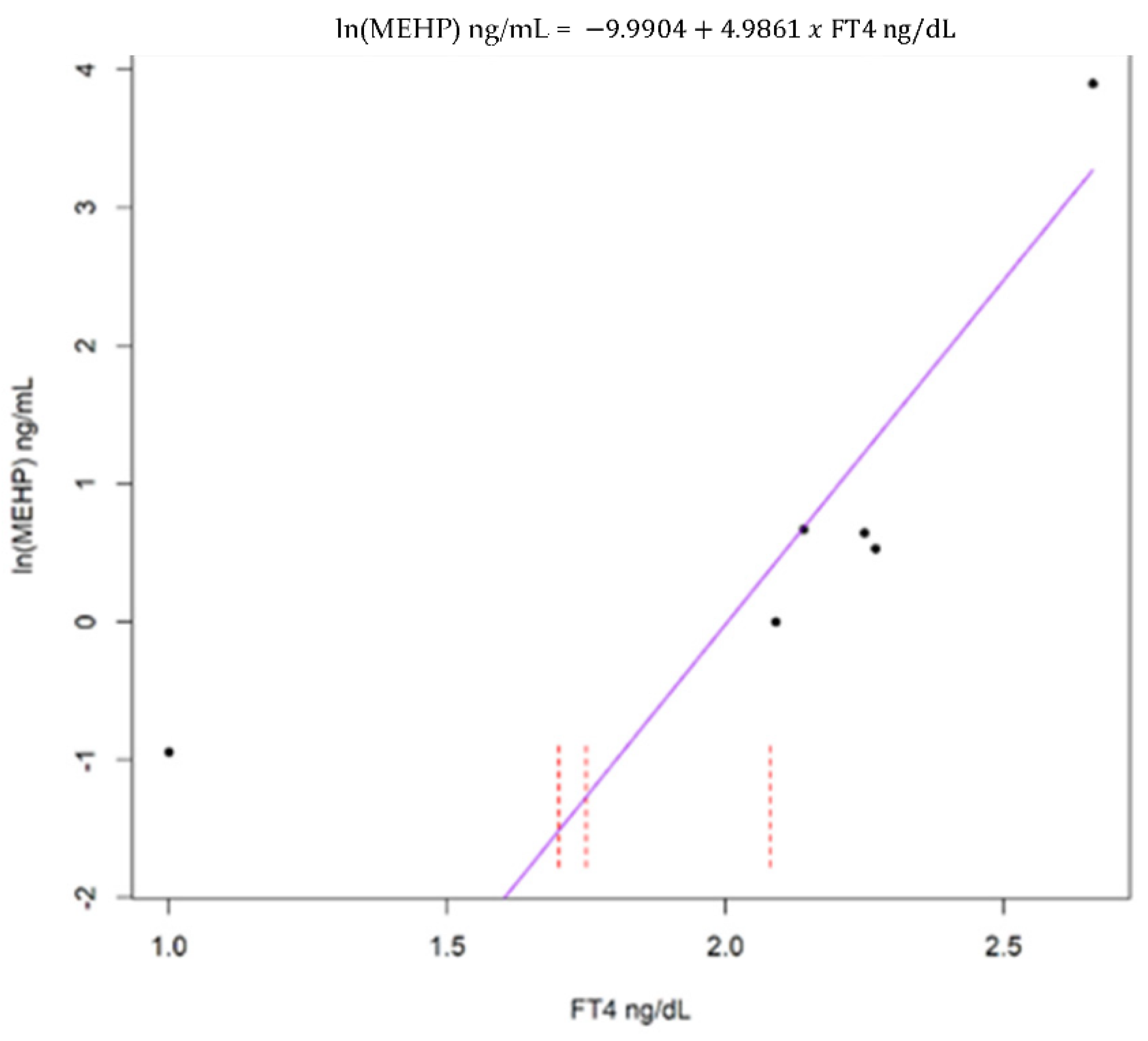
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Overall Findings
4.2. Mechanisms of Disruption
4.3. Implications of Thyroid Dysfunction
4.4. Triiodothyronine (T3)
4.5. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Di(2-Ethylhexyl)Phthalate (DEHP); Draft for Public Comment; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019.
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Diethyl Phthalate; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1995. [CrossRef]
- ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Di-n-Butyl Phthalate; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2001.
- Aurela, B.; Kulmala, H.; Soderhjelm, L. Phthalates in Paper and Board Packaging and Their Migration into Tenax and Sugar. Food Addit. Contam. 1999, 16, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Safety Assessment of Di (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) Released from PVC Medical Devices; FDA: White Oak, MA, USA, 2001.
- Sugino, M.; Hatanaka, T.; Todo, H.; Mashimo, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Hosoya, O.; Jinno, H.; Juni, K.; Sugibayashi, K. Safety Evaluation of Dermal Exposure to Phthalates: Metabolism-Dependent Percutaneous Absorption. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 328, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serrano, S.E.; Braun, J.; Trasande, L.; Dills, R.; Sathyanarayana, S. Phthalates and Diet: A Review of the Food Monitoring and Epidemiology Data. In Environmental Health: A Global Access Science Source; BioMed Central Ltd.: London, UK, 2014; p. 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fromme, H.; Lahrz, T.; Kraft, M.; Fembacher, L.; Dietrich, S.; Sievering, S.; Burghardt, R.; Schuster, R.; Bolte, G.; Völkel, W. Phthalates in German Daycare Centers: Occurrence in Air and Dust and the Excretion of Their Metabolites by Children (LUPE 3). Environ. Int. 2013, 61, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.; Hauser, R.; Calafat, A.M.; Weuve, J.; Schettler, T.; Ringer, S.; Huttner, K.; Hu, H. Use of Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate-Containing Medical Products and Urinary Levels of Mono(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Infants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Genuis, S.J.; Beesoon, S.; Lobo, R.A.; Birkholz, D. Human Elimination of Phthalate Compounds: Blood, Urine, and Sweat (BUS) Study. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 615068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staples, C.A.; Peterson, D.R.; Parkerton, T.F.; Adams, W.J. The Environmental Fate of Phthalate Esters: A Literature Review. Chemosphere 1997, 35, 667–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, E.; Rattan, S.; Gao, L.; Flaws, J.A. Prenatal Exposure to Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Causes Long-Term Transgenerational Effects on Female Reproduction in Mice. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, J.D.; Ferguson, K.K. Urinary Phthalate Metabolites Are Associated with Decreased Serum Testosterone in Men, Women, and Children from NHANES 2011–2012. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 4346–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sathyanarayana, S.; Barrett, E.; Butts, S.; Wang, C.; Swan, S.H. Phthalate Exposure and Reproductive Hormone Concentrations in Pregnancy. Reproduction 2014, 147, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Arguelles, D.B.; Campioli, E.; Lienhart, C.; Fan, J.; Culty, M.; Zirkin, B.R.; Papadopoulos, V. In Utero Exposure to the Endocrine Disruptor Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Induces Long-Term Changes in Gene Expression in the Adult Male Adrenal Gland. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meeker, J.D.; Calafat, A.M.; Hauser, R. Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Metabolites May Alter Thyroid Hormone Levels in Men. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, J.D.; Calafat, A.M.; Hauser, R. Urinary Metabolites of Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Are Associated with Decreased Steroid Hormone Leveis in Adult Men. J. Androl. 2009, 30, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, W.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Tao, Y.; et al. Dose-Response Relationships between Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Serum Thyroid Hormones among Waste Plastic Recycling Workers in China. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, L.E.; Ferguson, K.K.; McElrath, T.F.; Mukherjee, B.; Meeker, J.D. Associations between Repeated Measures of Maternal Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Thyroid Hormone Parameters during Pregnancy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, K.J.; McDowell, E.N.; Viereck, M.P.; Xia, J.Q. Species-Specific Dibutyl Phthalate Fetal Testis Endocrine Disruption Correlates with Inhibition of SREBP2-Dependent Gene Expression Pathways. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgenstern, R.; Whyatt, R.M.; Insel, B.J.; Calafat, A.M.; Liu, X.; Rauh, V.A.; Herbstman, J.; Bradwin, G.; Factor-Litvak, P. Phthalates and Thyroid Function in Preschool Age Children: Sex Specific Associations. Environ. Int. 2017, 106, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Ha, E.H.; Kim, E.J.; Park, H.; Ha, M.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, Y.C.; Chang, N.; Kim, B.N. Prenatal Exposure to Phthalates and Infant Development at 6 Months: Prospective Mothers and Children’s Environmental Health (MOCEH) Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.J.; Moon, S.; Oh, B.C.; Jung, D.; Choi, K.; Park, Y.J. Association between Diethylhexyl Phthalate Exposure and Thyroid Function: A Meta-Analysis. Thyroid 2019, 29, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederiksen, H.; Skakkebæk, N.E.; Andersson, A.M. Metabolism of Phthalates in Humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapinskas, P.J.; Brown, S.; Leesnitzer, L.M.; Blanchard, S.; Swanson, C.; Cattley, R.C.; Corton, J.C. Role of PPARα in Mediating the Effects of Phthalates and Metabolites in the Liver. Toxicology 2005, 207, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borch, J.; Metzdorff, S.B.; Vinggaard, A.M.; Brokken, L.; Dalgaard, M. Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-Androgenic Effects of Diethylhexyl Phthalate in Fetal Rat Testis. Toxicology 2006, 223, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals-Casas, C.; Desvergne, B. Endocrine Disruptors: From Endocrine to Metabolic Disruption. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2011, 73, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, Y.; Kamijima, M.; Nakajima, T. Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate-Induced Toxicity and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha: A Review. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2019, 24, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parks, L.G.P.; Ostby, J.S.; Lambright, C.R.; Abbott, B.D.; Klinefelter, G.R.; Barlow, N.J.; Gray Jr, L.E. The Plasticizer Diethylhexyl Phthalate Induces Malformations by Decreasing Fetal Testosterone Synthesis during Sexual Differentiation in the Male Rat. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 58, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swan, S.H.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Barrett, E.S.; Janssen, S.; Liu, F.; Nguyen, R.H.N.N.; Redmon, J.B.; TIDES Study Team. First Trimester Phthalate Exposure and Anogenital Distance in Newborns. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duty, S.M.; Silva, M.J.; Barr, D.B.; Brock, J.W.; Ryan, L.; Chen, Z.; Herrick, R.F.; Christiani, D.C.; Hauser, R.; Silva, M.; et al. Phthalate Exposure and Human Semen Parameters. Epidemiology 2003, 14, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, R.; Meeker, J.D.; Singh, N.P.; Silva, M.J.; Ryan, L.; Duty, S.; Calafat, A.M. DNA Damage in Human Sperm Is Related to Urinary Levels of Phthalate Monoester and Oxidative Metabolites. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toft, G.; Jönsson, B.A.G.; Lindh, C.H.; Jensen, T.K.; Hjollund, N.H.; Vested, A.; Bonde, J.P. Association between Pregnancy Loss and Urinary Phthalate Levels around the Time of Conception. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crobeddu, B.; Ferraris, E.; Kolasa, E.; Plante, I. Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) Increases Proliferation of Epithelial Breast Cancer Cells through Progesterone Receptor Dysregulation. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Beattie, M.C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Liu, J.; Traore, K.; Papadapolous, V.; Zirkin, B.R.; Chen, H. Oxidative Stress and Phthalate-Induced down-Regulation Ofsteroidogenesis in MA-10 Leydig Cells. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brucker-Davis, F. Effects of Environmental Synthetic Chemicals on Thyroid Function. Thyroid 1998, 8, 827–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghassabian, A.; Trasande, L. Disruption in Thyroid Signaling Pathway: A Mechanism for the Effect of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals on Child Neurodevelopment. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, C.; Flaws, J.A. Subchronic Exposure to Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate and Diisononyl Phthalate during Adulthood Has Immediate and Long-Term Reproductive Consequences in Female Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 168, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neier, K.; Cheatham, D.; Bedrosian, L.D.; Gregg, B.E.; Song, P.X.K.; Dolinoy, D.C. Longitudinal Metabolic Impacts of Perinatal Exposure to Phthalates and Phthalate Mixtures in Mice. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 1613–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, L.B.; Beckingham, B.; Wells, R.S.; Flagg, M.A.; Wischusen, K.; Moors, A.; Kucklick, J.; Pisarski, E.; Wirth, E. Urinary Phthalate Metabolites in Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Sarasota Bay, FL, USA. GeoHealth 2018, 2, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziobak, M.K.; Wells, R.S.; Pisarski, E.C.; Wirth, E.F.; Hart, L.B. Demographic Assessment of Mono(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (MEHP) and Monoethyl Phthalate (MEP) Concentrations in Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Sarasota Bay, FL, USA. GeoHealth 2021, 5, e2020GH000348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, L.B.; Dziobak, M.K.; Pisarski, E.C.; Wirth, E.F.; Wells, R.S. Sentinels of Synthetics—A Comparison of Phthalate Exposure between Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) and Human Reference Populations. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e024050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. Toxic Chemical Release Inventory Reporting Forms and Instructions: Revised 2005 Version; Section 313 of the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (Title III of the Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986); EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Deng, T.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Teng, X.; Hua, X.; Yuan, X.; Yao, Y.; Guo, N.; Li, Y. The Associations of Urinary Phthalate Metabolites with the Intermediate and Pregnancy Outcomes of Women Receiving IVF/ICSI Treatments: A Prospective Single-Center Study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 188, 109884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yordy, J.E.; Wells, R.S.; Balmer, B.C.; Schwacke, L.H.; Rowles, T.K.; Kucklick, J.R. Life History as a Source of Variation for Persistent Organic Pollutant (POP) Patterns in a Community of Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) Resident to Sarasota Bay, FL. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.W.; Wen, Z.D. Phthalate Esters in the Environment: A Critical Review of Their Occurrence, Biodegradation, and Removal during Wastewater Treatment Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, R.S. Social structure and life history of Bottlenose dolphins near Sarasota Bay, Florida: Insights from four decades and five generations. In Primates and Cetaceans; Yamagiwa, J., Karczmarski, L., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; pp. 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.S. Learning from Nature: Bottlenose Dolphin Care and Husbandry. Zoo Biol. 2009, 28, 635–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.S.; Tornero, V.; Borrell, A.; Aguilar, A.; Rowles, T.K.; Rhinehart, H.L.; Hofmann, S.; Jarman, W.M.; Hohn, A.A.; Sweeney, J.C. Integrating Life-History and Reproductive Success Data to Examine Potential Relationships with Organochlorine Compounds for Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in Sarasota Bay, Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 349, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, R.S.; Rhinehart, H.L.; Hansen, L.J.; Sweeney, J.C.; Townsend, F.I.; Stone, R.; Casper, D.R.; Scott, M.D.; Hohn, A.A.; Rowles, T.K. Bottlenose Dolphins as Marine Ecosystem Sentinels: Developing a Health Monitoring System. EcoHealth 2004, 1, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.J.; Wells, R.S.; Sweeney, J.C.; Townsend, F.I.; Balmer, B.C.; Hohn, A.A.; Rhinehart, H.L. Annual, Seasonal and Individual Variation in Hematology and Clinical Blood Chemistry Profiles in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Sarasota Bay, Florida. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 148, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwacke, L.H.; Hall, A.J.; Townsend, F.I.; Wells, R.S.; Hansen, L.J.; Hohn, A.A.; Bossart, G.D.; Fair, P.A.; Rowles, T.K. Hematologic and Serum Biochemical Reference Intervals for Free-Ranging Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) and Variation in the Distributions of Clinicopathologic Values Related to Geographic Sampling Site. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 70, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galligan, T.M.; Balmer, B.C.; Schwacke, L.H.; Bolton, J.L.; Quigley, B.M.; Rosel, P.E.; Ylitalo, G.M.; Boggs, A.S.P. Examining the Relationships between Blubber Steroid Hormones and Persistent Organic Pollutants in Common Bottlenose Dolphins. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsel, D.R. Nondetects and Data Analysis: Statistics for Censored Environmental Data; Helsel, D.R., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Helsel, D.R. Much Ado about next to Nothing: Incorporating Nondetects in Science. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2009, 54, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Aubin, D.J.; Ridgway, S.H.; Wells, R.S.; Rhinehart, H. Dolphin Thyroid and Adrenal Hormones: Circulating Levels in Wild and Semidomesticated Tursiops truncatus, and Influence of Sex, Age, and Season. Mar. Mammal Sci. 1996, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, K.L.; Ramer, J.; Brown, J.L.; Sweeney, J.; Hanahoe, E.M.; Reidarson, T.; Proudfoot, J.; Bergfelt, D.R. Thyroid Hormone Concentrations in Relation to Age, Sex, Pregnancy, and Perinatal Loss in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 197, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwacke, L.H.; Zolman, E.S.; Balmer, B.C.; De Guise, S.; George, R.C.; Hoguet, J.; Hohn, A.A.; Kucklick, J.R.; Lamb, S.; Levin, M.; et al. Anaemia, Hypothyroidism and Immune Suppression Associated with Polychlorinated Biphenyl Exposure in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2012, 279, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fair, P.A.; Montie, E.; Balthis, L.; Reif, J.S.; Bossart, G.D. Influences of Biological Variables and Geographic Location on Circulating Concentrations of Thyroid Hormones in Wild Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2011, 174, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, T.I.; Chen, M.H.; Lien, G.W.; Chen, P.S.; Lin, J.C.C.; Fang, C.C.; Chen, P.C. Effects of Gender on the Association of Urinary Phthalate Metabolites with Thyroid Hormones in Children: A Prospective Cohort Study in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollowell, J.G.; Staehling, N.W.; Flanders, W.D.; Hannon, W.H.; Gunter, E.W.; Spencer, C.A.; Braverman, L.E. Serum TSH, T4, and Thyroid Antibodies in the United States Population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baksi, S.; Pradhan, A. Thyroid Hormone: Sex-Dependent Role in Nervous System Regulation and Disease. Biol. Sex Differ. 2021, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.; Perez, R.; Hernandez, A.; Tejada, P.; Arteta, M.; Ramos, J.T. Factors and Mechanisms for Pharmacokinetic Differences between Pediatric Population and Adults. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheuplein, R.; Charnley, G.; Dourson, M. Differential Sensitivity of Children and Adults to Chemical Toxicity. I. Biological Basis. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 35, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasper-Sonnenberg, M.; Koch, H.M.; Wittsiepe, J.; Wilhelm, M. Levels of Phthalate Metabolites in Urine among Mother-Child-Pairs—Results from the Duisburg Birth Cohort Study, Germany. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2012, 215, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütze, A.; Pälmke, C.; Angerer, J.; Weiss, T.; Brüning, T.; Koch, H.M. Quantification of Biomarkers of Environmental Exposure to Di(Isononyl)Cyclohexane-1,2-Dicarboxylate (DINCH) in Urine via HPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 895–896, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Kannan, N.; Subramanian, A.; Watanabe, S.; Tatsukawa, R. Highly Toxic Coplanar PCBs: Occurrence, Source, Persistency and Toxic Implications to Wildlife and Humans. Environ. Pollut. 1987, 47, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.J. Endocrine organs: Hypophysis, thyroid and adrenal. In The Biology of Marine Mammal; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1969; pp. 349–390. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, T.J.B.; Gangolli, S.D. Aspects of the Testicular Toxicity of Phthalate Esters. Environ. Health Perspect. 1986, 65, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meeker, J.D.; Calafat, A.M.; Hauser, R. Urinary Phthalate Metabolites and Their Biotransformation Products: Predictors and Temporal Variability among Men and Women. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirahanchi, Y.; Jialal, I. Physiology, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH); StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gayathri, N.S.; Dhanya, C.R.; Indu, A.R.; Kurup, P.A. Changes in Some Hormones by Low Doses of Di (2-Ethyl Hexyl) Phthalate (DEHP), a Commonly Used Plasticizer in PVC Blood Storage Bags & Medical Tubing. Indian J. Med. Res. 2004, 119, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Price, S.C.; Chescoe, D.; Grasso, P.; Wright, M.; Hinton, R.H. Alterations in the Thyroids of Rats Treated for Long Periods with Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate or with Hypolipidaemic Agents. Toxicol. Lett. 1988, 40, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.-P.; Ma, Y.-B.; Lu, C.-J.; Mirza, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jia, Y.-F.; Li, W.-G.; Pei, D.-S. The Effects of Disturbance on Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid (HPT) Axis in Zebrafish Larvae after Exposure to DEHP. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, J.H. Role of Plasma Proteins in the Binding, Distribution and Metabolism of the Thyroid Hormones. N. Engl. J. Med. 1968, 278, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.P.; Feng, S.; Li, Y.L.; Li, R.; Lv, J.; Ren, W.Q.; Feng, Q.W.; Liu, P.; Wang, Q.N. Di-(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate Inhibits Expression and Internalization of Transthyretin in Human Placental Trophoblastic Cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 394, 114960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, A.; Nishiyama, N.; Sugiyama, S.I.; Yamauchi, K. The Effect of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals on Thyroid Hormone Binding to Japanese Quail Transthyretin and Thyroid Hormone Receptor. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2003, 134, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, N.; Yamauchi, K. Characteristics of 3,5,3′-Triiodothyronine (T3)-Uptake System of Tadpole Red Blood Cells: Effect of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals on Cellular T3 Response. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 183, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahid, M.A.; Sharma, S. Physiology, Thyroid Hormone; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yeap, B.B.; Alfonso, H.; Chubb, S.A.P.; Walsh, J.P.; Hankey, G.J.; Almeida, O.P.; Flicker, L. Higher Free Thyroxine Levels Are Associated with Frailty in Older Men: The Health In Men Study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2011, 76, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeap, B.B.; Alfonso, H.; Hankey, G.J.; Flicker, L.; Golledge, J.; Norman, P.E.; Chubb, S.A.P. Higher Free Thyroxine Levels Are Associated with All-Cause Mortality in Euthyroid Older Men: The Health in Men Study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwangbo, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.W.; Park, Y.J.; Park, D.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Shin, C.S.; Cho, N.H. High-Normal Free Thyroxine Levels Are Associated with Low Trabecular Bone Scores in Euthyroid Postmenopausal Women. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, J.J.; Grundy, S.M. Cholesterol Metabolism in Hypothyroidism and Hyperthyroidism in Man. J. Lipid Res. 1981, 22, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habra, M.A.; Hijazi, R.; Verstovsek, G.; Marcelli, M. Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Associated with Hyperthyroidism: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Thyroid. Thyroid 2004, 14, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazaitou-Panayiotou, K.; Perros, P.; Boudina, M.; Siardos, G.; Drimonitis, A.; Patakiouta, F.; Vainas, I. Mortality from Thyroid Cancer in Patients with Hyperthyroidism: The Theagenion Cancer Hospital Experience. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 159, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, D.A. Fetal Thyroid Function: Diagnosis and Management of Fetal Thyroid Disorders. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 1997, 40, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, B.M.; Knight, B.A.; Hill, A.; Hattersley, A.T.; Vaidya, B. Fetal Thyroid Hormone Level at Birth Is Associated with Fetal Growth. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E934–E938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anselmo, J.; Cao, D.; Karrison, T.; Weiss, R.E.; Refetoff, S. Fetal Loss Associated with Excess Thyroid Hormone Exposure. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 292, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weingartner, G.M.; Thornton, S.J.; Andrews, R.D.; Enstipp, M.R.; Barts, A.D.; Hochachka, P.W. The Effects of Experimentally Induced Hyperthyroidism on the Diving Physiology of Harbor Seals (Phoca vitulina). Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, D.A. Physiological Variations in Thyroid Hormones: Physiological and Pathophysiological Considerations. Clin. Chem. 1996, 42, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis. J. Am. Psychol. Soc. 1992, 1, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.C.; Salvatore, D.; Gereben, B.; Berry, M.J.; Larsen, P.R. Biochemistry, Cellular and Molecular Biology, and Physiological Roles of the Iodothyronine Selenodeiodinases. Endocrine Reviews. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 38–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, T.J.; Kaptein, E.; Terpstra, O.T.; Krenning, E.P. Deiodination of Thyroid Hormone by Human Liver. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 67, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, A.C.; Kim, B.W. Deiodinases: Implications of the Local Control of Thyroid Hormone Action. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarasota Water Temp. Available online: https://seatemperature.info/sarasota-water-temperature.html (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Rian, M.B.; Vike-Jonas, K.; Gonzalez, S.V.; Ciesielski, T.M.; Venkatraman, V.; Lindstrøm, U.; Jenssen, B.M.; Asimakopoulos, A.G. Phthalate Metabolites in Harbor Porpoises (Phocoena phocoena) from Norwegian Coastal Waters. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossi, M.C.; Coppola, D.; Baini, M.; Giannetti, M.; Guerranti, C.; Marsili, L.; Panti, C.; de Sabata, E.; Clò, S. Large Filter Feeding Marine Organisms as Indicators of Microplastic in the Pelagic Environment: The Case Studies of the Mediterranean Basking Shark (Cetorhinus maximus) and Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus). Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 100, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucklick, J.; Schwacke, L.; Wells, R.; Hohn, A.; Guichard, A.; Yordy, J.; Hansen, L.; Zolman, E.; Wilson, R.; Litz, J.; et al. Bottlenose Dolphins as Indicators of Persistent Organic Pollutants in the Western North Atlantic Ocean and Northern Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4270–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woshner, V.; Knott, K.; Wells, R.; Willetto, C.; Swor, R.; O’Hara, T. Mercury and Selenium in Blood and Epidermis of Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Sarasota Bay, FL: Interaction and Relevance to Life History and Hematologic Parameters. EcoHealth 2008, 5, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monosson, E. Chemical Mixtures: Considering the Evolution of Toxicology and Chemical Assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiandanese, N.; Borromeo, V.; Berrini, A.; Fischer, B.; Schaedlich, K.; Schmidt, J.S.; Secchi, C.; Pocar, P. Maternal Exposure to a Mixture of Di(2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) and Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) Causes Reproductive Dysfunction in Adult Male Mouse Offspring. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 65, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, R.N.; Tomlinson, M.; Craigon, J.; England, G.C.W.; Lea, R.G. Independent and Combined Effects of Diethylhexyl Phthalate and Polychlorinated Biphenyl 153 on Sperm Quality in the Human and Dog. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, R.M.; Long, B.; Casper, D.; Ortiz, L.L.; Williams, T.M. Biochemical and Hormonal Changes during Acute Fasting and Re-Feeding in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Mar. Mammal Sci. 2010, 26, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, B.; Stengel, C.; Neiger, R. Dietary Hyperthyroidism in Dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 53, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivalle, C.; Doucet, J.; Chassagne, P.; Landrin, I.; Kadri, N.; Menard, J.-F.; Bercoff, E. Differences in the Signs and Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism in Older and Younger Patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1996, 44, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC). Prohibition of Children’s Toys and Child Care Articles Containing Specified Phthalates; 16 CFR Part 1307; Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC): Bethesda, MA, USA, 2018.
- AB-2762. Assembly Bill No. 2762. 2020. Available online: https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billTextClient.xhtml?bill_id=201920200AB2762 (accessed on 9 February 2022).

| Analyte | Minimum | Median | Maximum | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP; ng/mL) | 0.17 | 0.49 | 76.60 | 56.00 |
| Triiodothyronine (T3; ng/dL) | <LOD | 86.55 | 175.00 | 60.00 |
| Total thyroxine (T4; μg/dL) | 7.94 | 15.00 | 22.02 | 100.00 |
| Free thyroxine (FT4; ng/dL) (n = 49) | 1.00 | 1.86 | 3.51 | 100.00 |
| Female (n = 29) | Male (n = 21) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyte | Minimum | Median | Maximum | % | Minimum | Median | Maximum | % |
| Mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP; ng/mL) | 0.17 | 2.10 | 76.60 | 56.00 | 0.17 | 0.55 | 49.20 | 65.52 |
| Triiodothyronine (T3; ng/dL) | <LOD | 97.40 | 158.00 | 60.00 | <LOD | 70.30 | 175.00 | 65.52 |
| Total thyroxine (T4; μg/dL) | 10.55 | 15.80 | 22.02 | 100.00 | 7.94 | 14.20 | 21.10 | 100.00 |
| Free thyroxine (FT4; ng/dL) (n = 49) | 1.11 | 1.81 | 2.77 | 100.00 | 1.00 | 2.09 | 3.51 | 100.00 |
| Adult (n = 33) | Juvenile (n = 17) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyte | Minimum | Median | Maximum | % | Minimum | Median | Maximum | % |
| Mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (MEHP; ng/mL) | 0.17 | 0.42 | 76.60 | 52.94 | 0.17 | 1.28 | 28.40 | 62.50 |
| Triiodothyronine (T3; ng/dL) | <LOD | 80.55 | 158.00 | 58.82 | <LOD | 102.50 | 175.00 | 62.50 |
| Total thyroxine (T4; μg/dL) | 7.94 | 13.97 | 20.90 | 100.00 | 12.00 | 18.85 | 22.02 | 100.00 |
| Free thyroxine (FT4; ng/dL) (n = 49) | 1.00 | 1.70 | 2.66 | 100.00 | 1.22 | 2.14 | 3.51 | 100.00 |
| Hormone | Sex | Age Class | (Sex) x (Age Class) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wald Statistic | p | Wald Statistic | p | Wald Statistic | p | |
| Triiodothyronine (T3) | 0.11 | 0.74 | 1.41 | 0.23 | 0.83 | 0.36 |
| Total thyroxine (T4) | 0.78 | 0.38 | 23.11 | <0.0001 | 2.24 | 0.13 |
| Free thyroxine (FT4) | 5.96 | 0.01 | 14.56 | 0.0001 | 0.91 | 0.34 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dziobak, M.K.; Wells, R.S.; Pisarski, E.C.; Wirth, E.F.; Hart, L.B. A Correlational Analysis of Phthalate Exposure and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Sarasota Bay, Florida (2010–2019). Animals 2022, 12, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12070824
Dziobak MK, Wells RS, Pisarski EC, Wirth EF, Hart LB. A Correlational Analysis of Phthalate Exposure and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Sarasota Bay, Florida (2010–2019). Animals. 2022; 12(7):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12070824
Chicago/Turabian StyleDziobak, Miranda K., Randall S. Wells, Emily C. Pisarski, Ed F. Wirth, and Leslie B. Hart. 2022. "A Correlational Analysis of Phthalate Exposure and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Sarasota Bay, Florida (2010–2019)" Animals 12, no. 7: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12070824
APA StyleDziobak, M. K., Wells, R. S., Pisarski, E. C., Wirth, E. F., & Hart, L. B. (2022). A Correlational Analysis of Phthalate Exposure and Thyroid Hormone Levels in Common Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) from Sarasota Bay, Florida (2010–2019). Animals, 12(7), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12070824







