Comparative Proteomics Study of Yak Milk from Standard and Naturally Extended Lactation Using iTRAQ Technique
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Yaks and Milk Sampling
2.2. iTRAQ Analysis of Skim Milk Proteins of Yaks
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Skim Milk Proteins of Yaks
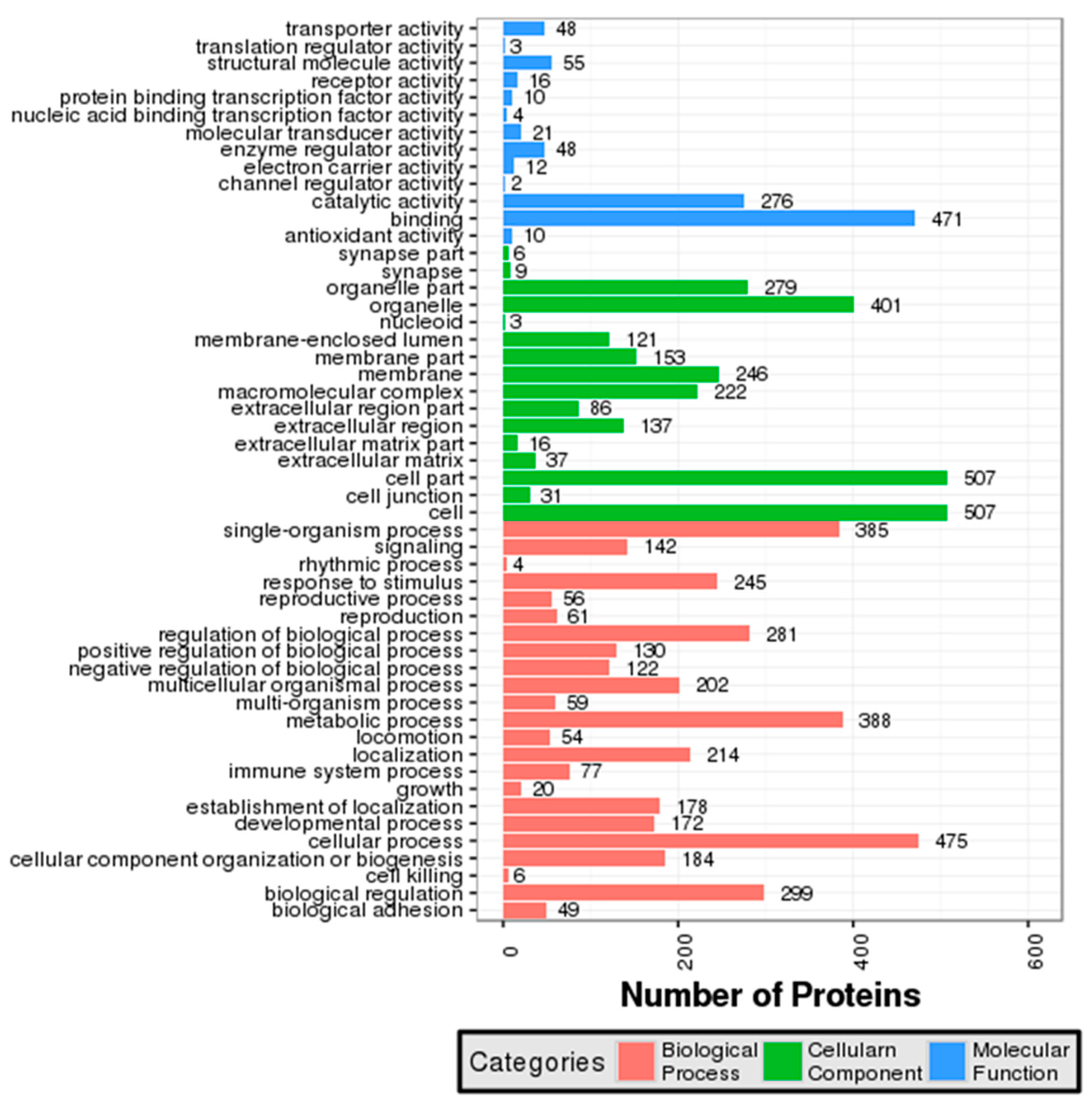
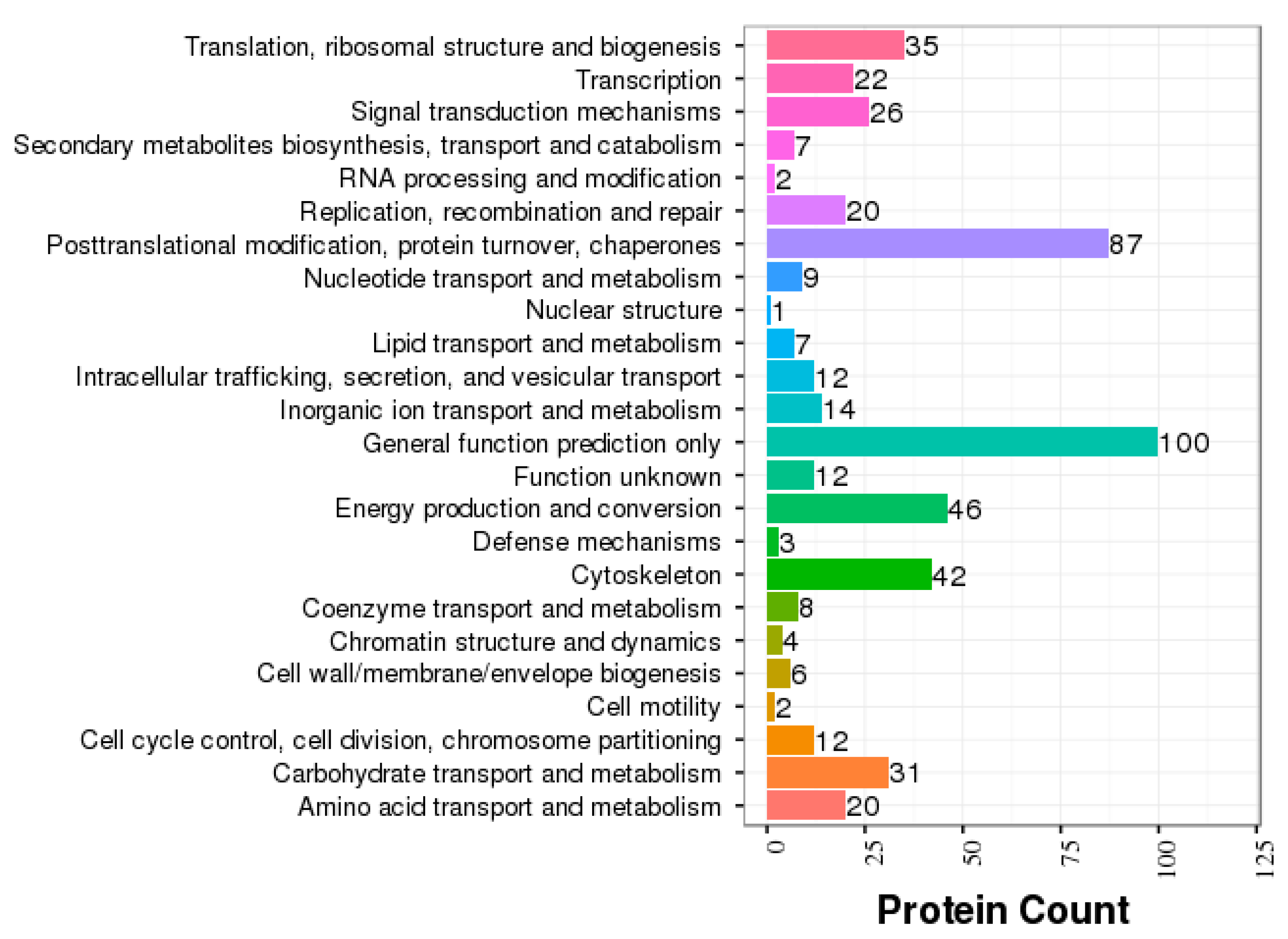
3.2. GO and COG Annotation of Identified Proteins
3.3. Differentially Expressed Milk Proteins of Yaks
3.4. GO Enrichment Analysis of DEPs
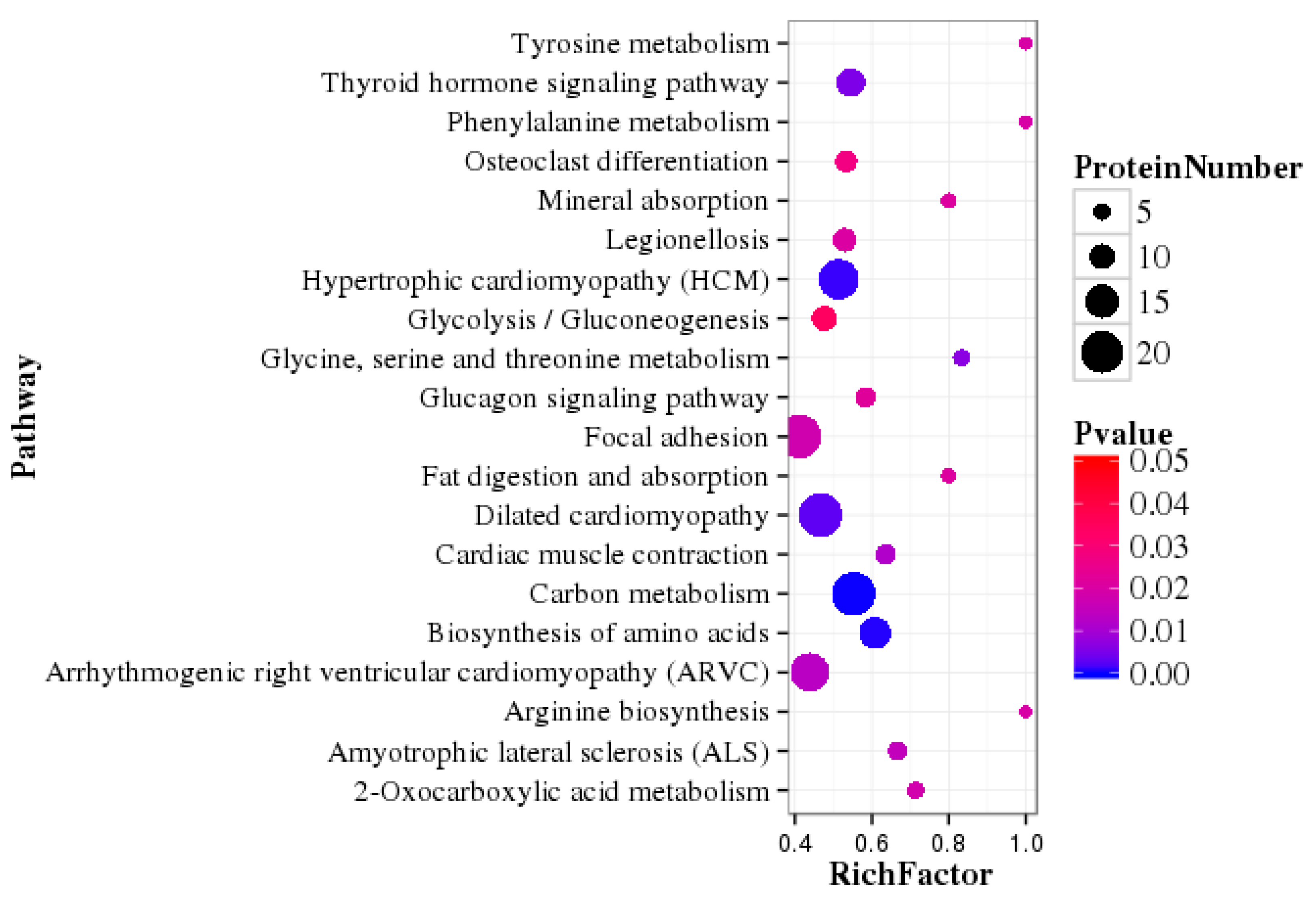
3.5. Pathway Enrichment Analysis of DEPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikkhah, A. Science of camel and yak milks: Human nutrition and health perspectives. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 2, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorensen, A.; Muir, D.D.; Knight, C.H. Extended lactation in dairy cows: Effects of milking frequency, calving season and nutrition on lactation persistency and milk quality. J. Dairy Res. 2008, 75, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, S.K.; Long, R.J.; Kang, M.Y. Milking performance of China yak (Bos grunniens): A preliminary report. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 2, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hurley, W.L. Mammary gland function during involution. J. Dairy Sci. 1989, 72, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.J.; Zhao, H.Q.; Gu, R.X. Protein composition and characteristics of yak milk. J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2013, 36, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.C.; Zhong, G.H.; WANG, Y.; Mao, Y.J.; Zou, S.X.; Chen, W.H.; Chen, J. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of lactation in half-lactating yak. Chin. Agric. Sci. 2002, 4, 421–425. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, M.S.; Hurley, W.L. Effects of secretion removal on bovine mammary gland function following an extended milk stasis. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, A.; Hostmark, A.T.; Harstad, O.M. Bovine milk in human nutrition—A review. Lipids Health Dis. 2007, 61, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Playford, R.J.; Weiser, M.J. Bovine colostrum: Its constituents and uses. Nutrients 2021, 13, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.L.; Huang, Y.N.; Marchese, J.N.; Williamson, B.; Parker, K.; Hattan, S.; Khainovski, N.; Pillai, S.; Dey, S.; Daniels, S.; et al. Multiplexed protein quantitation in saccharomyces cerevisiae using amine-reactive isobaric tagging reagents. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2004, 3, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinhardt, T.A.; Lippolis, J.D. Developmental changes in the milk fat globule membrane proteome during the transition from colostrum to milk-science direct. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Boeren, S.; Hageman, J.A.; Hooijdonk, T.V.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K. Perspective on calf and mammary gland development through changes in the bovine milk proteome over a complete lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 5362–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roncada, P.; Piras, C.; Soggiu, A.; Turk, R.; Urbani, A.; Bonizzi, L. Farm animal milk proteomics. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4259–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Alvarado, R.; Phinney, B.; Lönnerdal, B. Proteomic characterization of human milk whey proteins during a twelve-month lactation period. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosch, M.; Lu, Y.; Hubbard, T.; Choudhary, J. Accurate and sensitive peptide identification with MASCOT percolator. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3176–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilocca, B.; Balmas, V.; Hassan, Z.U.; Jaoua, S.; Migheli, Q. A proteomic investigation of Aspergillus carbonarius exposed to yeast volatilome or to its major component 2-phenylethanol reveals major shifts in fungal metabolism. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 306, 108265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gallego, C.; Garcia-Mantrana, I.; Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C. The human milk microbiome and factors influencing its composition and activity. Semin. Fetal Neonatal. Med. 2016, 21, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auldist, M.J.; Grainger, C.; Houlihan, A.V.; Mayes, J.J.; Williams, R.P. Composition, coagulation properties, and cheesemaking potential of milk from cows undergoing extended lactations in a pasture-based dairying system. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnykowska-Ukacka, M.; Królak-Olejnik, B.; Orczyk-Pawiowicz, M. Breast milk macronutrient components in prolonged lactation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prentice, P.; Ong, K.K.; Schoemaker, M.H.; Vantol, E.A.; Vervoort, J.; Hughes, I.A.; Acerini, C.L.; Dunger, D.B. Breast milk nutrient content and infancy growth. Acta Paediatr. 2016, 105, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yu, S.; Cao, S. Quantitative proteomic analysis of whey proteins in the colostrum and mature milk of yak (Bos grunniens). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenica, S.; Francesca, T.; Ludovica, D.; Antonio, C.; Giusi, P.; Laura, T.; Giorgio, V.; Alessia, L.; Daniela, M.; Giovanni, C. Proteomics-driven analysis of ovine whey colostrum. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117433. [Google Scholar]
- Macias, H.; Hinck, L. Mammary gland development. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2012, 1, 533–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ollier, S.; Zhao, X.; Lacasse, P. Effect of prolactin-release inhibition on milk production and mammary gland involution at drying-off in cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jena, M.K.; Jaswal, S.; Kumar, S.; Mohanty, A.K. Molecular mechanism of mammary gland involution: An update. Dev. Biol. 2019, 445, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayton, V.J.; Beckman, A.; Linden, M. Myeloid sarcoma expressing keratins and mimicking carcinoma-case report and literature review. Lab. Med. 2021, 13, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belardin, L.; Camargo, M.; Intasqui, P.; Antoniassi, M.; Fraietta, R.; Bertolla, R. Cysteine-rich secretory protein 3: Inflammation role in adult varicocoele. Andrology 2019, 7, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.C.; Day, B.; Harper, L.; Yee, J.; Rancourt, D.E. Fluid shear stress promotes embryonic stem cell pluripotency via interplay between β-catenin and vinculin in bioreactor culture. Stem Cells 2021, 39, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, B.; Wu, Q.; Guo, Y. An in vitro vesicle formation assay reveals cargo clients and factors that mediate vesicular trafficking. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101287118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Pang, X.; Ma, C.; Jiang, S. Comparative proteomics analysis of human and ruminant milk serum reveals variation in protection and nutrition. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cao, X.; Wu, R.; Liu, B.; Ye, W.; Yue, X. Comparative proteomic exploration of whey proteins in human and bovine colostrum and mature milk using iTRAQ-coupled LC-MS/MS. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, B.; Ji, C.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Jiang, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, G.; Min, L.; et al. Quantitative Label-Free Proteomic Analysis of Milk Fat Globule Membrane in Donkey and Human Milk. Front. Nutr. 2021, 22, 670099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| No. | NCBInr Accession | NCBInr Description | Mass (kDa) | Protein Coverage (%) | Fold Change * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | gi|440897559 | 14-3-3 protein theta, partial | 29.1 | 11.7 | 10 |
| 2 | gi|440898761 | Spliceosome RNA helicase BAT1 | 50.5 | 5.5 | 6.82 |
| 3 | gi|440897815 | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide-protein glycosyltransferase 48 kDa subunit, partial | 50.8 | 2.4 | 6.49 |
| 4 | gi|440892840 | Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein-associated protein N, partial | 24.7 | 3.3 | 5.73 |
| 5 | gi|440892885 | Protein S100-A1, partial | 13.9 | 11.9 | 5.56 |
| 6 | gi|440896162 | Tubulin beta-7 chain | 50.1 | 28.6 | 5.35 |
| 7 | gi|15718687 | 40S ribosomal protein S3 isoform 1 | 26.8 | 3.7 | 5.13 |
| 8 | gi|115498012 | Glycogen phosphorylase, liver form | 88.3 | 3.4 | 4.87 |
| 9 | gi|440895215 | Hemoglobin subunit beta, partial | 18.0 | 38.3 | 4.64 |
| 10 | gi|440906467 | D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase | 56.8 | 8.1 | 4.6 |
| 11 | gi|440905390 | Haptoglobin, partial | 45.5 | 4.3 | 4.21 |
| 12 | gi|440907809 | Annexin A4, partial | 36.1 | 25.4 | 4.21 |
| 13 | gi|32189334 | ADP/ATP translocase 2 | 33.1 | 10.1 | 3.90 |
| 14 | gi|326933110 | PREDICTED: histone-binding protein RBBP4-like | 47.3 | 1.9 | 3.88 |
| 15 | gi|440895216 | Hemoglobin subunit epsilon-1, partial | 16.5 | 23.8 | 3.87 |
| 16 | gi|7106387 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-5 | 25.4 | 5.2 | 3.79 |
| 17 | gi|440912614 | Annexin A1 | 39.2 | 3.8 | 3.69 |
| 18 | gi|440903260 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 42 | 51.5 | 5.6 | 3.58 |
| 19 | gi|440901472 | Secretoglobin family 1D member 2 | 11.5 | 8.8 | 3.45 |
| 20 | gi|440900805 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-1, partial | 115.9 | 2.6 | 3.42 |
| 21 | gi|440907817 | Hypothetical protein M91_09610 | 27.6 | 4.9 | 3.4 |
| 22 | gi|440903642 | T-complex protein 1 subunit gamma, partial | 64.1 | 1.9 | 3.28 |
| 23 | gi|62460420 | Heterogeneousnuclear ribonucleoprotein F | 46.0 | 4.1 | 3.1 |
| 24 | gi|440899875 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, partial | 89.1 | 1.4 | 3.06 |
| 25 | gi|351702463 | Calponin-3 | 19.7 | 6.2 | 3.03 |
| 26 | gi|440902212 | Adenosylhomocysteinase, partial | 47.5 | 1.9 | 2.97 |
| 27 | gi|444513904 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1, partial | 20.6 | 23.9 | 2.95 |
| 28 | gi|440902100 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C | 33.8 | 7.5 | 2.79 |
| 29 | gi|73955372 | PREDICTED: profilin-1-like | 10.5 | 40.6 | 2.77 |
| 30 | gi|440908857 | Clathrin heavy chain 1, partial | 191.6 | 5.5 | 2.76 |
| 31 | gi|195157178 | GL12416 | 50.8 | 42.6 | 2.75 |
| 32 | gi|440900693 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8, partial | 54.4 | 14.8 | 2.75 |
| 33 | gi|440901320 | Synaptophysin-like protein 1 | 28.3 | 4.3 | 2.69 |
| 34 | gi|4504447 | Heterogeneousnuclear ribonucleoproteins A2/B1 isoform A2 | 35.8 | 24.2 | 2.66 |
| 35 | gi|115495959 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX1 | 83.1 | 1.5 | 2.62 |
| 36 | gi|440900692 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 18, partial | 49.2 | 5.0 | 2.5 |
| 37 | gi|440900744 | Alpha-S2-casein, partial | 25.7 | 21.5 | 2.48 |
| 38 | gi|440909809 | Hypothetical protein M91_11302, partial | 50.1 | 20.7 | 2.48 |
| 39 | gi|344290140 | PREDICTED: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-1-like | 17.3 | 7.6 | 2.45 |
| 40 | gi|331284195 | Nucleolin | 77.2 | 2.0 | 2.45 |
| 41 | gi|431895946 | NMDA receptor-regulated protein 2 | 39.3 | 30.9 | 2.44 |
| 42 | gi|114051505 | Serpin H1 precursor | 46.6 | 19.9 | 2.44 |
| 43 | gi|440899031 | Heat shock protein HSP 90-alpha, partial | 37.7 | 29.1 | 2.36 |
| 44 | gi|4505585 | Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit beta isoform a | 25.7 | 3.9 | 2.36 |
| 45 | gi|440900746 | Alpha-S1-casein, partial | 24.5 | 91.6 | 2.35 |
| 46 | gi|440908101 | L-lactate dehydrogenase B chain | 37.4 | 13.6 | 2.33 |
| 47 | gi|440895669 | Triosephosphate isomerase | 30.9 | 12.9 | 2.31 |
| 48 | gi|440900959 | 60S ribosomal protein L12, partial | 21.2 | 7.8 | 2.26 |
| 49 | gi|78369302 | Catalase | 60.1 | 3.0 | 2.21 |
| 50 | gi|440904790 | Annexin A6, partial | 75.7 | 7.9 | 2.18 |
| No. | NCBInr Accession | NCBInr Description | Mass (kDa) | Protein Coverage (%) | Fold Change * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | gi|440897611 | 6-phosphofructokinase, muscle type | 94.3 | 2.8 | 0.1 |
| 2 | gi|311257294 | PREDICTED: cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit Rieske, mitochondrial-like | 29.8 | 2.6 | 0.1 |
| 3 | gi|440913466 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha-1, partial | 16.4 | 6.0 | 0.12 |
| 4 | gi|440904354 | Cytochrome c1, heme protein, mitochondrial, partial | 31.5 | 4.9 | 0.14 |
| 5 | gi|440893900 | Primary amine oxidase, liver isozyme, partial | 86.9 | 1.3 | 0.17 |
| 6 | gi|410964723 | PREDICTED: integrin alpha-7 isoform 2 | 129.1 | 1.0 | 0.21 |
| 7 | gi|110350683 | Biglycan precursor | 41.9 | 10.8 | 0.21 |
| 8 | gi|440901307 | Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain | 37.7 | 6.4 | 0.25 |
| 9 | gi|440904898 | Transgelin, partial | 23.0 | 35.8 | 0.27 |
| 10 | gi|114052094 | Calponin-1 | 33.4 | 36.7 | 0.31 |
| 11 | gi|440910551 | Platelet glycoprotein 4 | 53.4 | 4.2 | 0.31 |
| 12 | gi|440897546 | Phosphate carrier protein, mitochondrial, partial | 42.3 | 5.1 | 0.32 |
| 13 | gi|109891934 | RecName: Full=Isocitrate dehydrogenase | 51.1 | 6.9 | 0.34 |
| 14 | gi|440893758 | PDZ and LIM domain protein 3 | 39.9 | 4.1 | 0.35 |
| 15 | gi|440910545 | Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain | 37.4 | 9.2 | 0.36 |
| 16 | gi|115497074 | S-formylglutathione hydrolase | 32.3 | 2.5 | 0.36 |
| 17 | gi|440903063 | 2-oxoglutaratedehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 118.6 | 1.5 | 0.39 |
| 18 | gi|440907850 | Desmoplakin, partial | 329.7 | 0.5 | 0.42 |
| 19 | gi|440907068 | Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 1, partial | 111.4 | 2.1 | 0.42 |
| 20 | gi|440911054 | Desmin, partial | 46.3 | 31.2 | 0.43 |
| 21 | gi|78369436 | 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, mitochondrial | 41.9 | 5.4 | 0.45 |
| 22 | gi|440909063 | Aspartate aminotransferase, cytoplasmic, partial | 47.2 | 2.4 | 0.47 |
| 23 | gi|431894354 | Myosin regulatory light polypeptide 9 | 20.2 | 39.2 | 0.47 |
| 24 | gi|426220158 | PREDICTED: tropomodulin-1 | 40.5 | 2.2 | 0.47 |
| 25 | gi|332634684 | Glutamate [NMDA] receptor subunit epsilon-3 precursor | 94.2 | 1.7 | 0.51 |
| 26 | gi|440896699 | Four and a half LIM domains protein 2, partial | 34.3 | 3.9 | 0.51 |
| 27 | gi|344253851 | Actin, gamma-enteric smooth muscle | 42.2 | 59.0 | 0.51 |
| 28 | gi|440904982 | Sodium-dependent phosphate transport protein 2B | 77.3 | 2.3 | 0.52 |
| 29 | gi|440897772 | Filamin-C | 293.4 | 2.1 | 0.52 |
| 30 | gi|440904421 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2 | 73.6 | 1.5 | 0.52 |
| 31 | gi|440897862 | Filamin-A | 283.1 | 18.1 | 0.53 |
| 32 | gi|440896802 | Myosin-11, partial | 176.4 | 4.3 | 0.55 |
| 33 | gi|440899469 | Citratesynthase, mitochondrial | 52.0 | 2.4 | 0.55 |
| 34 | gi|74354891 | GLUD1 protein | 57.4 | 1.8 | 0.56 |
| 35 | gi|120419518 | enigma protein | 50.8 | 4.8 | 0.56 |
| 36 | gi|440898241 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 75 kDa subunit, mitochondrial, partial | 80.5 | 1.8 | 0.56 |
| 37 | gi|440898951 | Creatine kinase B-type, partial | 43.2 | 18.2 | 0.58 |
| 38 | gi|444518229 | Myosin light chain 6B | 17.1 | 23.2 | 0.58 |
| 39 | gi|440912794 | Calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier protein Aralar1, partial | 73.9 | 1.5 | 0.59 |
| 40 | gi|440901372 | Fibrinogen alpha chain, partial | 86.6 | 12.8 | 0.59 |
| 41 | gi|114053019 | alpha-1B-glycoprotein precursor | 36.3 | 12.9 | 0.59 |
| 42 | gi|119888979 | PREDICTED: basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein | 474.8 | 1.2 | 0.59 |
| 43 | gi|440909830 | Factor XIIa inhibitor, partial | 56.1 | 15.3 | 0.61 |
| 44 | gi|440902649 | Aspartate aminotransferase, mitochondrial | 47.9 | 2.3 | 0.61 |
| 45 | gi|440893207 | Myosin-7, partial | 223.1 | 4.9 | 0.61 |
| 46 | gi|77404217 | Phosphoglycerate mutase 1 | 28.9 | 10.2 | 0.63 |
| 47 | gi|296489917 | TPA: cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes | 17.5 | 22.9 | 0.64 |
| 48 | gi|139948177 | Cysteine and glycine-rich protein 1 | 21.4 | 25.9 | 0.64 |
| 49 | gi|410932519 | PREDICTED: uncharacterized protein LOC101077311 | 11.4 | 35.9 | 0.65 |
| 50 | gi|440901371 | Fibrinogen beta chain, partial | 56.7 | 19.8 | 0.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, M.; Huang, L.; Jin, S.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, Y. Comparative Proteomics Study of Yak Milk from Standard and Naturally Extended Lactation Using iTRAQ Technique. Animals 2022, 12, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030391
Cao M, Huang L, Jin S, Zhao M, Zheng Y. Comparative Proteomics Study of Yak Milk from Standard and Naturally Extended Lactation Using iTRAQ Technique. Animals. 2022; 12(3):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030391
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Mingxing, Lin Huang, Suyu Jin, Mengbo Zhao, and Yucai Zheng. 2022. "Comparative Proteomics Study of Yak Milk from Standard and Naturally Extended Lactation Using iTRAQ Technique" Animals 12, no. 3: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030391
APA StyleCao, M., Huang, L., Jin, S., Zhao, M., & Zheng, Y. (2022). Comparative Proteomics Study of Yak Milk from Standard and Naturally Extended Lactation Using iTRAQ Technique. Animals, 12(3), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030391





