Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Beef Cattle in China
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.3. Detection of BRSV
2.4. Amplification of Complete G and F Gene Sequences from Clinical Samples
2.5. Genome Amplification
2.6. Sequences, Phylogenetic, and Recombination Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of BRSV
3.2. Molecular Characterization of the G Gene Sequences
3.3. Molecular Characterization of the F Gene Sequences
3.4. Genomic Characterization of BRSV Strains
4. Discussion
4.1. Prevalence of BRSV in China
4.2. Molecular Characterization of the G Gene Sequences
4.3. Molecular Characterization of the F Gene Sequences
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stott, E.J.; Taylor, G. Respiratory syncytial virus. Brief review. Arch. Virol. 1985, 84, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerch, R.A.; Stott, E.J.; Wertz, G.W. Characterization of bovine respiratory syncytial virus proteins and mRNAs and generation of cDNA clones to the viral mRNAs. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotti, L.; Giammarioli, M.; Rosati, S. Genetic characterization of bovine respiratory syncytial virus strains isolated in Italy: Evidence for the circulation of new divergent clades. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento-Silva, R.E.; Nakamura-Lopez, Y.; Vaughan, G. Epidemiology, molecular epidemiology and evolution of bovine respiratory syncytial virus. Viruses 2012, 4, 3452–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furze, J.M.; Roberts, S.R.; Wertz, G.W.; Taylor, G. Antigenically distinct G glycoproteins of BRSV strains share a high degree of genetic homogeneity. Virology 1997, 231, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvander, M.; Vilcek, S.; Baule, C.; Uttenthal, A.; Ballagi-Pordány, A.; Belák, S. Genetic and antigenic analysis of the G attachment protein of bovine respiratory syncytial virus strains. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79 Pt. 12, 2939–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, N.; Cernicchiaro, N.; Torres, S.; Li, F.; Hause, B.M. Metagenomic characterization of the virome associated with bovine respiratory disease in feedlot cattle identified novel viruses and suggests an etiologic role for influenza D virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Yao, X.; Yang, Y.; Niu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pan, R.; Jiang, X.; Xiaobo, S.; Qiao, X.; et al. Isolation, identification, and phylogenetic analysis of subgroup III strain of bovine respiratory syncytial virus contributed to outbreak of acute respiratory disease among cattle in Northeast China. Virulence 2021, 12, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazici, Z.; Ozan, E.; Tamer, C.; Muftuoglu, B.; Barry, G.; Kurucay, H.N.; Elhag, A.E.; Cagirgan, A.A.; Gumusova, S.; Albayrak, H. Circulation of Indigenous Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus Strains in Turkish Cattle: The First Isolation and Molecular Characterization. Animals 2020, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, U.J.; Finke, S.; Conzelmann, K.K. Generation of bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV) from cDNA: BRSV NS2 is not essential for virus replication in tissue culture, and the human RSV leader region acts as a functional BRSV genome promoter. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valarcher, J.F.; Schelcher, F.; Bourhy, H. Evolution of bovine respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10714–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leme, R.A.; Dall Agnol, A.M.; Balbo, L.C.; Pereira, F.L.; Possatti, F.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Molecular characterization of Brazilian wild-type strains of bovine respiratory syncytial virus reveals genetic diversity and a putative new subgroup of the virus. Vet. Q. 2020, 40, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, A.; Kawauchi, K.; Andoh, K.; Hatama, S. Sequence and unique phylogeny of G genes of bovine respiratory syncytial viruses circulating in Japan. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.; Stott, E.J.; Furze, J.; Ford, J.; Sopp, P. Protective epitopes on the fusion protein of respiratory syncytial virus recognized by murine and bovine monoclonal antibodies. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73 Pt. 9, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.H.; Cook, R.S.; Wyld, S.G.; Furze, J.M.; Taylor, G. Passive protection of gnotobiotic calves using monoclonal antibodies directed at different epitopes on the fusion protein of bovine respiratory syncytial virus. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 177, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.; Bruce, C.; Barbet, A.F.; Wyld, S.G.; Thomas, L.H. DNA vaccination against respiratory syncytial virus in young calves. Vaccine 2005, 23, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.; Rijsewijk, F.A.; Thomas, L.H.; Wyld, S.G.; Gaddum, R.M.; Cook, R.S.; Morrison, W.I.; Hensen, E.; van Oirschot, J.T.; Keil, G. Resistance to bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV) induced in calves by a recombinant bovine herpesvirus-1 expressing the attachment glycoprotein of BRSV. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79 Pt. 7, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W. Isolation and Identification of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Establishment of an Indirect ELISA Diagnostic Method with the Recombinant Nucleocapsid Protein. Master’s Thesis, HeilongjiangBayi Agricultural University, Daqing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W. Serosurvey of Major Bovine Resporitary Viruses and Identification of BVDV Isolates and Vaccine Development. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Wei, X.; Wu, C.; Cui, Q.; Hao, Y. Investigation of viral pathogens in cattle with bovine respiratory disease complex in Inner Mongolia, China. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 153, 104594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Guo, L. Development of a nanoparticle-assisted PCR assay for detection of bovine respiratory syncytial virus. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, M.; Lin, J.; Xue, F.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, X. Development of a One-Step Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Detection of Viral Pathogens Associated with the Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 825257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headley, S.A.; Balbo, L.C.; Alfieri, A.F.; Saut, J.P.E.; Baptista, A.L.; Alfieri, A.A. Bovine respiratory disease associated with Histophilus somni and bovine respiratory syncytial virus in a beef cattle feedlot from Southeastern Brazil. Semin. Cienc. Agrar. 2017, 38, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timurkan, M.O.; Aydin, H.; Sait, A. Identification and Molecular Characterisation of Bovine Parainfluenza Virus-3 and Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus-First Report from Turkey. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 63, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valarcher, J.F.; Taylor, G. Bovine respiratory syncytial virus infection. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 153–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentova, V. The antigenic and genetic variability of bovine respiratory syncytial virus with emphasis on the G protein. Vet. Med. 2003, 48, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doreleijers, J.F.; Langedijk, J.P.; Hård, K.; Boelens, R.; Rullmann, J.A.; Schaaper, W.M.; van Oirschot, J.T.; Kaptein, R. Solution structure of the immunodominant region of protein G of bovine respiratory syncytial virus. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 14684–14688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furze, J.; Wertz, G.; Lerch, R.; Taylor, G. Antigenic heterogeneity of the attachment protein of bovine respiratory syncytial virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75 Pt. 2, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langedijk, J.P.; Meloen, R.H.; Taylor, G.; Furze, J.M.; van Oirschot, J.T. Antigenic structure of the central conserved region of protein G of bovines respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4055–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ai, H.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Shi, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, C.; Han, Z.; Liu, S. Surveillance of Class I Newcastle Disease Virus at Live Bird Markets in China and Identification of Variants with Increased Virulence and Replication Capacity. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0024122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, R.A.; Anderson, K.; Amann, V.L.; Wertz, G.W. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the bovine respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein mRNA and expression from a recombinant vaccinia virus. Virology 1991, 181, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 Indicates the province or municipality of the sample collected in this study,
Indicates the province or municipality of the sample collected in this study, 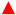 Indicates provinces with BRSV positive-sample distribution.
Indicates provinces with BRSV positive-sample distribution.
 Indicates the province or municipality of the sample collected in this study,
Indicates the province or municipality of the sample collected in this study,  Indicates provinces with BRSV positive-sample distribution.
Indicates provinces with BRSV positive-sample distribution.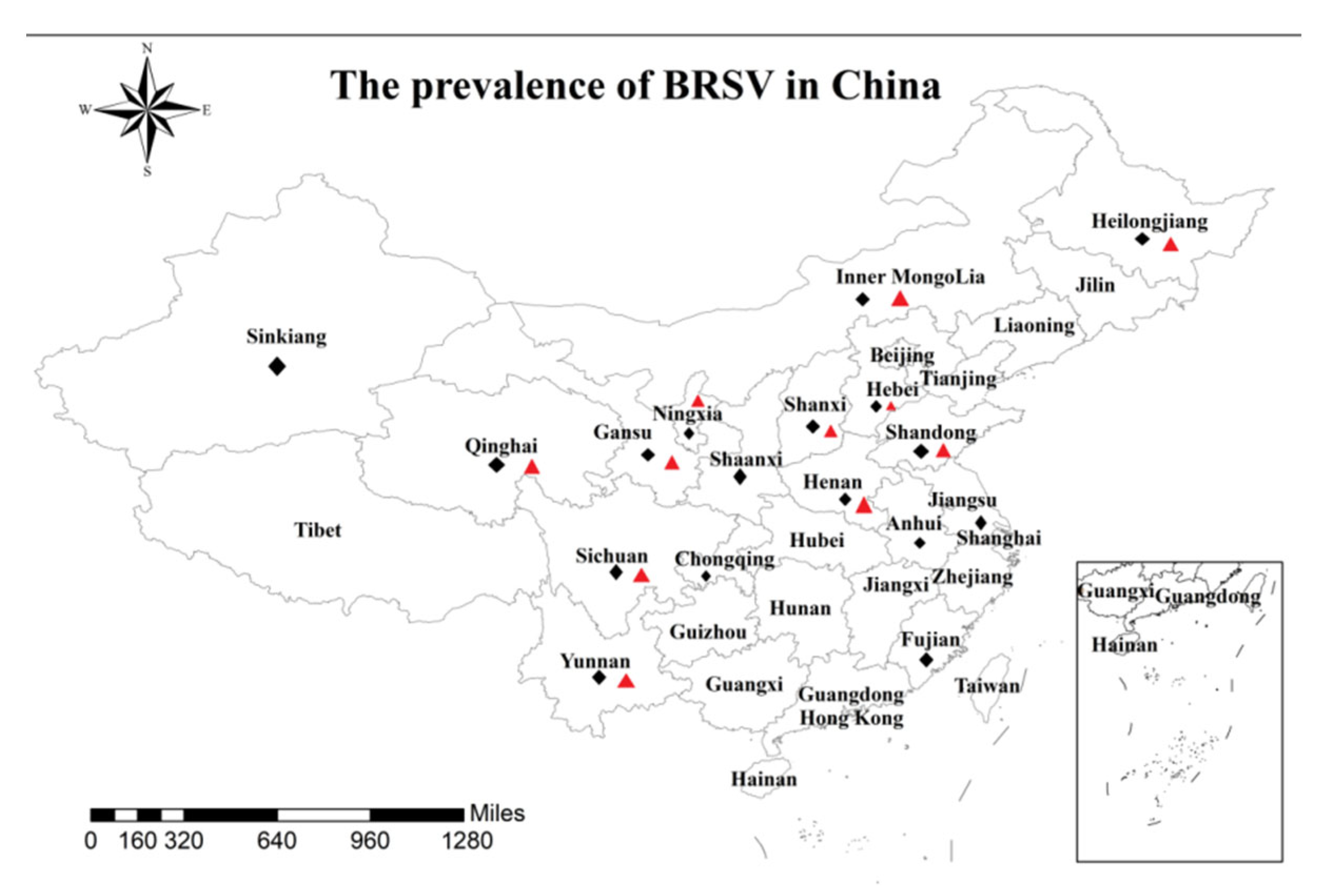
 represents the G gene sequences of other strains in China.
represents the G gene sequences of other strains in China.
 represents the G gene sequences of other strains in China.
represents the G gene sequences of other strains in China.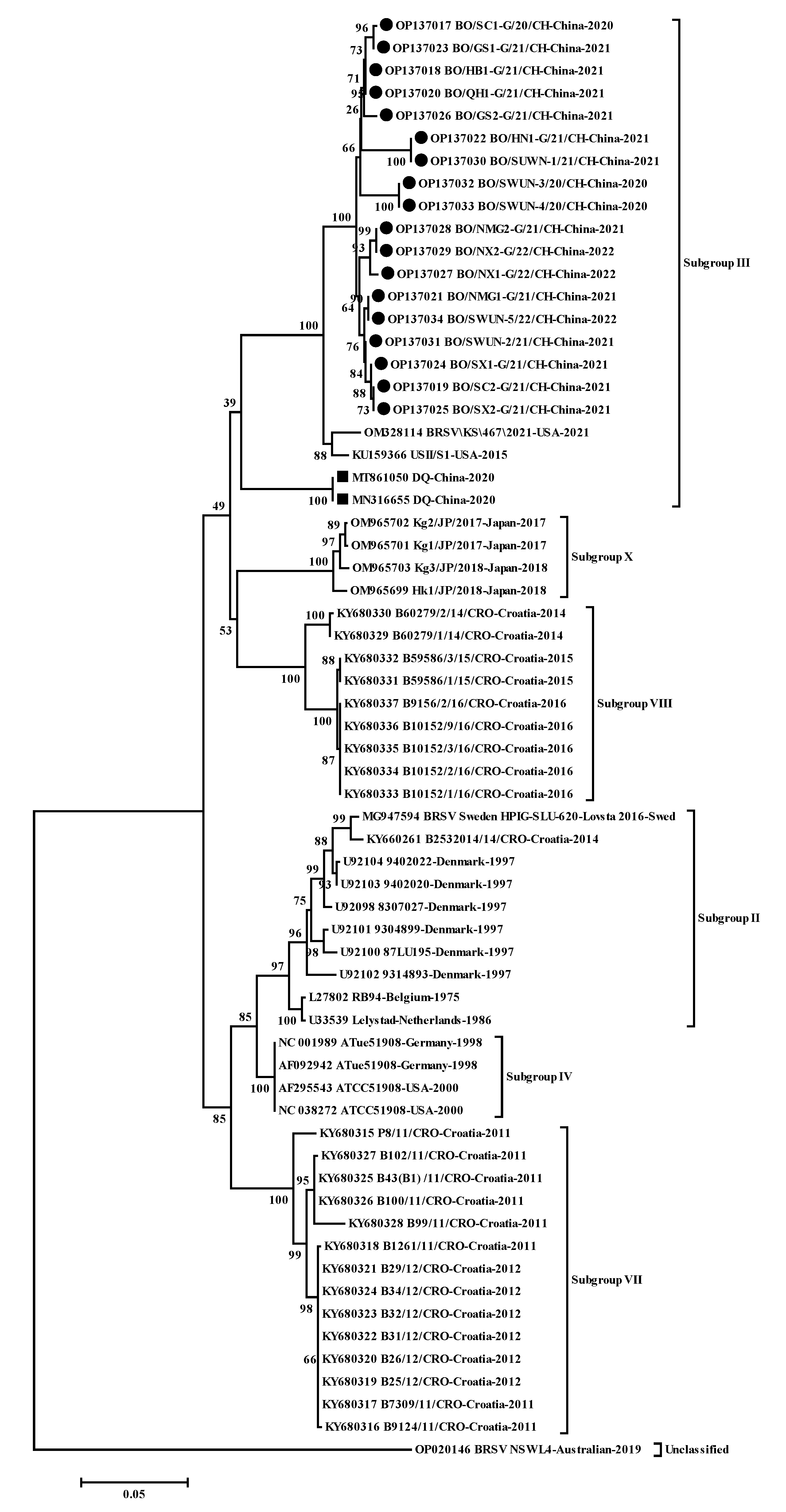
 represents the F gene sequences of other isolates in China.
represents the F gene sequences of other isolates in China.
 represents the F gene sequences of other isolates in China.
represents the F gene sequences of other isolates in China.
 represents the complete genome of other isolates in China.
represents the complete genome of other isolates in China.
 represents the complete genome of other isolates in China.
represents the complete genome of other isolates in China.
| Province or Municipality | Number of Farms | Number of Samples | Positive Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gansu | 2 | 40 | 37.50% (15/40) |
| Ningxia | 2 | 30 | 36.67% (11/30) |
| Sichuan | 7 | 136 | 36.02% (49/136) |
| Inner Mongolia | 5 | 58 | 34.48% (20/58) |
| Yunnan | 1 | 10 | 20.00% (2/10) |
| Heilongjiang | 1 | 12 | 16.67% (2/12) |
| Shanxi | 6 | 52 | 15.38% (8/52) |
| Hebei | 4 | 41 | 14.63% (6/41) |
| Shandong | 2 | 30 | 13.33% (4/30) |
| Henan | 7 | 210 | 13.33% (28/210) |
| Qinghai | 2 | 16 | 12.50% (2/16) |
| Chongqing | 6 | 83 | 0.00% (0/83) |
| Sinkiang | 2 | 20 | 0.00% (0/20) |
| Jiangsu | 1 | 15 | 0.00% (0/15) |
| Anhui | 1 | 15 | 0.00% (0/15) |
| Shaanxi | 1 | 10 | 0.00% (0/10) |
| Fujian | 1 | 10 | 0.00% (0/10) |
| Total | 51 | 788 | 18.65% (147/788) |
| Name | Primer Sequence | Amplified Fragment | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | ACGCGAAAAAATGCGTATA | 1–1175 | 1176 |
| R1175 | GTCTCATTTAGTTTGACCTTGC | ||
| F1028 | AATGTCAACCAAATTCCCAC | 1028–2966 | 1938 |
| R2966 | TCTTTTCACTTTCTTCATCCC | ||
| F2809 | TGTGGCTAGTGCAGGACC | 2809–4878 | 2069 |
| R4878 | GGCTGTTATGACGAGTGATG | ||
| F4468 | GATAACAAGAGCACATGAAGG | 4468–6592 | 2124 |
| R6592 | CCACCCACGATCTGTCCT | ||
| F6381 | AAAAGCTAATGTCAAGTAATGTTC | 6381–8269 | 1888 |
| R8269 | AGCTCCTGTGATGTCCAATAG | ||
| F8100 | TTCCCAGAAAAATACCCTTG | 8100–9956 | 1856 |
| R9956 | CAGACAATATAATCAAATCAGCTTC | ||
| F9713 | CGGCAAGCAATGGATG | 9713–11,598 | 2281 |
| R11598 | CCTAAAGCTTGTGGATCTCTC | ||
| F11351 | ATGTTATTTGGTGGTGGAGAC | 11,351–12,979 | 1628 |
| R12979 | ATCAGTTATATATCCTTCACCCC | ||
| F12790 | CAATAAAACACTTAAGAATAGTCCAC | 12,790–14,540 | 1750 |
| R14540 | CTGAATCCTTGTCAATCTTCTTAG | ||
| F14404 | AGGTTCTGAGGTTTATTTAGTCC | 14,404–15,122 | 718 |
| R15122 | AGAAAAAAAGTATCAAAAACTATCCT |
| G Protein | Amino Acid Mutations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acid sites | 93 | 100 | 105 | 151 | 180 | 198 | 251 |
| Strains in this study | R | Y | R | L | S | L | D |
| Other subgroup III strains | K | H | S | S | L | P | N |
| G Protein | Amino Acid Mutations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acid sites | 24 | 41 | 82 | 90 | 93 | 96 | 100 |
| Strains in this study | L | M | H | S | R | H | Y |
| Chinese DQ strain | I | L | L | F | K | Y | H |
| Amino acid sites | 105 | 126 | 128 | 147 | 151 | 165 | 168 |
| Strains in this study | R | A | D | S | L | L | S |
| Chinese DQ strain | S | T | E | P | S | I | L |
| Amino acid sites | 177 | 180 | 198 | 226 | 229 | 246 | 251 |
| Strains in this study | K | S | L | K | P | L | D |
| Chinese DQ strain | E | L | P | E | L | P | N |
| Stains | OP137030 BO/SUWN-1/21/CH | OP137031 BO/SUWN-2/21/CH | OP137032 BO/SUWN-3/20/CH | OP137033 BO/SUWN-4/20/CH | OP137034 BO/SUWN-5/22/CH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DQ MT861050 | 96.7 | 96.8 | 96.7 | 96.7 | 96.8 |
| 97 | 97.1 | 97 | 97 | 97.1 | |
| USII/S1 KU159366 | 98.7 | 98.8 | 98.7 | 98.7 | 98.8 |
| 99 | 99.1 | 99 | 99 | 99.1 | |
| BRSV\KS\467 OM328114 | 98.6 | 98.7 | 98.6 | 98.6 | 98.7 |
| 98.8 | 98.9 | 98.8 | 98.8 | 98.9 | |
| HPIG-SLU-620-Lovsta MG947594 | 95.4 | 95.5 | 95.5 | 95.5 | 95.5 |
| 96.4 | 96.5 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.5 | |
| Kg3/JP/2018 OM965703 | 95.4 | 95.5 | 95.5 | 95.5 | 95.5 |
| 97 | 97.1 | 97 | 97 | 97.1 | |
| Kg2/JP/2017 OM965702 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.5 |
| 97 | 97.1 | 97 | 97 | 97.1 | |
| Kg1/JP/2017 OM965701 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.5 |
| 97 | 97.1 | 97.1 | 97.1 | 97.1 | |
| Hk1/JP/2018 OM965699 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.4 | 96.4 |
| 96.9 | 96.9 | 96.9 | 96.9 | 96.9 | |
| ATCC51908 NC038272 | 96.6 | 96.7 | 96.6 | 96.6 | 96.7 |
| 97.4 | 97.5 | 97.4 | 97.4 | 97.5 | |
| ATue51908 NC001989 | 96.6 | 96.7 | 96.6 | 96.6 | 96.7 |
| 97.4 | 97.5 | 97.4 | 97.4 | 97.5 | |
| ATCC51908 AF295543 | 96.6 | 96.7 | 96.6 | 96.6 | 96.7 |
| 97.4 | 97.5 | 97.4 | 97.4 | 97.5 | |
| ATue51908 AF092942 | 96.6 | 96.7 | 96.6 | 96.6 | 96.7 |
| 97.4 | 97.5 | 97.4 | 97.4 | 97.5 | |
| BRSV-NSWL4 OP020146 | 76.8 | 76.9 | 76.8 | 76.8 | 76.9 |
| 79.9 | 79.9 | 79.8 | 79.8 | 79.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.; Yue, H.; Tang, C. Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Beef Cattle in China. Animals 2022, 12, 3511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12243511
Chang Y, Yue H, Tang C. Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Beef Cattle in China. Animals. 2022; 12(24):3511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12243511
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Yiming, Hua Yue, and Cheng Tang. 2022. "Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Beef Cattle in China" Animals 12, no. 24: 3511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12243511
APA StyleChang, Y., Yue, H., & Tang, C. (2022). Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics of Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Beef Cattle in China. Animals, 12(24), 3511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12243511






